Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
|
|
|
- Clinton Smith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies and bones. The Sternocleidomastoid muscle separates the posterior triangle from the anterior. Each of these is further divided into sub triangles. The Posterior triangle: There is one triangle on each side of the neck and each is bounded by: The Sternocleidomastoid The Trapezius and The middle third of the Clavicle. The Posterior triangle is divided by the Inferior belly of the Omohyoid muscle into: The Occipital triangle (bounded by the Sternocleidomastoid, Trapezius and Inferior belly of Omohyoid muscle) The Subclavian / Supraclavicular / Omoclavicular triangle (bounded by the Sternocleidomastoid, middle third of the Clavicle and the Inferior belly of Omohyoid). The Occipital triangle is larger than the Subclavian triangle The Anterior triangle: There is one triangle on each side of the neck and each is bounded by: The Sternocleidomastoid The Inferior border of the Mandible, and The Midline of the Neck. It is further subdivided into: The Digastric triangle, bounded by the anterior and posterior bellies of the Digastric muscle and the inferior border of the Mandible. The Submental triangle, bounded by the two anterior bellies of the Digastric muscles and the body of the Hyoid bone. The Carotid triangle bounded by the Sternocleidomastoid, the Posterior belly of the Digastric muscle, and the Superior belly of the Omohyoid muscle, and The Muscular triangle, which is bounded by the Sternocleidomastoid, Superior belly of the Omohyoid and the Midline of the Neck. 1 P age
2 The Posterior Triangle Boundaries: Anterior: Posterior border of Sternocleidomastoid muscle Posterior: Anterior border of Trapezius muscle Inferior (Base): Middle third of the Clavicle Roof: Investing layer of deep Cervical fascia. It encircles the neck, covers the posterior triangle, splits to envelop the Sternocleidomastoid and Trapezius and attaches to the clavicle. In the lower part, Platysma also forms part of the roof Floor: the floor is formed (from above downwards) by the Splenius capitis, Levator scapulae, Scalenus anterior, Scalenus Medius and Scalenus posterior muscles. These muscles are covered by the Prevertebral fascia CONTENTS OF THE POSTERIOR TRIANGLE: Cutaneous Nerves and Spinal part of Accessory Nerve The External Jugular Vein Brachial Plexus (Roots and Trunks) Inferior belly of Omohyoid muscle Lymph nodes Subclavian artery and vein, Suprascapular and transverse cervical arteries, Dorsal scapular artery and Occipital artery STRUCTURES DEEP TO THE STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID: The Carotid Sheath The Internal Jugular Vein THE CAROTID ARTERIES Sternocleidomastoid & Trapezius: These split from one sheet of embryonic muscle. Above, these two muscles have a continuous 2 P age
3 attachment extending from the mastoid process (behind the ear) to the inion (in the midline). Since this attachment is aponeurotic, it produces a ridge, the Superior Nuchal line. These two muscles separate as they descend below. Therefore, they have discontinuous attachment on the clavicle. A part of the sternocleidomastoid crosses the sternoclavicular joint. Spinal Part of the Accessory nerve: It is the nerve to sternocleidomastoid and Trapezius muscles and spans the gap between the two. Here it is quite superficial It divides the triangle into nearly two equal parts: The upper part is carefree part for there is no important structure to damage but below one must be very careful As it emerges from the jugular foramen (Accompanied with other nerves and vessels) it passes obliquely downwards and backwards from the transverse process of the atlas to the superior angle of the scapula. Along its course it burrows through the sternocleidomastoid a short distance below the mastoid process. Here lymph nodes surround it. It crosses the posterior triangle and disappears under cover of the trapezius, just above the clavicle. Sensory twigs from C2, C3 and C4 join it. Injury to this nerve in the posterior triangle results in a dropping of the shoulder downward and forward. In the posterior triangle there is an area about the size of a coin whose center is at the midpoint of the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. From here, the cutaneous nerves of the cervical plexus radiate. All of them leave the triangle in various directions. The lesser occipital (from cervical segment C2) parallels the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle after hooking around the 11 th nerve and ascends to the occipital region; The great auricular (C2 and C3) crosses the sternocleidomastoid obliquely toward the lobe of the ear; The anterior / transverse cutaneous (C2 and C3) 3 P age
4 leaves the triangle by crossing the sternocleidomastoid muscle transversely to reach the skin of the anterior triangle. The medial, intermediate, and lateral supraclavicular nerves stem from a trunk formed by anterior rami of C3 and C4 and supply the skin over the lower part of the posterior triangle. In addition, the medial and intermediate supraclaviculars cross the clavicle to supply the skin of the upper pectoral region. The lateral supraclavicular crosses the anterior border of the trapezius muscle superficial to the angle of the trapezius and clavicle to supply the skin over the shoulder tip. Inferior belly of Omohyoid Muscle: It passes about an inch above the clavicle to which it is bound by an inverted sling of fascia. It subdivides the posterior triangle into a smaller lower subclavian triangle and a larger upper occipital triangle. External Jugular vein: This large vein descends subcutaneously across the sternocleidomastoid and pierces the deep fascia to end in the subclavian vein. Its tributaries in the posterior triangle are the transverse cervical, suprascapular, and anterior jugular veins. The last communicate with each other. The Floor: The fibres of the muscles of the floor run obliquely downward and backward. Levator scapulae occupies a middle position. It lies deep to the accessory nerve and runs parallel to it. Above it lies the Splenius Capitis. Below it are the three Scalene muscles. Above the Splenius Capitis a small part of Semispinalis capitis can sometimes be seen. The muscular floor of the triangle is carpeted with a layer of fascia (The prevertebral fascia). This carpet covers the subclavian vessels and the roots of the brachial plexus and thus provides them with a covering (the Axillary sheath) as they enter the axilla. It also covers and guards the motor nerves to four important muscles (Levator scapulae, Rhomboids, Serratus anterior and Diaphragm) Lymph Nodes: They are embedded in the fat between the fascial roof and the fascial floor and form the lateral group of Inferior deep cervical (Supraclavicular) lymph nodes. 4 P age
5 They drain the back of the scalp and neck. Usually they receive some efferent vessels from the upper deep cervical, axillary and deltopectoral nodes. These nodes empty into the subclavian lymph trunk. The axillary nodes empty into the subclavian lymph trunk, which follows the subclavian vein to the thoracic or right lymph duct. They Get enlarged in Infections of the Scalp and Rubella. Subclavian Artery: Its only branch given off in the posterior triangle is the dorsal scapular artery. The branches from the subclavian artery usually come from the second part (behind scalenus anterior) and first part (proximal to that muscle). Other Arteries in the Posterior Triangle: The Suprascapular and Transverse cervical arteries, which arise from the first part of the artery via thyrocervical trunk. They pass laterally in front of the scalenus anterior and its fascia and the phrenic nerve. Across the apex of the triangle one can have the glimpse of the occipital artery Brachial Plexus: Roots are located behind the Scalenus anterior muscle. Trunks are located in the lower part of the triangle. The roots receive gray rami from the middle and inferior cervical ganglia and first and second thoracic ganglia. Cutaneous Nerves: C1 has no cutaneous branch. The ventral rami of C5 to T1 form the brachial plexus. Thus C2, C3 and C4 supply the cutaneous territory between the Trigeminal nerve above and T2 below. They do this by means of FOUR nerves that radiate from about the middle of the posterior border of sternocleidomastoid The Lesser Occipital Nerve (C2, C3): It hooks around the accessory nerve and ascends just behind and parallel to the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid to supply the scalp. The Greater Auricular Nerve (C2, C3): It runs vertically across the sternocleidomastoid to the lobe of the ear, with the external jugular vein. It has mastoid, auricular and facial branches 5 P age
6 The Anterior Cutaneous Nerve of the Neck / Transverse Cervical nerve (C2,C3): It crosses the sternocleidomastoid and the external jugular vein and supplies the skin between the jaw and the sternum The Supraclavicular Nerves (C3, C4): These are three sensory branches to the lower part of the posterior triangle and upper chest wall down to the level of the second rib. 6 P age
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
The Neck. BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat
 The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh
 3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
Gateway to the upper limb. An area of transition between the neck and the arm.
 Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes
 Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes Introduction about nervous system nervous system central nervous system periphral nervous system brain spinal cord 31 pairs of spinal nerves 12 paris of cranial
Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes Introduction about nervous system nervous system central nervous system periphral nervous system brain spinal cord 31 pairs of spinal nerves 12 paris of cranial
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck. M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick. Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974.
 Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck.
 Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Chapter 28: The neck. Fascia of the neck
 Chapter 28: The neck Fascia of the neck The superficial fascia is a fatty areolar layer between the skin and the more obvious deep fascia. It contains the platysma muscles and the external jugular veins
Chapter 28: The neck Fascia of the neck The superficial fascia is a fatty areolar layer between the skin and the more obvious deep fascia. It contains the platysma muscles and the external jugular veins
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
CHAPTER 9. The Neck THE "CERVICAL CAVITY" TRACHEA ESOPHAGUS THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLANDS
 281 CHAPTER 9 The Neck CERVICAL VERTEBRAE POSTERIOR TRIANGLE OF NECK Trapezius and Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING TRAPEZIUS Sternocleidomastoid CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS
281 CHAPTER 9 The Neck CERVICAL VERTEBRAE POSTERIOR TRIANGLE OF NECK Trapezius and Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING TRAPEZIUS Sternocleidomastoid CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Lab Activity 11: Group I
 Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns
 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns CLAVICLE Examine an isolated clavicle and compare it with a clavicle on an articulated skeleton. Viewed from above,
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns CLAVICLE Examine an isolated clavicle and compare it with a clavicle on an articulated skeleton. Viewed from above,
The pectoral region. University of Babylon College of Medicine Dr.HaythemAli Alsayigh M.B.CH.B.-F.I.M.B.S. Surgical Clinical Anatomy
 The pectoral region University of Babylon College of Medicine Dr.HaythemAli Alsayigh M.B.CH.B.-F.I.M.B.S. Surgical Clinical Anatomy Objective Study the Bones and Joints A. Clavicle (collarbone) B. Scapula
The pectoral region University of Babylon College of Medicine Dr.HaythemAli Alsayigh M.B.CH.B.-F.I.M.B.S. Surgical Clinical Anatomy Objective Study the Bones and Joints A. Clavicle (collarbone) B. Scapula
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla
 Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 1 Pectoral region Intercostal nerve Anterior branch of lateral cutaneous branch Lateral cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous
Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 1 Pectoral region Intercostal nerve Anterior branch of lateral cutaneous branch Lateral cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions.
 Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
VENOUS DRAINAGE O US F UPPER UPPER LIM B BY dr.fahad Ullah
 VENOUS DRAINAGE OF UPPER LIMB BY dr.fahad Ullah Venous drainage of the supper limb The venous system of the upper limb drains deoxygenated blood from the arm, forearm and hand It can anatomically be divided
VENOUS DRAINAGE OF UPPER LIMB BY dr.fahad Ullah Venous drainage of the supper limb The venous system of the upper limb drains deoxygenated blood from the arm, forearm and hand It can anatomically be divided
Muscles of the Upper Limb that are dissected in the Back Region Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes
 Muscles of Upper Limb that are dissected in Back Region Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes floor of thoraco thoraco inserting spines from intertubercular arm nerve (C7,8) a. tendon
Muscles of Upper Limb that are dissected in Back Region Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes floor of thoraco thoraco inserting spines from intertubercular arm nerve (C7,8) a. tendon
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page. Deltoid. Trapezius. Latissimus Dorsi
 Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page All Fibers Abduct the shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid Anterior Fibers Flex the shoulder (G/H joint) Horizontally adduct the shoulder
Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page All Fibers Abduct the shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid Anterior Fibers Flex the shoulder (G/H joint) Horizontally adduct the shoulder
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides
 The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
THE DESCENDING THORACIC AORTA
 Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
MUSCLE MECHANICS AND CONTROL
 MUSCLE MECHANICS AND CONTROL STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE NEUROVASCULAR BUNDLE - CONTAINS THE BLOOD VESSELS AND THE NERVES TO A MUSCLE SKELETAL MUSCLE - LONGITUDINAL SECTION MUSCLE ATTACHMENTS: TENDONS
MUSCLE MECHANICS AND CONTROL STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE NEUROVASCULAR BUNDLE - CONTAINS THE BLOOD VESSELS AND THE NERVES TO A MUSCLE SKELETAL MUSCLE - LONGITUDINAL SECTION MUSCLE ATTACHMENTS: TENDONS
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm
 Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Melissa McGinn. Welcome to Gross and Developmental Anatomy
 Welcome to Gross and Developmental Anatomy M1 Anatomy Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Richard Krieg Dr. Milton Sholley Dr. David Simpson 1 2 Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Steve Gudas Dr.
Welcome to Gross and Developmental Anatomy M1 Anatomy Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Richard Krieg Dr. Milton Sholley Dr. David Simpson 1 2 Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Steve Gudas Dr.
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta.
 Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
The Back OUTLINE. Vertebral Column (review) Craniovertebral Joints Dorsal Scapular Region(review) Muscles of the Back Suboccipital Region
 The Back OUTLINE Vertebral Column (review) Craniovertebral Joints Dorsal Scapular Region(review) Muscles of the Back Suboccipital Region Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com
The Back OUTLINE Vertebral Column (review) Craniovertebral Joints Dorsal Scapular Region(review) Muscles of the Back Suboccipital Region Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm
 Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Lecture 01. The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018
 Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
thoracic cage inlet and outlet landmarks of the anterior chest wall muscles of the thoracic wall sternum joints ribs intercostal spaces diaphragm
 Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including inlet and outlet. Describe the anatomical landmarks of the anterior chest wall. List various structures making
Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including inlet and outlet. Describe the anatomical landmarks of the anterior chest wall. List various structures making
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus.
 *Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
G24: Shoulder and Axilla
 G24: Shoulder and Axilla Syllabus - Pg. 2 ANAT 6010- Medical Gross Anatomy David A. Morton, Ph.D. Objectives Upper limb Systemically: Bones (joints) Muscles Nerves Vessels (arteries/veins) Fascial compartments
G24: Shoulder and Axilla Syllabus - Pg. 2 ANAT 6010- Medical Gross Anatomy David A. Morton, Ph.D. Objectives Upper limb Systemically: Bones (joints) Muscles Nerves Vessels (arteries/veins) Fascial compartments
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy. Raleigh E. Lingeman
 Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Microsurgical anatomy of the transcondylar, supracondylar, and paracondylar extensions of the far-lateral approach
 J Neurosurg 87:555 585, 1997 Microsurgical anatomy of the transcondylar, supracondylar, and paracondylar extensions of the far-lateral approach HUNG T. WEN, M.D., ALBERT L. RHOTON, JR., M.D., TOSHIRO KATSUTA,
J Neurosurg 87:555 585, 1997 Microsurgical anatomy of the transcondylar, supracondylar, and paracondylar extensions of the far-lateral approach HUNG T. WEN, M.D., ALBERT L. RHOTON, JR., M.D., TOSHIRO KATSUTA,
The Upper Limb III. The Brachial Plexus. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Upper Limb III The Brachial Plexus Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Brachial plexus Network of nerves supplying the upper limb Compression of the plexus results in motor & sensory changes
The Upper Limb III The Brachial Plexus Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Brachial plexus Network of nerves supplying the upper limb Compression of the plexus results in motor & sensory changes
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
BRACHIAL PLEXUS. DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae
 THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
STERNUM. Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts:
 STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Head & Neck Contouring
 Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position
General Anatomic Layout
 General Anatomic Layout 2 Core Messages At the start of the dissection exercise, we must take a panoramic look for orientation. We then establish the limits of the area of operation and the main landmarks.
General Anatomic Layout 2 Core Messages At the start of the dissection exercise, we must take a panoramic look for orientation. We then establish the limits of the area of operation and the main landmarks.
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓
 Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Note : I put the sheet's info within the slides to easily understand this lecture Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 Note : I put the sheet's info within the slides to easily understand this lecture Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including
Note : I put the sheet's info within the slides to easily understand this lecture Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including
The ultrasound-guided superficial cervical plexus block for anesthesia and analgesia in emergency care settings,
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2011) xx, xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Clinical Notes The ultrasound-guided superficial cervical plexus block for anesthesia and analgesia in emergency care
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2011) xx, xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Clinical Notes The ultrasound-guided superficial cervical plexus block for anesthesia and analgesia in emergency care
_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]
![_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come] _CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]](/thumbs/81/84146690.jpg) 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Thyroid gland. importance. relations and connections. external laryngeal nerves. malformations.
 Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D.
 Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D. Chest cavity - bony structures Chest cavity- bony structures Sternum Ribs True ribs: first seven pairs connect
Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D. Chest cavity - bony structures Chest cavity- bony structures Sternum Ribs True ribs: first seven pairs connect
Anatomy of the Shoulder Girdle. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde FMCS (Orthop)
 Anatomy of the Shoulder Girdle Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde FMCS (Orthop) www.oluwadiya.com Bony Anatomy Shoulder Complex: Sternum(manubrium) Clavicle Scapula Proximal humerus Manubrium Sterni Upper part of
Anatomy of the Shoulder Girdle Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde FMCS (Orthop) www.oluwadiya.com Bony Anatomy Shoulder Complex: Sternum(manubrium) Clavicle Scapula Proximal humerus Manubrium Sterni Upper part of
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system
 Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
1TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE
 TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
Classification of the nervous system. Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 2
 1 1. Formation and general organization 2. Spinal ganglia 3. Zonal and segmental innervation 4. Dorsal rami of the spinal nerves 5. Ventral rami of the spinal nerves 6. Cervical plexus Classification of
1 1. Formation and general organization 2. Spinal ganglia 3. Zonal and segmental innervation 4. Dorsal rami of the spinal nerves 5. Ventral rami of the spinal nerves 6. Cervical plexus Classification of
This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration-
 This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration- Slides of Anatomy Please note : These slides are Dr. Maher Hadidi s slides of spring 2016 and were edited
This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration- Slides of Anatomy Please note : These slides are Dr. Maher Hadidi s slides of spring 2016 and were edited
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy of thoracic wall
 Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Axilla and Brachial Region
 L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
Resection of malignant tumors invading the thoracic inlet
 Resection of Superior Sulcus Tumors: Anterior Approach Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc Resection of malignant tumors invading the thoracic inlet represents a technical challenge because of the complex anatomy
Resection of Superior Sulcus Tumors: Anterior Approach Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc Resection of malignant tumors invading the thoracic inlet represents a technical challenge because of the complex anatomy
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
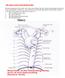 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
Pectoral region. Lecture 2
 Pectoral region Lecture 2 Muscle Action Each muscle has: Origin Beginning. Insertion End. Body (belly). Law: When a muscle performs its action, its insertion, moves towards its origin. Spring 2016 Dr.
Pectoral region Lecture 2 Muscle Action Each muscle has: Origin Beginning. Insertion End. Body (belly). Law: When a muscle performs its action, its insertion, moves towards its origin. Spring 2016 Dr.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013
![[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013 [ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013](/thumbs/86/93473883.jpg) Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Peripheral Circulation
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Peripheral Circulation Structures of the Splanchnopleure: receive unpaired vessels of the abdominal aorta. Structures of the
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Peripheral Circulation Structures of the Splanchnopleure: receive unpaired vessels of the abdominal aorta. Structures of the
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
