Updated Version of GTR9-1-07r1. March 28-29, 2012 Japan Automobile Standards Internationalization Center (JASIC) 1
|
|
|
- Zoe Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Informal Group on GTR9 Phase2 (IG GTR9-PH2) 2 nd Meeting Technical Discussion Benefit Updated Version of GTR9-1-07r1 March 28-29, 2012 Japan Automobile Standards Internationalization Center (JASIC) 1
2 Outline 1. Anticipated Factors for Enhanced Injury Mitigation 2. Estimation of Reduction due to Tibia Fracture Mitigation 3. Summary 2
3 1. Anticipated Factors for Enhanced Component Level Injury Mitigation - Improved Biofidelity - Tibia 4. Comparison of Component Responses Moment (Nm) Flex-GT (test 1) Flex-GT (test 2) PMHS Corridor (upper) PMHS Corridor (lower) TRL(calculated value) - Tibia Bending - TEG Flex-GT (test 1) Flex-GT (test 2) 550 PMHS Corridor (upper) 500 PMHS Corridor (lower) TRL (from corridor) 450 Knee GTR9-1-07r1 4. Comparison of Component Responses - Knee Bending - Moment (Nm) TEG Deflection (mm) Flex-PLI tibia response characteristics are much closer to those of human compared to TRL legform Tibia Knee angle (deg.) Flex-PLI knee joint is stiffer than that of human Flex-PLI stiffness is much more comparable to human stiffness than TRL legform Knee (ACL) Assembly Level 5. Correlation of Assembly Impact Responses el /s 2 ) TRL Legform Mode Upper Tibia Accel. (m/ CAE Correlation Study - Correlation of Tibia Injury Measures TRL Legform Flex-PLI y = x R = Human Model Tibia Bending Moment (Nm) Konosu et al. (2009) (Nm) Flex-PLI Model Tibia Bending Moment TEG-096 (Flex-PLI) y = 1.259x R = Human Model Tibia Bending Moment (Nm) No correlation between TRL legform upper tibia acceleration and human tibia bending moment Good correlation between Flex-PLI and human tibia bending moment Reference : Konosu, A. et al., Evaluation of the Validity of the Tibia Fracture Assessment Using the Upper Tibia Acceleration Employed in the TRL Legform Impactor, IRCOBI Conference (2009) 5. Correlation of Assembly Impact Responses - CAE Correlation Study - Correlation of ACL Injury Measures m) TRL Legform Model Knee Shear Displacement (mm TRL Legform y = x R = 0.13 Flex-PLI Model ACL Elongation (mm) Flex-PLI y = x R = Human Model ACL Elongation (mm) Human Model ACL Elongation (mm) No correlation between TRL legform knee shear displacement and human ACL elongation Good correlation between Flex-PLI and human ACL elongation
4 1. Anticipated Factors for Enhanced TRL Legform Injury Criterion Upper Tibia Acceleration Injury Mitigation - Enhanced Injury Assessment Capabilities - Knee center 64 mm Tibia Flex-PLI Injury Criteria Femur-3 BM Femur-2 BM Femur-1 BM 217 mm 137 mm 297 mm Upper end of tibia Individual Measurement Bending Angle Knee GTR9-1-07r1 Injury Criteria Femur-3 BM Femur-2 BM Femur-1 LCL MCL BM Knee-ACL PCL ACL EL Knee-PCL Disp. EL Shearing force Bending force + Knee-MCL EL Shear Tibia-1 BM 134 mm Tibia-1 BM No instrumentation Tibia-2 BM Tibia-3 BM Tibia-4 BM 214 mm 294 mm 374 mm Tibia-2 BM Tibia-3 BM Tibia-4 BM Combination BM: Bending Moment EL: Elongation Wider coverage of tibia fracture Use of bending moment that best describes human tibia fracture Flex-PLI ligaments elongate due to combined knee loading Use of ligament elongation provides better correlation with human injuries 4
5 1. Anticipated Factors for Enhanced Injury Mitigation - Otte et al. (2007) - GTR9-1-07r GIDAS data 143 pedestrians with leg fractures (tibia/fibula) documented by X-rays Reference: Otte, D., Haasper, C., Characteristics on Fractures of Tibia and Fibula in Car Impacts to Pedestrians Influences of Car Bumper Height and Shape, IRCOBI Conference (2007) 5
6 1. Anticipated Factors for Enhanced Injury Mitigation - Otte et al. (2007) - GTR9-1-07r1 Fracture location was identical to the bumper height only in 17.5 % of the cases 82.5% of fractures are presumed to be due to indirect loading Reference: Otte, D., Haasper, C., Characteristics on Fractures of Tibia and Fibula in Car Impacts to Pedestrians Influences of Car Bumper Height and Shape, IRCOBI Conference (2007) 6
7 1. Anticipated Factors for Enhanced Ankle/Foot Injury 6% Injury Mitigation - Japanese In-depth Accident Data (ITARDA) - Bumper Load Femur Fracture 8% Patella Fracture 2% Leg Fracture at Bumper 14% Knee Ligament Damage 6% Knee Bending Angle GTR9-1-07r1 TRL Legform Knee Shear Disp. Upper Tibia Accel. Bending Leg Fracture Away from Bumper 65% Knee Ligament Elongation Flex-PLI References: (1) FY2005 ITARDA Report : Investigation of Vehicle Safety Measures by Accident Reconstruction, ITARDA (2006) (in Japanese) (2) Otte et al., Characteristics on Fractures on Tibia and Fibula in Car Impacts to Pedestrians Influence of Car Bumper Height and Shape, IRCOBI (2007) Tibia Bending Moment Most significant improvement is with leg fracture mitigation 7 Tibia-1 Tibia-2 Tibia-3 Tibia-4
8 Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by MAIS Fatality Ratio by MAIS GTR9-1-07r1 - Estimated Reduction in Annual Medical (US, JPN) - MAIS Total PCDS, age > 15 with Tibia Fracture without Tibia Fracture Fatality MAIS Ratio 2 1.0% 3 5.3% % % % Reference : Goertz A., Accident Statistical Distributions from NAS CDS, SAE Paper # (2010) Percentage of Tibia Fracture by Injury Severity With Tibia Fracture (%) Without Tibia Fracture (%) Fatal 32.7% 67.3% Severe 22.6% 77.4% Minor 0.0% 100.0% 8
9 GTR9-1-07r1 - Estimated Reduction in Annual Medical (US, JPN) - Percentage of Tibia Fracture by Injury Severity With Tibia Fracture (%) Without Tibia Fracture (%) Fatal 32.7% 67.3% Severe 22.6% 77.4% Minor 0.0% 100.0% Annual Medical due to Tibia Fracture Country US $ 171,901,940 JPN $ 88,010,679 Pedestrians by Injury 16YO and older 0-15YO Severity US JPN US JPN Fatal Severe Minor US Fatal : FARS US Non-fatal : NASS-PCDS (Weighed) JPN : ITARDA Average Medical per Case Tibia count AIS Weighed For Tibia Fracture = $44,684 ($1 = \80) (coverage increase) (Protection Level) Annual Medical Reduction from Country US $ 99,273,370 JPN $ 50,826,167 9
10 - Overview of Estimation Procedure - Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by MAIS Percentage of Tibia Fracture by Pedestrians with Tibia Fracture by per Case In-depth accident data Multiply Fatality Ratio by MAIS Pedestrians by National accident statistics Annual due to Tibia Fracture Multiply Coverage Increase by Introducing FlexPLI Protection Level Annual Reduction from Annual Reduction from by Introducing FlexPLI 10
11 - Overview of Estimation Procedure - Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by MAIS Percentage of Tibia Fracture by Pedestrians with Tibia Fracture by per Case In-depth accident data Multiply Fatality Ratio by MAIS Pedestrians by National accident statistics Annual due to Tibia Fracture Multiply Coverage Increase by Introducing FlexPLI Protection Level Annual Reduction from Annual Reduction from by Introducing FlexPLI 11
12 - Estimation of Percentage of Tibia Fracture by - Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia FX by MAIS MAIS with Tibia FX 1 0 n 1 without Tibia FX FX: fracture Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia FX by with Tibia FX without Tibia FX MAIS Fatal Severe Minor Fatal Severe Minor 2 N 2 n n 1 3 N 3 n 3 2 N 2 xr 2 N 2 x(1-r 2 ) 0 n 2 xr 2 n 2 x(1-r 2 ) 0 4 N 4 n 4 5 N 5 n 5 3 N xr 3 3 N x(1-r ) n xr 3 3 n x(1-r ) N 6 n 6 4 N 4 xr 4 N 4 x(1-r 4 ) 0 n 4 xr 4 n 4 x(1-r 4 ) 0 5 N 5 xr 5 N 5 x(1-r 5 ) 0 n 5 xr 5 n 5 x(1-r 5 ) 0 Fatality Ratio 6 N 6 xr 6 N 6 x(1-r 6 ) 0 n 6 xr 6 n 6 x(1-r 6 ) 0 by MAIS MAIS Ratio SUM N f N s N m n f n s n m 1 R 1 2 R 2 3 R 3 4 R 4 5 R 5 6 R 6 Percentage of Tibia Fracture by with Tibia Fracture without Tibia Fracture Fatal N f /(N f + n f ) n f /(N f + n f ) Severe N s / (N s + n s ) n s / (N s + n s ) Minor N m / (N m + n m ) n m / (N m + n m ) 12
13 Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by MAIS MAIS total US (NASS-PCDS) JPN (ITARDA) US (NASS-PCDS) Numbers Numbers age>15 with Tibia FX without Tibia FX total with Tibia FX without Tibia FX Fatality Ratio by MAIS JPN (ITARDA) age>15, collision with passenger car or wagon FX: fracture Reference : Goertz A., Accident Statistical Distributions from NAS CDS, SAE Paper # (2010) MAIS Non-fatal Fatal Fatality Ratio Raw Weighted Raw Weighted Raw Weighted % 0.1%-> 0.0% % 1.0% % 5.3% % 22.5% % 47.6% % 99.0% 13
14 - Estimated Percentage of Tibia Fracture by - Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by MAIS US (NASS-PCDS) JPN (ITARDA) age > 15 with without with without MAIS Total Tibia Tibia Total Tibia Tibia Fracture Fracture Fracture Fracture Fatality Ratio by MAIS Fatality MAIS Ratio 2 1.0% 3 5.3% % % % Reference : Goertz A., Accident Statistical Distributions from NAS CDS, SAE Paper # (2010) Percentage of Tibia Fracture by US JPN Injury Severity With Tibia Fracture (%) Without Tibia Fracture (%) With Tibia Fracture (%) Without Tibia Fracture (%) Fatal 32.7% 67.3% 12.9% 87.1% Severe 22.6% 77.4% 19.4% 80.6% Minor 0.0% 100.0% 0.0% 100.0% 14
15 - Overview of Estimation Procedure - Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by MAIS Percentage of Tibia Fracture by Pedestrians with Tibia Fracture by per Case In-depth accident data Multiply Fatality Ratio by MAIS Pedestrians by National accident statistics Annual due to Tibia Fracture Multiply Coverage Increase by Introducing FlexPLI Protection Level Annual Reduction from Annual Reduction from by Introducing FlexPLI 15
16 US Injury Severity - Pedestrians by - 16 YO and older 0-15 YO Fatal was derived from FARS(2009) Fatal Severe Severe and Minor was Minor derived from NASS-GES (2009) NASS-GES data NASS-GES Variable: INJSEV 16 YO and older 0-15 YO Case Weighted case Case Weighted case No Injury (O) Possible Injury (C) Non-incapacitating Evident Injury (B) Number for Minor Injury Incapacitating Injury (A) Fatal Injury (K) Number for Severe Injury JPN Injury 16 YO and 0-15 YO All of Japanese data were derived from ITARDA (2009) Severity older Fatal: Died within 24 hours from accident Fatal Severe: Injury that requires 30 days or more for cure Severe Minor : injury that requires less than 30 days for cure Minor
17 - Overview of Estimation Procedure - Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by MAIS Percentage of Tibia Fracture by Pedestrians with Tibia Fracture by per Case In-depth accident data Multiply Fatality Ratio by MAIS Pedestrians by National accident statistics Annual due to Tibia Fracture Multiply Coverage Increase by Introducing FlexPLI Protection Level Annual Reduction from Annual Reduction from by Introducing FlexPLI 17
18 - Pedestrians with Tibia Fracture by - Percentage of Tibia Fracture by Pedestrians by With Tibia Without Tibia Injury Injury 16YO and older 0-15YO Fracture (%) Fracture (%) Severity Severity US JPN US JPN US JPN US JPN Fatal Fatal 32.7% 12.9% 67.3% 87.1% Severe Severe 22.6% 19.4% 77.4% 80.6% Minor Minor 0.0% 0.0% 100.0% 100.0% US Fatal : FARS US Non-fatal : NASS-GES (Weighed) JPN : ITARDA Pedestrians with Tibia Fracture by Injury 16YO and older 0-15YO Severity US JPN US JPN Fatal Severe Minor
19 - Overview of Estimation Procedure - Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by MAIS Percentage of Tibia Fracture by Pedestrians with Tibia Fracture by per Case In-depth accident data Multiply Fatality Ratio by MAIS Pedestrians by National accident statistics Annual due to Tibia Fracture Multiply Coverage Increase by Introducing FlexPLI Protection Level Annual Reduction from Annual Reduction from by Introducing FlexPLI 19
20 - per Case (US) - per case for MAIS 2 and 3 injuries 20
21 Injury Level - per Case (US) - per Case by MAIS (NHTSA,2002) Economic Human Property Company Public Agency Intangible Consequences Comprehensive MAIS 2 $47,964 $3,954 $1,953 $12,948 $91,137 $157,956 MAIS 3 $139,024 $6,799 $4,266 $36,009 $128,107 $314,205 Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by AIS (NASS-PCDS, age>15) MAIS count Weighted per Case Economic Human Property Company Public Agency Intangible Consequences Comprehensive $126,464 $6,407 $3,947 $32,828 $123,008 $292,654 21
22 Injury Level - per Case (JPN) - Unpublished data for average human cost by MAIS Based on Japanese insurance data Human cost only per Case by MAIS Exchange rate used : $1=107.4 Economic Human Property Company Public Agency Intangible Consequences Comprehensive MAIS 2 $16,760 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A MAIS 3 $38,175 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A fpedestrians ti Sustaining Tibia Fracture by AIS (NASS-PCDS, age>15) MAIS count Weighted per Case Economic Human Property Company Public Agency Intangible Consequences Comprehensive $24,650 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 22
23 Definition - per Case Comparison - Economic Human Property Company Medical Market Productivity Household Productivity Property Damage Workplace s Public Agency Emergency Services Insurance Administration Legal s Travel Delay Intangible Consequences QALYs Comprehensive Sum of Economic and Intangible Consequence US $126,464 $6,407 $3,947 $32,828 $123,008 $292,654 JPN $24,650 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A Breakdown of Human Medical Human Market Productivity Household Productivity US $42,237 $65,049 $19,178 JPN $24,650 QALY : Quality-Adjusted Life Years lost 23
24 - Overview of Estimation Procedure - Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by MAIS Percentage of Tibia Fracture by Pedestrians with Tibia Fracture by per Case In-depth accident data Multiply Fatality Ratio by MAIS Pedestrians by National accident statistics Annual due to Tibia Fracture Multiply Coverage Increase by Introducing FlexPLI Protection Level Annual Reduction from Annual Reduction from by Introducing FlexPLI 24
25 - Estimated Annual due to Tibia Fracture - Pedestrians with Tibia Fracture by Injury 16 YO and older Severity US JPN Fatal Severe Minor 0 0 Country per Case Economic Intangible Consequences Comprehensive US $169,646 $123,008 $292,654 JPN $24,650 N/A N/A JPN: Economic includes Human only Annual due to Tibia Fracture Country Economic Intangible Consequences Comprehensive US $652,628,162 $473,211,776 $1,125,839,938 JPN $36,555,950 N/A N/A JPN: Economic includes Human only 25
26 - Overview of Estimation Procedure - Pedestrians Sustaining Tibia Fracture by MAIS Percentage of Tibia Fracture by Pedestrians with Tibia Fracture by per Case In-depth accident data Multiply Fatality Ratio by MAIS Pedestrians by National accident statistics Annual due to Tibia Fracture Multiply Coverage Increase by Introducing FlexPLI Protection Level Annual Reduction from Annual Reduction from by Introducing FlexPLI 26
27 - Estimated Annual Reduction - Country Protection Level Annual due to Tibia Fracture Economic Intangible Consequences Comprehensive US $652,628,162 $473,211,776 $1,125,839,938 JPN $36,555,950 N/A N/A JPN: Economic includes Human only Coverage increase relative to TRL legform Otte et al. (2007) : Tibia fracture due to indirect loading = 82.5% Coverage Increase by Introducing FlexPLI 07 Protection Level by complying with injury 0.7 thresholds that correspond to 30% injury probability Annual Reduction from by Introducing FlexPLI Country Economic Intangible Comprehensive Consequences US $376,892, $273,279, $650,172, JPN $21,111,061 N/A N/A JPN: Economic includes Human only 27
28 - Comparison with Previous Results - JPN Previous per Case # Ped Ann. w/tib Human Property Company Public Intangible Total Fx Tib Fx $44,684 N/A N/A N/A N/A $44, $88M Coeff *0.7 JPN $24,650 N/A N/A N/A N/A $24, $37M Current *0.7 US Previous US Current $44,684 Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included $44, $172M $126,464 $6,407 $3,947 $32,828 $123,008 $292, $1,126M * *0.7 Benefit $51M $21M $99M $650M 28
29 3. Summary The Flex-PLI provides improved biofidelity of the tibia and knee at both assembly and component levels Accident data show that tibia fracture is most frequent in pedestrian severe (AIS 2+) injuries Most significant factor that would contribute to injury mitigation is enhanced biofidelity of the tibia and much wider coverage of injury measurements over the tibia Additional annual cost reduction due to tibia fracture mitigation by introducing the Flex-PLI was estimated to be approximately $377M of Economic and $650M of Comprehensive in the US, relative to the use of TRL legform Japan data could not be processed in the same way as performed with the US data due to the lack of information may require further study 29
30 References Otte, D., Haasper, C., Characteristics on Fractures of Tibia and Fibula in Car Impacts to Pedestrians Influences of Car Bumper Height and Shape, IRCOBI Conference (2007) FY2005 ITARDA Report : Investigation of Vehicle Safety Measures by Accident Reconstruction, ITARDA (2006) (in Japanese) Goertz A., Accident Statistical Distributions from NAS CDS, 2010 SAE World Congress, SAE Paper Number (2010) NHTSA, The Economic Impact of Motor Vehicle Crashes 2000, DOT HS (2002) 30
31 Thank you for your attention 31
Re-examination examination of Number of Pedestrians by Injury Severity
 Informal Group on GTR9 Phase2 (IG GTR9-PH2) 2 nd Meeting Re-examination examination of Number of Pedestrians by Severity March 29, 2012 Japan Automobile Standards Internationalization Center (JASIC) 1
Informal Group on GTR9 Phase2 (IG GTR9-PH2) 2 nd Meeting Re-examination examination of Number of Pedestrians by Severity March 29, 2012 Japan Automobile Standards Internationalization Center (JASIC) 1
FlexPLI vs. EEVC LFI Correlation
 FlexPLI vs. EEVC LFI Correlation Action List Item 1. j) Evaluate and decide on performance / injury criteria and threshold values 5 th IG GTR9-PH2 Meeting 6-7/December/212 Japan Automobile Standards Internationalization
FlexPLI vs. EEVC LFI Correlation Action List Item 1. j) Evaluate and decide on performance / injury criteria and threshold values 5 th IG GTR9-PH2 Meeting 6-7/December/212 Japan Automobile Standards Internationalization
Flex-GTR: Open questions and proposals for ACL, PCL and MCL injury thresholds
 Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen (Federal Highway Research Institute) TEG-078 Flex-GTR: Open questions and proposals for ACL, PCL and MCL injury thresholds 7th Meeting of the GRSP Flex PLI Technical Evaluation
Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen (Federal Highway Research Institute) TEG-078 Flex-GTR: Open questions and proposals for ACL, PCL and MCL injury thresholds 7th Meeting of the GRSP Flex PLI Technical Evaluation
NHTSA Evaluation of the Flex-GTR Legform on US Vehicles
 NHTSA Evaluation of the Flex-GTR Legform on US Vehicles Brian Suntay & Ann Mallory Transportation Research Center Inc. Jason Stammen NHTSA Vehicle Research and Test Center 1 This is a work of the U.S.
NHTSA Evaluation of the Flex-GTR Legform on US Vehicles Brian Suntay & Ann Mallory Transportation Research Center Inc. Jason Stammen NHTSA Vehicle Research and Test Center 1 This is a work of the U.S.
Flexible Pedestrian Legform Impactor Type GT (FLEX-GT) Car Test Results JAMA
 TEG- 2 April 27 4 th Flex-TEG MT BASt, Bergisch Gladbach Flexible Pedestrian Legform Impactor Type GT (FLEX-GT) Car Test Results JAMA Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association, Inc. Flex-GT Information
TEG- 2 April 27 4 th Flex-TEG MT BASt, Bergisch Gladbach Flexible Pedestrian Legform Impactor Type GT (FLEX-GT) Car Test Results JAMA Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association, Inc. Flex-GT Information
History of Development of the Flexible Pedestrian Legform Impactor (Flex-PLI)
 GTR9-C-04 History of Development of the Flexible Pedestrian Legform Impactor (Flex-PLI) November 3 rd, 2011 Japan 1 Contents 1. Back ground 2. History of Flex-PLI Development (Overview) 2 1. Back ground
GTR9-C-04 History of Development of the Flexible Pedestrian Legform Impactor (Flex-PLI) November 3 rd, 2011 Japan 1 Contents 1. Back ground 2. History of Flex-PLI Development (Overview) 2 1. Back ground
Validation of Pedestrian Lower Limb Injury Assessment using Subsystem Impactors
 Validation of Pedestrian Lower Limb Injury Assessment using Subsystem Impactors Yukou Takahashi Miwako Ikeda Iwao Imaizumi Yuji Kikuchi Satoru Takeishi Honda R&D Co., Ltd. 212 IRCOBI Conference September
Validation of Pedestrian Lower Limb Injury Assessment using Subsystem Impactors Yukou Takahashi Miwako Ikeda Iwao Imaizumi Yuji Kikuchi Satoru Takeishi Honda R&D Co., Ltd. 212 IRCOBI Conference September
Flex-GTR: Proposal for ACL/PCL injury threshold
 Flex-GTR: for ACL/PCL injury threshold 11th Meeting of the GRSP Flex PLI Technical Evaluation Group Bergisch Gladbach, April 21 st, 2010 Oliver Zander Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen
Flex-GTR: for ACL/PCL injury threshold 11th Meeting of the GRSP Flex PLI Technical Evaluation Group Bergisch Gladbach, April 21 st, 2010 Oliver Zander Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen
Information on the Flexible Pedestrian Legform Impactor GT Alpha (Flex-GTa)
 24 April 26 3 rd Flex-TEG MT BASt, Bergisch Information on the Flexible Pedestrian Legform Impactor GT Alpha (Flex-GTa) Atsuhiro Konosu Flex-TEG Chairperson /Japan Background At At the the 2 nd nd Flex-TEG
24 April 26 3 rd Flex-TEG MT BASt, Bergisch Information on the Flexible Pedestrian Legform Impactor GT Alpha (Flex-GTa) Atsuhiro Konosu Flex-TEG Chairperson /Japan Background At At the the 2 nd nd Flex-TEG
Development of a Flex-PLI LS-DYNA Model
 Development of a Flex-PLI LS-DYNA Model Shinya Hayashi 1, Masahiro Awano 2, Isamu Nishimura 2 1 JSOL Corporation, 2 Mitsubishi Motors Corporation Aichi, Japan Summary: A biofidelic flexible pedestrian
Development of a Flex-PLI LS-DYNA Model Shinya Hayashi 1, Masahiro Awano 2, Isamu Nishimura 2 1 JSOL Corporation, 2 Mitsubishi Motors Corporation Aichi, Japan Summary: A biofidelic flexible pedestrian
Consolidated Technical Specifications for the Advanced Pedestrian Legform Impactor (apli)
 IRC-18-42 IRCOBI conference 218 Consolidated Technical Specifications for the Advanced Pedestrian Legform Impactor (apli) Takahiro Isshiki, Jacobo Antona Makoshi, Atsuhiro Konosu, Yukou Takahashi Abstract
IRC-18-42 IRCOBI conference 218 Consolidated Technical Specifications for the Advanced Pedestrian Legform Impactor (apli) Takahiro Isshiki, Jacobo Antona Makoshi, Atsuhiro Konosu, Yukou Takahashi Abstract
TEG th May th Flex-TEG Meeting JAMA/JARI
 TEG-96 19 th May 29 8th Flex-TEG Meeting JAMA/JARI Development of a FE model and Analysis of the Correlation between the Flex- GTR-prototype and Human Lower Limb Outputs using Computer Simulation Models
TEG-96 19 th May 29 8th Flex-TEG Meeting JAMA/JARI Development of a FE model and Analysis of the Correlation between the Flex- GTR-prototype and Human Lower Limb Outputs using Computer Simulation Models
Impactor version. JARI Flex-G preparation manual Flex-G test preparation impactor design, certification testing EEVC LFI
 TEG doc no. Rev. Meeting no. Source Name Impactor version Main subject Other subjects 001 1 Chair/ Agenda for the first meeting of Flex-PLI Technical replaced by TEG-005 Evaluation Group 002 1 JARI Flex-G
TEG doc no. Rev. Meeting no. Source Name Impactor version Main subject Other subjects 001 1 Chair/ Agenda for the first meeting of Flex-PLI Technical replaced by TEG-005 Evaluation Group 002 1 JARI Flex-G
Dynamic full assembly certification test procedure (inverse test setup) in conjunction with functional test
 Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen (Federal Highway Research Institute) Dynamic full assembly certification test procedure (inverse test setup) in conjunction with functional test TEG-075 7th Meeting of the
Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen (Federal Highway Research Institute) Dynamic full assembly certification test procedure (inverse test setup) in conjunction with functional test TEG-075 7th Meeting of the
(48th GRSP, 7-10 December 2010, agenda item 4)
 Transmitted by the Chair of GRSP Informal document No. GRSP-48-41 (48th GRSP, 7-10 December 2010, agenda item 4) Amendments agreed to during the 48th session of GRSP Proposal for Amendment 2 I. Proposal
Transmitted by the Chair of GRSP Informal document No. GRSP-48-41 (48th GRSP, 7-10 December 2010, agenda item 4) Amendments agreed to during the 48th session of GRSP Proposal for Amendment 2 I. Proposal
FlexPLI Biofidelic Assesment Interval (BAI): Open Issues
 Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen (Federal Highway Research Institute) FlexPLI Biofidelic Assesment Interval (BAI): Open Issues 8 th Meeting of Informal Group GTR9 Phase 2 Paris, September 9 th - 10 th, 2013
Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen (Federal Highway Research Institute) FlexPLI Biofidelic Assesment Interval (BAI): Open Issues 8 th Meeting of Informal Group GTR9 Phase 2 Paris, September 9 th - 10 th, 2013
INJURY THRESHOLDS AND A MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE FOR THE THIGH AND LEG OF A PEDESTRIAN DUMMY
 INJURY THRESHOLDS AND A MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE FOR THE THIGH AND LEG OF A PEDESTRIAN DUMMY Yukou Takahashi, Masayoshi Okamoto, Yuji Kikuchi, Akihiko Akiyama Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center ABSTRACT
INJURY THRESHOLDS AND A MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE FOR THE THIGH AND LEG OF A PEDESTRIAN DUMMY Yukou Takahashi, Masayoshi Okamoto, Yuji Kikuchi, Akihiko Akiyama Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center ABSTRACT
First Technology Safety Systems. Design Freeze Status. Flex-PLI-GTR Development
 Based on TEG-047 29 Nov. 2007 JAMA-JARI JARI First Technology Safety Systems Design Freeze Status Flex-PLI-GTR Development Full Calibration Test Procedures Bernard Been FTSS Europe Comments addressed from
Based on TEG-047 29 Nov. 2007 JAMA-JARI JARI First Technology Safety Systems Design Freeze Status Flex-PLI-GTR Development Full Calibration Test Procedures Bernard Been FTSS Europe Comments addressed from
Virtual Evaluation of Vehicle Passive and Active Safety with ESI Solutions
 Virtual Evaluation of Vehicle Passive and Active Safety with ESI Solutions ASEAN AUTOMOBILE SAFETY FORUM https://blog.esi.co.jp/pro-sivic/pedestrian Copyright ESI Copyright Group, 2015. ESI Group, All
Virtual Evaluation of Vehicle Passive and Active Safety with ESI Solutions ASEAN AUTOMOBILE SAFETY FORUM https://blog.esi.co.jp/pro-sivic/pedestrian Copyright ESI Copyright Group, 2015. ESI Group, All
Summary of ACEA Tests. ACEA Comments
 8 th TEG FlexPLI Meeting on 19.05.2009 Offices of TÜV Rheinland, Cologne Summary of ACEA Tests ACEA Comments Page 1 Content: ACEA previous and latest test series Problems related to Flex-GTα and Flex-GTR
8 th TEG FlexPLI Meeting on 19.05.2009 Offices of TÜV Rheinland, Cologne Summary of ACEA Tests ACEA Comments Page 1 Content: ACEA previous and latest test series Problems related to Flex-GTα and Flex-GTR
CONCEPT DESIGN OF A 4-DOF PEDESTRIAN LEGFORM
 CONCEPT DESIGN OF A 4-DOF PEDESTRIAN LEGFORM Qing Zhou Michael Quade* Huiliang Du State Key Laboratory of Automotive Safety and Energy Tsinghua University China * Exchange student from RWTH-Aachen, Germany
CONCEPT DESIGN OF A 4-DOF PEDESTRIAN LEGFORM Qing Zhou Michael Quade* Huiliang Du State Key Laboratory of Automotive Safety and Energy Tsinghua University China * Exchange student from RWTH-Aachen, Germany
Injury Criteria for Tibia - JAMA Proposal -
 1 TEG-084 Injury Criteria for Tibia - JAMA Proposal - The Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association Inc. Pedestrian Safety WG Original Proposal (TEG-035) 2 Based on Nyquist et al. (1985) Originally proposed
1 TEG-084 Injury Criteria for Tibia - JAMA Proposal - The Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association Inc. Pedestrian Safety WG Original Proposal (TEG-035) 2 Based on Nyquist et al. (1985) Originally proposed
Optimization of a Lower Bumper Support regarding Pedestrian Protection Requirements using ANSA and LS-Opt
 Optimization of a Lower Bumper Support regarding Pedestrian Protection Requirements using ANSA and LS-Opt Isabelle Wetzstein, Beate Lauterbach, Matthias Erzgräber, Lothar Harzheim Adam Opel AG, Rüsselsheim
Optimization of a Lower Bumper Support regarding Pedestrian Protection Requirements using ANSA and LS-Opt Isabelle Wetzstein, Beate Lauterbach, Matthias Erzgräber, Lothar Harzheim Adam Opel AG, Rüsselsheim
Pedestrian CAE Models & Codes Version 1.2 September 2013 TB 013
 Technical Bulletin Pedestrian CAE Models & Codes Version 1.2 September 2013 TB 013 Title Pedestrian CAE Models & Codes Version 1.2 Document Number TB013 Author Secretariat Date September 2013 Related Documents
Technical Bulletin Pedestrian CAE Models & Codes Version 1.2 September 2013 TB 013 Title Pedestrian CAE Models & Codes Version 1.2 Document Number TB013 Author Secretariat Date September 2013 Related Documents
COMPARISON OF ANKLE INJURY MECHANISM IN FULL FRONTAL AND OBLIQUE FRONTAL CRASH MODES WITH THOR DUMMY AND HUMAN FE MODELS
 COMPARISON OF ANKLE INJURY MECHANISM IN FULL FRONTAL AND OBLIQUE FRONTAL CRASH MODES WITH THOR DUMMY AND HUMAN FE MODELS Kaitaro,Nambu Hisaki, Sugaya Hiroyuki, Mae Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center
COMPARISON OF ANKLE INJURY MECHANISM IN FULL FRONTAL AND OBLIQUE FRONTAL CRASH MODES WITH THOR DUMMY AND HUMAN FE MODELS Kaitaro,Nambu Hisaki, Sugaya Hiroyuki, Mae Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center
Pedestrian CAE Models & Codes Version 1.4 June 2015 TB 013
 Technical Bulletin Pedestrian CAE Models & Codes Version 1.4 June 2015 TB 013 Title Pedestrian CAE Models & Codes Version 1.4 Document Number TB013 Author Secretariat Date June 2015 Related Documents Pedestrian
Technical Bulletin Pedestrian CAE Models & Codes Version 1.4 June 2015 TB 013 Title Pedestrian CAE Models & Codes Version 1.4 Document Number TB013 Author Secretariat Date June 2015 Related Documents Pedestrian
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF EEVC WG17 LOWER LEGFORM FE MODEL FOR PEDESTRIAN SAFETY
 DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF EEVC WG17 LOWER LEGFORM FE MODEL FOR PEDESTRIAN SAFETY Khoo Y.C 1, F. Tarlochan 2 1, 2 Center for Innovation and Design, College of Engineering, Universiti TenagaNasional,
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF EEVC WG17 LOWER LEGFORM FE MODEL FOR PEDESTRIAN SAFETY Khoo Y.C 1, F. Tarlochan 2 1, 2 Center for Innovation and Design, College of Engineering, Universiti TenagaNasional,
Robustness of SN02 prototype test results
 Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen (Federal Highway Research Institute) Robustness of SN02 prototype test results 2 nd Meeting of Informal Group GTR9 Phase 2 Osaka, March 28 th and 29 th 2012 Oliver Zander
Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen (Federal Highway Research Institute) Robustness of SN02 prototype test results 2 nd Meeting of Informal Group GTR9 Phase 2 Osaka, March 28 th and 29 th 2012 Oliver Zander
EFFECT OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION ON KNEE LOADING FOR A STANDING PEDESTRIAN IN LATERAL IMPACTS
 EFFECT OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION ON KNEE LOADING FOR A STANDING PEDESTRIAN IN LATERAL IMPACTS Anurag Soni Anoop Chawla Sudipto Mukherjee Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology
EFFECT OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION ON KNEE LOADING FOR A STANDING PEDESTRIAN IN LATERAL IMPACTS Anurag Soni Anoop Chawla Sudipto Mukherjee Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology
Humanetics Innovative Solutions, Inc.
 Humanetics Innovative Solutions, Inc. TF-RUCC FLEX PLI TASK FORCE PRESENTATION Mark Burleigh, Mike Beebe, Kurt Bambach, Len Benfant JANUARY 27,2012 Content Introduction Long rubber verses short rubber
Humanetics Innovative Solutions, Inc. TF-RUCC FLEX PLI TASK FORCE PRESENTATION Mark Burleigh, Mike Beebe, Kurt Bambach, Len Benfant JANUARY 27,2012 Content Introduction Long rubber verses short rubber
KNEE JOINT INJURY MECHANISMS AND INJURY CRITERIA IN FULL ²SCALE TESTS ACCORDING TO IMPACT POSITION
 KNEE JOINT INJURY MECHANISMS AND INJURY CRITERIA IN FULL ²SCALE TESTS ACCORDING TO IMPACT POSITION ARNOUX P.J. 1, THOLLON L. 1, BEHR M. 1, BRUNET C. 1 CESARI D. 2 1 Laboratoire de Biomécanique Appliquée,
KNEE JOINT INJURY MECHANISMS AND INJURY CRITERIA IN FULL ²SCALE TESTS ACCORDING TO IMPACT POSITION ARNOUX P.J. 1, THOLLON L. 1, BEHR M. 1, BRUNET C. 1 CESARI D. 2 1 Laboratoire de Biomécanique Appliquée,
EFFECT OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION IN HIGH SPEED CAR- PEDESTRIAN IMPACT SIMULATIONS FOR WALKING POSTURE
 EFFECT OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION IN HIGH SPEED CAR- PEDESTRIAN IMPACT SIMULATIONS FOR WALKING POSTURE Soni A., Chawla A., Mukherjee S. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology,
EFFECT OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION IN HIGH SPEED CAR- PEDESTRIAN IMPACT SIMULATIONS FOR WALKING POSTURE Soni A., Chawla A., Mukherjee S. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology,
First Technology Safety Systems. Optional Instrumentation
 TEG-057 First Technology Safety Systems Design Freeze Status FLEX-PLI-GTR Development Optional Instrumentation Bernard Been FTSS Europe Comments addressed from Design Freeze meeting February 20 th 2008,
TEG-057 First Technology Safety Systems Design Freeze Status FLEX-PLI-GTR Development Optional Instrumentation Bernard Been FTSS Europe Comments addressed from Design Freeze meeting February 20 th 2008,
Project overview.
 Project overview Background Demographic change Source: Federal Statistics Office Germany, 2003 Share of elderly fatalities Background Vulnerable road users 30% Share of elderly fatalities 25% 20% 15% 10%
Project overview Background Demographic change Source: Federal Statistics Office Germany, 2003 Share of elderly fatalities Background Vulnerable road users 30% Share of elderly fatalities 25% 20% 15% 10%
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW BIOFIDELIC LEG FOR USE WITH A PEDESTRIAN DUMMY. A. Akiyama, M. Okamoto, R. Yoshizawa Honda R& D, Tochigi, JAPAN
 DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW BIOFIDELIC LEG FOR USE WITH A PEDESTRIAN DUMMY M Artis, J McDonald, R White, TJ Huang, T Shams, N Rangarajan GESAC, Inc, Boonsboro, MD, USA A Akiyama, M Okamoto, R Yoshizawa Honda
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW BIOFIDELIC LEG FOR USE WITH A PEDESTRIAN DUMMY M Artis, J McDonald, R White, TJ Huang, T Shams, N Rangarajan GESAC, Inc, Boonsboro, MD, USA A Akiyama, M Okamoto, R Yoshizawa Honda
DEVELOPMENT OF A BIOFIDELIC DUMMY FOR CAR-PEDESTRIAN ACCIDENT STUDIES
 DEVELOPMENT OF A BIOFIDELIC DUMMY FOR CARPEDESTRIAN ACCIDENT STUDIES T.J. Huang, J. McDonald, M. Artis, N. Rangarajan, T. Shams, R.P. White Jr., D. Beach, R. Campbell Jr. GESAC, lnc., USA A. Akiyama, S.
DEVELOPMENT OF A BIOFIDELIC DUMMY FOR CARPEDESTRIAN ACCIDENT STUDIES T.J. Huang, J. McDonald, M. Artis, N. Rangarajan, T. Shams, R.P. White Jr., D. Beach, R. Campbell Jr. GESAC, lnc., USA A. Akiyama, S.
Anterior Tibia Impacts: A Biofidelity Study between Post-Mortem Human Subjects and Anthropomorphic Test Devices
 Anterior Tibia Impacts: A Biofidelity Study between Post-Mortem Human Subjects and Anthropomorphic Test Devices H.M. Gustafson 1, J. McFadden 2 and R. Herriott 3, J.H. Bolte IV 1 1 The Ohio State University;
Anterior Tibia Impacts: A Biofidelity Study between Post-Mortem Human Subjects and Anthropomorphic Test Devices H.M. Gustafson 1, J. McFadden 2 and R. Herriott 3, J.H. Bolte IV 1 1 The Ohio State University;
EFFECT OF ACTIVE MUSCLE FORCES ON KNEE INJURY RISKS FOR PEDESTRIAN STANDING POSTURE AT LOW SPEED IMPACTS
 EFFECT OF ACTIVE MUSCLE FORCES ON KNEE INJURY RISKS FOR PEDESTRIAN STANDING POSTURE AT LOW SPEED IMPACTS Chawla A, Mukherjee S, Soni A Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology,
EFFECT OF ACTIVE MUSCLE FORCES ON KNEE INJURY RISKS FOR PEDESTRIAN STANDING POSTURE AT LOW SPEED IMPACTS Chawla A, Mukherjee S, Soni A Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology,
Improvements and Validation of an Existing LS- DYNA Model of the Knee-Thigh-Hip of a 50 th Percentile Male Including Muscles and Ligaments
 Improvements and Validation of an Existing LS- DYNA Model of the Knee-Thigh-Hip of a 50 th Percentile Male Including Muscles and Ligaments Dr. Chiara Silvestri, Mario Mongiardini, Prof. Dr. Malcolm H.
Improvements and Validation of an Existing LS- DYNA Model of the Knee-Thigh-Hip of a 50 th Percentile Male Including Muscles and Ligaments Dr. Chiara Silvestri, Mario Mongiardini, Prof. Dr. Malcolm H.
Flex PLI GTR User Manual
 Flex PLI GTR User Manual 133-9900 User Manual FLEX PLI GTR Rev F (Draft) Page 1 of 82 No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means,
Flex PLI GTR User Manual 133-9900 User Manual FLEX PLI GTR Rev F (Draft) Page 1 of 82 No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means,
Ikeda 1. Comparison of Thorax Responses between WorldSID-5th and SID-IIs in Lateral and Oblique Impacts
 Comparison of Thorax Responses between WorldSID-5th and SID-IIs in Lateral and Oblique Impacts Miwako Ikeda Hiroyuki Mae Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center Japan Paper Number 17-364 ABSTRACT Recently,
Comparison of Thorax Responses between WorldSID-5th and SID-IIs in Lateral and Oblique Impacts Miwako Ikeda Hiroyuki Mae Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center Japan Paper Number 17-364 ABSTRACT Recently,
Flex PLI GTR User Manual
 Flex PLI GTR User Manual 133-9900 User Manual FLEX PLI GTR Rev C Page 1 of 79 For information on Humanetics products, please visit our web site at www.humaneticsatd.com or contact: Humanetics Innovative
Flex PLI GTR User Manual 133-9900 User Manual FLEX PLI GTR Rev C Page 1 of 79 For information on Humanetics products, please visit our web site at www.humaneticsatd.com or contact: Humanetics Innovative
TECHNICAL PARAMETERS AND MECHANISMS FOR THE INJURY RISK OF THE KNEE JOINT OF VULNERABLE ROAD USERS IMPACTED BY CARS IN ROAD TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS
 TECHNICAL PARAMETERS AND MECHANISMS FOR THE INJURY RISK OF THE KNEE JOINT OF VULNERABLE ROAD USERS IMPACTED BY CARS IN ROAD TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS Dietmar Otte*, Carl Haasper** * Accident Research Unit, **
TECHNICAL PARAMETERS AND MECHANISMS FOR THE INJURY RISK OF THE KNEE JOINT OF VULNERABLE ROAD USERS IMPACTED BY CARS IN ROAD TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS Dietmar Otte*, Carl Haasper** * Accident Research Unit, **
Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation. Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures
 Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures June 2009 Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation Document Revisions: The June 2009 revision of this document clarifies
Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures June 2009 Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation Document Revisions: The June 2009 revision of this document clarifies
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A CHILD FINITE ELEMENT MODEL FOR USE IN PEDESTRIAN ACCIDENT SIMULATIONS
 DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A CHILD FINITE ELEMENT MODEL FOR USE IN PEDESTRIAN ACCIDENT SIMULATIONS Yunzhu Meng Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A CHILD FINITE ELEMENT MODEL FOR USE IN PEDESTRIAN ACCIDENT SIMULATIONS Yunzhu Meng Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
REVIEW OF THE EURO NCAP UPPER LEG TEST
 REVIEW OF THE EURO NCAP UPPER LEG TEST Nils Lubbe Toyota Motor Europe, Belgium Hiromi Hikichi Hiroyuki Takahashi Toyota Motor Corporation, Japan Johan Davidsson Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden
REVIEW OF THE EURO NCAP UPPER LEG TEST Nils Lubbe Toyota Motor Europe, Belgium Hiromi Hikichi Hiroyuki Takahashi Toyota Motor Corporation, Japan Johan Davidsson Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden
Side Impact Simulations using THUMS and WorldSID
 Side Impact Simulations using THUMS and WorldSID 25 th September, 213 Tsuyoshi Yasuki, Yuichi Kitagawa, Shinobu Tanaka, Satoshi Fukushima TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION CONTENTS 1. Background 2. Objective 3.
Side Impact Simulations using THUMS and WorldSID 25 th September, 213 Tsuyoshi Yasuki, Yuichi Kitagawa, Shinobu Tanaka, Satoshi Fukushima TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION CONTENTS 1. Background 2. Objective 3.
The Development of the Lower Extremity of a Human FE Model and the Influence of Anatomical Detailed Modelling in Vehicle to Pedestrian Impacts
 The Development of the Lower Extremity of a Human FE Model and the Influence of Anatomical Detailed Modelling in Vehicle to Pedestrian Impacts Shouhei Kunitomi, Yoshihiro Yamamoto, Ryosuke Kato, Jacobo
The Development of the Lower Extremity of a Human FE Model and the Influence of Anatomical Detailed Modelling in Vehicle to Pedestrian Impacts Shouhei Kunitomi, Yoshihiro Yamamoto, Ryosuke Kato, Jacobo
CHARACTERISTICS ON FRACTURES OF TIBIA AND FIBULA IN CAR IMPACTS TO PEDESTRIANS INFLUENCES OF CAR BUMPER HEIGHT AND SHAPE
 CHARACTERISTICS ON FRACTURES OF TIBIA AND FIBULA IN CAR IMPACTS TO PEDESTRIANS INFLUENCES OF CAR BUMPER HEIGHT AND SHAPE Otte, D.*; Haasper, C. ** * Accident Research Unit ** Trauma Department Medical
CHARACTERISTICS ON FRACTURES OF TIBIA AND FIBULA IN CAR IMPACTS TO PEDESTRIANS INFLUENCES OF CAR BUMPER HEIGHT AND SHAPE Otte, D.*; Haasper, C. ** * Accident Research Unit ** Trauma Department Medical
A NEW DETAILED MULTI-BODY MODEL OF THE PEDESTRIAN LOWER EXTREMITY: DEVELOPMENT AND PRELIMINARY VALIDATION
 A NEW DETAILED MULTI-BODY MODEL OF THE PEDESTRIAN LOWER EXTREMITY: DEVELOPMENT AND PRELIMINARY VALIDATION Jason Kerrigan, Dan Parent, Costin Untaroiu, Jeff Crandall, Bing Deng* University of Virginia Center
A NEW DETAILED MULTI-BODY MODEL OF THE PEDESTRIAN LOWER EXTREMITY: DEVELOPMENT AND PRELIMINARY VALIDATION Jason Kerrigan, Dan Parent, Costin Untaroiu, Jeff Crandall, Bing Deng* University of Virginia Center
Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation. Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures
 Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures May 2001 Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures Injury measures obtained from an
Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures May 2001 Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures Injury measures obtained from an
THE STRAIN-RATE DEPENDENCE OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF RABBIT KNEE LIGAMENTS
 THE STRAIN-RATE DEPENDENCE OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF RABBIT KNEE LIGAMENTS Sota Yamamoto Akinori Saito Kei Nagasaka Satoshi Sugimoto Koji Mizuno Eiichi Tanaka Nagoya University Japan Masaki Kabayama
THE STRAIN-RATE DEPENDENCE OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF RABBIT KNEE LIGAMENTS Sota Yamamoto Akinori Saito Kei Nagasaka Satoshi Sugimoto Koji Mizuno Eiichi Tanaka Nagoya University Japan Masaki Kabayama
Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates!
 7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
Collaboration Works (USA & JAPAN) Preliminary (Tentative) Results for HR-GTR 7 Meeting on December 5 and 6
 Collaboration Works (USA & JAPAN) Neck Injury Parameters based on PMHS Tests Preliminary (Tentative) Results for HR-GTR 7 Meeting on December 5 and 6 J-MLIT/JASIC/JARI Japan Validation Kinematics USA Research
Collaboration Works (USA & JAPAN) Neck Injury Parameters based on PMHS Tests Preliminary (Tentative) Results for HR-GTR 7 Meeting on December 5 and 6 J-MLIT/JASIC/JARI Japan Validation Kinematics USA Research
ASPECTS REGARDING THE IMPACT SPEED, AIS AND HIC RELATIONSHIP FOR CAR-PEDESTRIAN TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS
 ASPECTS REGARDING THE IMPACT SPEED, AIS AND HIC RELATIONSHIP FOR CAR-PEDESTRIAN TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS 1 drd.eng. George TOGANEL, 2 Conf.dr.eng. Adrian SOICA Transilvania University of Brasov, Mechanical Engineery
ASPECTS REGARDING THE IMPACT SPEED, AIS AND HIC RELATIONSHIP FOR CAR-PEDESTRIAN TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS 1 drd.eng. George TOGANEL, 2 Conf.dr.eng. Adrian SOICA Transilvania University of Brasov, Mechanical Engineery
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Side Impact Crashworthiness Evaluation. Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures
 Side Impact Crashworthiness Evaluation Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures October 2003 Side Impact Crashworthiness Evaluation Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures Injury measures obtained from instrumented
Side Impact Crashworthiness Evaluation Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures October 2003 Side Impact Crashworthiness Evaluation Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures Injury measures obtained from instrumented
DYNAMIC CHARACTERIZATION OF BOVINE MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENTS
 DYNAMIC CHARACTERIZATION OF BOVINE MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENTS A. Chawla, S. Mukherjee, H. Warhatkar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi, INDIA R. Malhotra Department
DYNAMIC CHARACTERIZATION OF BOVINE MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENTS A. Chawla, S. Mukherjee, H. Warhatkar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi, INDIA R. Malhotra Department
THORAX FP7 Workshop Task 2.4 Dummy Concepts
 Thoracic Injury Assessment for Improved Vehicle Safety THORAX FP7 Workshop Task 2.4 Dummy Concepts Meeting: Date of issue: Prepared by: May 11, 2010, London, UK May 7, 2010 Bernard Been Contents THOR history
Thoracic Injury Assessment for Improved Vehicle Safety THORAX FP7 Workshop Task 2.4 Dummy Concepts Meeting: Date of issue: Prepared by: May 11, 2010, London, UK May 7, 2010 Bernard Been Contents THOR history
Hayashi 1. Investigation of front seat occupants' acetabulum injury in front impact
 Investigation of front seat occupants' acetabulum injury in front impact Shinichi Hayashi Ryuuji Ootani Tsuyoshi Matsunaga Taisuke Watanabe Chinmoy Pal Shigeru Hirayama Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. Japan Paper
Investigation of front seat occupants' acetabulum injury in front impact Shinichi Hayashi Ryuuji Ootani Tsuyoshi Matsunaga Taisuke Watanabe Chinmoy Pal Shigeru Hirayama Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. Japan Paper
Sports Medicine 15. Unit I: Anatomy. The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin. Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs
 Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
BIOMECHANICAL RESPONSES OF HEAD/NECK/TORSO TO LATERAL IMPACT LOADING ON SHOULDERS OF MALE AND FEMALE VOLUNTEERS
 BIOMECHANICAL RESPONSES OF HEAD/NECK/TORSO TO LATERAL IMPACT LOADING ON SHOULDERS OF MALE AND FEMALE VOLUNTEERS Koshiro Ono 1), Susumu Ejima 1), Koji Kaneoka 2), Makoto Fukushima 2), Shintaro Yamada 3),
BIOMECHANICAL RESPONSES OF HEAD/NECK/TORSO TO LATERAL IMPACT LOADING ON SHOULDERS OF MALE AND FEMALE VOLUNTEERS Koshiro Ono 1), Susumu Ejima 1), Koji Kaneoka 2), Makoto Fukushima 2), Shintaro Yamada 3),
NHTSA s Ease of Use Rating System for Child Restraint Systems
 Transmitted by the expert from the United States of America NHTSA s Ease of Use Rating System for Child Restraint Systems Informal document No. GRSP-43-14 (43rd GRSP, 19-23 May 2008 agenda items 12(a))
Transmitted by the expert from the United States of America NHTSA s Ease of Use Rating System for Child Restraint Systems Informal document No. GRSP-43-14 (43rd GRSP, 19-23 May 2008 agenda items 12(a))
PEDESTRIAN INJURY MECHANISMS & CRITERIA A COUPLED EXPERIMENTAL AND FINITE ELEMENT APPROACH
 PEDESTRIAN INJURY MECHANISMS & CRITERIA A COUPLED EXPERIMENTAL AND FINITE ELEMENT APPROACH Catherine Masson Pierre-Jean Arnoux Christian Brunet Laboratory of Applied Biomechanics. French National Institute
PEDESTRIAN INJURY MECHANISMS & CRITERIA A COUPLED EXPERIMENTAL AND FINITE ELEMENT APPROACH Catherine Masson Pierre-Jean Arnoux Christian Brunet Laboratory of Applied Biomechanics. French National Institute
The Knee. Two Joints: Tibiofemoral. Patellofemoral
 Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Fusako Sato, Jacobo Antona, Susumu Ejima, Koshiro Ono Japan Automobile Research Institute
 Influence on Cervical Vertebral Motion of the Interaction between Occupant and Head Restraint/Seat, based on the Reconstruction of Rear-End Collision Using Finite Element Human Model Fusako Sato, Jacobo
Influence on Cervical Vertebral Motion of the Interaction between Occupant and Head Restraint/Seat, based on the Reconstruction of Rear-End Collision Using Finite Element Human Model Fusako Sato, Jacobo
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
Keywords Knee Joint Injury, Biomechanics, Pedestrian Safety, Connective Soft Tissue, Finite Elements Method
 www.jbpe.org Crash Injury Analysis of Knee Joint Considering Pedestrian Safety Original 1 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, K. N. Toosi University of Technology, Tehran, Iran Asgari M. 1 *, Keyvanian
www.jbpe.org Crash Injury Analysis of Knee Joint Considering Pedestrian Safety Original 1 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, K. N. Toosi University of Technology, Tehran, Iran Asgari M. 1 *, Keyvanian
Reviews on Injury Parameters and Injury Criteria for Minor Neck Injuries during Rear-end Impacts
 Informal GTR7 Experts Meeting on Minor Neck Injury Criteria Reviews on Injury Parameters and Injury Criteria for Minor Neck Injuries during Rear-end Impacts Koshiro Ono Japan Automobile Research Institute
Informal GTR7 Experts Meeting on Minor Neck Injury Criteria Reviews on Injury Parameters and Injury Criteria for Minor Neck Injuries during Rear-end Impacts Koshiro Ono Japan Automobile Research Institute
BIOFIDELITY AND REPEATABILITY EVALUATION OF THE THOR DUMMY THORAX, ABDOMEN AND FEMUR, THROUGH A SET OF TESTS
 BIOFIDELITY AND REPEATABILITY EVALUATION OF THE THOR DUMMY THORAX, ABDOMEN AND FEMUR, THROUGH A SET OF TESTS L. Martínez INSIA G. Ferichola INSIA L.J.Guerra INSIA M.Van Ratingen TNO D. Hynd TRL ABSTRACT
BIOFIDELITY AND REPEATABILITY EVALUATION OF THE THOR DUMMY THORAX, ABDOMEN AND FEMUR, THROUGH A SET OF TESTS L. Martínez INSIA G. Ferichola INSIA L.J.Guerra INSIA M.Van Ratingen TNO D. Hynd TRL ABSTRACT
Joseph M. Cormier PhD PE Curriculum Vitae
 Joseph M. Cormier PhD PE Curriculum Vitae Education Ph.D. Biomedical Engineering 2009 Virginia Tech Wake Forest School of Biomedical Engineering and Sciences Research focus: Facial Biomechanics M.S. Mechanical
Joseph M. Cormier PhD PE Curriculum Vitae Education Ph.D. Biomedical Engineering 2009 Virginia Tech Wake Forest School of Biomedical Engineering and Sciences Research focus: Facial Biomechanics M.S. Mechanical
VERIFICATION OF LOWER NECK SHEAR FORCE AS A REAR IMPACT INJURY CRITERION
 VERIFICATION OF LOWER NECK SHEAR FORCE AS A REAR IMPACT INJURY CRITERION Brian D. Stemper, Steven G. Storvik, Narayan Yoganandan, and Frank A. Pintar Department of Neurosurgery, Medical College of Wisconsin
VERIFICATION OF LOWER NECK SHEAR FORCE AS A REAR IMPACT INJURY CRITERION Brian D. Stemper, Steven G. Storvik, Narayan Yoganandan, and Frank A. Pintar Department of Neurosurgery, Medical College of Wisconsin
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Department of Biomedical Engineering and Mechanics, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, USA
 Review Article A Review of Pediatric Lower Extremity Data for Pedestrian Numerical Modeling: Injury Epidemiology, Anatomy, Anthropometry, Structural, and Mechanical Properties Yunzhu Meng and Costin D.
Review Article A Review of Pediatric Lower Extremity Data for Pedestrian Numerical Modeling: Injury Epidemiology, Anatomy, Anthropometry, Structural, and Mechanical Properties Yunzhu Meng and Costin D.
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Injury Criteria Analysis Plan
 GTR 7 Informal Working Group June 10, 2011 Washington DC GTR7-07-06 Injury Criteria Analysis Plan Kevin Moorhouse, Ph.D. NHTSA Yun-Seok Kang Ohio State University Rear Impact Research Objectives Evaluate
GTR 7 Informal Working Group June 10, 2011 Washington DC GTR7-07-06 Injury Criteria Analysis Plan Kevin Moorhouse, Ph.D. NHTSA Yun-Seok Kang Ohio State University Rear Impact Research Objectives Evaluate
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy. Stephanie E. Siegrist, MD, LLC
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
EM Cases Course 2017 Knee Emergencies Module
 EM Cases Course 2017 Knee Emergencies Module Arun Sayal Podcasts to listen to prior to the course Link to: Occult Knee Injuries Pearls & Pitfalls Knee injuries in the ED are much more than fractures and
EM Cases Course 2017 Knee Emergencies Module Arun Sayal Podcasts to listen to prior to the course Link to: Occult Knee Injuries Pearls & Pitfalls Knee injuries in the ED are much more than fractures and
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Objectives. The BIG Joint. Case 1. Boney Architecture. Presenter Disclosure Information. Common Knee Problems
 3:30 4:15 pm Common Knee Problems SPEAKER Christopher J. Visco, MD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher J. Visco, MD: Speaker s Bureau
3:30 4:15 pm Common Knee Problems SPEAKER Christopher J. Visco, MD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher J. Visco, MD: Speaker s Bureau
Hikida 1. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Upper Thorax Reponses of THOR-50M ATDs
 Repeatability and Reproducibility of Upper Thorax Reponses of -5M s Kazuki, Hikida Kazunori, Maehara Hidenori, Mikami, Hiroyuki, Mae Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center Japan Paper Number 7-8 ABSTRACT
Repeatability and Reproducibility of Upper Thorax Reponses of -5M s Kazuki, Hikida Kazunori, Maehara Hidenori, Mikami, Hiroyuki, Mae Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center Japan Paper Number 7-8 ABSTRACT
DOSE-RESPONSE MODELS AND EDR DATA FOR ASSESSMENT OF INJURY RISK AND EFFECTIVENESS OF SAFETY SYSTEMS
 DOSE-RESPONSE MODELS AND EDR DATA FOR ASSESSMENT OF INJURY RISK AND EFFECTIVENESS OF SAFETY SYSTEMS Anders Kullgren Folksam Research and Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Section of Personal Injury
DOSE-RESPONSE MODELS AND EDR DATA FOR ASSESSMENT OF INJURY RISK AND EFFECTIVENESS OF SAFETY SYSTEMS Anders Kullgren Folksam Research and Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Section of Personal Injury
Femoral Shaft Fracture
 Femoral Shaft Fracture The femoral shaft is well padded with muscles(an advantage in protecting the bone from all but the most powerful forces)but the disadvantage is that fractures are often severely
Femoral Shaft Fracture The femoral shaft is well padded with muscles(an advantage in protecting the bone from all but the most powerful forces)but the disadvantage is that fractures are often severely
Progress Report on Neck Injury Criteria Works for Discussion
 GTR 7 Informal Working Group September 10/11, 2013 Progress Report on Neck Injury Criteria Works for Discussion Collaboration works with NHTSA(VRTC) Part I JAPAN JMLIT/JASIC/JARI This year's Contents 2
GTR 7 Informal Working Group September 10/11, 2013 Progress Report on Neck Injury Criteria Works for Discussion Collaboration works with NHTSA(VRTC) Part I JAPAN JMLIT/JASIC/JARI This year's Contents 2
CASPER. CASPER 1 YO child human FE model CHILD ADVANCED SAFETY PROJECT FOR EUROPEAN ROADS
 CHILD ADVANCED SAFETY PROJECT FOR EUROPEAN ROADS 1 YO child human FE model Jikuang Yang Chalmers University of Technology SAFER-Vehicle Traffic Safety Center Co-workers: Sunan Huang (Chalmers) Frank Meryer,
CHILD ADVANCED SAFETY PROJECT FOR EUROPEAN ROADS 1 YO child human FE model Jikuang Yang Chalmers University of Technology SAFER-Vehicle Traffic Safety Center Co-workers: Sunan Huang (Chalmers) Frank Meryer,
Knee Injury Assessment
 Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #2 Blunt Trauma
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #2 Blunt Trauma Blunt trauma is the most common cause of traumatic death and disability. The definition
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #2 Blunt Trauma Blunt trauma is the most common cause of traumatic death and disability. The definition
OSLO SPORTS TRAUMA RESEARCH CENTER KNEE INJURY SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE
 OSLO SPORTS TRAUMA RESEARCH CENTER KNEE INJURY SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE 2A - Information on previous knee injuries LEFT KNEE Number of previous acute knee injuries (sprains): 0 1 2 3 4 5 >5 If you answered
OSLO SPORTS TRAUMA RESEARCH CENTER KNEE INJURY SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE 2A - Information on previous knee injuries LEFT KNEE Number of previous acute knee injuries (sprains): 0 1 2 3 4 5 >5 If you answered
Development and Evaluation of Mathematical Model to Simulate Thoracic Response to Impact in Lateral and Oblique Directions
 Development and Evaluation of Mathematical Model to Simulate Thoracic Response to Impact in Lateral and Oblique Directions Undergraduate Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Development and Evaluation of Mathematical Model to Simulate Thoracic Response to Impact in Lateral and Oblique Directions Undergraduate Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Driver Lower Extremity Response to Out of Position Knee Airbag Deployment. Xin Ye, Matthew B. Panzer, Greg Shaw, Jeff R. Crandall
 Driver Lower Extremity Response to Out of Position Knee Airbag Deployment Xin Ye, Matthew B. Panzer, Greg Shaw, Jeff R. Crandall Abstract The 5 th percentile female was chosen for an investigation of knee
Driver Lower Extremity Response to Out of Position Knee Airbag Deployment Xin Ye, Matthew B. Panzer, Greg Shaw, Jeff R. Crandall Abstract The 5 th percentile female was chosen for an investigation of knee
Alcohol. Gordon Smith, MD (MB, ChB Otago), MPH Professor University of Maryland National Study Center for Trauma and EMS
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
(1) Experimental Verification of the Relationship between Pedal-to- Pedal Distance and Pedal Misapplication
 (1) Experimental Verification of the Relationship between Pedal-to-Pedal Distance and Pedal Misapplication (2) Detection of Distress Caused by Pedal Misapplication and Its Application to Accident Prevention
(1) Experimental Verification of the Relationship between Pedal-to-Pedal Distance and Pedal Misapplication (2) Detection of Distress Caused by Pedal Misapplication and Its Application to Accident Prevention
Kinetic Energy Energy in Motion KE = Mass (weight) X Velocity (speed)² 2 Double Weight = Energy Double Speed = Energy IS THE GREATEST DETERMINANT
 1 Chapter 17 Blunt Trauma 2 Introduction to Blunt Trauma Most common cause of trauma death and disability exchange between an object and the human body, without intrusion through the skin 3 Blunt trauma
1 Chapter 17 Blunt Trauma 2 Introduction to Blunt Trauma Most common cause of trauma death and disability exchange between an object and the human body, without intrusion through the skin 3 Blunt trauma
The Severity of Pedestrian Injuries in Alcohol-Related Collisions
 The Severity of Pedestrian Injuries in -Related Collisions AUTHORS: Stanley Sciortino, PhD Elyse Chiapello San Francisco Department of Public Health Community Health Education Section The California Statewide
The Severity of Pedestrian Injuries in -Related Collisions AUTHORS: Stanley Sciortino, PhD Elyse Chiapello San Francisco Department of Public Health Community Health Education Section The California Statewide
Common Knee Injuries
 Common Knee Injuries In 2010, there were roughly 10.4 million patient visits to doctors' offices because of common knee injuries such as fractures, dislocations, sprains, and ligament tears. Knee injury
Common Knee Injuries In 2010, there were roughly 10.4 million patient visits to doctors' offices because of common knee injuries such as fractures, dislocations, sprains, and ligament tears. Knee injury
Development of Age and Sex-Specific Thorax Finite Element Models
 Development of Age and Sex-Specific Thorax Finite Element Models S. L. Schoell 1,2, A. A. Weaver 1,2, N.A. Vavalle 1,2 and J. D. Stitzel 1,2 1 Virginia Tech Wake Forest University Center for Injury Biomechanics
Development of Age and Sex-Specific Thorax Finite Element Models S. L. Schoell 1,2, A. A. Weaver 1,2, N.A. Vavalle 1,2 and J. D. Stitzel 1,2 1 Virginia Tech Wake Forest University Center for Injury Biomechanics
Please understand that the values set forth here estimated ranges of of value for New York pain and
 LOWER LEG INJURIES ISSUE 3 How New York Juries Decide the Value of obligation. You re invited to call John toll free at Pain and Suffering in Lower Leg Fracture 1-800-530-4660, or locally, 914-686-0900.
LOWER LEG INJURIES ISSUE 3 How New York Juries Decide the Value of obligation. You re invited to call John toll free at Pain and Suffering in Lower Leg Fracture 1-800-530-4660, or locally, 914-686-0900.
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE and LOWER LEG
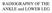 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE and LOWER LEG Patient Position: ANKLE AP Projection Part Position: True Slight to place foot s long axis Center to Central Ray: to IR Midway Note: Ankle joint is to tips of malleoli
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE and LOWER LEG Patient Position: ANKLE AP Projection Part Position: True Slight to place foot s long axis Center to Central Ray: to IR Midway Note: Ankle joint is to tips of malleoli
