Tibial Tuberosity Advancement For the Treatment of Cranial Cruciate Deficiency
|
|
|
- Gillian Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tibial Tuberosity Advancement For the Treatment of Cranial Cruciate Deficiency Cranial cruciate ligament deficiency in the dog is the most common orthopedic lameness seen in practice today. Many reasons are reported to be at cause, to include; genetic conformational abnormalities, obesity (either genetic or overfeeding), excessive athleticism, and chronic degenerative joint disease. Large breed dogs seem to be over represented when compared with small breed dogs and cats. This is probably in due part to their higher levels of physical activity when compared with smaller animals. There are two cruciate ligaments in the dog knee, termed cranial and caudal. The caudal cruciate ligament rarely tears, but when it does, it is usually concurrently torn with the cranial cruciate ligament. The most common physical reason the cranial cruciate ligament tears is thought to be a result of excessive internal rotation with the knee in slight extension. Your pet will usually yelp when this happens, and will limp either slightly or very severely afterwards. To some degree, they appear to get better in the next few days or so, only to become chronically lame over the next few weeks. During this time, your pet will shift its weight to the good rear leg, increasing the strain on it. Tearing of the cranial cruciate ligament results in instability of the knee termed cranial tibial thrust. Think of the top part of the knee (the femur) as being a car, and the bottom part of knee (the tibia) as being a hill. The cranial cruciate ligament is the parking brake. When it breaks, the car rolls down hill. This is cranial tibial thrust. During the examination process, the doctor will want to take 2-3 radiographs of the affected leg, the opposite leg, and the hips. This is done to look for additional evidence of a torn cranial cruciate ligament, evaluate for bone abnormalities that may have caused the instability in the knee, and the check for osteoarthritis of the hips. These radiographs will also be used to measure the knee for the proper sized implants for a corrective osteotomy to stabilize the knee. The literature routinely cites over 100 procedures as being available for the treatment of cruciate ligament tear in dogs. All of these procedures show some success, but it seems apparent that this success to some degree is operator dependent. In the last 10 years or so, the list of procedures in use has probably dwindled down to 4-5 procedures. More recent research has shown little differences in the success rates amongst these procedures in long term studies. The exception to this idea becomes apparent with procedures like tibial plateau leveling osteotomy ( TPLO, Slocum) from Oregon, and the more recently proposed tibial tuberosity advancement ( TTA, Montavan, Tepic, et al) from Zurich.
2 TPLO was developed in The purpose of the procedure is to realign the tibial portion of the knee joint in such a manner that the knee is no longer in need of stabilization by the cranial cruciate ligament. TPLO in effect eliminates the hill in the knee. Although the recovery period could be considered long (12-16 weeks), the immediate results are considerably better than more traditional procedures. The lengthy healing time is a result of the extensive cut made into the bone. Disadvantages to the procedure include; extensive surgical invasiveness, implant failure, and the procedure itself require a high degree of skill to perform. While only currently a small percentage of cases result in failure, as more practitioners become certified to perform the procedure, the failure rate is certain to climb, and has been reported in the literature to be as high as 36%. It has also been proposed that TPLO might over-correct the limb. TTA is a new-comer to the arena of procedures advocated to stabilize the cranial cruciate deficient knee in the canine. The theory of TTA arose out of a modification of the proposed model by Slocum, in that the net joint reaction is approximately parallel to the patellar tendon, and that if the patellar tendon is perpendicular to the tibial plateau (joint surface), the cruciate ligaments are not under any load. If we move the patellar tendon forward to the point that it is perpendicular to the tibial plateau in a standing angle, we relieve the load on the cranial cruciate ligament. The net result being that the patellar tendon takes over the load of the cranial cruciate ligament. Since we know the patellar tendon is capable of loads many times greater than what the cranial cruciate ligament withstood, the joint reaction should not be capable of exceeding the force of the patellar tendon. The net result is a stable knee. In more simple terms, TTA is an upside-down TPLO. Apparent advantages to TTA when compared to TPLO include; 1. Quicker recovery as a result of less invasive surgical technique, less swelling, shorter surgical time, and improved postoperative stability. Many patients are walking better when they leave the hospital postoperatively. 2. Less implant failure the implants are made of titanium and are therefore less reactive and less likely to break. The strain put on the implants is less than what is seen with TPLO. 3. Ease of procedure less technically demanding procedures are less likely to have operator-dependent failures, resulting in better clinical results. 4. Good results with chronically arthritic knees since TTA does not require a rolling of the tibial plateau (like TPLO), stability is easily achieved even in the most chronic knees. 5. Ability to operate on both knees at once a small percentage of dogs will have the condition undiagnosed in the opposite knee. TPLO surgery is currently not recommended for both knees at the same time due to stability problems. TTA has been successfully performed in dogs up to 140# on both knees. The only real disadvantage to TTA at this point is the lack of clinical cases. New procedures mean we do not have a huge case load to reflect upon when things go wrong. No surgery is perfect, and problems can arise. Should something go wrong with a TTA procedure, the knowledge base on dealing with the outcome is limited at this point. TPLO has been around long enough that the majority of the problems that arise have more than one solution.
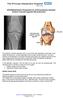
3 Postoperative recovery from knee surgery, regardless if TPLO or TTA is performed, requires that your pet be kept quiet. Bones have been cut and repositioned to alleviate the cranial cruciate ligament deficit. TTA, more so than TPLO, has resulted in such rapid recovery that many patients begin using the leg too much, too soon. It is imperative to avoid running, jumping, and rough-housing with other pets for a minimum of 8 weeks until the bone has had a chance to adequately heal. Excessive strain placed on the osteotomy in either procedure too early will result in implant failure. In the immediate postoperative period, you will see some swelling in the mid-tibial area, just past the end of the implants. Applying warm compresses to the leg 3-4 times daily for the first week will help with this. Some dogs will have some drainage from the surgical site for up to 1 week. Staples are irritating to some dogs, and they may try and chew them out. Others will feel so good when they go home that they immediately begin to play with the other dog, or want to run in the backyard. You must keep your pet quiet during the recovery period, even if this means temporarily medicating him/her. Some patients have good luck with diphenhydramine (Benadryl ), while others may require tramadol (Ulltram ), acepromazine, or even phenobarbital to keep them quiet during the convalescent period. Once the swelling is gone, you can begin short leash walks once Dr. Mayo has removed the staples. Do not swim the dog until instructed to do so by Dr. Mayo. Swimming too soon may result in severe patellar tendonitis, or possibly implant failure. The 8-week postoperative follow up radiograph is important. We are evaluating the leg for proper long-term alignment of the implants, failures, and to assure adequate healing of the osteotomy site. Once healed, a regimen of increased exercise as tolerated by the dog will result in a quick recovery to full use of the limb. Generally, this is about another 1-2 months. A postoperative x-ray of a tibial tuberosity advancement
4 Post-Operative Instructions Tibial Tuberosity Advancement Historically, rehabilitation on knee surgeries in general has been limited to one common recommendation cage rest! Veterinarians have been reluctant to allow their patients to perform even the slightest of exercise movements postoperative, for fear that the patient will ruin the work (and expense) already performed. If we have learned one thing from human medicine, the sooner the patient is up and using the leg, the quicker will be the recovery. There is only one modification to this thought that should be stated here, if the leg does not hurt, the dog will use it, and premature overuse of the leg will result in critical damage to the proper healing process. We cannot overemphasize enough, do not let your dog run loose until the doctor has pronounced the surgery a success. First Two Weeks: The first couple days when your pet comes home, the pain will be the worst. Why? Dogs are pretty smart, and they figure out right away that when they act like they are in pain, they will get more attention from their owners. It is important to not let your pet loose to run freely, particularly up and down stairs without assistance. They can go outside ON A LEASH to go to the bathroom, and then they must return inside and rest. (1) First 48 hours ice packs 3-4 times daily for minutes. This will help significantly with the swelling. (2) Pain medication as written by the doctor. If this is not working, do not overdose; call the office for further recommendations or additional medications. (3) After 48 hours, apply heat to the area 2-3 times daily for minutes. Afterwards, begin GENTLE range of motion of the leg that was operated on after the heat pack has been applied. If you are not clear about this, ASK! (4) No other exercise is recommended for the first two weeks. (5) Clean the wound daily if needed with dilute hydrogen peroxide, and do not allow the dog to lick it. If he attempts to lick the wound, please get an e- collar. Second Two Weeks: At this point, walking on leash is tolerated. (1) Pain medication should be off of prescription medicine, however, giving one aspirin for the average # dog 30 minutes prior to any physical therapy is advisable. (2) Apply heat to the leg for 20 minutes, then exercise the leg through range of motion. (3) Walking on a leash is acceptable, but begin with one block and stop. If the dog returns home and is not in pain, you may increase this in 1 block increments every 4-5 days as tolerated, provided your dog is not in pain when the walk is over. (4) While walking, push the dog s hips towards the operated leg slightly to help convince him/her that the leg can be used. (5) Lift the front end of the dog for 5 second intervals prior to starting the walk to increase the strength of the leg. Try several repetitions.
5 Third Two Weeks: By this time, walks should be in the 20 minute range or better, and tolerated well. Do not run yet. Increase the duration of walking as much as you can without causing the dog pain. Do not exceed the 20 minute range. If you have access to a pool, some hydrotherapy is ok, but NOT unattended nor allowed to swim in water over the dog s head. Any hydrotherapy over 10 minutes is more likely to exaggerate patellar tendon inflammation and result in lameness. Fourth Two Weeks: At the end of this period, it is time to come in for the follow up x- ray. We want to make sure everything has healed prior to increasing the exercise as tolerated. Be forewarned that if you just go home and turn the dog loose, he will be in pain. This is the point where you can SLOWLY build back up to full exercise.
Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease
 24- hour Emergency Service 01635 47170 The Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA) procedure is one of the advanced procedures for the treatment of cranial cruciate ligament disease in dogs. TTA is now available
24- hour Emergency Service 01635 47170 The Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA) procedure is one of the advanced procedures for the treatment of cranial cruciate ligament disease in dogs. TTA is now available
THE PET HEALTH LIBRARY By Wendy C. Brooks, DVM, DipABVP Educational Director, VeterinaryPartner.com. Ruptured Anterior (Cranial) Cruciate Ligament
 THE PET HEALTH LIBRARY By Wendy C. Brooks, DVM, DipABVP Educational Director, VeterinaryPartner.com Ruptured Anterior (Cranial) Cruciate Ligament First, the Basics There are two cruciate ligaments that
THE PET HEALTH LIBRARY By Wendy C. Brooks, DVM, DipABVP Educational Director, VeterinaryPartner.com Ruptured Anterior (Cranial) Cruciate Ligament First, the Basics There are two cruciate ligaments that
Ruptured Anterior (Cranial) Cruciate Ligament
 THE PET HEALTH LIBRARY By Wendy C. Brooks, DVM, DipABVP Educational Director, VeterinaryPartner.com Ruptured Anterior (Cranial) Cruciate Ligament First, the Basics The knee is a fairly complicated joint.
THE PET HEALTH LIBRARY By Wendy C. Brooks, DVM, DipABVP Educational Director, VeterinaryPartner.com Ruptured Anterior (Cranial) Cruciate Ligament First, the Basics The knee is a fairly complicated joint.
TIBIAL PLATEAU LEVELING OSTEOTOMY (TPLO)
 TIBIAL PLATEAU LEVELING OSTEOTOMY (TPLO) Cruciate disease in the dog Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) disease is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in the dog. It affects the stifle joint, the equivalent
TIBIAL PLATEAU LEVELING OSTEOTOMY (TPLO) Cruciate disease in the dog Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) disease is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in the dog. It affects the stifle joint, the equivalent
Cruciate ligament injury
 Cruciate ligament injury This is an extremely common injury in dogs, less so in cats. Let s start by looking at the anatomy of the stifle (knee) joint of the dog. The important differences between the
Cruciate ligament injury This is an extremely common injury in dogs, less so in cats. Let s start by looking at the anatomy of the stifle (knee) joint of the dog. The important differences between the
Cranial cruciate ligament rupture in Dogs
 Clinical sheet - Surgery Cranial cruciate ligament rupture in Dogs Cranial cruciate ligament rupture is one of the most common orthopedic conditions in dogs. Rupture of the cranial cruciate ligament is
Clinical sheet - Surgery Cranial cruciate ligament rupture in Dogs Cranial cruciate ligament rupture is one of the most common orthopedic conditions in dogs. Rupture of the cranial cruciate ligament is
Cranial Cruciate disease
 Cranial Cruciate disease Anatomy The Cranial cruciate ligament is located in the stifle joint (or knee). It is a thick fibrous band that runs from the distal femur to the proximal tibia. It is designed
Cranial Cruciate disease Anatomy The Cranial cruciate ligament is located in the stifle joint (or knee). It is a thick fibrous band that runs from the distal femur to the proximal tibia. It is designed
Ruptured cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) Ruptured cruciate, Ruptured ligament, Ruptured anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), Torn ACL, Torn ligament
 1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net Category: Canine Ruptured cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) Ruptured cruciate, Ruptured ligament, Ruptured anterior cruciate ligament
1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net Category: Canine Ruptured cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) Ruptured cruciate, Ruptured ligament, Ruptured anterior cruciate ligament
CRUCIATE DISEASE - LATERAL SUTURE STABILISATION (LSS)
 CRUCIATE DISEASE - LATERAL SUTURE STABILISATION (LSS) Cruciate disease in the dog Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) disease is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in the dog. It affects the stifle
CRUCIATE DISEASE - LATERAL SUTURE STABILISATION (LSS) Cruciate disease in the dog Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) disease is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in the dog. It affects the stifle
Post Surgical Care of Distal Femoral Fracture
 Post Surgical Care of Distal Femoral Fracture Home patient care after orthopedic surgery is critical to the success of the surgery. Allowing your pet too much activity may alter the anticipated outcome
Post Surgical Care of Distal Femoral Fracture Home patient care after orthopedic surgery is critical to the success of the surgery. Allowing your pet too much activity may alter the anticipated outcome
Earlswood Veterinary Hospital Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA)
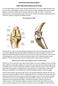 Earlswood Veterinary Hospital Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA) TTA is the abbreviation used for Tibital Tuberosity Advancement. This is the surgical procedure used to treat cranial cruciate ligament
Earlswood Veterinary Hospital Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA) TTA is the abbreviation used for Tibital Tuberosity Advancement. This is the surgical procedure used to treat cranial cruciate ligament
Cruciate Ligament Disease
 The Cranial Cruciate Ligament Cruciate Ligament Disease The cranial cruciate ligament (CrCL, aka anterior cruciate ligament or ACL) is one of several structures in the stifle (equivalent to our knee) that
The Cranial Cruciate Ligament Cruciate Ligament Disease The cranial cruciate ligament (CrCL, aka anterior cruciate ligament or ACL) is one of several structures in the stifle (equivalent to our knee) that
Patellar Instability. OrthoInfo Patella Instability Page 1 of 5
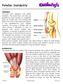 Patellar Instability OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with patella instability. This means that your knee cap (patella) has been partially or completely going out of place and is not tracking well against
Patellar Instability OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with patella instability. This means that your knee cap (patella) has been partially or completely going out of place and is not tracking well against
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis
 Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella)
 Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE POST-OPERATIVE CARE
 Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE POST-OPERATIVE CARE
Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE POST-OPERATIVE CARE
Cruciate Ligament Disease
 The Cranial Cruciate Ligament Cruciate Ligament Disease The cranial cruciate ligament (CrCL, aka in humans anterior cruciate ligament or ACL) is one of several structures in the stifle (equivalent to our
The Cranial Cruciate Ligament Cruciate Ligament Disease The cranial cruciate ligament (CrCL, aka in humans anterior cruciate ligament or ACL) is one of several structures in the stifle (equivalent to our
FEMORAL FRACTURE SURGERY: AT HOME CARE
 Your pet has had surgery for the treatment of a fractured femur. The femur has been put back together with: Stainless steel plate and screws Stainless steel pin(s) The objective of the operation is to
Your pet has had surgery for the treatment of a fractured femur. The femur has been put back together with: Stainless steel plate and screws Stainless steel pin(s) The objective of the operation is to
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress CRANIAL CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURIES SURGICAL MANAGEMENT Warrick J. Bruce BVSc(dist), MVM, DSAS(orthopaedics),
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress CRANIAL CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURIES SURGICAL MANAGEMENT Warrick J. Bruce BVSc(dist), MVM, DSAS(orthopaedics),
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Case history. swim to recovery
 Case history Name:......... Ralph Breed:......... Labradoodle Age:...... 2 Sex: Male Weight (at start):... 30.3kg (4.77st) Condition:....... Bilateral hip dysplasia Owned by: Phil and Maggie Crathern Surgical
Case history Name:......... Ralph Breed:......... Labradoodle Age:...... 2 Sex: Male Weight (at start):... 30.3kg (4.77st) Condition:....... Bilateral hip dysplasia Owned by: Phil and Maggie Crathern Surgical
Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture
 6910 Carpenter Fire Station Road, Cary NC 27519 Phone (919) 545-1001 www.quartetvet.com Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture This information is provided to help you understand the condition that has been
6910 Carpenter Fire Station Road, Cary NC 27519 Phone (919) 545-1001 www.quartetvet.com Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture This information is provided to help you understand the condition that has been
Midvalley Animal Clinic 6047 S. Redwood Road Salt Lake City, UT Office Phone (801) Paul Haderlie, DVM
 Midvalley Animal Clinic 6047 S. Redwood Road Salt Lake City, UT 84123 Office Phone (801) 269-1213 Paul Haderlie, DVM Cranial Cruciate post-operative information, care and rehabilitation Alertness Your
Midvalley Animal Clinic 6047 S. Redwood Road Salt Lake City, UT 84123 Office Phone (801) 269-1213 Paul Haderlie, DVM Cranial Cruciate post-operative information, care and rehabilitation Alertness Your
Knee Pain Solutions. Assess Your Pain. Make a Plan. Take Action
 Knee Pain Solutions Assess Your Pain Make a Plan Take Action By Jared Evans Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist Giammalva Fitness Director There are many different causes of knee pain and understanding
Knee Pain Solutions Assess Your Pain Make a Plan Take Action By Jared Evans Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist Giammalva Fitness Director There are many different causes of knee pain and understanding
Straight Spine Safe Spine Newsletter May Is National Correct Posture Month, but Every Day Should Be Perfect Posture Day
 Straight Spine Safe Spine Newsletter May Is National Correct Posture Month, but Every Day Should Be Perfect Posture Day May is Correct Posture Month, but every day should be Perfect Posture Day. This may
Straight Spine Safe Spine Newsletter May Is National Correct Posture Month, but Every Day Should Be Perfect Posture Day May is Correct Posture Month, but every day should be Perfect Posture Day. This may
This page is intentionally blank
 This page is intentionally blank 1 Focus on Canine Sports Medicine Cranial Cruciate Ligament Injury in Agility Dogs Part 1 By Sherman O. Canapp, Jr., DVM, MS, Diplomate ACVS TIEN TRAN PHOTOGRAPHY Kili,
This page is intentionally blank 1 Focus on Canine Sports Medicine Cranial Cruciate Ligament Injury in Agility Dogs Part 1 By Sherman O. Canapp, Jr., DVM, MS, Diplomate ACVS TIEN TRAN PHOTOGRAPHY Kili,
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
What is arthroscopy? Normal knee anatomy
 What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS
 SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
ACL Reconstruction. Role of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament. Treatment of ACL tears. ACL Reconstruction
 Role of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament The ACL stabilizes the knee when jumping, pivoting, or cutting. It prevents the shinbone (tibia) from sliding forward on the thigh bone (femur). ACL tears often occur
Role of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament The ACL stabilizes the knee when jumping, pivoting, or cutting. It prevents the shinbone (tibia) from sliding forward on the thigh bone (femur). ACL tears often occur
Basic Therapeutic Exercise for the Dog 65
 Stifle Region (Distal Femur to Hock) Rehabilitation Following Stifle (Knee)/Distal Femoral Surgery and Trauma Recovery following knee surgery may take 12 weeks or more. For the first 10 weeks, your dog
Stifle Region (Distal Femur to Hock) Rehabilitation Following Stifle (Knee)/Distal Femoral Surgery and Trauma Recovery following knee surgery may take 12 weeks or more. For the first 10 weeks, your dog
May 2011, Issue 31. In addition to our regular ER hours, AMVS is providing emergency and critical care services to your patients: Fridays, all day
 Page 1 of 5 Having Trouble Viewing this Email? Click Here You're receiving this email because of your relationship with Aspen Meadow Veterinary Specialists. Please confirm your continued interest in receiving
Page 1 of 5 Having Trouble Viewing this Email? Click Here You're receiving this email because of your relationship with Aspen Meadow Veterinary Specialists. Please confirm your continued interest in receiving
PARTIAL CARPAL ARTHRODESIS: AT HOME CARE
 Your pet has had surgery for the treatment of severely damaged ligaments of the carpus (wrist). The aim of the surgery is to convert the small joint spaces within the wrist into one fused bone. This replaces
Your pet has had surgery for the treatment of severely damaged ligaments of the carpus (wrist). The aim of the surgery is to convert the small joint spaces within the wrist into one fused bone. This replaces
Physical Therapy/Core Strengthening Exercises
 303 91 st Ave. NE Ste. A106 Lake Stevens, WA 98258 425-377-8620 www.lakestevensanimalhospital.com Physical Therapy/Core Strengthening Exercises Dogs with osteoarthritis or those recovering from a major
303 91 st Ave. NE Ste. A106 Lake Stevens, WA 98258 425-377-8620 www.lakestevensanimalhospital.com Physical Therapy/Core Strengthening Exercises Dogs with osteoarthritis or those recovering from a major
Patellar Luxation. The Patella. Dr. PJ Rocheleau, DVM and Associates 138 Tudhope St, Espanola ON, P5E 1S6
 Patellar Luxation The Patella The patella (equivalent to the knee cap ) is one of several structures in the stifle (equivalent to our knee) that provide joint stability and allow normal function. The stifle
Patellar Luxation The Patella The patella (equivalent to the knee cap ) is one of several structures in the stifle (equivalent to our knee) that provide joint stability and allow normal function. The stifle
What is an ACL Tear?...2. Treatment Options...3. Surgical Techniques...4. Preoperative Care...5. Preoperative Requirements...6
 Table of Contents What is an ACL Tear?....2 Treatment Options...3 Surgical Techniques...4 Preoperative Care...5 Preoperative Requirements...6 Postoperative Care...................... 7 Crutch use...8 Initial
Table of Contents What is an ACL Tear?....2 Treatment Options...3 Surgical Techniques...4 Preoperative Care...5 Preoperative Requirements...6 Postoperative Care...................... 7 Crutch use...8 Initial
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries One of the most common knee injuries is an anterior cruciate ligament sprain or tear.athletes who participate in high demand sports like soccer, football, and basketball
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries One of the most common knee injuries is an anterior cruciate ligament sprain or tear.athletes who participate in high demand sports like soccer, football, and basketball
Patellar Luxation. Anatomy, Function, and Dysfunction
 6910 Carpenter Fire Station Road, Cary NC 27519 Phone (919) 545-1001 Patellar Luxation This information is provided to help you understand the condition that has been diagnosed in your pet. We find that
6910 Carpenter Fire Station Road, Cary NC 27519 Phone (919) 545-1001 Patellar Luxation This information is provided to help you understand the condition that has been diagnosed in your pet. We find that
(Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage)
 Lateral Meniscus Tear (Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage) What is a lateral meniscus tear? The knee joint comprises of the union of two
Lateral Meniscus Tear (Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage) What is a lateral meniscus tear? The knee joint comprises of the union of two
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tears
 WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY ORTHOPEDICS Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tears Knowing what to expect for ACL surgery is key for a healthy surgery and recovery. Our sports medicine specialists are committed
WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY ORTHOPEDICS Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tears Knowing what to expect for ACL surgery is key for a healthy surgery and recovery. Our sports medicine specialists are committed
Postoperative Days 1-7
 ACL RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Postoperative Days 1-7 *IT IS EXTREMELY IMPORTANT THAT YOU WORK ON EXTENSION IMMEDIATELY Goals: * Control pain and swelling * Care for the knee and dressing *
ACL RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Postoperative Days 1-7 *IT IS EXTREMELY IMPORTANT THAT YOU WORK ON EXTENSION IMMEDIATELY Goals: * Control pain and swelling * Care for the knee and dressing *
Hip Pain. Anatomy of the hip
 Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
 GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
Tendon pain. What can be done?
 Tendon pain What can be done? Contents 1. Introduction to tendon s (what are they?). 2. Common Tendon s that become painful. 3. Tendon pain (Why is my tendon painful?). 4. Treatments for Tendon pain (what
Tendon pain What can be done? Contents 1. Introduction to tendon s (what are they?). 2. Common Tendon s that become painful. 3. Tendon pain (Why is my tendon painful?). 4. Treatments for Tendon pain (what
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
 What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
Arthritis of the Knee
 Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries
 A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries Learn About: Common ankle injuries Feet and Ankle Diagnosis and Treatment Ankle exercises Beginning your recovery Frequently asked questions Do s and Don t s Arthroscopy
A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries Learn About: Common ankle injuries Feet and Ankle Diagnosis and Treatment Ankle exercises Beginning your recovery Frequently asked questions Do s and Don t s Arthroscopy
Patellar Ligament Disease.
 Patellar Ligament Disease. The patellar ligament disease is a condition of the stifle where the cartilage keeping the patella in place over knee joint is weakened or damaged. The patella is held in place
Patellar Ligament Disease. The patellar ligament disease is a condition of the stifle where the cartilage keeping the patella in place over knee joint is weakened or damaged. The patella is held in place
PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY
 Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle Introduction Surgery to replace the ankle joint with an artificial joint (called ankle arthroplasty) is becoming more common. This surgery
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle Introduction Surgery to replace the ankle joint with an artificial joint (called ankle arthroplasty) is becoming more common. This surgery
Knee arthroscopy. Physiotherapy Department. Patient information leaflet
 Knee arthroscopy Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet What is a knee arthroscopy? A knee arthroscopy is a type of keyhole surgery performed through small cuts in the skin. An instrument
Knee arthroscopy Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet What is a knee arthroscopy? A knee arthroscopy is a type of keyhole surgery performed through small cuts in the skin. An instrument
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT (ACL) INJURIES
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT (ACL) INJURIES WHAT IS THE ACL? The ACL is a very strong ligament on the inside of the knee. It runs from the femur (thigh bone) obliquely down to the Tibia (shin bone). The
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT (ACL) INJURIES WHAT IS THE ACL? The ACL is a very strong ligament on the inside of the knee. It runs from the femur (thigh bone) obliquely down to the Tibia (shin bone). The
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101
 Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Non Surgical Management of Soft Tissue Injuries. Megan LeFave, DVM cvma
 Non Surgical Management of Soft Tissue Injuries Megan LeFave, DVM cvma Non Surgical Management of Soft Tissue Injuries Biomechanical Principles Common front limb and hind limb injuries In hospital treatments
Non Surgical Management of Soft Tissue Injuries Megan LeFave, DVM cvma Non Surgical Management of Soft Tissue Injuries Biomechanical Principles Common front limb and hind limb injuries In hospital treatments
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
A Patient s Guide to Collateral Ligament Injuries
 A Patient s Guide to Collateral Ligament Injuries 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
A Patient s Guide to Collateral Ligament Injuries 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
Achilles Tendonitis and Tears
 Achilles Tendonitis and Tears The Achilles tendon is an important structure for normal ankle motion and normal function, even for daily activities such as walking. Achilles tendonitis can occur in patients
Achilles Tendonitis and Tears The Achilles tendon is an important structure for normal ankle motion and normal function, even for daily activities such as walking. Achilles tendonitis can occur in patients
Post Surgical Care of Cruciate Ligament Rupture Repair
 Post Surgical Care of Cruciate Ligament Rupture Repair Home patient care after orthopedic surgery is critical to the success of the surgery. Allowing your pet too much activity may alter the anticipated
Post Surgical Care of Cruciate Ligament Rupture Repair Home patient care after orthopedic surgery is critical to the success of the surgery. Allowing your pet too much activity may alter the anticipated
BICEPS TENDON TENDINITIS (PROXIMAL) AND TENOSYNOVITIS
 BICEPS TENDON TENDINITIS (PROXIMAL) AND TENOSYNOVITIS Description Proximal biceps tendon tendinitis and tenosynovitis is characterized by pain at the front of the shoulder and upper arm caused by inflammation
BICEPS TENDON TENDINITIS (PROXIMAL) AND TENOSYNOVITIS Description Proximal biceps tendon tendinitis and tenosynovitis is characterized by pain at the front of the shoulder and upper arm caused by inflammation
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #7: Clinical Applications
 Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #7: Clinical Applications 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. www.benbenjamin.com 3 Webinar Goal To stretch and challenge your ability
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #7: Clinical Applications 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. www.benbenjamin.com 3 Webinar Goal To stretch and challenge your ability
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE
 ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
BACK SPASM. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
Everything. You Should Know. About Your Ankles
 Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Arthritis Clermont Animal Hospital, Inc.
 Arthritis Introduction The term arthritis refers to joint inflammation and swelling which leads to discomfort, stiffness, decreased ease of movement, and pain. There are a number of causes of arthritis
Arthritis Introduction The term arthritis refers to joint inflammation and swelling which leads to discomfort, stiffness, decreased ease of movement, and pain. There are a number of causes of arthritis
What Are Sports Injuries?
 What Should I Do if I Get Injured? Never try to "work through" the pain of a sports injury. Stop playing or exercising when you feel pain. Playing or exercising more only causes more harm. Some injuries
What Should I Do if I Get Injured? Never try to "work through" the pain of a sports injury. Stop playing or exercising when you feel pain. Playing or exercising more only causes more harm. Some injuries
Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents
 A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Patellofemoral Joint Allison Mourad December 20, 2013
 Patellofemoral Joint Allison Mourad December 20, 2013 The patellofemoral joint is located in the hind leg of a canine and plays a key role in dynamic mobility. This joint enables the dog to sit, walk,
Patellofemoral Joint Allison Mourad December 20, 2013 The patellofemoral joint is located in the hind leg of a canine and plays a key role in dynamic mobility. This joint enables the dog to sit, walk,
MEDVET TTA & TPLO. Use Only. Home Recovery Guide. A resource for families of MedVet Surgery patients
 A resource for families of MedVet Surgery patients Home Recovery Guide TTA & TPLO Preparing the home for your pet s recovery after surgery Rehabilitation and strengthening exercises your family can perform
A resource for families of MedVet Surgery patients Home Recovery Guide TTA & TPLO Preparing the home for your pet s recovery after surgery Rehabilitation and strengthening exercises your family can perform
TTA. Common Tangent Method
 TTA Common Tangent Method This document is derived from a presentation by Dr. Randy Boudrieau DVM, Dipl. ACVS, ECVS, Prof. of Surgery, Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine, Tufts University IVET DESIG
TTA Common Tangent Method This document is derived from a presentation by Dr. Randy Boudrieau DVM, Dipl. ACVS, ECVS, Prof. of Surgery, Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine, Tufts University IVET DESIG
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
Vibration (i.e., driving a Lack of exercise
 What is low back pain? Almost everyone has back pain at one time or another. The pain may be in the center of the back or to one side, or may move down the leg. Besides pain in the back, the symptoms may
What is low back pain? Almost everyone has back pain at one time or another. The pain may be in the center of the back or to one side, or may move down the leg. Besides pain in the back, the symptoms may
TRAINING GUIDE S H O U L D E R H E A L T H & P E R F O R M A N C E P A R T N E R W I T H
 TRAINING GUIDE S H O U L D E R PA R T N E R W I T H H E A L T H & P E R F O R M A N C E ABOUT Crossover Symmetry provides equipment, education, and training for athletes who want to end shoulder pain and
TRAINING GUIDE S H O U L D E R PA R T N E R W I T H H E A L T H & P E R F O R M A N C E ABOUT Crossover Symmetry provides equipment, education, and training for athletes who want to end shoulder pain and
Cytology of Neoplasia An Essential Component of Diagnosis
 A Peer-Reviewed Journal Cytology of Neoplasia An Essential Component of Diagnosis September/October 2012 Volume 2, Issue 5 Internal MedIcIne Practice Pearls defeating ticks Preventing Tick-Borne Disease
A Peer-Reviewed Journal Cytology of Neoplasia An Essential Component of Diagnosis September/October 2012 Volume 2, Issue 5 Internal MedIcIne Practice Pearls defeating ticks Preventing Tick-Borne Disease
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty
![Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty](/thumbs/90/102636395.jpg) Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Copyright Vanderbilt Sports Medicine. Table of Contents. The Knee Cap and Knee Joint...2. What is Patellofemoral Pain?...4
 Table of Contents The Knee Cap and Knee Joint...2 What is Patellofemoral Pain?....4 What to Expect From a Medical Evaluation....6 What to Expect After Therapy....7 1 The Kneecap and Knee Joint The knee
Table of Contents The Knee Cap and Knee Joint...2 What is Patellofemoral Pain?....4 What to Expect From a Medical Evaluation....6 What to Expect After Therapy....7 1 The Kneecap and Knee Joint The knee
A Patient s Guide. ACL Injury: Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, Ø Preoperative and postoperative. surgery and recovery.
 ACL Injury: A Patient s Guide Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, surgery and recovery Ø Preoperative and postoperative guidelines Mia S. Hagen, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics
ACL Injury: A Patient s Guide Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, surgery and recovery Ø Preoperative and postoperative guidelines Mia S. Hagen, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics
Biceps Femoris Muscle in Dogs Diana Powell 11/25/2016
 Biceps Femoris Muscle in Dogs Diana Powell 11/25/2016 The Biceps Femoris is the largest muscle in the muscle group that makes up the hamstring. The Biceps Femoris is covered only by fascia and skin and
Biceps Femoris Muscle in Dogs Diana Powell 11/25/2016 The Biceps Femoris is the largest muscle in the muscle group that makes up the hamstring. The Biceps Femoris is covered only by fascia and skin and
Osteochondritis Dissecans
 Osteochondritis Dissecans Carrie Lane, MA, SAMP October 14, 2011 Table of Contents Introduction What is Osteochondritis Dissecans? (OCD) The Nature of the Condition Common Treatment Approaches Rehabilitation
Osteochondritis Dissecans Carrie Lane, MA, SAMP October 14, 2011 Table of Contents Introduction What is Osteochondritis Dissecans? (OCD) The Nature of the Condition Common Treatment Approaches Rehabilitation
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
ACTIVE AGING.
 Shoulder Pain Rehabilitation Protocol Rotator Cuff Syndrome Shoulder impingement The Resistance Chair Solution Shoulder Impingement a. Shoulder impingement is one of the most common causes of shoulder
Shoulder Pain Rehabilitation Protocol Rotator Cuff Syndrome Shoulder impingement The Resistance Chair Solution Shoulder Impingement a. Shoulder impingement is one of the most common causes of shoulder
Dr. Berkson offers a list of some of the most common exercise-related injuries:
 AS we get older, we become more vulnerable to injuries, in part because we are less agile than we used to be, and we have also lost some of our former bone and muscle mass, says the October 2013 issue
AS we get older, we become more vulnerable to injuries, in part because we are less agile than we used to be, and we have also lost some of our former bone and muscle mass, says the October 2013 issue
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers
 CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
Total Hip Replacement Surgery
 Total Hip Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview What is Total hip replacement (THA)? Anatomy Preparing for surgery The Operation Post-Operative Possible Complications Exercise Restrictions Overview
Total Hip Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview What is Total hip replacement (THA)? Anatomy Preparing for surgery The Operation Post-Operative Possible Complications Exercise Restrictions Overview
This information leaflet has been produced by Senior Physiotherapists working at Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
 Hip Osteoarthritis This information leaflet has been produced by Senior Physiotherapists working at Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Osteoarthritis (OA) is a painful inflammatory condition
Hip Osteoarthritis This information leaflet has been produced by Senior Physiotherapists working at Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Osteoarthritis (OA) is a painful inflammatory condition
Chapter 2: Safe and Smart Physical Activity. Lesson 2.2: Physical Activity and Injury Taking Charge: Building Self-Confidence
 Chapter 2: Safe and Smart Physical Activity Lesson 2.2: Physical Activity and Taking Charge: Building Self-Confidence Lesson Objectives: List and describe some activity-related physical injuries. List
Chapter 2: Safe and Smart Physical Activity Lesson 2.2: Physical Activity and Taking Charge: Building Self-Confidence Lesson Objectives: List and describe some activity-related physical injuries. List
The S.T.A.R. Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement. Patient Information
 The S.T.A.R. Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement Patient Information Patient Information This patient education brochure is presented by Small Bone Innovations, Inc. Patient results may vary. Please
The S.T.A.R. Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement Patient Information Patient Information This patient education brochure is presented by Small Bone Innovations, Inc. Patient results may vary. Please
Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain
 What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
Cataracts in Animals
 Cataracts in Animals Cataracts in Animals Cross section of the Eye WHAT IS A CATARACT? A cataract is an opacity of the lens inside the eye. The lens is usually clear and transparent. The lens helps focus
Cataracts in Animals Cataracts in Animals Cross section of the Eye WHAT IS A CATARACT? A cataract is an opacity of the lens inside the eye. The lens is usually clear and transparent. The lens helps focus
ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE. Description
 Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
THE RECOVERY PROCESS
 THE RECOVERY PROCESS PART II If you're considering a major Orthopaedic surgical procedure to relieve pain in your back, knee, or hip, there's a lot to consider. These procedures, while common, do come
THE RECOVERY PROCESS PART II If you're considering a major Orthopaedic surgical procedure to relieve pain in your back, knee, or hip, there's a lot to consider. These procedures, while common, do come
Arthritis. in dogs & cats
 Arthritis in dogs & cats What is Arthritis? Degenerative joint disease or arthritis is a common problem in dogs and cats as they age. In fact, arthritis affects one in five adult dogs. It is more prevalent
Arthritis in dogs & cats What is Arthritis? Degenerative joint disease or arthritis is a common problem in dogs and cats as they age. In fact, arthritis affects one in five adult dogs. It is more prevalent
Partial Knee Replacement
 Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Official reprint from UpToDate UpToDate
 UpToDate L* & Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2012 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
UpToDate L* & Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2012 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
