Percutaneous Multiple Kirschner Wire Fixation in the Treatment of Hand Fractures
|
|
|
- Mary Rich
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn eissn J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2013;18(3): JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Percutaneous Multiple Kirschner Wire Fixation in the Treatment of Hand Fractures Seong Jae Hong 1, Hyeung Gyo Seo 2, Jong Ick Whang 2, Sanghun Cho 1 Department of 1 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang; 2 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Duson Hospital, Ansan, Korea Received: June 5, 2013 Revised: September 3, 2013 Accepted: September 7, 2013 Correspondence to: Hyeung Gyo Seo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Duson Hospital, 114 Seonbugwangjang 1-ro, Danwon-gu, Ansan , Korea TEL: FAX: blueginget@google.com This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( licenses/bync/3.0/) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Purpose: We reported results of percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation technique without passing through the joint in patients with a hand fracture. Methods: We evaluated a total of 116 cases in 94 patients who underwent percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation on dorsal cortex over a 10-year period between 2001 and The treatment outcomes were evaluated based on total active motion (TAM), as proposed by Widegrow. Results: Our clinical series of patients achieved good functional outcomes. Of total patients, 89% (84/94) had excellent TAM, 2% (2/94) did good TAM and 9% (8/94) did poor TAM. Postoperatively, our clinical series of patients had such a good compliance as to achieve a TAM of >181 when performing the early active movement. There were no notable postoperative complications during the follow-up period. Conclusion: Our results indicate that percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation technique without passing through the joint from normal bone density patients is effective in providing the rigid fixation. Thus, our patients could perform the early movement as promptly as possible and maintaining the full mobility of the rest of the hand. Keywords: Hand, Fractures, bone, Fracture fixation, Bone wires, Motion INTRODUCTION The hand fracture is one of the most common traumas, and it accounts for up to 10% of all the human body fractures 1,2. Its etiologic factors include sports activities, traffic accidents and industrial work activities. There is a variability in the management of hand fracture. This poses challenging problems for surgeons. The treatment goal is to obtain good outcomes, for which surgeons should consider 1) restoration of the normal alignment, 2) achievement of the appropriate union, 3) recovery of the early range of movement and earlier return to full activities, and 4) absence of residual disabilities or deformities It is difficult to maintain reduction without causing undesirable side effects. The complications of hand fracture include infection, non-union, malunion, tendon adhesion and joint stiffness 3. Of these, the most serious potential problem is an inability to attain a full range of movement. There Copyright c The Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand
2 Seong Jae Hong, et al. Percutaneous Multiple K-Wire Fixation are multiple factors which limit the range of motion, and these include structural problems such as concurrent injuries to the joint or tendon, i.e., the overlying structures that perform a gliding function, and soft tissue injuries including neurovascular injuries. Moreover, the limited range of motion is correlated with infection, swelling, pain and nonrigid, unstable fixation 4. All of these factors cause tendon adhesion or joint stiffness by maintaining the immobilized hand. For the effective treatment of hand fracture, the early active motion as well as the rigid fixation should be achieved. In addition, the postoperative complications should be prevented and the normal functions of the hand based on the maximum range of motion should be restored 5. We performed the percutaneous multiple K-wire technique on dorsal cortex without passing through the joint in patients with hand fracture and obtained good treatment outcomes. Here, we present our surgical methods and their outcomes based on our 10-year single institution experience. MATERIALS AND METHODS 1. Patients A total of 94 patients (116 cases) underwent percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation over a 10-year period between 2001 and We performed a retrospective analysis of such variables as location, direction of the fracture line, amount of displacement, degree of malalignment, angulation, subluxation, dislocation, rotational deformity (malrotation), presence or absence of comminution and articular involvement. Inclusion/exclusion criteria for the current study are as follows: 1) Inclusion criteria, patients with phalangeal or metacarpal fractures of the hand with normal bone density. 2) Exclusion criteria, patients with low bone density; patients with concurrent carpal fractures; patients with fractures with large bone defects; patients with fractures associated with replantation; patients with severely multilated injuries requiring primary amputation; patients who required skin grafting. We finally enrolled a total of 94 patients (116 cases) in the current study. The current study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of our medical institution. Because of its retrospective nature, the requirement for obtaining a written informed consent was waived. 2. Surgical techniques The basic principle of the surgical treatment for hand fractures is to realign the mobile segment to the less mobile one. Under local anesthesia, axillary block anesthesia in some cases, with or without standard C-arm fluoroscopic guidance, the fractures were properly treated with closed or open reduction when there was a concurrent presence of injury. Reduction of the fracture was done by pulling or traction of the finger with an even distribution of the sufficient pressure. After the fractures were well aligned and good reduction was obtained by closed or open manipulation, multiple K-wires were placed using a power driver percutaneously starting from the dorsal cortex to the other side dorsal cortex above the mid-lateral line for maximizing rigidity. In metacarpal fractures, multiple K-wires were percutaneously inserted in a transverse direction and then horizontally placed in the stable unit of the hand. The non-fractured adjacent bone was served as the stable unit that is expected to plays a role as the cornerstone of the bridge (Fig. 1). In comminuted fractures, we passed multiple K-wires through the largest segment into the smaller one and then fixed to each other, thus attempting to increase the rigidity, and thereby stabilized the fracture without passing K-wires through the joint (Figs. 2, 3). Then, we encouraged the patients to perform the early movement. We applied the sufficient compression by manual forces or encouraged the patients to move the hand for daily activities. Thus, we attempted to evaluate whether the range of motion and the stability of fixation are so sufficient as to maintain the reduction (Figs. 3, 4). Unless the fixation had been sufficient or bone fractures had been immobilized, we would have performed the longitudinal percutaneous K-wire fixation. But there were no such cases. The pins were withdrawn within a mean period of four weeks postoperatively (range, 3-6 weeks). 3. Postoperative management After the internal fixation, we initiated the early mobilization without delay while maintaining the adequate alignment of the fragments with rigid fixation. When there were no con
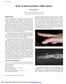
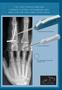
3 J Korean Soc Surg Hand Vol. 18, No. 3, September 2013 Fig. 1. Spiral metacarpal fracture with rotational malalignment. (A) Spiral fractures with rotational deformity of the index metacarpal shaft and long metacarpal base. (B) Closed reduction and internal fixation of each spiral fracture with percutaneous multiple K-wires stabilized the fracture yet allow movement. The third and fourth metacarpal function as a foundation stone. No wire was transfixed through the metacarpophalangeal joint surface. (C) On postoperative year 1, no rotational malalignment was observed and patient restored alignment with a full range of motion. Fig. 2. Rigid fixation of comminuted diaphyseal fracture. (A) Diaphyseal fracture of the index proximal phalanx with comminution. (B) Immediately after surgery, with the fixation by percutaneous multiple K-wires without passing through the joint, the rigid fixation was maintained during the active flexion. current injuries in such body areas as the tendon, collateral ligament and neurovascular structures, the patients were allowed to perform early mobilization within 7 to 14 days postoperatively. We encouraged the patients to perform active motion. In addition, we also added the passive range of motion when there was a limitation in the movement because of swelling or pain. Postoperatively, there were no patients who needed splint protection because there was a sufficient stability due to a rigid fixation with multiple K-wires although the patients with concurrent tendon injuries were 126
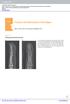
4 Seong Jae Hong, et al. Percutaneous Multiple K-Wire Fixation Fig. 3. Early mobilization after percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation. (A) Proximal phalangeal shaft, base fracture with comminution of the index finger. (B) Closed reduction and percutaneous multiple K-wires. (C) With the rigid fixation without passing through the joint, the early active movement was promoted. The degree of motion was satisfactory on postoperative day 3. Fig. 4. Multiple transverse fractures with concurrent injures. (A) Multiple transverse fractures of the shaft with the tendon injures in the proximal phalanges accompanied by the dorsal, concave angulation. (B) Immediately after surgery, the rigid fixation and the early active motion were achieved using the percutaneous multiple K-wire technique. (C) On postoperative year 1, the full range of motion was restored and there were no residual disabilities or deformities. in need of dynamic splinting. In patients who had injuries to neurovascular structures, however, the early mobilization was permitted after 14 days postoperatively. 4. Evaluation of outcomes The treatment outcomes are based on such variables as the range of joint motion, the degree of deformity, grasping function, pain and sensory recovery. In an actual clinical setting, however, it is difficult to objectively evaluate all the above variables. Moreover, there was a variability in the period of long-term follow-up. We therefore evaluated the total active movement (TAM), as proposed by Widgerow (Table 1). The TAM refers to an additive sum of three movements: the flexion at the metacarpophalangeal, the proximal interphalangeal, and the distal interphalangeal joints minus the extension deficit at the same joints 6. Thus, we classified the treatment outcomes based on the TAM into three grades: excellent (TAM >250 ), good (181 <TAM<249 ), and poor (TAM <180 )
5 J Korean Soc Surg Hand Vol. 18, No. 3, September 2013 RESULTS 1. Characteristics of the patients The mean age of the patients was 53-year-old (range, year-old), and they consisted of 54 men and 40 women. The most common fracture was metacarpal fracture, accounting for 48% (56/116) of total cases (Table 2). Our clinical series of patients include six cases of intra-articular fracture, 18 cases of spiral fracture and 12 cases of comminuted fracture. 2. Clinical outcomes As shown in Table 1, our clinical series of patients achieved good functional outcomes. Of total patients, 89% (84/94) had excellent TAM, 2% (2/94) did good TAM and 9% (8/94) did poor TAM. Postoperatively, our clinical series of patients had such a good compliance as to achieve a TAM of >181 when performing the early active movement. All of our clinical series of patients were followed up postoperatively, and underwent uneventful course and achieved a recovery of hand motion. Furthermore, there were no patients who had malunion or nonunion of the fracture as well as residual deformities (Figs. 1, 4). DISCUSSION The hand is one the most essential organs of the human Table 1. Functional outcomes based on the total active movement Outcomes TAM No. of patients (%) Excellent > (89) Good (2) Poor <180 8 (9) The total active motion (TAM) refers to an additive sum of three movements: the flexion at the metacarpophalangeal, the proximal interphalangeal and the distal interphalangeal joints minus the extension deficit at the same joints. body, and it is characterized by the sophisticated functions and complicated architecture. In addition, it is vulnerable to trauma with the industrial development and the increased use of transportation. The hand fracture accounts for 30% of all industrial fractures, and it is the most frequently seen 7. The management of hand fracture is a Cinderella subject; it is subject to the extent and mechanism of injury, patient s age, concurrent injuries and surgeons technical expertise. To put this in another way, there is no established treatment modality for hand fracture. The optimal treatment modality should be chosen on a case-by-case basis. According to Swanson, patients with hand fracture may be complicated; it may lead to the deformity when left untreated, stiffness when overtreated and both deformity and stiffness when incorrectly treated 8. This suggests that it would be mandatory to select the optimal treatment modality for each case although many cases of hand fracture can be treated by conservative management at the present 9. In an actual clinical setting, there are some patients who achieve a recovery even when almost or completely left untreated. If overtreated or incorrectly treated, however, patients will present with deformity or other severe complications than the deformity. According to Curry 10, the basic principle of the surgical treatment for hand fractures is to realign the mobile distal segment to the less mobile proximal one. Active measures can be taken if a satisfactory reduction cannot be achieved or if there are concurrent injuries in such areas the vessels, nerves, tendons or other soft tissues. Surgical treatments of hand fracture can be classified into the internal fixation and the external one. In the internal fixation, the reduction is achieved by percutaneous K-wire pinning, interosseous wiring and the fixation with a plate and a screw. Percutaneous K-wire pinning is a common surgical technique that is both simple and cost-effective. In addition, it is advantageous in that it can be versatile used for skeletal stabi- Table 2. Fracture site and accompanying injuries Fracture site No concurrent injuries Tendon injuries Neurovascular structure injuries Total no. of cases Distal phalanx Middle phalanx (S: 2, C: 2) Proximal phalanx (I: 6, S: 2, C: 6) Metacarpal (S: 14, C: 4) I, intra-articular fracture; S, spiral fracture; C, comminuted fracture
6 Seong Jae Hong, et al. Percutaneous Multiple K-Wire Fixation lization and it causes less complications 11. Black et al. 12 analyzed the rigidity of three methods, 1) the dorsal plating with or without lag screws, 2) the intraosseous wiring, and 3) the K-wire pinning, for the treatment of metacarpal fracture. This showed that the dorsal plate fixation and the wired techniques provided the most and the least rigid fixation, respectively. With the most stable fixation, patients can initiate the early active movement as promptly as possible. Despite the stable fixation, the plate system reveals several disadvantages due to a plate and a screw. That is, the plate is somewhat huge and then cannot be easily used for the fixation of hand phalanges. In addition, it needs an wide exposure for the extensive periosteal stripping. With the inappropriate location of the plate, the normal gliding of the tendon would be compromised 13. Moreover, it would be mandatory to remove both a screw and a plate at the second operation. To date, however, no attempts have been made to stabilize the rigidity of K-wire fixation because it has the great advantages. By contrast, the K-wire fixation minimally needs the periosteal elevation, but it is also known to provide the unstable fixation that limits the early active movement in patients with hand fracture 12. Rush and Rush 14 attempted the use of immediate intramedullary wiring in the treatment of patients with metacarpal fracture. But these authors did not use splints but recommended that patients perform the early movement of the hand and finger. To date, many authors have emphasized the importance of the early mobilization in patients with hand fracture. In association with this, Dobyns et al. 15 reported that final treatment outcomes would be improved if at least a partial arc of motion is restored as promptly as possible. The treatment outcomes would vary depending on the type of treatment methods and the duration of immobilization. It is well known that the small joints of the hand are prone to stiffen with immobilization. In the rehabilitation program, the early active mobilization based on the flexion and extension of the hand and finger should be considered of primary concern and it can attained when patients maintain the rigid fixation of reduction. Other digits and joints of the extremities should be mobilized as promptly as possible. Thus, attempts can be made to prevent the sympathetic dystrophy as well as total loss of hand function 8. Our clinical series of patients had no immobilized joints and they were permitted to perform the early mobilization. According to Clifford 16, the treatment goal of hand fracture is to reduce the fractures and to immobilize them. But we assume that the treatment goal of hand fracture is to reduce the fractures with stable fixation and to provide patients with the early active movement without immobilization. We treated patients with hand fracture simply with percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation without passing through the joint and thereby obtained such satisfactory outcomes that it achieved a sufficiently rigid fixation in the reduced position without joint immobilization. Then, we could shorten the usual postoperative course by subsequently performing the early active movement. In our series, the early movement including both the active and passive motion was effective in minimizing the occurrence of soft tissue swelling, achieving a recovery of the gliding function of tendon around the joints, thus preventing the occurrence of posttraumatic tendon adhesions, and allowing unrestricted motion of the joint, thus preventing the occurrence of joint stiffness and enabling patients to return to the daily lives. After achieving a rigid fixation, patients appeared to recover joint stability and could initiate the early mobilization without delay. Our surgical methods were also effective in correcting rotational deformities in patients with spiral fracture or comminuted one because the percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation provided such a sufficient stability as to maintain the reduction. In particular, the percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation technique is appropriate for patients with metacarpal fracture. Therefore, our clinical series of patients achieved an adequate fixation even when they had a concurrent presence of rotational malalignment. Unlike the plate and screw system, the percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation is a costeffective procedure that it does not need a second operation. Moreover, there is no need to pass the K-wire through the joint. Furthermore, the periosteal elevation for the direct visualization of the fracture is needed only at a minimal level in patients who are indicated in open reduction. Our results cannot be applied to patients with vascular diseases, those with low bone density and pediatric ones who had epiphyseal growth plate. In addition, surgeons cannot 129
7 J Korean Soc Surg Hand Vol. 18, No. 3, September 2013 use the K-wire fixation in patients with hemodynamic derangement 13. With the percutaneous insertion of multiple K-wires into the soft tissues, the range of early mobilization can be limited because of the restricted tendon gliding or intrinsic muscle movement. In our series, however, the above findings promptly disappeared immediately after the removal of pins. In addition, there were also a small number of patients where the final range of active movement was left intact. These patients restored the functions of the hand. To summarize, for the past ten years, we have used the percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation technique in 94 patients with hand fracture and thereby obtained satisfactory treatment outcomes. Our clinical series of patients showed no postoperative complications and a good prognosis. Our surgical technique is straightforward and fairly simple but the effect of surgeon experience is required for overcoming the learning curve. CONCLUSION In conclusion, our results indicate that the percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation technique without passing through the joint is effective in providing the rigid fixation. Thus, our patients could perform the early movement as promptly as possible and maintaining the full mobility of the rest of the hand. REFERENCES 1. Green DP, Rowland SP. Fractures and dislocations in the hand. In: Rockwood CA Jr, Green DP, editors. Fractures in adults. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Emmett JE, Breck LW. A review and analysis of 11,000 fractures seen in a private practice of orthopaedic surgery, J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1958;40: Brown PW. The management of phalangeal and metacarpal fractures. Surg Clin North Am. 1973;53: Jupiter JB, Koniuch MP, Smith RJ. The management of delayed union and nonunion of the metacarpals and phalanges. J Hand Surg Am. 1985;10: Wright TA. Early mobilization in fractures of the metacarpals and phalanges. Can J Surg. 1968;11: Widgerow AD, Edinburg M, Biddulph SL. An analysis of proximal phalangeal fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1987;12: Watson-Jones R. Fractures and joint injuries. 4th ed. London: E.&S. Livingstone; Swanson AB. Fractures involving the digits of the hand. Orthop Clin North Am. 1970;1: Stern PJ. Management of fractures of the hand over the last 25 years. J Hand Surg Am. 2000;25: Curry GJ. Treatment of finger fractures, simple and compound. Am J Surg. 1946;71: Hsu LP, Schwartz EG, Kalainov DM, Chen F, Makowiec RL. Complications of K-wire fixation in procedures involving the hand and wrist. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36: Black D, Mann RJ, Constine R, Daniels AU. Comparison of internal fixation techniques in metacarpal fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1985;10: Lamphier TA. Improper reduction of fractures of the proximal phalanges of fingers. Am J Surg. 1957;94: Rush LV, Rush HL. Evolution of medullary fixation of fractures by the longitudinal pin. Am J Surg. 1949;78: Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL, Cooney WP 3rd. Fractures and dislocations of the wrist and hand, then and now. J Hand Surg Am. 1983;8: Clifford RH. Intramedullary wire fixation of hand fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946). 1953;11:
8 Seong Jae Hong, et al. Percutaneous Multiple K-Wire Fixation 다발성 K- 강선을이용한수부골절의치료 홍성재 1 서형교 2 황종익 2 조상헌 1 1 동국대학교일산병원성형외과, 2 두손병원성형외과 목적 : 정상골밀도소견을보이는환자군의수부골절치료에있어다발성 K-강선을이용하여관절면의통과없이고정한결과를보고하고자한다. 대상및방법 : 2001년부터 2010년까지 94명 116예의수부골절환자들을대상으로다발성 K-강선을이용하여배측피질골에고정을시행하였으며 Widegrow 가제안한총능동운동 (total active motion, TAM) 으로수술후결과를측정, 평가하였다. 결과 : 대부분의환자에서만족할만한결과를보였다. 89% (84/94) 에서 TAM 250 를보였으며 2% (2/94) 에서 181 <TAM<250, 그리고 9% (8/94) 에서 TAM <180 의결과를보였다. 견고한고정후조기운동을실시한환자군에서 TAM >181 의좋은결과를얻었다. 추적기간동안합병증은발생하지않았다. 결론 : 정상골밀도소견을보이는환자의수부골절치료에있어다발성 K-강선을이용하여관절면의관통없이골절편을견고하게고정한다면조기에능동및수동운동을시행할수있으며이것은수부의빠른기능회복에도움을줄것으로생각된다. 색인단어 : 수부, 골절, 골절고정, 금속강선, 운동 접수일 2013 년 6 월 5 일수정일 2013 년 9 월 3 일게재확정일 2013 년 9 월 7 일교신저자서형교경기도안산시단원구선부광장 1 로 114 두손병원성형외과 TEL FAX blueginget@google.com 131
Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Tarek Aly* Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tanta University School of
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Tarek Aly* Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tanta University School of
Manual Kirschner-Wire Insertion through the Soft Tissue for Finger Immobilization after Scar Contracture Release
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):8-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.8 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Manual Kirschner-Wire
ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):8-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.8 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Manual Kirschner-Wire
Dynamic treatment for proximal phalangeal fracture of the hand
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):211-5 Dynamic treatment for proximal phalangeal fracture of the hand G Rajesh, WY Ip, SP Chow, BKK Fung Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):211-5 Dynamic treatment for proximal phalangeal fracture of the hand G Rajesh, WY Ip, SP Chow, BKK Fung Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
A Patient s Guide to Adult Metacarpal Fractures of the Hand
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Metacarpal Fractures of the Hand 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
A Patient s Guide to Adult Metacarpal Fractures of the Hand 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
Closed Proximal Phalangeal Fracture Management in Hand: An Outcome Analysis
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/577 Closed Proximal Phalangeal Fracture Management in Hand: An Outcome Analysis R Senthilkumar 1, E Kovarthini 2, Heber
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/577 Closed Proximal Phalangeal Fracture Management in Hand: An Outcome Analysis R Senthilkumar 1, E Kovarthini 2, Heber
A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Failed Extensor Indicis Proprius Tendon Transfer for Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon Rupture after Distal Radial Fracture
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):23-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.23 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Failed Extensor
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):23-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.23 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Failed Extensor
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The information
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The information
Post-Traumatic Malunion of the Proximal Phalanx of the Finger. Medium- Term Results in 24 Cases Treated by In Situ Osteotomy
 Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.org 468 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 468-472 Open Access Post-Traumatic Malunion of the Proximal Phalanx of the Finger. Medium- Term Results
Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.org 468 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 468-472 Open Access Post-Traumatic Malunion of the Proximal Phalanx of the Finger. Medium- Term Results
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
INTERNAL FIXATION OF THE METACARPALS AND PHALANGES P. BURGE
 Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 INTERNL FIXTION OF THE METCRPLS ND PHLNGES P. URGE Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford, UK SUMMRY Techniques and instrumentation for open reduction and internal fixation
Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 INTERNL FIXTION OF THE METCRPLS ND PHLNGES P. URGE Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford, UK SUMMRY Techniques and instrumentation for open reduction and internal fixation
Analysis of Bone Fixation Methods in Digital Replantation
 Analysis of Bone Fixation Methods in Digital Replantation Seung Woo Lee, Dong Chul Lee, Jin Soo Kim, Si Young Roh, Kyung Jin Lee Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Gwangmyeong Sungae General
Analysis of Bone Fixation Methods in Digital Replantation Seung Woo Lee, Dong Chul Lee, Jin Soo Kim, Si Young Roh, Kyung Jin Lee Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Gwangmyeong Sungae General
Comparison between Intramedullary Nailing and Percutaneous K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone
 Comparison between Nailing and K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone Original Article Sung Jun Moon 1, Jae-Won Yang 2, Si Young Roh 1, Dong Chul Lee 1, Jin Soo Kim 1
Comparison between Nailing and K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone Original Article Sung Jun Moon 1, Jae-Won Yang 2, Si Young Roh 1, Dong Chul Lee 1, Jin Soo Kim 1
Finger Mobility Deficits Fracture of metacarpal Fracture of phalanx of phalanges
 1 Finger Mobility Deficits ICD-9-CM codes: 715.4 Osteoarthrosis of the hand 815.0 Fracture of metacarpal 816.0 Fracture of phalanx of phalanges ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4301 Carrying
1 Finger Mobility Deficits ICD-9-CM codes: 715.4 Osteoarthrosis of the hand 815.0 Fracture of metacarpal 816.0 Fracture of phalanx of phalanges ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4301 Carrying
Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study Mohammed KM Ali 1, Abid Hussain 1, CA Mbah 1, Alaa Mustafa 1,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study Mohammed KM Ali 1, Abid Hussain 1, CA Mbah 1, Alaa Mustafa 1,
A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report
 CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Hand injuries. The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck.
 Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Study of clinical problems: Mallet injuries
 Review Article Study of clinical problems: Mallet injuries Hin-Keung WONG Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology, Princess Margaret Hospital, Hong Kong SAR INTRODUCTION The extensor mechanism of the
Review Article Study of clinical problems: Mallet injuries Hin-Keung WONG Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology, Princess Margaret Hospital, Hong Kong SAR INTRODUCTION The extensor mechanism of the
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
IC 30: Tips and Tricks for Management of Hand Fractures-Simple to Complex
 IC 30: Tips and Tricks for Management of Hand Fractures-Simple to Complex Moderator(s): Randip R. Bindra, FRCS, MCh Orth Faculty: Andrea Atzei, MD, Donald H. Lalonde, MD, David S. Ruch, MD Session Handouts
IC 30: Tips and Tricks for Management of Hand Fractures-Simple to Complex Moderator(s): Randip R. Bindra, FRCS, MCh Orth Faculty: Andrea Atzei, MD, Donald H. Lalonde, MD, David S. Ruch, MD Session Handouts
Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal Radius Fracture
 60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol.13, No.4, October, 2000
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol13, No4, October, 2000,, 16, ) : 2 29-1 TEL : (02) 2210-3474 FAX : (02) 2217-1897 1004, 4 (16%), 18,, (72%), 3 ( 12 %),,, 15 1994 1 1998 1 2 - (scapholunate
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol13, No4, October, 2000,, 16, ) : 2 29-1 TEL : (02) 2210-3474 FAX : (02) 2217-1897 1004, 4 (16%), 18,, (72%), 3 ( 12 %),,, 15 1994 1 1998 1 2 - (scapholunate
Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Epidemiology in USA: Metacarpal fractures: Page 1
 Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Robert J Strauch MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Columbia University New York City Epidemiology in USA: 2009 Distal radius fx s: 16/10,000 Phalangeal fx
Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Robert J Strauch MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Columbia University New York City Epidemiology in USA: 2009 Distal radius fx s: 16/10,000 Phalangeal fx
The Efficacy of Transverse Fixation and Early Exercise in the Treatment of Fourth Metacarpal Bone Fractures
 The Efficacy of Transverse Fixation and Early Exercise in the Treatment of Fourth Metacarpal Bone Fractures Suk-Ho Moon, Hak-Soo Kim, Sung-No Jung, Ho Kwon Department of Plastic Surgery, College of Medicine,
The Efficacy of Transverse Fixation and Early Exercise in the Treatment of Fourth Metacarpal Bone Fractures Suk-Ho Moon, Hak-Soo Kim, Sung-No Jung, Ho Kwon Department of Plastic Surgery, College of Medicine,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Hand Clin 21 (2005)
 Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Bilateral Trans-Scaphoid Perilunate Fracture Dislocation
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(3):127-132. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.127 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Bilateral Trans-Scaphoid
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(3):127-132. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.127 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Bilateral Trans-Scaphoid
Fracture and Dislocation of Metacarpal Bones, Metacarpophalangeal Joints, Phalanges, and Interphalangeal Joints ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Comparison of Miniplate and K-wire in Treatment of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fractures
 The THAI Journal of SURGERY 2009; 30:5-10. Official Publication of the Royal College of Surgeons of Thailand Comparison of Miniplate and K-wire in Treatment of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fractures Somboon
The THAI Journal of SURGERY 2009; 30:5-10. Official Publication of the Royal College of Surgeons of Thailand Comparison of Miniplate and K-wire in Treatment of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fractures Somboon
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Management of Mallet Fracture by Closed Extension-Block Pinning A case based review of a novel technique
 Management of Mallet Fracture by Closed Extension-Block Pinning A case based review of a novel technique Sharat Agarwal 1, Mohammad Nasim Akhtar 2 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics & Trauma,
Management of Mallet Fracture by Closed Extension-Block Pinning A case based review of a novel technique Sharat Agarwal 1, Mohammad Nasim Akhtar 2 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics & Trauma,
THE FIRST PERCUTANEOUS LOCKED FLEXIBLE INTRAMEDULARY NAIL SYSTEM FOR HAND FRACTURES
 THE FIRST PERCUTANEOUS LOCKED FLEXIBLE INTRAMEDULARY NAIL SYSTEM FOR HAND FRACTURES Intramedullary Nail & Slotted Awl Proximal Locking Device New Radio Opaque Soft Tissue Protection Cap Pre Operative Post
THE FIRST PERCUTANEOUS LOCKED FLEXIBLE INTRAMEDULARY NAIL SYSTEM FOR HAND FRACTURES Intramedullary Nail & Slotted Awl Proximal Locking Device New Radio Opaque Soft Tissue Protection Cap Pre Operative Post
SPORTS RELATED HAND INJURIES
 HKJOT 2010;20(1):13 18 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPORTS RELATED HAND INJURIES IN HONG KONG Hercy C.K. Li 1 and Cecilia W.P. Li-Tsang 2 Objective: This study attempted to review the incidence of sports related hand
HKJOT 2010;20(1):13 18 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPORTS RELATED HAND INJURIES IN HONG KONG Hercy C.K. Li 1 and Cecilia W.P. Li-Tsang 2 Objective: This study attempted to review the incidence of sports related hand
Intratendinous Ganglion of the Extensor Digitorum Tendon
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2014;19(4):195-199 http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.4.195 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Intratendinous
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2014;19(4):195-199 http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.4.195 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Intratendinous
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures:
 Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
Percutaneous Cannulated Compression Screw Osteosynthesis in Phalanx Fractures: The Surgical Technique, the Indications, and the Results
 Percutaneous Cannulated Compression Screw Osteosynthesis in Phalanx Fractures: The Surgical Technique, the Indications, and the Results Eirini Liodaki, MD, Tobias Kisch, MD, Eike Wenzel, MD, Peter Mailänder,
Percutaneous Cannulated Compression Screw Osteosynthesis in Phalanx Fractures: The Surgical Technique, the Indications, and the Results Eirini Liodaki, MD, Tobias Kisch, MD, Eike Wenzel, MD, Peter Mailänder,
Management of metacarpal and phalangeal fractures with JESS fixator: A prospective study
 2018; 4(1): 383-387 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 383-387 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-11-2017 Accepted: 06-12-2017 Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konaseema Institute
2018; 4(1): 383-387 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 383-387 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-11-2017 Accepted: 06-12-2017 Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konaseema Institute
Visualize, stabilize, mobilize. Wristore * Distal Radius Fracture Fixator Abbreviated Surgical Technique
 Visualize, stabilize, mobilize Wristore * Distal Radius Fracture Fixator Abbreviated Surgical Technique Wristore Distal Radius Fracture Fixator 1 Pin Placement Identify anatomy and make a direct (open)
Visualize, stabilize, mobilize Wristore * Distal Radius Fracture Fixator Abbreviated Surgical Technique Wristore Distal Radius Fracture Fixator 1 Pin Placement Identify anatomy and make a direct (open)
Functional outcome of Metacarpal Fracture managed with Miniplate and Screws. Bir Hospital & Patan Hospital, Kathmandu
 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3126/jmcjms.v6i1.20575 JMCJMS Research Article Functional outcome of Metacarpal Fracture managed with Miniplate and Screws Gyanendra Shah 1*, Bachchu Ram KC 2, Pankaj chand 3,
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3126/jmcjms.v6i1.20575 JMCJMS Research Article Functional outcome of Metacarpal Fracture managed with Miniplate and Screws Gyanendra Shah 1*, Bachchu Ram KC 2, Pankaj chand 3,
Humerus shaft - Reduction & Fixation - Compression plate - AO Surgery Reference. Compression plating
 Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Open Reduction of Proximal Interphalangeal Fracture-Dislocation through a Midlateral Incision Using Absorbable Suture Materials
 Open Reduction of Proximal Interphalangeal Fracture-Dislocation through a Midlateral Incision Using Absorbable Suture Materials Jae Jun Lee, Hyoung Joon Park, Hyun Gon Choi, Dong Hyeok Shin, Ki Il Uhm
Open Reduction of Proximal Interphalangeal Fracture-Dislocation through a Midlateral Incision Using Absorbable Suture Materials Jae Jun Lee, Hyoung Joon Park, Hyun Gon Choi, Dong Hyeok Shin, Ki Il Uhm
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Hand Surgery, Nagoya University School of Medicine ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 74. 167 ~ 171 2012 ORIGINAL PAPER TILT OF THE RADIUS FROM FOREARM ROTATIONAL AXIS RELIABLY PREDICTS ROTATIONAL IMPROVEMENT AFTER CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY FOR MALUNITED FOREARM FRACTURES
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 74. 167 ~ 171 2012 ORIGINAL PAPER TILT OF THE RADIUS FROM FOREARM ROTATIONAL AXIS RELIABLY PREDICTS ROTATIONAL IMPROVEMENT AFTER CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY FOR MALUNITED FOREARM FRACTURES
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Fractures and dislocations of the fingers
 Chapter 1 Fractures and dislocations of the fingers Felix S. Chew, M.D., and Catherine Maldjian, M.D. Case 1 1 Phalangeal tuft avulsion fracture 31-year-old woman injured in a ground-level fall. Lateral
Chapter 1 Fractures and dislocations of the fingers Felix S. Chew, M.D., and Catherine Maldjian, M.D. Case 1 1 Phalangeal tuft avulsion fracture 31-year-old woman injured in a ground-level fall. Lateral
2/1/2018. Clinical Reasoning for Fracture Management
 Clinical Reasoning for Fracture Management AO: Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen (German for "Association for the Study of Internal Fixation") Fracture is an event with immediate multi-tissue
Clinical Reasoning for Fracture Management AO: Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen (German for "Association for the Study of Internal Fixation") Fracture is an event with immediate multi-tissue
EXTRAARTICULAR ANTEGRADE FIXATION OF PROXIMAL PHALYNX FRACTURES WITH BENT K WIRE
 EXTRAARTICULAR ANTEGRADE FIXATION OF PROXIMAL PHALYNX FRACTURES WITH BENT K WIRE Research article Orthopaedics Mohammed Sadiq 1, Raju Kulkarni 2 1 - Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, ESIC
EXTRAARTICULAR ANTEGRADE FIXATION OF PROXIMAL PHALYNX FRACTURES WITH BENT K WIRE Research article Orthopaedics Mohammed Sadiq 1, Raju Kulkarni 2 1 - Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, ESIC
Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries. Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013
 Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013 Overview Trigger Digits: diagnosis and treatment Bonus: approach in children Mallet
Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013 Overview Trigger Digits: diagnosis and treatment Bonus: approach in children Mallet
Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure?
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Interesting Case Series. Perilunate Dislocation
 Interesting Case Series Perilunate Dislocation Tom Reisler, BSc (Hons), MB ChB, MRCS (Ed), Paul J. Therattil, MD, and Edward S. Lee, MD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Perilunate Dislocation Tom Reisler, BSc (Hons), MB ChB, MRCS (Ed), Paul J. Therattil, MD, and Edward S. Lee, MD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Technique Guide. Rotation Correction Plates 1.5 and 2.0. Reposition plates for fractures and osteotomies at the metacarpals and phalanges.
 Technique Guide Rotation Correction Plates 1.5 and 2.0. Reposition plates for fractures and osteotomies at the metacarpals and phalanges. Table of Contents Introduction Rotation Correction Plates 1.5
Technique Guide Rotation Correction Plates 1.5 and 2.0. Reposition plates for fractures and osteotomies at the metacarpals and phalanges. Table of Contents Introduction Rotation Correction Plates 1.5
Original Article Mini External Fixator in Metacarpal And Phalangeal Fractures Pak Armed Forces Med J 2016; 66(5):715-19
 Open Access Original Article Mini External Fixator in Metacarpal And Phalangeal Fractures Pak Armed Forces Med J 2016; 66(5):715-19 RESULTS OF MINI EXTERNAL FIXATOR IN METACARPAL AND PHALANGEAL FRACTURES
Open Access Original Article Mini External Fixator in Metacarpal And Phalangeal Fractures Pak Armed Forces Med J 2016; 66(5):715-19 RESULTS OF MINI EXTERNAL FIXATOR IN METACARPAL AND PHALANGEAL FRACTURES
SURGERY OF THE HAND. Basosquamous Carcinoma of the Hand in a Radiologist with Prolonged Radiation Exposure INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT CASE REPORT
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2016;21(3):162-166. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.3.162 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Basosquamous
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2016;21(3):162-166. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.3.162 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Basosquamous
The Birmingham Hook Plate Treatment Of Irreduceable Displaced Mallet Avulsion Fractures: A Technical Note
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Hand Surgery Volume 1 Number 1 The Birmingham Hook Plate Treatment Of Irreduceable Displaced Mallet Avulsion Fractures: A Technical S Tan, D Power Citation S Tan, D Power..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Hand Surgery Volume 1 Number 1 The Birmingham Hook Plate Treatment Of Irreduceable Displaced Mallet Avulsion Fractures: A Technical S Tan, D Power Citation S Tan, D Power..
PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger A Patient's Guide to PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger
 PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger A Patient's Guide to PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger Introduction We use our hands constantly, placing them in harm's way continuously. Injuries to the finger joints are
PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger A Patient's Guide to PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger Introduction We use our hands constantly, placing them in harm's way continuously. Injuries to the finger joints are
Upper Extremity Fractures
 Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
분절성쇄골골절의수술적치료와비수술적치료 - 증례보고 -
 CSE REPORT J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(3):151-155 ISSN 1225-1682 (Print) ㆍ ISSN 2287-9293 (Online) https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.151 분절성쇄골골절의수술적치료와비수술적치료 - 증례보고 - 하성식ㆍ홍기도ㆍ심재천ㆍ서이락ㆍ남태석 삼육서울병원정형외과
CSE REPORT J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(3):151-155 ISSN 1225-1682 (Print) ㆍ ISSN 2287-9293 (Online) https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.151 분절성쇄골골절의수술적치료와비수술적치료 - 증례보고 - 하성식ㆍ홍기도ㆍ심재천ㆍ서이락ㆍ남태석 삼육서울병원정형외과
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 76/ Sept. 21, 2015 Page 13162
 A CLINICAL STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE BOTH BONES FOREARM WITH INTERNAL FIXATION BY TWO DIFFERENT METHODS D. Venkateswara Rao 1, Chinta Shyam Kumar 2, Anvesh Sangepu 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D.
A CLINICAL STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE BOTH BONES FOREARM WITH INTERNAL FIXATION BY TWO DIFFERENT METHODS D. Venkateswara Rao 1, Chinta Shyam Kumar 2, Anvesh Sangepu 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D.
Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria
 TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y.
 Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
Finger fractures and dislocations may
 Common Finger Fractures and Dislocations JAMES R. BORCHERS, MD, MPH, and THOMAS M. BEST, MD, PhD, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio Finger fractures and dislocations are common injuries that are
Common Finger Fractures and Dislocations JAMES R. BORCHERS, MD, MPH, and THOMAS M. BEST, MD, PhD, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio Finger fractures and dislocations are common injuries that are
The Use of the S-Quattro Dynamic External Fixator for the Treatment of Intra-Articular Phalangeal Fractures: A Review of the Literature
 54 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, (Suppl 1: M6) 54-59 Open Access The Use of the S-Quattro Dynamic External Fixator for the Treatment of Intra-Articular Phalangeal : A Review of the Literature
54 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, (Suppl 1: M6) 54-59 Open Access The Use of the S-Quattro Dynamic External Fixator for the Treatment of Intra-Articular Phalangeal : A Review of the Literature
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 The Stiff Hand: Boutonniere & Sylvia Dávila, PT, CHT San Antonio, Texas Extensor Mechanism Central slip inserts into base of the middle phalanx Lateral bands lie dorsal to the PIP joint center of rotation
The Stiff Hand: Boutonniere & Sylvia Dávila, PT, CHT San Antonio, Texas Extensor Mechanism Central slip inserts into base of the middle phalanx Lateral bands lie dorsal to the PIP joint center of rotation
Early motion or immobilisation of Hand Fractures? Nikki Burr Consultant Hand Therapist Royal Free Hospital London Mount Vernon Hospital
 Early motion or immobilisation of Hand Fractures? Nikki Burr Consultant Hand Therapist Royal Free Hospital London Mount Vernon Hospital Hand Fractures (distal to carpus) Soft tissue injury with an underlying
Early motion or immobilisation of Hand Fractures? Nikki Burr Consultant Hand Therapist Royal Free Hospital London Mount Vernon Hospital Hand Fractures (distal to carpus) Soft tissue injury with an underlying
Identification of Double Compression Lesion of Ulnar Nerve after Cubital Tunnel Release
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(3):148-152. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.148 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Identification
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(3):148-152. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.148 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Identification
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Acute Rupture of Flexor Digitorum Profundus Tendon Associated with Distal Radius Fracture: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(4):198-203. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.4.198 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Acute Rupture
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(4):198-203. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.4.198 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Acute Rupture
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
CASE REPORT. Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
SURGERY OF THE HAND. Reverse Digital Island Flap with Skin Strip Retention to Prevent Flap Congestion INTRODUCTION ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 598-3889 eissn 34-998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 6;():7-76. http://dx.doi.org/.79/jkssh.6...7 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Reverse Digital Island Flap with Skin
ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 598-3889 eissn 34-998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 6;():7-76. http://dx.doi.org/.79/jkssh.6...7 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Reverse Digital Island Flap with Skin
SURGERY OF THE HAND. Results of Iliac Bone Graft with Kirschner Wire Fixation for Scaphoid Nonunions INTRODUCTION ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2017;22(3):174-179. http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2017.22.3.174 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Results of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2017;22(3):174-179. http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2017.22.3.174 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Results of
Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture Dislocation of the Elbow in an Adult
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Hand and wrist emergencies
 Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger Flaps and Vigorous Postoperative Exercises
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.574 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):574-578, 2010 Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.574 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):574-578, 2010 Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger
Recurrent subluxation or dislocation after surgical
 )263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
)263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures
 Journal of the Accident and Medical Practitioners Association (JAMPA) 2006; Vol. 3 (No. 1) Accident and Medical Practitioners Association, New Zealand Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures Sarah Cooper, MBChB
Journal of the Accident and Medical Practitioners Association (JAMPA) 2006; Vol. 3 (No. 1) Accident and Medical Practitioners Association, New Zealand Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures Sarah Cooper, MBChB
Other Upper Extremity Trauma. Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin
 Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
Pediatric Phalanx Fractures
 Pediatric Phalanx Fractures Julie Balch Samora, MD/PhD/MPH March 1, 2019.... Disclosures Board/committee member: AOA, AAOS, ASSH, RJOS, POSNA Globus (spouse) Goals To identify the most common phalanx fractures
Pediatric Phalanx Fractures Julie Balch Samora, MD/PhD/MPH March 1, 2019.... Disclosures Board/committee member: AOA, AAOS, ASSH, RJOS, POSNA Globus (spouse) Goals To identify the most common phalanx fractures
Carpal rows injuries!
 Carpal rows injuries! Michael Papaloïzos! Center for Hand Surgery and Therapy Geneva, Switzerland no conflict of interest to declare Fractures of carpal bones! The fractured scaphoid! Fracture-dislocations
Carpal rows injuries! Michael Papaloïzos! Center for Hand Surgery and Therapy Geneva, Switzerland no conflict of interest to declare Fractures of carpal bones! The fractured scaphoid! Fracture-dislocations
The Metacarpal Locked Intramedullary Nail: Comparative Biomechanical Evaluation of New Implant Design for Metacarpal Fractures
 The Metacarpal Locked Intramedullary Nail: Comparative Biomechanical Evaluation of New Implant Design for Metacarpal Fractures Chinnakart Boonyasirikool MD*, Sakkarin Tanakeatsakul MD**, Sunyarn Niempoog
The Metacarpal Locked Intramedullary Nail: Comparative Biomechanical Evaluation of New Implant Design for Metacarpal Fractures Chinnakart Boonyasirikool MD*, Sakkarin Tanakeatsakul MD**, Sunyarn Niempoog
Lunate and Perilunate Dislocations: Our Experience
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 8 Number 1 Lunate and Perilunate Dislocations: Our Experience J Ogunlusi, S St. Rose, T Davids Citation J Ogunlusi, S St. Rose, T Davids. Lunate
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 8 Number 1 Lunate and Perilunate Dislocations: Our Experience J Ogunlusi, S St. Rose, T Davids Citation J Ogunlusi, S St. Rose, T Davids. Lunate
