Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
|
|
|
- Bertram Rogers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An Original Study Effects of a Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitor on Fracture Healing in a Rat Model Michael A. Herbenick, MD, Dominic Sprott, MBBS, Harold Stills, DVM, and Matthew Lawless, MD Abstract Since the advent of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX- 2) inhibitors, little research has been done on the effects of these medications on fracture healing. In the study reported here, we sought to determine whether a COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, affects strength and amount of healing callus formed after a fracture. Forty-eight male Sprague-Dawley rats were evaluated for impairment of fracture healing with celecoxib use. Compared with controls, celecoxib-treated rats had a significant decrease in force required for refracture (P =.0199). We do not recommend routine use of celecoxib in postfracture pain control, particularly when fracture union is tenuous. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have been one of the mainstays of treatment for pain after surgery and in patients with fractures or soft-tissue injuries. The influence of NSAIDs on bone metabolism has been well documented. There is evidence supporting and refuting the notion that NSAIDs inhibit bone healing. 1-5 However, some authors believe that differences in protocol methodology (eg, drug dosage, dosing rates, timing and method of evaluating fracture healing) account for some of the variations in study outcomes. 6 Several investigators have reported on the inhibitory effects of NSAIDs on bone formation, bone remodeling, and mineralization in animal models NSAIDs have been shown to induce qualitative histologic changes in the healing process. Immaturity of histologic grade of callus formation with NSAID use was noted early during the inflammatory process and continued throughout the course of healing. 3,6,16 Local blood flow to the site of an osteotomy was shown to be markedly impaired early in the course of healing. 17 NSAIDs have also been shown to decrease mechanical rigidity and the bending moment at a fracture or osteotomy Dr. Herbenick is Assistant Professor, Dr. Sprott is Research Assistant, Dr. Stills is Associate professor, and Dr. Lawless is Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Wright State University School of Medicine, Dayton, Ohio. Address correspondence to: Michael A. Herbenick, MD, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Wright State University School of Medicine, 30 E Apple St, Suite 2200, Dayton, OH (tel, ; fax, ; , maherbenick@mvh.org). Am J Orthop. 2008;37(7):E133-E137. Copyright Quadrant HealthCom Inc All rights reserved. site. 6,14,18,19 Many investigators have reported no difference in quantitative amount of direct or radiographically measured callus formed during NSAID use. 2,19,20 However, as testing in these studies demonstrated significantly decreased mechanical strength of healing callus with NSAID use, it may not be advisable to rely solely on radiographs to demonstrate completion of healing. With respect to fracture healing, cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) inhibitors have not been scrutinized as much as nonselective NSAIDs have. In the study reported here, we sought to examine the effects of a COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, on mechanical strength and amount of callus formed in a fracture model. As COX-2 inhibitors (like nonselective NSAIDs) inhibit the inflammatory process, we hypothesized that we would find a decrease in the mechanical strength of callus and a quantitative difference in the amount of callus. Materials and Methods Fifty male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing approximately 350 g were acclimated to their environment with food and water for 7 days before surgery. The animals were maintained with standard laboratory feed and water for the duration of the experiment. All surgery, recovery, and housing of the rats in this study were conducted at the Wright State University Animal Laboratory Facility. Each rat underwent a surgical procedure after anesthesia was applied. Ketamine 35 mg/kg plus xylazine 5 mg/kg intraperitoneal was used for induction. Inhaled isoflurane was used for maintenance anesthesia. Once the rat was anesthetized, its right knee and back (just posterior to the scapulae) were shaved and surgically scrubbed. A 21- gauge needle (0.9 mm in diameter, 2.5 cm in length) was inserted percutaneously into the intramedullary canal of the femur in a retrograde fashion. A fracture was then accomplished without violating the skin using a jig and a pneumatic device. The ends of the femur were supported laterally while the pneumatic device was applied to the medial aspect of the femur to cause a mid-diaphyseal fracture. An anteroposterior radiograph was then obtained of the affected limb under anesthesia to ensure that a transverse, mid-diaphyseal fracture was created. A small incision was made in the area prepared on the back of the neck, and a subcutaneous pocket was created with a hemostat. An Alzet 2001 osmotic pump (200 ul volume) filled with sufentanil (2.5 μg/ml) was placed subcutaneously in this space. The wound was then closed with staples. Postoperative care consisted of routine wound checks and evaluation of behavior, including motion and appetite. July 2008 E133
2 Effects of a Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitor on Fracture Healing in a Rat Model Mean Force Body Weights Mean Force control study Weight (g) All Weeks Figure 1. Mean load to failure for control and treatment (celecoxib) groups of rats. Animal weights were obtained on arrival at the laboratory, at time of surgery, and every 2 weeks thereafter. The rats were not immobilized after surgery. Pain management consisted of sufentanil administered by osmotic pump for 1 week at a rate of approximately 1 μl/h. Beginning on the day of surgery, rats were placed in the control group or the treatment group. The control group received water and food without any COX-2 inhibitor. The effective daily dose of celecoxib in rats is 5 to 30 mg/kg. The amount of rat chow consumed daily by a rat of the size used in this study is 32 g. 21 For the treatment group, the drug was administered by grinding a 100-mg tablet of celecoxib into 1 kg of feed and mixing thoroughly. Treatment group rats received celecoxib at a mean of 3.2 mg/d, well within the 1.6- to 10-mg/d dosing range. This delivery method and this dosing range have been used in similar studies. 21 Rats were housed 2 per cage during the study, and limitations on their activity after the index procedure were minimal. Soon after the procedure, 2 of the 50 rats were euthanized (see Results). Osmotic pumps were removed between postoperative days 7 and 10, per manufacturer recommendation. Each of the remaining 48 rats received ketamine 35 mg/kg plus xylazine 5 mg/kg intraperitoneal for induction and maintenance with inhaled isoflurane. The site of the pump was prepared in a similar manner to the initial surgery, with shaving and surgical scrubbing. Staples were removed and the incision reopened. The osmotic pump was removed, and the wound was closed once again with staples. This procedure produced very minimal discomfort in the animals, and no additional pain medication was required. Twelve animals (6 control, 6 treatment) were randomly selected for sacrifice (by carbon dioxide overdose) at each of 4 intervals (2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks). Fractured femurs were removed en bloc, and all soft tissue was carefully dissected free. Calipers were used to measure the length and maximum width of the callus. Specimens were set aside in moist physiologic saline solution and refrigerated until mechanical testing. Before mechanical testing, a needle driver was used to remove the intramedullary needle. A Days after Surgery Figure 2. Mean weights of rats over course of study. 3-point bending technique was used in measuring the loadbearing capability of the healing bone. Each specimen was supported on 2 parallel bars with the callus in the center; a constant load was applied until fracture occurred. The load/deformation data were acquired and the load at failure recorded. The t test was used to compare the control and treatment groups with respect to amount of force needed for fracture and cross-sectional elliptical area. We planned for a 20% difference in mean amount of force needed for fracture (control, 100 N; treatment, 80 N) and considerable variability among animals in amount of force (ie, 75% of anticipated group means: control, 75 N; treatment, 60 N). With a at.05, b at.20, and power at 80%, 15 rats per group were needed. Thus, we had an adequate sample size for the overall comparison between the 2 groups (actual sample size per group, 24) but inadequate power for comparisons of the sacrifice intervals (2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks). The practicalities of our study and its limited budget permitted only 6 animals per interval. Inferences were made at P =.05. All analyses were conducted with SAS version 8.2. Results We began the study with 50 rats. Soon after the index procedure, 1 rat had an intramedullary needle misplaced in the soft tissues and then a fracture created. After multiple failed attempts to blindly insert the intramedullary needle past the fracture site, we had to euthanize this rat. Another rat had adequate intramedullary fixation, but a comminuted fracture pattern was found on postfracture radiographs. This rat also was euthanized. The remaining 48 rats were divided into 2 groups, control (n = 24) and treatment (n = 24). Figure 1 shows mean load to failure for the control and treatment groups. Mean force needed to break femurs in the treatment group ( N) was significantly (P =.02) lower than that in the control group ( N) when taken across all healing times. Mechanical load comparisons between control and treatment groups at the 4 sacrifice intervals (2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks) were not significant. In 6 of the 48 rats, the fracture remodeled enough that E134 The American Journal of Orthopedics
3 M. A. Herbenick et al fracture height could not be accurately determined with calipers. Two of these 6 rats were from the week 8 control group, 2 were from the week 12 control group, and 2 were from the week 12 treatment group. Subtracting these 6 rats left 42 (20 control, 22 treatment) for analysis of the crosssectional elliptical area. Callus area (A) was calculated as an elliptical area in which A = P height/2 width/2. In the overall comparison, there was no statistically significant difference in mean cross-sectional elliptical area between the control group ( mm 2 ) and the treatment group ( mm 2 ). In addition, none of the weekly interval comparisons was significant for cross-sectional area. Weight data appear in Figure 2. The rats gained weight during the acclimation period and, as a whole, lost weight by the 2-week postoperative weighing. We believe the weight loss is secondary to increased metabolic need after surgery. On daily recorded observations, the rats were noted to be moving with minimal discomfort and eating regularly. Drug delivery may have been compromised during the 2 weeks after surgery, but that explanation is less plausible given the noticeable difference in fracture strength. Discussion NSAID use is extremely common in the treatment of patients with fracture, soft-tissue injury, and postoperative pain. Narcotic medications are used acutely for pain in these situations as well, but they are often supplemented with an NSAID. To guard against dependency and abuse, many physicians try to limit their patients narcotic use. Often, pain persists after narcotics are stopped, and patients are continued or started on an anti-inflammatory medication for the many weeks of fracture healing. However, many studies have shown that NSAID use delays and impairs fracture healing. 6-8,10,13-20,22 Use of anti-inflammatory medications during fracture care remains a clinical concern. Reports of nonunion and delayed union of fractures are abundant. 23 Study results that show NSAID-related decreases in spinal fusion 24,25 and femoral shaft union rates 26 have changed the practice habits of many orthopedic surgeons, such that they avoid NSAID use during fracture care. Celecoxib was the first drug in a relatively new class of NSAIDs, the COX-2 inhibitors. Nonselective NSAIDs block both COX-2 and cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1), whereas these new selective medications target only COX-2. COX-1 is found in almost all tissues and appears to provide homeostatic control for prostaglandin levels in tissues but does not have a role in inflammation. 21,27 COX-2 is an inducible enzyme found in tissues and is produced only at inflammation sites. 28,29 The obvious advantage of COX- 2 specific inhibitors is their ability to block inflammation without disrupting the normal homeostatic functions of prostaglandins throughout the body. In several studies, celecoxib has been shown to provide arthritis patients with pain relief comparable to what nonselective NSAIDs provide, but without increased incidence of gastrointestinal or bleeding complication Celecoxib and other COX-2 inhibitors have been used for acute pain after surgery and in patients with fractures or soft-tissue injuries. There is some indication that COX-2 inhibitors may adversely affect ligament healing. 21 Since the advent of COX-2 selective inhibitors, however, not much research has been conducted on the effect of these medications on fracture healing. Three COX-2 inhibitors have been introduced for clinical use: celecoxib, rofecoxib, and valdecoxib. Recently, rofecoxib was removed from the market because of reported cardiac side effects. Celecoxib preferentially inhibits the cyclooxygenase activity of COX-2 with approximately 8-fold selectivity relative to COX The COX-2 enzyme has the primary role in prostaglandin production with respect to the inflammatory process. Inhibition of prostaglandin and cytokines in the acute inflammatory phase is theorized to decrease the vascular and cellular responses that lead to bone regeneration and healing. 19,36-38 Prostaglandins are known to promote angiogenesis 39 and have direct effects on increasing osteoblast cell division and osteoid production. 40,41 Tanaka and colleagues 42 also found that stimulation of prostaglandin E2 receptors accelerated bone repair and stimulated osteogenesis. Therefore, we would expect a more dramatic effect on fracture inhibition with a COX-2 inhibitor than with a nonselective NSAID. Simon and colleagues 22 showed that COX-2 has an essential function during normal fracture healing and that COX-2 selective NSAID inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis stops normal fracture healing. In addition, Robertson and colleagues 43 demonstrated that the COX-2 enzyme has an important regulatory role in bone homeostasis in mice. Our observations support the hypothesis that inhibition of the COX-2 enzyme impairs fracture healing. We used a rat closed femur fracture model to show that biomechanical strength is markedly (P =.0199) decreased in animals given celecoxib. Mean force needed to break femurs in our treatment group ( N) was significantly (P =.02) lower than that in our control group ( N) when taken across all healing times. In addition, we found no statistical difference between these groups at the 4 sacrifice intervals (2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks). Directly measured callus did not differ significantly between the treatment and control groups a result that may be related to an imperceptible sensitivity error in the calipers used. However, previous studies have had similar quantitative callus results. Our raw data show that celecoxib had the most pronounced effect on the strength of fracture callus early in the inflammatory phase (2 weeks). During this phase, there was a 50% reduction in fracture strength in our treatment group compared with the control group. Brown and colleagues 44 found that rats treated with celecoxib had reduced stiffness, strength, radiographic evidence of healing, and histologic grade of callus 4 weeks after fracture. In their study, fractures were produced in the manner described by Bonnarens and Einhorn 45 (with use of a materials testing machine), and the drug was delivered with chocolate. We used a different July 2008 E135
4 Effects of a Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitor on Fracture Healing in a Rat Model fracture method and a different drug-delivery method. Our results showed that impairment of fracture healing at 4 intervals was not statistically significant. The findings of Brown and colleagues are consistent with the data from our study. The estimated plasma half-life of celecoxib after a single dose is 4 hours in male rats (vs 12 hours in humans). 46 Consequently, we thought that our rats blood drug levels might be an underestimation of humans COX-2 inhibition levels over a 24-hour period. Orally dosing rats every 4 hours for up to 12 weeks was felt to be an extremely difficult undertaking. Brown and colleagues 44 dosed their study animals with drug plus chocolate just once a day. In their scheme, blood drug levels would be high for only a very short time. Their dosing regimen ensures that rats receive the drug, but we believe that blood drug levels throughout most of the day would be negligible. Appropriate drug delivery remains an issue in fracture studies. The goal of providing laboratory animals with reasonable blood drug levels comparable to human levels, both in quantity and duration, has not been achieved in any fracture study. More work needs to be done to determine the true effects that a steady dose of anti-inflammatory medication has on fracture healing. Our study rats received celecoxib daily until they were sacrificed. This scenario is unlike clinical scenarios in which COX-2 inhibitors are used acutely to manage early pain, inflammation, and swelling after a fracture. Investigators have thought that anti-inflammatory drugs, even those given daily only for a short time after injury, can impair the early inflammatory processes enough to affect bone formation and healing. 20,47 Gerstenfeld and colleagues 48 recently demonstrated that COX-2 specific drugs inhibit fracture healing more than nonspecific NSAIDs do and that the magnitude of this effect is related to treatment duration. After treatment was discontinued, however, prostaglandin E2 levels were gradually restored, and fracture callus strength returned to levels similar to those of controls. In another recent study, Simon and O Connor 49 demonstrated that higher doses and longer periods of celecoxib treatment were more detrimental to fracture healing than were lower doses and shorter periods. In contrast to Gerstenfeld and colleagues, Simon and O Connor found that short-term use of a high-dose COX-2 inhibitor had a deleterious effect on ultimate fracture healing. Drug dosage levels may contribute to the discrepancy in these study results. We dosed our animals at approximately 3.2 mg/kg/d, similar to the 4-mg/kg/d dose used by Simon and O Connor. Although we did not stop the drug during our study, we found a similar trend for continued impairment of fracture callus strength throughout the healing process in our treatment group compared with our control group. Some authors have recommended avoiding or discontinuing use of these medications during bone healing. 22,38,49,50 Clearly, continued research on fracture healing is needed so that clinicians can be appropriately advised regarding use of NSAIDs and COX-2 inhibitors during fracture healing. Conclusions This study was designed to examine the effects of COX-2 inhibitors on biomechanical strength and direct callus measurement in fracture healing. We found a statistically significant difference in the biomechanical strength of fracture callus in the pooled data from our treatment rats and control rats, but we did not find any statistically significant difference in biomechanical strength at 4 sacrifice intervals (2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks). At the 8-week interval, more callus was noted in our treatment group relative to the control group. However, no statistically significant difference was found in mean elliptical area of callus formation at any interval. Our data suggest that COX-2 enzyme function is important for fracture healing and that caution should be used when considering use of COX-2 inhibitors in patients with fractures. Authors Disclosure Statement This study was funded by a Wright State University Seed Grant and a Dayton Area Graduate Medical Education Consortium Grant. The authors report no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article. References 1. Adolphson P, Abbaszadegan H, Jonsson U, Dalén N, Sjöberg HE, Kalén S. No effects of piroxicam on osteopenia and recovery after Colles fracture. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1993;112(3): Ho ML, Chang JK, Wang GJ. Effects of ketorolac on bone repair: a radiographic study in modeled demineralized bone matrix grafted rabbits. Pharmacology. 1998;57(3): Mbugua SW, Skoglund LA, Lokken P. Effects of phenylbutazone and indomethacin on the post-operative course following experimental orthopaedic surgery in dogs. Acta Vet Scand. 1989;30(1): Moed BR, Resnick RB, Fakhouri AJ, Nallamothu B, Wagner RA. Effect of two nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on heterotopic bone formation in a rabbit model. J Arthroplasty. 1994;9(1): More RC, Kody MH, Kabo JM, Dorey FJ, Meals RA. The effects of two nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on limb swelling, joint stiffness, and bone torsional strength following fracture in a rabbit model. Clin Orthop. 1989;(247): Altman RD, Latta LL, Keer R, Renfree K, Hornicek FJ, Banovac K. Effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on fracture healing: a laboratory study in rats. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(5): Allen HL, Wase A, Bear WT. Indomethacin and aspirin: effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents on the rate of fracture repair in the rat. Acta Orthop Scand. 1980;51(4): Elves MW, Bayley I, Roylance PJ. The effect of indomethacin upon experimental fractures in the rat. Acta Orthop Scand. 1982;53(1): Huo MH, Troiano NW, Pelker RR, Gundberg CM, Friedlaender GE. The influence of ibuprofen on fracture repair: biomechanical, biochemical, histologic, and histomorphometric parameters in rats. J Orthop Res. 1991;9(3): Lindholm TS, Tornkvist H. Inhibitory effect on bone formation and calcification exerted by the anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen: an experimental study on adult rat with fracture. Scand J Rheumatol. 1981;10(1): Obeid G, Zhang X, Wang X. Effect on ibuprofen on the healing and remodeling of bone and articular cartilage in the rabbit temporomandibular joint. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992;50(8): Ro J, Langeland N, Sander J. Effect of indomethacin on collagen metabolism of rat fracture callus in vitro. Acta Orthop Scand. 1978;49(4): Bo J, Sudmann E, Marton PF. Effect of indomethacin on fracture healing in rats. Acta Orthop Scand. 1976;47(6): Sudmann E, Dregelid E, Bessesen, Mørland J. Inhibition of fracture healing by indomethacin in rats. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979;9(5): Tornkvist H, Henrik Bauer FC, Nilsson OS. Influence of indomethacin on experimental bone metabolism in rats. Clin Orthop. 1985;(193): Reikeraas O, Engebretsen L. Effects of ketorolac tromethamine and indomethacin on primary and secondary bone healing: an experimental study in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998;118(1-2): E134 The American Journal of of Orthopedics
5 M. A. Herbenick et al 17. Keller J, Bunger C, Andereassen TT, Bak B, Lucht U. Bone repair inhibited by indomethacin: effects on bone metabolism and strength of rabbit osteotomies. Acta Orthop Scand. 1987;58(4): Engesaeter LB, Sudmann B, Sudmann E. Fracture healing in rats inhibited by locally administered indomethacin. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992;63(3): Keller J. Effects of indomethacin and local prostaglandin E2 on fracture healing in rabbits. Dan Med Bull. 1996;43(4): Hogevold HE, Grogaard B, Reikeraas O. Effect of short-term treatment with corticosteroids and indomethacin on bone healing: a mechanical study of osteotomies in rats. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992;63(6): Elder CL, Dahners LE, Weinhold PS. A cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor impairs ligament healing in the rat. Am J Sports Med. 2001;29(6): Simon AM, Manigrasso MB, O Connor JP. Cyclo-oxygenase 2 function is essential for bone fracture healing. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(6): Khan MI. Fracture healing: role of NSAIDs. Am J Orthop. 1997;26(6): Dimar JR, Ante WA, Zhang YP, Glassman SD. The effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on posterior spinal fusions in the rat. Spine. 1996;21(16): Glassman SD, Rose SM, Dimar JR, Puno RM, Campbell MJ, Johnson JR. The effect of postoperative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug administration on spinal fusion. Spine. 1998;23(7): Giannoudis PV, MacDonald DA, Matthews SJ, Smith RM, Furlong AJ, De Boer P. Nonunion of the femoral diaphysis: the influence of reaming and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(5): Jouzeau JY, Terlain B, Abid A, Nédélec E, Netter P. Cyclo-oxygenase isozymes: how recent findings affect thinking about nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Drugs. 1997;53(4): Crofford LJ. COX-1 and COX-2 tissue expression: implications and predictions. J Rheumatol. 1997;24(suppl 49): Lipsky PE. Role of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in health and disease. Am J Orthop. 1999;28(3 suppl): Bensen WG, Fiechtner JJ, McMillen JI, et al. Treatment of osteoarthritis with celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor: a randomized controlled trial. Mayo Clin Proc. 1999;74(11): Bensen WG, Zhao SZ, Burke TA, et al. Upper gastrointestinal tolerability of celecoxib, a COX-2 specific inhibitor, compared to naproxen and placebo. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(8): Goldstein JL, Correa P, Zhao WW, et al. Reduced incidence of gastroduodenal ulcers with celecoxib, a novel cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, compared to naproxen in patients with arthritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(4): Simon LS, Lanza FL, Lipsky PE, et al. Preliminary study of the safety and efficacy of SL-58635, a novel cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor: efficacy and safety in two placebo-controlled trials in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, and studies of gastrointestinal and platelet effects. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(9): Simon LS, Weaver AL, Graham DY, et al. Anti-inflammatory and upper gastrointestinal effects of celecoxib in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999;282(20): Riendeau D, Percival MD, Brideau C, et al. Etoricoxib (MK-0663): preclinical profile and comparison with other agents that selectively inhibit cyclooxygenase-2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;296(2): Banovac K, Renfree K, Makowski AL, Latta LL, Altman RD. Fracture healing and mast cells. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(6): Goldring MB, Goldring SR. Skeletal tissue response to cytokines. Clin Orthop. 1990;(258): Simmons DJ. Fracture healing perspectives. Clin Orthop. 1985;(200): Form DM, Auerbach R. PGE2 and angiogenesis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983;172(2): Hakeda Y, Hotta T, Kurihara N, et al. Prostaglandin E1 and F2 alpha stimulate differentiation and proliferation, respectively, of clonal osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells by different second messengers in vitro. Endocrinology. 1987;121(6): Kaneki H, Takasugi I, Fujieda M, Kiriu M, Mizuochi S, Ide H. Prostaglandin E2 stimulates the formation of mineralized bone nodules by a camp-independent mechanism in the culture of adult rat calvarial osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 1999;73(1): Tanaka M, Sakai A, Uchida S, et al. Prostaglandin E2 receptor (EP4) selective agonist (ONO-4819.CD) accelerates bone repair of femoral cortex after drill-hole injury associated with local upregulation of bone turnover in mature rats. Bone. 2004;34(6): Robertson G, Xien C, Chen D, et al. Alteration of femoral bone morphology and density in COX-2-/- mice. Bone. 2006;39(4): Brown KM, Saunders MM, Kirsch T, Donahue HJ, Reid JS. Effect of Cox- 2 specific inhibition on fracture-healing in the rat femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(1): Bonnarens F, Einhorn TA. Production of a standard closed fracture in laboratory animal bone. J Orthop Res. 1984;2(1): Davies NM, McLachlan AJ, Day RO, Williams KM. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of celecoxib: a selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitor. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2000;38(3): Gebuhr P, Wilbek H, Soelberg M. Naproxen for 8 days can prevent heterotopic ossification after hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop. 1995;(314): Gerstenfeld LC, Al-Ghawas M, Alkhiary YM, et al. Selective and nonselective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and experimental fracture-healing. Reversibility of effects after short-term treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1): Simon AM, O Connor JP. Dose and time-dependent effects of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition on fracture-healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(3): Einhorn TA. Do inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2 impair bone healing? J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(6): July 2008 E135 E137
N on-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
 65 REVIEW Do non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs adversely affect stress fracture healing? A short review P Wheeler, M E att... A literature search was performed to determine whether non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
65 REVIEW Do non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs adversely affect stress fracture healing? A short review P Wheeler, M E att... A literature search was performed to determine whether non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis
 Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
NSAIDs and tissue healing - bone. Sigbjørn Dimmen and Lars Engebretsen, Orthopaedic Center, Ullevaal University Hospital, Oslo, Norway
 NSAIDs and tissue healing - bone. Sigbjørn Dimmen and Lars Engebretsen, Orthopaedic Center, Ullevaal University Hospital, Oslo, Norway Prevalence of use of NSAIDs in sport Most used drug class in Olympic
NSAIDs and tissue healing - bone. Sigbjørn Dimmen and Lars Engebretsen, Orthopaedic Center, Ullevaal University Hospital, Oslo, Norway Prevalence of use of NSAIDs in sport Most used drug class in Olympic
Tobacco and Bone Health
 Tobacco and Bone Health Prof. Dr. Alok Chandra Agrawal MS Orthopaedics, DNB Orthopaedics, PhD Orthopaedics MAMS All India Institute of Medical Sciences Raipur CG Cigarette smoking is commonly identified
Tobacco and Bone Health Prof. Dr. Alok Chandra Agrawal MS Orthopaedics, DNB Orthopaedics, PhD Orthopaedics MAMS All India Institute of Medical Sciences Raipur CG Cigarette smoking is commonly identified
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
This document has not been circulated to either the industry or Consultants within the Suffolk system.
 New Medicine Report Document Status COX II Inhibitors In Acute Analgesia For Suffolk Drug & Therapeutics Committee Date of Last Revision 15 th February 2002 Reviewer s Comments There seems to be a growing
New Medicine Report Document Status COX II Inhibitors In Acute Analgesia For Suffolk Drug & Therapeutics Committee Date of Last Revision 15 th February 2002 Reviewer s Comments There seems to be a growing
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Title: Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs for Analgesia in Patients with Fracture: Evidence for Use
 Title: Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs for Analgesia in Patients with Fracture: Evidence for Use Date: 03 June 2008 Context and policy issues: In 2000-2001, 3.4 million Canadians aged 12 years or
Title: Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs for Analgesia in Patients with Fracture: Evidence for Use Date: 03 June 2008 Context and policy issues: In 2000-2001, 3.4 million Canadians aged 12 years or
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 Award Number: W81XWH-13-1-0188 TITLE: CaMKK2 Inhibition in Enhancing Bone Fracture Healing PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Uma Sankar, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Indiana University Bloomington, IN 47405 REPORT
Award Number: W81XWH-13-1-0188 TITLE: CaMKK2 Inhibition in Enhancing Bone Fracture Healing PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Uma Sankar, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Indiana University Bloomington, IN 47405 REPORT
Indomethacin and Celecoxib Impair Rotator Cuff Tendon-to-Bone Healing
 Excellence in Research Award Indomethacin and Celecoxib Impair Rotator Cuff Tendon-to-Bone Healing David B. Cohen,* MD, Sumito Kawamura, MD, John R. Ehteshami, MD, and Scott A. Rodeo, MD From Connecticut
Excellence in Research Award Indomethacin and Celecoxib Impair Rotator Cuff Tendon-to-Bone Healing David B. Cohen,* MD, Sumito Kawamura, MD, John R. Ehteshami, MD, and Scott A. Rodeo, MD From Connecticut
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Gastrointestinal Safety of Coxibs and Outcomes Studies: What s the Verdict?
 Vol. 23 No. 4S April 2002 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S5 Proceedings from the Symposium The Evolution of Anti-Inflammatory Treatments in Arthritis: Current and Future Perspectives Gastrointestinal
Vol. 23 No. 4S April 2002 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S5 Proceedings from the Symposium The Evolution of Anti-Inflammatory Treatments in Arthritis: Current and Future Perspectives Gastrointestinal
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons.
 Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
Effect of Post-Operative Ketorolac Administration on Bone Healing in Ankle Fractures
 Effect of Post-Operative Ketorolac Administration on Bone Healing in Ankle Fractures Elizabeth McDonald, BA Brian Winters, MD Rachel Shakked, MD David I. Pedowitz, MD Steven M. Raikin, MD Joseph N. Daniel,
Effect of Post-Operative Ketorolac Administration on Bone Healing in Ankle Fractures Elizabeth McDonald, BA Brian Winters, MD Rachel Shakked, MD David I. Pedowitz, MD Steven M. Raikin, MD Joseph N. Daniel,
Clinical Review Criteria
 Clinical Review Criteria Autologous Platelet Derived Wound Healing Factors for Treatment of: Non Healing Cutaneous Wounds (Procuren) Non-Healing Fractures and the Associated GEM 21STM Device Platelet Rich
Clinical Review Criteria Autologous Platelet Derived Wound Healing Factors for Treatment of: Non Healing Cutaneous Wounds (Procuren) Non-Healing Fractures and the Associated GEM 21STM Device Platelet Rich
AN NSAID WITH A BALANCED COX-1 & COX-2 INHIBITORY EFFECT
 AN NSAID WITH A BALANCED COX-1 & COX-2 INHIBITORY EFFECT A balanced cox-1 and cox-2 inhibitor Metabolisim and Bioavailabillty of Lornoxicam (3) Relative selectivity of agents as inhibitors of cox-1 and
AN NSAID WITH A BALANCED COX-1 & COX-2 INHIBITORY EFFECT A balanced cox-1 and cox-2 inhibitor Metabolisim and Bioavailabillty of Lornoxicam (3) Relative selectivity of agents as inhibitors of cox-1 and
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4
 Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Month/Year of Review: January 2012 Date of Last Review: February 2007
 Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-945-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Month/Year of Review: January 2012 Date of Last Review:
Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-945-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Month/Year of Review: January 2012 Date of Last Review:
Arthritis of the Shoulder
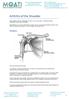 Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Treatment of open tibial shaft fractures using intra medullary interlocking
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
Arthritis of the Knee
 Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
InternationalJournalofAgricultural
 www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.2,May2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc &
www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.2,May2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc &
Inflammation is Not the Enemy
 6/22/2017 Inflammation is Not the Enemy Sean Mulvaney, MD 1 6/22/2017 2 6/22/2017 Lascaux 7.4 Billion 3 This image cannot currently be displayed. 6/22/2017 Goals 4 ANTI INFLAMMATORY THERAPIES NSAIDS 5
6/22/2017 Inflammation is Not the Enemy Sean Mulvaney, MD 1 6/22/2017 2 6/22/2017 Lascaux 7.4 Billion 3 This image cannot currently be displayed. 6/22/2017 Goals 4 ANTI INFLAMMATORY THERAPIES NSAIDS 5
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture
 Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures
 Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Metha Short Hip Stem System
 Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
Intra-Articular Tibiofemoral Injection of a Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug has no Detrimental Effects on Joint Mechanics in a Rat Model
 Intra-Articular Tibiofemoral Injection of a Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug has no Detrimental Effects on Joint Mechanics in a Rat Model Corinne N. Riggin, Jennica J. Tucker, Louis J. Soslowsky, PhD,
Intra-Articular Tibiofemoral Injection of a Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug has no Detrimental Effects on Joint Mechanics in a Rat Model Corinne N. Riggin, Jennica J. Tucker, Louis J. Soslowsky, PhD,
Celecoxib versus ibuprofen in the prevention of heterotopic ossification following total hip replacement: a prospective randomised trial
 Article Celecoxib versus ibuprofen in the prevention of heterotopic ossification following total hip replacement: a prospective randomised trial SAUDAN, Marc, et al. Abstract We examined whether a selective
Article Celecoxib versus ibuprofen in the prevention of heterotopic ossification following total hip replacement: a prospective randomised trial SAUDAN, Marc, et al. Abstract We examined whether a selective
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery
 PATIENT INFORMATION Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery The Midfoot The midfoot refers to the bones and joints that make up the arch and connect the forefoot to the hindfoot. Metatarsals
PATIENT INFORMATION Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery The Midfoot The midfoot refers to the bones and joints that make up the arch and connect the forefoot to the hindfoot. Metatarsals
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
WVJ World's Veterinary Journal
 WVJ World's Veterinary Journal World's Vet. J. 4(1): 06-10, 2014 2014, Scienceline Publication Osteo-synthesis Use in Dogs Femur Surgical Fractures Repair: An Experimental and Comparative Study Bouknine
WVJ World's Veterinary Journal World's Vet. J. 4(1): 06-10, 2014 2014, Scienceline Publication Osteo-synthesis Use in Dogs Femur Surgical Fractures Repair: An Experimental and Comparative Study Bouknine
Title:Effects of prostaglandin E1 on callus formation in rabbit
 Author's response to reviews Title:Effects of prostaglandin E1 on callus formation in rabbit Authors: Pawel V Lipinsky (lipper@inbox.ru) Ivan V Sirotin (ivsir@mail.ru) Alexandr V Skoroglyadov (pskor@bk.ru)
Author's response to reviews Title:Effects of prostaglandin E1 on callus formation in rabbit Authors: Pawel V Lipinsky (lipper@inbox.ru) Ivan V Sirotin (ivsir@mail.ru) Alexandr V Skoroglyadov (pskor@bk.ru)
Patient Guide. Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening
 Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6
 Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study Mohammed KM Ali 1, Abid Hussain 1, CA Mbah 1, Alaa Mustafa 1,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study Mohammed KM Ali 1, Abid Hussain 1, CA Mbah 1, Alaa Mustafa 1,
COMPARING KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION TO A NEW DEVICE USED FOR PROXIMAL INTERPHALANGEAL FUSION
 C H A P T E R 3 0 COMPARING KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION TO A NEW DEVICE USED FOR PROXIMAL INTERPHALANGEAL FUSION Scott R. Roman, DPM INTRODUCTION The most common fixation for proximal interphalangeal fusion
C H A P T E R 3 0 COMPARING KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION TO A NEW DEVICE USED FOR PROXIMAL INTERPHALANGEAL FUSION Scott R. Roman, DPM INTRODUCTION The most common fixation for proximal interphalangeal fusion
Original Article Remove orthopedic fracture implant with minimal invasive surgery is good for the patient s early rehabilitation
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(12):22377-22381 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016560 Original Article Remove orthopedic fracture implant with minimal invasive surgery is good for the patient s early rehabilitation
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(12):22377-22381 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016560 Original Article Remove orthopedic fracture implant with minimal invasive surgery is good for the patient s early rehabilitation
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0188 TITLE: CaMKK2 Inhibition in Enhancing Bone Fracture Healing PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Uma Sankar, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Indiana University Bloomington, IN 47402 REPORT
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0188 TITLE: CaMKK2 Inhibition in Enhancing Bone Fracture Healing PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Uma Sankar, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Indiana University Bloomington, IN 47402 REPORT
Successful Bone Healing of Nonunion After Ulnar Shortening Osteotomy for Smokers Treated With Teriparatide
 Successful Bone Healing of Nonunion After Ulnar Shortening Osteotomy for Smokers Treated With Teriparatide Takuya Uemura, MD, PhD; Mitsuhiro Okada, MD, PhD; Takuya Yokoi, MD; Kosuke Shintani, MD; Hiroaki
Successful Bone Healing of Nonunion After Ulnar Shortening Osteotomy for Smokers Treated With Teriparatide Takuya Uemura, MD, PhD; Mitsuhiro Okada, MD, PhD; Takuya Yokoi, MD; Kosuke Shintani, MD; Hiroaki
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy
 Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy ISHA Annual Scientific Meeting 2012 Boston, MA Crispin Ong MD, Michael Hall MD, Thomas Youm MD Disclosures Consultancy: Arthrex, Depuy Lectures/speakers
Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy ISHA Annual Scientific Meeting 2012 Boston, MA Crispin Ong MD, Michael Hall MD, Thomas Youm MD Disclosures Consultancy: Arthrex, Depuy Lectures/speakers
Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic, 501 N. 10th Street, Manitowoc, WI Procedure. Subtalar arthrodesis
 OSTEOAMP Allogeneic Morphogenetic Proteins Subtalar Nonunions OSTEOAMP Case Report SUBTALAR NONUNIONS Dr. Jason George DeVries and Dr. Brandon M. Scharer Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic,
OSTEOAMP Allogeneic Morphogenetic Proteins Subtalar Nonunions OSTEOAMP Case Report SUBTALAR NONUNIONS Dr. Jason George DeVries and Dr. Brandon M. Scharer Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic,
The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
Fracture fixation. Types. Mechanical considerations. Biomechanics of fracture fixation. External fixation. Internal fixation
 Fracture fixation Biomechanics of fracture fixation Types External fixation Mechanical considerations Internal fixation Mechanical considerations in treatment of 1. In the external fixation: fracture When
Fracture fixation Biomechanics of fracture fixation Types External fixation Mechanical considerations Internal fixation Mechanical considerations in treatment of 1. In the external fixation: fracture When
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Fractures of the Proximal Tibia (Shinbone)
 Fractures of the Proximal Tibia (Shinbone) A fracture, or break, in the shinbone just below the knee is called a proximal tibia fracture. The proximal tibia is the upper portion of the bone where it widens
Fractures of the Proximal Tibia (Shinbone) A fracture, or break, in the shinbone just below the knee is called a proximal tibia fracture. The proximal tibia is the upper portion of the bone where it widens
EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION
 EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION SINCE 1983 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING EXPLANTATION OPTIONS the cement from inside the cement canal until the bone/ cement bond
EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION SINCE 1983 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING EXPLANTATION OPTIONS the cement from inside the cement canal until the bone/ cement bond
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Running head: THE EFFECT OF NSAIDS ON THE BONE HEALING PROCESS IN RATS. The Effect of NSAIDs on the Bone Healing Process in Rats
 1 Running head: The Effect of NSAIDs on the Bone Healing Process in Rats The Center for Advanced Studies and Research Word count: 4102 (without citations) Keywords: NSAIDs, bone healing, osteoblasts, bone
1 Running head: The Effect of NSAIDs on the Bone Healing Process in Rats The Center for Advanced Studies and Research Word count: 4102 (without citations) Keywords: NSAIDs, bone healing, osteoblasts, bone
Fracture and Dislocation of Metacarpal Bones, Metacarpophalangeal Joints, Phalanges, and Interphalangeal Joints ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Hip Fractures. Anatomy. Causes. Symptoms
 Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
ORTHOPEDICS BONE Recalcitrant nonunions In total hip replacement total knee surgery increased callus volume
 ORTHOPEDICS Orthopedics has to do with a variety of tissue: bone, cartilage, tendon, ligament, muscle. In this regard orthopedic and sports medicine share the same tissue targets. Orthopedics is mostly
ORTHOPEDICS Orthopedics has to do with a variety of tissue: bone, cartilage, tendon, ligament, muscle. In this regard orthopedic and sports medicine share the same tissue targets. Orthopedics is mostly
TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY (Total Hip Replacement)
 (Total Hip Replacement) The Hip Joint The hip is a ball and socket joint. The joint is formed by the head of the femur (thighbone) and the acetabulum (pelvis). The bones are coated in cartilage, which
(Total Hip Replacement) The Hip Joint The hip is a ball and socket joint. The joint is formed by the head of the femur (thighbone) and the acetabulum (pelvis). The bones are coated in cartilage, which
JOURNALOF ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA
 JOT Special Case Report Series CASE REPORTS www.jorthotrauma.com JOURNALOF ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF Orthopaedic Trauma Association Belgian Orthopaedic Trauma Association Canadian Orthopaedic
JOT Special Case Report Series CASE REPORTS www.jorthotrauma.com JOURNALOF ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF Orthopaedic Trauma Association Belgian Orthopaedic Trauma Association Canadian Orthopaedic
A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Cigarette smoking delays bone healing: A prospective study of 200 patients operated on by the hemicallotasis technique
 Cigarette smoking delays bone healing: A prospective study of 200 patients operated on by the hemicallotasis technique W-Dahl, Annette; Toksvig-Larsen, Sören Published in: Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica
Cigarette smoking delays bone healing: A prospective study of 200 patients operated on by the hemicallotasis technique W-Dahl, Annette; Toksvig-Larsen, Sören Published in: Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica
Midfoot - Reduction & Fixation - ORIF - screw fixation - AO Surgery Reference. ORIF - screw fixation
 Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
An Owner's Guide to Natural Healing. Autologous Conditioned Plasma (ACP)
 An Owner's Guide to Natural Healing Autologous Conditioned Plasma (ACP) Healing after an injury involves a well-orchestrated and complex series of events where proteins in the blood have primary roles,
An Owner's Guide to Natural Healing Autologous Conditioned Plasma (ACP) Healing after an injury involves a well-orchestrated and complex series of events where proteins in the blood have primary roles,
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH
 PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH Headline Contents Headline Appendix 4 5 7 8 13 14 Clinical Benefits Self-Forming Porous Scaffold
PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH Headline Contents Headline Appendix 4 5 7 8 13 14 Clinical Benefits Self-Forming Porous Scaffold
NSAIDs: Side Effects and Guidelines
 NSAIDs: Side Effects and James J Hale FY1 Department of Anaesthetics Introduction The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a diverse group of drugs that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory
NSAIDs: Side Effects and James J Hale FY1 Department of Anaesthetics Introduction The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a diverse group of drugs that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory
Biologics in ACL: What s the Data?
 Biologics in ACL: What s the Data? Jo A. Hannafin, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery, Weill Cornell Medical College Attending Orthopaedic Surgeon and Senior Scientist Sports Medicine and Shoulder
Biologics in ACL: What s the Data? Jo A. Hannafin, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery, Weill Cornell Medical College Attending Orthopaedic Surgeon and Senior Scientist Sports Medicine and Shoulder
PediNail Pediatric Femoral Nail
 PediNail Pediatric Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Table of Contents Indications...3 Patient Positioning...3 Approach...4 Reaming...5 Nail Placement...6 Proximal Interlocking...7 Distal Interlocking...8
PediNail Pediatric Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Table of Contents Indications...3 Patient Positioning...3 Approach...4 Reaming...5 Nail Placement...6 Proximal Interlocking...7 Distal Interlocking...8
Locked Plating: Clinical Indications
 Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(3):181 185 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Clinical Indications Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John Munz, M.D. Summary: As shown in the previous article,
Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(3):181 185 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Clinical Indications Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John Munz, M.D. Summary: As shown in the previous article,
Cankaya Ortopedi. Outpatient TKA in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Prof. N. Reha Tandogan, M.D
 IMUKA 2016 Transatlantic Current Concepts in Outpatient Arthroplasty Dr. N. Reha Tandoğan Outpatient TKA in Rheumatoid Arthritis Prof. N. Reha Tandogan, M.D Ortoklinik / Çankaya Orthopaedics, Ankara, Turkey
IMUKA 2016 Transatlantic Current Concepts in Outpatient Arthroplasty Dr. N. Reha Tandoğan Outpatient TKA in Rheumatoid Arthritis Prof. N. Reha Tandogan, M.D Ortoklinik / Çankaya Orthopaedics, Ankara, Turkey
Risk Management Plan Etoricoxib film-coated tablets
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
The Use of Analgesics in Rodents and Rabbits Deborah M. Mook, DVM
 The Use of Analgesics in Rodents and Rabbits Deborah M. Mook, DVM (Last updated August, 2005) Rationale. Well-established studies have shown repeatedly that effective analgesia enhances locomotion, increases
The Use of Analgesics in Rodents and Rabbits Deborah M. Mook, DVM (Last updated August, 2005) Rationale. Well-established studies have shown repeatedly that effective analgesia enhances locomotion, increases
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System. Surgical Technique
 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Unlocked Nailing vs. Interlocking Nailing for Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fractures. Is there a Difference?
 Unlocked Nailing vs. Interlocking Nailing for Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fractures. Is there a Difference? CK Yu, MBBS (UM), HY Wong*, MD (UKM), AS Vivek, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To*, FRCS (Edin)
Unlocked Nailing vs. Interlocking Nailing for Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fractures. Is there a Difference? CK Yu, MBBS (UM), HY Wong*, MD (UKM), AS Vivek, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To*, FRCS (Edin)
Knee Arthroscopy. Anatomy
 Knee Arthroscopy Knee arthroscopy is a surgical procedure that allows doctors to view the knee joint without making a large incision (cut) through the skin and other soft tissues. Arthroscopy is used to
Knee Arthroscopy Knee arthroscopy is a surgical procedure that allows doctors to view the knee joint without making a large incision (cut) through the skin and other soft tissues. Arthroscopy is used to
Posterior Tibial Tendon Problems
 A Patient s Guide to Posterior Tibial Tendon Problems 2659 Professional Circle Suite 1110 Naples, FL 34119 Phone: 239-596-0100 Fax: 239-596-6737 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Posterior Tibial Tendon Problems 2659 Professional Circle Suite 1110 Naples, FL 34119 Phone: 239-596-0100 Fax: 239-596-6737 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Integra. Titan Modular Shoulder System, 2.5
 Titan Modular Shoulder System, 2.5 Limit uncertainty with a shoulder implant system that redefines modularity, addresses multiple indications, and allows for reproducible results. Titan Modular Shoulder
Titan Modular Shoulder System, 2.5 Limit uncertainty with a shoulder implant system that redefines modularity, addresses multiple indications, and allows for reproducible results. Titan Modular Shoulder
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Are You Living with. Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you.
 Are You Living with Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Understanding Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Are You Living with Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Understanding Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Tibiotalocalcaneal fusion over retrograde SIGN Nail
 Tibiotalocalcaneal fusion over retrograde SIGN Nail PROF (DR.) SYED ANWARUZZAMAN Professor and Head Department of Orthopedic &trauma Comilla Medical college & Hospital Comilla, Bangladesh Introduction
Tibiotalocalcaneal fusion over retrograde SIGN Nail PROF (DR.) SYED ANWARUZZAMAN Professor and Head Department of Orthopedic &trauma Comilla Medical college & Hospital Comilla, Bangladesh Introduction
A U X I L I A R Y C O N N E C T O R S Surgical Technique
 A U X I L I A R Y C O N N E C T O R S Surgical Technique AUXILIARY CONNECTORS ISSYS LP Auxiliary Connectors The ISSYS LP auxiliary connectors were designed to provide medial-lateral variability for the
A U X I L I A R Y C O N N E C T O R S Surgical Technique AUXILIARY CONNECTORS ISSYS LP Auxiliary Connectors The ISSYS LP auxiliary connectors were designed to provide medial-lateral variability for the
Arthritis. What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available?
 Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
Arthroplasty Of The Shoulder
 Arthroplasty Of The Shoulder 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Arthroplasty Of The Shoulder About Your Shoulder. Ligaments and tendons hold it together. Ligaments connect the bones, while tendons connect muscles to the
Arthroplasty Of The Shoulder 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Arthroplasty Of The Shoulder About Your Shoulder. Ligaments and tendons hold it together. Ligaments connect the bones, while tendons connect muscles to the
KNEE MICROFRACTURE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE
 KNEE MICROFRACTURE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Progression is time and criterion-based, dependent on soft tissue healing, patient demographics and clinician evaluation. Contact Ohio State Sports Medicine
KNEE MICROFRACTURE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Progression is time and criterion-based, dependent on soft tissue healing, patient demographics and clinician evaluation. Contact Ohio State Sports Medicine
CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO :
 CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Name : XXXX Age : 53yr Sex : Female Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO : 201518441 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : - Pain in the right knee since
CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Name : XXXX Age : 53yr Sex : Female Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO : 201518441 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : - Pain in the right knee since
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis is the most common type of joint disease. It represents a group of conditions that result in changes
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis is the most common type of joint disease. It represents a group of conditions that result in changes
Surgical Technique. Intramedullary locked Nailing With Screws for Humerus Fractures Solid/Cannulated. Humeral Interlocking Nail.
 Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
ENHANCED RECOVERY PROTOCOLS FOR KNEE REPLACEMENT
 ENHANCED RECOVERY PROTOCOLS FOR KNEE REPLACEMENT Jeff Gadsden, MD, FRCPC, FANZCA Associate Professor Duke University Department of Anesthesiology Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain Medicine DISCLOSURES
ENHANCED RECOVERY PROTOCOLS FOR KNEE REPLACEMENT Jeff Gadsden, MD, FRCPC, FANZCA Associate Professor Duke University Department of Anesthesiology Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain Medicine DISCLOSURES
Review Article. Safety Profile of Nonsteroidal Antiflammatory Drugs (NSAID) Safety Profile of NSAID
 Safety Profile of Nonsteroidal Antiflammatory Drugs (NSAID) R. Stoilov: University Hospital St Ivan Rilski, Clinic of Rheumatology Contact: Rumen Stoilov, Clinic of Rheumatology, University Hospital St
Safety Profile of Nonsteroidal Antiflammatory Drugs (NSAID) R. Stoilov: University Hospital St Ivan Rilski, Clinic of Rheumatology Contact: Rumen Stoilov, Clinic of Rheumatology, University Hospital St
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Papers. Abstract. Introduction. Methods. Jonathan J Deeks, Lesley A Smith, Matthew D Bradley
 Efficacy, tolerability, and upper gastrointestinal safety of celecoxib for treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review of randomised controlled trials Jonathan J Deeks, Lesley
Efficacy, tolerability, and upper gastrointestinal safety of celecoxib for treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review of randomised controlled trials Jonathan J Deeks, Lesley
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What?
 Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What? Anish R. Kadakia MD Associate Professor Northwestern University: Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern Memorial Hospital Department of
Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What? Anish R. Kadakia MD Associate Professor Northwestern University: Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern Memorial Hospital Department of
