Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching.
|
|
|
- Bertha Walton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching
2 Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport
3 Part One: The Skeletal System
4 Main Part Bones Main Function Skeletal System Support the weight of the body Secondary Functions Leverage Protection Storage Blood Cell Production
5 Skeletal System Con t Types of Bones Long Short Flat Irregular Sesmoid Cells in Bones Osteocytes Osteoclasts Osteoblasts
6 Skeletal System Con t Bone and Growth Development Starts six weeks after fertilization Ends between 18 and 25 years Bone Closures different from bone to bone Babies do not fully develop their patella (knee caps) until around 18 months old Usual closures are 18 in women and 20 in men differences in sex hormones
7 Requirements for Normal Bone Growth Calcium and Phosphate Vitamin D Vitamins A and C Injury and Repair Fracture Classified based on appearance Transverse- break across the bone at a right angle Oblique- bone breaks at an angle Spiral- easily confused with oblique- bone is broken in more then 1 plane Comminuted- crushed bone
8 Skeletal Divisions 206 Separate Bones Axial Skull Vertebrae Thoracic Cage Ribs Sternum
9 Skeletal Divisions Con t Appendicular Skeleton Arms Legs Pectoral / Pelvic Girdles Major Bones Involved in Sports Upper Body Lower Body Joints / Articulations Synarthrosis- offer no mobility (skull) Amphiarthrosis- Some mobility (vertebrae) Diarthrosis- freely moveable joints (shoulder, hip)
10 Movements Gliding Special Movements Inversion Eversion Dorsiflexion Plantarflexion Opposition Protraction Retraction Elevation Depression Angular Motions Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Circumduction Rotation Pronation Supination
11 Types of Joints Gliding Clavicle and Manubrium Hinge Knee and Elbow Pivot - Vertebrae Ellipsoidal - Scaphoid Saddle Thumb and Trapezium Ball and Socket Hip and Shoulder
12 Part Two: The Muscular System
13 Muscular System The three types/ Main Functions Cardiac- Heart (involuntary) Smooth- controlled directly by the autonomic nervous system. (involuntary) ex: intestines, lunges Skeletal- control movement of the body (voluntary) Movements Flexors Extensors Adductors Abductors
14 Tendons Muscular System Connect muscles to bones Muscles contract=> pull on the tendons=> pull on the muscles => causes movement Strain tendons and muscles Ligaments Connect bone to bone Connect at the ends of muscles and keep them from slipping and sliding, and force them to bend Sprain ligaments
15 Major Skeletal Muscles Facial Neck Shoulder Arm Forearm Thorax/ Back Abdomen Hip Pelvis Thigh Leg Lower Leg
16 HEAD Injuries Concussions Lacerations Fractures Eye Teeth
17 Neck Injuries Whiplash Strains Hyperextension
18 Shoulder Injuries Dislocations Separations Rotator cuff
19 Shoulder injuries Bursitis Impingement Stingers/ Burners
20 Arm Injuries Bicep tendonitis Strains Torn Biceps
21 Elbow Injuries Medial Epicondylitis (Little League elbow) Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis elbow) Bursitis Dislocations
22 Forearm Injuries Breaks Radius Ulna
23 Wrist Injuries Sprains Strains Tendonitis Dislocations Breaks
24 Finger Injuries Dislocations Breaks Boutonniere Finger Deformity Swan neck deformity Dislocated Finger
25 Most Common Injuries Thorax Ribs: Break Fractures Intercostals Muscle Strain Contusions Abdomen Strains Internal Injuries Back Strains Sprains Discs Problems
26 Most Common Injuries Hip Pointer Pelvis/ Hip Hip Pointer Groin Strains Contusions Bursitis Tendonitis Sports Hernia Sciatica Fractures Hip Flexor Lower Body Quad/ Hamstring Strains Tears
27 Knee Injuries ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL Dislocation Dislocated Patella ACL Tear MCL Tear LCL Tear
28 Knee Injuries Cont. Patellar Tendonitis Tendonitis (Patella) Bursitis IT Band Syndrome Chondromalacia Osgood- Schlatter Bursitis of the knee Osgood- Schlatter
29 Lower Leg Injuries Shin Splints Strains Fractures Stress Fractures Calf Strain Tears Achilles Tendonitis Bursitis Stress Fx of Tibia Shin Splints
30 Dislocations Fractures Sprains Tendonitis Ankle Injuries
31 Feet/ Toe Injuries Turf Toe Stress Fractures Turf Toe Tendonitis Plantar Fasciitis
32 Feet/ Toe Injuries Heel Spurs Bursitis Bunions Corns/ Calluses Bunion
33 Toe/ Feet Cont. Flat Feet Falling Arch Hammer Toe Plantar Warts Flat Foot Hammer Toe
34 Questions???????
Chapter 09 Articulations Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
Introduction. Physiology. Classification of Bones. Anatomy of a Long Bone. Anatomy of a Long Bone. Skeletal System and Joint Movements.
 Chapter 13 Skeletal System and Joint Movements Susan G. Salvo Introduction Skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints 206 bones in the body Bone is living tissue Skeletal system
Chapter 13 Skeletal System and Joint Movements Susan G. Salvo Introduction Skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints 206 bones in the body Bone is living tissue Skeletal system
Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems
 Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems Review the Types of Bones Articulations Classification of Joints (Articulations) Joint Where two bones interact Three functional classes of joint
Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems Review the Types of Bones Articulations Classification of Joints (Articulations) Joint Where two bones interact Three functional classes of joint
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Bellwork: Copy the vocabulary.
 Bellwork: Copy the vocabulary. Arthr- joint Burs- sac Carp- wrist Chondr- cartilage Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Meta- beyond Myelo- bone marrow Osteo- bone Peri- around Pod- foot Poro- pores in the
Bellwork: Copy the vocabulary. Arthr- joint Burs- sac Carp- wrist Chondr- cartilage Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Meta- beyond Myelo- bone marrow Osteo- bone Peri- around Pod- foot Poro- pores in the
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 9 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 9 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Joints can be classified structurally as A) bony. B) fibrous. C) cartilaginous. D) synovial. E) All of the answers are correct. 2)
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 9 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Joints can be classified structurally as A) bony. B) fibrous. C) cartilaginous. D) synovial. E) All of the answers are correct. 2)
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE. CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?
 PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Assignment 2: Human Anatomy
 Assignment 2: Human Anatomy Chapter 2 Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Anatomy? 1. Which of the following is not a feature of the anatomical position: A) The body stands erect. B) The body is facing forward.
Assignment 2: Human Anatomy Chapter 2 Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Anatomy? 1. Which of the following is not a feature of the anatomical position: A) The body stands erect. B) The body is facing forward.
Arthrology the study of joint structure, function and dysfunction. Sentenced to Life in the Joint
 Arthrology Arthrology the study of joint structure, function and dysfunction Sentenced to Life in the Joint Kinesiology study of musculo-skeletal movement Articulations any point where two bones meet (joint)
Arthrology Arthrology the study of joint structure, function and dysfunction Sentenced to Life in the Joint Kinesiology study of musculo-skeletal movement Articulations any point where two bones meet (joint)
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
Skeletal System. Chapter 7.1. Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction:
 Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL
 CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
The Skeletal System: Articulations Pearson Education, Inc.
 8 The Skeletal System: Articulations Introduction The body cannot move without joints Movements are linked to the range of joint action Joints (arthroses) are connections between bones that may or may
8 The Skeletal System: Articulations Introduction The body cannot move without joints Movements are linked to the range of joint action Joints (arthroses) are connections between bones that may or may
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 9 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 229) 1. A joint or articulation or arthrosis is a point of contact between neighboring bones, between cartilage and bones, or
Chapter 9 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 229) 1. A joint or articulation or arthrosis is a point of contact between neighboring bones, between cartilage and bones, or
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Chapter 5-Skeletal System
 Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Introduction 1. List the functions of joints. 2. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Introduction 1. List the functions of joints. 2. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Types of Joints 1. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible at the joint. (p. 268) 2.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Types of Joints 1. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible at the joint. (p. 268) 2.
Boardworks Ltd Types of Synovial Joint
 1 of 37 Types of Synovial Joint Definition: 2 of 37 3 of 37 3. Freely movable or synovial joints 90% of the joints in the body are synovial joints. They are freely movable. Synovial joints contain synovial
1 of 37 Types of Synovial Joint Definition: 2 of 37 3 of 37 3. Freely movable or synovial joints 90% of the joints in the body are synovial joints. They are freely movable. Synovial joints contain synovial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R. Joints: Part A. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
Muscle Tissue. Isometric Contraction. Isotonic Contractions 11/22/2016. Muscles. Anatomy Two Joints And Movements
 Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL
 LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
9.1 Joints. Objectives Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints
 Joints 9.1 Joints Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints Joints have both structural and functional classifications: The criteria for classifying joints structurally are anatomical
Joints 9.1 Joints Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints Joints have both structural and functional classifications: The criteria for classifying joints structurally are anatomical
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
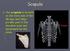 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Exercise 13. Articulations and Body Movements
 Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Joints. Agenda. Joints. Structural and Functional Classification of Articulations
 Joints Structural and Functional Classification of Articulations Agenda Joint Basics Classification Structural Joint Details Joint Stability Movements of Synovial Joints Shape Classification of Synovial
Joints Structural and Functional Classification of Articulations Agenda Joint Basics Classification Structural Joint Details Joint Stability Movements of Synovial Joints Shape Classification of Synovial
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Chapter 8 Joints & Skeletal Movement
 Chapter 8 Joints & Skeletal Movement Classification of joints is by functional group (the amount of movement possible), and structural group (how the bones are held together). Functional Group Structural
Chapter 8 Joints & Skeletal Movement Classification of joints is by functional group (the amount of movement possible), and structural group (how the bones are held together). Functional Group Structural
Chapter 6 part 2. Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 6 part 2 Skeletal Muscles of the Body Basic Principles 600 + muscles in the human body (you are required to learn 45, lucky kids)! Skeletal Muscles pull on bones Origin of a muscle = point of attachment
Chapter 6 part 2 Skeletal Muscles of the Body Basic Principles 600 + muscles in the human body (you are required to learn 45, lucky kids)! Skeletal Muscles pull on bones Origin of a muscle = point of attachment
Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Three systems of the body work in coordination to perform various movements of the body. These are: A System of Bones (Osteology), A System of Muscles
Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Three systems of the body work in coordination to perform various movements of the body. These are: A System of Bones (Osteology), A System of Muscles
COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION
 COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION Definition of sports medicine Pre-participation physical exam Epidemiology of sports injuries injury rates for various sports sports risks relative to
COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION Definition of sports medicine Pre-participation physical exam Epidemiology of sports injuries injury rates for various sports sports risks relative to
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology
 Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Articulations Chapter 9
 Articulations Chapter 9 Biology 210 Instructor: John McGill Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell Supplemental Notes: Beth Wyatt Last updated: October 2, 2007 INTRODUCTION TO ARTICULATIONS DEFINITION Articulations
Articulations Chapter 9 Biology 210 Instructor: John McGill Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell Supplemental Notes: Beth Wyatt Last updated: October 2, 2007 INTRODUCTION TO ARTICULATIONS DEFINITION Articulations
Chapter 7 Skeletal System. Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions.
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles tendonitis, criteria for full competition in, 164 165 description of, 164 patient education in, 165 prophylactic support in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles tendonitis, criteria for full competition in, 164 165 description of, 164 patient education in, 165 prophylactic support in,
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION
 SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers. Workbook 11 The articular system
 NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 11 The articular system Contents Workbook 11 The articular system 1 11.1 Aim 3 11.2 Learning outcomes 3 11.3 The articular system 4 11.4 Individual
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 11 The articular system Contents Workbook 11 The articular system 1 11.1 Aim 3 11.2 Learning outcomes 3 11.3 The articular system 4 11.4 Individual
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
Human Body. Bones, Joints and Muscles
 Human Body Bones, Joints and Muscles 1 Bone cranium mandible clavicle sternum humerus ribs pelvis ulna femur patella phalanges phalanges vertebrae Also known as skull lower jaw collarbone breastplate upper
Human Body Bones, Joints and Muscles 1 Bone cranium mandible clavicle sternum humerus ribs pelvis ulna femur patella phalanges phalanges vertebrae Also known as skull lower jaw collarbone breastplate upper
Notes: The Skeletal System
 Date: Notes: The Skeletal System Humans have an endoskeleton that develops from of the mesoderm. Composed of o o o : connects bone-to-bone o : connects muscle-to-bone Functions: o o o o Divided into two
Date: Notes: The Skeletal System Humans have an endoskeleton that develops from of the mesoderm. Composed of o o o : connects bone-to-bone o : connects muscle-to-bone Functions: o o o o Divided into two
Types of Body Movements
 Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by
 Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by structure and by function: Structural classification focuses
Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by structure and by function: Structural classification focuses
Skeletal System: Articulations (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Skeletal System: Articulations (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Skeletal System: Articulations (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
The skeleton supports the body. The skeleton protects soft body parts The skeleton produces blood cells. The skeleton stores minerals and fat.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton supports the body. The bones of the legs support the entire body when we are standing, and the coxal bones of the pelvic girdle support the abdominal cavity.
SKELETAL SYSTEM SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton supports the body. The bones of the legs support the entire body when we are standing, and the coxal bones of the pelvic girdle support the abdominal cavity.
Understand the skeletal system:
 Understand the skeletal system: Including axial and appendicular skeleton All joints in the body All major bones Development of bones & bone growth Training effects on the skeletal system All movements
Understand the skeletal system: Including axial and appendicular skeleton All joints in the body All major bones Development of bones & bone growth Training effects on the skeletal system All movements
The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide
 DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
The Articular System OBJECTIVES ACTIVITIES. A. Completion
 C H A P T E R 8 The Articular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name and describe the three types of joints. 2. Name the two types of synarthroses joints. 3. Name
C H A P T E R 8 The Articular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name and describe the three types of joints. 2. Name the two types of synarthroses joints. 3. Name
YOGA ANATOMY. Part Three - Bones. Yoga Teacher Training Robin Bennett 200 RYT
 YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
Body Organizations Flashcards
 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
Diarthrosis Joints - Freely Moveable Joints
 Reprinted with permission from the Aquatic Exercise Association (AEA) www.aeawave.com Anatomy Gets Real By June M Chewning BS, MS For fitness professionals, anatomy is the never-ending learning challenge.
Reprinted with permission from the Aquatic Exercise Association (AEA) www.aeawave.com Anatomy Gets Real By June M Chewning BS, MS For fitness professionals, anatomy is the never-ending learning challenge.
WTC II Term 3 Notes & Assessments
 Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Introduction. Fibrous Joints. 8.1: Types of Joints. Cartilaginous Joints. Fibrous Joints 12/14/2016. Chapter 08 Lecture Outline
 Introduction Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Joints (Articulations): Functional junctions between bones Bind
Introduction Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Joints (Articulations): Functional junctions between bones Bind
Articulations. Articulation. Joint between bones. Does not mean movement! Some joints are immovable; sutures.
 Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Skeletal System A&P Week 11
 Skeletal System A&P Week 11 Bones 206 bones in the body Smallest are in the middle ear cavity Malleus, incus, stapes Functions of Bone Framework and support Protection Contains/protects red bone marrow
Skeletal System A&P Week 11 Bones 206 bones in the body Smallest are in the middle ear cavity Malleus, incus, stapes Functions of Bone Framework and support Protection Contains/protects red bone marrow
Ch. 8 Joints of the Skeletal System
 Ch. 8 Joints of the Skeletal System Part 1: Classifying Joints & Joint Movements Interactive pages 269-278 Types of Joints (AKA: Articulations) Structural Classification (type of tissue that binds the
Ch. 8 Joints of the Skeletal System Part 1: Classifying Joints & Joint Movements Interactive pages 269-278 Types of Joints (AKA: Articulations) Structural Classification (type of tissue that binds the
B DAYS SKELETAL SYSTEM UNIT GUIDE DUE THURSDAY 11/17
 B DAYS SKELETAL SYSTEM UNIT GUIDE DUE THURSDAY 11/17 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 10/10 10/11 - B 10/12 - A 10/13 - B 10/14 - A NO SCHOOL Unit quiz Presentations 10/17 - B 10/18 - A 10/19 -
B DAYS SKELETAL SYSTEM UNIT GUIDE DUE THURSDAY 11/17 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 10/10 10/11 - B 10/12 - A 10/13 - B 10/14 - A NO SCHOOL Unit quiz Presentations 10/17 - B 10/18 - A 10/19 -
Movement Terminology. The language of movement is designed to allow us to describe how the body moves through space.
 Movement Terminology The language of movement is designed to allow us to describe how the body moves through space. In exercise it allows us to communicate with other movement professionals so we can describe
Movement Terminology The language of movement is designed to allow us to describe how the body moves through space. In exercise it allows us to communicate with other movement professionals so we can describe
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES
 UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY Prof. Oluwadiya KS MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) http://www.oluwadiya.com What is anatomy? The study of the gross structure of the human body with the naked eyes and as well as microscopy.
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY Prof. Oluwadiya KS MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) http://www.oluwadiya.com What is anatomy? The study of the gross structure of the human body with the naked eyes and as well as microscopy.
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
Chapter 9 Joints. Classification of Joints. Fibrous Joints. Structural classification based upon: Functional classification based upon movement:
 Chapter 9 Joints Joints hold bones together but permit movement Point of contact between 2 bones between cartilage and bone between teeth and bones Arthrology = study of joints Kinesiology = study of motion
Chapter 9 Joints Joints hold bones together but permit movement Point of contact between 2 bones between cartilage and bone between teeth and bones Arthrology = study of joints Kinesiology = study of motion
Student Objectives. When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives:
 Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: Classification of Joints 1. Define joint or articulation. 2. Classify joints
Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: Classification of Joints 1. Define joint or articulation. 2. Classify joints
Joints. Vi Michelle Austin
 Joints Vi Michelle Austin Joints Overview A joint, otherwise known as an articulation, is a point at which points connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull bones) and provide mechanical
Joints Vi Michelle Austin Joints Overview A joint, otherwise known as an articulation, is a point at which points connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull bones) and provide mechanical
9/26/2012. Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & Arthrokinematics (how the joints move) Planes & Axes. Planes & Axes continued
 Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & (how the joints move) Planes & Axes Planes of Action = Three fixed lines of reference along which the body is divided. Each plane is at right angles (or perpendicular)
Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & (how the joints move) Planes & Axes Planes of Action = Three fixed lines of reference along which the body is divided. Each plane is at right angles (or perpendicular)
QUICK ASSESSMENT: CONCEPT MAP
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Body Planes & Positions
 Learning Objectives Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how it is used to reference the body. Distinguish
Learning Objectives Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how it is used to reference the body. Distinguish
CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS
 CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt
CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt
The Skeletal System. Chapter 8
 The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme
 YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme Half Term/Term Learning objective Learning activity Differentiation and extension Bones. Knowledge of the bones at the following locations: head/neck cranium, vertebrae
YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme Half Term/Term Learning objective Learning activity Differentiation and extension Bones. Knowledge of the bones at the following locations: head/neck cranium, vertebrae
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect. Two classification methods are used to categorize joints:
 Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect Two classification methods are used to categorize joints: Functional classification Structural classification Functional classification
Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect Two classification methods are used to categorize joints: Functional classification Structural classification Functional classification
I. Introduction. Unit Two. of the Skeletal System. II. Classification of Joints. URLs for this chapter:
 8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
2º ESO - PE Workbook - IES Joan Miró Physical Education Department THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
17a A&P:! Skeletal System - Joint Actions and Articulations
 17a A&P:! Skeletal System - Joint Actions and Articulations 17a A&P:! Skeletal System - Joint Actions and Articulations! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes
17a A&P:! Skeletal System - Joint Actions and Articulations 17a A&P:! Skeletal System - Joint Actions and Articulations! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Joints. Articulations Arthroses
 Joints Articulations Arthroses 1 Joints, defined Points of contact between Two bones Bone and teeth Joint classification: 2 schemes Functional classification degree of movement permitted Structural classification
Joints Articulations Arthroses 1 Joints, defined Points of contact between Two bones Bone and teeth Joint classification: 2 schemes Functional classification degree of movement permitted Structural classification
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
Table of Contents. Introduction to the Teacher...1. Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
