Biological evects of extracorporeal shockwave in bone healing: a study in rabbits
|
|
|
- Louise May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI /s BASIC SCIENCE Biological evects of extracorporeal shockwave in bone healing: a study in rabbits Ching-Jen Wang Feng-Sheng Wang Kuender D. Yang Received: 31 July 2007 Springer-Verlag 2008 Abstract Introduction This study is an investigation of the biological evects of extracorporeal shockwave treatment (ESWT) on bone healing in a rabbit model. Materials and methods Sixteen 12-month-old New Zealand white rabbits with body weight ranging from 2.5 to 3.5 kg were used in the study. An intra-medullary pin was inserted retrograde into the femur canal. A closed fracture of the femur was created with a three-point bend method. The animals were randomly divided into the study group and the control group with eight rabbits in each group. The study group received shockwave treatment, whereas the control group did not. The animals were killed at 12 weeks, and a 5-cm long femur bone including the callus was harvested. The specimens were subjected to biomechanical study, histomorphological examination, and immunohistochemical analysis. Results The shockwave group showed signiwcantly better bone strength in biomechanical study, more cortical bone formation in histomorphological examination and higher number of neo-vessels and angiogenic and osteogenic C.-J. Wang (&) Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Ta-Pei Road, Niao-Sung Hsiang, Kaohsiung 833, Taiwan w281211@adm.cgmh.org.tw F.-S. Wang K. D. Yang Department of Medical Research, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Kaohsiung, Taiwan growth markers including VEGF, enos, PCNA, and BMP- 2 on immunohistochemical stains than the control group. Conclusion ESWT signiwcantly improved bone healing after fracture of the femur in rabbit. ESWT promoted the formation of cortical bone what might have been associated with increased biomechanical results. ESWT-promoted bone healing was associated with increased neovascularization and up-regulation of angiogenic and osteogenic growth factors. Keywords Shockwave Bone healing Biological evect Rabbits Introduction Extracorporeal shockwave treatment (ESWT) was shown evective in non-union of long bone fracture with a success rate ranging from 65 to 85% [3, 9 14]. The positive evect of shockwave in promoting bone healing was demonstrated in both acute fracture and chronic non-union in animal experiments [2, 4, 6, 7, 15]. Despite the success in clinical application and the positive evect in animal study, the exact mechanism of shockwave in bone healing remains unknown. Recently, ESWT was shown to induce the ingrowths of neovascularization and increased angiogenic growth factors at the Achilles tendon-bone junction in dog and rabbit models [17, 20]. We hypothesized that shockwave-promoted bone healing may show similar biological evects. The purpose of this study was to investigate the eycacy of shockwave in bone healing and to unveil the working mechanism through the biological evects of shockwave-promoted bone healing in rabbits.
2 Materials and methods The Institutional Review Board of our hospital approved the study. The animal experiments were performed under the guidelines and the care and use of animals in research. Sixteen New Zealand white rabbits, 12 months old, with body weight ranging from 2.5 to 3.5 kg were used in this study. The rabbits were anesthetized with intra-muscular ketamine (25 mg/kg) and phenobarbital (30 mg/kg). The right lower limb was scrubbed and draped in surgically sterile fashion. A mini-arthrotomy of the knee was made through a medial parapatellar incision. A drill hole was made at the center of the intercondylar notch, and a 2.0 mm Kirschnur pin was inserted retrograde into the canal of the femur. The proximal end of the pin was exited through a separate incision over the trochanter, and the tip of the pin was bent to prevent it from migration. The distal end of the pin was cut Xush with the articular surface of the distal femur condyles. The incisions were closed in routine fashion after irrigation with normal saline. A closed fracture of the right femur was created with a three-point bend method [5]. The hip and knee were supported on a three point bending apparatus, and a closed fracture of the right femur was created at the mid-third with a loading anvil. Special care was undertaken to avoid bending of the intra-medullary pin when the fracture occurred. The fracture was conwrmed with radiographic examination (Fig. 1). Postoperative prophylaxis included ampicillin (50 mg/kg) every 12 h given intramuscularly for 5 days. The rabbits were kept in the housing cage and cared for by a veterinarian. The surgical wounds, the alignment and stability of the fractured limb and the overall activities of the rabbit were monitored daily. The rabbits were randomly divided into two groups with eight rabbits in the study group and eight in the control group. The study group received 2,000 impulses of shockwaves at 20 kv (equivalent to 0.47 mj/mm 2 energy Xux density) to the fracture site in 1 week after the fracture when the surgical wounds had healed. The source of shockwave was from an electrohydraulic OssaTron (Sanuwave, Alpharetta, GA, USA). The fracture site and the depth of treatment were conwrmed with the control guide of the machine under C-arm imaging. Surgical lubricate was placed onto the skin in contact with the shockwave tube. ESWT was applied in two planes at 90 with 1,000 shocks in each plane as a single session. Immediately after the treatment, the avected limb was inspected for local redness, swelling, or hematoma. The control group received no shockwave. The rabbits were returned to the housing cages with no additional immobilization. Serial radiographs of the right femur in A-P and lateral views were performed at 1, 4, 8 and 12 weeks. The fracture Fig. 1 Radiographs of the right femur in anteroposterior and lateral views showed fracture of the femur with an intra-medullary pin Wxation healing was evaluated by clinical assessment and conwrmed with radiographs. Clinical assessments included local tenderness and motion at the fracture site. Radiographs evaluated the amount of callus formation and the bridging bone across the fracture site. All fractures healed radiographically in 12 weeks. The rabbits were killed at 12 weeks. The K-pin was removed and a 5-cm long segment of the femur bone including the callus was harvested. The bone specimens were subjected to biomechanical study, histomorphological examination, and immunohistochemical analysis. Biomechanical study The bone strength tests including peak load, peak stress, and modulus of elasticity were performed using a slow load compression test on Material Testing System OT 10 (MST Corp., Minneapolis, MN). A supporting apparatus with two supporting points 30 mm apart was placed on the stage of the machine. The specimens were tested on a supported beam using an actuator displacement rate of 2 mm/min. To avoid rotation of the bone during testing, the bending load was applied to the concave surface of the femur bone. The press head was rounded ov to avoid cutting into the bone when loaded. The fracture load (lb) and the dexection of bone (mm) were read from the load dexection curve (Fig. 2).
3 Two pathologists blinded to the treatment regimens performed the measurements on all sections. Statistical analysis Data were analyzed with a two-way analysis of variance followed by Mann Whitney U test to determine the signiwcance between the shockwave group and the control group. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically signiwcant. Results Fig. 2 The load dexection displacement curves of the bone on slow load compression test performed on MTS machine (Material Testing System). The upper curve showed the shockwave group and the control group in the lower curve Histomorphological examination The harvested bone specimens were Wxed in 4% PBSbuVered paraformaldehyde for 48 h and decalciwed in PBS-buVered 10% EDTA. DecalciWed tissues were embedded in parayn. Bone specimens were cut longitudinally into 5-μm thick sections and transferred to poly-lysine-coated slides for conventional hematoxylin-eosin, alcian blue, or alizarin red staining (Sigma Chemicals Inc, St Louis, MO, USA) for the purpose of distinguishing Wbrous tissue, cartilagenous, and bony tissues within the specimens. Immunohistochemical analysis Sections of the bone specimens were immunostained for VEGF-A, enos, PCNA, and BMP-2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc, CA, USA) to identify angiogenesis and osteogenesis-related growth and proliferating indicators. The immuno-reactivity in specimens was demonstrated using a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-3 -, 3 -diaminobenzidine (DAB) cell and tissue staining kit (R&D Systems Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA). The immuno-activities were quanti- Wed from Wve areas in three sections of the callus site from each animal using a Zeiss Axioskop 2 plus microscope (Carl Zeiss, Gottingen, Germany). All the images of each specimen were captured using a Cool CCD camera (SNAP- Pro cf. Digital kit; Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD, USA). Images were analyzed using an Image-Pro Plus image-analysis software (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD, USA). The actual number and the percentage of positive immuno-labeled cells over the total cells in each area were counted. An antibody against von Willebrand factor (vwf) was used to identify the immunolocalization of neovessels in the callus sites of shockwave and control groups. Bone strength tests The results of bone strength including peak load, peak stress, and modulus of elasticity of the shockwave and control groups are summarized in Table 1. All specimens showed a typical load dexection displacement curve with an initial non-linear response followed by an upward linear slop and a failure response at the time of fracture. The shockwave group showed signiwcantly higher peak load, peak stress, and elastic modulus than the control (P < 0.05). Histomorphological examination The results of tissue distributions of the shockwave and control groups are summarized in Table 2. The shockwave group showed signiwcantly more cortical bone (P = 0.048), less Wbrous tissue (P = 0.053), and comparable woven bone (P = 0.116) as compared to the control (Fig. 3). Immunohistochemical analysis Data on the numbers of neo-vessels and positive immunostained cells for VEGF, enos, PCNA, and BMP-2 in the callus site of the shockwave and control groups are summarized in Table 3 and illustrated microscopically in Table 1 The results of biomechanical study The data were shown in mean SD Control (N = 8) Shockwave (N = 8) P value Peak load (lb) Median (range) 68.1 ( ) ( ) Peak stress (in-lb) Median (range) 3.4 ( ) 12.4 ( ) Modulus of elasticity Median (range) 18,332 (9,658 26,788) 18,663 6,888 71,053 25, P values are based on Mann Whitney U test 71,858 (30, ,645)
4 Table 2 Tissue distribution in histomorphological examination The data are shown in mean SD P values are based on Mann Whitney U test Control (N = 8) Shockwave (N = 8) P value Cortical bone Area in mm 2 (%) 2, ,130.5 ( %) 4, ( %) Median (range) 2,270.4 (1,159 3,540.3) 4,194.9 (3, ,812.7) Woven bone Area in mm 2 (%) 2, ( %) 1, ( %) Median (range) 2,372.3 (1, ,348.7) 1,762.5 (1,594 2,738.2) Fibrous tissue Area in mm 2 (%) ( %) ( %) Median (range) ( ) 96.7 ( ) Fig. 3 The histomorphological features of the callus site showed more cortical bone, less Wbrous tissue and comparable woven bone in shockwave group than the control group Table 3 The results of immunohistochemical analysis Control (N = 8) Shockwave (N = 8) P value Neo-vessels Median (range) 39 (23 53) 72 (36 96) VEGF Median (range) 174 (75 205) 277 ( ) enos Median (range) 175 ( ) 294 ( ) PCNA Median (range) 210 ( ) 305 ( ) BMP Median (range) 224 ( ) 367 ( ) The data represent the total numbers of positive immunostained cells and are shown in mean SD The P values are based on Mann Whitney U test Fig. 4. The shockwave group showed signiwcantly higher numbers of neo-vessels and immuno positive cells including VEGF, enos, PCNA, and BMP-2 than the control (P < 0.05). Complications There was no systemic or local complication including wound infection. There was no device-related problem. Fig. 4 The immunohistochemical stains showed signiwcantly higher numbers of neo-vessels (vwf) and VEGF, enos, PCNA and BMP-2 in the shockwave group than the control group
5 Discussion The exact mechanism of shockwave in bone healing remains unknown. It was speculated that shockwave produced micro-fracture that in turn caused hematoma formation and subsequent callus formation and eventual fracture healing [8]. However, there were insuycient data to scientiwcally substantiate the theory. The results of the current study demonstrated that ESWT signiwcantly promotes bone healing after fracture. Many studies investigated the evects of ESWT in bone healing from diverent elements of experiment including histological examination [2, 6, 7, 15], biomechanical study [22], and molecular biology [1, 16, 18 20, 23]. However, most studies are fragmented and the experiments are focused on single element. Some studies reported that shockwave promoted bone healing primarily by increased cortical bone formation [7, 15]. Other study demonstrated a dose-dependent enhancement of bone mass and bone strength with shockwave treatment [22]. The results of the current study showed that shockwave promoted more cortical bone formation and better bone strength. Some authors demonstrated that shockwave enhanced pertussis toxin-sensitive bone formation in segmental defect in rats [1]. Others showed that physical shockwaves mediated membrane hyperpolarization and Ras activation for osteogenesis in human bone marrow stromal cells [16], and superoxide mediated shockwave induction of ERKdependent osteogenic transcription factor (CBFA 1) and mesenchymal cell diverentiation toward osteoprogenitors [18, 19, 23]. Another study showed that temporal and spatial expressions of bone morphogenetic protein in extracorporeal shockwave-promoted healing of segmental defect [21]. The results of the current study demonstrated that ESWT-promoted bone healing was associated with increased numbers of neo-vessels and angiogenic and osteogenic growth factors including VEGF, enos, PCNA, and BMP-2. In conclusion, the current study systemically analyzed the biological evects of ESWT in bone healing. ESWT signiwcantly promoted the formation of cortical bone, what might have been associated with increased biomechanical results after fracture in rabbits. Shockwave-promoted bone healing was associated with increases in neovascularization and angiogenic and osteogenic growth factors. It appears that the working mechanism of ESWT in bone healing may be linked to the biological evects as demonstrated in this study. Acknowledgments Funds were received in total or partial support of the research or clinical study presented in this article. The funding sources were National Health Research Institute (NHRI-EX EP) and Chang Gung Research Fund (CMRPG8049). The authors thank Ms Yi-Chih Sun, Ya-Ju Yang and Ya-Hsueh Chuang for their technical assistance in animal experiments and data collection in this study. No benewts in any form have been received or will be received from any commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. References 1. Chen YJ, Kuo YR, Yang KD, Wang CJ, Huang HC, Wang FS (2003) Shock wave application enhances pertussis toxin-sensitive bone formation in segmental defect in rats. J Bone Miner Res 18: Delius M, Draenert K, Al Diek Y, Draenert Y (1995) Biological evect of shockwave: in vivo evect of high-energy pulses on rabbit bone. Ultrasound Med Biol 21: Haupt G (1997) Use of extracorporeal shock wave in the treatment of pseudoarthrosis, tendinopathy and other orthopaedic disease. J Urol 158: Haupt G, Haupt A, Ekkernkamp A, Gerety B, Chvapil M (1992) InXuence of shockwave on fracture healing. Urology 39: Jamsa T, Jalovaara P, Peng Z, Vaananen HK, Tuukkanen J (1998) Comparison of three-point bending test and peripheral quantitative computed tomography analysis in the evaluation of the strength in mouse femur and tibia. Bone 23: Johannes EJ, Kaulesar Sukul DM, Matura E (1994) High-energy shockwave for treatment of nonunion. An experiment on dogs. J Surg Res 57: Kaulesar Sukul DM, Johannes EJ, Pierik EG, van Eijck GJ, Kristelijn MJ (1993) The evect of high-energy shock waves focused on cortical bone: an in vitro study. J Surg Res 54: Ogden JA, Tóth-Kischkat A, Schultheiss R (2001) Principles of shock wave therapy. Clin Orthop 387: Rompe JD, Rosendahl T, Schöllner C, Theis C (2001) High-energy extracorporeal shock wave treatment of nonunions. Clin Orthop 387: Schaden W, Fischer A, Sailer A (2001) Extracorporeal shock wave therapy of nonunion or delayed osseous union. Clin Orthop 387: Schleberger R, Senge T (1992) Noninvasive treatment of long bone pseudoarthrosis by shock waves (ESWL). Arch Ortho Trauma Surg 111: Valchanou VD, Michailov P (1991) High energy shock waves in the treatment of delayed and nonunion of fractures. Int Orthop 15: Vogel J, Hopf C, Eysel P, Rompe JD (1997) Application of extracorporeal shock waves in the treatment of pseudarthrosis of the lower extremity: preliminary results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 116: Wang CJ, Chen HS, Chen CE, Yang KD (2001) Treatment of nonunions of long bone fractures with shock waves. Clin Orthop 387: Wang CJ, Huang HY, Chen HH, Pai CH, Yang KD (2001) The evect of shock wave therapy on acute fractures of the tibia. A study in a dog model. Clin Orthop 387: Wang FS, Wang CJ, Huang HC, Chung H, Chen RF, Yang KD (2001) Physical shock wave mediates membrane hyperpolarization and Ras activation for osteogenesis in human bone marrow stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 287: Wang CJ, Huang HY, Pai CH (2002) Shock wave enhanced neovascularization at the bone-tendon junction. A study in a dog model. J Foot Ankle Surg 41: Wang FS, Wang CJ, Sheen-Chen SM, Chen RF, Kuo YR, Yang KD (2002) Superoxide mediates shock wave induction of ERKdependent osteogenic transcription factor (CBFA1) and mesenchymal cells diverentiation toward osteoprogenitors. J Biol Chem 277:
6 19. Wang FS, Yang KD, Chen RF, Wang CJ, Sheen-Chen SM (2002) Extracorporeal shock wave promotes growth and diverentiation of bone-marrow stromal cells towards osteoprogenitors associated with induction of TGF-beta1. J Bone Joint Surg 84B: Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD, Huang CS, Hsu CC (2003) Shockwave therapy induced neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction. A study in rabbits. J Orthop Res 21: Wang FS, Yang KD, Kuo YR, Wang CJ, Huang HJ, Chen YJ (2003) Temporal and spatial expression of bone morphogenetic proteins in extracorporeal shock wave-promoted healing of fracture defect. Bone 32: Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD (2004) Shock wave treatment produced dose-dependent enhancement in bone mass and bone strength after fracture. Bone 34: Yang C, Heston WDW, Gulati S, Fair WR (1988) The evects of high-energy shock waves (HESW) on human bone marrow. Urol Res 16:
INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY - ISMST NEWSLETTER
 WANG, Ching-Jen; YANG, Kuender D. - Biological mechanism of musculoskeletal shockwaves. ISMST Newsletter [Em linha]. 1:1 (2006) 5 11. [Consult. 6 jan. 2015]. Disponível na Internet:
WANG, Ching-Jen; YANG, Kuender D. - Biological mechanism of musculoskeletal shockwaves. ISMST Newsletter [Em linha]. 1:1 (2006) 5 11. [Consult. 6 jan. 2015]. Disponível na Internet:
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders Abstract Keywords:
 J Orthop Surg Res. 2012; 7: 11. Published online 2012 Mar 20. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders Ching-Jen Wang1 Author information Article notes Copyright and License information
J Orthop Surg Res. 2012; 7: 11. Published online 2012 Mar 20. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders Ching-Jen Wang1 Author information Article notes Copyright and License information
ESWT Mechanisms of Action in Veterinary Applications
 ESWT Mechanisms of Action in Veterinary Applications Extracorporeal Shock Wave Technology (ESWT) is a high energy acoustic pressure wave technology that has been demonstrated to treat a variety of musculoskeletal
ESWT Mechanisms of Action in Veterinary Applications Extracorporeal Shock Wave Technology (ESWT) is a high energy acoustic pressure wave technology that has been demonstrated to treat a variety of musculoskeletal
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows a number of treatment related chondroprotective effect in osteoarthritis of the knee in rats
 Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:44 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows a number of treatment related chondroprotective effect in osteoarthritis of the
Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:44 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows a number of treatment related chondroprotective effect in osteoarthritis of the
Shock wave therapy induces neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction A study in rabbits
 ELSEVIER Journal of Orthopaedic Research 21 (2003) 984-989 ~~~ Journal of Ort hopaedic Research www.ei3ebier comilocateiorthres Shock wave therapy induces neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction
ELSEVIER Journal of Orthopaedic Research 21 (2003) 984-989 ~~~ Journal of Ort hopaedic Research www.ei3ebier comilocateiorthres Shock wave therapy induces neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction
Shock waves are high-energy acoustic waves generated under water with high voltage
 Review Article 220 An Overview of Shock Wave Therapy in Musculoskeletal Disorders Ching-Jen Wang, MD Shock waves are high-energy acoustic waves generated under water with high voltage explosion and vaporization.
Review Article 220 An Overview of Shock Wave Therapy in Musculoskeletal Disorders Ching-Jen Wang, MD Shock waves are high-energy acoustic waves generated under water with high voltage explosion and vaporization.
orthopace Noninvasive Regenerative Medicine for Musculoskeletal Conditions
 orthopace Noninvasive Regenerative Medicine for Musculoskeletal Conditions SANUWAVE Health, Inc. is a regenerative medicine company focused on the development and commercialization of noninvasive, biological
orthopace Noninvasive Regenerative Medicine for Musculoskeletal Conditions SANUWAVE Health, Inc. is a regenerative medicine company focused on the development and commercialization of noninvasive, biological
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) Jeff Blea, DVM Von Bluecher, Blea, Hunkin, Inc. Equine Medicine and Surgery Sierra Madre, CA
 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) Jeff Blea, DVM Von Bluecher, Blea, Hunkin, Inc. Equine Medicine and Surgery Sierra Madre, CA History Shock waves used in human medicine as early as 1980s: Break
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) Jeff Blea, DVM Von Bluecher, Blea, Hunkin, Inc. Equine Medicine and Surgery Sierra Madre, CA History Shock waves used in human medicine as early as 1980s: Break
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Resistant Stress Fracture in Athletes
 AJSM PreView, published on February 9, 2007 as doi:10.1177/0363546506297540 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Resistant Stress Fracture in Athletes A Report of 5 Cases Masanori Taki,* MD, Osamu Iwata,
AJSM PreView, published on February 9, 2007 as doi:10.1177/0363546506297540 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Resistant Stress Fracture in Athletes A Report of 5 Cases Masanori Taki,* MD, Osamu Iwata,
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Fracture Nonunions
 An Original Study Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Fracture Nonunions Maria Chiara Vulpiani, MD, Mario Vetrano, MD, Federica Conforti, MD, Lucia Minutolo, MD, Donatella Trischitta, MD, John
An Original Study Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Fracture Nonunions Maria Chiara Vulpiani, MD, Mario Vetrano, MD, Federica Conforti, MD, Lucia Minutolo, MD, Donatella Trischitta, MD, John
The Mechanical Properties Of Fixing Greater Trochanter Or Lesser Trochanter In Complex Four Part Intertrochanteric Fractures
 The Mechanical Properties Of Fixing Greater Trochanter Or Lesser Trochanter In Complex Four Part Intertrochanteric Fractures Chih-Hui Chen 1, Kui-Chou Huang 2, Cheng-Kung Cheng, PhD 3, Hung-Chan Kao 4.
The Mechanical Properties Of Fixing Greater Trochanter Or Lesser Trochanter In Complex Four Part Intertrochanteric Fractures Chih-Hui Chen 1, Kui-Chou Huang 2, Cheng-Kung Cheng, PhD 3, Hung-Chan Kao 4.
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS
 BACKGROUND EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS REVIEW OF THE MEDICAL LITERATURE FOR EFFICACY, SAFETY, AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS Low energy ESWT is a byproduct
BACKGROUND EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS REVIEW OF THE MEDICAL LITERATURE FOR EFFICACY, SAFETY, AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS Low energy ESWT is a byproduct
E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy. Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science
 E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science Objectives Following completion of this lecture the student will be able to: Describe the mechanical characteristics
E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science Objectives Following completion of this lecture the student will be able to: Describe the mechanical characteristics
Cellular and molecular basis for shock wave application to the musculo-skeletal system
 Cellular and molecular basis for shock wave application to the musculo-skeletal system Dr. Christoph Schmitz, MD Dept. Psychiat. Neuropsychol., Div. Cell. Neurosci. Maastricht University Maastricht The
Cellular and molecular basis for shock wave application to the musculo-skeletal system Dr. Christoph Schmitz, MD Dept. Psychiat. Neuropsychol., Div. Cell. Neurosci. Maastricht University Maastricht The
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT. Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad
 Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad Osteonecrosis(ON) of the knee SPONK- Spontaneous ON of the knee Secondary ON of the knee Postarthrosopic ON of the
Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad Osteonecrosis(ON) of the knee SPONK- Spontaneous ON of the knee Secondary ON of the knee Postarthrosopic ON of the
CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO :
 CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Name : XXXX Age : 53yr Sex : Female Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO : 201518441 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : - Pain in the right knee since
CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Name : XXXX Age : 53yr Sex : Female Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO : 201518441 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : - Pain in the right knee since
Knee spanning solutions
 Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis. American University of Beirut Medical Center
 Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis Nagham HADDAD, PT Nagham HADDAD, PT American University of Beirut Medical Center Introduction: Tendinosis is the
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis Nagham HADDAD, PT Nagham HADDAD, PT American University of Beirut Medical Center Introduction: Tendinosis is the
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4
 Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Kevin Jones Medical Services Director
 Kevin Jones Medical Services Director MSK 2016 Extra Corporeal Shockwave Therapy Shock! Some Examples Of A Shockwave Atomic Bomb John Non Neumann 1945 Mathematician. Invented the WWII 1945 Atomic Bomb
Kevin Jones Medical Services Director MSK 2016 Extra Corporeal Shockwave Therapy Shock! Some Examples Of A Shockwave Atomic Bomb John Non Neumann 1945 Mathematician. Invented the WWII 1945 Atomic Bomb
Patient Guide. Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening
 Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
US Patent No. 6,309,396B1. G. David Ritland, M.D.
 US Patent No. 6,309,396B1 G. David Ritland, M.D. The Femur Finder is designed to direct the guide wire into the medullary canal. Do not use it to manipulate the fracture fragments, reduce the fracture,
US Patent No. 6,309,396B1 G. David Ritland, M.D. The Femur Finder is designed to direct the guide wire into the medullary canal. Do not use it to manipulate the fracture fragments, reduce the fracture,
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis
 Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
H.P. Teng, Y.J. Chou, L.C. Lin, and C.Y. Wong Under general or spinal anesthesia, the knee was flexed gently. In the cases of limited ROM, gentle and
 THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows regeneration in hip necrosis
 Rheumatology 2008;47:542 546 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken020 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows regeneration in hip necrosis C.-J. Wang 1, F.-S. Wang 2, J.-Y. Ko 1, H.-Y. Huang 3, C.-J. Chen 4, Y.-C.
Rheumatology 2008;47:542 546 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken020 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows regeneration in hip necrosis C.-J. Wang 1, F.-S. Wang 2, J.-Y. Ko 1, H.-Y. Huang 3, C.-J. Chen 4, Y.-C.
Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing and Dynamic Hip Screw in Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur *
 Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
AcUMEDr. LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary
 SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
A Locking IM Rod that won't back out. Simple and straight to the point! SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 A Locking IM Rod that won't back out. Simple and straight to the point! SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The SLIM (Simple Locking IntraMedullary) System is a new generation of pediatric orthopedic nails specifically
A Locking IM Rod that won't back out. Simple and straight to the point! SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The SLIM (Simple Locking IntraMedullary) System is a new generation of pediatric orthopedic nails specifically
EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D.
 1 of 5 7/8/2005 1:47 PM EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Abstract: Chronic proximal plantar fasciitis is an extremely common
1 of 5 7/8/2005 1:47 PM EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Abstract: Chronic proximal plantar fasciitis is an extremely common
Orthospec. ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy
 Orthospec ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy TM There are many things in life that seemed impossible to us. For example walking on the moon; or getting from London to Paris in just an hour; or talking
Orthospec ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy TM There are many things in life that seemed impossible to us. For example walking on the moon; or getting from London to Paris in just an hour; or talking
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points. Christopher Iobst, MD
 Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature
 Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT)
 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Gladys L.Y. Cheing, PhD 1 Hua Chang, MSc 2 Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is an emerging treatment modality for managing pain caused by various musculoskeletal
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Gladys L.Y. Cheing, PhD 1 Hua Chang, MSc 2 Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is an emerging treatment modality for managing pain caused by various musculoskeletal
Microstructural changes in the bone tissue and in the bone callus of diabetic rats with and without insulin treatment
 Microstructural changes in the bone tissue and in the bone callus of diabetic rats with and without insulin treatment A. Zamarioli 1, M.S. Campos 1, A. Guimarães 1, M. Butezloff 1, G.B. Leoni 2, M.D. Sousa-Neto
Microstructural changes in the bone tissue and in the bone callus of diabetic rats with and without insulin treatment A. Zamarioli 1, M.S. Campos 1, A. Guimarães 1, M. Butezloff 1, G.B. Leoni 2, M.D. Sousa-Neto
Fracture and Dislocation of Metacarpal Bones, Metacarpophalangeal Joints, Phalanges, and Interphalangeal Joints ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
Resurfacing Distal Femur. Orthopaedic Salvage System
 Resurfacing Distal Femur Orthopaedic Salvage System Primary Arthroplasty OSS 3cm Resurfacing Distal Femur Distal Femoral Resection Drill and ream the distal femur in the following sequence: (Figure 1)
Resurfacing Distal Femur Orthopaedic Salvage System Primary Arthroplasty OSS 3cm Resurfacing Distal Femur Distal Femoral Resection Drill and ream the distal femur in the following sequence: (Figure 1)
Promoting Fracture Healing Through Systemic or Local Administration of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Promoting Fracture Healing Through Systemic or Local Administration of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Gang Li Dept. of Orthopaedics and Traumatology School of Biomedical Sciences, The Chinese University
Promoting Fracture Healing Through Systemic or Local Administration of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Gang Li Dept. of Orthopaedics and Traumatology School of Biomedical Sciences, The Chinese University
Editorial Editor s Note
 MC 540/05 03-2006-ACX-05-BR-540-PB Chief Editor Paulo Roberto Dias dos Santos, MD (Brazil) - prds@uol.com.br Associate Editor Ching-Jen Wang, MD (Taiwan) w281211@adm.cgmh.org.tw Editorial Board Ana Claudia
MC 540/05 03-2006-ACX-05-BR-540-PB Chief Editor Paulo Roberto Dias dos Santos, MD (Brazil) - prds@uol.com.br Associate Editor Ching-Jen Wang, MD (Taiwan) w281211@adm.cgmh.org.tw Editorial Board Ana Claudia
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
THE NANCY NAIL. The End Caps ADVANTAGES OF NANCY NAIL
 NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
Tobacco and Bone Health
 Tobacco and Bone Health Prof. Dr. Alok Chandra Agrawal MS Orthopaedics, DNB Orthopaedics, PhD Orthopaedics MAMS All India Institute of Medical Sciences Raipur CG Cigarette smoking is commonly identified
Tobacco and Bone Health Prof. Dr. Alok Chandra Agrawal MS Orthopaedics, DNB Orthopaedics, PhD Orthopaedics MAMS All India Institute of Medical Sciences Raipur CG Cigarette smoking is commonly identified
Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic calcific rotator cuff tendonitis.
 Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic calcific rotator cuff tendonitis. From the Brisbane Hand & Upper Limb Clinic, Arnold Janssen Centre, Brisbane Private Hospital, 259 Wickham Terrace, Brisbane,
Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic calcific rotator cuff tendonitis. From the Brisbane Hand & Upper Limb Clinic, Arnold Janssen Centre, Brisbane Private Hospital, 259 Wickham Terrace, Brisbane,
Clover Staple. Surgical Technique
 Clover Staple Surgical Technique Contents Product The BioPro Clover Staple is a permanent implant that removes minimal cross-sectional fusion area, allows easy radiographical monitoring and may permit
Clover Staple Surgical Technique Contents Product The BioPro Clover Staple is a permanent implant that removes minimal cross-sectional fusion area, allows easy radiographical monitoring and may permit
Fractures Healing & Management. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4
 Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Surgical Technique. Customer Service:
 Patent and Patent Pending CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Axis Charcot Fixation System in diameters of 5.5, 6.5 and 7.5mm
Patent and Patent Pending CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Axis Charcot Fixation System in diameters of 5.5, 6.5 and 7.5mm
Neurologic Damage. The most common neurologic injury following intramedullary tibial nailing is injury to the peroneal nerve.
 COMPLICATIONS Knee Pain Anterior knee pain was present in 55% Affects younger more than older patients A significant number of the patients with anterior knee pain had pain with kneeling [90%] They also
COMPLICATIONS Knee Pain Anterior knee pain was present in 55% Affects younger more than older patients A significant number of the patients with anterior knee pain had pain with kneeling [90%] They also
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT
 EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
NeoGen Femoral Nail System
 NeoGen Femoral Nail System LESS IS MORE TE-2070-04 Surgical Technique BLE OF CONTENT Preface Standard Femoral Mode Recon Mode Post-Operative Management Appendix Products Information Indication Patient
NeoGen Femoral Nail System LESS IS MORE TE-2070-04 Surgical Technique BLE OF CONTENT Preface Standard Femoral Mode Recon Mode Post-Operative Management Appendix Products Information Indication Patient
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM 90-SRK-700000 B.0 0 Contents 1. Implant Sizing 2. Surgical Technique a. Incision and Exposure b. Distal Femoral Resection c. Tibial Resection d. Femoral
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM 90-SRK-700000 B.0 0 Contents 1. Implant Sizing 2. Surgical Technique a. Incision and Exposure b. Distal Femoral Resection c. Tibial Resection d. Femoral
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Practical Reduction Techniques: Diaphyseal Reduction. Philip Wolinsky University of California at Davis Medical Center
 OTA Specialty Day 2016 Practical Reduction Techniques: Diaphyseal Reduction Philip Wolinsky University of California at Davis Medical Center 8:55 am 9:55 am Tips and Tricks: Practical Reduction Techniques
OTA Specialty Day 2016 Practical Reduction Techniques: Diaphyseal Reduction Philip Wolinsky University of California at Davis Medical Center 8:55 am 9:55 am Tips and Tricks: Practical Reduction Techniques
TTA-Rapid Protocol. i. Where possible, calibrate the radiograph on the screen to real size.
 Legeweg 157 i 8020 Oostkamp Tel: 050/31.18.76 Fax: 050/31.58.86 www.instrulife.be TTA-Rapid Protocol The dog is placed in a dorsal recumbency with the affected limb suspended from a stand. Make sure that
Legeweg 157 i 8020 Oostkamp Tel: 050/31.18.76 Fax: 050/31.58.86 www.instrulife.be TTA-Rapid Protocol The dog is placed in a dorsal recumbency with the affected limb suspended from a stand. Make sure that
Large Distractor Femur
 Fracture Reduction and Provisional Stabilization Large Distractor Femur Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Standard Femoral Distraction 2 Large Distractor System 4 Surgical Technique Prepare
Fracture Reduction and Provisional Stabilization Large Distractor Femur Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Standard Femoral Distraction 2 Large Distractor System 4 Surgical Technique Prepare
TTA Rapid with Patellar Luxation
 TTA Rapid with Patellar Luxation The dog is placed in a dorsal recumbency with the affected limb suspended from a stand. Make sure that the dog s paws are not fixed too tightly, since the affected limb
TTA Rapid with Patellar Luxation The dog is placed in a dorsal recumbency with the affected limb suspended from a stand. Make sure that the dog s paws are not fixed too tightly, since the affected limb
IMPLANT REMOVAL: AN UNSOLVED CHALLENGE TO ORTHOPAEDICIAN Varunjikar M. D 1, S. C. Joshi 2, Bejoy E Jayan 3, A. M. Varunjikar 4, C. R.
 IMPLANT REMOVAL: AN UNSOLVED CHALLENGE TO ORTHOPAEDICIAN Varunjikar M. D 1, S. C. Joshi 2, Bejoy E Jayan 3, A. M. Varunjikar 4, C. R. Joshi 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Varunjikar M. D, S. C. Joshi, Bejoy
IMPLANT REMOVAL: AN UNSOLVED CHALLENGE TO ORTHOPAEDICIAN Varunjikar M. D 1, S. C. Joshi 2, Bejoy E Jayan 3, A. M. Varunjikar 4, C. R. Joshi 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Varunjikar M. D, S. C. Joshi, Bejoy
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee): A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee):
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee):
Lapidus Arthrodesis System Instructions for Use
 Lapidus Arthrodesis System Instructions for Use Description The AlignMATE Lapidus Arthrodesis System consists of bone plates and bone screws (locking, non-locking and interfragmentary), which are intended
Lapidus Arthrodesis System Instructions for Use Description The AlignMATE Lapidus Arthrodesis System consists of bone plates and bone screws (locking, non-locking and interfragmentary), which are intended
Plate and Bone Stresses for Single- and Double-Plated Femoral Fractures. D.R. Carter and R. Vasu
 Plate and Bone Stresses for Single- and Double-Plated Femoral Fractures D.R. Carter and R. Vasu J. Biomech 14: 55-62, 1981 Loading Koch Conditions Intact Trans-cortical stress Composite Beam Representation
Plate and Bone Stresses for Single- and Double-Plated Femoral Fractures D.R. Carter and R. Vasu J. Biomech 14: 55-62, 1981 Loading Koch Conditions Intact Trans-cortical stress Composite Beam Representation
Clinical Evaluation Surgical Technique
 Clinical Evaluation Surgical Technique Table of Contents EMPERION Specifications 3 EMPERION Surgical Technique 9 EMPERION Catalog 18 Nota Bene: This technique description herein is made available to the
Clinical Evaluation Surgical Technique Table of Contents EMPERION Specifications 3 EMPERION Surgical Technique 9 EMPERION Catalog 18 Nota Bene: This technique description herein is made available to the
Titanium Distal Femoral Nail System
 For Retrograde Insertion Titanium Distal Femoral Nail System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Titanium Distal Femoral Nail System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Clinical Cases 6 Surgical
For Retrograde Insertion Titanium Distal Femoral Nail System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Titanium Distal Femoral Nail System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Clinical Cases 6 Surgical
The Effect of Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC) and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) during Distraction Osteogenesis of the Tibia
 The Effect of Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC) and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) during Distraction Osteogenesis of the Tibia Dong Hoon Lee, MD, Ph.D, Keun Jung Ryu MD Limb Lengthening and Deformity
The Effect of Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC) and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) during Distraction Osteogenesis of the Tibia Dong Hoon Lee, MD, Ph.D, Keun Jung Ryu MD Limb Lengthening and Deformity
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE SKS Total Knee Replacement
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE SKS Total Knee Replacement Femoral preparation A40577 1 2 5 1: Alignment rod A30049 + A30124 2: Centromedullary rod A40224 4: T-handle A40232 6: Femoral measuring device A40411 + A40414
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE SKS Total Knee Replacement Femoral preparation A40577 1 2 5 1: Alignment rod A30049 + A30124 2: Centromedullary rod A40224 4: T-handle A40232 6: Femoral measuring device A40411 + A40414
Method & Sites for Intra-osseous Needle Insertion. Main Insertion Sites suggested for paediatric use are:
 Method & Sites for Intra-osseous Needle Insertion There are 8 potential sites for the insertion of an intraosseous needle using the EZ-IO device or standard intraosseous needle, these include proximal
Method & Sites for Intra-osseous Needle Insertion There are 8 potential sites for the insertion of an intraosseous needle using the EZ-IO device or standard intraosseous needle, these include proximal
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique
 PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique Surgical Technique Contour Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the healthcare professional to illustrate the
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique Surgical Technique Contour Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the healthcare professional to illustrate the
THE HUMERUS 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW
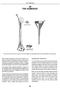 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
Shockwave Therapy. Also referred to as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
 Shockwave Therapy Also referred to as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy TensCare Shockwave Therapy Unit Introduction ESWT Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive therapy that uses acoustic waves
Shockwave Therapy Also referred to as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy TensCare Shockwave Therapy Unit Introduction ESWT Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive therapy that uses acoustic waves
2016 SIGN Conference: Treatment of Difficult Fractures Around The World
 2016 SIGN Conference: Treatment of Difficult Fractures Around The World September 21-24, 2016 Long Bone Osteosynthesis Failure DUONG BUNN Trauma-Orthopedique ward Preah Kossamak Preah Sihaknouk Ville Beach
2016 SIGN Conference: Treatment of Difficult Fractures Around The World September 21-24, 2016 Long Bone Osteosynthesis Failure DUONG BUNN Trauma-Orthopedique ward Preah Kossamak Preah Sihaknouk Ville Beach
Biologically-Assisted ACL Reconstruction. Surgical Technique
 Biologically-Assisted ACL Reconstruction Surgical Technique One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized care to one patient. The science and art
Biologically-Assisted ACL Reconstruction Surgical Technique One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized care to one patient. The science and art
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Bowed Femur Plate Surgical Technique
 PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Bowed Femur Plate Surgical Technique 2957 Bow Broch_REV_B.indd 1 2/10/11 12:47 PM Surgical Technique Bowed Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Bowed Femur Plate Surgical Technique 2957 Bow Broch_REV_B.indd 1 2/10/11 12:47 PM Surgical Technique Bowed Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the
Unlocked Nailing vs. Interlocking Nailing for Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fractures. Is there a Difference?
 Unlocked Nailing vs. Interlocking Nailing for Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fractures. Is there a Difference? CK Yu, MBBS (UM), HY Wong*, MD (UKM), AS Vivek, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To*, FRCS (Edin)
Unlocked Nailing vs. Interlocking Nailing for Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fractures. Is there a Difference? CK Yu, MBBS (UM), HY Wong*, MD (UKM), AS Vivek, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To*, FRCS (Edin)
Efficacy of a Kirschner-Wire Guide in Distal Linear Metatarsal Osteotomy for Correction of Hallux Valgus
 Efficacy of a Kirschner-Wire Guide in Distal Linear Metatarsal Osteotomy for Correction of Hallux Valgus Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka University Takefumi Nishino MD,
Efficacy of a Kirschner-Wire Guide in Distal Linear Metatarsal Osteotomy for Correction of Hallux Valgus Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka University Takefumi Nishino MD,
Case Study: David. Conditions Treated Femoral Neck Fracture with Avascular Necrosis of the Hip. Age Range During Treatment 16 Years
 Case Study: David Conditions Treated Femoral Neck Fracture with Avascular Necrosis of the Hip Age Range During Treatment 16 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of
Case Study: David Conditions Treated Femoral Neck Fracture with Avascular Necrosis of the Hip Age Range During Treatment 16 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of
SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
 Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
Repair of large segmental bone defects in rabbits using BMP and FGF composite xenogeneic bone
 Repair of large segmental bone defects in rabbits using BMP and FGF composite xenogeneic bone X. Li 1 *, Z. Lin 2 *, Y. Duan 2, X. Shu 2, A. Jin 2, S. Min 2 and W. Yi 1 1 Department of Spinal Surgery,
Repair of large segmental bone defects in rabbits using BMP and FGF composite xenogeneic bone X. Li 1 *, Z. Lin 2 *, Y. Duan 2, X. Shu 2, A. Jin 2, S. Min 2 and W. Yi 1 1 Department of Spinal Surgery,
Principles of intramedullary nailing. Management for ORP
 Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Technique Guide Small Bone Fusion System
 Technique Guide Small Bone Fusion System The Pinit Plate Small Bone Fusion System is a super low profile, modular bone plate and screw system designed to stabilize a bunionectomy with a medial to lateral
Technique Guide Small Bone Fusion System The Pinit Plate Small Bone Fusion System is a super low profile, modular bone plate and screw system designed to stabilize a bunionectomy with a medial to lateral
Surgical Technique. Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90
 Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
InternationalJournalofAgricultural
 www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.2,May2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc &
www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.2,May2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc &
Knee Surgical Technique
 Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
Surgical Technique Final Trial Reduction and Component Implantation of
 Surgical Technique Final Trial Reduction and Component Implantation of TC *smith&nephew TC-PLUS PRIMARY Mobile Bearing TC-PLUS PRIMARY Mobile Bearing Final Trial Reduction and Component Implantation of
Surgical Technique Final Trial Reduction and Component Implantation of TC *smith&nephew TC-PLUS PRIMARY Mobile Bearing TC-PLUS PRIMARY Mobile Bearing Final Trial Reduction and Component Implantation of
Evaluation of the functional outcome in open tibial fractures managed with an Ilizarov fixator as a primary and definitive treatment modality
 2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
LCP Distal Tibia Plate
 Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
