The Effect Of Metatarsal Padding On Pain And Functional. Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland 2
|
|
|
- Veronica McDowell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 683090SJS / Metatarsal paddingk. Männikkö, J. Sahlman research-article2017 Original Research Article SJS SCANDINAVIAN JOURNAL OF SURGERY The Effect Of Metatarsal Padding On Pain And Functional Ability In Metatarsalgia K. Männikkö 1,2, J. Sahlman 1 1 Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland 2 Department of Applied Physics, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland Abstract Background and Aims: Many kinds of insoles and pads are commonly used as a conservative treatment of metatarsalgia. However, earlier studies of insole treatment provide contradictory results, and the natural progression of metatarsalgia is still unknown. The aims of this study were to (1) determine whether simple custom-made metatarsal pad insoles reduce pain and improve functional ability, (2) find out patients satisfaction with padding treatment, and (3) investigate predisposing factors for metatarsalgia. Material and Methods: All metatarsalgia patients provided with metatarsal pad insoles during a 2-year period at Kuopio University Hospital (n = 45) were included in the study and observed at least a year. In all, 25 patients were interviewed about their situation before and after treatment. The Numeric Rating Scale for pain and American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society forefoot questionnaire included questions about predisposing factors, other diseases, exercise, work, shoes, and satisfaction with insoles. Foot X-rays taken from 45 patients during treatment were analyzed. Results: The mean age of the patients was 56 years (range years); 87% of them were women. In all, 47% of patients had osteoarthritic changes in the first metatarsophalangeal joint, and 42% had hallux valgus. In the interviewed subgroup (n = 25) body mass index was normal in 44%, and 36% were mildly overweight. High-heeled shoes were used by 40% daily, and 68% had done standing work for several years. Pain decreased significantly on the Numeric Rating Scale: 3.2 points in all patients (p < 0.001), 3.1 points among women, and 4.25 points among men. The American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society score improved 24.2 points in all patients (p < 0.001, range 0 100), among women 19 points, and among men 29 points. Conclusion: Metatarsalgia affects mostly women and is often preceded by extensive use of high heels and standing work. Also, a high association of first metatarsophalangeal Correspondence: Katri J. Männikkö, M.D. Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Kuopio University Hospital Puijonlaaksontie 2 PL Kuopio Finland katri.mannikko@fimnet.fi Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 2017, Vol. 106(4) The Finnish Surgical Society 2017 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav DOI: journals.sagepub.com/home/sjs
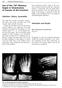
2 Metatarsal padding 333 arthrosis and hallux valgus was found. Metatarsal pads reduce pain and improve the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society score. We recommend metatarsal padding as a safe and inexpensive alternative in treating metatarsalgia patients. Key words: Metatarsalgia; horizontal arch; forefoot; insole; metatarsal pad; plantar pressure; gait Introduction Pain under the distal heads of the metatarsal bones, usually in the second and third rays, is called metatarsalgia (Fig. 1). Most of the pressure during the toe-off phase of the gait concentrates on this area (1, 2). Metatarsalgia is a quite common condition; it can restrict movement or even totally prevent walking. Metatarsalgia is often related to common foot malpositions such as hallux valgus, hammer toe and flat foot, or hypermobility of the first ray (2 4). In spite of associations with malpositionings, there are only a few x-ray measurements in the literature about anatomic characteristics of bony structures among metatarsalgia patients. Predisposing factors for metatarsalgia might also be rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes (2). In addition to increased pressure load, there can also be inflammation, neuropathy, or malpositioning of the fat pad under the forefoot (2). The natural progression of metatarsalgia is still unknown. Different kinds of insoles and metatarsal pads or toe orthoses are commonly used as a conservative treatment of metatarsalgia (1, 2, 5). Kang et al. (2) found out that metatarsal pads (Fig. 2) can diminish plantar pressure under painful metatarsal heads by spreading it to a larger area and by elevating the possibly fallen horizontal arch of the forefoot (2). It also seems that this arch elevation creates more space between metatarsal heads; this feature could play a role in pain reduction especially in Morton s neuralgy, where increased load on the forefoot causes interdigital nerve compression and irritation (6). Morton s neuralgia is quite common and is usually treated conservatively with metatarsal pads, corticoid injections, and physiotherapy. Interdigital neurinectomy could help in incalcitrant cases. The placement, size, and material of metatarsal pads are important (1, 2). Changes in pressure distribution caused by the pad correlate with pain reduction (2, 7, 8). However, the effects of conservative treatments vary considerably, including the use of insoles and pads. The aims of this study were to (1) determine whether simple custom-made metatarsal pad insoles reduce pain under the forefoot and improve functional ability, (2) find out patients satisfaction with padding treatment, and (3) investigate predisposing factors for metatarsalgia using a questionnaire and X-ray analysis for foot morphology and deformities. Our working hypotheses were as follows: 1. Metatarsal pad insoles relieve metatarsal overload pain (at least two points on the Numeric Rating Scale (NRS)) 2. Hallux valgus, high-heeled shoes, and standing work predispose for metatarsalgia. Fig. 1. Metatarsalgia is usually located under the distal parts of the second and third metatarsal bones. Fig. 2. The insole with metatarsal pad. Materials And Methods Participants And Selection All patients diagnosed with metatarsalgia and provided with metatarsal pad insoles during a 2-year period at Kuopio University Hospital were included in the study. The exclusion criteria were age under 18, incompetency, serious mental disorder, or failure to see a physician during treatment. Of 59, 14 were thus excluded. An invitation letter for a telephone interview was sent to the remaining 45, and 25 participated. X-rays and diagnoses from case histories were analyzed for all 45 patients. The subjects gave informed consent, and the study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Kuopio University Hospital. Treatment All patients selected were first evaluated by an orthopedic surgeon and then provided with metatarsal pad insoles by a cast technician in Kuopio University
3 334 K. Männikkö, J. Sahlman Hospital. The insoles were made by the cast technician by gluing a pad to a simple flat leather insole. The pads were made of 14-mm high foam rubber (Camp Scandinavia, Sweden), which was suitably cut (Fig. 2). The purpose of metatarsal padding is to elevate the horizontal arch of the forefoot. Patients visited the hospital every 2 weeks to have the pads and insoles changed because they wear out, and the right position may have to be reassessed. During these visits, patients were asked about pain relief; if the pads helped, custom-made foot orthoses including metatarsal pads were provided. The Interview Patients were interviewed by telephone, and during the interview, their symptoms before the insole treatment and at the time of the interview were asked. To evaluate pain and ability to function, the interviewer used the NRS and American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society (AOFAS) forefoot questionnaires (9). A decrease in two points or 33% on the NRS is clinically relevant (10). The interviewer also sought information about predisposing factors, other diseases, medications, exercise, former treatment, and satisfaction with metatarsal pad insoles. Patient s professions were divided into seven categories (11) based on the physical heaviness involved. X-Ray Observations During treatment, foot X-rays were taken from most patients as a part of normal treatment practice. These X-rays were analyzed to measure the length of the first and second metatarsal bones, intermetatarsal angle (IMA), hallux valgus angle (HVA), and Meary s angle. An experienced orthopedic surgeon analyzed these X-rays. Signs of increased stress on the second metatarsal were noted, and the level of arthrosis in the first to third metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints was evaluated using the Kellgren- Lawrence scale (8). Statistical Analysis All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 17.0 for Windows, IBM Corporation. The paired samples t-test was used to compare changes in NRS and AOFAS scores. The X-rays were measured using Sectra Workstation IDS7, version , Linköping, Sweden. Results Subject characteristics There were 45 patients, 25 of whom consented for an interview. Most of the patients were women: 86.7% of all and 84% of the interviewed subgroup. The average age of all our patients was 56 years (range years); it was 59 years (40 74 years) in the interviewed subgroup. In the interviewed subgroup, 44% were normal weight, and 36% were mildly overweight (body mass index (BMI) 25 30). Other Diseases Patients in the interviewed subgroup were requested for information about other health problems, and the case histories of all the patients were checked. The most common diseases were degenerative diseases, for example, sciatica, prolapsus disci, spinal stenosis (56%), and osteoarthrosis of major joints (44%). The prevalence of hypertension was 27%, that of hypothyreosis was 27%, and that of rheumatoid arthritis was 16%. Only 7% had osteoporosis, 11% had diabetes, and 4% had polyneuropathy. However, 24% had various shoulder problems, and 16% had various ligament and meniscus ruptures; 7% patients had scleroderma. Work, Exercise, And Shoes Of the interviewed subgroup, 52% were not working at the time of the interview. Most of them were retired because of age. Most (68% of all, 53% of females, 100% of males) had done standing work for 3 40 years during their working career; the average was 23. Aromaa and Koskinen (11) used a work heaviness classification divided into seven categories: 0 = never worked (0%), 1 2 = light or sitting work (24%), 3 4 = light standing and standing work (40%), and 5 6 = hard manual and really heavy work (36%). Most men were placed in categories 5 and 6 (75%). All the patients interviewed exercised in varying degrees. There were no competing athletes, but 64% exercised regularly, 24% sometimes, and 12% rarely. In all, 40% of our patients used or had used high-heeled shoes (heel over 2 cm) daily for many years. Those who could no longer wear them had to stop because of pain in the ball of the foot. Previous Treatment In all, 64% of the patients had used some kind of insole or other device in the shoes before attending our study: insoles with heel paddings, medial arch supports, and even metatarsal pads. Most of those were commercial and non-customized products. Some patients were unable to describe the insoles they had used. Of the patients, 16% had had physical therapy for metatarsalgia; 60% had had lower extremity or back operations before this study. Of those operations, 60% (36% of the patients interviewed) were in the forefoot area. The Effects Of Treatment Metatarsal pad insole use In all, 72% of the patients interviewed used their insoles all day long; 16% used them sometimes, and 8% had not used them at all. The average duration of insole use was 11.2 months (range 1 month to 3 years). Insole treatment was considered beneficial by 68% of our patients. Finally, 56% of the patients got individually made custom orthoses. Only 52% would start the insole treatment again if they got metatarsalgia a second time, 20% were unsure, and 28% would not. Those who refused to start again
4 Metatarsal padding 335 either had had an operation and been healed or wanted to have more effective insoles or deemed insole use too laborious. After treatment for at least 1 year, 48% were still using insoles because those devices relieved pain. Patients who had discontinued had obtained permanent help and had no need for insoles anymore (4%), had had an operation (20%), or had had some help but not enough (8%) or no help at all (20%). The reasons for quitting insole use were that the insoles caused pain (16%), insoles did not help (16%), a shoe did not fit anymore (8%), or the patient had had an operation (20%). Of our patients, 24% had had an operation, and one of them is still using insoles. The majority (83%) of the operated patients were diagnosed for Morton s neuralgy, and neurinectomy was performed. One Weil osteotomy was conducted to decrease metatarsal pressure. During insole treatment, among patients who had some pain, 76% of the whole group perceived no location change in lower limb pain and 84% in lower back pain. Simultaneous conservative treatments During insole treatment, most patients interviewed were advised to do forefoot muscle exercises and calf stretching. In all, 64% of them had done the former and 52% the latter. A few (12%) had also had physiotherapy. Change in pain and function Pain on the NRS was reduced in 84% of the patients, stayed the same in 8%, and increased in 8%. A clinically relevant reduction of at least two points on the NRS was evident in 72% of the patients. The pain decreased significantly: 3.2 points in all patients (average 2.8, p < 0.001), 3.1 points among women (n = 21), and 4.25 points among men (n = 4). The AOFAS score increased in 88% of patients, stayed unchanged in 8%, and decreased in 4%. In all our patients, the total increase was 24.2 points (scale 0 100, p < 0.001): among women 19 points and among men 29 points (Table 1). In the AOFAS questionnaire, patients reported 12.9 points of improvement in pain (scale 0 40, p < 0.001), and 10.0 points of increase in function (0 45, p < 0.001). Metatarsal padding had no effect on patient-evaluated foot alignment scores. Activity limitations improved by 1.9 (0 10, p = 0.003), gait abnormalities by 2.4 (0 10, p = 0.001), and maximum walking distance by 3.5 (0 10, p = 0.001). There was no significant change in footwear requirement or walking surfaces (Table 2). X-ray findings Seven out of 45 patients had thickening of the second metatarsal. One patient s foot had a markedly short first metatarsal (Morton s foot) (12). The mean MT1 length was 60.6 mm, and the MT1/MT2 ratio The HVA was measured in 31 patients. When categorized according to the level of HVA (foot with wider angle chosen), 58% of the patients had normal HVA (<15 ), Table 1 Pain in NRS and AOFAS midfoot scale before and after insole treatment, n = 25. Before treatment NRS Mean Median Standard deviation Range AOFAS (total) Mean Median Standard deviation Range After treatment NRS: Numeric Ratind Scale; AOFAS: American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society. 10% had mild (15 20 ), 29% moderate (21 40 ), and 3% severe (>40 ) hallux valgus. The mean IMA was 11.1, and the mean Meary s angle was 3.2 (Table 3). The most arthrotic MTP joints were the first, then the second, followed by the third. Overall, 69.5% had arthritic changes in their first to third MTP joints. Discussion Specially made insoles and insoles with metatarsal pads are commonly used as in the treatment of metatarsalgia. However, reports of this conservative treatment are conflicting (1, 2, 7, 13). The position, size, and material of the pad may be important factors for the success of the treatment (1, 2). There is no standardized manner to determine the best position, size, and material of the pad, so the placing is still based on an approximation by the insole maker. This could be one reason for the varying results reported in studies. Metatarsalgia affects men infrequently; only 13% percent of our patients were men. Similar proportions have been found in previous studies (2, 14). The use of high-heeled shoes was quite common in our patients 40% had used heels higher than 2 cm most of their lives. Also, doing work standing was common our patients had been working mainly on their feet 23 years on average. All men in our study had done standing work, which might be the main cause for metatarsalgia in the male population. Their work was also categorized heavier than that of women. The difference in the level of arthrosis in the MTP joints would be an interesting issue too, but our study lacked enough foot X-rays of male patients to enable a discussion. Age and weight had no significant role in the development of metatarsalgia. In agreement with our working hypothesis, most patients treated with metatarsal pad insoles obtained pain relief. We found a decrease in two or more points on the NRS in 72% and an improvement on the AOFAS pain score in 71% (average 12.9 points, p < 0.001). The AOFAS score for function improved 10 points (p < 0.001), and the overall AOFAS score improved 24.2 points (p < 0.001). Patient satisfaction for the insole treatment was found to be quite good as 48% of the
5 336 K. Männikkö, J. Sahlman Table 2 AOFAS Midfoot Scale comparison after and before insole treatment, n = 25. Number of patients before treatment Number of patients after treatment Pain None 0 2 Mild, occasional 2 9 Moderate, daily 9 10 Severe, almost always present 13 3 Function No limitation, no support 2 12 no limitation of daily activities, limitation of recreational 8 4 activities, no support Limited daily and recreational activities, cane 14 8 Severe limitations of daily and recreational activities, walker, 1 1 crutches, wheelchair Footwear requirements Fashionable, conventional shoes, no insert required 2 2 Comfort footwear, shoe insert Modified shoes or brace 0 0 Maximum walking distance >1.2 km m 1.2 km m 800 m 7 4 <200 m 7 0 Walking surfaces No difficulty in any surface Some difficulty on uneven terrain, stairs, incliners, ladders 5 4 Severe difficulty on uneven terrain, stairs, incliners, ladders 9 4 Gait abnormality None, slight 8 15 Obvious 10 8 Marked 7 2 Alignment Good, plantigrade, foot, midfoot well aligned Fair, plantigrade foot, some degree of midfoot malalignment, no 7 9 symptoms Poor, nonplantigrade foot, severe malalignment, symptoms 5 2 AOFAS: American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society. Table 3 Bone lengths and angles. Mean Median Standard deviation Range MT1, length MT2, length Intermetatarsal angle Hallux valgus angle MTT angle to 13.7 MTT: metatarsotarsal angle (Meary angle). patients were still using insoles at the time of the interview, 4% have had permanent help (no need for insoles anymore), and 68% reported that insole treatment was beneficial. But only 52% would start the metatarsal pad insole treatment again. The compliance for this treatment was surprisingly low despite good results in pain relief. The patients felt insole treatment laborious, and perhaps it restricted choosing fashionable shoes too. In all, 42% of patients whose X-rays were analyzed had hallux valgus. This result supports earlier findings that hallux valgus is related to first ray instability and metatarsalgia (2 4). The MT1-MT2 ratio was 0.89 on average; the range was and the standard deviation Davitt et al. (15) reported an MT1-MT2 ratio of 0.77 in patients with midfoot arthrosis and 0.82 in the control group.
6 Metatarsal padding 337 Our patients did not have short first metatarsals as compared to the second metatarsals. The increased pressure under the painful second and third metatarsal heads in metatarsalgia patients is caused by increased mobility of the first ray. Gong et al. (16) found a positive correlation between metatarsal pain and IMA in patients with hallux valgus. In our study, 42% had hallux valgus and 52% IMA over 10. The incidence of first metatarsophalangeal (MTP1) joint arthrosis (Kellgren-Lawrence categories 1 4 (8)) was high in our patients (97.4%). This might be due to increased mechanical stress in the MTP joint line caused by instability and elevation of the first ray, which has been found to be common in metatarsalgia patients (3, 4, 17, 18). There are certain limitations in this study. First, the study is retrospective, so the patients might not have precisely remembered their pre-treatment symptoms. Not all patients had X-rays, and in some X-rays, the patients might not have been standing as the radiological documentation was sometimes vague. More than half of the patients interviewed had also had other conservative treatments: forefoot muscle exercises and calf stretching. Further research is needed to determine the optimal positioning of the metatarsal pad and how the pad affects the biomechanics of the foot, leg, and lower back. Another point of interest is why so many of these metatarsalgia patients had hypothyreosis (26.7% vs 3.3% in the Finnish population) and scleroderma (7%), which is a very rare disease. No correlation between metatarsalgia and hypothyreosis has been reported earlier. Hypothyroidism is known to cause arthralgias and arthritis of the small joints of the hands and feet (19). Scleroderma causes synovitis of the joints and joint contractures, which may explain metatarsalgia (20). Metatarsalgia affects mostly women (87%) and is often preceded by extensive use of high heels and standing work. Also, we found a high association of MTP1 arthrosis and hallux valgus with metatarsal pain. We recommend metatarsal padding as a safe and inexpensive alternative in treating metatarsalgia patients. Acknowledgements We owe a great deal to our cast technician Raimo Hoffren for pads and insoles and Dr Gerald Netto for doing a language check and correcting our English. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. Declaration Of Conflicting Interests The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Ethical Approval The subjects had given informed consent, and the study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Kuopio University Hospital. Funding A research grant from the Kuopio University Hospital was received to support this study. References 1. Hsi WL, Kang JH, Lee XX: Optimum position of metatarsal pad in metatarsalgia for pressure relief. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2005;84(7): Kang JH, Chen MD, Chen SC et al: Correlations between subjective treatment responses and plantar pressure parameters of metatarsal pad treatment in metatarsalgia patients: A prospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2006;7: Greisberg J, Sperber L, Prince DE: Mobility of the first ray in various foot disorders. Foot Ankle Int 2012;33(1): Morton DJ: Hypermobility of the first metatarsal bone: The interlinking factor between metatarsalgia and longitudinal arch strains. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1928;10(2): Maddali Bongi S, Del Rosso A, Mikhaylova S et al: A comparison of two podiatric protocols for metatarsalgia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2014;32(6): Koenraadt KL, Stolwijk NM, van den Wildenberg D et al: Effect of a metatarsal pad on the forefoot during gait. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2012;102(1): Hodge MC, Bach TM, Carter GM: Orthotic management of plantar pressure and pain in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Biomech 1999;14(8): Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS: Radiological assessment of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 1957;16(4): Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS et al: Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int 1994;15(7): Salaffi F, Stancati A, Silvestri CA et al: Minimal clinically important changes in chronic musculoskeletal pain intensity measured on a numerical rating scale. Eur J Pain 2004;8(4): Aromaa A, Koskinen S: Health and Functional Capacity in Finland: Baseline Results of the Health 2000 Health Examination Survey. National Public Health Institutes, Helsinki, Morton DJ: Metatarsus atavicus. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1927;9(3): Postema K, Burm PE, Zande ME et al: Primary metatarsalgia: The influence of a custom moulded insole and a rockerbar on plantar pressure. Prosthet Orthot Int 1998;22(1): Bhutta MA, Chauhan D, Zubairy AI et al: Second metatarsophalangeal joint instability and second metatarsal length association depends on the method of measurement. Foot Ankle Int 2010;31(6): Davitt JS, Kadel N, Sangeorzan BJ et al: An association between functional second metatarsal length and midfoot arthrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005;87(4): Gong H, Sang ZC, Wen JM et al: Correlative analysis on metatarsalgia and the X-ray measurement indexes under weightbearing and non-weight-bearing of hallux valgus. Zhongguo Gu Shang 2014;27(4): Lee KT, Young K: Measurement of first-ray mobility in normal vs. hallux valgus patients. Foot Ankle Int 2001;22(12): Van Beek C, Greisberg J: Mobility of the first ray: Review article. Foot Ankle Int 2011;32(9): McLean RM, Podell DN: Bone and joint manifestations of hypothyroidism. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1995;24(4): Avouac J, Walker U, Tyndall A et al: Characteristics of joint involvement and relationships with systemic inflammation in systemic sclerosis: Results from the EULAR Scleroderma Trial and Research Group (EUSTAR) database. J Rheumatol 2010;37(7): Received: April 12, 2015 Accepted: November 6, 2016
BUCKS MSK: FOOT AND ANKLE PATHWAY GP MANAGEMENT. Hallux Valgus. Assessment: Early Management. (must be attempted prior to any referral to imsk):
 Hallux Valgus Common condition: affecting around 28% of the adult population. Prevalence increases with age and in females. Observation: Lateral deviation of the great toe. May cause secondary irritation
Hallux Valgus Common condition: affecting around 28% of the adult population. Prevalence increases with age and in females. Observation: Lateral deviation of the great toe. May cause secondary irritation
17 OSTEOARTHRITIS. What is it?
 17 OSTEOARTHRITIS What is it? Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most dominant form of arthritis, affecting 13% of Canadian adults. In the foot, the most commonly affected sites for OA are the midfoot joints and
17 OSTEOARTHRITIS What is it? Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most dominant form of arthritis, affecting 13% of Canadian adults. In the foot, the most commonly affected sites for OA are the midfoot joints and
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months.
 Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
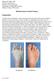
Bunions. A bunion is a painful bony bump that develops on the inside of the foot at the big toe joint. Bunions are often referred to as hallux valgus.
 Bunions A bunion is a painful bony bump that develops on the inside of the foot at the big toe joint. Bunions are often referred to as hallux valgus. Bunions develop slowly. Pressure on the big toe joint
Bunions A bunion is a painful bony bump that develops on the inside of the foot at the big toe joint. Bunions are often referred to as hallux valgus. Bunions develop slowly. Pressure on the big toe joint
6/5/2018. Forefoot Disorders. Highgate Private Hospital (Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust (Barnet & Chase Farm Hospitals) Hallux Rigidus
 Forefoot Disorders Mr Pinak Ray (MS, MCh(Orth), FRCS, FRCS(Tr&Orth)) Highgate Private Hospital (Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust (Barnet & Chase Farm Hospitals) E: ray.secretary@uk-conslutants Our
Forefoot Disorders Mr Pinak Ray (MS, MCh(Orth), FRCS, FRCS(Tr&Orth)) Highgate Private Hospital (Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust (Barnet & Chase Farm Hospitals) E: ray.secretary@uk-conslutants Our
Are you suffering from heel pain? We can help you!
 Are you suffering from heel pain? We can help you! STOP THE PAIN! Heel pain can be effectively combated with the proven Body Armor Night Splint. Heel spurs and heel pain Why? Heel pain is among the most
Are you suffering from heel pain? We can help you! STOP THE PAIN! Heel pain can be effectively combated with the proven Body Armor Night Splint. Heel spurs and heel pain Why? Heel pain is among the most
Your Orthotics service is changing
 Your Orthotics service is changing Important information for service users on changes effective from July 2015 Why is the service changing? As demand for the Orthotics service increases, Livewell Southwest
Your Orthotics service is changing Important information for service users on changes effective from July 2015 Why is the service changing? As demand for the Orthotics service increases, Livewell Southwest
Lesser toe deformities
 PATIENT INFORMATION Lesser toe deformities What are lesser toe deformities? Lesser toe deformities are caused by changes in normal anatomy that create an imbalance between the foot s muscle groups (intrinsic
PATIENT INFORMATION Lesser toe deformities What are lesser toe deformities? Lesser toe deformities are caused by changes in normal anatomy that create an imbalance between the foot s muscle groups (intrinsic
The electronic version of this article is the complete one and can be found online at:
 Correlations between subjective treatment responses and plantar pressure parameters of metatarsal pad treatment in metatarsalgia patients: a prospective study Jiunn-Horng Kang 1, Min-Der Chen 2, Shih-Ching
Correlations between subjective treatment responses and plantar pressure parameters of metatarsal pad treatment in metatarsalgia patients: a prospective study Jiunn-Horng Kang 1, Min-Der Chen 2, Shih-Ching
Orthopaedic (Ankles & Feet) Referral Guidelines
 Orthopaedic (Ankles & Feet) Referral Guidelines Austin Health Orthopaedic Clinic holds weekly multidisciplinary meetings to discuss and plan the treatment of patients with Orthopaedic and Fracture conditions.
Orthopaedic (Ankles & Feet) Referral Guidelines Austin Health Orthopaedic Clinic holds weekly multidisciplinary meetings to discuss and plan the treatment of patients with Orthopaedic and Fracture conditions.
ORTHOTIC ARCH SUPPORTS
 ORTHOTIC ARCH SUPPORTS COMMON FOOT PROBLEMS & ORTHOTIC THERAPY The foot and ankle are the foundation for the overall posture of the skeletal body. Many problems with the feet, legs, knees, hips and lower
ORTHOTIC ARCH SUPPORTS COMMON FOOT PROBLEMS & ORTHOTIC THERAPY The foot and ankle are the foundation for the overall posture of the skeletal body. Many problems with the feet, legs, knees, hips and lower
A Patient s Guide to Bunions. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Bunions Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Bunions Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Comparison of Postoperative Outcomes between Modified Mann Procedure and Modified Lapidus Procedure for Hallux Valgus
 Comparison of Postoperative Outcomes between Modified Mann Procedure and Modified Lapidus Procedure for Hallux Valgus Yui Akiyama, Takaaki Hirano, Hiroyuki Mitsui Shingo Maeda, Hisateru Niki Department
Comparison of Postoperative Outcomes between Modified Mann Procedure and Modified Lapidus Procedure for Hallux Valgus Yui Akiyama, Takaaki Hirano, Hiroyuki Mitsui Shingo Maeda, Hisateru Niki Department
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Long-term results of the Hohmann and Lapidus procedure for the correction of hallux valgus
 FOOT AND ANKLE Long-term results of the Hohmann and Lapidus procedure for the correction of hallux valgus F. W. M. Faber, P. M. van Kampen, M. W. Bloembergen From HAGA Hospital, Den Haag, the Netherlands
FOOT AND ANKLE Long-term results of the Hohmann and Lapidus procedure for the correction of hallux valgus F. W. M. Faber, P. M. van Kampen, M. W. Bloembergen From HAGA Hospital, Den Haag, the Netherlands
1. Orthoapedic Associates of Michigan, PC, Grand Rapids, MI 2. Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, Grand Rapids, MI
 Second Metatarsal Osteotomy Shortening with Tarsometatarsal Arthrodesis: Comparison of Outcomes Between MSP TM Metatarsal Shortening System and Plates and Screws Donald R. Bohay, MD, FACS 1 ; John G. Anderson,
Second Metatarsal Osteotomy Shortening with Tarsometatarsal Arthrodesis: Comparison of Outcomes Between MSP TM Metatarsal Shortening System and Plates and Screws Donald R. Bohay, MD, FACS 1 ; John G. Anderson,
Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe
 Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe A bunion (hallux valgus) is a deformity of the base joint of the big toe. The cause is not clear in many cases. The deformity may cause the foot to rub
Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe A bunion (hallux valgus) is a deformity of the base joint of the big toe. The cause is not clear in many cases. The deformity may cause the foot to rub
CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS
 CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS ABC s of Comprehensive Musculoskeletal Care December 1 st, 2007 Stephen Pinney MD Chief, UCSF Foot and Ankle Service Chronic problems typically occur gradually
CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS ABC s of Comprehensive Musculoskeletal Care December 1 st, 2007 Stephen Pinney MD Chief, UCSF Foot and Ankle Service Chronic problems typically occur gradually
Bunions. Compliments of: Institute of Sports Medicine & Orthopaedics
 A Patient s Guide to Bunions 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Bunions 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
WHAT IS ARTHRITIS OF THE BIG TOE (HALLUX RIGIDUS)?
 Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT IS ARTHRITIS OF THE BIG TOE (HALLUX RIGIDUS)? A common term for arthritis of the metatarsophalangeal
Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT IS ARTHRITIS OF THE BIG TOE (HALLUX RIGIDUS)? A common term for arthritis of the metatarsophalangeal
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery
 Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery Bunion surgery is generally reserved for bunions that are severe and impacting on function. There most frequent surgical procedure used involves a medial incision
Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery Bunion surgery is generally reserved for bunions that are severe and impacting on function. There most frequent surgical procedure used involves a medial incision
A Patient s Guide to Inter Digital Neuralgia (Morton s Neuroma)
 A Patient s Guide to Inter Digital Neuralgia (Morton s Neuroma) The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of two specialist
A Patient s Guide to Inter Digital Neuralgia (Morton s Neuroma) The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of two specialist
Bunionectomy-Forefoot Surgery
 Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Bunionectomy-Forefoot Surgery A bunion (also called hallux
Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Bunionectomy-Forefoot Surgery A bunion (also called hallux
WHAT IS THIS CONDITION? COMMON CAUSES:
 Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT IS THIS CONDITION? The posterior tibial tendon is an important structure that is normally
Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT IS THIS CONDITION? The posterior tibial tendon is an important structure that is normally
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS?
 WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain
 PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
Medincenter GlavUpDK by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia, Moscow.
 Medincenter GlavUpDK by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia, Moscow. Berezhnoy Sergey. Percutaneous First Metatarsocuneiform Joint Arthrodesis in a Treatment of Metatarsus Primus Varus: a Prospective
Medincenter GlavUpDK by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia, Moscow. Berezhnoy Sergey. Percutaneous First Metatarsocuneiform Joint Arthrodesis in a Treatment of Metatarsus Primus Varus: a Prospective
Case Report: Diabetic Foot
 Sergio Puigcerver (1) ; Juan Carlos González (1) ; Roser Part (1) ; Eduardo Brau (1) ; Ana León (2), Juan Ignacio Acosta (2) (1) Instituto de Biomecánica de Valencia, UPV. Valencia, Sapin; ibv@ibv.upv.es
Sergio Puigcerver (1) ; Juan Carlos González (1) ; Roser Part (1) ; Eduardo Brau (1) ; Ana León (2), Juan Ignacio Acosta (2) (1) Instituto de Biomecánica de Valencia, UPV. Valencia, Sapin; ibv@ibv.upv.es
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Common Foot Disorders Justin Wernick, DPM, C.Ped. NY College of Podiatric Medicine Orthopedic Department, New York, NY 2 Common
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Common Foot Disorders Justin Wernick, DPM, C.Ped. NY College of Podiatric Medicine Orthopedic Department, New York, NY 2 Common
Your Orthotics service is changing
 Your Orthotics service is changing Important for referrers on changes effective from January 2015 Why is the service changing? As demand for the orthotics service increases and budgets remain relatively
Your Orthotics service is changing Important for referrers on changes effective from January 2015 Why is the service changing? As demand for the orthotics service increases and budgets remain relatively
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Tips to Treat Bunion and avoid Surgery
 Tips to Treat Bunion and avoid Surgery DR JK i Important Legal Disclaimer Before beginning using any of our tips or our bunion relief products, consult your physician first to be sure it is appropriate
Tips to Treat Bunion and avoid Surgery DR JK i Important Legal Disclaimer Before beginning using any of our tips or our bunion relief products, consult your physician first to be sure it is appropriate
A patient s guide to. Inferior Heel Pain
 A patient s guide to Inferior Heel Pain The Foot & Ankle Unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital is made up of a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of four specialist orthopaedic foot and
A patient s guide to Inferior Heel Pain The Foot & Ankle Unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital is made up of a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of four specialist orthopaedic foot and
Surgical correction of Hallux Valgus
 Surgical correction of Hallux Valgus complicated with adult type Pes planus Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang-si, Korea * W Institute for Foot and Ankle Diseases
Surgical correction of Hallux Valgus complicated with adult type Pes planus Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang-si, Korea * W Institute for Foot and Ankle Diseases
Big toe (Hallux) corrective surgery Including Scarf, Weils, Akin/Chevron
 Big toe (Hallux) corrective surgery Including Scarf, Weils, Akin/Chevron Orthopaedic Department Patient information leaflet This patient information booklet is designed to provide you with information
Big toe (Hallux) corrective surgery Including Scarf, Weils, Akin/Chevron Orthopaedic Department Patient information leaflet This patient information booklet is designed to provide you with information
Bunion Surgery. This article provides information on surgery for bunions. For more general information: Bunions (topic.cfm? topic=a00155).
 Bunion Surgery This article provides information on surgery for bunions. For more general information: Bunions (topic.cfm? topic=a00155). Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments
Bunion Surgery This article provides information on surgery for bunions. For more general information: Bunions (topic.cfm? topic=a00155). Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments
Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment
 119 Pictorial Essay H............ - Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment David Karasick1 and Keith L. Wapner An estimated 40% of the American adult population experiences foot problems,
119 Pictorial Essay H............ - Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment David Karasick1 and Keith L. Wapner An estimated 40% of the American adult population experiences foot problems,
Degenerative knee disorders. Management of knee pain An Orthotists perspective
 Degenerative knee disorders Management of knee pain An Orthotists perspective Orthotists role Reduce pain Help to preserve the joint Delay surgery Allow continued activity -Exercise /walking -Recreation
Degenerative knee disorders Management of knee pain An Orthotists perspective Orthotists role Reduce pain Help to preserve the joint Delay surgery Allow continued activity -Exercise /walking -Recreation
PROstep Minimally Invasive Surgery HALLUX VALGUS CORRECTION USING PROSTEP MICA MINIMALLY INVASIVE FOOT SURGERY: TWO CASE STUDIES
 PROstep Minimally Invasive Surgery HALLUX VALGUS CORRECTION USING PROSTEP MICA MINIMALLY INVASIVE FOOT SURGERY: TWO CASE STUDIES AS PRESENTED BY: JOEL VERNOIS M.D. 016798A Case Study 1 PROstep Minimally
PROstep Minimally Invasive Surgery HALLUX VALGUS CORRECTION USING PROSTEP MICA MINIMALLY INVASIVE FOOT SURGERY: TWO CASE STUDIES AS PRESENTED BY: JOEL VERNOIS M.D. 016798A Case Study 1 PROstep Minimally
1. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2010;18:
 1. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2010;18: 474-485 1. it is frequently accompanied by deformity of the first and fiah rays as well as of the toes. 2. related to gait mechanics, foot anatomy, and foot and ankle
1. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2010;18: 474-485 1. it is frequently accompanied by deformity of the first and fiah rays as well as of the toes. 2. related to gait mechanics, foot anatomy, and foot and ankle
Weil Osteotomy. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Weil Osteotomy Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Following your consultation with a member of the Foot and Ankle team you have been diagnosed with metatarsalgia and advised to have a Weil osteomy.
Weil Osteotomy Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Following your consultation with a member of the Foot and Ankle team you have been diagnosed with metatarsalgia and advised to have a Weil osteomy.
Healthy feet. Everything you need to keep your feet in good condition. medi. I feel better.
 Healthy feet Everything you need to keep your feet in good condition. medi. I feel better. Outstanding performance for healthy feet On average, our feet are exposed to the stresses and strains of about
Healthy feet Everything you need to keep your feet in good condition. medi. I feel better. Outstanding performance for healthy feet On average, our feet are exposed to the stresses and strains of about
Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
BUNION (AND OTHER PAINFUL TOE CONDITION) SURGICAL TREATMENT POLICY PRIOR APPROVAL
 BUNION (AND OTHER PAINFUL TOE CONDITION) SURGICAL TREATMENT POLICY PRIOR APPROVAL Version: 1718.v3 Recommendation by: Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum (CCPF) Date Ratified: 12 July 2017
BUNION (AND OTHER PAINFUL TOE CONDITION) SURGICAL TREATMENT POLICY PRIOR APPROVAL Version: 1718.v3 Recommendation by: Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum (CCPF) Date Ratified: 12 July 2017
right Initial examination established that you have 'flat feet'. Additional information left Left foot is more supinated possibly due to LLD
 Motion analysis report for Feet In Focus at 25/01/2013 Personal data: Mathew Vaughan DEMO REPORT, 20 Churchill Way CF10 2DY Cardiff - United Kingdom Birthday: 03/01/1979 Telephone: 02920 644900 Email:
Motion analysis report for Feet In Focus at 25/01/2013 Personal data: Mathew Vaughan DEMO REPORT, 20 Churchill Way CF10 2DY Cardiff - United Kingdom Birthday: 03/01/1979 Telephone: 02920 644900 Email:
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Weil osteotomy for the treatment of metatarsalgia. Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery
 Weil osteotomy for the treatment of metatarsalgia Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is metatarsalgia? Metatarsalgia is a type of pain that occurs in the ball of the foot, also
Weil osteotomy for the treatment of metatarsalgia Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is metatarsalgia? Metatarsalgia is a type of pain that occurs in the ball of the foot, also
Common Foot and Ankle Pathology DOTS 17th April Nick Savva Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon. Monday, 29 April 13
 Common Foot and Ankle Pathology DOTS 17th April 2013 Nick Savva Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon Monday, 29 April 13 Topics Forefoot pain Hindfoot/Ankle pain Hallux rigidus Bunions Toe deformity Mortons
Common Foot and Ankle Pathology DOTS 17th April 2013 Nick Savva Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon Monday, 29 April 13 Topics Forefoot pain Hindfoot/Ankle pain Hallux rigidus Bunions Toe deformity Mortons
Financial Disclosure. Turf Toe
 Seth O Brien, CP, LP Financial Disclosure Mr. Seth O'Brien has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Turf Toe Common in athletes playing on firm, artificial turf Forceful
Seth O Brien, CP, LP Financial Disclosure Mr. Seth O'Brien has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Turf Toe Common in athletes playing on firm, artificial turf Forceful
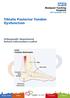
Designing a Prognostic Scoring System for Predicting the Outcomes of Proximal Fifth Metatarsal Fractures at 20 Weeks
 IJMS Vol 40, No 2, March 2015 Original Article Designing a Prognostic Scoring System for Predicting the Outcomes of Proximal Fifth Metatarsal Fractures at 20 Weeks Mohammad Ali Tahririan 1, MD; Amir Momeni
IJMS Vol 40, No 2, March 2015 Original Article Designing a Prognostic Scoring System for Predicting the Outcomes of Proximal Fifth Metatarsal Fractures at 20 Weeks Mohammad Ali Tahririan 1, MD; Amir Momeni
Diagnosing and treating hallux valgus: A conservative approach for a common problem
 REVIEW BRIAN G. DONLEY, MD Orthopaedic surgeon, Cleveland Clinic, specializing in foot and ankle disorders. CHRISTOPHER L. TISDEL, MD Orthopaedic surgeon. Cleveland Clinic. JAMES J. SFERRA, MD Orthopaedic
REVIEW BRIAN G. DONLEY, MD Orthopaedic surgeon, Cleveland Clinic, specializing in foot and ankle disorders. CHRISTOPHER L. TISDEL, MD Orthopaedic surgeon. Cleveland Clinic. JAMES J. SFERRA, MD Orthopaedic
Foot & Ankle Products with Clinical Data
 Foot & Ankle Products with Clinical Data Podalux post-op shoe Podalux Developers Dr Determe Toulouse Dr Cermolacci - Marseille Dr Coillard Lyon Dr Laffenetre - Bordeaux Podalux Indications Post-operative
Foot & Ankle Products with Clinical Data Podalux post-op shoe Podalux Developers Dr Determe Toulouse Dr Cermolacci - Marseille Dr Coillard Lyon Dr Laffenetre - Bordeaux Podalux Indications Post-operative
Injuries to the Foot. NOCROP Sports Medicine and Therapy
 Injuries to the Foot Arches of the Foot Plantar Fascia - a flat band of connective tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. It supports the arch of your foot. Muscle of the Foot and Lower Leg
Injuries to the Foot Arches of the Foot Plantar Fascia - a flat band of connective tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. It supports the arch of your foot. Muscle of the Foot and Lower Leg
Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief?
 Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief? Your Feet and Ankles are Workhorses They bear a lot of weight They perform various movements Common Conditions That Cause Foot/Ankle Pain Plantar
Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief? Your Feet and Ankles are Workhorses They bear a lot of weight They perform various movements Common Conditions That Cause Foot/Ankle Pain Plantar
Pedographic, clinical, and functional Outcome after Scarf Osteotomy Timo J. Lorei, MD Christian Kinast,
 Zentrum FuSS & Sprunggelenk Dr. Kinast Prof. Dr. Hamel Pedographic, clinical, and functional Outcome after Scarf Osteotomy Timo J. Lorei, MD Christian Kinast, MD Hans Klärner, MD and Dieter Rosenbaum,
Zentrum FuSS & Sprunggelenk Dr. Kinast Prof. Dr. Hamel Pedographic, clinical, and functional Outcome after Scarf Osteotomy Timo J. Lorei, MD Christian Kinast, MD Hans Klärner, MD and Dieter Rosenbaum,
Beyond the Rearfoot. Here are some modifications that your sports medicine patients will love. By Brant McCartan, DPM
 SPORTS PODIATRY Beyond the Rearfoot Here are some modifications that your sports medicine patients will love. By Brant McCartan, DPM This article is part of a sports medicine series written exclusively
SPORTS PODIATRY Beyond the Rearfoot Here are some modifications that your sports medicine patients will love. By Brant McCartan, DPM This article is part of a sports medicine series written exclusively
WHAT DO HALLUX VALGUS AND BUNION MEAN?
 Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT DO HALLUX VALGUS AND BUNION MEAN? Hallux is Latin for great toe and Valgus is Latin
Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT DO HALLUX VALGUS AND BUNION MEAN? Hallux is Latin for great toe and Valgus is Latin
Halux rigidus or arthritis of the big toe
 PATIENT INFORMATION Halux rigidus or arthritis of the big toe Hallux rigidus Metatarso-phalangeal joint What is Hallux rigidus? Hallux rigidus (Latin for a "stiff great toe") is a condition caused by arthritis
PATIENT INFORMATION Halux rigidus or arthritis of the big toe Hallux rigidus Metatarso-phalangeal joint What is Hallux rigidus? Hallux rigidus (Latin for a "stiff great toe") is a condition caused by arthritis
How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia
 220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
Appendix H: Description of Foot Deformities
 Appendix H: Description of Foot Deformities The following table provides the description for several foot deformities: hammer toe, claw toe, hallux deformity, pes planus, pes cavus and charcot arthropathy.
Appendix H: Description of Foot Deformities The following table provides the description for several foot deformities: hammer toe, claw toe, hallux deformity, pes planus, pes cavus and charcot arthropathy.
Plantar Fasciitis. Physiotherapy Department. Patient information leaflet
 Plantar Fasciitis Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet Name of patient: Date: Name of Physiotherapist: Telephone: 01483 464153 This leaflet has been designed to provide information about
Plantar Fasciitis Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet Name of patient: Date: Name of Physiotherapist: Telephone: 01483 464153 This leaflet has been designed to provide information about
PRESCRIPTION FOOTWEAR
 PRESCRIPTION FOOTWEAR Standards of Practice for Chiropodists and Podiatrists I. Introduction Prescription footwear is an integral part of patient care for the management of lower extremity pathology and
PRESCRIPTION FOOTWEAR Standards of Practice for Chiropodists and Podiatrists I. Introduction Prescription footwear is an integral part of patient care for the management of lower extremity pathology and
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION. At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral)
 PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
Lesser metatarsal cuneiform joint fusion for the treatment of midfoot osteoarthritis. Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery
 Lesser metatarsal cuneiform joint fusion for the treatment of midfoot osteoarthritis Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is midfoot osteoarthritis? Midfoot arthritis is 'wear
Lesser metatarsal cuneiform joint fusion for the treatment of midfoot osteoarthritis Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is midfoot osteoarthritis? Midfoot arthritis is 'wear
Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction. Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet What is Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction? The Tibialis Posterior Tendon (see diagram) is an important structure
Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet What is Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction? The Tibialis Posterior Tendon (see diagram) is an important structure
Anatomy 1% 29% 64% 6%
 Mortons Neuroma Perineural fibrosis of the plantar digital nerve Females 8-10 3 rd plantar webspace most commonly effected Burning pain Sensory changes 3&4 digits / interdigital space Etiology Excessive
Mortons Neuroma Perineural fibrosis of the plantar digital nerve Females 8-10 3 rd plantar webspace most commonly effected Burning pain Sensory changes 3&4 digits / interdigital space Etiology Excessive
Patient information. Forefoot surgery. Barts Health Physiotherapy Website:
 Patient information Forefoot surgery Barts Health Physiotherapy Website: www.bartshealth.nhs.uk/physiotherapy This booklet is for patients following surgery to the front of their foot. This may include
Patient information Forefoot surgery Barts Health Physiotherapy Website: www.bartshealth.nhs.uk/physiotherapy This booklet is for patients following surgery to the front of their foot. This may include
SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT
 C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
Excision of Morton s Neuroma
 Excision of Morton s Neuroma Day Surgery Unit Patient information leaflet This leaflet outlines the risks, general advice and information about foot surgery called an excision of a Morton s Neuroma. If
Excision of Morton s Neuroma Day Surgery Unit Patient information leaflet This leaflet outlines the risks, general advice and information about foot surgery called an excision of a Morton s Neuroma. If
Mid-Term Results of Triple Osteotomy in Hallux Valgus with Highly Increased Distal Metatarsal Articular Angle
 AOFAS Annual Meeting 2012 The Korean Foot & Ankle Society Mid-Term Results of Triple Osteotomy in Hallux Valgus with Highly Increased Distal Metatarsal Articular Angle Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Ki Won Young,
AOFAS Annual Meeting 2012 The Korean Foot & Ankle Society Mid-Term Results of Triple Osteotomy in Hallux Valgus with Highly Increased Distal Metatarsal Articular Angle Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Ki Won Young,
JUVENILE AND ADOLESCENT HALLUX VALGUS. George E. Quill, Jr., M.D.
 JUVENILE AND ADOLESCENT HALLUX VALGUS George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. The development of a hallux valgus deformity in children and adolescents is actually an uncommon entity. Most of these occurrences can be
JUVENILE AND ADOLESCENT HALLUX VALGUS George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. The development of a hallux valgus deformity in children and adolescents is actually an uncommon entity. Most of these occurrences can be
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
PATIENT INFORMATION Bunion Surgery - Metatarsal Osteotomy
 PATIENT INFORMATION Bunion Surgery - Metatarsal Osteotomy What is a bunion? (Hallux Valgus) A bunion, (Hallux Valgus) is a lump at the base of the big toe caused by sideways drifting and angulation of
PATIENT INFORMATION Bunion Surgery - Metatarsal Osteotomy What is a bunion? (Hallux Valgus) A bunion, (Hallux Valgus) is a lump at the base of the big toe caused by sideways drifting and angulation of
MEDIROYAL FUNCTIONAL INSOLES
 MEDIROYAL FUNCTIONAL INSOLES mediroyal.se MOW MEDIAL ORTHOTIC WEDGE Your feet are the foundation that the body rests on. They should be able to stand up to four times the body weight and excessive loading
MEDIROYAL FUNCTIONAL INSOLES mediroyal.se MOW MEDIAL ORTHOTIC WEDGE Your feet are the foundation that the body rests on. They should be able to stand up to four times the body weight and excessive loading
Combination of First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Arthrodesis and Proximal Correction for Severe Hallux Valgus Deformity
 FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2012.0400 Combination of First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Arthrodesis and Proximal Correction for Severe Hallux Valgus Deformity Pascal F. Rippstein, MD; Young-Uk
FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2012.0400 Combination of First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Arthrodesis and Proximal Correction for Severe Hallux Valgus Deformity Pascal F. Rippstein, MD; Young-Uk
!"#$%&'(")'$*)'&+"$,-./$
 !!"#%&'(")'*)'&+",-./! 0-1&2345&'"6666666666666666666666 5&'"-78(.'966666666:66666666:6666666666,(.4'!&/"66666666666666666666666666;(1111."4466666666666666666666666666666666?('2666666666666666666666@'&'"66666666A(B?-1"666666666666666
!!"#%&'(")'*)'&+",-./! 0-1&2345&'"6666666666666666666666 5&'"-78(.'966666666:66666666:6666666666,(.4'!&/"66666666666666666666666666;(1111."4466666666666666666666666666666666?('2666666666666666666666@'&'"66666666A(B?-1"666666666666666
NON-CONSTRAINED TITANIUM-POLYETHYLENE TOTAL ENDOPROSTHESIS IN THE TREATMENT OF HALLUX RIGIDUS A prospective clinical 2-year follow-up study
 Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 91: 202 207, 2002 NON-CONSTRAINED TITANIUM-POLYETHYLENE TOTAL ENDOPROSTHESIS IN THE TREATMENT OF HALLUX RIGIDUS A prospective clinical 2-year follow-up study P. Ess, M.
Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 91: 202 207, 2002 NON-CONSTRAINED TITANIUM-POLYETHYLENE TOTAL ENDOPROSTHESIS IN THE TREATMENT OF HALLUX RIGIDUS A prospective clinical 2-year follow-up study P. Ess, M.
FUNCTIONAL METATARSAL LENGTH IN PATIENTS WITH MIDFOOT ARTHRITIS
 FUNCTIONAL METATARSAL LENGTH IN PATIENTS WITH MIDFOOT ARTHRITIS Smita Rao, PT, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Physical Therapy New York University Judith F. Baumhauer Department of Orthopedics,
FUNCTIONAL METATARSAL LENGTH IN PATIENTS WITH MIDFOOT ARTHRITIS Smita Rao, PT, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Physical Therapy New York University Judith F. Baumhauer Department of Orthopedics,
Lapidus procedure and Akin osteotomy
 Lapidus procedure and Akin osteotomy Bunion surgery Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is a bunion? A bunion is a bony deformity of the joint at the base of the big toe (hallux).
Lapidus procedure and Akin osteotomy Bunion surgery Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is a bunion? A bunion is a bony deformity of the joint at the base of the big toe (hallux).
BIG TOE FUSION. Patient Information
 Patient Information BIG TOE FUSION This may have been caused by an old injury, previous surgery or a long-standing bunion deformity. Pain at the joint can start to affect your daily activities and even
Patient Information BIG TOE FUSION This may have been caused by an old injury, previous surgery or a long-standing bunion deformity. Pain at the joint can start to affect your daily activities and even
RECURRENT INTERMETATARSAL NEUROMA
 4 th Foot & Ankle Symposium RECURRENT INTERMETATARSAL NEUROMA Martin Berli, MD Department of Prosthetics and Orthotics Uniklinik Balgrist, Zurich martin.berli@balgrist.ch Recurrence: General Topics Pain
4 th Foot & Ankle Symposium RECURRENT INTERMETATARSAL NEUROMA Martin Berli, MD Department of Prosthetics and Orthotics Uniklinik Balgrist, Zurich martin.berli@balgrist.ch Recurrence: General Topics Pain
Localized collection of pus in a cavity
 Localized collection of pus in a cavity Loss of feeling or sensation induced to permit surgery Common example: Injection given to numb up the toe prior to performing an ingrown toenail procedure Mechanical
Localized collection of pus in a cavity Loss of feeling or sensation induced to permit surgery Common example: Injection given to numb up the toe prior to performing an ingrown toenail procedure Mechanical
Issue No 165: Dated 1st Feb 2018
 It s a bony bump that forms on the joint where your big toe meets your foot -- called the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint. It happens slowly over time, and eventually gets bigger and sticks out. It can
It s a bony bump that forms on the joint where your big toe meets your foot -- called the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint. It happens slowly over time, and eventually gets bigger and sticks out. It can
Information about. Common conditions affecting the big toe (bunion and arthritis)
 Information about Common conditions affecting the big toe (bunion and arthritis) 2 Statement of Use The information in this leaflet is intended solely for the person to whom it was given by the health
Information about Common conditions affecting the big toe (bunion and arthritis) 2 Statement of Use The information in this leaflet is intended solely for the person to whom it was given by the health
Lesser toe sequential repair
 Lesser toe sequential repair For the correction of lesser toe deformity Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is lesser toe deformity? The lesser toes are those other than your
Lesser toe sequential repair For the correction of lesser toe deformity Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is lesser toe deformity? The lesser toes are those other than your
AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery
 AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis 11-9-17 Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery Anatomy 3 bands of dense connective tissue, which originate
AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis 11-9-17 Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery Anatomy 3 bands of dense connective tissue, which originate
Case Report: Metatarsalgia (by first ray insufficiency)
 Sergio Puigcerver (1) ; Juan Carlos González (1) ; Roser Part (1) ; Eduardo Brau (1) ; Felip Salinas (2) (1) Instituto de Biomecánica de Valencia, UPV. Valencia, España; ibv@ibv.upv.es ; www.ibv.org (2)
Sergio Puigcerver (1) ; Juan Carlos González (1) ; Roser Part (1) ; Eduardo Brau (1) ; Felip Salinas (2) (1) Instituto de Biomecánica de Valencia, UPV. Valencia, España; ibv@ibv.upv.es ; www.ibv.org (2)
Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot. Glossary of Terms
 Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Warren Woods, Certified Orthotist, Health Sciences Centre, Rehabilitation Engineering Department What you need to know Glossary of Terms Neuropathic
Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Warren Woods, Certified Orthotist, Health Sciences Centre, Rehabilitation Engineering Department What you need to know Glossary of Terms Neuropathic
Geoffrey Watson, MD Matthew McKean, MD Siddhant K. Mehta, MD Thom A. Tarquinio, MD
 Geoffrey Watson, MD Matthew McKean, MD Siddhant K. Mehta, MD Thom A. Tarquinio, MD University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson, Mississippi American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society ANNUAL MEETING
Geoffrey Watson, MD Matthew McKean, MD Siddhant K. Mehta, MD Thom A. Tarquinio, MD University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson, Mississippi American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society ANNUAL MEETING
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Morton s Neuroma PATIENT INFORMATION. What is Morton s Neuroma?
 PATIENT INFORMATION Morton s Neuroma What is Morton s Neuroma? A Morton s neuroma is swelling and inflammation of a nerve that lies between two metatarsal bones of your foot. It causes pain in the ball
PATIENT INFORMATION Morton s Neuroma What is Morton s Neuroma? A Morton s neuroma is swelling and inflammation of a nerve that lies between two metatarsal bones of your foot. It causes pain in the ball
5 COMMON CONDITIONS IN THE FOOT & ANKLE
 5 COMMON CONDITIONS IN THE FOOT & ANKLE MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA IN A NUTSHELL ~ ALL ANATOMY & BIOMECHANICS >90% OF CONDITIONS IN FOOT & ANKLE DIAGNISED FROM GOOD
5 COMMON CONDITIONS IN THE FOOT & ANKLE MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA IN A NUTSHELL ~ ALL ANATOMY & BIOMECHANICS >90% OF CONDITIONS IN FOOT & ANKLE DIAGNISED FROM GOOD
Increased pressures at
 Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Silicoplant. Well-being for your feet
 Silicoplant Well-being for your feet EMO designs, develops and manufactures using innovation as the way to offer advanced products and help the patients and users that need our products, solve their problems.
Silicoplant Well-being for your feet EMO designs, develops and manufactures using innovation as the way to offer advanced products and help the patients and users that need our products, solve their problems.
Efficacy of a Kirschner-Wire Guide in Distal Linear Metatarsal Osteotomy for Correction of Hallux Valgus
 Efficacy of a Kirschner-Wire Guide in Distal Linear Metatarsal Osteotomy for Correction of Hallux Valgus Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka University Takefumi Nishino MD,
Efficacy of a Kirschner-Wire Guide in Distal Linear Metatarsal Osteotomy for Correction of Hallux Valgus Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka University Takefumi Nishino MD,
Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot
 168 Forefoot Reconstruction Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot Definition, History, Generalities This staple first provides a permanent compression both in the prongs
168 Forefoot Reconstruction Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot Definition, History, Generalities This staple first provides a permanent compression both in the prongs
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique. Description of Plate
 Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Long Oblique Distal Osteotomy of the Fifth Metatarsal for Correction of Tailor s Bunion: A Retrospective Review
 Long Oblique Distal Osteotomy of the Fifth Metatarsal for Correction of Tailor s Bunion: A Retrospective Review Barry P. London, DPM, 1 Stephen F. Stern, DPM, 2 Mark A. Quist, DPM, 3 Robert K. Lee, DPM,
Long Oblique Distal Osteotomy of the Fifth Metatarsal for Correction of Tailor s Bunion: A Retrospective Review Barry P. London, DPM, 1 Stephen F. Stern, DPM, 2 Mark A. Quist, DPM, 3 Robert K. Lee, DPM,
The Ludloff Osteotomy
 Techniques in Foot and Ankle Surgery 4(4):263 268, 2005 Ó 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia The Ludloff Osteotomy T E C H N I Q U E Hans-Jörg Trnka, MD, PhD and Stefan Hofstätter, MD Foot
Techniques in Foot and Ankle Surgery 4(4):263 268, 2005 Ó 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia The Ludloff Osteotomy T E C H N I Q U E Hans-Jörg Trnka, MD, PhD and Stefan Hofstätter, MD Foot
