ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chubu Rosai Hospital, Nagoya, Japan ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Berniece Dixon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nagoya J. Med. Sci ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT KEIGO ITO, MD, PhD; YASUTSUGU YUKAWA, MD, PhD; MASAAKI MACHINO, MD; AKINORI KOBAYAKAWA, MD; and FUMIHIKO KATO, MD, PhD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chubu Rosai Hospital, Nagoya, Japan ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to measure range of motion (ROM) in patients with cervical ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament (C-OPLL) by multidetector-row computed tomography (MDCT), and to investigate the influence of dynamic factors. The study included 101 patients with C-OPLL and 99 normal control patients. Preoperative MDCT were taken in all subjects in maximum neck flexion and extension. ROM at each disc level between C2/3 and C7/T1 in sagittal view was measured. Ossification morphology at each disc segment was divided into 6 groups: covered disc, covered vertebra, unconnected vertebra, connected vertebra (continuous), connected vertebra (localized), and others. The relationship between ROM and the group of ossification morphology was also investigated. ROM of adjacent intervertebral disc in connected vertebrae (continuous and localized) and those of others were investigated for each group. The average ROM of covered disc group was significantly higher than that of connected vertebra (continuous, localized). The average ROM of connected vertebra (continuous) group was significantly lower than that of covered disc group, others group, and normal control. There was no significant difference between ROM of adjacent intervertebral disc in connected vertebrae and others, but the average ROM of the connected vertebra group was significantly lower than that of the covered disc group and normal control group. Dynamic factor was reduced at continuous segment, but it was not increased in adjacent intervertebral disc. Key Words: Cervical ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament, Range of motion, Cervical spinal cord injuries without radiographic evidence of trauma, Multidetector-row computed tomography, Ossification morphology INTRODUCTION Dynamic factors have a significant role in causing cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM). 1) In patients with cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (C-OPLL), mild symptoms of myelopathy are experienced even if the spinal canal narrows. The pathomechanism of cervical myelopathy caused by C-OPLL remains unknown. Despite spinal stenosis (6 mm < space available for the spinal cord < 14 mm), myelopathy may not develop in patients with severe range limitations of the cervical spine. 2) This possibility indicates that not only static factors but also Received: September 30, 2014; accepted: January 7, 2015 Corresponding author: Keigo Ito, MD, PhD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chubu Rosai Hospital, Koumei, Minato-ku, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan TEL: / FAX: , keiort@aol.com 221
2 222 Keigo Ito et al. dynamic factors, such as listhesis or hypermobility at the discontinuity of the ossified lesion, have important roles in the development of myelopathy, especially in mixed and segmental OPLLs. Multidetector-row computed tomography (MDCT) has given a better understanding of spinal ligament ossification. Unlike the Tsuyama classification based on lateral radiographs, 3) ossification morphology and bone continuity between each vertebrae are shown more clearly by MDCT. Previously, we reported 4) that ossification morphology at each disc segment was divided into 3 groups: the connection department, coating part, and non-connection department of OPLL. We previously used MDCT to measure spinal cord cross-sectional areas (SCCSAs) during flexion and extension. In that report, the SCCSA did not show statistically significant differences in ossification morphology. It is the possible that myelopathy is aggravated by dynamic factors, even in the connection department of OPLL. However, we did not investigate the sagittal range of motion (ROM) and ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligaments. Previously, we reported that the incidence of spinal cord injury in the stoppage department of ossification was 64%. 5) However, morphology of stoppage department had been unclear. The purpose of this study was to measure ROM by MDCT, to investigate the influence of dynamic factors on the spinal cord of patients with C-OPLL. And the ROMs of adjacent intervertebral disc in connected vertebrae and those of others were investigated for each morphology. MATERIALS AND METHODS From January 2006 to August 2010, a total, of 110 patients (80 men and 30 women) with C-OPLL were enrolled in this study. Their mean age was 62 years (range: years). All patients had undergone surgical treatment for cervical myelopathy due to C-OPLL. Patients with spinal cord injury without radiological evidence of trauma were excluded. In addition, 99 patients (64 men and 35 women) who had lumbar disc herniation determined by MDCT were defined as normal controls. Patients with OPLL, fused vertebrae, and spinal instability were excluded from this normal control. Their mean age was 47 years (range: years). This study was approved by the institutional review board. The aims of this study were explained to all patients before myelography and CT scanning, and all patients gave informed consent to their participation. Preoperative CT scans after myelography were performed in all subjects in maximum neck flexion and extension. The position of the pillow was changed. The shoulder pillow was used in the extension. 6) CT scans were obtained (1-mm-thick axial helical) with sagittal and coronal reconstruction using 64-line, multi-slice unit (Light Speed VCT; GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences, Piscataway, NJ, USA). The ROM at each disc level between C2/3 and C7/T1 in sagittal view was measured using SYNAPSE Enterprise-PACS (FUJIFILM Medical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Ossification morphology at each disc segment was divided into 6 groups: covered disc, covered vertebra, unconnected vertebra, connected vertebra (continuous), connected vertebra (localized), and others (Fig. 1). The covered disc group was defined as comprising either cranial or caudal vertebra connected by ossification, with the other intervertebral disc not completely covered by ossification. The covered vertebra group was defined as comprising either cranial or caudal vertebra connected by ossification, with the other intervertebral disc completely covered by ossification. The unconnected vertebra group was defined as coprising either cranial or caudal vertebra connected by ossification, with ossification completely covering the vertebra, including other cranial and caudal intervertebral discs or vertebrae. The connected vertebra (continuous) group was defined as comprising both cranial and caudal vertebrae connected by ossification, of the continuous type according to the Tsuyama classification. In addition, the connected vertebra (localized) group was defined as comprising both cranial and caudal vertebrae connected by
3 ROM OF PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OPLL 223 Fig. 1 Ossification morphology at each disc segment was divided into 6 groups: covered disc, covered vertebra, unconnected vertebra, connected vertebra (continuous), connected vertebra (localized), and others. Table 1 C2/3 C3/4 C4/5 C5/6 C6/7 C7T1 Total C-OPLL Normal ossification, that was the localized type according to the Tsuyama classification. The others group was defined as vertebrae with osteophytes, disc ossification, or no problematic features. The ossification morphology was defined at the biggest and longest place in much MDCT slice. The relationship between ROM and the ossification morphology groups was also investigated. In addition, the ROMs of adjacent intervertebral disc in connected vertebrae (continuous and localized) and those of others were investigated for each group. ROMs during neck flexion and extension were measured once on two different days by a spinal surgeon, and average values were adopted. 6) The Stat View 5.0 software (ABACUS, Berkeley, CA) was used to perform data analysis. All values are expressed as the means ± standard deviations. Analysis of variance with a post hoc test (Kruskal -Wallis test) was used to perform comparisons between the groups. A P-value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS The ROM results at each level are summarized in Table 1. The ROM of the patients with C-OPLL was significantly smaller than that of the normal controls. There were 122 disc levels in the covered disc group, 114 disc levels in the covered vertebra group, 12 disc levels in the unconnected vertebra group, 40 disc levels in the connected vertebra (continuous) group, 20 disc levels in the connected vertebra (localized) group, and 340 disc levels in the others group (Fig. 2). The average ROMs were 6.4 ± 4.6 in the covered disc group, 4.8 ± 4.3 in the covered
4 224 Keigo Ito et al. Fig. 2 Number of intervertebral disc according to each classification Fig. 3 The average ROM according to each classification
5 ROM OF PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OPLL 225 Table 2 Number of intervertebral Adjacent Others Covered disc Covered vertebra Unconnected vertebra 4 8 Connected vertebra (Continuous) Connected vertebra (Localized) 9 11 Others Fig. 4 The average ROM of adjacent connected vertebra (continuous and localized) and that of except adjacent connected vertebra (continuous and localized) vertebra group, 4.8 ± 3.8 in the unconnected vertebra group, 2.9 ± 2.3 in the connected vertebra (continuous) group, 2.8 ± 2.4 in the connected vertebra (localized) group, 6.0 ± 4.3 in the others group, and 8.1 ± 4.2 in the normal control. The average ROM of the covered disc group was significantly higher than that of the connected vertebra (continuous) group and connected vertebra (localized) group. In addition, the average ROM of the normal control was significantly higher than those of the covered disc group, covered vertebra group, connected vertebra (continuous), and connected vertebra (localized) groups. The average ROM of the connected vertebra (continuous) group was significantly lower than those of the covered disc group, others group, and normal control group (Fig. 3). The average ROMs of the ROMs of adjacent intervertebral disc in connected vertebrae (continuous and localized) and those of others were investigated for each group shown in Table 2 and Fig. 4, were 5.9 ± 4.8 and, 6.5 ± 4.6 in the covered disc group, 5.5 ± 4.3 and, 4.5 ± 4.3 in the covered vertebra group, 3.8 ± 1.7 and, 5.3 ± 4.5 in the unconnected vertebra group,
6 226 Keigo Ito et al. 2.9 ± 2.5 and, 2.9 ± 2.2 in the connected vertebra (continuous) group, 3.0 ± 2.5 and, 2.5 ± 2.3 in the connected vertebra (localized) group, and 4.8 ± 4.7 and, 6.0 ± 4.3 in the others group, respectively. There were no significant differences between the adjacent intervertebral disc in connected vertebrae and others. DISCUSSION The Tsuyama classification is the most widely used criteria for classifying C-OPLL. 3) On the basis of lateral radiographs alone, C-OPLL can be roughly classified into 4 types: (1) continuous type, which is a continuous ossified mass extending over several vertebrae; (2) segmental type, which is a segmental ossification behind each vertebral body; (3) mixed type, which is a mixture of these 2 types; and (4) localized type, which includes other types, (e.g., circumscribed ossification of the ligament corresponding to the level of the intervertebral disc). This classification is not suitable for examining local areas. In addition, MDCT has enabled better understanding of ossification of spinal ligaments than provided by lateral radiographs, because the ossification morphology and bone continuity between each vertebrae have become clear. Previously, we had described ossification morphology at each disc segment that had been divided into 3 groups: the connection department, coating part, and non-connection department of OPLL. We had used MDCT to measure SCCSA during flexion and extension, and SCCSA did not show statistically significant differences in ossification morphology. It is possible that myelopathy is aggravated by dynamic factors, even in the connection department of OPLL. 4) However, those classifications were rough. Therefore, we reclassified these groups more finely, and examined ROM at each segment using a new classification. Ossification morphology at each disc segment was divided into 6 groups: covered disc, covered vertebra, unconnected vertebra, connected vertebra (continuous), connected vertebra (localized), and others. The average ROM in the covered vertebra group was quite similar to that in the unconnected vertebra group. The average ROM in the connected vertebra (continuous) was quite similar to that in the connected vertebra (localized) group. We used the former classification to classify the covered vertebra group and unconnected vertebra group as the coating part. Similarly, we had classified the connected vertebra (continuous) group and connected vertebra (localized) group as the connection department. It is not necessary to each distribute, re-classification that we increase cases is desirable. The influence of dynamic factors on the cervical spine has been investigated by flexion extension magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). 7) Dynamic factors have been proposed to be involved in the pathogenesis of CSM. However, the pathomechanism of myelopathy in C-OPLL remains unknown. Matsunaga et al. 8,9) showed that in patients with C-OPLL, involvement of not only chronic pathological compressive factors caused by OPLL but also of circulatory and dynamic factors were thought to be important in the development and aggravation of myelopathy. Morio et al. 10) suggested that important factors in the onset or aggravation of myelopathy are related to pathological compression by OPLL, cervical soft disc herniation, a developmentally narrow spinal canal, and a local or non-proportional hypermobility. Previously, we 4) reported that SCCSA by MDCT was measured to elucidate the influence of dynamic factors. There were no significant differences in the dynamic changes of SCCSA between the connection department, coating part, and non-connection department of OPLL. It is thought that SCCSA in patients with C-OPLL gradually becomes narrower. 11) It has also been suggested that the influence of dynamic factors is less in patients with mature continuous OPLL. However, this concept does not always apply to patients with continuous OPLL. Acute spinal cord injury associated with C-OPLL can be induced by minor cervical trauma,
7 ROM OF PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OPLL 227 and there is often radiographic evidence of trauma, termed cervical spinal cord injuries without radiographic evidence of trauma (SCIWORET). Schneider et al. 12) described the pathogenesis of central cord injury in the cervical spine as the result of a hyperextension mechanism, with subsequent compression of bony spur, a herniated disc, or a buckled ligamentum flavum. Onishi et al. 13) reported that SCIWORET with C-OPLL occurred at the edge of OPLL or OALL. Previously, we reported that the incidence of spinal cord injury in the stoppage department of ossification was 64%. 5) However, morphology of stoppage department had been unclear. There were no significant differences between the adjacent intervertebral disc in connected vertebrae and others for each group, but the average ROM of the connected vertebra (continuous and localized) group was significantly lower than that of the covered disc group and normal control group. Dynamic factors were reduced at the continuous segment: therefore, frequency of SCIWORET at the continuous segment may be less likely to happen from other segments. The limitations of this study were that the examination of the spinal cord changes relied on MRI signal intensities. Second, it will be necessary to examine the differences between ROM based on MDCT and ROM based on X-ray. Examination of these relationships will be necessary to help select the appropriate surgical method. We should closely observe the natural course of patients with C-OPLL from dynamic factors even in patients with mature C-OPLL, and it will be necessary to consider SCIWORET with respect to dynamic factors. CONCLUSIONS This study was performed to measure ROM in patients with C-OPLL by MDCT, and to investigate the influence of dynamic factors on the spinal cord. And ROM of adjacent intervertebral disc in connected vertebrae (continuous and localized) and those of others were investigated for each group. Ossification morphology at each disc segment was divided into 6 groups: covered disc, covered vertebra, unconnected vertebra, connected vertebra (continuous), connected vertebra (localized), and others. The average ROM of covered disc group was significantly higher than that of connected vertebra (continuous, localized). The average ROM of connected vertebra (continuous) group was significantly lower than that of covered disc group, others group, and normal control. There was no significant difference between ROM of adjacent intervertebral disc in connected vertebrae and others, but the average ROM of the connected vertebra group was significantly lower than that of the covered disc group and normal control group. Dynamic factor was reduced at continuous segment, but it was not increased in adjacent intervertebral disc. CONFLICT OF INTEREST Each author certifies that they had no commercial associations (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest/licensing arrangement, etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article. REFERENCES 1) Sumi M, Kataoka O, Sawamura S, Ikeda M, Mukai H. Radiological analysis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Rinsho seikei geka, 1998; 33(11): (in Japanease). 2) Liu H, Li Y, Chen Y, Wu W, Zou D. Cervical curvature, spinal cord MRIT2 signal, and occupying ratio
8 228 Keigo Ito et al. impact surgical approach selection in patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Eur Spine J, 2013; 22(7): ) Tsuyama N. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1984; 184: ) Ito K, Yukawa Y, Machino M, Kato F. Spinal cord cross-sectional area during flexion and extension in the patients with cervical ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament. Eur Spine J, 2013; 22(11): ) Ito K, Yukawa Y, Machino M, Kato F. Range of motion and spinal cord cross-sectional areas according to the ossification type of cervical ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament. Rinsho seikei geka, 2013; 48(9): (in Japanease). 6) Morita D, Yukawa Y, Nakashima H, Ito K, Yoshida G, Machino M, Kanbara S, Iwase T, Kato F. Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane. Eur Spine J, 2014 Mar; 23(3): ) Iwasaki M, Kawaguchi Y, Kimura T, Yonenobu K. Long-term results of expansive laminoplasty for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine: more than 10 years follow up. J Neurosurg, 2002; 96 (2 Suppl): ) Matsunaga S, Nakamura K, Seichi A, Yokoyama T, Toh S, Ichimura S, Satomi K, Endo K, Yamamoto K, Kato Y, Ito T, Tokuhashi Y, Uchida K, Baba H, Kawahara N, Tomita K, Matsuyama Y, Ishiguro N, Iwasaki M, Yoshikawa H, Yonenobu K, Kawakami M, Yoshida M, Inoue S, Tani T, Kaneko K, Taguchi T, Imakiire T, Komiya S. Radiographic predictors for the development of myelopathy in patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: a multicenter cohort study. Spine, 2008; 33(24): ) Matsunaga S, Komiya S, Toyama Y. Risk factors for development of myelopathy in patients with cervical spondylotic cord compression. Eur Spine J, 2013; May 23. [Epub ahead of print] 10) Morio Y, Nagashima H, Teshima R, Nawata K. Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy in 60 consecutive patients with cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spinal Cord, 1999; 37(12): ) Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Taketomi E, Yamaguchi M, Okano T. The natural course of myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in cervical spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1994; 305: ) Schneider RC, Cherry G, Pantek H. The syndrome of acute central cervical spinal cord injury; with special reference to the mechanisms involved in hyperextension injuries of cervical spine. J Neurosurg, 1954; 11(6): ) Onishi E, Sakamoto A, Murata S, Matsushita M. Risk factors for acute cervical spinal cord injury associated with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine, 2012; 37(8):
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery,Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine,Nagoya,Japan 2
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 583 589, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.4.583 ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of sagittal alignment and range of motion of the cervical spine using multi-detector- row computed tomography
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 583 589, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.4.583 ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of sagittal alignment and range of motion of the cervical spine using multi-detector- row computed tomography
Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane
 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
Disclosures: T. Yoshii: None. T. Yamada: None. T. Taniyama: None. S. Sotome: None. T. Kato: None. S. Kawabata: None. A. Okawa: None.
 Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy in 60 consecutive patients with cervical ossi cation of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Original Investigation. Byung-Wan CHOI. INTRODUCTION Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament ABSTRACT
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.16196-15.1 Received: 25.09.2015 / Accepted: 07.12.2015 Published Online: 01.06.2016 Original Investigation Clinical and Radiological Characteristics of Ossification of the Posterior
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.16196-15.1 Received: 25.09.2015 / Accepted: 07.12.2015 Published Online: 01.06.2016 Original Investigation Clinical and Radiological Characteristics of Ossification of the Posterior
Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion
 Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion of the cervical spine: a comparative study of radiographic data from 1016 patients with cervical spondylotic
Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion of the cervical spine: a comparative study of radiographic data from 1016 patients with cervical spondylotic
Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy. Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86
 Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy 1 Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86 Yukawa, Yasutsugu; Kato, Fumihiko; Ito, Keigo; Horie, Yumiko; Nakashima,
Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy 1 Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86 Yukawa, Yasutsugu; Kato, Fumihiko; Ito, Keigo; Horie, Yumiko; Nakashima,
S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA
 AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics
 Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging
 Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
Narrative Review Cervical Ossified Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
 Narrative Review Cervical Ossified Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Introduction Cervical ossified posterior longitudinal ligament is a common cause of myelopathy. It is frequently encountered in busy spine
Narrative Review Cervical Ossified Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Introduction Cervical ossified posterior longitudinal ligament is a common cause of myelopathy. It is frequently encountered in busy spine
CMEARTICLE * * * Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed
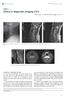 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
ASJ. Risk Factor Analysis for C5 Palsy after Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Asian Spine Journal.
 Asian Spine Journal 298 Satoshi Clinical Baba et al. Study http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2016.10.2.298 Risk Factor Analysis for C5 Palsy after Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
Asian Spine Journal 298 Satoshi Clinical Baba et al. Study http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2016.10.2.298 Risk Factor Analysis for C5 Palsy after Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
We performed CT myelography in 38 patients
 Posterior movement and enlargement of the spinal cord after cervical laminoplasty Ikuo Aita, Koichiro Hayashi, Yasuyoshi Wadano, Takeshi Yabuki From the University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan We performed
Posterior movement and enlargement of the spinal cord after cervical laminoplasty Ikuo Aita, Koichiro Hayashi, Yasuyoshi Wadano, Takeshi Yabuki From the University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan We performed
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Introduction SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Radiological Examination of Postoperative Cervical Alignment and Stability in Patients with Dialysis-Associated Spondylosis Excluding Destructive Spondyloarthropathy:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Radiological Examination of Postoperative Cervical Alignment and Stability in Patients with Dialysis-Associated Spondylosis Excluding Destructive Spondyloarthropathy:
Kazunari Takeuchi Æ Toru Yokoyama Æ Atsushi Ono Æ Takuya Numasawa Æ Kanichiro Wada Æ Taito Itabashi Æ Satoshi Toh
 Eur Spine J (2008) 17:415 420 DOI 10.1007/s00586-007-0553-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Limitation of activities of daily living accompanying reduced neck mobility after laminoplasty preserving or reattaching the
Eur Spine J (2008) 17:415 420 DOI 10.1007/s00586-007-0553-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Limitation of activities of daily living accompanying reduced neck mobility after laminoplasty preserving or reattaching the
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 J Neurosurg Spine 19:431 435, 2013 AANS, 2013 Upper cervical cord compression due to a C-1 posterior arch in a patient with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and a kyphotic cervical spine
J Neurosurg Spine 19:431 435, 2013 AANS, 2013 Upper cervical cord compression due to a C-1 posterior arch in a patient with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and a kyphotic cervical spine
Minamide A*, Yoshida M*, Yamada H*, Hashizume H*, NakagawaY*, Iwasaki H*, Tsutsui S*, Hiroyuki Oka H**.
 Efficacy of Posterior Segmental Decompression Surgery for Pincer Mechanism in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy -A retrospective case control study using propensity score matching Minamide A*, Yoshida M*,
Efficacy of Posterior Segmental Decompression Surgery for Pincer Mechanism in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy -A retrospective case control study using propensity score matching Minamide A*, Yoshida M*,
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 06
 What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
Key Primary CPT Codes: Refer to pages: 7-9 Last Review Date: October 2016 Medical Coverage Guideline Number:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
Dynamic Mri of the Cervical Spine An Important Tool in Planning Surgical Treatment of Cervical Compressive Myelopathy
 International Journal of Neurosurgery 2018; 2(1): 17-22 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijn doi: 10.11648/j.ijn.20180201.14 Dynamic Mri of the Cervical Spine An Important Tool in Planning Surgical
International Journal of Neurosurgery 2018; 2(1): 17-22 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijn doi: 10.11648/j.ijn.20180201.14 Dynamic Mri of the Cervical Spine An Important Tool in Planning Surgical
흉추척수증을유발한황색인대골화증의골절 - 증례보고 -
 대한척추외과학회지제 14 권제 1 호 Journal of Korean Spine Surg. Vol. 14, No. 1, pp 52~56, 2007 흉추척수증을유발한황색인대골화증의골절 - 증례보고 - 하기용 김영훈 # 지원희 $ 가톨릭대학교의과대학강남성모병원정형외과, 성모자애병원정형외과 #, 강남성모병원영상의학과 $ Fracture of Ossification
대한척추외과학회지제 14 권제 1 호 Journal of Korean Spine Surg. Vol. 14, No. 1, pp 52~56, 2007 흉추척수증을유발한황색인대골화증의골절 - 증례보고 - 하기용 김영훈 # 지원희 $ 가톨릭대학교의과대학강남성모병원정형외과, 성모자애병원정형외과 #, 강남성모병원영상의학과 $ Fracture of Ossification
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Introduction SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Cervical Kyphotic Deformity after Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament with Normal Sagittal Spinal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Cervical Kyphotic Deformity after Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament with Normal Sagittal Spinal
Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI /s
 Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0515-1 TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access Intraoperative evaluation using mobile computed tomography in anterior cervical
Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0515-1 TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access Intraoperative evaluation using mobile computed tomography in anterior cervical
Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki 3), Masatsune Yamagata 1), Yoshikazu Ikeda 1), Fumitake Nakajima 1)
 Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review
 Systematic review Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy 35 35 42 Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review Authors Anoushka
Systematic review Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy 35 35 42 Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review Authors Anoushka
Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis
 35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
Yoshifumi Kudo, 1 Tomoaki Toyone, 1 Toshiyuki Shirahata, 1 Tomoyuki Ozawa, 1 Akira Matsuoka, 1 Yoichi Jin, 2 and Katsunori Inagaki 1. 1.
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1250810, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1250810 Case Report A Case of Successful Foraminotomy for Severe Bilateral C5 Palsy following Posterior
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1250810, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1250810 Case Report A Case of Successful Foraminotomy for Severe Bilateral C5 Palsy following Posterior
Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up
 Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up Minori Kato*, Hiroaki Nakamura**, Koji Tamai**, Kazunori Hayashi**, Akira Matsumura**, Sadahiko
Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up Minori Kato*, Hiroaki Nakamura**, Koji Tamai**, Kazunori Hayashi**, Akira Matsumura**, Sadahiko
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS
 Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
Spinal Imaging. ssregypt.com. Mamdouh Mahfouz MD
 Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Magnetic resonance image (MRI) is a useful tool for
 SPINE Volume 40, Number 6, pp 392-398 2015, Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved. DIAGNOSTICS Abnormal Findings on Magnetic Resonance Images of the Cervical Spines in 1211 Asymptomatic Subjects
SPINE Volume 40, Number 6, pp 392-398 2015, Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved. DIAGNOSTICS Abnormal Findings on Magnetic Resonance Images of the Cervical Spines in 1211 Asymptomatic Subjects
INTRODUCTION.
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.5.442 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (5) : 442-447, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.5.442 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (5) : 442-447, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures
 9 Cervical Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures that have been in use for a long time with established efficacy in the treatment of radiculopathy and myelopathy caused by pathologies including
9 Cervical Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures that have been in use for a long time with established efficacy in the treatment of radiculopathy and myelopathy caused by pathologies including
Department of Neurological Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
 online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2014;10(2):60-65 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.60 Midline Splitting Cervical Laminoplasty Using Allogeneic
online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2014;10(2):60-65 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.60 Midline Splitting Cervical Laminoplasty Using Allogeneic
Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic resonance imaging study evidence
 See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
Jing Tao Zhang 1, Lin Feng Wang 1, Yue Ju Liu 2, Jun Ming Cao 1, Jie Li 1, Shuai Wang 1 and Yong Shen 1*
 Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:267 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0728-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between developmental canal stenosis and surgical results of anterior decompression
Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:267 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0728-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between developmental canal stenosis and surgical results of anterior decompression
SpineFAQs. Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment
 SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy
 Original Study Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy Lorenzo Nigro 1, Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Marika Rullo 2, Antonio Santoro 1, Roberto Delfini 1
Original Study Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy Lorenzo Nigro 1, Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Marika Rullo 2, Antonio Santoro 1, Roberto Delfini 1
Morphological Patterns of the Anterior Median Fissure in the Cervical Spinal Cord Evaluated by Computed Tomography After Myelography
 Neurospine 2018;15(4):388-393. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1836112.056 Neurospine pissn 2586-6583 eissn 2586-6591 Original Article Corresponding Author Yuki Oichi https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0225-8158
Neurospine 2018;15(4):388-393. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1836112.056 Neurospine pissn 2586-6583 eissn 2586-6591 Original Article Corresponding Author Yuki Oichi https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0225-8158
Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD
 CSRS 21st Instructional Course Wednesday, November 30, 2016 Laminoplasty/Foraminotomy: Why Fuse the Spine at all? Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD John A. Jane Distinguished Professor Departments of Neurosurgery
CSRS 21st Instructional Course Wednesday, November 30, 2016 Laminoplasty/Foraminotomy: Why Fuse the Spine at all? Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD John A. Jane Distinguished Professor Departments of Neurosurgery
Clinical Article. Key Words : Ossification Posterior longitudinal ligament Volume 3D analysis MIMICS.
 Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (4) : 441-447, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.0708.014 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Inter- and Intra-Observer Variability of the Volume of Cervical
Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (4) : 441-447, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.0708.014 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Inter- and Intra-Observer Variability of the Volume of Cervical
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
ORIGINAL PAPER. Surgical outcomes of decompressive laminoplasty with spinous process osteotomy to treat lumbar spinal stenosis
 Editors Choice ORIGINAL PAPER Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 1 9, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.1.1 Surgical outcomes of decompressive laminoplasty with spinous process osteotomy to treat lumbar spinal stenosis
Editors Choice ORIGINAL PAPER Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 1 9, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.1.1 Surgical outcomes of decompressive laminoplasty with spinous process osteotomy to treat lumbar spinal stenosis
Efficacy and results of expansive laminoplasty in patients with severe cervical myelopathy due to cervical canal stenosis
 Original Article Efficacy and results of expansive laminoplasty in patients with severe cervical myelopathy due to cervical canal stenosis D. Agrawal, B. S. Sharma, A. Gupta, V. S. Mehta Department of
Original Article Efficacy and results of expansive laminoplasty in patients with severe cervical myelopathy due to cervical canal stenosis D. Agrawal, B. S. Sharma, A. Gupta, V. S. Mehta Department of
Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C Anterior Cervical Interbody Fusion
 Journal of Surgery 2016; 4(6): 141-145 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20160406.14 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C
Journal of Surgery 2016; 4(6): 141-145 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20160406.14 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C
Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment of multi-segmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
Symptomatic ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament with stenosis of the cervical spine
 Spine Symptomatic ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament with stenosis of the cervical spine A REPORT OF SEVEN CASES J. Mizuno, H. Nakagawa, J. Song From Aichi Medical University, Aichi-gun
Spine Symptomatic ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament with stenosis of the cervical spine A REPORT OF SEVEN CASES J. Mizuno, H. Nakagawa, J. Song From Aichi Medical University, Aichi-gun
The Occupancy of the Components in the Cervical Spine and Their Changes with Extension and Flexion
 396 Original Article GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME The Occupancy of the Components in the Cervical Spine and Their Changes with Extension and Flexion Emrah Sayıt 1 Bayan Aghdasi 2 Michael D. Daubs 3 Jeffrey
396 Original Article GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME The Occupancy of the Components in the Cervical Spine and Their Changes with Extension and Flexion Emrah Sayıt 1 Bayan Aghdasi 2 Michael D. Daubs 3 Jeffrey
Surgical outcomes for lumbar spinal canal stenosis with coexisting cervical stenosis (tandem spinal stenosis): a retrospective analysis of 565 cases
 Yamada et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:60 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0765-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Surgical outcomes for lumbar spinal canal stenosis with coexisting
Yamada et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:60 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0765-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Surgical outcomes for lumbar spinal canal stenosis with coexisting
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment
 Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Outcomes of Secondary Laminoplasty for Patients with Unsatisfactory Results after Anterior Multilevel Cervical Surgery
 online ML Comm www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.57.1.36 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 57 (1) : 36-41, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical
online ML Comm www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.57.1.36 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 57 (1) : 36-41, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yi Yang, Hao Liu, Yueming Song, Tao Li
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
 283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
Junming Cao, Yongsheng Lin, Xiangbei Qi, Zhihong Wang, Yipeng Yang, Hehuan Xia, Bin Xu
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):741-746 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0067327 Original Article Effect of intramedullary signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images on prognosis in patients
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):741-746 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0067327 Original Article Effect of intramedullary signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images on prognosis in patients
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is a progressive
 literature review J Neurosurg Spine 24:77 99, 2016 A systematic review of clinical and surgical predictors of complications following surgery for degenerative cervical myelopathy Lindsay Tetreault, BSc,
literature review J Neurosurg Spine 24:77 99, 2016 A systematic review of clinical and surgical predictors of complications following surgery for degenerative cervical myelopathy Lindsay Tetreault, BSc,
ASJ. Analysis of the Prevalence and Distribution of Cervical and Thoracic Compressive Lesions of the Spinal Cord in Lumbar Degenerative Disease
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Cervical and thoracic Asian compressive Spine J 2014;8(1):19-26 lesions in http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.19 lumbar degenerative disease 19
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Cervical and thoracic Asian compressive Spine J 2014;8(1):19-26 lesions in http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.19 lumbar degenerative disease 19
We have reviewed the cervical spine radiographs
 THE CERVICAL SPINE IN ATHETOID CEREBRAL PALSY A RADIOLOGICAL STUDY OF 180 PATIENTS TAKEO HARADA, SOHEI EBARA, MONZOOR M. ANWAR, ATSUKO OKAWA, ICHIRO KAJIURA, KAZUO HIROSHIMA, KEIRO ONO From Osaka Police
THE CERVICAL SPINE IN ATHETOID CEREBRAL PALSY A RADIOLOGICAL STUDY OF 180 PATIENTS TAKEO HARADA, SOHEI EBARA, MONZOOR M. ANWAR, ATSUKO OKAWA, ICHIRO KAJIURA, KAZUO HIROSHIMA, KEIRO ONO From Osaka Police
Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients
 Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients Shota Takenaka* a, MD; Takashi Kaito b, MD; Noboru Hosono a, MD; Toshitada Miwa c, MD; Takenori Oda d, MD; Shinya Okuda d, MD; Tomoya
Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients Shota Takenaka* a, MD; Takashi Kaito b, MD; Noboru Hosono a, MD; Toshitada Miwa c, MD; Takenori Oda d, MD; Shinya Okuda d, MD; Tomoya
DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE PRABIN SHRESTHA ANISH M SINGH B&B HOSPITAL
 SPINAL CHAPTER, NESON DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE PRABIN SHRESTHA ANISH M SINGH B&B HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE Gradual loss of normal structure and function of spine with time Also
SPINAL CHAPTER, NESON DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE PRABIN SHRESTHA ANISH M SINGH B&B HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE Gradual loss of normal structure and function of spine with time Also
ELY ASHKENAZI Israel Spine Center at Assuta Hospital Tel Aviv, Israel
 nterior cervical decompression using the Hybrid Decompression Fixation technique, a combination of corpectomies and or discectomies, in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy J ORTHOP TRUM SURG
nterior cervical decompression using the Hybrid Decompression Fixation technique, a combination of corpectomies and or discectomies, in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy J ORTHOP TRUM SURG
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Spinal Cord (2005) 43, & 2005 International Spinal Cord Society All rights reserved /05 $
 (2005) 43, 503 507 & 2005 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/sc Case Report Postmortem study of the spinal cord showing snake-eyes appearance due to damage by
(2005) 43, 503 507 & 2005 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/sc Case Report Postmortem study of the spinal cord showing snake-eyes appearance due to damage by
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 J Neurosurg Spine 13:319 323, 2010 Using the T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging signal intensity ratio and clinical manifestations to assess the prognosis of patients with cervical ossification of
J Neurosurg Spine 13:319 323, 2010 Using the T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging signal intensity ratio and clinical manifestations to assess the prognosis of patients with cervical ossification of
Is high T-1 slope a significant risk factor for developing interlaminar bony fusion after cervical laminoplasty? A retrospective cohort study
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Spine 27:627 632, 2017 Is high T-1 slope a significant risk factor for developing interlaminar bony fusion after cervical laminoplasty? A retrospective cohort study Takeshi
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Spine 27:627 632, 2017 Is high T-1 slope a significant risk factor for developing interlaminar bony fusion after cervical laminoplasty? A retrospective cohort study Takeshi
Original Date: July 2008 Cervical ACDF - Anterior Decompression with Fusion Single or Multiple Levels
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: Original Date: July 2008 Cervical ACDF - Anterior Decompression with Fusion Single or Multiple Levels Page 1 of 13 Cervical Posterior Decompression
National Imaging Associates, Inc. CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: Original Date: July 2008 Cervical ACDF - Anterior Decompression with Fusion Single or Multiple Levels Page 1 of 13 Cervical Posterior Decompression
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY A NEUROSURGEON S VIEW A Preventable Journey to a wheelchair bound-life Dr H. BOODHOO F.C.S (Neurosurgery) Cervical Spondylosis Spinal Osteoarthritis
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY A NEUROSURGEON S VIEW A Preventable Journey to a wheelchair bound-life Dr H. BOODHOO F.C.S (Neurosurgery) Cervical Spondylosis Spinal Osteoarthritis
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma. Introduction. Anatomic Considerations 7/23/2018
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
En Bloc Cervical Laminoplasty While Preserving the Posterior Structure with Arcocristectomy in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.17440-16.0 Received: 03.03.2016 / Accepted: 05.03.3016 Published Online: 12.08.2016 Original Investigation En Bloc Cervical Laminoplasty While Preserving the Posterior Structure
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.17440-16.0 Received: 03.03.2016 / Accepted: 05.03.3016 Published Online: 12.08.2016 Original Investigation En Bloc Cervical Laminoplasty While Preserving the Posterior Structure
Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire: Part 3. Determination of reliability
 J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:321 326 DOI 10.1007/s00776-007-1131-4 Original article Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire: Part 3. Determination of reliability Mitsuru
J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:321 326 DOI 10.1007/s00776-007-1131-4 Original article Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire: Part 3. Determination of reliability Mitsuru
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
3D imaging reformation was obtained. The 3D color imaging reformation was reviewed in a different high resolution setting.
 POST OPERATIVE SPINE WITH CONTRAST CLINICAL INDICATION: Low back pain, Patient is post operative status for L4/5 diskectomy TECHNIQUE: MRI of the lumbosacral spine was performed with multiplanar imaging
POST OPERATIVE SPINE WITH CONTRAST CLINICAL INDICATION: Low back pain, Patient is post operative status for L4/5 diskectomy TECHNIQUE: MRI of the lumbosacral spine was performed with multiplanar imaging
Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Expansive Open-door Laminoplasty With Titanium Miniplate Versus Sutures
 Expansive Open-door Laminoplasty With Titanium Miniplate Versus Sutures Guangdong Chen, MD; Zongping Luo, MD, PhD; Badri Nalajala, MD; Tao Liu, MD, PhD; Huilin Yang, MD, PhD abstract Full article available
Expansive Open-door Laminoplasty With Titanium Miniplate Versus Sutures Guangdong Chen, MD; Zongping Luo, MD, PhD; Badri Nalajala, MD; Tao Liu, MD, PhD; Huilin Yang, MD, PhD abstract Full article available
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome
 Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...)
 Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Soccer causes degenerative changes in the cervical spine. European Spine Journal, February 2004, 13(1):76-82
 Soccer causes degenerative changes in the cervical spine European Spine Journal, February 2004, 13(1):76-82 Alparslan Kartal, Brahim Yldran, Alparslan Enköylü and Feza Korkusuz FROM ABSTRACT: Background
Soccer causes degenerative changes in the cervical spine European Spine Journal, February 2004, 13(1):76-82 Alparslan Kartal, Brahim Yldran, Alparslan Enköylü and Feza Korkusuz FROM ABSTRACT: Background
Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Description
 Subject: Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Description Positional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows imaging
Subject: Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Description Positional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows imaging
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Influence of hinge position on the effectiveness of opendoor expansive laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 . 6. Influence of hinge position on the effectiveness of opendoor expansive laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy WAN Jun, XU Tian-tong*, SHEN Qing-feng, LI Hui-nan and XIA Ying-peng Abstract
. 6. Influence of hinge position on the effectiveness of opendoor expansive laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy WAN Jun, XU Tian-tong*, SHEN Qing-feng, LI Hui-nan and XIA Ying-peng Abstract
Abstract Study Design Prospective clinical study.
 812 Technical Report GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME Resection of Beak-Type Thoracic Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament from a Posterior Approach under Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring
812 Technical Report GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME Resection of Beak-Type Thoracic Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament from a Posterior Approach under Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring
Bony framework of the vertebral column Structure of the vertebral column
 5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
Cervical Degenerative Disease - Surgical Approaches to CSM 가톨릭의대인천성모병원척추센터 김종태
 KNS Main Topic Session Spine Surgery : Case-Based Lecture of Spinal Disease Cervical Degenerative Disease - Surgical Approaches to CSM 가톨릭의대인천성모병원척추센터 김종태 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy ( CSM ) (1984,
KNS Main Topic Session Spine Surgery : Case-Based Lecture of Spinal Disease Cervical Degenerative Disease - Surgical Approaches to CSM 가톨릭의대인천성모병원척추센터 김종태 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy ( CSM ) (1984,
Am I eligible for the TOPS study? Possibly, if you suffer from one or more of the following conditions:
 Am I eligible for the TOPS study? Possibly, if you suffer from one or more of the following conditions: Radiating leg pain Greater leg / buttock pain than back pain Severe pain sets in when walking as
Am I eligible for the TOPS study? Possibly, if you suffer from one or more of the following conditions: Radiating leg pain Greater leg / buttock pain than back pain Severe pain sets in when walking as
Key words: Professional Med J 2018;25(8): CERVICAL LAMINOPLASTY
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.29309/TPMJ/18.4872 1. MBBS Post graduate Trainee, 2. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 3. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 4. MBBS Honorary Researcher, 5. MBBS, FCPS
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.29309/TPMJ/18.4872 1. MBBS Post graduate Trainee, 2. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 3. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 4. MBBS Honorary Researcher, 5. MBBS, FCPS
Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Medicine Fuculty of Medical Sciences University of Fukui
 Quantitative analysis and prognostic value of changes in spinal cord signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Medicine
Quantitative analysis and prognostic value of changes in spinal cord signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Medicine
A Patient s Guide to Neck Pain. William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Neck Pain Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves in
A Patient s Guide to Neck Pain Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves in
The most common cause of CSM after middle age
 J Neurosurg Spine 19:288 292, 2013 AANS, 2013 Dynamic somatosensory evoked potentials to determine electrophysiological effects on the spinal cord during cervical spine extension Clinical article Yuichiro
J Neurosurg Spine 19:288 292, 2013 AANS, 2013 Dynamic somatosensory evoked potentials to determine electrophysiological effects on the spinal cord during cervical spine extension Clinical article Yuichiro
Neck Pain Following Cervical Laminoplasty: Does Preservation of the C2 Muscle Attachments and/or C7 Matter?
 42 Systematic Review Neck Pain Following Cervical Laminoplasty: Does Preservation of the C2 Muscle Attachments and/or C7 Matter? K. Daniel Riew 1 Annie L. Raich 3 Joseph R. Dettori 3 John G. Heller 2 1
42 Systematic Review Neck Pain Following Cervical Laminoplasty: Does Preservation of the C2 Muscle Attachments and/or C7 Matter? K. Daniel Riew 1 Annie L. Raich 3 Joseph R. Dettori 3 John G. Heller 2 1
Pott s kyphosis. University Affiliated Sixth People s Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai , P.
 QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine
 J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 99:251 256, 2003 Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine NAOHISA MIYAKOSHI, M.D., YOICHI SHIMADA,
J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 99:251 256, 2003 Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine NAOHISA MIYAKOSHI, M.D., YOICHI SHIMADA,
Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Spine Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Indiana University School of Medicine
 Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
Evaluation of Canal Diameter by MRI in Sudanese Population
 American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (ASRJETS) ISSN (Print) 2313-4410, ISSN (Online) 2313-4402 Global Society of Scientific Research and Researchers http://asrjetsjournal.org/
American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (ASRJETS) ISSN (Print) 2313-4410, ISSN (Online) 2313-4402 Global Society of Scientific Research and Researchers http://asrjetsjournal.org/
ASJ. Magnification Error in Digital Radiographs of the Cervical Spine Against Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measurements. Asian Spine Journal
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
