OUTCOME IN PATIENTS WITH FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES DEPENDS ON THE TREATMENT USED
|
|
|
- Charlene George
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Zdrav Vestn 2007; 76: I-3 8 I-3 Research article/raziskovalni prispevek OUTCOME IN PATIENTS WITH FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES DEPENDS ON THE TREATMENT USED KONČNI REZULTAT ZDRAVLJENJA STAROSTNIKA Z ZLOMOM VRATU STEGNENICE JE POVEZAN Z METODO OPERACIJE Drago Brilej, 1 Radko Komadina, 1 Miran Vrabl 2 1 Department of Traumatology, General and Teaching Hospital Celje, Oblakova 5, 3000 Celje 2 Zavarovalnica Maribor d. d., Cankarjeva ul. 3, 2000 Maribor Abstract Background Patients and methods Results Conclusions Key words Hip fractures among the elderly are related to a high degree of mortality and disability. The views of the treatment methods of elderly patients with femoral neck fractures are opposing. In the 4-year period the General and Teaching Hospital Celje admitted 164 patients older than 65 years for treatment due to a dislocated femoral neck fracture (Garden 3,4). The patients were divided into two groups according to the fracture management approach. 52 patients were treated for dislocated femoral neck fracture through internal fixation with three screws (Group A). 81 patients were treated for dislocated femoral neck fracture through cemented bipolar partial prosthesis (Group B). The one-year survivability was examined and compared between the two groups. A multivariant analysis was used to examine the impact on the final outcome of the treatment and one-year survivability. A good treatment outcome was reported in 44 % elderly managed with osteosynthesis and in 66 % patients treated with prosthesis. A cumulative one-year survivability rate was 64.6 % in patients treated with osteosynthesis while in patients treated with prosthesis the rate was 75.7 %. The pre-fracture medical condition (3.88 odds ratio), treatment approach (0.33 odds ratio) and clinical rehabilitation efficiency (0.07 odds ratio) had a statistically significant impact on the functional one-year post-fracture result. The age of the patients (0.30 odds ratio) and hospital rehabilitation efficiency (2.89 odds ratio) had a significant impact on the post-fracture survivability. The authors claim that a primary cemented partial bipolar prosthesis is the treatment choice for elderly with dislocated femoral neck fracture. elderly; femoral neck fracture; osteosynthesis; partial hip replacement Izvleček Izhodišča Prebivalstvo Slovenije se stara. Med starostniki so zlomi kolkov pomemben vzrok umrljivosti in invalidnosti. Incidenca zlomov vratu stegnenice dosega na prebivalcev letno. Mnenja o načinu zdravljenja starostnikov z zlomom vratu stegnenice si nasprotujejo. Kar 94 % dislociranih zlomov vratu stegnenice pri starostnikih na Nizozemskem zdravijo s hemiartroplastiko, v Švedski pa praktično vse primarno oskrbijo z osteosintezo. V SUB Celje so do leta 1994 večino dislociranih zlomov vratu stegnenice oskrbeli z osteo- Corresponding author / Avtor za dopisovanje: Drago Brilej, Department of Traumatology, General and Teaching Hospital Celje, Oblakova 5, 3000 Celje, Slovenia, fax: , Drago.Brilej@guest.arnes.si
2 I-4 Zdrav Vestn 2007; 76: SUPPL I sintezo s tremi vijaki. Leta 1995 so spremenili protokol zdravljenja. Poškodovance, starejše od 65 let z dislociranim zlomom vratu stegnenice so oskrbeli z delno cementirano bipolarno protezo. Obe skupini so primerjali med sabo, da bi ugotovili upravičenost menjave metode zdravljenja. Hipoteza je bila, da vstavitev delno cementirane bipolarne endoproteze izboljša preživetje starostnikov z dislociranim zlomom vratu stegnenice in da preživelim omogoči uspešnejšo rehabilitacijo. Bolniki in metode V SUB Celje so od januarja 1993 do decembra 1996 zaradi svežega dislociranega zloma vratu stegnenice (Garden 3,4) zdravili 164 poškodovancev, starejših od 65 let. Praviloma so v letih 1993 in 94 zdravili te zlome z osteosintezo s tremi vijaki, v letih 1995 in 96 z vstavitvijo delne bipolarne endoproteze. 131 (80 %) poškodovancev so spremljali 1 leto. Glede na način oskrbe zloma so jih razdelili v dve skupini. V letih 1993 in 94 so zdravili 52 starostnikov zaradi dislociranega zloma vratu stegnenice z osteosintezo s tremi vijaki. V letih 1995 in 96 so zdravili 81 starostnikov zaradi dislociranega zloma vratu stegnenice z delno cementirano bipolarno protezo. Pred operativnim posegom so ocenili zdravstveno stanje poškodovanca po ASA lestvici. Ugotavljali so zaplete med zdravljenjem in trajanje hospitalizacije. Ob koncu zdravljenja in po enem letu so ocenili samostojnost poškodovancev pri hoji. Z metodo po Kaplan Meier so ugotavljali 1-letno preživetje in ga z Log-Rank testom primerjali med obema skupinama. Z multivariantno analizo so ugotavljali vpliv neodvisnih spremenljivk na končni rezultat zdravljenja in na enoletno preživetje. Rezultati Zaključki Ključne besede V skupini A (osteosinteze) je bilo 52 poškodovancev. Povprečno trajanje hospitalizacije je bilo 18,75 dneva. Zapleti so se pojavili pri 11 (21 %) poškodovancih. V bolnišnici so umrli štirje (8 %) poškodovanci. Ob odpustu iz bolnišnice je bilo 18 (37,5 %) poškodovancev samostojnih pri hoji. Eno leto po poškodbi so analizirali 43 poškodovancev (89,6 %). Pri 16 (33,5 %) poškodovancih so se pojavile motnje celjenja zloma (pseudoartroza, avaskularna nekroza glavice stegnenice). Dober rezultat zdravljenja po enem letu je bil ugotovljen pri 19 (44 %) starostnikih z zlomom vratu stegnenice, zdravljenih z osteosintezo. V skupini B (proteze) je bilo 81 poškodovancev. Povprečno trajanje hospitalizacije je bilo 17,8 dneva. Zapleti so se pojavili pri 14 (17,3 %) poškodovancih. Umrljivost v bolnišnici je bila 7,5 %. Eno leto po poškodbi smo analizirali 68 poškodovancev (89,5 %). Ponovnih operativnih posegov na operiranem kolku ni bilo. Dober rezultat zdravljenja po enem letu je bil ugotovljen pri 45 (66 %) poškodovancev. Kumulativno enoletno preživetje poškodovancev z zlomom vratu stegnenice in osteosintezo je bilo 64,6 %, pri poškodovancih s protezami 75,7 %. Zdravstveno stanje pred poškodbo (razmerje obetov 3,88), metoda zdravljenja (razmerje obetov 0,33) in uspešnost bolnišnične rehabilitacije (razmerje obetov 0,07) so statistično signifikantno vplivali na funkcionalni rezultat eno leto po poškodbi. Starost poškodovanca (razmerje obetov 0,30) in uspešnost bolnišnične rehabilitacije (razmerje obetov 2,89) sta statistično signifikantno vplivala na preživetje po poškodbi. Cilj zdravljenja starostnika z zlomom vratu stegnenice mora biti zgodnja mobilizacija in možnost obremenjevanja operirane noge. Le-to mu omogoča hitro vrnitev v njegovo socialno okolje. Prednost oskrbe zloma vratu stegnenice s cementirano bipolarno endoprotezo je v tem, da lahko starostnik nogo takoj polno obremenjuje, ponovnih operacij je malo (0,4 4 %). Rezultati analize v SUB Celje so pokazali, da so zdravstveno stanje pred poškodbo, metoda zdravljenja in uspešnost bolnišnične rehabilitacije statistično signifikantno vplivali na funkcionalni rezultat eno leto po poškodbi. Rezultati analize v SUB Celje so tudi pokazali boljše enoletno preživetje tistih starostnikov, ki so bili operirani s protezo (razlika 11,1 %), vendar razlika ni bila statistično značilna. Med bolnišničnim zdravljenjem ni bilo pomembnih razlik v zapletih in umrljivosti poškodovancev. Statistično pomemben vpliv na enoletno preživetje sta imela starost poškodovancev in uspešnost rehabilitacije v bolnišnici. Ocenjujemo, da je zdravljenje dislociranega zloma vratu stegnenice pri starostnikih s cementno delno bipolarno protezo boljše kot osteosinteza in predstavlja kirurško metodo izbora. starostniki; zlom vratu stegnenice; osteosinteza; delna proteza
3 Brilej D, Komadina R, Vrabl M. Outcome in patients with femoral neck fractures depends on the treatment used I-5 Introduction The number of people in Slovenia aged 65 and older is projected to increase by 50 % over the next 20 years to reach 19 % of the whole population. 1 Hip fractures among the elderly are related to a high degree of mortality and disability. The incidence of femoral neck fractures is approximately per 100,000 people annually. 2 The mortality rate among the hip fracture patients is nearly 30 % in the first post-fracture year and only half of those who survive manage to regain their pre-injury level of function. 3 It has been estimated that the overall costs of treatment in the USA account for about $ 16,000 20,000 per patient. 4 The views of the treatment methods of elderly patients with femoral neck fractures are opposing. In the Netherlands, as many as 94 % of dislocated femoral neck fractures in elderly are treated with hemiarthroplasty, while in Sweden practically all are treated with osteosynthesis. 5 At the General and Teaching Hospital Celje (»SUB Celje«) until 1994 most of the dislocated femoral neck fractures were treated by osteosynthesis with three screws. In the year 1995, the treatment protocol was changed. The patients older than 65 years were treated with cemented bipolar prosthesis for dislocated femoral neck fracture. The comparison of the two groups was made in order to examine the reasons for practice variation. The hypothesis was that the use of a cemented bipolar endoprosthesis contributed to the survivability of elderly patients with dislocated femoral neck fracture and to the efficiency of their rehabilitation. Patients and methods In the period between January 1993 and December 1996 the General and Teaching Hospital Celje admitted 164 patients older than 65 years for treatment due to a dislocated femoral neck fracture (Garden 3,4). In the years 1993 and 1994, such fractures would normally be treated with osteosynthesis through internal fixation with three screws, and in the years 1995 and 1996, using the bipolar endoprosthesis. A 1-year follow-up study of 131 patients (80 %) was conducted. The patients were divided into two groups according to the fracture management approach. Group A In the years 1993 and 1994, fifty-two elderly patients were treated for dislocated femoral neck fracture with osteosynthesis through internal fixation with three screws. The mean age of the patients was 79.7 years with 16 of them being male and 36 female. Forty-nine percent of the patients were operated within two days after the injury. After the closed reposition on the extension table under the control of the radiological amplifier the fracture was stabilised with three parallel spongious screws. 6 The patients were mobilised out of bed by the first post-operative day and with the assistance of physiotherapists they were taught to walk using crutches and to apply the weight bearing restrictions on the operated leg. The outpatient follow-up was conducted at 6-week intervals until the fracture healing or occurrence of any healing disturbances (redislocation, pseudoarthrosis, avascular necrosis). Full weight bearing was normally allowed 2 3 months after the fracture. Group B In the years 1995 and 1996 eighty-one patients were treated for dislocated femoral neck fracture through cemented bipolar prosthesis. The average age of the patients was 79.2 years, with 14 of male and 67 of female gender. The cemented bipolar prosthesis was anchored using either the lateral or anterolateral approach according to Watson Jones. 7 The patients were mobilised out of bed by the first post-operative day and with the assistance of physiotherapists they were taught to walk using crutches. Full weight bearing of the operated leg was allowed. The pre-surgical physical condition of the patients was assessed using the ASA scale. 8 Analysed were any complications during the treatment and the duration of hospitalisation. At the end of the treatment the functional independence of the patients was assessed: 1 (immobile), 2 (walking using crutches or with the assistance of another person), 3 (independent mobility using crutches), 4 (totally independent mobility). The patients assessed with 3 and 4 were considered as independent when walking. Independence in walking was analysed again one year after the fracture. If the elderly needed assistance in walking (score 1 and 2) and if re-operation was required of the injured hip (fracture healing disturbances, replacement of prosthesis), this was assessed as a poor treatment outcome. The Kaplan Meier method was used to examine the one-year survivability to be compared through the Log-Rank test between the two groups. 9 A multivariant analysis was used to examine the impact of independent variables on the final outcome of the treatment and one-year survivability. 10 The dependent variable was the functional result after one year (dichotomous variable: good, bad). The independent variables were age (dichotomous variable: years, > 75 years), pre-fracture mobility (dichotomous variable: independent, dependent), pre-fracture medical condition according to the ASA scale (dichotomous variable: 1 and 2, 3 and 4), treatment method (dichotomous variable: osteosynthesis or prosthesis) and level of function upon discharge (dichotomous variable: independent, dependent). The analysis was made using the SPSS program (Statistical package for social sciences, SPSS Inc.). The values p < 0.05 were regarded as statistically typical. Results Group A (osteosyntheis) comprised 52 patients. The average hospitalisation duration was days. The complications occurred in 11 patients (21 %): three suffered from pneumonia, two from stomach ulcer haemorrhage, two had a heart failure, one case of deep venous thrombosis with pulmonary embolus and three
4 I-6 Zdrav Vestn 2007; 76: SUPPL I 1,0 0,9 0,8 0,7 0,6 0,5 0,4 0,3 0,2 0,1 prosthesis / proteza osteosynthesis / osteosinteza 0, Months / Meseci Figure 1. Cumulative survivability of elderly patients with femoral neck fracture by treatment approach. Sl. 1. Kumulativno preživetje starostnikov z zlomom vratu stegnenice glede na metodo zdravljenja. cases of complications in surgical wound were reported. Four patients (8 %) died at the hospital: two due to stomach ulcer haemorrhage, one due to heart failure and one due to respiration failure. All these patients who died were pre-surgically assessed as 3 or 4 according to the ASA. Upon the discharge from the hospital 18 patients (37.5 %) had a full walking ability. One year after the fracture 43 patients (89.6 %) were analysed. In 16 patients (33.5 %) fracture healing complications were reported (pseudoarthrosis, avascular necrosis of femoral neck). In 8 patients (16.7 %) a total endoprosthesis was used due to healing fracture complications. A good treatment outcome was reported in nineteen (44 %) elderly patients with femoral neck fracture whose fracture was managed with osteosynthesis. Group B (prostheses) comprised 81 patients. The average duration of hospitalisation was 17.8 days. Complications occurred in 14 patients (17.3 %): four cases of pneumonia, one heart failure and one respiration failure, one multiple organ failure, four deep venous thromboses with pulmonary embolus, and in one patient complications in surgical wound occurred. The dislocation of prosthesis occurred in two patients (2.5 %). The mortality rate at the hospital was 7.5 %. One patient died due to a pulmonary embolus, two due to respiration failure and one due to a multiple organ failure. All the patients who died, except one, were scored 4 prior to surgery according to the ASA. One year after the injury, 68 patients (89.5 %) were analysed. No re-operation interventions were required. A good treatment outcome was reported in 45 patients (66 %). A cumulative one-year survivability rate was 64.6 % in femoral neck fracture patients treated with osteosynthesis while in patients with prosthesis the rate was 75.7 % (Figure 1). The difference was not statistically typical (log rank test, p = 0.20). Table 1 shows the results of the multivariant analysis aimed at assessing the parameters impacting a good treatment outcome. The pre-fracture medical condition (3.88 odds ratio), treatment approach (0.33 odds ratio) and clinical rehabilitation efficiency (0.07 odds ratio) had a statistically significant impact on the functional one-year post-fracture result. Table 1. Impact on rehabilitation of elderly patients treated for dislocated femoral neck fractures after one year results of multivariant analysis. Razpr. 1. Vpliv na preživetje starostnikov, zdravljenih zaradi dislociranega zloma vratu stegnenice po enem letu rezultati multivariantne analize. (p) ratio confidence interval (p) ratio interval zaupanja Age Starost Medical condition ASA lestvica 1, Mobility Morbilnost Prosthesis Proteza Discharge Odpust Constant Konstanta Table 2 shows the results of the multivariant analysis aimed at assessing the parameters impacting a oneyear post-fracture survivability. The age of the patients (0.30 odds ratio) and hospital rehabilitation efficiency (2.89 odds ratio) had a significant statistical impact on the post-fracture survivability. Table 2. Impact on survivability of elderly patients treated for dislocated femoral neck fractures one year after the fracture results of multivariant analysis. Razpr. 2. Vpliv na preživetje starostnikov, zdravljenih zaradi dislociranega zloma vratu stegnenice po enem letu rezultati multivariantne analize. (p) ratio confidence interval (p) ratio interval zaupanja Age Starost 1,18 4,64 1 0,03 0,30 0,12 0,76 Medical condition ASA lestvica 0,35 1,64 1 0,20 0,71 0,45 1,10 Mobility Mobilnost 0,35 1,26 1 0,26 1,42 0,85 2,37 Prosthesis Proteza 0,29 1,52 1 0,22 1,33 0,90 1,96 Discharge Odpust 1,06 6,67 1 0,01 2,89 1,47 5,70 Constant Konstanta 1,94 10,08 1 0,0015
5 Brilej D, Komadina R, Vrabl M. Outcome in patients with femoral neck fractures depends on the treatment used I-7 Discussion The aim of the treatment of femoral neck fracture in elderly patients is early mobilisation and immediate weight bearing of surgically treated leg. This allows the patients an early return to their community. 2, 3 The surgeons who prefer osteosynthesis state the preservation of the joint as their main reason for the treatment choice. If the fracture is healed the function of the joint is the best. 11, 12 The fact that there is a significant rate of fracture healing disturbances (up to 35 % of pseudoarthroses and secondary necroses of femoral neck) and that a reoperation is required in 15 % of the cases is well supported in the literature. 2, 13, 14 By examining 3000 hip fracture elderly patients Palmer found a high level of morbidity and high reoperation expenses. 15 The advantage of femoral neck fracture care through cemented bipolar endoprosthesis lies in that an elderly patient can immediately apply full weight bearing on the leg and that there are few reoperations required (0.4 4 %). 7 The authors reported two cases of dislocation of prosthesis (2.5 %) and both were successfully treated without any additional surgical intervention on the hip. Given the high post-hip fracture mortality rate in elderly (up to 40 % during the post-fracture year) and the prosthesis life span of 12 to 15 years, the number of late surgical interventions is low. 2 Van Vugt compared 43 elderly with femoral neck fracture in a randomised study by the treatment method. Among the elderly treated with osteosynthesis or prosthesis no difference was reported in the mortality rate, complications at the hospital and the number of reoperations. 16 Conversely, in a study, comprising 367 femoral neck fracture patients 8 years post fracture, Hudson found a significant difference in the survivability rate, which was most obvious in the 65 to 80-year age group. 4 The results of the analysis conducted at the SUB Celje showed a better one-year survivability rate in elderly patients treated with prosthesis (11.1 % difference), though this difference was not statistically typical. During the hospital treatment there were no differences in the number of complications and the mortality rate of the patients. The age of the patients and rehabilitation efficiency had a statistically significant impact on one-year survivability, as proved by the findings 2, 17 of other authors. The goal of the elderly hip fracture rehabilitation is to achieve a functional independence. 2 Through a multivariant analysis the authors examined the parameters, which had an impact on functional independence after the first year post fracture. According to the authors, rehabilitation in the acute phase of the treatment is key to success. An elderly patient who manages to achieve foot-flat weight bearing by the end of the hospital treatment has 14.3 times better chances to regain full walking ability after one year and 2.86 times better survivability chances first year after the fracture than an elderly patient who stays in bed or needs additional assistance in walking. Koval found that the rehabilitation was more efficient in the first post-fracture months, as proved by the postoperative rehabilitation programme. 3, 17 High rehabilitation programme expenses raise doubts about their efficiency. Characteristics should be identified of the elderly patients who benefit most from intensive rehabilitation. 17 The use of a prosthesis allowed for a more successful rehabilitation of post femoral neck fracture in elderly patients. This is confirmed also by the views of numerous authors who support the primary care of femoral neck fractures in elderly with a cemented partial 2, 4, 7 endoprosthesis. This study proves that an intensive rehabilitation in the first months after the fracture is urgent for a successful treatment of elderly with femoral neck fracture. The use of a cemented partial endoprosthesis allows for an immediate verticalisation and weight bearing applied on the injured leg. There is no need for early second surgical interventions to interfere in the vulnerable early rehabilitation. The authors claim that a primary cemented bipolar prosthesis is the treatment choice for elderly with dislocated femoral neck fracture. References 1. Anon. Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Slovenia. Ljubljana: Statistični urad; Beck A, Ruter A. Schenkelhalsfrakturen Diagnostik und therapeutisches Vorgehen. Unfallchirurg 1998; 101: Koval KJ, Skovron ML, Aharonoff GB, Zuckerman JD. Predictors of functional recovery after hip fracture in the elderly. Clin Orthop 1998; 348: Hudson JI, Kenzora JE, Hebel JR, Gardner JF, Scherlis L, Epstein RS, Magaziner JS. Eight-year outcome associated with clinical options in the management of femoral neck fractures. Clin Orthop 1998; 348: Chua D, Jaglal SB, Schatzker J. An orthopedic surgeon survey on the treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures: opposing views. Canadian Journal of Surgery 1997;40: Swiontkowski MF. Intracapsular hip fractures. In: Browner BD, Jupiter JB, Levine AM, Trafton PG, eds. Skeletal trauma. Phyladelphia: Saunders; p McGann WA. Surgical approaches. In: Callaghan JJ, Rosenberg AG. Rubash HE, eds. The adult hip. Lipnicot Raven Publishers; Camporesi EM, Greeley WJ, Lumb PD, Watkins WD. Anesthesia. In: Sabiston DC, ed. Textbook of Surgery. Philadelphia: Saunders; p Mathews DE, Farewell VT. Using and understanding medical statistics. Basel: Krager; Glantz SA, Slinker BK. Primer of applied regression and analysis of variance. New York: McGraw Hill; Berglund-Roden M, Swierstra BA, Wingstrand H, Thorngren K. Prospective comparison of hip fracture treatment. 856 cases followed for 4 months in The Netherlands and Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand 1994; 65: Robinson CM, Saran D, Annan IH. Intracapsular hip fractures. Results of management adopting a treatment protocol. Clin Orthop 1994; 302: Chua D, Jaglal SB, Schatzker J. Predictors of early failure of fixation in the treatment of displaced subcapital hip fractures. J Orthop Trauma 1998; 12: Elmerson S, Sjostedt A, Zetterberg C. Fixation of femoral neck fracture. A randomized 2 year follow-up study of hook pins and sliding screw plate in 222 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 1995; 66: Palmer SJ, Parker MJ, Hollingworth W. The cost and implications of reoperation after surgery for fracture of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg 2000; 82A: 864.
6 I-8 Zdrav Vestn 2007; 76: SUPPL I 16. Van Vugt AB, Oosterwijk WM, Goris RJ. Osteosynthesis versus endoprosthesis in the treatment of unstable intracapsular hip fractures in the elderly. A randomised clinical trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1993; 113: Michele JP, Hoffmeyer P, Klopfenstein C, Bruchez M. Prognosis and functional recovery 1 year after hip fracture: Typical patient profiles through cluster analysis. J Gerontol 2000; 55A: Arrived , accepted
Outcome after surgery for fracture of the hip in patients aged over 95 years
 Outcome after surgery for fracture of the hip in patients aged over 95 years G. Holt, D. Macdonald, M. Fraser, A. T. Reece From Western Infirmary, Glasgow, Scotland Despite the increase in numbers of the
Outcome after surgery for fracture of the hip in patients aged over 95 years G. Holt, D. Macdonald, M. Fraser, A. T. Reece From Western Infirmary, Glasgow, Scotland Despite the increase in numbers of the
Effect of age, sex, co morbidities, delay in surgery and complications on outcome in elderly with proximal femur fractures
 2018; 4(3): 498-506 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 498-506 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 27-05-2018 Accepted: 28-06-2018 P Venu Gopala Reddy Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
2018; 4(3): 498-506 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 498-506 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 27-05-2018 Accepted: 28-06-2018 P Venu Gopala Reddy Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement
 Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2011 Vol 5 No 1 doi: /MOJ
 doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients
 Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Outcome of Replacement Hemi-arthroplasty by Non-Cemented Bipolar Prosthesis of Femoral Component of Hip
 Outcome of Replacement Hemi-arthroplasty by Non-Cemented Bipolar Prosthesis of Femoral Component of Hip *Hossain SN, 1 Hoque E, 2 Islam MM, 3 Rahman M, 4 Alam MS 5 Most femoral neck fractures are osteoporotic
Outcome of Replacement Hemi-arthroplasty by Non-Cemented Bipolar Prosthesis of Femoral Component of Hip *Hossain SN, 1 Hoque E, 2 Islam MM, 3 Rahman M, 4 Alam MS 5 Most femoral neck fractures are osteoporotic
Femoral Neck Fractures
 Femoral Neck Fractures Michael Monge, Harvard Medical School Agenda Epidemiology Normal anatomy of the femur Garden classifications Patients Summary 1 Epidemiology 1 250,000 yearly hip fractures in the
Femoral Neck Fractures Michael Monge, Harvard Medical School Agenda Epidemiology Normal anatomy of the femur Garden classifications Patients Summary 1 Epidemiology 1 250,000 yearly hip fractures in the
Failed internal fixation of femoral neck fractures
 Original article Failed internal fixation of femoral neck fractures 1343 7 Summary Background. There are two main types of surgical treatment for fractures of the femoral neck; internal fixation and arthroplasty.
Original article Failed internal fixation of femoral neck fractures 1343 7 Summary Background. There are two main types of surgical treatment for fractures of the femoral neck; internal fixation and arthroplasty.
DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP. Dr Károly Fekete
 DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP Dr Károly Fekete 1 OUTLINE Epidemiology Incidence Anatomy Patient s examination, clinical symptons Diagnosis Classification Management Special complications 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY,
DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP Dr Károly Fekete 1 OUTLINE Epidemiology Incidence Anatomy Patient s examination, clinical symptons Diagnosis Classification Management Special complications 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY,
Costs of internal fixation and arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomized study of 68 patients.
 Costs of internal fixation and arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomized study of 68 patients. Rogmark, Cecilia; Carlsson, Åke; Johnell, Olof; Sembo, Ingemar Published in: Acta Orthopaedica
Costs of internal fixation and arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomized study of 68 patients. Rogmark, Cecilia; Carlsson, Åke; Johnell, Olof; Sembo, Ingemar Published in: Acta Orthopaedica
Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
 M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
Femoral neck fractures in elderly, treated by hemiarthroplasty: AMIS vs. anterolateral and lateral surgical approaches
 Femoral neck fractures in elderly, treated by hemiarthroplasty: AMIS vs. anterolateral and lateral surgical approaches Matjaž Veselko, M.D., Ph.D. Miha Ambrožič Departement of Traumatology University Medical
Femoral neck fractures in elderly, treated by hemiarthroplasty: AMIS vs. anterolateral and lateral surgical approaches Matjaž Veselko, M.D., Ph.D. Miha Ambrožič Departement of Traumatology University Medical
AO Debate Controversies in Management
 46 AODIALOGUE 2 07 Jan Tidermark and Hans Törnqvist AO Debate Controversies in Management Case 1 A 72-year-old active lady (Fig 1). Sustained a displaced femoral neck fracture (Fig 2) after a simple fall.
46 AODIALOGUE 2 07 Jan Tidermark and Hans Törnqvist AO Debate Controversies in Management Case 1 A 72-year-old active lady (Fig 1). Sustained a displaced femoral neck fracture (Fig 2) after a simple fall.
Hip Fractures. Compliments of: Champlain Valley Orthopedics
 A Patient s Guide to Hip Fractures 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Hip Fractures 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
National Registration of Hip Fractures in Sweden
 Preface This is the 9th volume of the European Instructional Lectures, which contains more new material, which will be presented during the 1th EFORT Congress in Vienna by distinguished authors from across
Preface This is the 9th volume of the European Instructional Lectures, which contains more new material, which will be presented during the 1th EFORT Congress in Vienna by distinguished authors from across
The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures. Martyn Parker Peterborough UK
 The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures Martyn Parker Peterborough UK PETERBOROUGH HIP FRACTURE PROJECT Avoid delays to surgery Minimally invasive surgery by experienced staff Unrestricted
The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures Martyn Parker Peterborough UK PETERBOROUGH HIP FRACTURE PROJECT Avoid delays to surgery Minimally invasive surgery by experienced staff Unrestricted
Quality of life after primary hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fracture: 6-year follow-up of 185 patients
 Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 000-0 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://wwwtandfonlinecom/loi/iort9 Quality of life after primary hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fracture: -year follow-up
Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 000-0 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://wwwtandfonlinecom/loi/iort9 Quality of life after primary hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fracture: -year follow-up
FOUR OR TWELVE MONTHS FOLLOW-UP IN THE EVALUATION OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER HIP FRACTURE SURGERY?
 Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 94: 59 66, 2005 FOUR OR TWELVE MONTHS FOLLOW-UP IN THE EVALUATION OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER HIP FRACTURE SURGERY? T. Heikkinen, P. Jalovaara University of Oulu University
Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 94: 59 66, 2005 FOUR OR TWELVE MONTHS FOLLOW-UP IN THE EVALUATION OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER HIP FRACTURE SURGERY? T. Heikkinen, P. Jalovaara University of Oulu University
DISCLOSURE FNFX ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? 11/21/2016 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET
 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? GEORGE HAIDUKEWYCH, MD ORLANDO, FLORIDA DISCLOSURE ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET CONSULTING DEPUY, SYNTHES, BIOMET, RESPONSIVE ORTHOPEDICS STOCK OWNERSHIP ORTHOPEDIATRICS
FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? GEORGE HAIDUKEWYCH, MD ORLANDO, FLORIDA DISCLOSURE ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET CONSULTING DEPUY, SYNTHES, BIOMET, RESPONSIVE ORTHOPEDICS STOCK OWNERSHIP ORTHOPEDIATRICS
Outcome of undisplaced and moderately displaced femoral neck fractures
 498 Acta Orthopaedica 2007; 78 (4): 498 504 Outcome of undisplaced and moderately displaced femoral neck fractures A prospective study of 466 patients treated by internal fixation Kristian Bjørgul 1 and
498 Acta Orthopaedica 2007; 78 (4): 498 504 Outcome of undisplaced and moderately displaced femoral neck fractures A prospective study of 466 patients treated by internal fixation Kristian Bjørgul 1 and
Internal fixation of femoral neck fractures
 Acta Orthop Scand 55, 423-429, 1984 Internal fixation of femoral neck fractures Compression screw compared with nail plate fixation In a prospective, randomized study of femoral neck fracture operations,
Acta Orthop Scand 55, 423-429, 1984 Internal fixation of femoral neck fractures Compression screw compared with nail plate fixation In a prospective, randomized study of femoral neck fracture operations,
Femoral Neck Fractures- Gold standards and breaking news. Anna Ekman, MD, PhD Stockholm South hospital Sweden
 Femoral Neck Fractures- Gold standards and breaking news Anna Ekman, MD, PhD Stockholm South hospital Sweden Learning outcomes Learning Outcomes Epidemiology Preoperative planning Reduction techniques
Femoral Neck Fractures- Gold standards and breaking news Anna Ekman, MD, PhD Stockholm South hospital Sweden Learning outcomes Learning Outcomes Epidemiology Preoperative planning Reduction techniques
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 22/ Mar 16, 2015 Page 3785
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Hip Fractures. Anatomy. Causes. Symptoms
 Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study
 Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER. undisplaced, but as a consequence of the delay in diagnosis displacement occurred SUMMARY
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 23-27 Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER Peterborough District Hospital, SUMMARY Thorpe Road, Peterborough From a series of 825 consecutive admissions with a hip
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 23-27 Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER Peterborough District Hospital, SUMMARY Thorpe Road, Peterborough From a series of 825 consecutive admissions with a hip
Dislocation of total hip replacement in patients with fractures of the femoral neck
 184 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 184 189 Dislocation of total hip replacement in patients with fractures of the femoral neck A prospective cohort study of 713 consecutive hips Anders Enocson 1, Carl-Johan
184 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 184 189 Dislocation of total hip replacement in patients with fractures of the femoral neck A prospective cohort study of 713 consecutive hips Anders Enocson 1, Carl-Johan
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38039 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Embden, Daphne van Title: Facts and fiction in hip fracture treatment Issue Date:
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38039 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Embden, Daphne van Title: Facts and fiction in hip fracture treatment Issue Date:
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol.16, No.1, January, 2003
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol16, No1, January, 2003 : 351 ( )463-712 TEL: (031) 780-5270/5271 FAX : (031) 708-3578 E-mail: bskima@netsgocom 16,, ( > 20mm ) 5, ) 20 % 1 ), 6,, 3 8 8
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol16, No1, January, 2003 : 351 ( )463-712 TEL: (031) 780-5270/5271 FAX : (031) 708-3578 E-mail: bskima@netsgocom 16,, ( > 20mm ) 5, ) 20 % 1 ), 6,, 3 8 8
Management of Hip Fractures
 Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
ISSN: (Print) (Online) Journal homepage:
 Acta Orthopaedica ISSN: 1745-3674 (Print) 1745-3682 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort20 Primary arthroplasty is better than internal fixation of displaced femoral neck fractures:
Acta Orthopaedica ISSN: 1745-3674 (Print) 1745-3682 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort20 Primary arthroplasty is better than internal fixation of displaced femoral neck fractures:
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL FEMORAL FRACTURES IN THE ELDERLY: FIXATION VS HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL FEMORAL FRACTURES IN THE ELDERLY: FIXATION VS HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Sławomir Dudko, Damian Kusz, Karolina Godyń, Marcin Kusz Department
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL FEMORAL FRACTURES IN THE ELDERLY: FIXATION VS HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Sławomir Dudko, Damian Kusz, Karolina Godyń, Marcin Kusz Department
Cemented Thompson versus cemented bipolar prostheses for femoral neck fractures
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(2):166-71 Cemented Thompson versus cemented bipolar prostheses for femoral neck fractures Stefan Bauer, 1 Patrick Isenegger, 1 Oliver P Gautschi, 1 Kwok M Ho, 2 Piers
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(2):166-71 Cemented Thompson versus cemented bipolar prostheses for femoral neck fractures Stefan Bauer, 1 Patrick Isenegger, 1 Oliver P Gautschi, 1 Kwok M Ho, 2 Piers
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Unipolar, Bipolar or Total Hip Endoprosthesis after Femoral Neck Fracture: What is a Right Decision?
 Clinical Science Unipolar, Bipolar or Total Hip Endoprosthesis after Femoral Neck Fracture: What is a Right Decision? Dragica Smrke 1, Mirza Biščević 2 1 Department of Traumatology, Clinical Center- Ljubljana,
Clinical Science Unipolar, Bipolar or Total Hip Endoprosthesis after Femoral Neck Fracture: What is a Right Decision? Dragica Smrke 1, Mirza Biščević 2 1 Department of Traumatology, Clinical Center- Ljubljana,
Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation of Patients With Acute Hip Fracture
 An Original Study Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation of Patients With Acute Hip Fracture Jonathan Cluett, MD, Jill Caplan, MD, and Warren Yu, MD Abstract The goals of the present study were to assess if there
An Original Study Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation of Patients With Acute Hip Fracture Jonathan Cluett, MD, Jill Caplan, MD, and Warren Yu, MD Abstract The goals of the present study were to assess if there
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.49 Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.49 Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
Hip Fracture in the Elderly: Partial or Total Arthroplasty?
 3 Hip Fracture in the Elderly: Partial or Total Arthroplasty? Samo K. Fokter 1 and Nina Fokter 2 1 Celje General and Teaching Hospital 2 Maribor University Clinical Centre Slovenia 1. Introduction The
3 Hip Fracture in the Elderly: Partial or Total Arthroplasty? Samo K. Fokter 1 and Nina Fokter 2 1 Celje General and Teaching Hospital 2 Maribor University Clinical Centre Slovenia 1. Introduction The
Comparitive Study of Fracture Neck of Femur Treated With Total Hip Replacement and Hemiarthroplasty in Elderly (Above 60 Years)
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 18-23 www.iosrjournals.org Comparitive Study of Fracture Neck
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 18-23 www.iosrjournals.org Comparitive Study of Fracture Neck
Hip Fracture Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet
 riginator: Anne Flavall Professional Development Lead, Mr Marsh and Mr Quraishi Orthopaedic Consultant Surgeons Date: March 2012 Version: 2 Date for Review: March 2015 DGOH Ref No: DGOH/PIL/00611 Hip Fracture
riginator: Anne Flavall Professional Development Lead, Mr Marsh and Mr Quraishi Orthopaedic Consultant Surgeons Date: March 2012 Version: 2 Date for Review: March 2015 DGOH Ref No: DGOH/PIL/00611 Hip Fracture
Structural Differences Between Hip Endoprostheses, and Implications on a Hip Kinetics
 & Structural Differences Between Hip Endoprostheses, and Implications on a Hip Kinetics Mirza Biščević 1 *, Dragica Smrke 2 1. Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Clinical centre Sarajevo, Bolnička
& Structural Differences Between Hip Endoprostheses, and Implications on a Hip Kinetics Mirza Biščević 1 *, Dragica Smrke 2 1. Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Clinical centre Sarajevo, Bolnička
Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
More than half of hip fracture patients do not regain mobility in the first postoperative yearggi_
 bs_bs_banner Geriatr Gerontol Int 2013; 13: 334 341 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PRACTICE AND HEALTH More than half of hip fracture patients do not regain mobility in the first postoperative
bs_bs_banner Geriatr Gerontol Int 2013; 13: 334 341 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PRACTICE AND HEALTH More than half of hip fracture patients do not regain mobility in the first postoperative
Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric
 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (5): 493 498 493 Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures A cohort study with 5 11 year follow-up of 88 consecutive patients Anders
Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (5): 493 498 493 Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures A cohort study with 5 11 year follow-up of 88 consecutive patients Anders
Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture
 Patient Information Leaflet Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture Produced By: Orthopaedic Department September 2013 Review due September 2016 1 If you require this leaflet in another language, large print or another
Patient Information Leaflet Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture Produced By: Orthopaedic Department September 2013 Review due September 2016 1 If you require this leaflet in another language, large print or another
PRIMARY BIPOLAR ARTHROPLASTY IN TREATMENT OF UNSTABLE INTERTROCHANTERIC FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
 PRIMARY BIPOLAR ARTHROPLASTY IN TREATMENT OF UNSTABLE INTERTROCHANTERIC FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS *Ibrahim M., Shah Sachin and Kothadia Pradeep Department of Orthopaedics, KBNIMS, Gulbarga, Karnataka,
PRIMARY BIPOLAR ARTHROPLASTY IN TREATMENT OF UNSTABLE INTERTROCHANTERIC FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS *Ibrahim M., Shah Sachin and Kothadia Pradeep Department of Orthopaedics, KBNIMS, Gulbarga, Karnataka,
Geriatric Hip Fractures: Pearls for the Hospitalist. Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Speakers Bureau-Synthes
 Geriatric Hip Fractures: Pearls for the Hospitalist Jason W. Stoneback, MD Assistant Professor, Univ. of Colorado SOM Director, Orthopedic Trauma and Fracture Surgery Service Director, Orthopedic Inpatient
Geriatric Hip Fractures: Pearls for the Hospitalist Jason W. Stoneback, MD Assistant Professor, Univ. of Colorado SOM Director, Orthopedic Trauma and Fracture Surgery Service Director, Orthopedic Inpatient
Medial circumflex artery Lateral circumflex artery
 Femoral Head Fractures: A Critical But Frequently Missed Injury Susanna C. Spence MD Manickam Kumaravel MBBS University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Background Femoral head fractures: A complication
Femoral Head Fractures: A Critical But Frequently Missed Injury Susanna C. Spence MD Manickam Kumaravel MBBS University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Background Femoral head fractures: A complication
Arthroplasty versus internal fixation for femoral neck fractures in the elderly
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2011) 6:7 12 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0099-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Arthroplasty versus internal for femoral neck fractures in the elderly Vassilios Nicolaides Spyridon Galanakos Andreas
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2011) 6:7 12 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0099-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Arthroplasty versus internal for femoral neck fractures in the elderly Vassilios Nicolaides Spyridon Galanakos Andreas
Mr Maulik J Gandhi (ST6 T&O) Mr Jan Herman Kuiper Ms Swati Bhasin Mr David J Ford Mr Alastair Marsh Mr Sohail Quraishi
 The Dudley Grid: An evidence-based audit/research tool to investigate mortality risk following a displaced intracapsular hip fracture. How can it be applied in practice? Mr Maulik J Gandhi (ST6 T&O) Mr
The Dudley Grid: An evidence-based audit/research tool to investigate mortality risk following a displaced intracapsular hip fracture. How can it be applied in practice? Mr Maulik J Gandhi (ST6 T&O) Mr
Total Hip Replacement
 Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Accompanied to walk Yes No Accompanied to walk Yes No Side of Fracture
 Fracture Neck Of Femur / Fast Track Criteria: Admission where femoral neck fracture is the primary diagnosis Accident & Emergency Assessment (To be completed by A/E Nurse and/or A/E doctor) Patient label
Fracture Neck Of Femur / Fast Track Criteria: Admission where femoral neck fracture is the primary diagnosis Accident & Emergency Assessment (To be completed by A/E Nurse and/or A/E doctor) Patient label
Hardware Related Pain and Hardware Removal after Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Ankle Fractures
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Hardware Related Pain and Hardware Removal after Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Ankle Fractures
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Hardware Related Pain and Hardware Removal after Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Ankle Fractures
Treatment results of displaced femoral neck fractures
 505 Treatment results of displaced femoral neck fractures Clinic of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Kaunas University of Medicine, Lithuania Key words: femoral neck fractures, osteosynthesis, hemiarthroplasty,
505 Treatment results of displaced femoral neck fractures Clinic of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Kaunas University of Medicine, Lithuania Key words: femoral neck fractures, osteosynthesis, hemiarthroplasty,
Osteoporotic hip fractures Three-year followup mortality rate in Malta
 Osteoporotic hip fractures Three-year followup mortality rate in Malta Abstract Introduction: Primary osteoporosis is a major factor in fragility hip fractures. The index fracture is loaded with morbidity
Osteoporotic hip fractures Three-year followup mortality rate in Malta Abstract Introduction: Primary osteoporosis is a major factor in fragility hip fractures. The index fracture is loaded with morbidity
Review Article Comparison of hemiarthroplasty versus internal fixation in treatment of displaced femoral neck fracture: a meta-analysis
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):15017-15025 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0028677 Review Article Comparison of hemiarthroplasty versus internal fixation in treatment of displaced femoral neck fracture:
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):15017-15025 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0028677 Review Article Comparison of hemiarthroplasty versus internal fixation in treatment of displaced femoral neck fracture:
Outcome of Cloverleaf Locking Plate Fixation for Femoral Neck Fractures in Young Adults
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1203.010 Outcome of Cloverleaf Locking Plate Fixation for Femoral Neck Fractures in Young Adults Ismail HD, Ph.D, Phedy*, MD, Oktavian Irawadi Purba*, MD, Bambang Gunawan,
http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1203.010 Outcome of Cloverleaf Locking Plate Fixation for Femoral Neck Fractures in Young Adults Ismail HD, Ph.D, Phedy*, MD, Oktavian Irawadi Purba*, MD, Bambang Gunawan,
Original Article Intertrochanteric hip fracture surgery in Chinese: risk factors for predicting mortality
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(2):2789-2793 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003119 Original Article Intertrochanteric hip fracture surgery in Chinese: risk factors for predicting mortality Peng Zhao 1*,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(2):2789-2793 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003119 Original Article Intertrochanteric hip fracture surgery in Chinese: risk factors for predicting mortality Peng Zhao 1*,
Original Article Effects of Hardinge versus Moore approach on postoperative outcomes in elderly patients with hip fracture
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4425-4431 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015681 Original Article Effects of Hardinge versus Moore approach on postoperative outcomes in elderly patients with hip fracture
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4425-4431 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015681 Original Article Effects of Hardinge versus Moore approach on postoperative outcomes in elderly patients with hip fracture
Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur
 CASE REPORT Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur WI Faisham, M.Med{Ortho)*, W Zulmi, M.S{Ortho)*, B M Biswal, MBBS** 'Department of Orthopaedic, "Department of Oncology and Radiotherapy, School of
CASE REPORT Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur WI Faisham, M.Med{Ortho)*, W Zulmi, M.S{Ortho)*, B M Biswal, MBBS** 'Department of Orthopaedic, "Department of Oncology and Radiotherapy, School of
Misdiagnosis of occult hip fracture is more likely in patients with poor mobility and cognitive impairment
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 341-346 ORIGINAL STUDY Misdiagnosis of occult hip fracture is more likely in patients with poor mobility and cognitive impairment Munier HOSSAIN, Syed A. AKBAR, Glynne ANDREW
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 341-346 ORIGINAL STUDY Misdiagnosis of occult hip fracture is more likely in patients with poor mobility and cognitive impairment Munier HOSSAIN, Syed A. AKBAR, Glynne ANDREW
Traumatic injuries of knee and hip
 Traumatic injuries of knee and hip Martin W. Korn, MD The United States secretary of transportation recently announced that highway deaths had risen from the previously announced 56,000 for 1969 to a new
Traumatic injuries of knee and hip Martin W. Korn, MD The United States secretary of transportation recently announced that highway deaths had risen from the previously announced 56,000 for 1969 to a new
Damir FRANIC 1*, Ivan VERDENIK 2. Outpatient Clinic for Obstetrics and Gynecology, Celjska cesta 10, 3250 Rogaska Slatina, Slovenia 2
 Franic D, Verdenik I. Risk factors for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women from the point of view of primary care gynecologist. Zdr Varst. 2018;57(1):33-38. doi: 10.2478/sjph-2018-0005. RISK FACTORS FOR
Franic D, Verdenik I. Risk factors for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women from the point of view of primary care gynecologist. Zdr Varst. 2018;57(1):33-38. doi: 10.2478/sjph-2018-0005. RISK FACTORS FOR
Association of a Modified Frailty Index with Postoperative Outcomes after Ankle Fractures in Patients Aged 55 and Older
 Association of a Modified Frailty Index with Postoperative Outcomes after Ankle Fractures in Patients Aged 55 and Older Rishin J. Kadakia MD; Cathy Vu MD; Andrew Pao MD; Shay Tenenbaum MD, Jason T. Bariteau
Association of a Modified Frailty Index with Postoperative Outcomes after Ankle Fractures in Patients Aged 55 and Older Rishin J. Kadakia MD; Cathy Vu MD; Andrew Pao MD; Shay Tenenbaum MD, Jason T. Bariteau
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
Ankle fractures are one of
 Elevated Risks of Ankle Fracture Surgery in Patients With Diabetes Nelson F. SooHoo, MD, Lucie Krenek, MD, Michael Eagan, MD, and David S. Zingmond, MD, PhD Ankle fractures are one of the most common types
Elevated Risks of Ankle Fracture Surgery in Patients With Diabetes Nelson F. SooHoo, MD, Lucie Krenek, MD, Michael Eagan, MD, and David S. Zingmond, MD, PhD Ankle fractures are one of the most common types
Subcapital hip fracture surgery. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Subcapital hip fracture surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
Subcapital hip fracture surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
AMP HEMIARTHROPLASTY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF INTRACAPSULAR FRACTURE FEMUR- STILL RELEVANT IN PRESENT ERA
 Original Article AMP HEMIARTHROPLASTY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF INTRACAPSULAR FRACTURE FEMUR- STILL RELEVANT IN PRESENT ERA Sudhir Mahadeoprasad Shandilya A, Nageswara Rao V. A, Gandharva Pradeep A, Jaganmohan
Original Article AMP HEMIARTHROPLASTY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF INTRACAPSULAR FRACTURE FEMUR- STILL RELEVANT IN PRESENT ERA Sudhir Mahadeoprasad Shandilya A, Nageswara Rao V. A, Gandharva Pradeep A, Jaganmohan
Conversion total hip arthroplasty Functional outcome in Egyptian population
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 549-554 ORIGINAL STUDY Conversion total hip arthroplasty Functional outcome in Egyptian population Akram HAMMAD, Ahmed ABDEL-AAL From Mansoura and Assiut University Hospitals,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 549-554 ORIGINAL STUDY Conversion total hip arthroplasty Functional outcome in Egyptian population Akram HAMMAD, Ahmed ABDEL-AAL From Mansoura and Assiut University Hospitals,
Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 703850, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703850 Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head Mehmet Elmadag,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 703850, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703850 Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head Mehmet Elmadag,
Appendix E : Evidence table 9 Rehabilitation: Other Key Documents
 Appendix E : Evidence table 9 Rehabilitation: Other Key Documents 1. Cameron et al. Geriatric rehabilitation following following fractures in older people: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment
Appendix E : Evidence table 9 Rehabilitation: Other Key Documents 1. Cameron et al. Geriatric rehabilitation following following fractures in older people: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment
The Result of In Situ Pinning for Valgus Impacted Femoral Neck Fractures of Patients over 70 Years Old
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 26(4): 263-268, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.263 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 The Result of In Situ Pinning for Valgus Impacted Femoral Neck Fractures
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 26(4): 263-268, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.263 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 The Result of In Situ Pinning for Valgus Impacted Femoral Neck Fractures
Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study Mohammed KM Ali 1, Abid Hussain 1, CA Mbah 1, Alaa Mustafa 1,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study Mohammed KM Ali 1, Abid Hussain 1, CA Mbah 1, Alaa Mustafa 1,
CC Wu, WJ Chen Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 129 136 inimally displaced intra-capsular femoral neck fractures in the elderly comparison of multiple threaded pins and sliding compression screws surgical
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 129 136 inimally displaced intra-capsular femoral neck fractures in the elderly comparison of multiple threaded pins and sliding compression screws surgical
The Risks of Hip Fracture in Older People from Private Homes and Institutions
 Age and Ageing 1996:25:381-385 The Risks of Hip Fracture in Older People from Private Homes and Institutions MEG BUTLER, ROBYN NORTON, TREVOR LEE-JOE, ADA CHENG, A. JOHN CAMPBELL Summary This study aimed
Age and Ageing 1996:25:381-385 The Risks of Hip Fracture in Older People from Private Homes and Institutions MEG BUTLER, ROBYN NORTON, TREVOR LEE-JOE, ADA CHENG, A. JOHN CAMPBELL Summary This study aimed
HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY
 HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY HOW TO PREPARE FOR SURGERY AND REC0VERY Before surgery: Arrange for someone to help you around the house for a week or two after coming home from the hospital. Arrange for transportation
HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY HOW TO PREPARE FOR SURGERY AND REC0VERY Before surgery: Arrange for someone to help you around the house for a week or two after coming home from the hospital. Arrange for transportation
Effects of Older Age and Multiple Comorbidities on Functional Outcome After Partial Hip Replacement Surgery for Hip Fractures
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Older Age and Multiple Comorbidities on Functional Outcome After Partial Hip Replacement Surgery for Hip Fractures Lukman Shebubakar*, Errol Hutagalung**, Subroto Sapardan*,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Older Age and Multiple Comorbidities on Functional Outcome After Partial Hip Replacement Surgery for Hip Fractures Lukman Shebubakar*, Errol Hutagalung**, Subroto Sapardan*,
When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip
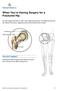 When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip The hip includes the head or ball of the thigh bone (femur). The thigh bone fits into the socket of the pelvis. Ligaments and muscles hold the joint in place.
When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip The hip includes the head or ball of the thigh bone (femur). The thigh bone fits into the socket of the pelvis. Ligaments and muscles hold the joint in place.
Learning Curve of Internal Fixation for Nondisplaced Femoral Neck Fractures: A Cumulative Sum Analysis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:9-13 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.9 Learning Curve of Internal Fixation for Nondisplaced Femoral Neck Fractures: A Cumulative Sum Analysis
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:9-13 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.9 Learning Curve of Internal Fixation for Nondisplaced Femoral Neck Fractures: A Cumulative Sum Analysis
Functional Recovery Following Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures Fixated with the Dynamic Hip Screw vs. the Percutaneous Compression Plate
 Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2005) 5, 221 229 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2005.29 Functional Recovery Following Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures Fixated with the Dynamic Hip Screw vs. the
Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2005) 5, 221 229 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2005.29 Functional Recovery Following Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures Fixated with the Dynamic Hip Screw vs. the
Progression of a Fracture Site Impaction as a Prognostic Indicator of Impacted Femoral Neck Fracture Treated with Multiple Pinning
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:66-71 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.1.66 Progression of a Fracture Site Impaction as a Prognostic Indicator of Impacted Femoral Neck Fracture
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:66-71 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.1.66 Progression of a Fracture Site Impaction as a Prognostic Indicator of Impacted Femoral Neck Fracture
Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw)
 Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a dynamic hip screw, sometimes also known as a sliding hip
Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a dynamic hip screw, sometimes also known as a sliding hip
Internal Fixation Compared with Arthroplasty for Displaced Fractures of the Femoral Neck A META-ANALYSIS
 1673 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Internal Fixation Compared with Arthroplasty for Displaced Fractures of the Femoral Neck A META-ANALYSIS BY MOHIT BHANDARI, MD,
1673 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Internal Fixation Compared with Arthroplasty for Displaced Fractures of the Femoral Neck A META-ANALYSIS BY MOHIT BHANDARI, MD,
Satisfaction analysis of Figure 8 (open heel) short leg cast
 Chan Kang, MD, PhD Dong-Hun Kang, MD Jae-Hwang Song, MD Min-Gu Jang, MD Ki-Jun Ahn, MD Ki-Soo, Lee, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine. Daejeon, Republic
Chan Kang, MD, PhD Dong-Hun Kang, MD Jae-Hwang Song, MD Min-Gu Jang, MD Ki-Jun Ahn, MD Ki-Soo, Lee, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine. Daejeon, Republic
Dr. Manojkumar HV, Dr. Hemanth HP, Dr. Ponnilavan Jayakanthan, Dr. Bhaskar Jyoti Pegu and Dr. Prathmesh MH
 2017; 3(3): 537-542 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 537-542 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 16-05-2017 Accepted: 17-06-2017 Dr. Manojkumar HV Professor Department of Dr. Hemanth HP Senior Resident,
2017; 3(3): 537-542 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 537-542 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 16-05-2017 Accepted: 17-06-2017 Dr. Manojkumar HV Professor Department of Dr. Hemanth HP Senior Resident,
Could Patient Undergwent Surgical Treatment for Periprosthetic Femoral Fracture after Hip Arthroplasty Return to Their Status before Trauma?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 28(2): 90-97, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.2.90 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Could Patient Undergwent Surgical Treatment for Periprosthetic Femoral
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 28(2): 90-97, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.2.90 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Could Patient Undergwent Surgical Treatment for Periprosthetic Femoral
Clinical Practice Guideline for Patients Requiring Total Hip Replacement
 Clinical Practice Guideline for Patients Requiring Total Hip Replacement Inclusions Patients undergoing elective total hip replacement Exclusions Patients with active local or systemic infection or medical
Clinical Practice Guideline for Patients Requiring Total Hip Replacement Inclusions Patients undergoing elective total hip replacement Exclusions Patients with active local or systemic infection or medical
The cost and consequences of proximal femoral fractures which require further surgery following initial fixation
 The cost and consequences of proximal femoral fractures which require further surgery following initial fixation C. Thakar, J. Alsousou, T. W. Hamilton, K. Willett From John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford,
The cost and consequences of proximal femoral fractures which require further surgery following initial fixation C. Thakar, J. Alsousou, T. W. Hamilton, K. Willett From John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford,
76 F: Plays tennis, lives independently, told she has weak bone
 Femoral Neck Fractures In the ELDERLY What to do, when and why Frank Liporace, MD Chairman & VP, Dept of Orthopaedics Chief of Trauma & Adult Reconstruction Jersey City Medical Center / RWJ Barnabas Health
Femoral Neck Fractures In the ELDERLY What to do, when and why Frank Liporace, MD Chairman & VP, Dept of Orthopaedics Chief of Trauma & Adult Reconstruction Jersey City Medical Center / RWJ Barnabas Health
E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus
 Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Displaced intra-capsular neck femur fractures in elderly: Austin Moore s prosthesis or Cemented Modular Bipolar Prosthesis
 Original Research Article Displaced intra-capsular neck femur fractures in elderly: Austin Moore s prosthesis or Cemented Modular Bipolar Prosthesis Bijith Balan 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3,
Original Research Article Displaced intra-capsular neck femur fractures in elderly: Austin Moore s prosthesis or Cemented Modular Bipolar Prosthesis Bijith Balan 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Hip Surgery and Mobility
 Orthopedic Nursing, Part 1 Hip Surgery and Mobility Nursing Best Practice Guidelines Clinical Indications for Hip Surgery Selected fractures of the hip Unremitting pain and irreversible damaged joint from
Orthopedic Nursing, Part 1 Hip Surgery and Mobility Nursing Best Practice Guidelines Clinical Indications for Hip Surgery Selected fractures of the hip Unremitting pain and irreversible damaged joint from
Short-term results of surgical treatment with cephalomedullary nails for basicervical proximal femoral fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 427-434 ORIGINAL STUDY Short-term results of surgical treatment with cephalomedullary nails for basicervical proximal femoral fractures Levent Tasyıkan, Ender Ugutmen, Selim
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 427-434 ORIGINAL STUDY Short-term results of surgical treatment with cephalomedullary nails for basicervical proximal femoral fractures Levent Tasyıkan, Ender Ugutmen, Selim
Chronic Lymphedema of the Lower Limb: A Rare Cause of Dislocation of Total Hip Arthroplasty
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.579 Chronic Lymphedema of the Lower Limb: A Rare Cause of Dislocation of Total Hip Arthroplasty Raju Vaishya 1, Amit Kumar Agarwal 1, Nishint Gupta 2, Vipul
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.579 Chronic Lymphedema of the Lower Limb: A Rare Cause of Dislocation of Total Hip Arthroplasty Raju Vaishya 1, Amit Kumar Agarwal 1, Nishint Gupta 2, Vipul
Effect of surgical approach on the early outcome of total hip replacement for femoral neck fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 23, 79, 667-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Effect of surgical approach on the early outcome of total hip replacement for femoral neck fractures Ahmed M. Mohamed, Daoud Makki, James Gibbs From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 23, 79, 667-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Effect of surgical approach on the early outcome of total hip replacement for femoral neck fractures Ahmed M. Mohamed, Daoud Makki, James Gibbs From the
Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of 20 Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of
A Patient s Guide to Stress Fractures of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Stress Fractures of the Hip Introduction Stress fractures of the hip once most commonly affected military personnel who marched and ran day after day. Today, stress fractures of the
A Patient s Guide to Stress Fractures of the Hip Introduction Stress fractures of the hip once most commonly affected military personnel who marched and ran day after day. Today, stress fractures of the
