Downloaded from
|
|
|
- Dorcas Goodman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 20. Lcmtin and Mvement Types f Mvement : Amebid mvement: This mvement takes place in phagcytes where leuccytes and macrphages migrate thrugh tissue. It is affected by pseudpdia frmed by the streaming f prtplasm (as in ameba) Ciliary mvement: These mvements ccur in internal rgans which are lined by ciliary epithelium. Muscular Mvement: This mvement invlves the muscle fibers, which have the ability t cntract and relax. MUSCLES : Prperties f Muscle : Excitability Cntractility Extensibility Elasticity Types f Muscles : Skeletal muscles r striated muscles Clsely assciated with skeletn. They are striped appearance under the micrscpe and called Striated muscles. They are under vluntary cntrl f nervus system, hence called vluntary muscles. These invlved in lcmtin and change f bdy pstures. Unbranched and multinucleated. Visceral muscles r smth muscles These are lcated in inner wall f hllw visceral rgan. Spindle shaped and uni-nucleated. They d nt exhibit any striatin and are smth in appearance. They are called smth muscles r nn-striated muscles. Their activities are nt under vluntary cntrl f nervus system hence called as invluntary muscles. They assist in transprt f fd thrugh digestive tract and gametes thrugh the genital tract. Cardiac muscles The muscles f heart, invluntary in nature. Cardiac muscle cells assemble in a branching pattern t frm a cardiac muscle. These are uni-nucleated with characteristic intercalated disc. Structure f skeletal muscle : Each rganized skeletal muscle in ur bdy is made f a number f muscle bundles called fascicles held tgether by cmmn fibrus cvering called fascia. Each fascicle cnsists f a number f muscle fibres (cell) cvered by a cmmn fibrus perimysium. Each muscle fibre is lined by the plasma membrane called sarclemma, enclsing cytplasm called sarcplasm. The sarcplasm cntain endplasmic reticulum, called sarcplasmic reticulum is the stre huse f calcium in.
2 Muscle fibre is a syncitium as the sarcplasm cntain many nuclei. Muscle fibres cntain a large number f parallelly arranged filaments in the sarcplasm called myfilaments rmyfibrils. There are tw types f myfibrils are present in the sarcplasm Thin filament Actin Thick filament Mysin. The arrangement f thick and thin filament gives the characteristic striated appearance. The light bands cntain nly actin filaments and are called I-band r istrpic band. The dark band called A r anistrpic band cntains bth actin and mysin. In the centre f each I band is an elastic fibre called Z line which bisects it. The thin filaments r actin are firmly attached with the Z line. The thick filaments r mysin in the A band are als held tgether in the middle by a thin fibrus membrane called M line. The prtin between tw successive Z lines is cnsidered as the functinal unit f the muscle called sarcmere. Each A band cntains tw verlap zne f thick and thin filament called O band. The central part f thick filament, nt verlapped by thin filament is called H band. A band = 2(O) + H. Structure f Cntractile prteins : Thin filament r Actin : Each actin filament is made f tw F actins helically wund t each ther. Each F actin is made f plymer f mnmeric G (Glbular) actin. Each F actin assciated with anther prtein, trpmysin als run thrughut its length. Anther cmplex prtein, Trpnin is distributed at regular intervals n the trpmysin. Each trpnin has three cmpnent Trpnin-C binds with calcium. Trpnin-M, binds with the trpmysin. Trpnin T, masks the active site n the G actin (thin filament) In the resting state a sub-unit f Trpnin (Tn-T), masks the active binding sites n the thin filaments fr mysin. Thick filament : Each mysin (thick) filament is cnsists f many mnmeric prtein called Mermysins. Each mermysin has tw parts Heavy mermysin (HMM) - A glbular head with a shrt arm. Light mermysin (LMM) a tail. The HMM cmpnent, i.e. the head and shrt arm prjects utwards at regular distance and angle frm each ther frm the surface f a plymerized mysin filament and is knwn as crss arm. The glbular head is an active ATPase enzyme and has binding sites fr ATP and active sites fr actin.
3 Mechanism f muscle cntractin : Mechanism f muscle cntractin is explained by sliding filament thery which states that cntractin f a muscle fibre takes place by the sliding f the thin filaments ver the thick filaments. Muscle cntractin is initiated by a signal sent by the central nervus system via a mtr neurn. A mtr neurn alng with the muscle fibres cnnected t it cnstitutes a mtr unit. The junctin between a mtr neurn and the sarclemma f the muscle fibre is called neurmuscular junctin rmtr-end plate. Neurtransmitter releases here which generates an actin ptential in sarclemma. These causes release f Ca++ int sarcplasm. These Ca++ binds with trpnin, thereby remve masking f active site. Mysin head binds t expsed active site n actin t frm a crss bridge, utilizing energy frm ATP hydrlysis. This pulls the actin filament twards the centre f A band. Z lines als pulled inward thereby causing a shrtening f sarcmere i.e. cntractin. I band get reduced, whereas the A band retain the length. During relaxatin, the crss bridge between the actin and mysin break. Ca++pumped back t sarcplasmic cisternae. Actin filament slide ut f A band and length f I band increases. This returns the muscle t its riginal state. Repeated muscle cntractin causes accumulatin f lactic acid, prduced frm anaerbic breakdwn f glycgen leads t muscle fatigue. Muscle cntains red clured xygen string pigment called myglbin. Muscle with myglbin called red muscle fibres, they are als cntain large number f mitchndria which can utilize large amunt f xygen stred in them fr ATP prductin als called aerbic muscle. Sme muscles pssess very less quantity f myglbin and less mitchndrin hence called white fibres. Amunt f sarcplasmic reticulum is high in these muscles. They depend n anaerbic prcess fr energy. SKELETAL SYSTEM : Human skeletn cnsists f 206 bnes in adult. Axial skeletn 80 bnes Appendicular skeletn 126 bnes. Axial skeletn : Skull 29 bnes. Cranium 8 bnes frms the brain bx. Facial 14 bnes frms the frnt part f the face. Hyid a single U-shaped bne at the base f the buccal cavity. Ear ssicles 6 bnes- 3 n either side (Malleus, Incus and stapes) The skull regin articulates with the superir regin f the vertebral clumn with the help f tw ccipital cndyles hence called dicndylic skull. Vertebral clumn 26 bnes Cervical 7 vertebrae.
4 Thracic 12 vertebrae. Lumber 5 vertebrae. Sacral 1 vertebra. (fused five bne) Caudal 1 vertebra (fused fur bnes) Sternum r breast bne 1 bne in the middle line f the thrax. Ribs 12 pairs (24 bnes) 1-7 are true ribs (cnnected t the sternum directly) 8 th, 9 th, 10 th pairs are called false ribs they attached t the 7th ribs. 11th and 12th nt cnnected ventrally hence called flating ribs. Ribs attaché drsally t the vertebra and ventrally with the sternum by hyaline cartilage. Thracic vertebrae, ribs and sternum tgether frm the rib cage. Appendicular skeletn: 126 bnes Fre limb 60 ( 30 in each) Humerus 1 bne Radius and ulna 2 bnes Carpals (wrist bnes) 8 in numbers. Metacarpals (palm bnes) 5 in numbers Phalanges (digits) 14 in number. Hind limb 60 (30 in each) Femur (thigh bne- the lngest and heaviest bne) 1 number. Tibia and fibula 2 bnes. Tarsals (ankle bne) 7 bnes. Metatarsals 5 in numbers. Phalanges (digits) 14 in numbers. Patella (knee cap) 1 bne. Pectral girdles: cnsists f 2 bnes each = 4 bnes. Helps in articulatin f fre limb with the axial skeletn. Each pectral girdle made f tw half. Each half made f tw bne the clavicle and scapula. Scapula is a large triangular flat bne situated in the drsal part f the thrax between the secnd and the seventh ribs. Scapula is characterized by spine with acrmin prcess. Belw acrmin, is glenid cavity t which head f humerus fits. Clavicle is cmmnly called cllar bne. Pelvic girdle: 2 bnes. Pelvic girdle cnsists f tw cxal bnes.
5 Each cxal bne is frmed f fusin f three bnes Ilium Ischium Pubis. At the pint f fusin f the three bnes is a cavity called acetabulum t which the femur articulates. Tw halves f the pelvic girdle meets ventrally t frm the pubic symphysis cntaining fibrus cartilage. JOINTS : Jints are the pints f cntact between bnes, r between bnes and cartilages. Frce generated by the muscles is used t carry ut mvement thrugh jints, where jint acts as a fulcrum. Jints are classified int three types: Fibrus jint Cartilaginus jint Synvial jint Fibrus jints : D nt allw any mvements. Fund in flat bnes which fuse end-t-end with the help f dense fibrus cnnective tissues in the frm f sutures. These types f jints are fund in the bnes f cranium. Cartilaginus jints : The bnes invlved are jined tgether with the help f cartilages. Permits very little mvements. Jint between the vertebral clumn are the example f such jints. Synvial jints : Characterized by the presence f a fluid filled synvial cavity between the articulating surfaces f the tw bnes. Allw free mvement between tw bnes. The fluid inside it called synvial fluid cvered by synvial membrane. Ball and scket jint - between humerus and pectral girdle Hinge jint knee jint Pivt jint between atlas and axis. Gliding jint between carpals. Saddle jint between carpals and metacarpals f thumb. DISORDERS OF MUSCULAR AND SKELETAL SYSTEM : Myasthenia gravis : It is an aut-immun disrder. Affects the neurmuscular junctin leads t fatigue. Caused weakening and paralysis f skeletal muscle. Muscular dystrphy : Prgressive degeneratin f skeletal muscle mstly due t genetic disrder. Tetany: rapid spasms (wild cntractins) in muscle due t lw Ca++ in bdy fluid.
6 Arthritis : inflammatin f jints. Osteprsis : age related disrder characterized by decreased bne mass and increased chances f fractures. Decrease levels f estrgen are a cmmn cause. Gut : inflammatin f jints due t accumulatin f uric acid crystals.
Can exert forces from a fraction of an ounce to > 70 lbs
 Anatmy & Physilgy Chapter 9 Ntes: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Name Muscle Cell = My / Mys = Sarc = Muscle Cell Plasma Membrane = Muscle Celly Cytplasm = Three types f muscle tissue: 1. 2. 3. Skeletal Muscle
Anatmy & Physilgy Chapter 9 Ntes: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Name Muscle Cell = My / Mys = Sarc = Muscle Cell Plasma Membrane = Muscle Celly Cytplasm = Three types f muscle tissue: 1. 2. 3. Skeletal Muscle
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 FORBUSH HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: SKELETAL SYSTEM GUIDE TO IDENTIFICATION Arranged by: M.Sewell Bnes and Prcesses t Knw Page 2 f 19 Cntents Bnes and prcesses needed t knw fr Anatmy:... 3 Be able
FORBUSH HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: SKELETAL SYSTEM GUIDE TO IDENTIFICATION Arranged by: M.Sewell Bnes and Prcesses t Knw Page 2 f 19 Cntents Bnes and prcesses needed t knw fr Anatmy:... 3 Be able
Class XI Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement Biology
 Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 114 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 20 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Match the following and mark the correct option Column I Column II A. Fast muscle fibres i. Myoglobin B. Slow
114 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 20 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Match the following and mark the correct option Column I Column II A. Fast muscle fibres i. Myoglobin B. Slow
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
BIO 137 AXIAL SKELETON BONE STUDY THE HUMAN SKELETON
 BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal
 Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Locomotion Movement. Topicwise Solved Previous Year Qs. synthesizes (in adults) the blood and its cells.
 208 Locomotion Movement and 1. Extremities of long bones possess cartilage [1989] (a) calcified (b) fibrous (c) elastic (d) hyaline Hyalin Cartilage forms the cushions or pads upon the articular surfaces
208 Locomotion Movement and 1. Extremities of long bones possess cartilage [1989] (a) calcified (b) fibrous (c) elastic (d) hyaline Hyalin Cartilage forms the cushions or pads upon the articular surfaces
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Section Chapter 36. The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems. Go to Section:
 Section 35-1 Chapter 36 The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems Section Outline Section 36-1 36 1 The Skeletal System A. The Skeleton B. Structure of Bones C. Development of Bones D. Types of
Section 35-1 Chapter 36 The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems Section Outline Section 36-1 36 1 The Skeletal System A. The Skeleton B. Structure of Bones C. Development of Bones D. Types of
5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW
 Unit 5 Skeletal System 5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW Section Objectives Identify the major structures and functions of the skeletal system. Differentiate between the two divisions (axial and appendicular) of
Unit 5 Skeletal System 5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW Section Objectives Identify the major structures and functions of the skeletal system. Differentiate between the two divisions (axial and appendicular) of
NOTES SKELETAL SYSTEM
 NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Characteristics. Bones. Functions of the Skeleton
 Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Vikasana Bridge Cource 2012
 Vikasana Bridge Cource 2012 Definition Learning Objectives Types of movement Muscle Skeletal system Joints Disorders of muscular and skeletal system What is locomotion? Displacement of an animal from one
Vikasana Bridge Cource 2012 Definition Learning Objectives Types of movement Muscle Skeletal system Joints Disorders of muscular and skeletal system What is locomotion? Displacement of an animal from one
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives
 Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Hand Pain & Problems
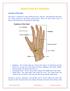 Anatmy f the hand: Hand Pain & Prblems The hand is cmpsed f many different bnes, muscles, and ligaments that allw fr a large amunt f mvement and dexterity. There are three majr types f bnes in the hand
Anatmy f the hand: Hand Pain & Prblems The hand is cmpsed f many different bnes, muscles, and ligaments that allw fr a large amunt f mvement and dexterity. There are three majr types f bnes in the hand
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
The Skeletal System. Chapter 4
 The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES
 UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
Sports Medicine Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX
 Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan 2008 Anatomy of the Upper Body In this section of the
Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan 2008 Anatomy of the Upper Body In this section of the
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Skeletal System. Chapter 7.1. Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction:
 Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE. CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?
 PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME
 TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Nov 20 12:02 PM I. Functions A. Support: Internal framework, Structure, Anchors & Supports soft tissue/organs B. Protection: Protects vital organs C. Movement: Provide attach
UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Nov 20 12:02 PM I. Functions A. Support: Internal framework, Structure, Anchors & Supports soft tissue/organs B. Protection: Protects vital organs C. Movement: Provide attach
Skeletal Considerations for Movement. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
TERMINOLOGY AS IT APPLIES TO TICA BREED STANDARDS. Interpretation by Marge Hanna
 TERMINOLOGY AS IT APPLIES TO TICA BREED STANDARDS Interpretation by Marge Hanna 1. Nose: The area, with its underlying cartilage, from the top edge of the nose leather up to the bottom of the bridge of
TERMINOLOGY AS IT APPLIES TO TICA BREED STANDARDS Interpretation by Marge Hanna 1. Nose: The area, with its underlying cartilage, from the top edge of the nose leather up to the bottom of the bridge of
Warm-Up Activity. Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram.
 Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
The Skeletal System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY PART A ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
A. Incorrect! The appendicular skeleton includes bones of the shoulder, arm, hand, pelvis, leg and foot.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Structural Support and Movement. Chapter 33
 Structural Support and Movement Chapter 33 33.1 Skeletons and Muscles Most animals move when the force of muscle contraction is applied to skeletal elements Animal Skeletons Hydrostatic skeleton A confined
Structural Support and Movement Chapter 33 33.1 Skeletons and Muscles Most animals move when the force of muscle contraction is applied to skeletal elements Animal Skeletons Hydrostatic skeleton A confined
Topic 11: Nervous System
 Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Skeletal System. By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr.
 Skeletal System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Learning Outcomes Describe the parts of a long
Skeletal System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Learning Outcomes Describe the parts of a long
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
QUICK ASSESSMENT: CONCEPT MAP
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
Extension: Flexion: Motor neurons: o Only excitatory neurons release acetylcholine (ACh)
 Interneurn -> A nerve cell fund entirely within the central nervus system that acts as a link between sensry neurns and mtr neurns Infrmatin sent frm brain t perfrm a gal, has a purpse Tw Types f Mtr Behavir:
Interneurn -> A nerve cell fund entirely within the central nervus system that acts as a link between sensry neurns and mtr neurns Infrmatin sent frm brain t perfrm a gal, has a purpse Tw Types f Mtr Behavir:
ASFYT Part I: The Skeletal System Module S3 (Joints)
 Mdule S3 (Jints) (1) Overview f Jints Classificatin f Jints Fibrus Jints Cartilaginus Jints Synvial Jints Factrs Determining the Stability f Synvial Jints Menisci and Articulating Discs Classificatin f
Mdule S3 (Jints) (1) Overview f Jints Classificatin f Jints Fibrus Jints Cartilaginus Jints Synvial Jints Factrs Determining the Stability f Synvial Jints Menisci and Articulating Discs Classificatin f
Section 11.1 Your Skeletal System
 Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system.
 L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
Chapter 30 How Animals Move
 Chapter 30 How Animals Move PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J.
Chapter 30 How Animals Move PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J.
10/12/2010. Upper Extremity. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle. Clavicle (collarbone) Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton
 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Skeletal System Notes
 Skeletal System Notes A. Introduction 1. Skeletal system is made of organs that are called bones 2. In the adult, there are 206 bones B. Functions of bones 1. Framework: support the body s muscle fat,
Skeletal System Notes A. Introduction 1. Skeletal system is made of organs that are called bones 2. In the adult, there are 206 bones B. Functions of bones 1. Framework: support the body s muscle fat,
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017
 IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017 Seneca Valley High School Mrs. Meaghan Stuckey meaghan_s_stuckey@mcpsmd.org meaghan.s.stuckey@mcpsmd.net DUE: First Day of School, September 5, 2017 Welcome to IB Sports,
IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017 Seneca Valley High School Mrs. Meaghan Stuckey meaghan_s_stuckey@mcpsmd.org meaghan.s.stuckey@mcpsmd.net DUE: First Day of School, September 5, 2017 Welcome to IB Sports,
Supporting systems and movement in Animals
 Supporting systems and movement in Animals Hydrostatic skeleton Types of skeletons Exoskeleton Endoskeleton Hydrostatic skeleton Exoskeleton Endoskeleton Description Consists of fluid under pressure in
Supporting systems and movement in Animals Hydrostatic skeleton Types of skeletons Exoskeleton Endoskeleton Hydrostatic skeleton Exoskeleton Endoskeleton Description Consists of fluid under pressure in
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
1.6. Topic 1: Cell Biology (Teacher) Essential Idea: Cell division is essential but must be controlled. 1.6 Cell Division
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
11.2 Muscles and Movement
 11.2 Muscles and Movement 11.2.1 - State the roles of bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves in human movement Bones Act as anchors for the muscles, and levers to control the movement of muscles,
11.2 Muscles and Movement 11.2.1 - State the roles of bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves in human movement Bones Act as anchors for the muscles, and levers to control the movement of muscles,
Aim: To detect the presence of albumin in the given sample of urine. NCERT
 Exercise 31 Aim: To detect the presence of albumin in the given sample of urine. Principle: Nitric acid causes the precipitation of albumin. When heated or treated with sulphosalicylic acid, albumin undergoes
Exercise 31 Aim: To detect the presence of albumin in the given sample of urine. Principle: Nitric acid causes the precipitation of albumin. When heated or treated with sulphosalicylic acid, albumin undergoes
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5. Subject: The Skeletal System
 Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Skeletal System A&P Week 11
 Skeletal System A&P Week 11 Bones 206 bones in the body Smallest are in the middle ear cavity Malleus, incus, stapes Functions of Bone Framework and support Protection Contains/protects red bone marrow
Skeletal System A&P Week 11 Bones 206 bones in the body Smallest are in the middle ear cavity Malleus, incus, stapes Functions of Bone Framework and support Protection Contains/protects red bone marrow
ASFYT Part I: The Skeletal System S1: Intro to Kinesiology
 S1: Intr t Kinesilgy (1) Intr t Kinesilgy Majr Divisins f the Human Bdy Jints Between Majr Bdy Parts Describing Mvement in the Bdy True Mvement vs. Ging Alng fr the Ride Anatmic Psitin Directinal Terms
S1: Intr t Kinesilgy (1) Intr t Kinesilgy Majr Divisins f the Human Bdy Jints Between Majr Bdy Parts Describing Mvement in the Bdy True Mvement vs. Ging Alng fr the Ride Anatmic Psitin Directinal Terms
B DAYS SKELETAL SYSTEM UNIT GUIDE DUE THURSDAY 11/17
 B DAYS SKELETAL SYSTEM UNIT GUIDE DUE THURSDAY 11/17 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 10/10 10/11 - B 10/12 - A 10/13 - B 10/14 - A NO SCHOOL Unit quiz Presentations 10/17 - B 10/18 - A 10/19 -
B DAYS SKELETAL SYSTEM UNIT GUIDE DUE THURSDAY 11/17 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 10/10 10/11 - B 10/12 - A 10/13 - B 10/14 - A NO SCHOOL Unit quiz Presentations 10/17 - B 10/18 - A 10/19 -
Exercise 11. The Appendicular Skeleton
 Exercise 11 The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones. Consists of the upper and lower limbs, the pectoral girdles, and the pelvic girdles. The pectoral
Exercise 11 The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones. Consists of the upper and lower limbs, the pectoral girdles, and the pelvic girdles. The pectoral
Contents. Section 1: Life s Building Blocks. Section 2: The Human Framework. Section 3: The Senses and the Respiratory System
 Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Support and protection. Body movement. Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
Topic 1: Cell Biology (Student) Essential Idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure that prokaryotes.
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
Chapter 20 The Heart
 Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: Objective for Portfolio #1: Part I: Skeletal Stations Station A: Bones of the Body
 SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
The Skeletal System. Support Systems Unit 2
 The Skeletal System Support Systems Unit 2 The Basic Functions of the Skeletal System Hematopoiesis Structure Support Muscle Attachment and Movement Mineral Storage Axial vs. Appendicular The Axial Skeleton
The Skeletal System Support Systems Unit 2 The Basic Functions of the Skeletal System Hematopoiesis Structure Support Muscle Attachment and Movement Mineral Storage Axial vs. Appendicular The Axial Skeleton
