ARM Brachium Musculature
|
|
|
- Amy Stafford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches of the brachial artery Nerve: musculocutaneous nerve, C5,6,(C7) Biceps brachii 1. long head- supraglenoid tubercle and glenohumeral labrum 2. short head- tip of the coracoid process of the scapula 1. radial tuberosity 2. bicipital aponeurosis 1. flexes the forearm at the elbow (when supinated) 2. supinates forearm from neutral 3. stabilizes anterior aspect of shoulder 4. flexes shoulder (weak if at all) Blood: muscular branches of brachial artery Nerve: musculocutaneous nerve, C5,6 Brachialis 1. lower 1/2 of anterior humerus 2. both intermuscular septa 1. ulnar tuberosity 2. coronoid process of ulna slightly elbow flexion (major mover) Blood: 1. muscular branches of brachial artery 2. radial recurrent artery Nerve: musculocutaneous nerve, C5,6 Triceps brachii 1. long head - infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula 2. lateral head - upper half of the posterior surface of the shaft of the humerus, and the upper part of the lateral intermuscular septum 3. medial head - posterior shaft of humerus, distal to radial groove and both the medial and lateral intermuscular septum (deep to the long & lateral heads) 1. posterior surface of the olecranon process of the ulna 2. deep fascia of the antebrachium 1
2 1. long - adducts the arm, extends at the shoulder, and a little elbow flexion 2. lateral - extends the forearm at the elbow 3. medial - extends the forearm at the elbow Blood: 1. muscular branches of the brachial artery 2. superior ulnar collateral artery 3. profunda brachii artery Nerve: radial nerve, C6,7 Anconeus posterior surface of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus lateral aspect of olecranon extending to the lateral part of ulnar body 1. extends the forearm at the elbow 2. supports the elbow when in full extension Blood: middle collateral artery from the profunda brachii artery Nerve: radial nerve, C7,8 Antebrachial Flexor Musculature Pronator teres 1. humeral head: a. upper portion of medial epicondyle via the CFT (common flexor tendon) b. medial brachial intermuscular septum 2. ulnar head - coronoid process of ulna lateral aspect of radius at the middle of the shaft (pronator tuberosity) 1. pronates forearm (during rapid or forced pronation) 2. weakly flexes the elbow Blood: 1. muscular branches of ulnar artery 2. muscular branches of radial artery Nerve: median nerve, C6,7 Flexor carpi radialis 1. medial epicondyle via the CFT (common flexor tendon) 2. antebrachial fascia Insertion: base of the 2nd and sometimes 3rd metacarpals 1. flexes the hand at the wrist 2. radially deviates the wrist 3. may assist to pronate the forearm Blood: muscular branches of radial artery Nerve: median nerve, C6,7 2
3 Palmaris longus 1. medial epicondyle via the CFT (common flexor tendon) 2. antebrachial fascia 1. central portion of the flexor retinaculum 2. superficial portion of the palmar aponeurosis flexes the hand at the wrist Blood: muscular branches of ulnar artery Nerve: median nerve, C6,7 Flexor carpi ulnaris 1. humeral head - medial epicondyle via the CFT (common flexor tendon) 2. ulnar head: a. medial aspect of olecranon b. proximal 3/5 of dorsal ulnar shaft c. antebrachial fascia 1. pisiform & hamate bones (via the pisohamate ligament) 2. base of the 5th metacarpal (via the pisometacarpal ligament) 1. flexes the hand at the wrist 2. ulnarly deviates the wrist 3. stabilizes wrist to permit powerful thumb motion Blood: muscular branches of ulnar artery Nerve: ulnar nerve, C8,T1 Flexor digitorum superficialis 1. humeral-ulnar head: a. medial epicondyle via the CFT (common flexor tendon) b. medial boarder of base of coronoid process of ulna c. medial (ulnar) collateral ligament d. antebrachial fascia 2. radial head: oblique line of radius along its upper anterior boarder Insertion: both sides of the base of each middle phalanx of the 4 fingers 1. flexes the proximal and middle phalanges 2. flexes the wrist if fingers are extended Blood: 1. muscular branches of ulnar artery 2. muscular branches of radial artery Nerve: median nerve, C7,8,T1 Flexor digitorum profundus 1. anterior & medial surface of upper 3/4 ulna 2. adjacent interosseous membrane distal phalanx of medial 4 digits (through FDS tunnel) 3
4 1. flexes the distal IP joints and in so doing flexes the proximal and middle IP joints 2. flexes the wrist if fingers are extended Blood: 1. muscular branches of the ulnar artery 2. muscular branches of the radial artery 3. anterior interosseous artery (from ulnar artery) Nerve: 1. medial portion - ulnar nerve, C8,T1 2. lateral portion - anterior interosseous branch of median nerve, C8,T1 Flexor pollicis longus 1. middle anterior surface of the radius 2. interosseous membrane 3. (may also originate from lateral boarder of coronoid process 4. or medial epicondyle) Insertion: palmar aspect of base of the distal phalanx of thumb (deep to flexor retinaculum) 1. flexes the distal phalanx of the thumb (IP joint) 2. flexes the other joints to the wrist (McP, CMc and weakly at the wrist) Blood: 1. muscular branches of radial artery 2. anterior interosseous artery Nerve: anterior interosseous branch of median nerve, C8,T1 Pronator quadratus distal 1/4 anteriomedial surface of ulna distal 1/4 anteriolateral surface of radius pronates the forearm and hand Blood: 1. anterior interosseous artery 2. muscular branches of the radial artery Nerve: anterior interosseous branch of median nerve, C8,T1 Antebrachial Extensor Musculature Brachioradialis 1. upper lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus (between the triceps and brachialis muscles) 2. lateral intermuscular septum of humerus 1. superior aspect of styloid process of radius 2. lateral side of the distal 1/2 to 1/3 of the radius 1. flexes the forearm at the elbow 2. pronates the forearm when supinated 3. supinates the forearm when pronated Blood: radial recurrent artery 4
5 Nerve: 1. radial nerve, C5,6 OR 2. deep branch of the radial nerve Extensor carpi radialis longus 1. lower lateral supracondylar ridge (below the brachioradialis) 2. lateral intermuscular septum of humerus Insertion: base of 2nd metacarpal 1. extends the hand at the wrist 2. radially deviates the hand at the wrist 3. weakly flexes the forearm at the elbow 4. weakly supinates the forearm Blood: radial recurrent artery Nerve: 1. radial nerve, C5,6 OR 2. deep branch of the radial nerve Extensor carpi radialis brevis 1. lateral epicondyle via the CET (common extensor tendon) 2. radial collateral ligament Insertion: base of 3rd metacarpal 1. extends the hand at the wrist 2. radially deviates the hand at the wrist Blood: radial recurrent artery Nerve: deep branch of the radial nerve, C6,7 Extensor digitorum 1. lateral epicondyle via the CET (common extensor tendon) 2. antebrachial fascia 1. base of middle phalanx of each of the four fingers (central band) 2. base of distal phalanx of each of the four fingers (2 lateral bands) 1. extends the four medial digits 2. extends the wrist if fingers flexed 3. abducts the digits (spreads the digits as it extends them) Blood: posterior interosseous artery Nerve: posterior interosseous nerve of the radial nerve, C6,7,8 Extensor digiti minimi 1. lateral epicondyl via the CET (common extensor tendon) 2. antebrachial fascia 3. ulnar aspect of extensor digitorum 5
6 Insertion: 1. base of middle phalanx of the 5th digit (central band) 2. base of distal phalanx of the 5th digit (2 lateral bands) 1. extends the 5th digit 2. abducts the 5th digit Blood: posterior interosseous artery Nerve: posterior interosseous nerve of the radial nerve, C6,7,8 Extensor carpi ulnaris 1. 1st head - lateral epicondyle via the CET (common extensor tendon) 2. 2nd head - posterior body of ulna Insertion: medial side of base of the 5th metacarpal 1. extends the hand at the wrist 2. ulnarly deviates the hand at the wrist Blood: posterior interosseous artery Nerve: posterior interosseous nerve of the radial nerve, C6,7,8 Supinator 1. lateral epicondyle of humerus 2. supinator crest of ulna 3. radial collateral ligament 4. annular ligament 5. antebrachial fascia proximal portion of anteriorlateral surface of the radius supinates the forearm Blood: radial recurrent artery Nerve: deep branch of the radial nerve, C6 Abductor pollicis longus 1. posterior surfaces of ulna and radius 2. interosseous membrane Insertion: lateral aspect of base of 1st metacarpal 1. abducts the 1st metacarpal 2. assists to extend & rotate the thumb 3. radially deviates the hand at the wrist 4. flexes the hand at the wrist Blood: posterior interosseous artery Nerve: posterior interosseous nerve of the radial nerve, C6,7,(C8) 6
7 Extensor pollicis brevis 1. posterior surfaces of radius (below abductor pollicis longus) 2. interosseous membrane base of proximal phalanx of thumb (often a slip inserts into extensor pollicis longus tendon) 1. extends the proximal phalanx and 1st metacarpal of the thumb 2. radially deviates the hand at the wrist Blood: posterior interosseous artery Nerve: posterior interosseous nerve of the radial nerve, C6,7,(C8) Extensor pollicis longus 1. posterior surface of ulna 2. interosseous membrane Insertion: distal phalanx of thumb 1. extends distal phalanx of thumb 2. extends proximal phalanx of thumb 3. assists to extend the hand at the wrist (if fingers flexed) Blood: posterior interosseous artery Nerve: posterior interosseous nerve of the radial nerve, C6,7,8 Extensor indicis 1. posterior surface of ulna (distal to extensor pollicis longus) 2. interosseous membrane Insertion: base of middle and distal phalanx of the index finger 1. extends the 2nd digit (McP & IP joints) 2. adducts the 2nd digit 3. assists to extend the hand at the wrist 4. stabilizes McP joint for flexion of IP solely Blood: posterior interosseous artery Nerve: posterior interosseous nerve of the radial nerve, C6,7,8 Hand & Wrist Musculature Abductor pollicis brevis 1. distal border of flexor retinaculum 2. trapezium (may be variable) 1. lateral aspect of base of proximal phalanx of the thumb 2. may also send a slip to the tendon of extensor pollicis longus 7
8 1. abducts thumb (at the McP joint) 2. participates to flex the thumb (at the McP joint) 3. if attached to extensor pollicis longus, it might assist to extend the thumb Blood: superficial palmar branches of radial artery Nerve: recurrent branch of median nerve, C8,T1 Flexor pollicis brevis 1. superficial head: a. distal border of flexor retinaculum b. trapezium 2. deep head: a. floor of carpal tunnel b. indirectly to scaphoid & trapezium 1. base of proximal phalanx of thumb 2. can also attach to the lateral sesamoid bone at the McP joint powerfully flexes the thumb (at the McP joint) Blood: superficial palmar branches of radial artery Nerve: 1. superficial head - recurrent branch of median nerve, C8,T1 2. deep head - deep branch of ulnar nerve, C8,T1 Opponens pollicis 1. distal border of flexor retinaculum 2. trapezium lateral aspect of the 1st metacarpal opposes the thumb to the fingers Blood: superficial palmar branches of radial artery Nerve: recurrent branch of median nerve, C8,T1 Adductor pollicis 1. transverse head: 3rd metacarpal 2. oblique head: a. base of 1st, 2nd and 3rd metacarpals b. floor of carpal tunnel 1. medial aspect of the base of proximal phalanx 2. medial sesamoid at McP 1. adducts the thumb 2. may assist to flex the thumb (at the McP joint) Blood: superficial palmar branches of radial artery Nerve: deep branch of ulnar nerve, C8,T1 8
9 Palmaris brevis medial margin of palmar aponeurosis 1. skin of ulnar border of palm 2. may insert on the pissiform tenses the skin on the ulnar side, which is used in a grip action Blood: superficial palmar branches of ulnar artery Nerve: superficial branch of ulnar nerve, C8,T1 Abductor digiti minimi pisiform & tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris 1. medial aspect of the base of proximal phalanx of the 5th digit 2. may send a slip to the ulnar side of the dorsal expansion 1. abduct 5th digit (requires pisiform stabilized by FCU) 2. assists to flex the 5th digit (at McP) 3. may assist in extension of 5th digit (at IP due to slips to extensor digitorum) Blood: deep palmar branches of ulnar artery Nerve: deep branch of ulnar nerve, C8,T1 Flexor digiti minimi brevis 1. distal border of flexor retinaculum 2. hook of the hamate medial aspect of the base of proximal phalanx flexes the 5th digit (at the McP joint) Blood: deep palmar branches of ulnar artery Nerve: deep branch of ulnar nerve, C8,T1 Opponens digiti minimi 1. distal border of flexor retinaculum 2. hook of the hamate Insertion: medial aspect of the 5th metacarpal 1. opposes the 5th digit with the thumb 2. assists to "cup" the palm Blood: deep palmar branches of ulnar artery Nerve: deep branch of ulnar nerve, C8,T1 Palmar interossei from the side of the metacarpal that faces the midline - to adduct them 1. on the base of the proximal phalanx of the digit of origin (same side toward the midline) 2. extensor hood of the same digit(s) 1. adducts the fingers (hint: PAD) 2. flexes the fingers (at the McP while IP joints are extended) Blood: palmar metacarpal artery of deep palmar arch 9
10 Nerve: deep branch of ulnar nerve, C8,T1 Dorsal interossei between each metacarpal 1. directly distal to the origin on the base of the proximal phalanx closest to the midline (to abduct them.) 2. extensor hood of the same digit(s) 1. abducts the fingers (hint: DAB) 2. flexes the fingers (at the McP while IP joints are extended) Blood: palmar metacarpal artery of deep palmar arch Nerve: deep branch of ulnar nerve, C8,T1 Lumbricals 1. tendon of flexor digitorum profundus 2. 1 & 2 have a single head of origin (from radial aspect of tendon) 3. 3 & 4 have two heads of origin (each head from an adjacent tendon) extensor hood of digits flexes the fingers (at the McP joints) 2. extend IPs Blood: palmar metacarpal arteryof deep palmar arch Nerve: 1. 1 & 2 - median nerve, C8,T & 4 - deep branch of ulnar nerve, C8,T1 10
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Thank You for Your Support! Hosford Muscle Tables
 Thank You for Your Support! This PDF document has been placed online for your enjoyment and I hope you find it useful. These tables are both a teaching tool, and a study / review tool. I created these
Thank You for Your Support! This PDF document has been placed online for your enjoyment and I hope you find it useful. These tables are both a teaching tool, and a study / review tool. I created these
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
divided by the bones ( redius and ulna ) and interosseous membrane into :
 fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
The Forearm 2. Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm
 The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION
 MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION Dr Bronwen Ackermann COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulation WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney
MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION Dr Bronwen Ackermann COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulation WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney
The Elbow and the cubital fossa. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm
 Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Wrist and Hand Anatomy
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla.
 1 region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla. Inferiorly, a number of important structures pass between arm & forearm through cubital fossa. 2 medial
1 region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla. Inferiorly, a number of important structures pass between arm & forearm through cubital fossa. 2 medial
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
compartments of the forearm
 " forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
" forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016
 LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016 BONES Ribs, sternum, clavicle Humerus: Head, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, intertubercular sulcus, surgical neck, anatomical
LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016 BONES Ribs, sternum, clavicle Humerus: Head, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, intertubercular sulcus, surgical neck, anatomical
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
Axilla and Brachial Region
 L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
# Anatomy. Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla. Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil. Page 0 of 16
 #10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
#10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides
 The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow
 Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
Dr. Mahir Alhadidi Anatomy Lecture #9 Feb,28 th 2012
 Quick Revision: Upper arm is divided into two compartments: 1. Anterior Compartment: Contains three muscles (Biceps brachii, Coracobrachialis, Brachialis). Innervated by Musculocutaneous nerve. 2. Posterior
Quick Revision: Upper arm is divided into two compartments: 1. Anterior Compartment: Contains three muscles (Biceps brachii, Coracobrachialis, Brachialis). Innervated by Musculocutaneous nerve. 2. Posterior
forearm posterior compartment
 Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Systematic Anatomy (For international students)
 Systematic Anatomy (For international students) Department of Anatomy,Fudan University Teaching contents Muscles of abdomen & upper limbs Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy (For international students) Department of Anatomy,Fudan University Teaching contents Muscles of abdomen & upper limbs Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen
Anatomy of the Forearm
 Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation.
 Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Supplied in part by the musculocutaneous nerve. Forms the axis of rotation in movements of pronation and supination
 Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES
 LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
Figure 27: The synovial membrane of the shoulder joint (anterior view)
 The coracoacromial ligament; is an accessory ligament that protects the superior aspect of the joint extending from the coracoid process to the acromion over the tendon of supraspinatus. The synovial membrane
The coracoacromial ligament; is an accessory ligament that protects the superior aspect of the joint extending from the coracoid process to the acromion over the tendon of supraspinatus. The synovial membrane
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader. Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS
 Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
Abduction of arm until your hand rich your head. Flexion of forearm at elbow joint. Extension of arm at elbow joint. Flexion of fingers 10.
 Num. answer 1. Medialy With the manubrium ( sternum ), and laterally with the acromion of the scapula 2. 1. Trapezius 2. Levator scapulae 3. Rhomboids 3. 1. Pectoralis major 2. Pectoralis minor 3. Latissiumus
Num. answer 1. Medialy With the manubrium ( sternum ), and laterally with the acromion of the scapula 2. 1. Trapezius 2. Levator scapulae 3. Rhomboids 3. 1. Pectoralis major 2. Pectoralis minor 3. Latissiumus
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology. Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]
![[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]] [[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]](/thumbs/84/91174469.jpg) In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
Anatomy Upper Limb Muscles
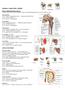 Anatomy Upper Limb Muscles Rotator cuff/scapulohumeral muscles 4 muscles (SITS) form musculotendinous rotator cuff around glenohumeral joint, provide stability of joint Supraspinatus Course: med 2/3 supraspinatous
Anatomy Upper Limb Muscles Rotator cuff/scapulohumeral muscles 4 muscles (SITS) form musculotendinous rotator cuff around glenohumeral joint, provide stability of joint Supraspinatus Course: med 2/3 supraspinatous
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints. Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint
 Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex. The ability to perform many activities of daily living (ADL) depends upon the elbow.
 Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex The ability to perform many activities of daily living (ADL) depends upon the elbow. Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Can you think of anything that you do to
Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex The ability to perform many activities of daily living (ADL) depends upon the elbow. Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Can you think of anything that you do to
The Arm and Cubital Fossa
 The Arm and Cubital Fossa Dr. Andrew Gallagher School of Anatomical Sciences University of the Witwatersrand Introduction The ARM (BRACHIUM) is the most proximal segment of the upper limb musculoskeletal
The Arm and Cubital Fossa Dr. Andrew Gallagher School of Anatomical Sciences University of the Witwatersrand Introduction The ARM (BRACHIUM) is the most proximal segment of the upper limb musculoskeletal
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow.
 MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
Cubital fossa and forearm
 Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Deep dry needling of the arm and hand muscles
 Deep dry needling of the arm and hand s 8 César Fernández-de-las-Peñas Javier González Iglesias Christian Gröbli Ricky Weissmann CHAPTER CONTENT Introduction................... 107 Clinical relevance of
Deep dry needling of the arm and hand s 8 César Fernández-de-las-Peñas Javier González Iglesias Christian Gröbli Ricky Weissmann CHAPTER CONTENT Introduction................... 107 Clinical relevance of
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Elbow Elbow Anatomy. Flexion extension. Pronation Supination. Anatomy. Anatomy. Romina Astifidis, MS., PT., CHT
 Elbow Elbow Anatomy Romina Astifidis, MS., PT., CHT Curtis National Hand Center Baltimore, MD October 6-8, 2017 Link between the arm and forearm to position the hand in space Not just a hinge Elbow = 70%
Elbow Elbow Anatomy Romina Astifidis, MS., PT., CHT Curtis National Hand Center Baltimore, MD October 6-8, 2017 Link between the arm and forearm to position the hand in space Not just a hinge Elbow = 70%
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology II REVIEW
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology II REVIEW MSAK101-II Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, the student will be
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology II REVIEW MSAK101-II Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, the student will be
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments
 Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Chapter 8. The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb
 Chapter 8 The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb Pectoral Girdle pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) supports the arm consists of two on each side of the body // clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
Chapter 8 The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb Pectoral Girdle pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) supports the arm consists of two on each side of the body // clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
13 13/3/2012. Adel Muhanna
 13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity RADIUS AND ULNA right
 11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
BRACHIAL PLEXUS. DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae
 THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓
 Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Upper Limb
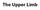 The Upper Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Upper Limb Table of Contents Upper Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Clavicle...3 2: Scapula...5 3: Shoulder (Glenohumeral) and Proximal Humerus...7 4:
The Upper Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Upper Limb Table of Contents Upper Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Clavicle...3 2: Scapula...5 3: Shoulder (Glenohumeral) and Proximal Humerus...7 4:
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Locomotor system - Part 6
 Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside
 Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
The hand. it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand**
 Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS
 TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
*the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone
 *the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone - muscles in the arm : *brachialis muscle *Biceps brachii
*the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone - muscles in the arm : *brachialis muscle *Biceps brachii
Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex
 Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex The ability to perform m any activities of daily living (ADL) d epends upon the elbow. Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Can you think of anything that you do
Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex The ability to perform m any activities of daily living (ADL) d epends upon the elbow. Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Can you think of anything that you do
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Anatomy of the Upper Limb
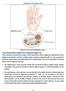 Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
The Free Upper Limb. Bone of the Arm. aus: Platzer, Locomotor System (ISBN ), 2009 Georg Thieme Verlag KG
 : ones, Ligaments, Joints The Free The bones of the free upper limb are The humerus The radius and ulna The carpal bones The metacarpal bones The phalanges one of the Arm Humerus (A H) The humerus articulates
: ones, Ligaments, Joints The Free The bones of the free upper limb are The humerus The radius and ulna The carpal bones The metacarpal bones The phalanges one of the Arm Humerus (A H) The humerus articulates
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Anatomy - Hand. Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics. Osteology. Carpal Arch. Property of VOMPTI, LLC
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락
 Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
1/13/2013. Anatomy Guy Dissection Sheet Extensor Forearm and Hand. Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Joints of the upper limb II
 Joints of the upper limb II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Elbow joint The elbow joint is connecting the upper arm to the forearm. It is classed
Joints of the upper limb II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Elbow joint The elbow joint is connecting the upper arm to the forearm. It is classed
David G. Simpson, Ph.D.
 David G. Simpson, Ph.D. ARM & CUBITAL FOSSA Revised 7/08 Text References Moores 3 rd ed., p402 408, 436 439, 439 443, 478, 481 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the humerus, indicating the sites of muscle
David G. Simpson, Ph.D. ARM & CUBITAL FOSSA Revised 7/08 Text References Moores 3 rd ed., p402 408, 436 439, 439 443, 478, 481 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the humerus, indicating the sites of muscle
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Small muscles of the hand
 By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
Appendix. Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance
 Appendix Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance Appendix Outline Respiratory System 426 Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426 Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426 Musculoskeletal
Appendix Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance Appendix Outline Respiratory System 426 Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426 Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426 Musculoskeletal
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S?
 Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
10/15/2014. Wrist. Clarification of Terms. Clarification of Terms cont
 Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful
 In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
Acknowledgement. Here are some flash cards all set up in a "pdf" format for you! Thanks to Laura H. (spring 08)
 Acknowledgement Here are some flash cards all set up in a "pdf" format for you! Thanks to Laura H. (spring 08) for her donation to all my anatomy students! t Here is her suggestion for making flashcards
Acknowledgement Here are some flash cards all set up in a "pdf" format for you! Thanks to Laura H. (spring 08) for her donation to all my anatomy students! t Here is her suggestion for making flashcards
The Foot. Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob:
 The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
Done By : Isra a Aweidah
 Anatomy Made Easy MSS هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة 10 المحاضرة 12 ابتداء من صفحة 13 وتفريغ part #9 Done By : Isra a Aweidah Edited by: AWN Academic Team Everything is included ( the drs slides in addition
Anatomy Made Easy MSS هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة 10 المحاضرة 12 ابتداء من صفحة 13 وتفريغ part #9 Done By : Isra a Aweidah Edited by: AWN Academic Team Everything is included ( the drs slides in addition
MUSCLES. Anconeus Muscle
 LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
ANATOMY. Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date :
 ANATOMY Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date : Median nerve Meaian nerve to Pronator teres Course: Enter cubital fossa. Pierce Pronat. teres Between to FDS, FOP Below and lateral
ANATOMY Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date : Median nerve Meaian nerve to Pronator teres Course: Enter cubital fossa. Pierce Pronat. teres Between to FDS, FOP Below and lateral
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
8/25/2014. Radiocarpal Joint. Midcarpal Joint. Osteology of the Wrist
 Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Ultrasound of the elbow joint - anatomical review of normal structures
 Ultrasound of the elbow joint - anatomical review of normal structures Poster No.: C-2089 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Castelo, E. Matos, F. C. Pires ; Vila Nova de Gaia/PT,
Ultrasound of the elbow joint - anatomical review of normal structures Poster No.: C-2089 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Castelo, E. Matos, F. C. Pires ; Vila Nova de Gaia/PT,
