Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
|
|
|
- Norman Short
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, Department of Radiology, V Medical Center, University of California San Diego, 3350 La Jolla Village Dr., San Diego, C ddress correspondence to C.. Chung. 2 Present address: Department of Radiology, askent University, Faculty of Medicine, nkara, Turkey. JR 2004;183: X/04/ merican Roentgen Ray Society Meniscal Tears: Role of xial MRI lone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes OJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to determine the reliability of standard axial MR images alone in the diagnosis of meniscal tears of the knee and in combination with other imaging planes. MTERILS ND METHODS. Sixty-two patients (55 men, seven women; age range, years) with a prior MRI examination who underwent arthroscopic surgery of the knee during a 1-year period were included in the study group. Images were independently reviewed for identification of meniscal tears by two musculoskeletal radiologists blinded to arthroscopic findings. Sequences for meniscal evaluation included axial fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density, coronal fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density, and sagittal fast spin-echo proton density with 4- to 5-mm slice thicknesses. Imaging groups for evaluation were axial, coronal, sagittal, axial and sagittal, axial and coronal, and coronal and sagittal. Observers reported a confidence level for the presence or absence of meniscal tear in all imaging groups based on a 5-point scale. Statistical analysis considered medial and lateral menisci separately. RESULTS. Forty patients had medial meniscal tears, and 16 had lateral meniscal tears at arthroscopy. For medial and lateral meniscal tears, the accuracy (79% and 71%, respectively) of imaging in the axial plane was comparable to other imaging groups but the mean confidence levels (2. and 3.00, respectively) were low. In one patient, the axial plane alone correctly showed that no tear was present. No statistically significant difference was observed between imaging plane groups of both menisci in the diagnosis of meniscal tears (p > 0.05). The axial plane increased the accuracy of sagittal and coronal planes of lateral meniscus when combined. CONCLUSION. In standard knee MRI examinations, the axial imaging plane may be valuable for the detection and characterization of meniscal tears. M RI is the preferred diagnostic method for evaluation of internal derangements of the knee. The suspicion of meniscal tear constitutes one of the leading indications for MRI examination of this articulation [1]. Imaging in the sagittal and coronal planes has been proven to be valuable in the MRI diagnosis of meniscal tears [2 4]. The use of the axial plane for meniscal evaluation has been investigated to a lesser degree but has been reported to be helpful in meniscal assessment, particularly with respect to characterization of tears [5 7]. No previous study has addressed the accuracy of the axial plane for the detection of meniscal disease. The aim of this study was to determine the value of standard axial MR images alone and in combination with other imaging planes in the diagnosis of meniscal tears of the knee. Materials and Methods fter approval from the investigational review board at our institution had been obtained, the medical records of all patients who had an MRI examination of the knee over a 14-month period were retrospectively reviewed to identify a subpopulation of patients who underwent arthroscopy. This review yielded 62 patients (55 men and seven women; age range, years; mean age, 46.8 years). The time interval between the MRI examination and arthroscopy ranged between 2 weeks and 16 months (mean, 20.8 weeks). MRI Protocol ll MRI examinations were performed with a 1.5-T unit (Signa, General Electric Medical Systems). Images were obtained using a dedicated knee coil. Three imaging sequences (one for each plane) from the standard knee imaging protocol were selected for this study and included axial fatsaturated fast spin-echo proton density (TR range/ JR:183, July
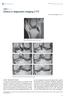
2 Tarhan et al. TE range, 2,650 2,717/12 54), coronal fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density (3,000 3,400/ 15 65), and sagittal spin-echo proton density (TR range/te, 2,117 2,367/30). Other imaging parameters included the following: number of excitations, 2; matrix, (axial and coronal) and (sagittal); and field of view, 160 units (axial) and 140 units (coronal and sagittal). The sequences were obtained with a 4-mm slice thickness in 43 patients and with a 5-mm slice thickness in 19 patients because it was a retrospective review. Imaging nalysis The imaging sequences were separated into six evaluation groups as follows: I, axial; II, coronal; III, sagittal; IV, axial and sagittal; V, axial and coronal; and VI, coronal and sagittal. To control bias associated with case recognition, we randomly distributed the studies within each group according to sequence, and interpretation sessions were separated by at least 1 day. Image groups were independently reviewed by two musculoskeletal radiologists with different levels of expertise (observer 1, 1 year 6 months of fellowship training; and observer 2, 4 years of experience as a musculoskeletal radiologist). Reviewers were blinded to arthroscopic findings. The data acquired were evaluated for the presence or absence of meniscal tear. Meniscal tears were characterized as increased signal intensity on MRI extending to the articular surface of the meniscus or abnormal morphology, or both [1]. Observers were requested to determine the confidence level for the di- agnosis of meniscal tear in all image groups based on a 5-point scale: 1, completely uncertain of tear; 2, small likelihood of tear; 3, equivocal for tear; 4, probable tear; and 5, very certain of tear. similar 5-point scale was used for the diagnosis of no tear. Medial and lateral menisci were evaluated as separate interpretations. ll discordant results were reviewed by consensus. MRI findings were then compared with those of arthroscopy. MRI reports of all patients were also reviewed by a radiologist not involved in imaging interpretation, and other associated findings were evaluated. Findings recorded were ligamentous tears; osteoarthritic changes, including osteochondral defects and osseous abnormalities; and the presence or absence of meniscal cysts, intraarticular bodies, and joint effusion. Statistical nalysis Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for the detection of meniscal tears were calculated for each observer separately and for interpretations in consensus. Statistical analysis was performed with the McNemar test to interpret the differences in diagnosis between the six imaging groups. Mean confidence levels for every group of interpretation were calculated for all observers in consensus, and the difference between the confidence levels was analyzed by the Wilcoxon s signed rank test. Interobserver agreement for detection of meniscal tears for each plane group was calculated using kappa values. Kappa values were interpreted as follows: 0, poor; , slight; , fair; , moderate; , high; and , almost perfect. Results t arthroscopy, 40 medial menisci and 16 lateral menisci were diagnosed as torn. The first observer correctly diagnosed 27 of 40 medial meniscal and four of 16 lateral meniscal tears, and the second observer correctly diagnosed 32 of 40 medial meniscal and seven of 16 lateral meniscal tears using the axial plane alone (Figs. 1 and 2). In one patient with no tear of the lateral meniscus, presence of no tear was correctly diagnosed on the basis of the axial plane. The findings of all other plane groups were false-positive. In 16 patients, on the basis of the axial plane alone the presence or absence of tear of the menisci was correctly diagnosed, whereas false-positive or false-negative findings based on other plane groups were recorded. In 14 of these patients, the lateral meniscus was involved; and in two, the medial meniscus was involved. The tears that were most often diagnosed with the axial plane alone were radial or complex tears of the posterior horn. ll findings of sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy are summarized in Table 1 for each imaging group and for each observer. In the evaluation of the medial meniscus, the highest sensitivity (95%) was observed in imaging group VI (coronal and sagittal planes). Sensitivity in the axial plane (%) was Fig year-old man with radial tear of lateral meniscus., xial fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density weighted image (TR/TE, 2,717/54; slice thickness, 4 mm) of right knee shows well-defined linear increased intensity (arrow) in body of lateral meniscus starting from free edge., Coronal fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density weighted image (3,750/60; slice thickness, 4 mm) shows tear as vertical defect in body of lateral meniscus (arrow). 10 JR:183, July 2004
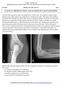
3 MRI of Meniscal Tears Fig year-old man with bucket-handle tear of medial meniscus., xial fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density weighted image (TR/TE, 2,717/54; slice thickness, 4 mm) of right knee reveals thinning and irregularity of medial meniscus body with bucket-handle component (arrows) extending from anterior to posterior., ucket-handle tear (arrow) is shown on coronal fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density weighted image (3,267/60; slice thickness, 4 mm). comparable to other imaging plane groups. Specificity was increased with group V (axial and coronal planes) when compared with group I (axial plane) and group III (coronal plane). Highest accuracy (92%) was obtained in group III (coronal plane) and group TLE 1 V (sagittal and coronal planes). ccuracy in the axial plane alone (79%) was comparable to that of other imaging plane groups. The axial plane when combined with other imaging planes did not result in a significant change in overall accuracy. In the evaluation of the lateral meniscus, highest sensitivities were found in group II (sagittal plane), group III (coronal plane), and group IV (axial and sagittal planes) (%). Sensitivity was lower (37.5%) in the axial plane when compared with the other MRI and rthroscopic Correlation for Each Observer First Observer Plane Second Observer In Consensus Group Sensitivity Specificity ccuracy Sensitivity Specificity ccuracy Sensitivity Specificity ccuracy Medial meniscus xial Sagittal Coronal xial and sagittal xial and coronal Coronal and sagittal I II III IV V VI Lateral meniscus xial Sagittal Coronal xial and sagittal xial and coronal Coronal and sagittal I II III IV V VI Note. ll numbers are percentages. p > JR:183, July
4 Tarhan et al. planes. Specificity was also increased in group V (axial and coronal planes) when compared with group I (axial plane) or with group III (coronal plane) for the lateral meniscus. The highest accuracy was observed in group III (coronal plane) and in group IV (axial and sagittal planes) (% and 94%, respectively). ccuracy in the axial plane alone for the lateral meniscal tears was also comparable to other imaging plane groups (71%). The axial plane when combined with other planes increased the accuracy of the sagittal plane for the first observer and the accuracy of the coronal plane for the second observer. Group IV (axial and sagittal planes) had the highest accuracy (94%) of any plane group with regard to consensus interpretation, including group VI (coronal and sagittal planes) (%). When diagnosis of meniscal tears was compared between the plane groups, no statistically significant difference was observed in assessment of the medial or lateral meniscus (p > 0.05). The mean confidence levels of each imaging group are summarized for both menisci in Table 2. The axial plane had the lowest mean confidence levels for both the medial and lateral menisci. These levels proved significantly lower for this imaging plane than all other imaging plane groups (p < 0.001). Group IV (axial and sagittal planes) had significantly higher mean confidence levels compared with group V (axial and coronal planes) and group III (coronal plane) for the TLE 2 second observer with regard to the lateral meniscus (p < 0.05). The kappa values are given in Table 3 for the assessment of both menisci. Interobserver agreement was high for the axial plane with regard to the medial meniscus (κ = 0.64) and moderate for the axial plane with regard to the lateral meniscus (κ = 0.41). The lowest kappa value was obtained for group III (coronal plane) with regard to the lateral meniscus (κ = 0.35, fair) and highest for group VI (sagittal and coronal planes) with regard to the medial meniscus (κ = 0., almost perfect). ssociated MRI findings that were identified included osteoarthritic changes (n = 39), anterior cruciate ligament tear (n = 12), medial collateral ligament tear (n = 5), posterior cruciate ligament tear (n = 1), patellar tendon rupture (n = 1), popliteus muscle injury (n = 1), semimembranosus tendon avulsion (n = 1), joint effusion (large, n = 10; small, n = 5), meniscal cyst (n = 5), intraarticular bodies (n = 5), and osteochondritis dissecans (n = 1). In three patients, either motion or metallic artifact was present leading to degradation of the MRI study. In 31 patients with erroneous interpretation of meniscal disease, osteoarthritic changes were noted (Fig. 3), including secondary osteoarthritis in one patient with osteochondritis dissecans. In nine of 12 patients with anterior cruciate ligament tears, meniscal disease was misinterpreted. In six of these patients, false-positive interpretation of a lateral meniscus tear was made (Fig. 4). Incorrect diagnosis Mean Confidence Levels of Each Plane for the First and Second Observers Plane Group First Observer Second Observer Medial meniscus xial I Sagittal II Coronal III xial and sagittal IV xial and coronal V Coronal and sagittal VI Lateral meniscus xial I Sagittal II Coronal III xial and sagittal IV xial and coronal V Coronal and sagittal VI Note. p < 0.01 for axial plane compared with other planes. occurred in four patients with variable amounts of joint effusion and in three patients with tendon injuries. In four patients who had only fraying of the lateral meniscus noted at arthroscopy, false-positive interpretations were rendered by both observers. In one patient with a small medial meniscal tear that was stable arthroscopically, both observers rendered falsenegative interpretations. Discussion In the evaluation of the menisci of the knee, MRI has been found to be highly accurate for the diagnosis of meniscal tears [1]. Many investigators have suggested that the sagittal imaging plane is the most useful for the detection of meniscal disease and that the coronal plane improves the overall diagnostic accuracy [2 4]. For most institutions, the axial fast spin-echo fat-saturated proton density sequence is the only technique used for evaluation in the axial plane [7]. There have been reports on thin-section axial 3D gradient-echo sequences in the evaluation of the menisci [5, 6]. These studies have shown that the extent and severity of meniscal tears were better delineated compared with coronal and sagittal images, especially when disease existed in the periphery of the meniscus. Small radial tears of the free edge and displaced fragments have also been reported to be better visualized in this plane [5, 6]. These sequences, however, are not routinely used in clinical practice, primarily related to con- TLE 3 Interobserver greement for Each Meniscus Plane Group κ Medial meniscus xial I 0.64 Sagittal II 0. Coronal III 0. xial and sagittal IV 0. xial and coronal V 0. Coronal and sagittal VI 0. Lateral meniscus xial I 0.41 Sagittal II 0.66 Coronal III 0.35 xial and sagittal IV 0.63 xial and coronal V 0.58 Coronal and sagittal VI JR:183, July 2004
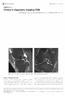
5 MRI of Meniscal Tears cerns regarding the study acquisition time. preliminary report [7] suggested that most of the different types of meniscal tears have discrete appearances in axial fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density images that provide additional information regarding lesion characterization. Their results, however, were not compared with those of arthroscopy. ccuracy for the diagnosis of meniscal tears with MRI has been studied by different authors, and several different sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy levels have been found [1, 8 10]. Sensitivity and specificity ranged between % and 97% and % and 91% for the medial meniscus and between C D Fig year-old man with osteoarthritis and chondromalacia with misinterpretation of axial images for lateral and medial menisci. and, Sequential axial fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density weighted images (TR/TE, 2,700/54; slice thickness, 4 mm) of right knee show medial and lateral menisci as intact. C, Coronal fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density weighted image (3,767/60; slice thickness, 4 mm) shows tear (arrow) of lateral meniscus as tapering and increased intensity. D, Sagittal spin-echo proton density weighted image (2,167/30; slice thickness, 4 mm) shows tear (arrow) on body of medial meniscus as vertical defect. JR:183, July
6 Tarhan et al. Fig year-old woman with anterior cruciate ligament tear with false-positive interpretation of lateral meniscus tear., xial fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density weighted image (TR/TE, 2,717/54; slice thickness, 4 mm) of right knee shows linear increased signal intensity (arrow) in anterior horn of lateral meniscus thought to be tear., Coronal fat-saturated fast spin-echo proton density weighted image (3,750/60; slice thickness, 4 mm) shows meniscus is intact. 69% and 92% and 91% and 98% for the lateral meniscus, respectively, in these previous studies [1, 8, 9]. Our findings were similar to the highest level of these ranges for both sensitivity and specificity. In these previous studies, only coronal and sagittal planes were used together with no consideration given to the value of the axial plane. Our study showed high accuracy levels for the detection of meniscal disease using the axial plane alone. Confidence levels, however, were low with regard to the assessment of both the medial and lateral menisci. In sagittal and coronal orientations, menisci are seen in almost 13 or 14 images, but in the axial plane with 4- to 5-mm slice thickness, they are seen only in two or three images. This is one potential reason for low confidence levels related to meniscal tears associated with assessment of the axial plane. We evaluated axial images that were characterized by a 4- to 5-mm slice thickness because such images are used in routine MRI protocols of the knee. lthough spatial resolution decreases with 5-mm-thick sections compared with thinner slices, signal-to-noise ratio increases and this may compensate, to some degree, for the lower spatial resolution. It has been shown that 5-mm-thick images 14 do not have lower diagnostic accuracy compared with that of thinner slices used for MRI studies of the knee [2]. With respect to the diagnosis of meniscal tears in axial images, confidence intervals may also reflect a relative lack of experience of the observers. s previously mentioned, the sagittal and coronal images are generally relied on for the diagnosis of meniscal disease. ecause no statistically significant difference was evident in the diagnosis of meniscal tears when comparing the axial imaging plane alone and all other imaging groups, it can be postulated that the axial plane is also valuable in the evaluation of meniscal tears. Our observations indicate that the overall accuracy for the diagnosis of medial meniscus tear was not increased by the addition of the axial plane to other imaging planes. ccuracy and specificity were, however, improved by the addition of the axial plane to other imaging planes for the lateral meniscus. The highest accuracy was observed in group IV (axial and sagittal planes) for assessment of the lateral meniscus, and mean confidence levels were significantly higher for this imaging group. Most of the true-positive and true-negative evaluations compared with other plane groups were found for the lateral meniscus. Therefore, the axial plane was especially helpful when interpreted with the sagittal plane in the evaluation of the lateral meniscus. We have found that most of the correctly diagnosed tears on the axial plane alone were radial or complex tears of the posterior horn. These findings will lead us to future studies of the accuracy of the characterization of meniscal tears with the addition of the standard axial plane to other planes. We believe that the low kappa values, particularly with regard to the lateral meniscus, may have been related to patient selection. Most of the patients who underwent arthroscopy had cartilage abnormalities and osteoarthritis (n = 39), which contributed to false-positive and false-negative evaluations when only one plane was used for assessment. We also had a significant number of patients with tears of the anterior cruciate ligament who had false-positive interpretations of meniscal disease. n anterior cruciate ligament tear is especially important in patients with false-positive diagnoses of lateral meniscal tears. Fraying and small stable tears of the menisci were also mistaken during our evaluation. In addition, a long interval (> 1 year) between MRI and arthroscopy JR:183, July 2004
7 MRI of Meniscal Tears in four patients may account for this finding as a result of interval healing or interval development of lesions or both. This study provided accuracy levels for the assessment of both meniscal tears in the axial plane alone and in combination with other imaging planes. The high levels of accuracy for detection of medial meniscal disease and increased levels of accuracy for detection of lateral meniscal disease with the addition of axial images shown in this study suggest that the axial imaging plane may prove helpful for the detection of meniscal tears in routine studies of the knee. References 1. Rubin D. MR imaging of the knee menisci. Radiol Clin North m 1997;35: Herman LJ, eltran J. Pitfalls in MR imaging of the knee. Radiology 1988;167: Tyrrell RL, Gluckert K, Pathria M, Modic MT. Fast three-dimensional MR imaging of the knee: comparison with arthroscopy. Radiology 1988;166: Reeder JD, Matz SO, ecker L, ndelman SM. MR imaging of the knee in the sagittal projection: comparison of three-dimensional gradient-echo and spin-echo sequences. JR 19;153: raki Y, Ootani F, Tsukaguchi I, et al. MR diagnosis of meniscal tears of the knee: value of axial three-dimensional Fourier transformation GRSS images. JR 1992;158: ubel S, Heyd RL, Thaete FL, Wozney P. MR knee imaging: axial 3DFT GRSS pulse sequence versus spin-echo imaging for detecting meniscal tears. Magn Reson Imaging 1992;10: Lee JHE, Singh TT, olton G. xial fat-saturated FSE imaging of the knee: appearance of meniscal tears. Skeletal Radiol 2002;31: Fischer SP, Fox JM, Del Pizzo W, Friedman MJ, Snyder SJ, Ferkel RD. ccuracy of diagnoses from magnetic resonance imaging of the knee: a multi-center analysis of one thousand and fourteen patients. J one Joint Surg m 1991;73: Crues JV, Mink J, Levy TL, Lotysch M, Stoller DW. Meniscal tears of the knee: accuracy of MR imaging. Radiology 19;164: oeve F, Davidson R, Staab EV. Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of knee injuries. South Med J 1991;: The full text and images from the merican Journal of Roentgenology may also be viewed online at or JR:183, July
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast Necessary?
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee
 Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Acute Injury of the Articular Cartilage and Subchondral Bone: A Common but Unrecognized Lesion in the Immature Knee
 Rachel S. Oeppen 1,2 Susan. Connolly 3 Jenny T. encardino 4 Diego Jaramillo 1 Received May 19, 2003; accepted after revision July 28, 2003. 1 Department of Pediatric Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital,
Rachel S. Oeppen 1,2 Susan. Connolly 3 Jenny T. encardino 4 Diego Jaramillo 1 Received May 19, 2003; accepted after revision July 28, 2003. 1 Department of Pediatric Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital,
Lesions of the Menisci of the Knee: Value of MR Imaging Criteria for Recognition of Unstable Lesions
 B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Diagnostic Accuracy of 0.2 Tesla Open MR Imaging Unit in Detecting Meniscal Tears: Correlation with Arthroscopy
 Original Article Diagnostic Accuracy of 0.2 Tesla Open MR Imaging Unit in Detecting Meniscal Tears: Correlation with Arthroscopy Mustafa Koplay 1, Elif Aksakallı 2, Serdar Toker 3, Seda Özbek 1, Ali Sami
Original Article Diagnostic Accuracy of 0.2 Tesla Open MR Imaging Unit in Detecting Meniscal Tears: Correlation with Arthroscopy Mustafa Koplay 1, Elif Aksakallı 2, Serdar Toker 3, Seda Özbek 1, Ali Sami
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma
 Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Original Research Article
 ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
MRI Characteristics of Healed and Unhealed Peripheral Vertical Meniscal Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kijowski et al. MRI of Peripheral Meniscal Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Richard Kijowski 1 Humberto G. Rosas 1 Kenneth S. Lee 1 rnold Cheung
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kijowski et al. MRI of Peripheral Meniscal Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Richard Kijowski 1 Humberto G. Rosas 1 Kenneth S. Lee 1 rnold Cheung
MRI of Acute Meniscal Injury Associated with Tibial Plateau Fractures: Prevalence, Type, and Location
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Mustonen et al. MRI of Meniscal Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research ntti O. T. Mustonen 1 Mika P. Koivikko 1 Jan Lindahl 2 Seppo K. Koskinen 1 Mustonen
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Mustonen et al. MRI of Meniscal Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research ntti O. T. Mustonen 1 Mika P. Koivikko 1 Jan Lindahl 2 Seppo K. Koskinen 1 Mustonen
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
Imaging of Articular Cartilage
 Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Key words: arthroscopy, orthopaedic examination, magnetic resonance imaging, knee injury.
 Original paper Videosurgery Arthroscopic verification of objectivity of the orthopaedic examination and magnetic resonance imaging in intra-articular knee injury. Retrospective study Julian Dutka, Michał
Original paper Videosurgery Arthroscopic verification of objectivity of the orthopaedic examination and magnetic resonance imaging in intra-articular knee injury. Retrospective study Julian Dutka, Michał
Elbow Effusions in Trauma in Adults and Children: Is There an Occult Fracture?
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 118 No 1209 ISSN 1175 8716 Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging for traumatic injury of the knee Keith Winters, Russell Tregonning Abstract Background: Magnetic
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 118 No 1209 ISSN 1175 8716 Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging for traumatic injury of the knee Keith Winters, Russell Tregonning Abstract Background: Magnetic
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Original Research Article. Atul Bucha 1, Sunita Dashottar 2 *, Surabhi Sharma 2, Preeth Pany 2, Rushabh Bhikhanhai Suthar 2
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy
 Open Access Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy Jamal Yaqoob 1, Muhammad Shahbaz Alam 2, Nadeem Khalid
Open Access Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy Jamal Yaqoob 1, Muhammad Shahbaz Alam 2, Nadeem Khalid
Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel
 ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
Available online at
 Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics
 Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Sonographic Detection of Baker s Cysts: Comparison with MR Imaging
 Eric E. Ward 1 Jon. Jacobson 2 David P. Fessell 2 Curtis W. Hayes 2 Marnix van Holsbeeck 1 Received June 20, 2000; accepted after revision ugust 14, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican
Eric E. Ward 1 Jon. Jacobson 2 David P. Fessell 2 Curtis W. Hayes 2 Marnix van Holsbeeck 1 Received June 20, 2000; accepted after revision ugust 14, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican
MRI of the Spine: Image Quality and Normal Neoplastic Bone Marrow Contrast at 3 T Versus 1.5 T
 Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Zhao et al. 3-T Versus 1.5-T MRI of the Spine Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research FOCUS ON: Jian Zhao 1,2 Roland Krug 1 Duan Xu 1 Ying Lu
Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Zhao et al. 3-T Versus 1.5-T MRI of the Spine Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research FOCUS ON: Jian Zhao 1,2 Roland Krug 1 Duan Xu 1 Ying Lu
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works
 UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
B one contusion is a finding substantiated by magnetic
 592 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The appearance of kissing contusion in the acutely injured knee in the athletes I P Terzidis, A G Christodoulou, A L Ploumis, S R Metsovitis, M Koimtzis, P Givissis... See end of article
592 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The appearance of kissing contusion in the acutely injured knee in the athletes I P Terzidis, A G Christodoulou, A L Ploumis, S R Metsovitis, M Koimtzis, P Givissis... See end of article
MRI of Cartilage. D. BENDAHAN (PhD)
 MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
How Much Tesla Is Too Much?
 How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping
 The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping Shinya Yamasaki, MD, PhD 1,2, Yusuke Hashimoto, MD, PhD 2, Takuya Kinoshita, MD 2, Kazuya Nishino,
The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping Shinya Yamasaki, MD, PhD 1,2, Yusuke Hashimoto, MD, PhD 2, Takuya Kinoshita, MD 2, Kazuya Nishino,
Imaging the Athlete s Knee. Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado
 Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
MENISCAL INJURY. Meniscus. Anterior Roots. Medial Meniscus. Lateral Meniscus. Posterior Roots. MRI and Arthroscopic Findings
 Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Original Report. Sonography of Tears of the Distal Biceps Tendon. Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. Adler 3
 Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. dler 3 Received October 15, 1999; accepted after revision March 21, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican Roentgen Ray Society, Washington, DC, May 2000.
Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. dler 3 Received October 15, 1999; accepted after revision March 21, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican Roentgen Ray Society, Washington, DC, May 2000.
Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears ABSTRACT
 1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 肌肉骨骼磁振造影. 本週課程內容 General Technical Considerations 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系
 本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Perspective
 Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective McMonagle et al. MRI of the PL Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective J. Scott McMonagle 1 lyde. Helms 1 William E. Garrett, Jr. 2 Emily N. Vinson 1 McMonagle
Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective McMonagle et al. MRI of the PL Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective J. Scott McMonagle 1 lyde. Helms 1 William E. Garrett, Jr. 2 Emily N. Vinson 1 McMonagle
The Meniscal Roots: Gross Anatomic Correlation with 3-T MRI Findings
 rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
MR Imaging of the Knee: Three-Dimensional Fourier Transform G RASS Technique 1
 심Journal of the Korean Radiological Society 1996: 34(4) : 543-549 MR Imaging of the Knee: Three-Dimensional Fourier Transform G RASS Technique 1 Oong Joo Kim, M.O., Young-uk Lee, M.O., Eun Kyung Youn,
심Journal of the Korean Radiological Society 1996: 34(4) : 543-549 MR Imaging of the Knee: Three-Dimensional Fourier Transform G RASS Technique 1 Oong Joo Kim, M.O., Young-uk Lee, M.O., Eun Kyung Youn,
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177)
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries
 MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Use of 3D SPCE Sequences for ssessment of nkle Syndesmosis Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Minchul Kim 1 Yun Sun Choi 1 Min Sun Jeong 1 Mira Park
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Use of 3D SPCE Sequences for ssessment of nkle Syndesmosis Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Minchul Kim 1 Yun Sun Choi 1 Min Sun Jeong 1 Mira Park
Frequency of Baker s Cysts in Cases of Meniscal Injury
 International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 4, Issue 1, January 2016, PP 10-14 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0365.0401003
International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 4, Issue 1, January 2016, PP 10-14 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0365.0401003
Knee dislocation in overweight patients. Peltola, Erno.
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Knee dislocation in overweight patients Peltola, Erno 2009 Peltola, E, Lindahl, J, Hietaranta, H & Koskinen, S K 2009, ' Knee dislocation in overweight patients ' merican Journal
https://helda.helsinki.fi Knee dislocation in overweight patients Peltola, Erno 2009 Peltola, E, Lindahl, J, Hietaranta, H & Koskinen, S K 2009, ' Knee dislocation in overweight patients ' merican Journal
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls
 Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Sensitivity of MR Arthrography in the Evaluation of Acetabular Labral Tears
 MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Ankle MRI for Anterolateral Soft Tissue Impingement: Increased Accuracy with the Use of Contrast-Enhanced Fat-Suppressed 3D-FSPGR MRI
 nkle MRI for nterolateral Soft Tissue Impingement: Increased ccuracy with the Use of Contrast-Enhanced Fat-Suppressed 3D-FSPGR MRI Hye Jung Choo, MD 2 Jin-Suck Suh, MD 1 Sung-Jun Kim, MD 1 Yong-Min Huh,
nkle MRI for nterolateral Soft Tissue Impingement: Increased ccuracy with the Use of Contrast-Enhanced Fat-Suppressed 3D-FSPGR MRI Hye Jung Choo, MD 2 Jin-Suck Suh, MD 1 Sung-Jun Kim, MD 1 Yong-Min Huh,
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears
 Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
A comparative study of MRI versus arthroscopic findings in ACL and meniscal injuries of the knee
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
Basic low - field MR imaging of meniscal injuries in children.
 Basic low - field MR imaging of meniscal injuries in children. Poster No.: C-2365 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Yakimov, M. Nikonova, E. Prokhorova, D. Vybornov,
Basic low - field MR imaging of meniscal injuries in children. Poster No.: C-2365 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Yakimov, M. Nikonova, E. Prokhorova, D. Vybornov,
Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions
 KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
High b Value Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Detecting Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Preliminary Results
 Diffusion-Weighted MRI to Detect Pancreatic denocarcinoma bdominal Imaging Original Research Tomoaki Ichikawa 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 2 Utarou Motosugi 1 Hironobu Sou 1 Hiroshi Iino 3 Tsutomu raki 1 Hideki
Diffusion-Weighted MRI to Detect Pancreatic denocarcinoma bdominal Imaging Original Research Tomoaki Ichikawa 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 2 Utarou Motosugi 1 Hironobu Sou 1 Hiroshi Iino 3 Tsutomu raki 1 Hideki
MRI Appearance of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations William Rodriguez, Jr. 1 Emily N. Vinson 1 Clyde. Helms 1 lison P. Toth 2 Rodriguez W Jr, Vinson EN, Helms C,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations William Rodriguez, Jr. 1 Emily N. Vinson 1 Clyde. Helms 1 lison P. Toth 2 Rodriguez W Jr, Vinson EN, Helms C,
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.84 Anatomical Differences Between T2 WI FSE
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.84 Anatomical Differences Between T2 WI FSE
MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and
 MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and Associated Knee Abnormalities 1 Hyang Mi Lee, M.D., Jae Chan Shim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim,
MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and Associated Knee Abnormalities 1 Hyang Mi Lee, M.D., Jae Chan Shim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim,
T HE clinical history and findings at physical examination in patients with abnormalities of the knee are known to be nonspecific in the determination
 Patrick A. Ruwe, MD #{149} James Wright, MD, MPH, FRCSC #{149}R. Lawr Randall, BA J. Kevin Lynch, MD #{149}Peter Joki, MD #{149}Shirley McCarthy, MD, PhD Can MR Imaging Effectively Replace Diagnostic Arthroscopy?
Patrick A. Ruwe, MD #{149} James Wright, MD, MPH, FRCSC #{149}R. Lawr Randall, BA J. Kevin Lynch, MD #{149}Peter Joki, MD #{149}Shirley McCarthy, MD, PhD Can MR Imaging Effectively Replace Diagnostic Arthroscopy?
Knee: Cruciate Ligaments
 72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations
 MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Necessity of MRI in Acute and Mild knee Problem
 SAUSSUREA (ISSN: 03732525) (2014)Volume 4(2):PP 15 Necessity of MRI in Acute and Mild knee Problem Ali Birjandinejad 1, Mohammad Taghi Peivandi 1, Amir Reza Kachooei 2, Amin Razi 3, Sara Amelfarzad 4,
SAUSSUREA (ISSN: 03732525) (2014)Volume 4(2):PP 15 Necessity of MRI in Acute and Mild knee Problem Ali Birjandinejad 1, Mohammad Taghi Peivandi 1, Amir Reza Kachooei 2, Amin Razi 3, Sara Amelfarzad 4,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/6/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 93 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/6/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 93 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
a - CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) CASE PRESENTATION
 !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a - - - Fig. 1 Sagittal
!Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a - - - Fig. 1 Sagittal
Rotator Cable: MRI Study of Its Appearance in the Intact Rotator Cuff With Anatomic and Histologic Correlation
 Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Sport Specific MRI. The symptoms of the majority, if not all sports injuries are experienced when upright, and weight-bearing
 Sport Specific MRI The symptoms of the majority, if not all sports injuries are experienced when upright, and weight-bearing A complete, accurate MRI assessment can only be made when in the position of
Sport Specific MRI The symptoms of the majority, if not all sports injuries are experienced when upright, and weight-bearing A complete, accurate MRI assessment can only be made when in the position of
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Laundre et al. MRI Detection of Meniscal Tears in Patients With CL Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research ryan J. Laundre 1 Mark S. Collins 1 Jeffrey
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Laundre et al. MRI Detection of Meniscal Tears in Patients With CL Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research ryan J. Laundre 1 Mark S. Collins 1 Jeffrey
Correlation between findings on stress X-rays (Telos) and MRI in patients with anterior knee instability
 Correlation between findings on stress X-rays (Telos) and MRI in patients with anterior knee instability Poster No.: C-1687 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit C. Prieto Santa Cruz 1,
Correlation between findings on stress X-rays (Telos) and MRI in patients with anterior knee instability Poster No.: C-1687 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit C. Prieto Santa Cruz 1,
Diagnostic Utility of MRI and MR Arthrography for Detection of Ligamentum Teres Tears: A Retrospective Analysis of 187 Patients With Hip Pain
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Datir et al. MRI and MR for Ligamentum Teres Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research bhijit Datir 1 Minzhi Xing 1 Jian Kang 2 Paul Harkey 1 parna Kakarala
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Datir et al. MRI and MR for Ligamentum Teres Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research bhijit Datir 1 Minzhi Xing 1 Jian Kang 2 Paul Harkey 1 parna Kakarala
n avulsion fracture of the head of the fibula has been described as an important
 Guo-Shu Huang 1 Joseph S. Yu 2 Muhammad Munshi 3 Wing P. Chan 4 Chian-Her Lee 5 Cheng-Yu Chen 1 Donald Resnick 3 Received December 6, 2001; accepted after revision July 30, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology,
Guo-Shu Huang 1 Joseph S. Yu 2 Muhammad Munshi 3 Wing P. Chan 4 Chian-Her Lee 5 Cheng-Yu Chen 1 Donald Resnick 3 Received December 6, 2001; accepted after revision July 30, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology,
MRI Findings of 26 Patients with
 MRI of Patients with Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Richard E. Scalf 1 Doris E. Wenger 1 Matthew. Frick 1 Jayawant N. Mandrekar 2 Mark C. dkins 1 Scalf RE, Wenger
MRI of Patients with Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Richard E. Scalf 1 Doris E. Wenger 1 Matthew. Frick 1 Jayawant N. Mandrekar 2 Mark C. dkins 1 Scalf RE, Wenger
Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging
 Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging cases. Hitachi Medical Systems America, Inc. 1959 Summit
Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging cases. Hitachi Medical Systems America, Inc. 1959 Summit
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN. David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging
 MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
Unlocking the locked Knee
 Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Recipient of the 2003 Sports Physical Therapy Section Excellence in Research Award
 Recipient of the 2003 Sports Physical Therapy Section Excellence in Research Award Clinical Diagnostic Accuracy and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Patients Referred by Physical Therapists, Orthopaedic Surgeons,
Recipient of the 2003 Sports Physical Therapy Section Excellence in Research Award Clinical Diagnostic Accuracy and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Patients Referred by Physical Therapists, Orthopaedic Surgeons,
Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review of Treatments
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
MRI of Osteochondral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle: Incidence and Pattern of Injury After Transient Lateral Dislocation of the Patella
 Sanders et al. MRI of Osteochond ral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:1332 1337 0361 803X/06/1875
Sanders et al. MRI of Osteochond ral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:1332 1337 0361 803X/06/1875
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, Davis
 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, Davis Lloyd W. Taylor Resident Award: Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI in SLAP Tears: A Retrospective Review of 444 Patients Utilizing Musculoskeletal
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, Davis Lloyd W. Taylor Resident Award: Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI in SLAP Tears: A Retrospective Review of 444 Patients Utilizing Musculoskeletal
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page 5490-5494 The Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Meniscal Injury Nada Sayed Mahdy*, Hossam Mousa Sakr, Allam Elsayed Allam Radiology
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page 5490-5494 The Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Meniscal Injury Nada Sayed Mahdy*, Hossam Mousa Sakr, Allam Elsayed Allam Radiology
