LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Spine. After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify:
|
|
|
- Briana Bruce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Positioning for Exams of the Spine. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify: 4-1. Identify specifications for proper placement of the anatomical structures of the spine listed below: AP thoracic spine. Lateral thoracic spine. Lateral cervical spine. AP C-spine. AP open mouth C-spine. RPO or LPO oblique C-spine. Swimmer s lateral cervico-thoracic spine. AP lumbar spine. Lateral lumbar spine. Lateral sumbosacral articulation. RPO and LPO lumbar spine. AP lumbosacral articulation joint. Lateral lumbosacral articulation joint. AP axial sacroiliac articulation. Biliateral posterior oblique. SUGGESTION After reading and studying the assignment, complete the exercises. These exercises will help you to achieve the lesson objectives. MD
2 LESSON 4 POSITIONING FOR EXAMS OF THE SPINE Section I. PROJECTIONS OF THE THORACIC SPINE 4-1. THE ANTERIOR-POSTERIOR THORACIC SPINE (T-SPINE) MD
3 MD
4 4-2. THE LATERAL THORACIC SPINE (T-SPINE) MD
5 Continue with Exercises MD
6 EXERCISES, LESSON 4, SECTION I MATCHING: For exercises 1 through 2, match the position with the anatomical structure(s) that the position demonstrates. Enter the letter that corresponds to your choice in the space provided. 1. AP thoracic spine. a. Thoracic vertebral bodies, intervertebral joint spaces. 2. Lateral thoracic b. Thoracic vertebral bodies, intervertebral joint spine. spaces, and spinous processes. MULTIPLE- CHOICE. For exercises 3-8, select the ONE word or phrase that BEST completes the statement or BEST answers the question. 3. What is the appropriate letter marker for a lateral thoracic spine? a. Side closest to the cassette. b. Corresponding to the side up. c. Outside of the conefield so it will not interfere with the part. 4. What is the appropriate letter marker for an AP thoracic spine? a. Side closest to the cassette. b. Side up. c. Corresponding side. d. Side down. 5. The technical factor for an AP or a lateral T-spine is: a. 14 x 17 LW B. b. 14 x 17 LW NB. c. 14 x 17 CW. d. 14 x 17 CW NB. MD
7 6. The conefield for an AP T-spine or a lateral T-spine is: a. FFC. b. 10 X 17. c. 7 X 17 LW. d. 5 X The proper patient and part position for an AP thoracic spine is: a. Patient in lateral recumbent position, knees flexed, arms at right angles to body, CR perpendicular to film holder. b. Patient supine, midsagittal plane perpendicular to the table, legs fully extended but not locked. c. Patient supine coronal plane rotated 45 degrees. d. Patient suipine, median plane perpendicular and over film centerline, knees flexed, soles of feet on table. 8. The proper patient and part position for a lateral thoracic spine is: a. Patient in lateral recumbent position, knees flexed, arms at right angles to body, CR perpendicular to film holder. b. Patient supine, midsagittal plane perpendicular to the table, legs extended. c. Patient supine coronal plane rotated 45 degrees. d. Median plane perpendicular and over film centerline, knees flexed, lower back making contact with the table so as to prevent injury, soles of feet on table. Check Your Answers on Next Page MD
8 SOLUTIONS, LESSON 4, SECTION I 1. b (para 4-1) 2. a (para 4-2) 3. a (para 4-2) 4. c (para 4-1) 5. a (paras 4-1, 4-2) 6. c (paras 4-1, 4-2) 7. d (para 4-1) 8. a (para 4-2) MD
9 Section II. PROJECTIONS OF THE CERCICAL SPINE 4-3. LATERAL CERVICAL SPINE (C-SPINE) a. C-Spine Routine. A cervical spine routine consist of an AP, a lateral (swimmer s view if the entire C-7 vertebra cannot be demonstrated on the lateral), and an AP open mouth. As a rule, the lateral C-spine is the first view that should be obtained since it shows all seven cervical vertebrae. Additional views that may be required are the obliques. b. Special Precautions. In the event of a trauma, be sure to obtain the authorization of the radiologist or the attending physician before removing the cervical collar. Only after viewing the radiographs for the lateral cervical spine and ascertaining that there is no fracture or other damage to the spine can the physician authorize removal of the collar. Never remove the cervical collar prior to having the lateral view cleared by a radiologist or the attending physician. MD
10 MD
11 4-4. ANTERIOR-POSTERIOR CERVICAL SPINE MD
12 MD
13 4-5. OPEN MOUTH C-SPINE MD
14 MD
15 4-6. RIGHT POSTERIOR OBLIQUE OR LEFT POSTERIOR OBLIQUE C-SPINE a. Right Posterior Oblique: The right posterior oblique (RPO) position in which the right post aspect of the body is closest to the film. b. Left Posterior Oblique: The left posterior oblique position (LPO) in which the left posterior aspect of the body is closest to the film. MD
16 MD
17 4-7. SWIMMER S LATERAL CERVICOTHORACIC SPINE MD
18 Continue with Exercises MD
19 EXERCISES, LESSON 4, SECTION II MATCHING: For exercises 1 through 5, match the position with the anatomical structure(s) that the position demonstrates. Enter the letter that corresponds to your choice in the space provided. 1. Lateral C-spine. a. Dens (odontoid process) and the vertebral body of C-2, lateral masses of C-1, and zygapophyseal joints between C-1 and C AP C-spine. b. Cervical vertebral bodies, intervertebral joint space, articular pillars, spinous processes, zygapophyseal joints. 3. AP open mouth. c. C-3 through C-7, to include vertebral bodies, C-spine. space between pedicles, intervertebral disc spaces, and spinous process. 4. RPO or LPO oblique d. Intervertebral foramina and pedicles farthest C-spine. from the film. 5. Swimmer s lateral e. Lower cervical upper thoracic vertebral bodies, cervico-thoracic intervertebral disc spaces, and zygapophyseal spine. joints. MULTIPLE- CHOICE. For exercises 6-9, select the ONE word or phrase that BEST completes the statement or BEST answers the question. 6. The body should be rotated for an oblique C-spine. a. 20 degrees. b. 30 degrees. c. 45 degrees. d. 90 degrees. MD
20 7. The proper patient and part position for an AP cervical spine is: a. Patient standing or seated; part centered; coronal plane rotated 45 degrees to film; if possible, median plane of head parallel to film; acanthiomeatal line parallel to floor. b. Patient upright; median plane perpendicular to and over film center; acanthiomeatal line perpendicular to film; mouth open to full extent. c. Patient seated/standing; shoulder against film; median plnae parallel to film; acanthiomeatal line parallel to floor; patient holding sandbags with shoulders relaxed and arms hanging to side. d. Patient upright; median plane perpendicular to and over the film center; acanthiomeatal line perpendicular to film. 8. When positioning the patient for a/an, one arm is raised and the other lowered, and the head is supported at the level of the spine with and the long axis of the thoracic and cervical spine. a. Swimmer s lateral cervico-thoracic spine. b. RPO or LPO oblique c-spine. c. AP open mouth c-spine. d. AP c-spine. e. Lateral c-spine. 9. Before the radiologist or attending physician authorizes removal of a cervical collar, he will have viewed the radiograph for the to ascertain that there is no fracture or other damage to the spine. a. AP c-spine. b. Lateral c-spine. c. AP open mouth c-spine. d. Oblique c-spine. Check Your Answers on Next Page MD
21 SOLUTIONS, LESSON 4, SECTION II 1. b (para 4-3) 2. c (para 4-4) 3. a (para 4-5) 4. d (para 4-6) 5. e (paras 4-7) 6. c (para 4-6) 7. d (para 4-4) 8. a (para 4-7) 9. b (para 4-3b) MD
22 Section III. PROJECTIONS OF THE LUMBAR SPINE 4-8. ANTERIOR-POSTERIOR LUMBAR SPINE A lumbo-sacral spine routine consists of the AP, lateral, and lateral lumbosacral articulation (spot L-5/S-1) views. Additional projections that may be requested are the obliques and the AP lumbosacral articulation. MD
23 MD
24 4-9. LATERAL LUMBAR SPINE MD
25 MD
26 4-10. LATERAL LUMBOSACRAL ARTICULATION MD
27 MD
28 4-11. RIGHT POSTERIOR OBLIQUE AND LEFT POSTERIOR OBLIQUE LUMBAR SPINE MD
29 Continue with Exercises MD
30 EXERCISES, LESSON 4, SECTION III MATCHING: For exercises 1 through 4, match the position with the anatomical structure(s) that the position demonstrates. Enter the letter that corresponds to your choice in the space provided. 1. AP lumbar spine. a. L-5/S-1 joint space in lateral position. 2. Lateral lumbar b. Zygapophyseal joints. spine. 3. Oblique lumbar. c. Lumbar vertebrae, intervertebral joints, L-5/S-1 spine. junction. 4. Lateral lumbosacral d. Lumbar vertebral bodies, intervertebral joints, articulation. laminae. MULTIPLE- CHOICE. For exercises 5-10, select the ONE word or phrase that BEST completes the statement or BESTanswers the question. 5. What is centered to the film for an AP lumbar spine? a. ASIS. b. Greater trochanter. c. Level of iliac crest. d. Xyphoid process. 6. When viewing an RPO lumbar spine film, what is being demonstrated? a. Intervertebral formina of side away. b. Interverbral foramina of side down. c. Zygapophyseal joints of left side. d. Zygapophyseal joints of right side. MD
31 7. Why is a radiolucent sponge placed under the patient s waist for a lateral lumbar spine? a. For the patient s comfort. b. To aid in immobilization. c. To bring the long axis of the spine parallel to the table. d. To decrease dorsal kyphosis. 8. What is centered to the film for a lumbosacral articulation? a. The level of the iliac chest. b. The level of the ASIS. c. The level of the greater trochanter. d. Midway between the superior prominence of the iliac crest and the ASIS. 9. What is the degree of rotation of the coronal plane for an oblique lumbar spine? a. 60 degrees. b. 45 degrees. c. 30 degrees. d. 15 to 20 degrees. 10. What is the routine for a lumbar spine exam? a. AP and lateral. b. AP, lateral, and lumbosacral articulation (L-5/S-1). c. AP, lateral, and obliques. d. AP, lateral, obliques, and lumbosacral articulation (L-5/S-1). Check Your Answers on Next Page MD
32 SOLUTIONS, LESSON 4, SECTION III 1. d (para 4-8) 2. c (para 4-9) 3. b (para 4-11) 4. a (para 4-10) 5. c (para 4-8) 6. d (para 4-11) 7. c (para 4-9) 8. d (para 4-10) 9. b (para 4-11) 10. b (para 4-8) MD
33 Section IV. PROJECTIONS OF THE LUMBOSACRAL AND SACROILIAC ARTICULATIONS ANTERIOR-POSTERIOR LUMBOSACRAL ARTICULATION (JOINT) A lumbo-sacral articulation routine consist of a AP lumbosacral articulation as well as a lateral view. MD
34 MD
35 4-13. LATERAL LUMBOSACRAL ARTICULATION (JOINT) MD
36 MD
37 4-14. ANTERIOR-POSTERIOR AXIAL SACROILIAC ARTICULATION A sacroiliac articulation (or sacroiliac joint) routine consist of a view of the AP axial sacroiliac as both (bilateral) posterior oblique sacroiliac joints. MD
38 MD
39 4-15. BILATERAL OBLIQUE SACROILIAC ARTICULATION For comparison, both posterior oblique sacroiliac joints are radiographed. MD
40 Continue with Exercises Return to Table of Contents MD
41 EXERCISES, LESSON 4, SECTION IV MATCHING: For exercises 1 through 4, match the position with the anatomical structure(s) that the position demonstrates. Enter the letter that corresponds to your choice in the space provided. 1. AP lumbosacral a. Sacroiliac joints, L-5/S-1 junction, sacrum, and articulation. coccyx. 2. Lateral lumbosacral b. Lumbosacral joint space (L-5/S-1) and articulation. sacroiliac joints in AP projection. 3. AP axial sacroiliac c. Sacroiliac joints on the elevated side. joint. 4. Posterior obliquel d. Lumbosacral joint space (L-5/S-1) in the lateral sacroiliac joint. position. MULTIPLE- CHOICE. For exercises 5-10, select the ONE word or phrase that BEST completes the statement or BEST answers the question. 5. What degree of rotation (posterior obliqueing) of the coronal plane is required for a posterior oblique sacroiliac joint? a. 25 to 30 degrees. b. 30 to 35 degrees. c. 40 to 45 degrees. d. 75 to 80 degrees. MD
42 6. The proper patient and part position for an AP axial sacroiliac articulation is: a. Patient supine with median plane perpendicular and over center line of film; legs fully extended with no support under the knees. b. Patient laterally recumbent; knees flexed and arms at right angle to body; radiolucent material under the small of the waist; coronal plane perpendicular to the film. c. Patient supine; legs fully extended with support under knees for comfort; midsagittal plane aligned to midline of film; no rotation of pelvis. d. Patient supine; coronal plane rotated 25 to 30 degrees to the center of the film. 7. The technical factors for a posterior oblique sacroiliac articulation is: a. 10 x 12 LW B. b. 8 x 10 LW B. c. 10 x 12 CW NB. d. 8 x 10 LW NB. 8. The central ray for an AP lumbosacral articulation is: a. Horizontal perpendicular. b. Vertical perpendicular. c. Males, 30 degrees cephalic; females 35 degrees cephalic. MD
43 9. The part position for a lateral lumbosacral articulation is: a. A point 1 inch to the elevated ASIS to the center of the film. b. Midway between the superior prominence of the iliac crest and the ASIS. c. Along the midsagittal plane, midway between the ASIS and the symphysis pubis to the center of the film. d. The midpoint between the AISI projected to the center of the film. 10. The CR for an AP axial sacroliac articulation is directed to: a. A point 1 inch to the elevated ASIS to the center of the film. b. A point 1.5 inches inferior to the iliac crest on the coronal plane to the center of the film. c. Along the midsagittal plane, midway between the ASIS and the symphysis pubis to the center of the film. d. The midpoint between the level of the ASIS and symphysis pubis. Check Your Answers on Next Page MD
44 SOLUTIONS,LESSON 4, SECTION IV 1. b (para 4-12) 2. d (para 4-13) 3. a (para 4-14) 4. c (para 4-15) 5. a (para 4-15) 6. c (para 4-14) 7. a (para 4-15) 8. c (para 4-12) 9. b (para 4-13) 10. d (para 4-14) Return to Table of Contents MD
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park):
 Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park): (Lower Extremity): patient is fully gowned / no artifacts / properly shielded (exposure for femur and below : hold still, don t move ) (exposure
Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park): (Lower Extremity): patient is fully gowned / no artifacts / properly shielded (exposure for femur and below : hold still, don t move ) (exposure
Proteus XR/f Patient positioning guide
 Proteus XR/f Patient positioning guide PROTEUS XR/F Now a single digital x-ray room accommodates nearly all your radiographic studies. With extended tube coverage and wireless detectors, Proteus XR/f gives
Proteus XR/f Patient positioning guide PROTEUS XR/F Now a single digital x-ray room accommodates nearly all your radiographic studies. With extended tube coverage and wireless detectors, Proteus XR/f gives
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
Barium Enema RD Sheet
 SIMS POSITION Instruct patient to turn onto the left side, lean forward and about 35 to 40 degree, and knees are flexed right knee on the table, above and in front of the slightly flexed left knee This
SIMS POSITION Instruct patient to turn onto the left side, lean forward and about 35 to 40 degree, and knees are flexed right knee on the table, above and in front of the slightly flexed left knee This
Bony Thorax. Anatomy and Procedures of the Bony Thorax Edited by M. Rhodes
 Bony Thorax Anatomy and Procedures of the Bony Thorax 10-526-191 Edited by M. Rhodes Anatomy Review Bony Thorax Formed by Sternum 12 pairs of ribs 12 thoracic vertebrae Conical in shape Narrow at top Posterior
Bony Thorax Anatomy and Procedures of the Bony Thorax 10-526-191 Edited by M. Rhodes Anatomy Review Bony Thorax Formed by Sternum 12 pairs of ribs 12 thoracic vertebrae Conical in shape Narrow at top Posterior
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Country Health SA Medical Imaging
 Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222)
 Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Routine Guide EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION. 14x17 CW* 14x17LW 14x17LW. 14x17LW 14x17LW 14x17LW
 EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
Radiology of Cervical Spine Trauma. Cervical Spine Trauma. Imaging Standards. Canadian C. Spine Rule 11/28/2016
 Radiology of Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Steven J. Gould, D.C. Board Certified Chiropractic Radiologist Cleveland Chiropractic College, KC. MO. Radiology Residency at CCC, KC Cervical Spine Trauma Vertebral
Radiology of Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Steven J. Gould, D.C. Board Certified Chiropractic Radiologist Cleveland Chiropractic College, KC. MO. Radiology Residency at CCC, KC Cervical Spine Trauma Vertebral
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column
 Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings
 Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Vertebral Column. Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions. Cervical
 Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify body part terminology.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Positioning Terminology. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-23. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify body part terminology.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Positioning Terminology. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-23. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify body part terminology.
Radiography Protocols
 Radiography Protocols Upper Limb Second through Fifth Digits (Standard 3 views) First Digit (Thumb) (Standard 3 views) Hand (Standard 3 views) Wrist (Standard 4 views) Forearm (Standard 2 views) Elbow
Radiography Protocols Upper Limb Second through Fifth Digits (Standard 3 views) First Digit (Thumb) (Standard 3 views) Hand (Standard 3 views) Wrist (Standard 4 views) Forearm (Standard 2 views) Elbow
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW
 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE
 MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE Vertebrae are your friends Matthew Harper MS-IV LECTURE OBJECTIVES INTRODUCE THE MOST COMMON MODALITIES OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND BASIC TECHNIQUES FOR READING THESE IMAGES
MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE Vertebrae are your friends Matthew Harper MS-IV LECTURE OBJECTIVES INTRODUCE THE MOST COMMON MODALITIES OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND BASIC TECHNIQUES FOR READING THESE IMAGES
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar
 BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques. Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright
 Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright 2001-2006 Objectives Understand how joint range of motion & goniometric assessment is an important component
Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright 2001-2006 Objectives Understand how joint range of motion & goniometric assessment is an important component
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN. Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms.
 THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Upper Extremities. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Upper Extremities. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-25. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 5-1. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Upper Extremities. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-25. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 5-1. Identify
MOTION PALPATION GUIDE
 MOTION PALPATION GUIDE C1 What s happening C1 is moving anterior and superior on the occipital condyles causing a Superior atlas. What you feel - The t.p. s will move, bilaterally in the anterior direction,
MOTION PALPATION GUIDE C1 What s happening C1 is moving anterior and superior on the occipital condyles causing a Superior atlas. What you feel - The t.p. s will move, bilaterally in the anterior direction,
Spine. aus: Möller u.a., Pocket Atlas of Radiographic Positioning (ISBN ) 2009 Georg Thieme Verlag KG
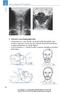 2 Cervical Spine: AP Projection Spine Criteria for a Good Radiographic View Odontoid process, axis and atlas are clearly visible through the open mouth, occiput does not obscure the odontoid, atlantoaxial
2 Cervical Spine: AP Projection Spine Criteria for a Good Radiographic View Odontoid process, axis and atlas are clearly visible through the open mouth, occiput does not obscure the odontoid, atlantoaxial
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives
 1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET
 Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET Purpose: It is the intention of this to provide a general description of the course, outline the required elements of the course and to lay the foundation for
Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET Purpose: It is the intention of this to provide a general description of the course, outline the required elements of the course and to lay the foundation for
Bone List Anatomy
 1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
How to use: Hold the Baseline scoliosis. Fabrication Enterprises Incorporated
 EVALUATION BASELINE BODY LEVEL / SCOLIOSIS METER 12-1090 12-1091 Baseline body level Use to determine whether body parts are properly aligned. Ideal for Scoliosis screening. Baseline scoliosis meter Measurements
EVALUATION BASELINE BODY LEVEL / SCOLIOSIS METER 12-1090 12-1091 Baseline body level Use to determine whether body parts are properly aligned. Ideal for Scoliosis screening. Baseline scoliosis meter Measurements
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology. ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations
 Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations Anthropology & Archaeology Anthropology is the study of the biological and cultural aspects of all humans in all places
Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations Anthropology & Archaeology Anthropology is the study of the biological and cultural aspects of all humans in all places
Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb AP; Lat. PA. PA; Lat.: Obls.; Elongated PA with ulnar deviation
 Projections Region Basic projections Additional / Modified projections Upper Limbs Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb ; Lat. PA Fingers PA; Lat. Wrist PA; Lat. Obls. Scaphoid Lunate Trapezium Triquetral
Projections Region Basic projections Additional / Modified projections Upper Limbs Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb ; Lat. PA Fingers PA; Lat. Wrist PA; Lat. Obls. Scaphoid Lunate Trapezium Triquetral
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Learning Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the bony structures of the pelvis. Describe in detail
PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Learning Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the bony structures of the pelvis. Describe in detail
Definition of Anatomy. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts.
 Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Types of Body Movements
 Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Information within the handout. Brief Introduction Anatomy & Biomechanics Assessment & Diagnosis Treatment through Muscle Energy
 Manual Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction of the Pelvis Through Muscle Energy Greenman s Priciples of Manual Medicine (5 th Ed.)- Lisa DeStefano,DO Speaker disclosure I declare I
Manual Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction of the Pelvis Through Muscle Energy Greenman s Priciples of Manual Medicine (5 th Ed.)- Lisa DeStefano,DO Speaker disclosure I declare I
human anatomy 2015 lecture four Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine
 Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam
 Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
SCALING Radiographic Technique
 SCALING Radiographic Technique SCALING FOR DIGITAL X-RAYS As images become filmless. Current planning practices with acetate sheets become difficult or obsolete. When images are printed to film sometimes
SCALING Radiographic Technique SCALING FOR DIGITAL X-RAYS As images become filmless. Current planning practices with acetate sheets become difficult or obsolete. When images are printed to film sometimes
Rotational Forces. : Their impact; our treatments
 Rotational Forces : Their impact; our treatments Lee Stang, LMT, LMBT, BCTMB NCBTMB Provider: 450217-06 bridgestohealthseminars.com bthseminars@gmail.com 860.985.5834 Facebook.com/BridgesToHealthSeminars
Rotational Forces : Their impact; our treatments Lee Stang, LMT, LMBT, BCTMB NCBTMB Provider: 450217-06 bridgestohealthseminars.com bthseminars@gmail.com 860.985.5834 Facebook.com/BridgesToHealthSeminars
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Imaging Decision Making: Recommended Radiographic Projections
 WSCC Clinics Protocol Adopted: 3/05 Imaging Decision Making: Recommended Radiographic Projections This document lists the routine, supplemental and alternative projections performed in the Diagnostic Imaging
WSCC Clinics Protocol Adopted: 3/05 Imaging Decision Making: Recommended Radiographic Projections This document lists the routine, supplemental and alternative projections performed in the Diagnostic Imaging
P V S MEMORIAL HOSPITAL LTD.
 SHOULDER XRAYS Instability Series o True AP (Grashey s) o Axillary o Stryker Notch view o True AP in Internal rotation o Scapular Y view o West Point view for Bony Bankart ( looks like modif axillary view)
SHOULDER XRAYS Instability Series o True AP (Grashey s) o Axillary o Stryker Notch view o True AP in Internal rotation o Scapular Y view o West Point view for Bony Bankart ( looks like modif axillary view)
bio4165 lab quiz 1 Posterior View Anterior View Lateral View Anterior View bio fall.quarter lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6
 B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
Guidelines for the Trunk test for Paracanoe Athletes. Trunk test guidelines for Paracanoe
 Guidelines for the Trunk test for Paracanoe Athletes Information Please note that the purpose of the pictures is to show the position of the athlete and classifier. The classifier s job is to assess function
Guidelines for the Trunk test for Paracanoe Athletes Information Please note that the purpose of the pictures is to show the position of the athlete and classifier. The classifier s job is to assess function
The sacrum is a complex anatomical structure.
 A Review Paper Rongming Xu, MD, Nabil A. Ebraheim, MD, and Nicholas K. Gove, MD Abstract Treatment in spinal disorders, sacroiliac joint disruption, and sacral fractures may involve instrumentation of
A Review Paper Rongming Xu, MD, Nabil A. Ebraheim, MD, and Nicholas K. Gove, MD Abstract Treatment in spinal disorders, sacroiliac joint disruption, and sacral fractures may involve instrumentation of
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Chiro-Tech IV Midterm Questions
 hiro-tech IV Midterm Questions 1. What is NOT a factor in shaping the Lumbar lordosis?. Wedge shaped L-S IV.. L5 vertebral body is wedge-shaped.. The size of the Sacrum.. Inclination of the vertebrae above
hiro-tech IV Midterm Questions 1. What is NOT a factor in shaping the Lumbar lordosis?. Wedge shaped L-S IV.. L5 vertebral body is wedge-shaped.. The size of the Sacrum.. Inclination of the vertebrae above
18th International Scientific Meeting of the VCFS Educational Foundation Steven M. Reich, MD. July 15-17, 2011 New Brunswick, New Jersey USA
 18th International Scientific Meeting of the VCFS Educational Foundation Steven M. Reich, MD July 15-17, 2011 New Brunswick, New Jersey USA SCOLIOSIS AND ITS TREATMENT Steven M. Reich, MD Assistant Clinical
18th International Scientific Meeting of the VCFS Educational Foundation Steven M. Reich, MD July 15-17, 2011 New Brunswick, New Jersey USA SCOLIOSIS AND ITS TREATMENT Steven M. Reich, MD Assistant Clinical
Digital Motion X-ray Cervical Spine
 NAME OF PATIENT: CASE STUDY 4 DATE OF REPORT: DATE OF EXAMINATION: REFERRING PHYSICIAN: TESTING FACILITY: Digital Motion X-ray Cervical Spine 1. In the neutral lateral projection: Shows reversal of the
NAME OF PATIENT: CASE STUDY 4 DATE OF REPORT: DATE OF EXAMINATION: REFERRING PHYSICIAN: TESTING FACILITY: Digital Motion X-ray Cervical Spine 1. In the neutral lateral projection: Shows reversal of the
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of th
 Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Spinal deformities, such as increased thoracic
 An Original Study Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation of Sagittal Imbalance: A New Radiographic Assessment Hossein Elgafy, MD, MCh, FRCS Ed, FRCSC, Rick Bransford, MD, Hassan Semaan, MD, and Theodore
An Original Study Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation of Sagittal Imbalance: A New Radiographic Assessment Hossein Elgafy, MD, MCh, FRCS Ed, FRCSC, Rick Bransford, MD, Hassan Semaan, MD, and Theodore
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Bone. Mental Foramen Mandible
 Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy.
 Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Functional Movement Test. Deep Squat
 Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Gonstead Technique Study Sheet Fall 2006
 Patient Lower Cervical Adjustments (C2-C7) PR Right index, distallateral Right posterior inferior spinous process P-A, R-L through pts opposite eye, *** along plane line of PL Left index, distallateral
Patient Lower Cervical Adjustments (C2-C7) PR Right index, distallateral Right posterior inferior spinous process P-A, R-L through pts opposite eye, *** along plane line of PL Left index, distallateral
Medical Terminology. Unit 2
 Medical Terminology Unit 2 Students will apply medical terminology. Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how
Medical Terminology Unit 2 Students will apply medical terminology. Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE
 THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
The vault bones Frontal Parietals Occiput Temporals Sphenoid Ethmoid
 The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
OMT Without An OMT Table Workshop. Dennis Dowling, DO FAAO Ann Habenicht, DO FAAO FACOFP
 OMT Without An OMT Table Workshop Dennis Dowling, DO FAAO Ann Habenicht, DO FAAO FACOFP Cervical Somatic Dysfunction (C5 SR RR) - Seated 1. Patient position: seated. 2. Physician position: standing facing
OMT Without An OMT Table Workshop Dennis Dowling, DO FAAO Ann Habenicht, DO FAAO FACOFP Cervical Somatic Dysfunction (C5 SR RR) - Seated 1. Patient position: seated. 2. Physician position: standing facing
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
OUTLINE ANATOMY, RADIOGRAPHY,
 16 ABDOMEN R OUTLINE SUMMARY OF PROJECTIONS, 84 ANATOMY, 85 Abdominopelvic cavity, 85 SUMMARY OF ANATOMY, 86 SUMMARY OF PATHOLOGY, 86 EXPOSURE TECHNIQUE CHART, 87 ABBREVIATIONS, 87 RADIOGRAPHY, 88 Abdominal
16 ABDOMEN R OUTLINE SUMMARY OF PROJECTIONS, 84 ANATOMY, 85 Abdominopelvic cavity, 85 SUMMARY OF ANATOMY, 86 SUMMARY OF PATHOLOGY, 86 EXPOSURE TECHNIQUE CHART, 87 ABBREVIATIONS, 87 RADIOGRAPHY, 88 Abdominal
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System)
 Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
OMT Without An OMT Table. Ann L. Habenicht DO, FAAO, FACOFP, CS AAO Convocation- Student Program March12, 2015
 OMT Without An OMT Table Ann L. Habenicht DO, FAAO, FACOFP, CS AAO Convocation- Student Program March12, 2015 BASIC STUFF WE HAVE TO WADE THROUGH TO MAKE SURE WE RE ALL ON THE SAME PAGE A.T. Still To find
OMT Without An OMT Table Ann L. Habenicht DO, FAAO, FACOFP, CS AAO Convocation- Student Program March12, 2015 BASIC STUFF WE HAVE TO WADE THROUGH TO MAKE SURE WE RE ALL ON THE SAME PAGE A.T. Still To find
Anatomy - Reconnect with your Spine Muscles by NFPT Idea World 2016 : Session 449 Friday July 15th 9:40-11:30am Beverly Hosford, MA
 Anatomy - Reconnect with your Spine Muscles by NFPT Idea World 2016 : Session 449 Friday July 15th 9:40-11:30am Beverly Hosford, MA Posture Core Anatomy Awareness Action 1. Anatomy *Know the muscle attachments.
Anatomy - Reconnect with your Spine Muscles by NFPT Idea World 2016 : Session 449 Friday July 15th 9:40-11:30am Beverly Hosford, MA Posture Core Anatomy Awareness Action 1. Anatomy *Know the muscle attachments.
Dualer IQ TM The Smarter Inclinometer TM
 Dualer IQ TM The Smarter Inclinometer TM Published by JTECH Medical 470 Lawndale Dr., Ste G Salt Lake City, Utah 84115 801 478-0680 800 985-8324 www.jtechmedical.com Copyright 2005 JTECH Medical. All rights
Dualer IQ TM The Smarter Inclinometer TM Published by JTECH Medical 470 Lawndale Dr., Ste G Salt Lake City, Utah 84115 801 478-0680 800 985-8324 www.jtechmedical.com Copyright 2005 JTECH Medical. All rights
The Thoracic Cage ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process
ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
A B C. Breathing Concentration Control Centring Precision Flow
 Session Two A B C Breathing Concentration Control Centring Precision Flow Will be based on your group of participants. Ensure that your lesson plan content links to objectives What is the reason for prep?
Session Two A B C Breathing Concentration Control Centring Precision Flow Will be based on your group of participants. Ensure that your lesson plan content links to objectives What is the reason for prep?
2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
 CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
TRAINING THE CORE BEGIN WITH ONE SET OF ALL 17 EXERCISES FOR A TOTAL OF 250 REPS. NEXT, MOVE TO TWO SETS FOR A TOTAL OF 500 REPS.
 TRAINING THE CORE 1. LATERAL SIT UPS.X 20 (10 EACH SIDE) 2. HYPEREXTENSIONS.X 10 3. LEG HUGS...X 15 4. RUSSIAN TWIST X 20 (10 EACH SIDE) 5. HIP CURLS..X 14 (7 EACH LEG) 6. JACK KNIFES..X 10 7. REVERSE
TRAINING THE CORE 1. LATERAL SIT UPS.X 20 (10 EACH SIDE) 2. HYPEREXTENSIONS.X 10 3. LEG HUGS...X 15 4. RUSSIAN TWIST X 20 (10 EACH SIDE) 5. HIP CURLS..X 14 (7 EACH LEG) 6. JACK KNIFES..X 10 7. REVERSE
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Outline. Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures
 C-Spine Plain Films Outline Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures Epidemiology 7000-10000 c-spine injuries treated each year Additional 5000 die at the
C-Spine Plain Films Outline Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures Epidemiology 7000-10000 c-spine injuries treated each year Additional 5000 die at the
The Lower Limb. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
Radiography Log Book
 Radiography Log Book Radiography teaching occurs in constituent hospitals as part of working week. This unit of the log book deals with diagnostic radiography. Tuition in radiography will be carried out
Radiography Log Book Radiography teaching occurs in constituent hospitals as part of working week. This unit of the log book deals with diagnostic radiography. Tuition in radiography will be carried out
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D.
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
What is HARA chair? Young Jae Huh, M.D. Orthopedic Surgery. April 2015
 What is HARA chair? Young Jae Huh, M.D. Orthopedic Surgery April 2015 1. Correlated human anatomy - ---------------------------------------------------- 2 2. Changes in the spine & pelvis during a single-seat
What is HARA chair? Young Jae Huh, M.D. Orthopedic Surgery April 2015 1. Correlated human anatomy - ---------------------------------------------------- 2 2. Changes in the spine & pelvis during a single-seat
Skeletal System. Axial Division
 Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
Myoskeletal Alignment for Low Back, Hip, and Leg Pain DVDs
 Myoskeletal Alignment for Low Back, Hip, and Leg Pain DVDs Use these handy time markers to locate the specific treatment techniques on the Level 4 Dynamic Body 6 DVD set as demonstrated by Erik Dalton
Myoskeletal Alignment for Low Back, Hip, and Leg Pain DVDs Use these handy time markers to locate the specific treatment techniques on the Level 4 Dynamic Body 6 DVD set as demonstrated by Erik Dalton
Bony framework of the vertebral column Structure of the vertebral column
 5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
