Functional Outcomes of Uni knee Arthroplasty for Medial Compartment Knee Arthropathy in Asian Patients
|
|
|
- Antony Tracy Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article 406 Functional Outcomes of Uni knee Arthroplasty for Medial Compartment Knee Arthropathy in Asian Patients To Wong 1, Ching Jen Wang 2, Jun Wen Wang 2, Jih Yang Ko 2 Background: Uni knee arthroplasty (UKA) has shown better knee kinematics and motion that may better suit the activities of daily living in Eastern countries. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the functional outcomes of UKA for medial compartment knee arthropathy in Asian patients. Methods: The study cohort consisted of 48 patients with 51 UK A knees. Only one type of prosthesis was used and all components were cemented. Postoperative management included ambulation with weight bearing, range of motion, and muscle strengthening exercises as tolerated until full recovery. The average follow up was 52.0 ± 24.0 (range 12-92) months. The evaluation included functional assessment, the Knee Society knee and functional scores, the International Knee Document Committee (IKDC) subjective and objective scores, and Results: radiographs of the knee. The overall clinical outcomes of the knee showed the functional outcome of the knee to be normal in 51%, nearly normal in 37%, abnormal in 8%, and severely abnormal in 4%. The functional activities included stair At a Glance Commentary Scientific background of the subject Uni-knee arthroplasty (UKA) is one of the surgical option for medial compartment knee arthropathy include osteoarthritis or osteonecrosis. Functional outcomes of UKA had been discussed among the western population. Better knee kinematics and motion in UKA design that consider more appropriate for the activities of daily living in Eastern countries. What this study adds to the field This study showed that UKA provides excellent pain relief and restoration knee daily activities that perfectly fit the oriental lifestyle and high patient satisfaction in Asian patients at medium-term follow-up. Low complications rate and good survival rate were found. climbing in 96%, squatting in 76%, jogging in 71% and kneeling in 47%. Three quarters of the patients were able to kneel for daily activities. Approximately 98% of the patients were satisfied with the operation. The survivorship of the prosthesis was 98% with one revision pending. Radiographic evaluations revealed the components were centered in 82% and off centered in 18%. Osteoarthritis was 22% preoperative and 27% postoperative for the patellofemoral compartment, and 0% before and 4% after surgery for the lateral compartment. The functional outcomes showed no difference between patients with and without patellofemoral arthritis. The complications included one component malposition and one knee pain of undetermined origin. Conclusions: UKA provides excellent pain relief and restoration of knee function including kneeling, squatting, and sit to stand activities that perfectly fit the oriental lifestyle and high patient satisfaction in Asian patients at medium term follow up. The complications were rare and the survival rate was 98% at medium term follow up. (Biomed J 2014;37: ) Key words: Asian, medial compartment knee arthropathy, uni knee arthroplasty From the 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Municipal United Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan; 2 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Kaohsiung, Taiwan Received: Jan. 25, 2013; Accepted: Jan. 15, 2014 Correspondence to: Dr. Ching Jen Wang, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital. 123, Tapei Rd., Niaosung, Kaohsiung 833, Taiwan (ROC). Tel: ; Fax: ; E mail: w281211@adm.cgmh.org.tw DOI: /
2 407 The surgical management options for medial compartment knee arthropathy (osteoarthritis or osteonecrosis) include uni knee arthroplasty (UKA), total knee arthroplasty (TKA), and high tibia osteotomy (HTO). [1 3] The surgeries are often used for different patient groups; however, there is considerable overlap in the indications for all three options and it is often difficult to decide whether a UKA or TKA is more appropriate. [3 5] Treatment of isolated compartmental osteoarthritis of the knee with UKA has mixed outcome and such procedure remains controversial. [6 9] However, there has been a resurgence of interest and a major increase in the use of UKA for the treatment of medial compartmental knee osteoarthritis in the past decades. [6,7,10 13] In the US market, UKA comprised approximately 1% of all knee arthroplasties in 1996 and 1997, and it increased to 6% in 2000 and [14] Improved prosthetic design, minimally invasive surgical techniques, and strict patient selection criteria have resulted in improved functional outcomes and survivorship rates. [15 22] The advantages of UKA included the preservation of knee kinematics and good range of knee motion that may better suit the need of kneeling in activities of daily living in oriental countries. [6,20] The purpose of this prospective study was to evaluate the functional outcomes of UKA for medial compartment knee arthropathy in Asian patients. METHODS The selection criteria of UKA included clinical, radiographic, and intraoperative assessments. [6,19] The clinical criteria included pain and tenderness localized to medial joint line, knee flexion more than 90, and fixed knee flexion deformity less than 10. The radiographic criteria included isolated medial compartment osteoarthritis with complete loss of cartilage, osteonecrosis of medial femoral condyle, varus deformity less than 15, and insignificant degenerative changes in other compartments. The intraoperative criteria included passively correctable varus deformity under anesthesia, intact anterior cruciate ligament, and full thickness cartilage wear on the anteromedial half of the medial tibia plateau. The exclusion criteria included inflammatory arthritis, patellofemoral joint symptoms, hemophilia, chondrocalcinosis, symptomatic knee instability, body mass index (BMI) of greater than 32, prior HTO, full thickness patellar cartilage loss, significant degenerative changes involving lateral or patellofemoral compartment, and severe angular deformity and flexion contracture. Forty eight patients with 51 knees who met the above criteria and underwent UKA were included in this study. The patient demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. The surgical tips consisted of minimally invasive medial parapatellar approach with quadriceps spared, lateral displacement of patella, but not everted, avoidance of incidental fracture of the vertical tibial cut, minimal or none soft Table 1: Patient demographic characteristics Numbers of patients/knees 48/51 Bilateral knees 3 Average age (years) (range) 65.71±7.27 (53-81) Gender (female/male) 35/13 Side (right/left) 23/28 Diagnosis Osteoarthritis (medial compartment) 82.4% (42/51) Osteonecrosis (MFC) 17.7% (9/51) Average duration of disease (months) (range) 18.3±15.23 (12-74) Average body weight (kg) (range) 68.13±10.08 (51-91) Average BMI (body wt/body ht in %) (range) 28.31±3.75 ( ) Average follow up (months) (range) 52.0±24.0 (12-92) Abbreviations: MFC: Medial femoral condle; BMI: Body mass index tissue release, equal flexion and extension gaps, replication of the tibia slope, centering of the femur component on the tibial component to reduce edge loading effect postoperatively and allow 2 mm medial laxity by undercorrection of 2-3 of varus angulation. In this series, only one type of prosthesis (Zimmer, Warsaw, IN, USA) was used and all components were cemented in all cases. Prophylaxis with broad spectrum antibiotics was routinely given for 24 h. However, prophylactic anticoagulation with low molecular weight heparin was given selectively in patients with high risk. Postoperative management included ambulation with weight bearing as tolerated, range of knee motion, and quadriceps and hamstring exercises starting from the second postoperative day. Patients were discharged from the hospital while independent on walking and continued outpatient physical therapy until full recovery. The evaluation parameters included knee and functional scores of The Knee Society, subjective and objective scores of the International Knee Document Committee (IKDC), and radiographs of the operated knees. Functional evaluation included pain, alignment and range of motion of the knee, and ability to do kneeling or squatting for activities of daily living. Radiographic evaluation included the overall alignment of the knee, component position, and radiolucency at the prosthesis bone interface. Statistical analysis The pre and postoperative data were compared statistically using Wilcoxon signed ranks test. The incidence of osteoarthritis in lateral and patellofemoral compartments was compared by Chi square test. The statistical significance was set at p < RESULTS The Knee Society knee and functional scores and the IKDC scores before and after surgery are summarized in Table 2. Significant improvements were noticed in pain and function of the knee after UKA (p < 0.001). The over
3 408 all clinical results showed the functional outcome of the knee to be normal in 51% (26 of 51), nearly normal in 37% (19 of 51), abnormal in 8% (4 of 51), and severely abnormal in 4% (2 of 51). The levels of functional activities included stair climbing in 96%, squatting in 76%, jogging in 71%, and kneeling in 47%. Approximately three quarters of the patients were able to kneel for activities of daily living including religious service and customary cross leg lifestyle. Approximately 98% of the patients were satisfied with the operation. The survivorship of the prosthesis was 98% at a follow up of 52.0 ± 24.0 (range 12-92) months, with one revision pending. The radiographic evaluation of the knee before and after surgery is summarized in Table 3. The femorotibial alignment was within normal physiological limits in all cases. Component position was centered in 82% and off centered in 18%. Osteoarthritis was 22% preoperative and 27% postoperative for the patellofemoral compartment, and 0% before and 4% after surgery for the lateral compartment. The functional activities of patients with and without patellofemoral arthritis are summarized in Table 4. The functional outcomes showed no differences between patients with and Table 2: Functional score, IKDC score, and range of knee motion Functional score (range) 51.1±18.6 (25-75) IKDC (range) 27.0±10.7 (15-50) Range of knee 115 ±5.0 5 motion (range) (0-125 ) Preoperative Postoperative p value a 86.8±12.3 (60-100) 79.5±19.4 (35-100) 125 ±10.5 (0-145 ) a The p values are obtained by Wilcoxon signed ranks test. Abbreviation: IKDC: International knee document committee Table 3: The radiographic evaluation <0.001 <0.001 a <0.001 a Femorotibial alignment Preoperative Postoperative p value Average (range) ± ±2.43 <0.001 a ( ) ( ) Tibial slope (range) 85.5 ± ±4.42 <0.001 a ( ) ( ) Patellar tilt 12% 13% 1.0 b Radiolucency 2% (1/51) Component position Center 82% (42/51) Medial (femur on tibia) 16% (8/51) (average 2.18±0.55 mm), (range mm) 2% (1/51) (3.5 mm) Lateral (femur on tibia) Degenerative changes Lateral compartment 0% 4% (2/51) b P/F compartment 22% (11/51) 27% (14/51) b Cement protrusion 9.8% (5/51) a The p-values are obtained statistically by Wilcoxon signed ranks test. b The p-values are obtained by McNemar s test without patellofemoral arthritis pre and postoperatively. Radiolucency was noted in only one case (2%) and was non progressive. Cement protrusion was identified in 9.8% and none was symptomatic. The pre and postoperative anteroposterior (AP) radiographs of the knee at 1, 4, and 6 years are shown in Figure 1. Complications included no infection, no deep vein thrombosis (DVT), one component malposition, and one knee pain of undetermined origin. DISCUSSION The initial results reported UKA to be unfavorable in the early stage of development. [8,9] However, there have been big changes with more favorable results in the past decades. The survivorship of UKA was reported to be between 96% and 98% at 7-10 years. [6,13,19] This was attributed to strict patient selection, improved prosthetic design, and minimally invasive surgery. [7,13,21 25] In the present study, the functional outcome of the knee was normal in 51%, nearly normal in 37%, abnormal in 8%, and severely abnormal in 4%. Approximately 98% of the patients were satisfied with the surgery. The survivorship of the prosthesis was 98% at a follow up of 52.0 ± 24.0 (range 12-92) months when the case of pending revision was counted as failure. Several studies reported nearly normal gait with preserved biphasic pattern and similar kinematic profiles of normal knee after UKA. [26 28] The gait velocity and muscle strength after UKA are superior to those after HTO. [2,27,28] UKA provided improved range of motion, decreased Table 4: Patellofemoral arthritis Preoperative Postoperative p-value 1 With P/F OA 22% (11/51) 27% (14/51) Without P/F OA 78% (40/51) 73% (37/51) <0.001 p-value 2 <0.001 <0.001 Function score With P/F OA 52.6±16.6 (25-71) 92.6±10.37 (69-100) Without P/F OA 53.9±18.8 (10-75) 87.0±12.2 (60-100) <0.001 p-value Kneeling With P/F OA 18% (2/11) 79% (11/14) Without P/F OA 20% (8/40) 81% (30/37) <0.001 p-value Squatting With P/F OA 18% (2/11) 71% (10/14) Without P/F OA 15% (6/40) 70% (26/37) <0.001 p-value Sit to stand With P/F OA 27% (3/11) 100% (14/14) Without P/F OA 23% (9/40) 97% (36/37) <0.001 p-value P/F OA: Patellofemoral arthritis; 1 p-value: Comparison of preoperative and postoperative data within the same group; 2 p-value: Comparison of data between two groups
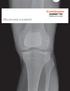
4 409 Figure 1: The pre- and postoperative AP radiographs of the knee at 1, 4, and 6 years showed centered UKA components in normal alignment and no radiolucency. rehabilitation time, and immediate weight bearing than HTO. However, HTO showed ability to maintain a higher level of activity without potential wear of arthroplasty components. Overall, UKA showed slightly better results in survival and functional outcome. [1,2,20] The majority of patients are able to return to recreational sports involving low and mid impact activities after UKA. [29,30] In this study, the levels of functional activities of the knee included stair climbing in 96%, squatting in 76%, jogging in 71%, and kneeling in 47%. Approximately three quarters of the patients are able to perform normal activities of daily living such as religious service and cross leg sitting lifestyle. One concern of UKA is the progression of osteoarthritic changes in the lateral and patellofemoral compartments and ultimately necessitated TKA. Progression of osteoarthritis to the lateral compartment was reported in 18% patients and to the patellofemoral compartment in 14% patients in 10 years. [6,31] The cumulative revision rate for UKA is 22% for patients younger than 60 years which is in part due to the progressive degenerative changes of other compartments. [32] UKA is reserved for knees with isolated uni compartmental osteoarthritis of the knee. However, early osteoarthritis of the patellofemoral joint with medial spur formation, but very subtle cartilage fissuring that is difficult to identify in clinical assessment and radiographic examination can only be verified intraoperatively. Under this circumstance, UKA and concomitant exostectomy and debridement of the patellofemoral joint were performed instead of TKA. In the present study, osteoarthritis of the patellofemoral joint was 22% before and 27% after surgery, and osteoarthritis of the lateral compartment was 0 before and 4% after surgery. The clinical outcomes were not affected when concomitant surgery was performed in the patellofemoral joint. Therefore, based on the results of the present study, medial compartmental osteoarthritis combined with early patellofemoral arthritis is not a contraindication for UKA. Some reports showed higher patient satisfaction after revision of a failed UKA than after revision of a failed TKA, and more surgeons recommend UKA because of functional superiority. [33] In this study, there was no revision or conversion of UKA to TKA due to progressive osteoarthritis of the knee at an average follow up 52.0 ± 24.0 months. The complications associated with TKA, such as infection, DVT, and stiffness, are rare after UKA. [21,24,31] In the present series, the complications included no infection, no DVT, one knee pain due to component malposition on X ray, and one knee pain of undetermined origin. This study has its own limitations. It is limited by virtue of the small number of patient population which may result in bias due to low power of statistical analysis. The average follow up time was approximately 4 years, and longer follow up is needed to ascertain the ultimate results of UKA in Asian patients. Other limitations include lack of control group in this study. The patients selected included those with a mixture of osteoarthritis and osteonecrosis of the medial compartment of the knee, and no stratification between the two diagnoses was performed. This study did not stratify patients younger than 60 years from the cohort population. The purpose of this study was not to compare the functional results of UKA with other procedures such as TKA or HTO, but to evaluate the functional results of UKA in Asian patients. Conclusion UKA provided excellent pain relief and restored the knee function in Asian patients with medial compartment knee arthropathy with a high rate of patient satisfaction at medium term follow up. Approximately three quarters of the patients are able to perform normal activities of daily living including kneeling for religious service and cross leg sitting lifestyle. Long term follow up is needed to further ascertain the ultimate outcome of UKA in Asian patients. Acknowledgments No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. REFERENCES 1. Dettoni F, Bonasia DE, Castoldi F, Bruzzone M, Blonna D, Rossi R. High tibial osteotomy versus unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for medial compartment arthrosis of the knee: A review of the literature. Iowa Orthop J 2010;30: Ivarsson I, Gillquist J. Rehabilitation after high tibial osteotomy and unicompartmental arthroplasty. A comparative study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1991;266: Rougraff BT, Heck DA, Gibson AE. A comparison of tricompartmental and unicompartmental arthroplasty for the treatment of gonarthrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1991;273:
5 Newman JH, Ackroyd CE, Shah NA. Unicompartmental or total knee replacement? Five year results of a prospective, randomised trial of 102 osteoarthritic knees with unicompartmental arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1998;80: Saldanha KA, Keys GW, Svard UC, White SH, Rao C. Revision of Oxford medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty to total knee arthroplasty Results of a multicentre study. Knee 2007;14: Berger RA, Meneghini RM, Jacobs JJ, Sheinkop MB, Della Valle CJ, Rosenberg AG, et al. Results of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty at a minimum of ten years of follow up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005;87: Emerson RH Jr, Higgins LL. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with the Oxford prosthesis in patients with medial compartment arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;90: Insall J, Walker P. Unicondylar knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1976;20: Laskin R. Unicompartmental tibiofemoral resurfacing arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1978;60: Koskinen E, Paavolainen P, Eskelinen A, Harilainen A, Sandelin J, Ylinen P, et al. Medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with Miller Galante II prosthesis: Mid term clinical and radiographic results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2009;129: Mercier N, Wimsey S, Saragaglia D. Long term clinical results of the Oxford medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 2010;34: Murray DW, Goodfellow JW, O Connor JJ. The Oxford medial unicompartmental arthroplasty: A ten year survival study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1998;80: Parmaksizoglu AS, Kabukcuoglu Y, Ozkaya U, Bilgili F, Aslan A. Short term results of the Oxford phase 3 unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for medial arthritis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2010;44: US markets for reconstructive devices Toronto: Millennum Research Group; Cinar BM, Akpinar S, Uysal M, Cesur N, Hersekli MA, Ozalay M, et al. Unicondylar knee arthroplasty in medial unicompartmental osteoarthritis: Technical faults and difficulties. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi 2010;21: Kaya Bicer E, Servien E, Lustig S, Demey G, Ait Si Selmi T, Neyret P. Sagittal flexion angle of the femoral component in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: Is it same for both medial and lateral UKAs? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2010;18: Kim KT, Lee S, Cho KH, Kim KS. Fracture of the medial femoral condyle after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2009;24:1143.e Luscombe KL, Lim J, Jones PW, White SH. Minimally invasive Oxford medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. A note of caution. Intern Orthop 2007;31: Pandit H, Jenkins C, Barker K, Dodd CA, Murray DW. The Oxford medial unicompartmental knee replacement using a minimally invasive approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2006;88: Price AJ, Dodd CA, Svard UG, Murray DW. Oxford medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in patients younger and older than 60 years of age. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2005;87: Daniilidis K, Skwara A, Skuginna A, Fischer F, Tibesku CO. Comparison of medium term clinical and radiological outcome between cemented and cementless medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Z Orthop Unfall 2009;147: Song MH, Kim BH, Ahn SJ, Yoo SH, Lee MS. Early complications after minimally invasive mobile bearing medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2009;24: Jenny JY. Comparative study of the use of computer assisted navigation system for axial correction in medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2010;18: Lim MH, Tallay A, Bartlett J. Comparative study of the use of computer assisted navigation system for axial correction in medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2009;17: Rudol G, Jackson MP, James SE. Medial tibial plateau fracture complicating unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2007;22: Webster KE, Wittwer JE, Feller JA. Quantitative gait analysis after medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoarthritis. J Arthroplasty 2003;18: Hollinghurst D, Stoney J, Ward T, Gill HS, Newman JH, Murray DW, et al. No deterioration of kinematics and cruciate function 10 years after medial unicompartmental arthroplasty. Knee 2006;13: Patil S, Colwell CW Jr, Ezzet KA, D Lima DD. Can normal knee kinematics be restored with unicompartmental knee replacement? J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005;87: Fisher N, Agarwal M, Reuben SF, Johnson DS, Turner PG. Sporting and physical activity following Oxford medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee 2006;13: Naal FD, Fischer M, Preuss A, Goldhahn J, von Knoch F, Preiss S, et al. Return to sports and recreational activity after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Am J Sports Med 2007;35: Ansari S, Warwick D, Ackroyd CE, Newman JH. Incidence of fatal pulmonary embolism after 1,390 knee arthroplasties without routine prophylactic anticoagulation, except in high risk cases. J Arthroplasty 1997;12: Harrysson OL, Robertsson O, Nayfeh JF. Higher cumulative revision rate of knee arthroplasties in younger patients with osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004;421: Robertsson O, Dunbar M, Pehrsson T, Knutson K, Lidgren L. Patient satisfaction after knee arthroplasty: A report on 27,372 knees operated on between 1981 and 1995 in Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand 2000;71:262 7.
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
Minimally invasive unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of osteonecrosis versus osteoarthritis : a matched-pair comparison
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 333-339 ORIGINAL STUDY Minimally invasive unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of osteonecrosis versus osteoarthritis : a matched-pair comparison Qidong Zhang,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 333-339 ORIGINAL STUDY Minimally invasive unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of osteonecrosis versus osteoarthritis : a matched-pair comparison Qidong Zhang,
Complications of Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:365-372 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.365 Complications of Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Jong Hun Ji, MD, Sang Eun Park, MD,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:365-372 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.365 Complications of Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Jong Hun Ji, MD, Sang Eun Park, MD,
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete
 Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Mid-Term Results of Oxford Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:178-183 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2011.3.3.178 Mid-Term Results of Oxford Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Won-Sik Choy, MD, Kap Jung
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:178-183 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2011.3.3.178 Mid-Term Results of Oxford Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Won-Sik Choy, MD, Kap Jung
why bicompartmental? A REVOLUTIONARY ALTERNATIVE TO TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 why bicompartmental? A REVOLUTIONARY ALTERNATIVE TO TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS TKR is not always the answer Today, many patients with medial or lateral disease and patellofemoral involvement receive a Total
why bicompartmental? A REVOLUTIONARY ALTERNATIVE TO TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS TKR is not always the answer Today, many patients with medial or lateral disease and patellofemoral involvement receive a Total
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Management of Periprosthetic Fracture in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Patients: A Case Series
 Management of Periprosthetic Fracture in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Patients: A Case Series Yew Lok Woo, MBBS, Pak Lin Chin, MBBS, FRCS, Ngai Nung Lo, MBBS, FRCS, Shi-Lu Chia, PhD, Darren Keng
Management of Periprosthetic Fracture in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Patients: A Case Series Yew Lok Woo, MBBS, Pak Lin Chin, MBBS, FRCS, Ngai Nung Lo, MBBS, FRCS, Shi-Lu Chia, PhD, Darren Keng
The influence of degeneration of the lateral patellofemoral joint on outcome of medial unicompartmental knee replacement
 2015 4 ORTHOPAEDIC BIOMECHANICS MATERIALS AND CLINICAL STUDY.29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn. 1672-5972.2015.02.008 swgk2015-03-0050 * 1 1 2 1 * 1 1 [ ] Oxford 2009 8 2013 12 126 (104 ) Ahlback Weidow 5 1 Hospital
2015 4 ORTHOPAEDIC BIOMECHANICS MATERIALS AND CLINICAL STUDY.29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn. 1672-5972.2015.02.008 swgk2015-03-0050 * 1 1 2 1 * 1 1 [ ] Oxford 2009 8 2013 12 126 (104 ) Ahlback Weidow 5 1 Hospital
The young patient and the medial unicompartmental knee replacement
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 283-288 ORIGINAL STUDY The young patient and the medial unicompartmental knee replacement Omar Faour Martín, Jose Antonio Valverde García, Miguel Ángel Martín Ferrero, Aurelio
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 283-288 ORIGINAL STUDY The young patient and the medial unicompartmental knee replacement Omar Faour Martín, Jose Antonio Valverde García, Miguel Ángel Martín Ferrero, Aurelio
Pre-operative clinical and radiological
 Pre-operative clinical and radiological assessment of the patellofemoral joint in unicompartmental knee replacement and its influence on outcome D. J. Beard, H. Pandit, S. Ostlere, C. Jenkins, C. A. F.
Pre-operative clinical and radiological assessment of the patellofemoral joint in unicompartmental knee replacement and its influence on outcome D. J. Beard, H. Pandit, S. Ostlere, C. Jenkins, C. A. F.
Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 0: 1 8, Department of Surgery, North Karelia Central Hospital, Joensuu, Finland 2
 577022SJS0010.1177/1457496915577022UKA mid-term resultss. S. A. Miettinen et al. research-article2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 0: 1 8, 2015 Mid-Term Results Of Oxford Phase 3 Unicompartmental
577022SJS0010.1177/1457496915577022UKA mid-term resultss. S. A. Miettinen et al. research-article2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 0: 1 8, 2015 Mid-Term Results Of Oxford Phase 3 Unicompartmental
With over 40 years clinical experience, the Oxford Partial Knee is the most widely used, 1 clinically proven 2 partial knee system in the world.
 Oxford Partial Knee A Definitive Implant With over 40 years clinical experience, the Oxford Partial Knee is the most widely used, 1 clinically proven 2 partial knee system in the world. Compared with total
Oxford Partial Knee A Definitive Implant With over 40 years clinical experience, the Oxford Partial Knee is the most widely used, 1 clinically proven 2 partial knee system in the world. Compared with total
Unicompartmental Knee Replacement
 Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Results and Techniques Alexander P. Sah, MD California Orthopaedic Association Meeting Laguna Niguel, CA May 20th, 2011 Overview Why partial knee replacement? - versus
Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Results and Techniques Alexander P. Sah, MD California Orthopaedic Association Meeting Laguna Niguel, CA May 20th, 2011 Overview Why partial knee replacement? - versus
Implant Overhang after Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Oxford Prosthesis versus Miller-Galante II Prosthesis
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2014;26(2):82-87 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2014.26.2.82 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Implant Overhang after Unicompartmental
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2014;26(2):82-87 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2014.26.2.82 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Implant Overhang after Unicompartmental
Assessment of radiolucent lines around the Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement
 KNEE Assessment of radiolucent lines around the Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY FOR LOOSENING S. Kalra, T. O. Smith, B. Berko, N. P. Walton From Norfolk and Norwich
KNEE Assessment of radiolucent lines around the Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY FOR LOOSENING S. Kalra, T. O. Smith, B. Berko, N. P. Walton From Norfolk and Norwich
Oxford. Partial Knee
 Oxford Partial Knee Oxford Partial Knee A Definitive Implant The Oxford Partial Knee is the most widely used 38 and clinically proven 22 partial knee replacement (PKR) system in the world, offering industry
Oxford Partial Knee Oxford Partial Knee A Definitive Implant The Oxford Partial Knee is the most widely used 38 and clinically proven 22 partial knee replacement (PKR) system in the world, offering industry
The Oxford phase III unicompartmental knee replacement in patients less than 60 years of age Kort, Nanne P.; van Raay, Jos J. A. M.; van Horn, Jim J.
 University of Groningen The Oxford phase III unicompartmental knee replacement in patients less than 60 years of age Kort, Nanne P.; van Raay, Jos J. A. M.; van Horn, Jim J. Published in: Knee surgery
University of Groningen The Oxford phase III unicompartmental knee replacement in patients less than 60 years of age Kort, Nanne P.; van Raay, Jos J. A. M.; van Horn, Jim J. Published in: Knee surgery
Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:386-392 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.386 Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up Kyung Tae
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:386-392 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.386 Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up Kyung Tae
Bicruciate-Retaining or Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis Pritchett 225 Fig. 3. The MP total knee prosthesis. Fig. 1. An anteroposterior radiograph o
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 26 No. 2 2011 Patients Prefer A Bicruciate-Retaining or the Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis James W. Pritchett, MD, FACS Abstract: Four-hundred forty patients underwent
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 26 No. 2 2011 Patients Prefer A Bicruciate-Retaining or the Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis James W. Pritchett, MD, FACS Abstract: Four-hundred forty patients underwent
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
Medium term results of the Miller-Galante unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with 10 year survivorship
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 197-204 ORIGINAL STUDY Medium term results of the Miller-Galante unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with 10 year survivorship Rajesh Rachha, Karunakar Veravalli, Manoj Sood
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 197-204 ORIGINAL STUDY Medium term results of the Miller-Galante unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with 10 year survivorship Rajesh Rachha, Karunakar Veravalli, Manoj Sood
Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Oxford phase 3 unicompartmental knee replacement in Korean patients
 KNEE Oxford phase 3 unicompartmental knee replacement in Korean patients H-C. Lim, J-H. Bae, S-H. Song, S-J. Kim From Guro Hospital, Korea University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea Medium-term survivorship
KNEE Oxford phase 3 unicompartmental knee replacement in Korean patients H-C. Lim, J-H. Bae, S-H. Song, S-J. Kim From Guro Hospital, Korea University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea Medium-term survivorship
The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
Unicompartmental or total knee replacement
 Unicompartmental or total knee replacement THE 15-YEAR RESULTS OF A PROSPECTIVE RANDOMISED CONTROLLED TRIAL J. Newman, R. V. Pydisetty, C. Ackroyd From Avon Orthopaedic Centre, Bristol, England Between
Unicompartmental or total knee replacement THE 15-YEAR RESULTS OF A PROSPECTIVE RANDOMISED CONTROLLED TRIAL J. Newman, R. V. Pydisetty, C. Ackroyd From Avon Orthopaedic Centre, Bristol, England Between
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Mid-Term Results of Oxford Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty in Young Asian Patients Less than 60 Years of Age: A Minimum 5-Year Follow-up
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(2):122-128 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.16.045 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Mid-Term Results of Oxford Medial Unicompartmental
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(2):122-128 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.16.045 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Mid-Term Results of Oxford Medial Unicompartmental
Gender Solutions Patello-Femoral Joint System
 Zimmer Biomet is the leading company in partial knee arthroplasty (PKA) 1 with over 40 years experience, offering a comprehensive range of anatomic and innovative solutions. Research shows that surgeons
Zimmer Biomet is the leading company in partial knee arthroplasty (PKA) 1 with over 40 years experience, offering a comprehensive range of anatomic and innovative solutions. Research shows that surgeons
The Survivorship and Clinical Results of Minimally Invasive Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty at 10-Year Follow-up
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:199-206 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.199 The Survivorship and Clinical Results of Minimally Invasive Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:199-206 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.199 The Survivorship and Clinical Results of Minimally Invasive Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty
15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 18 No. 8 2003 15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jun Ito, MD, PhD, Tomihisa Koshino, MD, PhD, Renzo Okamoto, MD, PhD,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 18 No. 8 2003 15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jun Ito, MD, PhD, Tomihisa Koshino, MD, PhD, Renzo Okamoto, MD, PhD,
Does a minimally invasive approach affect positioning of components in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty? Early results with survivorship analysis
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 709-715 ORIGINAL STUDY Does a minimally invasive approach affect positioning of components in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty? Early results with survivorship analysis
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 709-715 ORIGINAL STUDY Does a minimally invasive approach affect positioning of components in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty? Early results with survivorship analysis
The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the
 The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year
 Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year H. Pandit, C. Jenkins, D. J. Beard, J. Gallagher, A. J. Price, C. A. F. Dodd, J. W. Goodfellow, D. W. Murray From
Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year H. Pandit, C. Jenkins, D. J. Beard, J. Gallagher, A. J. Price, C. A. F. Dodd, J. W. Goodfellow, D. W. Murray From
Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven Partial Knee in the World. Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation
 Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven Partial Knee in the World Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation 1 Microplasty Instrumentation Innovative, Accurate, Reproducible Microplasty instrumentation
Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven Partial Knee in the World Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation 1 Microplasty Instrumentation Innovative, Accurate, Reproducible Microplasty instrumentation
Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven 1 Partial Knee in the World. Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation
 Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven 1 Partial Knee in the World Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation 1 Microplasty Instrumentation Innovative, Accurate, Reproducible Microplasty Instrumentation
Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven 1 Partial Knee in the World Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation 1 Microplasty Instrumentation Innovative, Accurate, Reproducible Microplasty Instrumentation
Stefan Rahm MD University Hospital Balgrist
 Knee Prosthesis Models & Materials, Surgical Techniques and Approaches Stefan Rahm MD University Hospital Balgrist INTRODUCTION VARUS VALGUS 46 Y OLD MALE Pain in the medial compartment left more than
Knee Prosthesis Models & Materials, Surgical Techniques and Approaches Stefan Rahm MD University Hospital Balgrist INTRODUCTION VARUS VALGUS 46 Y OLD MALE Pain in the medial compartment left more than
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
For Commercial products, please refer to the following policy: Preauthorization via Web-Based Tool for Procedures
 Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing
 A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
The Knee. The Twin Peg Oxford partial knee replacement: The first 100 cases. Stephen H. White a,, Sharon Roberts a, Peter W.
 The Knee 19 (2012) 36 40 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect The Knee The Twin Peg Oxford partial knee replacement: The first 100 cases Stephen H. White a,, Sharon Roberts a, Peter W. Jones b a Department
The Knee 19 (2012) 36 40 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect The Knee The Twin Peg Oxford partial knee replacement: The first 100 cases Stephen H. White a,, Sharon Roberts a, Peter W. Jones b a Department
H.P. Teng, Y.J. Chou, L.C. Lin, and C.Y. Wong Under general or spinal anesthesia, the knee was flexed gently. In the cases of limited ROM, gentle and
 THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
The KineSpring Knee Implant System Product Information
 The KineSpring Knee Implant System Product Information The Treatment Gap Increasing numbers of young, active OA patients with longer life expectancy and higher activity demands. 1 Large increase in arthroplasty
The KineSpring Knee Implant System Product Information The Treatment Gap Increasing numbers of young, active OA patients with longer life expectancy and higher activity demands. 1 Large increase in arthroplasty
Midterm results of cemented Press Fit Condylar Sigma total knee arthroplasty system
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005:13(3):280-284 Midterm results of cemented Press Fit Condylar Sigma total knee arthroplasty system S Asif, DSK Choon Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005:13(3):280-284 Midterm results of cemented Press Fit Condylar Sigma total knee arthroplasty system S Asif, DSK Choon Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements:
 Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 934-938 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee Sandesh
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 934-938 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee Sandesh
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC. Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Case Report Meniscal Bearing Dislocation of Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty with Faint Symptom
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 217842, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/217842 Case Report Meniscal Bearing Dislocation of Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty with Faint Symptom
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 217842, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/217842 Case Report Meniscal Bearing Dislocation of Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty with Faint Symptom
Why Consider Partial Knee Arthroplasty?
 Why Consider Partial Knee Arthroplasty? Andrew A. Freiberg, MD Chief, Adult Reconstruction Service Massachusetts General Hospital Surgeon, Newton Wellesley Hospital Associate Professor, Harvard Medical
Why Consider Partial Knee Arthroplasty? Andrew A. Freiberg, MD Chief, Adult Reconstruction Service Massachusetts General Hospital Surgeon, Newton Wellesley Hospital Associate Professor, Harvard Medical
Original Date: December 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
Umile Giuseppe Longo, Mattia Loppini, Ugo Trovato, Giacomo Rizzello, Nicola Maffulli,, *, and Vincenzo Denaro. Abstract
 British Medical Bulletin, 2015, 114:65 73 doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldv009 Advance Access Publication Date: 4 March 2015 No difference between unicompartmental versus total knee arthroplasty for the management
British Medical Bulletin, 2015, 114:65 73 doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldv009 Advance Access Publication Date: 4 March 2015 No difference between unicompartmental versus total knee arthroplasty for the management
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Tissue-sparing surgery with the bi-unicompartmental knee prosthesis: retrospective study with minimum follow-up of 36 months
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2006) 7:108 112 DOI 10.1007/s10195-005- - TSS SECTION N. Confalonieri A. Manzotti Tissue-sparing surgery with the bi-unicompartmental knee prosthesis: retrospective study with minimum
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2006) 7:108 112 DOI 10.1007/s10195-005- - TSS SECTION N. Confalonieri A. Manzotti Tissue-sparing surgery with the bi-unicompartmental knee prosthesis: retrospective study with minimum
Is There A Difference In Uni- And Multi-compartmental Knee Arthroplasty Kinematics?
 Is There A Difference In Uni- And Multi-compartmental Knee Arthroplasty Kinematics? Toshifumi Watanabe, MD, PhD 1, Stefan Kreuzer, MD, MS 2, Jennifer Amanda Christopher, BS 3, Michael Conditt, PhD 3, Brian
Is There A Difference In Uni- And Multi-compartmental Knee Arthroplasty Kinematics? Toshifumi Watanabe, MD, PhD 1, Stefan Kreuzer, MD, MS 2, Jennifer Amanda Christopher, BS 3, Michael Conditt, PhD 3, Brian
Day of Surgery Discharge after Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty (UKA): An Effective Perioperative Pathway. Jay Patel, MD Hoag Orthopedic Institute
 Day of Surgery Discharge after Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty (UKA): An Effective Perioperative Pathway Jay Patel, MD Hoag Orthopedic Institute UKA Rapid Recovery Protocol Purpose of Study Describe
Day of Surgery Discharge after Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty (UKA): An Effective Perioperative Pathway Jay Patel, MD Hoag Orthopedic Institute UKA Rapid Recovery Protocol Purpose of Study Describe
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference?
 Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Knee Surg Relat Res 2011;23(3): pissn eissn Knee Surgery & Related Research
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2011;23(3):142-148 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2011.23.3.142 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research A Comparison of Patella Retention versus
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2011;23(3):142-148 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2011.23.3.142 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research A Comparison of Patella Retention versus
No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery
 DOI 10.1007/s00167-014-2849-0 KNEE No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery Bart Kerens Martijn G. M. Schotanus Bert Boonen Nanne P. Kort Received:
DOI 10.1007/s00167-014-2849-0 KNEE No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery Bart Kerens Martijn G. M. Schotanus Bert Boonen Nanne P. Kort Received:
08:00 08:10 Welcome from the Chairmen J-N. Argenson / E. Thienpont. 08:10 08:20 Interactivity at this meeting C. Dodd / A. Baldini
 Knee² International Sports Medicine and Knee Arthroplasty Meeting 2015 Gothenburg, Sweden 28-31 October 2015 WEDNESDAY 28 OCTOBER Arrivals THURSDAY 29 OCTOBER 08:00 08:10 Welcome from the Chairmen J-N.
Knee² International Sports Medicine and Knee Arthroplasty Meeting 2015 Gothenburg, Sweden 28-31 October 2015 WEDNESDAY 28 OCTOBER Arrivals THURSDAY 29 OCTOBER 08:00 08:10 Welcome from the Chairmen J-N.
1. White SH, Nazarian NA, McEwen Smith AM, Balfour TW. Periampullary adenoma causing pancreatitis. Br Med J 1981; 283:527.
 Mr Steve White, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Peer-reviewed original papers: 1. White SH, Nazarian NA, McEwen Smith AM, Balfour TW. Periampullary adenoma causing pancreatitis. Br Med J 1981; 283:527.
Mr Steve White, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Peer-reviewed original papers: 1. White SH, Nazarian NA, McEwen Smith AM, Balfour TW. Periampullary adenoma causing pancreatitis. Br Med J 1981; 283:527.
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. M.S. Barrow Barrow Physiotherapy MBBch (Wits), FCS (SA) Orth. Waterfall City Hospital Orthopaedic Surgeon Tel: 011 304 7829 Suite 5, East Wing, Sunninghill Hospital www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. M.S. Barrow Barrow Physiotherapy MBBch (Wits), FCS (SA) Orth. Waterfall City Hospital Orthopaedic Surgeon Tel: 011 304 7829 Suite 5, East Wing, Sunninghill Hospital www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za
Clinical Study Cemented versus Uncemented Oxford Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Is There a Difference?
 Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 245915, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/245915 Clinical Study Cemented versus Uncemented Oxford Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Is There a Difference?
Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 245915, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/245915 Clinical Study Cemented versus Uncemented Oxford Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Is There a Difference?
Total Joints and Arthritis. Marc A. Roux, M.D. Chief of Surgery, Baylor Medical Center at Waxahachie August 25, 2012
 Total Joints and Arthritis Marc A. Roux, M.D. Chief of Surgery, Baylor Medical Center at Waxahachie August 25, 2012 Joint Replacement Will focus on Knee and Hip OA amd joint replacement Over 500,000
Total Joints and Arthritis Marc A. Roux, M.D. Chief of Surgery, Baylor Medical Center at Waxahachie August 25, 2012 Joint Replacement Will focus on Knee and Hip OA amd joint replacement Over 500,000
Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella Treated with a Different Method in Each Knee
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890315, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890315 Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890315, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890315 Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella
Why precision is powerful
 Why precision is powerful A new answer for isolated patellofemoral OA First generation PFJ implants had sharp, constraining trochlear grooves and were prone to complications such as maltracking and catching
Why precision is powerful A new answer for isolated patellofemoral OA First generation PFJ implants had sharp, constraining trochlear grooves and were prone to complications such as maltracking and catching
Results of arthroscopic surgery, with or without high Tibial osteotomy, in osteoarthritis of knee
 2018; 2(3): 100-105 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(3): 100-105 Received: 17-05-2018 Accepted: 18-06-2018 Dr. Tarkik Amin Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(3): 100-105 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(3): 100-105 Received: 17-05-2018 Accepted: 18-06-2018 Dr. Tarkik Amin Assistant Professor,
Correlation between Knee Kinematics and Patello-femoral Contact Pressure in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Correlation between Knee Kinematics and Patello-femoral Contact Pressure in Total Knee Arthroplasty Takuya Konno, MD 1, Tomohiro Onodera, MD, PhD 1, Yasuhiko Kasahara, MD, PhD 1, Daisuke Takahashi 1, Norimasa
Correlation between Knee Kinematics and Patello-femoral Contact Pressure in Total Knee Arthroplasty Takuya Konno, MD 1, Tomohiro Onodera, MD, PhD 1, Yasuhiko Kasahara, MD, PhD 1, Daisuke Takahashi 1, Norimasa
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers
 CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
Analysis of factors affecting range of motion after Total Knee Arthroplasty
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. II (Sep. 2015), PP 01-10 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of factors affecting range of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. II (Sep. 2015), PP 01-10 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of factors affecting range of
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Save the meniscus Mais pourquoi?
 Save the meniscus Mais pourquoi? #$%&' ()"*+!," Philippe Neyret E Servien S Lustig P Verdonk One or more of the authors of the next presentation have identified no potential conflicts of interest 2 Consequences
Save the meniscus Mais pourquoi? #$%&' ()"*+!," Philippe Neyret E Servien S Lustig P Verdonk One or more of the authors of the next presentation have identified no potential conflicts of interest 2 Consequences
Shaoqi Tian 1*, Bin Wang 2, Yuanhe Wang 1, Chengzhi Ha 1, Lun Liu 1 and Kang Sun 1*
 Tian et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:327 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-1186-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
Tian et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:327 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-1186-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
Oxford Phase 3 unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: medium-term results of a minimally invasive surgical procedure
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2011) 19:277 284 DOI 10.1007/s00167-010-1213-2 KNEE Oxford Phase 3 unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: medium-term results of a minimally invasive surgical procedure
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2011) 19:277 284 DOI 10.1007/s00167-010-1213-2 KNEE Oxford Phase 3 unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: medium-term results of a minimally invasive surgical procedure
Sasaki E 1,2, Otsuka H 2, Sasaki N 2, and Ishibashi Y 1
 Influence of osteophyte resection of the posterior femoral condyle on extension range of motion and gap balance in cruciate retaining type total knee arthroplasty. - Intraoperative evaluation using navigation
Influence of osteophyte resection of the posterior femoral condyle on extension range of motion and gap balance in cruciate retaining type total knee arthroplasty. - Intraoperative evaluation using navigation
Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W.
 University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis
 Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with an Ankylosing Knee after Previous Patellectomy
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2014;26(3):182-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2014.26.3.182 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2014;26(3):182-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2014.26.3.182 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with
Full Function, Faster Medial-Pivot
 Full Function, Faster Medial-Pivot Total Knee Replacement Patient Brochure Does your knee prevent you from performing and enjoying everyday activities? Osteoarthritis affects nearly 350 million people
Full Function, Faster Medial-Pivot Total Knee Replacement Patient Brochure Does your knee prevent you from performing and enjoying everyday activities? Osteoarthritis affects nearly 350 million people
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates!
 7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping
 Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Limb alignment in computer-assisted minimally-invasive unicompartmental knee replacement
 Limb alignment in computer-assisted minimally-invasive unicompartmental knee replacement G. Keene, D. Simpson, Y. Kalairajah From Sportsmed-SA Orthopaedic Clinic, Adelaide, South Australia Twenty patients
Limb alignment in computer-assisted minimally-invasive unicompartmental knee replacement G. Keene, D. Simpson, Y. Kalairajah From Sportsmed-SA Orthopaedic Clinic, Adelaide, South Australia Twenty patients
Some illustrations are from the internet and intended for educational purpose only
 Some illustrations are from the internet and intended for educational purpose only นพ. ส หธ ช งามอ โฆษ ภาคว ชา ออร โธป ด กส คณะแพทย ศาสตร จ ฬาลงกรณ มหาว ทยาล ย Knee anatomy Femur Pathophysiology Symptoms
Some illustrations are from the internet and intended for educational purpose only นพ. ส หธ ช งามอ โฆษ ภาคว ชา ออร โธป ด กส คณะแพทย ศาสตร จ ฬาลงกรณ มหาว ทยาล ย Knee anatomy Femur Pathophysiology Symptoms
Partial Knee Replacement
 Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success. Zimmer Natural-Knee II System
 Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success Zimmer Natural-Knee II System CSTi Porous Coating Structurally similar to human bone CSTi porous coating combines the excellent biocompatibility of titanium with
Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success Zimmer Natural-Knee II System CSTi Porous Coating Structurally similar to human bone CSTi porous coating combines the excellent biocompatibility of titanium with
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
Medial unicompartmental knee replacement in the under-50s
 Medial unicompartmental knee replacement in the under-50s S. Parratte, J.-N.A.Argenson, O. Pearce, V. Pauly, P. Auquier, J.-M. Aubaniac From Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France We retrospectively
Medial unicompartmental knee replacement in the under-50s S. Parratte, J.-N.A.Argenson, O. Pearce, V. Pauly, P. Auquier, J.-M. Aubaniac From Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France We retrospectively
Life. Uncompromised. The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout
 Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Noninvasive Assessment of Sagittal Knee Kinematics After Total Knee Arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 16 Number 2 Noninvasive Assessment of Sagittal Knee Kinematics After Total Knee Arthroplasty V Chester, E Biden, T Barnhill Citation V Chester,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 16 Number 2 Noninvasive Assessment of Sagittal Knee Kinematics After Total Knee Arthroplasty V Chester, E Biden, T Barnhill Citation V Chester,
21/01/10. Disclosures. Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature. Introduction. OW osteotomy and bone graft
 3rd Annual Advanced Course on Knee Surgery January 17-22, 2010, Val D Isere, Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature Disclosures Conflict of interest related to this presentation:
3rd Annual Advanced Course on Knee Surgery January 17-22, 2010, Val D Isere, Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature Disclosures Conflict of interest related to this presentation:
Conversion of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty to total knee arthroplasty : The challenges and need for augments
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 699-705 ORIGINAL STUDY Conversion of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty to total knee arthroplasty : The challenges and need for augments Zeeshan Khan, Syed Z. Nawaz, Steven
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 699-705 ORIGINAL STUDY Conversion of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty to total knee arthroplasty : The challenges and need for augments Zeeshan Khan, Syed Z. Nawaz, Steven
Patellofemoral Replacement
 Patellofemoral Replacement During knee replacement surgery, damaged bone and cartilage is resurfaced with metal and plastic components. Patellofemoral replacement is a type of "partial" knee replacement
Patellofemoral Replacement During knee replacement surgery, damaged bone and cartilage is resurfaced with metal and plastic components. Patellofemoral replacement is a type of "partial" knee replacement
Fixed or Mobile bearing in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty
 Fixed or Mobile bearing in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Jean-Noel Argenson, Matthieu Ollivier, Xavier Flecher, Sebastien Parratte Institute for Locomotion Sainte Marguerite Hospital, Marseille, France
Fixed or Mobile bearing in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Jean-Noel Argenson, Matthieu Ollivier, Xavier Flecher, Sebastien Parratte Institute for Locomotion Sainte Marguerite Hospital, Marseille, France
