Results of All-Inside Meniscal Repair With the FasT-Fix Meniscal Repair System
|
|
|
- Isaac Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Results of All-Inside Meniscal Repair With the FasT-Fix Meniscal Repair System Elias S. Kotsovolos, M.D., Michael E. Hantes, M.D., Dimitrios S. Mastrokalos, M.D., Olaf Lorbach, M.D., and Hans H. Paessler, M.D. Purpose: The goal of this prospective study was to evaluate the results of arthroscopic meniscal repair using the FasT-Fix repair system. Type of Study: Prospective case series. Methods: Sixty-one meniscal repairs with the FasT-Fix meniscal repair system in 58 patients with a mean age of 32.6 years were performed between 2001 and Concurrent anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction was performed in 36 patients (62%). All tears were longitudinal and located in the red/red or red/white zone. Criteria for clinical success included absence of joint-line tenderness, locking, swelling, and a negative McMurray test. Clinical evaluation also included the Tegner and Lysholm knee scores, and KT-1000 arthrometry. In addition, all patients were evaluated preoperatively with magnetic resonance imaging. Results: The average follow-up was 18 months (range, 14 to 28 months). Six of 61 repaired menisci (9.8%) were considered failures according to our criteria. Therefore, the success rate was 90.2%. Time required for meniscal repair averaged 11 minutes. Postoperatively, the majority of the patients had no restrictions in sports activities. The mean Lysholm significantly improved from 43.6 preoperatively to 87.5 postoperatively (P.001). Fifty-one patients (88%) had an excellent or good result according to the Lysholm knee score. Four patients had a restriction of knee joint motion postoperatively, and an arthroscopic arthrolysis was performed in 1 of them. Analysis showed that age, length of tear, simultaneous anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, chronicity of injury, and location of tear did not affect the clinical outcome. Conclusions: Our results show that arthroscopic meniscal repair with the FasT-Fix repair system provided a high rate of meniscus healing and appeared to be safe and effective in this group of patients. Level of Evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study, case series (no control group). Key Words: Meniscus repair All-inside technique Clinical results. From the Center for Knee, Foot Surgery and Sports Trauma, ATOS Clinic, Heidelberg, Germany. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Elias S. Kotsovolos, M.D., 2 Parodos Platias G. Stavrou str., Ioannina, Greece. lias14@hotmail.com 2006 by the Arthroscopy Association of North America /06/ $32.00/0 doi: /j.arthro Although meniscal repair was first reported more than 100 years ago by Annandale, 1 it did not gain appreciation until the last 2 decades. This is because the importance of the meniscus for the knee has been well established owing to laboratory and clinical investigations during the last 2 decades. 2-4 In addition, improvements in arthroscopic techniques and instrumentation in recent years permit a large number of surgeons to easily perform this procedure. Among the 3 arthroscopic techniques that are known today (inside-out, outside-in, and all-inside), the all-inside fixation with biodegradable products has increased in popularity because of its fast application and reduction of the risk of serious neurovascular complications. 5,6 However, there are several reports in the literature of complications directly associated with these devices such as chondral injuries and synovitis. 7-9 Another concern is the inferior strength of these devices in comparison with vertical sutures, which could be a critical factor contributing to meniscal healing according to some biomechanical studies There is today a plethora of devices for all-inside meniscal repair. Most of these have been tested in vitro but clinical results are not available for the Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery, Vol 22, No 1 (January), 2006: pp 3-9 3
2 4 E. S. KOTSOVOLOS ET AL. majority of them. One of these devices that has been recently introduced is the FasT-Fix meniscal repair system (Smith & Nephew). It combines the advantages of all-inside technique while providing high biomechanical properties. 13,14 Therefore, we designed a study to evaluate the clinical results and complications of arthroscopic meniscal repairs in a consecutive series using the FasT- Fix meniscal repair system, and to evaluate factors that could affect the healing rate. Our hypothesis was that the FasT-Fix meniscal repair system will provide clinical results equal to other similar meniscal repair systems. METHODS From June 2001 through December 2002, 64 arthroscopic meniscal repairs in 61 consecutive patients were performed by the senior author (H.H.P) with the FasT-Fix Meniscal Repair Suture System (Smith & Nephew) using the arthroscopic technique detailed below. During this period only this system was used for meniscal repair in our institution. Ten meniscal repairs using a hybrid fixation of sutures and the FasT-Fix System were performed but these cases were not part of this study. Inclusion criteria were (1) vertical full-thickness tear greater than 10 mm in length, (2) location of the tear less than 6 mm from the meniscocapsular junction, (3) no former meniscus surgery, (4) no evidence of arthritis during arthroscopy, and (5) fixation of the meniscus only with FasT-Fix. Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)-deficient knees were reconstructed using hamstrings autograft at the time of the meniscal repair. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained before initiating the study. All patients gave their informed consent to participate. Preoperatively, diagnosis of meniscal tear was based on clinical examination; special attention was paid to signs of meniscal tear, such as locking, tenderness on palpation of the joint line, presence or absence of effusion, and meniscal tests like McMurray and Appley test. Knee laxity was measured with the KT-1000 Arthrometer (MEDmetric, San Diego, CA). The Lysholm knee score 15 and Tegner activity score 16 were obtained to evaluate knee function. In addition, all patients underwent preoperative evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging. Surgical Technique Each device of FasT-Fix contains two 5-mm polymer suture bar anchors with a pre-tied self-sliding FIGURE 1. Components of the FasT-Fix meniscal repair system: delivery needle with the implant, depth penetration limiter, and split cannula. knot of No. 0 nonabsorbable USP braided polyester suture material. Also, there is a split cannula for easier introduction of the device into the knee joint, a depth penetration limiter, and a knot pusher suture cutter (Fig 1). General anesthesia was used in all patients. After diagnostic arthroscopy, the morphology of the meniscus tear was determined. The tear length and the rim width were recorded at the time of surgery. In case of a dislocated bucket-handle tear, reduction was performed. Tear edges were freshened with a meniscus rasp and shaver. Multiple perforations were made with microfracture awls in the meniscus rim to produce vascular channels and encourage bleeding in order to stimulate healing response. Using a meniscal depth probe the desired length of penetration is determined and then the depth limiter is trimmed accordingly, followed by the introduction of the Fast-Fix delivery needle through the split cannula. It was positioned so that it perpendicularly pierced the surface of the inner meniscal fragment and then was advanced into the peripheral meniscal fragment to the end of the depth penetration limiter (Fig 2). The needle was then withdrawn from the meniscus with a gentle oscillating motion, releasing the first anchor. Then the gold trigger was slid forward to advance the second implant. For a horizontal suture, the delivery needle was transferred 5 mm sideways and for a vertical one we placed it perpendicular to the tear (Fig 3). As soon as the second implant was inserted, the delivery needle was removed from the knee joint, leaving the free end of the sutures (Fig 4). Finally, the pre-tied self sliding knot was tensioned with the aid of the knot pusher suture cutter. The sutures could be cut with the knot
3 RESULTS OF MENISCAL REPAIR WITH FAST-FIX 5 FIGURE 4. Both suture bar anchors have been placed and the free end of the sutures is used to tighten the knot (demonstration in a cadaver knee). FIGURE 2. Placement of the first suture bar anchor in a medial meniscus tear (demonstration in a cadaver knee). pusher suture cutter or arthroscopic scissors. Sutures were applied to the femoral and the tibial site of the lesion. Postoperatively, all patients (isolated meniscal repair and meniscal repair with an ACL reconstruction) used a hinged brace and motion was restricted between 0 and 60 for the first 3 weeks with partial weight bearing, followed by another 3 weeks with an increase of range of motion between 0 and 90, and progression to full weight bearing by postoperative week 6. Jogging was permitted after week 10, and full activity at 5 months for all patients. Evaluation Methods An experienced sports medicine fellow (D.S.M) performed all the postoperative examinations. Using Barrett s criteria, 17 a repaired meniscus was considered healed if there was no joint-line tenderness or effusion, and a negative McMurray s test at the latest follow-up. If one or more of these parameters was present, the result was classified as a failure. Knee laxity was measured with the KT-1000 Arthrometer postoperatively and knee function in activities of daily living and in recreational and competitive sports was assessed using the Lysholm and Tegner activity scores. Statistics The paired t test was used for comparison of the preoperative and postoperative Lysholm and Tegner scores. Comparisons between subgroups of patients were performed using the Fisher Exact test as appropriate. Significance was set at P.05. RESULTS Two of 61 patients were lost to follow-up (they are living abroad) and 1 patient had a new severe trau- FIGURE 3. (A) After deployment of the first implant (arrow), the delivery needle is ready to pierce the meniscus again in order to release the second implant. (B) The second implant (arrow) is in place 4 to 5 mm from the first implant (demonstration in a cadaver knee).
4 6 E. S. KOTSOVOLOS ET AL. matic incidence 4 months postoperatively, resulting in ACL and medial meniscus rerupture plus a malleolar fracture. Consequently, all 3 of them (5%) were excluded from the study. Thus, 58 patients (61 menisci) constitute the subjects of this report. The mean follow-up period was 18 months (range, 14 to 28 months). Thirty-seven men (64%) and 21 women (36%) were included in the study population. The average age at the time of meniscal repair was 32.6 years (range, 16 to 54 years). The period from injury to meniscal repair ranged from 2 to 196 days (median, 76 days). Thirty (48%) meniscal tears were rated acute (injury-to-repair interval 3 weeks), and 31 (52%) tears were rated chronic (injury-to-repair interval 3 weeks). There were 22 (36%) isolated meniscal tears, and 39 (64%) were combined with arthroscopic ACL reconstruction. Three patients who underwent ACL reconstruction had medial and lateral meniscus tear. There were 25 right knees (43%) and 33 left knees (57%). The medial meniscus was affected in 34 cases (56%) and the lateral meniscus in 27 cases (44%). Twenty-two (36%) meniscal tears were located within a rim width of less than 3 mm (red-red zone), whereas 39 (64%) were within a rim width of 3 to 6 mm. The meniscal tears morphology included 61 (100%) longitudinal tears. The average length of the tears was 31.6 mm (range, 13 to 45 mm). There were 22 buckethandle tears (36%) and 10 of them were displaced at the time of operation. The number of FasT-Fix anchors used averaged 4.4 (range, 1 to 8). Additional operation time required for meniscal repair averaged 11 minutes per procedure. At the last follow-up, we found no symptoms of meniscal tears in 55 (90.2%) cases. One patient (1.6%) had a positive McMurray test and tenderness on joint-line palpation, 3 patients (5%) had tenderness on joint-line palpation, and 2 patients (3.2%) had tenderness on joint-line palpation plus effusion. No patient had locking episodes. These 6 cases (9.8%) were considered as failures. However, revision arthroscopy and a partial meniscectomy was necessary only in 2 cases, 1 and 9 months postoperatively. Overall, the Lysholm score increased to a mean value of 87.5 (range, ), which was statistically significant compared with the preoperative mean value of 43.6 (range, 18-61) (P.001, paired t test). Fifty-one patients (88%) had an excellent or good outcome, 6 patients (10.3%) had a fair result, and 1 patient (1.7%) had a poor result. For patients with concurrent ACL reconstruction, the Lysholm score improved significantly (P.001) from an average of 49.3 (range, 25-61) preoperatively to 88.2 (range, ) postoperatively. For patients with isolated meniscal repair, the Lysholm score improved significantly (P.001) from an average of 41.2 (range, 18-60) preoperatively to 86.8 (range, ) postoperatively. Overall, the mean preinjury Tegner activity score was 6.42 (range, 5-9). Preoperatively the mean preinjury Tegner activity score was 3.21 (range, 2-5) whereas the postoperative mean value was 5.7 (range, 5-8) and this difference was statistically significant (P.001, paired t test). For patients with concurrent ACL reconstruction, the Tegner activity score improved significantly (P.01) from an average of 2.9 (range, 2-5) preoperatively to 5.7 (range, 5-8) postoperatively. For patients with isolated meniscal repair, the Tegner activity score improved significantly (P.01) from an average of 3.5 (range, 2-5) preoperatively to 5.9 (range, 5-7) postoperatively. All patients had returned to full-time work. Also, at the last follow-up, all the knees were considered stable with negative Lachman and pivot-shift test and an average side-to-side difference of 1.9 mm (range, 0-5 mm) on maximum-manual KT-1000 arthrometer testing. Complications occurred in 7 of 58 patients. One patient, after combined meniscal repair and ACL reconstruction, had a painful hemarthrosis and underwent aspiration. Four patients, also after combined meniscal refixation and ACL reconstruction, had difficulties in regaining full flexion of the knee. In only 1 of them was an arthroscopic arthrolysis considered necessary, 3 months postoperatively; the rest of them had only 10 of flexion deficit after intensive physical therapy. Two patients with isolated meniscal repair complained of persistent knee joint swelling and erythema 1 month after the operation. They were treated with arthroscopic debridement, synovectomy, and antibiotic therapy. However, cultures obtained at debridement surgery were negative for bacteria. In both cases, diffuse synovitis was present but no chondral lesions were noted, the suture knot was barely visible, and the sides of the tear were maintained in good position. It is difficult to conclude if the menisci were healed because the time interval from the index operation was short. In addition, no chondral injuries were observed associated with the device. One of these patients had a persistent joint-line tenderness and underwent a revision arthroscopy and a partial meniscectomy. There were no neurovascular or other complications directly associated with the device. In an effort to identify factors that affect the results of meniscus repair, we compared patients with clinically healed menisci with the patients with
5 RESULTS OF MENISCAL REPAIR WITH FAST-FIX 7 TABLE 1. Factor Effect of 7 Factors on Outcome of Meniscus Repair Asymptomatic: No. of Repairs (%) clinically failed repairs. Parameters that were examined for their influence in the clinical result were age, chronicity of tear (time from injury to repair), length of tear, repair side (medial or lateral), location of tear (distance from the meniscocapsular junction), presence of complications, and ACL reconstruction at the time of meniscal repair (Table 1). Statistical analysis showed that none of these factors significantly affected the clinical outcome. DISCUSSION Symptomatic: No. of Repairs (%) Total P Value Chronicity 3 weeks 26 (84) 5 (16) weeks 29 (96.7) 1 (3.3) 30 Age 30 years 30 (90.9) 3 (9.1) years 25 (89.3) 3 (10.7) 28 Meniscus side.167 Medial 29 (85.3) 5 (14.7) 34 Lateral 26 (96.3) 1 (3.7) 27 Length of tear mm 30 (90.9) 3 (9.1) mm 25 (89.3) 3 (10.7) 28 Location of tear.256 Red/red 21 (95.5) 1 (4.5) 22 Red/white 34 (87.2) 5 (12.8) 39 ACL reconstruction.823 No 20 (90.9) 2 (9.1) 22 Yes 35 (89.8) 4 (10.2) 39 Complications.284 No 49 (90.8) 5 (9.2) 54 Yes 6 (85.7) 1 (14.3) 7 After the introduction of the biodegradable Meniscus Arrow by Bionx Implants (Blue Bell, PA) in 1993, 6 a large number of all-inside arthroscopic meniscal repair devices have been introduced to the market. Perhaps the most popular device is the Meniscus Arrow, and therefore several reports with clinical results using this device are available. 5,18-21 However, very few clinical studies are available for some of the newer meniscal devices, and for the majority of them no clinical data exist. In this study, the clinical results of 61 repaired menisci with the FasT-Fix meniscal repair system with an average follow-up of 18 months are presented. The success rate in this series was 90% (55 clinically healed menisci out of 61) according to the criteria of Barrett et al., 17 and 51 patients (88%) had an excellent or good result. Evaluation of meniscal healing after meniscal repair is performed using these or similar clinical criteria by the vast majority of the studies today Of course, we acknowledge that a meniscal repair without symptoms postoperatively does not always reflect the true status of the meniscus and that only second-look arthroscopy can verify healing of the meniscus or not, and this is a limitation of our study. According to Albrecht-Olsen et al., 6 the healing rate of the repaired menisci after second-look arthroscopy is lower than the clinical estimation. However, we used strict criteria to consider a clinical result as a success. For example, patients who had occasional soreness or minor symptoms in our study population were classified as failures, although their symptoms were not so intense as to require revision surgery. On the other hand, Morgan et al. 25 showed that clinical examination seems to be a reliable method of evaluating the status of repaired menisci. In this study, it was proved that clinical examination accurately predicted all failures in second-look arthroscopy, with no false positives. Clinical results similar to those in our study have been reported in other studies with meniscal repair devices. The success rate for the Meniscus Arrow ranged from 88% to 95% according to most recent studies. 6,18-21 The healing rate with the T-Fix system has been reported to be nearly 90%. 22 Laprell et al. 23 reported a success rate of 86% with the Mitek meniscal repair system. However, comparison is not always possible because several study groups used a different evaluation system. The need for repeat surgery (partial meniscectomy) was defined as failure in some studies. 20,26 When more strict criteria are used as in our study (joint-line tenderness, McMurray test, effusion), Barrett et al., 27 using the T-Fix system, reported an 81% healing rate. In our series, 4 patients had difficulty in regaining a full range of motion of their knee. All these patients underwent meniscal refixation in combination with ACL reconstruction. It is known from the literature that the risk of arthrofibrosis is increased in this type of surgery. 28 Because no patient with isolated meniscal repair developed such a problem, it seems unlikely that this restriction of knee motion was caused by the implants. We had 2 patients with knee joint swelling and erythema after meniscal refixation. Perhaps these 2 cases represent aseptic synovitis since no bacteria were identified. Aseptic synovitis after meniscal fixation with implants has been reported by others as a
6 8 E. S. KOTSOVOLOS ET AL. foreign-body reaction, 29,30 although the mechanism of synovitis is not yet fully understood. We had no other complications directly associated with the device in our series, such as broken implants or migration of the implants, as has been reported with other devices. 7-9 We believe also, as Barber et al. 13 stated, that since the implants of the FasT-Fix are embedded into the peripheral capsule chondral injury is unlikely, although we had the chance to document it only in the 2 cases of second-look arthroscopy. However, we agree with Miller et al. 31 that to avoid penetration of superficial structures including the skin, premeasurement of the desired depth using meniscal depth probe is required followed by trimming of the depth-limitation device. Although the strength of the repair device is only one factor contributing to meniscal healing, it is our opinion that our low failure rate is due to the fact that the FasT-Fix provides a high load at failure and stiffness at the repair site. Two biomechanical studies 13,14 found that the strength of the FasT-Fix meniscal repair system is comparable to that of vertical mattress sutures and superior to all the available meniscal devices in the market including the Meniscus Arrow. Even when the device is placed not vertically but horizontally as we did in most of the cases (which is technically much easier), the load to failure is not reduced. 13 Of course, we have no control group in our study to compare the FasT-Fix meniscal repair system to another alternative method, and this is another limitation of our study. It would be interesting if future studies compared this device with traditional suture techniques or other meniscal devices. However, our study has the advantage of a consecutive series of patients, operated by a single surgeon, using the same technique. Many factors such as age, chronicity of tear, length of tear, location of tear, and ACL reconstruction at the time of meniscal repair influence the outcome of meniscal repair according to reports in the literature. However, disagreement exists regarding the effect of each of these factors on meniscal healing. Our analysis showed that none of these factors significantly affects the clinical outcome. Some studies reported a higher healing rate (with a success rate of more than 90%) for meniscal tears with a rim width of less than 3 mm, 17,32 acute tears, 33,34 and tears in the lateral meniscus. 17,32 However, other studies found that the tear site (medial or lateral) or chronicity of the tear does not influence meniscal healing. Our results are in concurrence with those of other investigators who found no significantly different results between younger and older age groups, 33,34 and that tear length 17 is not a significant factor in meniscal healing. Most authors agree that simultaneous meniscal repair and ACL reconstruction creates a more favorable environment for meniscal healing because of greater intra-articular bleeding and fibrin clot formation. 17,18 However, De Haven et al. 35 reported that they had only 4% failures in isolated meniscal repairs with rim widths less than 3 mm; in their opinion, rim width is the primary factor and not simultaneous ACL reconstruction. CONCLUSIONS Meniscal repair with the FasT-Fix meniscal repair system provides excellent clinical results in the vast majority of patients, with a success rate of 90%, which is comparable to those of traditional suture techniques in this short-term follow-up study. However, studies with a long-term follow-up are needed to determine if the repaired menisci will maintain structural and functional integrity over time. In addition, we found that the system has the advantage of avoiding neurovascular complications. An acceptable failure rate using this device can be expected, even in chronic tears, in tears that extent to the red/white zone, and in patients older than 30 years. REFERENCES 1. Annandale T. An operation for displaced semilunar cartilage. BMJ 1885;1: Levy IM, Torzilli PA, Warren RF. The effects of medial meniscectomy on anterior-posterior motion of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1982;64: Shrive NG, O Connor JJ, Goodfellow JW. Load-bearing in the knee joint. Clin Orthop 1978;131: Walker PS, Erkman MJ. The role of menisci in force transmission across the knee. Clin Orthop 1975;109: Albrecht-Olsen P, Kristensen G, Burgaard P, Joengersen U, Toerholm C. The arrow versus horizontal suture in arthroscopic meniscus repair. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 1999;7: Albrecht-Olsen P, Kristensen G, Törmälä P. Meniscus buckethandle fixation with an absorbable Biofix tack: Development of a new technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 1993;1: Anderson K, Marx RG, Hannafin J, Warren RF. Chondral injury following meniscal repair with a biodegradable implant. Arthroscopy 2000;16: Bonshahi AY, Hopgood P, Shepard CJ. Migration of a broken arrow: A case report and review of the literature. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2004;12: Calder S, Myers PT. Broken arrow: A complication of meniscal repair. Arthroscopy 1999;15: Arnoczky SP, Lavagnino M. Tensile fixation strengths of absorbable meniscal repairs as a function of hydrolysis time. Am J Sports Med 2001;29:
7 RESULTS OF MENISCAL REPAIR WITH FAST-FIX Asik M, Sener N. Failure strength of repair devices versus meniscus suturing techniques. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2002;10: McDermott ID, Richards SW, Hallam P, Tavares S, Lavelle JR, Amis AA. A biomechanical study of four different meniscal repair systems, comparing pull-out strengths and gapping under cyclic loading. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2003;11: Barber FA, Herbert MA, Richards DP. Load to failure testing of new meniscal repair devices. Arthroscopy 2004;20: Borden P, Nyland J, Caborn DN, Pienkowski D. Biomechanical comparison of the FasT-Fix meniscal repair suture system with vertical mattress sutures and Meniscus Arrows. Am J Sports Med 2003;31: Lysholm J, Gillquist J. Evaluation of knee ligament surgery results with special emphasis on use of a scoring scale. Am J Sports Med 1982;10: Tegner Y, Lysholm J. Rating systems in the evaluation of knee ligament injuries. Clin Orthop 1985;198: Barrett GR, Field MH, Treacy SH, Ruff CG. Clinical results of meniscus repair in patients 40 years and older. Arthroscopy 1998;14: Gill SS, Diduch DR. Outcomes after meniscal repair using the Meniscus Arrow in knees undergoing concurrent anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy 2002;18: Huerel C, Mertens F, Verdonk R. Biofix resorbable Meniscus Arrow for meniscal ruptures: Results of a 1-year follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2000;8: Petsche TS, Selesnick H, Rochman A. Arthroscopic meniscal repair with bioabsorbable arrows. Arthroscopy 2002;18: Steenbrugge F, Verdonk R, Huerel C, Verstraete K. Arthroscopic meniscus repair: Inside-out technique vs. Biofix Meniscus Arrow. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2004; 12: Asik M, Sen C, Erginsu M. Arthroscopic meniscal repair using T-fix. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2002;10: Laprell H, Stein V, Petersen W. Arthroscopic all-inside meniscus repair using a new refixation device: A prospective study. Arthroscopy 2002;18: Tsai AM, McAllister DR, Chow S, Young CR, Hame SL. Results of meniscal repair using a bioabsorbable screw. Arthroscopy 2004;20: Morgan CD, Wojtys EM, Casscells CD, Casscells SW. Arthroscopic meniscal repair evaluated by second look arthroscopy. Am J Sports Med 1991;19: Jones HP, Lemos MJ, Wilk RM, Smiley PM, Gutierrez R, Schepsis AA. Two-year follow-up of meniscal repair using a bioabsorbable arrow. Arthroscopy 2002;18: Barrett GR, Treacy SH, Ruff CH. Preliminary results of the T-Fix endoscopic meniscus technique in an anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction population. Arthroscopy 1997;13: Austin KS, Sherman OH. Complications of arthroscopic meniscal repair. Am J Sports Med 1990;21: Song EK, Lee KB, Yoon TR. Aseptic synovitis after meniscal repair using the biodegradable Meniscus Arrow. Arthroscopy 2001;17: Friden T, Rydholm U. Severe aseptic synovitis of the knee after biodegradable internal fixation: A case report. Acta Orthop Scand 1992;63: Miller MD, Kline AJ, Gonzales J, Beach WR. Pitfalls associated with FasT-Fix meniscal repair. Arthroscopy 2002;18: Eggli S, Wegmüller H, Kosina J, Huckell C, Jakob RP. Long term results of arthroscopic meniscal repair. Am J Sports Med 1995;23: Perdue PS, Hummer CD, Colosimo AJ, Heidt RS, Dormer SG. Meniscal repair: Outcomes and clinical follow up. Arthroscopy 1996;12: Stone RG, Frewin PR, Gonzales S. Long-term assessment of arthroscopic meniscus repair: A two- to six-year follow-up study. Arthroscopy 1990;6: De Haven KE, Black KP, Griffiths HJ. Open meniscus repair. Technique and two to nine year results. Am J Sports Med 1989;17:
The meniscus plays a key role in the functioning. Clinical Results of All-inside Meniscal Repair Using the FasT-Fix Meniscal Repair System
 Original Article 298 Clinical Results of All-inside Meniscal Repair Using the FasT-Fix Meniscal Repair System Chih-Wei Chiang, MD; Chung-Hsun Chang, MD; Chun-Ying Cheng, MD; Alvin Chao-Yu Chen, MD; Yi-Sheng
Original Article 298 Clinical Results of All-inside Meniscal Repair Using the FasT-Fix Meniscal Repair System Chih-Wei Chiang, MD; Chung-Hsun Chang, MD; Chun-Ying Cheng, MD; Alvin Chao-Yu Chen, MD; Yi-Sheng
)179( COPYRIGHT 2015 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
 )179( COPYRIGHT 2015 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Clinical Results of Meniscal Repair Using Submeniscal Horizontal Sutures Amir Mohammad Navali, MD; Hossein Aslani, MD Research
)179( COPYRIGHT 2015 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Clinical Results of Meniscal Repair Using Submeniscal Horizontal Sutures Amir Mohammad Navali, MD; Hossein Aslani, MD Research
An arthroscopic meniscal repair is a commonly. Meniscal Repair With the RapidLoc Meniscal Repair Device
 Meniscal Repair With the RapidLoc Meniscal Repair Device F. Alan Barber, M.D., David A. Coons, D.O., and Michell Ruiz-Suarez, M.D. Background: The RapidLoc is an all-inside, self-adjusting, flexible meniscal
Meniscal Repair With the RapidLoc Meniscal Repair Device F. Alan Barber, M.D., David A. Coons, D.O., and Michell Ruiz-Suarez, M.D. Background: The RapidLoc is an all-inside, self-adjusting, flexible meniscal
The first reported meniscal repair was performed in. Results of Meniscal Repair Using a Bioabsorbable Screw
 Results of Meniscal Repair Using a Bioabsorbable Screw Albert M. Tsai, M.D., David R. McAllister, M.D., Stephen Chow, M.D., Charles R. Young, B.S., and Sharon L. Hame, M.D. Purpose: With most all-inside
Results of Meniscal Repair Using a Bioabsorbable Screw Albert M. Tsai, M.D., David R. McAllister, M.D., Stephen Chow, M.D., Charles R. Young, B.S., and Sharon L. Hame, M.D. Purpose: With most all-inside
Arthroscopic Meniscus Repair
 Arthroscopic Meniscus Repair Don Johnson MD Director Sports Medicine Clinic Carleton University Associate Professor Orthopedic Surgery University of Ottawa Ottawa ON Canada Introduction Sutures, stingers,
Arthroscopic Meniscus Repair Don Johnson MD Director Sports Medicine Clinic Carleton University Associate Professor Orthopedic Surgery University of Ottawa Ottawa ON Canada Introduction Sutures, stingers,
The Meniscus. History. Anatomy. Anatomy. Blood Supply. Attachments
 History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
All inside suture device is superior to meniscal arrows in meniscal repair: a prospective randomized multicenter clinical trial with 2 year follow up
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2015) 23:211 218 DOI 10.1007/s00167-014-3423-5 KNEE All inside suture device is superior to meniscal arrows in meniscal repair: a prospective randomized multicenter
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2015) 23:211 218 DOI 10.1007/s00167-014-3423-5 KNEE All inside suture device is superior to meniscal arrows in meniscal repair: a prospective randomized multicenter
Inside-Out Meniscal Repair Still the Gold Standard?
 Inside-Out Meniscal Repair Still the Gold Standard? ERIC BERKSON, MD MGH SPORTS MEDICINE TEAM PHYSICIAN, BOSTON RED SOX ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL JULY 26, 2018 Disclosures Neither I nor
Inside-Out Meniscal Repair Still the Gold Standard? ERIC BERKSON, MD MGH SPORTS MEDICINE TEAM PHYSICIAN, BOSTON RED SOX ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL JULY 26, 2018 Disclosures Neither I nor
A novel technique for modified all-inside repair of bucket-handle meniscus tears using standard arthroscopic portals
 Yik et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:188 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0692-y TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access A novel technique for modified all-inside repair of bucket-handle meniscus
Yik et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:188 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0692-y TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access A novel technique for modified all-inside repair of bucket-handle meniscus
CLINICAL ANALYSIS ON ARTHOSCOPIC MENISCAL REPAIR BY FAST-FIX SYSTEM
 CLINICAL ANALYSIS ON ARTHOSCOPIC MENISCAL REPAIR BY FAST-FIX SYSTEM Ashutosh Kumar Das, Liu Jun and Lu Hougen (Orthopaedics Department of Jingzhou Central hospital, Yangtze University) Jingzhou, Hubei,
CLINICAL ANALYSIS ON ARTHOSCOPIC MENISCAL REPAIR BY FAST-FIX SYSTEM Ashutosh Kumar Das, Liu Jun and Lu Hougen (Orthopaedics Department of Jingzhou Central hospital, Yangtze University) Jingzhou, Hubei,
Meniscus Problems - Torn Meniscus Repair
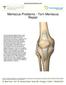 Meniscus Problems - Torn Meniscus Repair The two crescent-shaped menisci in each knee absorb shock, disperse weight, and reduce friction when the knee moves. Activities such as walking or jumping transfer
Meniscus Problems - Torn Meniscus Repair The two crescent-shaped menisci in each knee absorb shock, disperse weight, and reduce friction when the knee moves. Activities such as walking or jumping transfer
The FasT-Fix Repair Technique for Ramp Lesion of the Medial Meniscus
 Technical Note Knee Surg Relat Res 2015;27(1):56-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.1.56 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research The FasT-Fix Repair Technique for Ramp Lesion
Technical Note Knee Surg Relat Res 2015;27(1):56-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.1.56 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research The FasT-Fix Repair Technique for Ramp Lesion
OMICS - 3rd Int. Conference & 2
 KNEE OBJECTIVE STABILITY AND ISOKINETIC THIGH MUSCLE STRENGTH AFTER ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT (ACL) RECONSTRUCTION: A Randomized Six-Month Follow-Up Study M. Sajovic Department of Orthopedics and Sports
KNEE OBJECTIVE STABILITY AND ISOKINETIC THIGH MUSCLE STRENGTH AFTER ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT (ACL) RECONSTRUCTION: A Randomized Six-Month Follow-Up Study M. Sajovic Department of Orthopedics and Sports
Modified all-inside meniscal repair using spinal needles for radial tear of the midbody of the lateral meniscus: a technical note
 Technical Note http://dx.doi.org/10.14517/aosm16003 pissn 2289-005X eissn 2289-0068 Modified all-inside meniscal repair using spinal needles for radial tear of the midbody of the lateral meniscus: a technical
Technical Note http://dx.doi.org/10.14517/aosm16003 pissn 2289-005X eissn 2289-0068 Modified all-inside meniscal repair using spinal needles for radial tear of the midbody of the lateral meniscus: a technical
All Inside Meniscus Repair in 2018
 All Inside Meniscus Repair in 2018 R O B E RT N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & S H O U L D E R S U RG E RY N E W TO N- W E L L ESLEY H O S P I TA L M E D I C A L D
All Inside Meniscus Repair in 2018 R O B E RT N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & S H O U L D E R S U RG E RY N E W TO N- W E L L ESLEY H O S P I TA L M E D I C A L D
Meniscus cartilage replacement with cadaveric
 Technical Note Meniscal Allografting: The Three-Tunnel Technique Kevin R. Stone, M.D., and Ann W. Walgenbach, R.N.N.P., M.S.N. Abstract: This technical note describes an improved arthroscopic technique
Technical Note Meniscal Allografting: The Three-Tunnel Technique Kevin R. Stone, M.D., and Ann W. Walgenbach, R.N.N.P., M.S.N. Abstract: This technical note describes an improved arthroscopic technique
Chart a course for meniscal preservation
 Chart a course for meniscal preservation 1 The clearly defined value of meniscal preservation A number of studies have been published that clearly define the benefits of preserving as much functional meniscus
Chart a course for meniscal preservation 1 The clearly defined value of meniscal preservation A number of studies have been published that clearly define the benefits of preserving as much functional meniscus
Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee
 Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee Introduction The following report mainly concerns the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, Michael. Given that Michael s clinical problem surrounds an injury about
Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee Introduction The following report mainly concerns the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, Michael. Given that Michael s clinical problem surrounds an injury about
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
Epidemiology. Meniscal Injury & Repair. Meniscus Anatomy. Meniscus Anatomy
 Epidemiology 60-70/100,000 per year Meniscal Injury & Repair Arthroscopic Mensiscectomy One of the most common orthopaedic procedures 20% of all surgeries at some centers Male:Female ratio - 2-4:1 Younger
Epidemiology 60-70/100,000 per year Meniscal Injury & Repair Arthroscopic Mensiscectomy One of the most common orthopaedic procedures 20% of all surgeries at some centers Male:Female ratio - 2-4:1 Younger
Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 357463, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/357463 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation Aki Fukuda,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 357463, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/357463 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation Aki Fukuda,
Visit Linvatec.com today to learn more. Surgical Technique: Sequential Meniscal Running Stitch
 ORDERING INFORMATION Sequent Meniscal Repair System MR004S MR007S MR004C MR007C SC047D Straight Needle, 4 Implants Straight Needle, 7 Implants Curved Needle, 4 Implants Curved Needle, 7 implants Sequent
ORDERING INFORMATION Sequent Meniscal Repair System MR004S MR007S MR004C MR007C SC047D Straight Needle, 4 Implants Straight Needle, 7 Implants Curved Needle, 4 Implants Curved Needle, 7 implants Sequent
Grant H Garcia, MD Sports and Shoulder Surgeon
 What to Expect from your Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Surgery A Guide for Patients Grant H Garcia, MD Sports and Shoulder Surgeon Important Contact Information Grant Garcia, MD Wallingford:
What to Expect from your Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Surgery A Guide for Patients Grant H Garcia, MD Sports and Shoulder Surgeon Important Contact Information Grant Garcia, MD Wallingford:
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
DK7215-Levine-ch12_R2_211106
 12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
The Impact of Age on Knee Injury Treatment
 The Impact of Age on Knee Injury Treatment Focus on the Meniscus Dr. Alvin J. Detterline, MD Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgery Towson Orthopaedic Associates University of Maryland St. Joseph Medical
The Impact of Age on Knee Injury Treatment Focus on the Meniscus Dr. Alvin J. Detterline, MD Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgery Towson Orthopaedic Associates University of Maryland St. Joseph Medical
A Patient s Guide. ACL Injury: Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, Ø Preoperative and postoperative. surgery and recovery.
 ACL Injury: A Patient s Guide Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, surgery and recovery Ø Preoperative and postoperative guidelines Mia S. Hagen, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics
ACL Injury: A Patient s Guide Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, surgery and recovery Ø Preoperative and postoperative guidelines Mia S. Hagen, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics
What to Expect from your Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Surgery A Guide for Patients
 What to Expect from your Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Surgery A Guide for Patients Sources of Information: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org http://www.orthoinfo.org/informedpatient.cfm http://www.sportsmed.org/patient/
What to Expect from your Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Surgery A Guide for Patients Sources of Information: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org http://www.orthoinfo.org/informedpatient.cfm http://www.sportsmed.org/patient/
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Meniscus Reconstruction: Trough Surgical Technique
 Meniscus Reconstruction: Trough Surgical Technique Technique Consultant Jeffrey L. Halbrecht, M.D. San Francisco, CA ABOUT THE TROUGH TECHNIQUE The trough technique for meniscal allograft reconstruction
Meniscus Reconstruction: Trough Surgical Technique Technique Consultant Jeffrey L. Halbrecht, M.D. San Francisco, CA ABOUT THE TROUGH TECHNIQUE The trough technique for meniscal allograft reconstruction
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using the Bio-TransFix femoral fixation device. with an anteromedial portal technique.
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2006) 14: 497 501 TECHNICAL NOTE DOI 10.1007/s00167-005-0705-y Michael E. Hantes Zoe Dailiana Vasilios C. Zachos Sokratis E. Varitimidis Anterior cruciate ligament
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2006) 14: 497 501 TECHNICAL NOTE DOI 10.1007/s00167-005-0705-y Michael E. Hantes Zoe Dailiana Vasilios C. Zachos Sokratis E. Varitimidis Anterior cruciate ligament
Lateral ligament injuries of the knee
 Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc (1998) 6:21 25 KNEE Springer-Verlag 1998 Y. Krukhaug A. Mølster A. Rodt T. Strand Lateral ligament injuries of the knee Received: 22 January 1997 Accepted: 20 June
Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc (1998) 6:21 25 KNEE Springer-Verlag 1998 Y. Krukhaug A. Mølster A. Rodt T. Strand Lateral ligament injuries of the knee Received: 22 January 1997 Accepted: 20 June
New Complication Associated With All-Inside Meniscal Repair Device: Ultrasound-Aided Diagnosis and Operative Localization of Foreign Body Reaction
 Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation Publications 9-2-2016 New Complication Associated With All-Inside Meniscal Repair Device: Ultrasound-Aided Diagnosis and Operative Localization of Foreign Body
Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation Publications 9-2-2016 New Complication Associated With All-Inside Meniscal Repair Device: Ultrasound-Aided Diagnosis and Operative Localization of Foreign Body
Long-term outcome after meniscal repair
 DOI 10.1007/s00167-010-1286-y KNEE Long-term outcome after meniscal repair Mike Tengrootenhuysen Geert Meermans Kathleen Pittoors Roger van Riet Jan Victor Received: 5 April 2010 / Accepted: 16 September
DOI 10.1007/s00167-010-1286-y KNEE Long-term outcome after meniscal repair Mike Tengrootenhuysen Geert Meermans Kathleen Pittoors Roger van Riet Jan Victor Received: 5 April 2010 / Accepted: 16 September
Resection of bucket-handle tears is one of the most
 Technical Note Arthroscopic Resection of Bucket-Handle Tears With the Help of a Suture Punch: A Simple Technique to Shorten Operating Time Mehmet S. Bı nnet, M.D., İlksen Gürkan, M.D., and Cem Çetı n,
Technical Note Arthroscopic Resection of Bucket-Handle Tears With the Help of a Suture Punch: A Simple Technique to Shorten Operating Time Mehmet S. Bı nnet, M.D., İlksen Gürkan, M.D., and Cem Çetı n,
W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco
 Knee Pain And Injuries In Adults W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco Pain Control Overview Narcotics rarely necessary after 1 st 1-2
Knee Pain And Injuries In Adults W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco Pain Control Overview Narcotics rarely necessary after 1 st 1-2
Does the location of placement of meniscal sutures have a clinical effect in the allinside repair of meniscocapsular tears?
 Tiftikçi and Serbest Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:87 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0591-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does the location of placement of meniscal sutures have a clinical
Tiftikçi and Serbest Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:87 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0591-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does the location of placement of meniscal sutures have a clinical
Medial Meniscal Root Tears: When to rehab? When to repair? When to debride. Christopher Betz, DO Orthopedics Sports Medicine Bristol, CT
 Medial Meniscal Root Tears: When to rehab? When to repair? When to debride Christopher Betz, DO Orthopedics Sports Medicine Bristol, CT Disclosure Consultant Mitek Smith and Nephew-biologic patch Good
Medial Meniscal Root Tears: When to rehab? When to repair? When to debride Christopher Betz, DO Orthopedics Sports Medicine Bristol, CT Disclosure Consultant Mitek Smith and Nephew-biologic patch Good
UNUSUAL ACL CASE: Tibial Eminence Fracture in a Female Collegiate Basketball Player
 UNUSUAL ACL CASE: Tibial Eminence Fracture in a Female Collegiate Basketball Player Cheri Drysdale, MEd,, ATC Margot Putukian,, MD Jeffery Bechler,, MD Princeton University How many of you have done an
UNUSUAL ACL CASE: Tibial Eminence Fracture in a Female Collegiate Basketball Player Cheri Drysdale, MEd,, ATC Margot Putukian,, MD Jeffery Bechler,, MD Princeton University How many of you have done an
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries Mark L. Wood, MD The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most commonly injured ligaments of the knee. The incidence of ACL injuries is currently estimated
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries Mark L. Wood, MD The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most commonly injured ligaments of the knee. The incidence of ACL injuries is currently estimated
Anatomy and Sports Injuries of the Knee
 Anatomy and Sports Injuries of the Knee I. Anatomy II. Assessment III. Treatment IV. Case Study V. Dissection Anatomy Not a hinge joint 6 degrees of freedom Flexion/Extension Rotation Translation Anatomy
Anatomy and Sports Injuries of the Knee I. Anatomy II. Assessment III. Treatment IV. Case Study V. Dissection Anatomy Not a hinge joint 6 degrees of freedom Flexion/Extension Rotation Translation Anatomy
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears
 Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
7/29/2016. None. Tim Doig DO, Todd Frush MD, Stephen E. Lemos MD PhD, Allison Cracchiolo BS, Alexandria Dupuie MPH 7/29/2016
 Tim Doig DO, Todd Frush MD, Stephen E. Lemos MD PhD, Allison Cracchiolo BS, Alexandria Dupuie MPH 7/29/2016 None Radial meniscus tears can be a challenging clinical scenario 10-23% incidence of radial
Tim Doig DO, Todd Frush MD, Stephen E. Lemos MD PhD, Allison Cracchiolo BS, Alexandria Dupuie MPH 7/29/2016 None Radial meniscus tears can be a challenging clinical scenario 10-23% incidence of radial
Bone&JointAppraisal Vol
 Bone&JointAppraisal Vol 01 No 03 December 2016 COBLATION Chondroplasty Versus Mechanical Debridement: Randomized Controlled Trial with 10-Year Outcomes -Year Four-Year Ten-Year Group A COBLATION technology
Bone&JointAppraisal Vol 01 No 03 December 2016 COBLATION Chondroplasty Versus Mechanical Debridement: Randomized Controlled Trial with 10-Year Outcomes -Year Four-Year Ten-Year Group A COBLATION technology
Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques
 Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques R O B E R T N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & SH O U L D E R S U R G E RY N E W TO N- W E L L E S L
Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques R O B E R T N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & SH O U L D E R S U R G E RY N E W TO N- W E L L E S L
Five year results of the first ten ACL patients treated with dynamic intraligamentary stabilisation
 Eggli et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:105 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-0961-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Five year results of the first ten ACL patients treated with dynamic intraligamentary
Eggli et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:105 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-0961-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Five year results of the first ten ACL patients treated with dynamic intraligamentary
TABLE E-1 Search Terms and Number of Resulting PubMed Search Results* Sear Search Terms
 Moksnes eappendix Page 1 of 15 TABLE E-1 Search Terms and Number of Resulting PubMed Search Results* Sear ch Search Terms No. of Studies #1 Anterior cruciate ligament [MeSH] 7768 #2 Child [MeSH] 1,371,559
Moksnes eappendix Page 1 of 15 TABLE E-1 Search Terms and Number of Resulting PubMed Search Results* Sear ch Search Terms No. of Studies #1 Anterior cruciate ligament [MeSH] 7768 #2 Child [MeSH] 1,371,559
OMNISPAN MENISCAL REPAIR SYSTEM Prominent in Strength, Subtle in Profile
 OMNISPAN MENISCAL REPAIR SYSTEM Prominent in Strength, Subtle in Profile This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The OMNISPAN Meniscal Repair System from DePuy
OMNISPAN MENISCAL REPAIR SYSTEM Prominent in Strength, Subtle in Profile This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The OMNISPAN Meniscal Repair System from DePuy
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT
 ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
Survivorship After Meniscal Allograft Transplantation According To Articular Cartilage Status
 # 154134 Survivorship After Meniscal Allograft Transplantation According To Articular Cartilage Status Jun-Gu Park, Seong-Il Bin, Jong-Min Kim, Bum Sik Lee Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asan Medical
# 154134 Survivorship After Meniscal Allograft Transplantation According To Articular Cartilage Status Jun-Gu Park, Seong-Il Bin, Jong-Min Kim, Bum Sik Lee Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asan Medical
PATIENT GUIDE TO CARTILAGE INJURIES
 Lucas Wymore, MD Sports Medicine 23000 Moakley Street Suite 102 Leonardtown MD 20650 Office Phone: 301-475-5555 Office Fax: 301-475- 5914 Email: lwymore@somdortho.com PATIENT GUIDE TO CARTILAGE INJURIES
Lucas Wymore, MD Sports Medicine 23000 Moakley Street Suite 102 Leonardtown MD 20650 Office Phone: 301-475-5555 Office Fax: 301-475- 5914 Email: lwymore@somdortho.com PATIENT GUIDE TO CARTILAGE INJURIES
A Patient s Guide to Meniscal Surgery. William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Meniscal Surgery Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves
A Patient s Guide to Meniscal Surgery Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves
Surgical Protocol written by Keith Lawhorn, M.D.
 Surgical Protocol written by Keith Lawhorn, M.D. The MaxFire Meniscal Repair System is an all-inside, all-suture meniscal repair system utilizing ZipLoop Technology. Anchors are preloaded on needle inserters,
Surgical Protocol written by Keith Lawhorn, M.D. The MaxFire Meniscal Repair System is an all-inside, all-suture meniscal repair system utilizing ZipLoop Technology. Anchors are preloaded on needle inserters,
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation
 A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
New Evidence Suggests that Work Related Knee Pain with Degenerative Complications May Not Require Surgery
 4 th Quarter 2017 New Evidence Suggests that Work Related Knee Pain with Degenerative Complications May Not Require Surgery By: Michael Erdil MD, FACOEM Introduction It is estimated there are approximately
4 th Quarter 2017 New Evidence Suggests that Work Related Knee Pain with Degenerative Complications May Not Require Surgery By: Michael Erdil MD, FACOEM Introduction It is estimated there are approximately
Overview Ligament Injuries. Anatomy. Epidemiology Very commonly injured joint. ACL Injury 20/06/2016. Meniscus Tears. Patellofemoral Problems
 Overview Ligament Injuries Meniscus Tears Pankaj Sharma MBBS, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Manchester Royal Infirmary Patellofemoral Problems Knee Examination Anatomy Epidemiology Very
Overview Ligament Injuries Meniscus Tears Pankaj Sharma MBBS, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Manchester Royal Infirmary Patellofemoral Problems Knee Examination Anatomy Epidemiology Very
CHANGING THE WAY YOU LOOK AT THINGS
 CHANGING THE WAY YOU LOOK AT THINGS At ConMed Linvatec, we re constantly challenging ourselves to develop truly innovative arthroscopic products that not only complement your technique, but also lead to
CHANGING THE WAY YOU LOOK AT THINGS At ConMed Linvatec, we re constantly challenging ourselves to develop truly innovative arthroscopic products that not only complement your technique, but also lead to
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery
 Anatomy Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery Roger Ostrander, MD Andrews Institute Anatomy Anatomy Function Primary restraint to anterior tibial translation Secondary restraint to internal tibial rotation
Anatomy Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery Roger Ostrander, MD Andrews Institute Anatomy Anatomy Function Primary restraint to anterior tibial translation Secondary restraint to internal tibial rotation
Arthroscopic Meniscal Repair using the Meniscal Cinch Surgical Technique
 Arthroscopic Meniscal Repair using the Meniscal Cinch Surgical Technique Arthroscopic Meniscal Repair Small PEEK implants and 2-0 FiberWire provide secure, low profile fixation Slotted, curved cannula
Arthroscopic Meniscal Repair using the Meniscal Cinch Surgical Technique Arthroscopic Meniscal Repair Small PEEK implants and 2-0 FiberWire provide secure, low profile fixation Slotted, curved cannula
Priorities Forum Statement GUIDANCE
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Department of Orthopaedics
 Department of Orthopaedics ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION SURGERY What is the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilize
Department of Orthopaedics ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION SURGERY What is the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilize
Does Cortical Non-Contact or Delayed Contact of an Adjustable-loop Femoral Button Affect Knee Stability after ACL Reconstruction?
 Does Cortical Non-Contact or Delayed Contact of an Adjustable-loop Femoral Button Affect Knee Stability after ACL Reconstruction? 2008. 1. 16 Kim CK, Sohn SE, Koh IJ, Kim MS, Song KY, In Y Seoul St. Mary
Does Cortical Non-Contact or Delayed Contact of an Adjustable-loop Femoral Button Affect Knee Stability after ACL Reconstruction? 2008. 1. 16 Kim CK, Sohn SE, Koh IJ, Kim MS, Song KY, In Y Seoul St. Mary
Evaluation of Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction using Hamstring Graft
 384 Clinicale Evaluation Evaluation of Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction using Hamstring Graft Swaroop Patel, Resident, Vijendra D. Chauhan, Professor, Anil Juyal, Professor, Rajesh
384 Clinicale Evaluation Evaluation of Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction using Hamstring Graft Swaroop Patel, Resident, Vijendra D. Chauhan, Professor, Anil Juyal, Professor, Rajesh
Lateral Meniscus Transplant
 Lateral Meniscus Transplant Using the CONMED Meniscus Allograft Transplant (MAT) Instruments A complete guide to Lateral Meniscus Transplant using the CONMED meniscus allograft transplant Instruments.
Lateral Meniscus Transplant Using the CONMED Meniscus Allograft Transplant (MAT) Instruments A complete guide to Lateral Meniscus Transplant using the CONMED meniscus allograft transplant Instruments.
Impact of surgical timing on the clinical outcomes of anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
 ISAKOS 2019 12 th -16 th May Cancun, Mexico Impact of surgical timing on the clinical outcomes of anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction Baba R. 1, Kondo E. 2, Iwasaki K. 1, Joutoku
ISAKOS 2019 12 th -16 th May Cancun, Mexico Impact of surgical timing on the clinical outcomes of anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction Baba R. 1, Kondo E. 2, Iwasaki K. 1, Joutoku
Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 706241, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/706241 Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst Shoji Fukuta,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 706241, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/706241 Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst Shoji Fukuta,
No Disclosures. Topics. Pediatric ACL Tears
 Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Rehab Considerations: Meniscus
 Rehab Considerations: Meniscus Steve Cox, PT, DPT Department of Orthopaedics School of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 -Anatomy/ Function/ Injuries -Treatment Options
Rehab Considerations: Meniscus Steve Cox, PT, DPT Department of Orthopaedics School of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 -Anatomy/ Function/ Injuries -Treatment Options
What Is The Optimal Penetration Depth For "All-Inside" Meniscal Repairs?
 What Is The Optimal Penetration Depth For "All-Inside" Meniscal Repairs? Jeffrey Lue 1, Hugh Jones 2, Jesal Parekh 2, Philip C. Noble 2,3, Patrick McCulloch 1. 1 Methodist Center for Sports Medicine, Houston
What Is The Optimal Penetration Depth For "All-Inside" Meniscal Repairs? Jeffrey Lue 1, Hugh Jones 2, Jesal Parekh 2, Philip C. Noble 2,3, Patrick McCulloch 1. 1 Methodist Center for Sports Medicine, Houston
Comparison of Postoperative Outcomes for Medial Meniscal Ramp Lesions between Left without Repair and All-Inside Suture
 Comparison of Postoperative Outcomes for Medial Meniscal Ramp Lesions between Left without Repair and All-Inside Suture Kazuhisa Hatayama 1), Masanori Terauchi 1), Ryota Takase 2), Satoshi Nonaka 2), Hiroshi
Comparison of Postoperative Outcomes for Medial Meniscal Ramp Lesions between Left without Repair and All-Inside Suture Kazuhisa Hatayama 1), Masanori Terauchi 1), Ryota Takase 2), Satoshi Nonaka 2), Hiroshi
Primary transosseous ACL repair in proximal lesions
 Primary transosseous ACL repair in proximal lesions G.L. Canata, V. Casale Centre of Sports Traumatology, Koelliker Hospital, Torino Institute of Sports Medicine, Torino, Italy Gian Luigi Canata, MD I
Primary transosseous ACL repair in proximal lesions G.L. Canata, V. Casale Centre of Sports Traumatology, Koelliker Hospital, Torino Institute of Sports Medicine, Torino, Italy Gian Luigi Canata, MD I
Human ACL reconstruction
 Human ACL reconstruction current state of the art Rudolph Geesink MD PhD Maastricht The Netherlands Human or canine ACL repair...!? ACL anatomy... right knees! ACL double bundles... ACL double or triple
Human ACL reconstruction current state of the art Rudolph Geesink MD PhD Maastricht The Netherlands Human or canine ACL repair...!? ACL anatomy... right knees! ACL double bundles... ACL double or triple
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Technical Note
 Technical Note Hybrid Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Introduction of a New Technique for Anatomic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Darren A. Frank, M.D., Gregory T. Altman, M.D., and
Technical Note Hybrid Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Introduction of a New Technique for Anatomic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Darren A. Frank, M.D., Gregory T. Altman, M.D., and
Knee Preservation System
 Knee Preservation System Sequential Meniscal Running Stitch Surgical Technique Multiple continuous stitches for repair of any size meniscal tear. COMMITTED TO INNOVATION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The Sequent
Knee Preservation System Sequential Meniscal Running Stitch Surgical Technique Multiple continuous stitches for repair of any size meniscal tear. COMMITTED TO INNOVATION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The Sequent
ACL repair in proximal lesions Vs. ACL reconstruction
 ACL repair in proximal lesions Vs. ACL reconstruction G.L. Canata, V. Casale Centre of Sports Traumatology, Koelliker Hospital, Torino Institute of Sports Medicine, Torino, Italy Gian Luigi Canata, MD
ACL repair in proximal lesions Vs. ACL reconstruction G.L. Canata, V. Casale Centre of Sports Traumatology, Koelliker Hospital, Torino Institute of Sports Medicine, Torino, Italy Gian Luigi Canata, MD
Jin Wan Kim, Youn Soo Hwang, Kyu Pill Moon, Kyung Taek Kim, Joon Yeon Song
 Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.14517/aosm15022 pissn 2289-005X eissn 2289-0068 rthroscopic fixation with a cannulated screw for avulsion fractures of the tibial spine in children: a report of two cases
Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.14517/aosm15022 pissn 2289-005X eissn 2289-0068 rthroscopic fixation with a cannulated screw for avulsion fractures of the tibial spine in children: a report of two cases
Remnant Preservation in ACL Reconstruction: Is it Worth Doing?
 Remnant Preservation in ACL Reconstruction: Is it Worth Doing? 1. Presentation (4 x approx. 5min.) i. Mitsuo Ochi ii. Freddie Fu, iii. Takeshi Muneta iv. Rainer Siebold, 2. Debate (approx. 10 min.) 1 ACL
Remnant Preservation in ACL Reconstruction: Is it Worth Doing? 1. Presentation (4 x approx. 5min.) i. Mitsuo Ochi ii. Freddie Fu, iii. Takeshi Muneta iv. Rainer Siebold, 2. Debate (approx. 10 min.) 1 ACL
Treatment of meniscal lesions and isolated lesions of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee in adults
 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Treatment of meniscal s and isolated s of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee in adults June 2008 AIM OF THE GUIDELINES To encourage good practices in the areas of meniscal
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Treatment of meniscal s and isolated s of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee in adults June 2008 AIM OF THE GUIDELINES To encourage good practices in the areas of meniscal
What s your diagnosis?
 Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These
AFX. Femoral Implant. System. The AperFix. AM Portal Surgical Technique Guide. with the. The AperFix System with the AFX Femoral Implant
 The AperFix System AFX with the Femoral Implant AM Portal Surgical Technique Guide The Cayenne Medical AperFix system with the AFX Femoral Implant is the only anatomic system for soft tissue ACL reconstruction
The AperFix System AFX with the Femoral Implant AM Portal Surgical Technique Guide The Cayenne Medical AperFix system with the AFX Femoral Implant is the only anatomic system for soft tissue ACL reconstruction
All-Soft Tissue Quadriceps Tendon Autograft for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Short to Intermediate-Term Clinical Outcomes
 All-Soft Tissue Quadriceps Tendon Autograft for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Short to Intermediate-Term Clinical Outcomes William Godfrey, BS Aaron Gebrelul, BA; John Xerogeanes, MD; Ajay
All-Soft Tissue Quadriceps Tendon Autograft for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Short to Intermediate-Term Clinical Outcomes William Godfrey, BS Aaron Gebrelul, BA; John Xerogeanes, MD; Ajay
On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective
 On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective Jessica Condliffe Physiotherapist / Clinic Manager TBI Health Wellington Presentation Outline Knee anatomy review
On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective Jessica Condliffe Physiotherapist / Clinic Manager TBI Health Wellington Presentation Outline Knee anatomy review
Management of neglected ACL avulsion fractures: a case series and systematic review
 Management of neglected ACL avulsion fractures: a case series and systematic review Presenter Dr. Devendra K chouhan Additional Professor PGIMER, Chandigarh India Co-Author Prof. Mandeep S Dhillon Department
Management of neglected ACL avulsion fractures: a case series and systematic review Presenter Dr. Devendra K chouhan Additional Professor PGIMER, Chandigarh India Co-Author Prof. Mandeep S Dhillon Department
Cartilage Repair Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Safety, feasibility, and radiographic outcomes of the anterior meniscal takedown technique to approach chondral defects on the tibia and posterior femoral
Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Safety, feasibility, and radiographic outcomes of the anterior meniscal takedown technique to approach chondral defects on the tibia and posterior femoral
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of partial replacement of the meniscus of the knee using a biodegradable scaffold
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of partial replacement of the meniscus of the knee using a biodegradable scaffold
Is Meniscectomy such a bad thing compared to meniscal repair?
 Is Meniscectomy such a bad thing compared to meniscal repair? Jack M. Bert, MD Adjunct Clinical Professor University of Minnesota Minnesota Bone & Joint Specialists, Ltd St. Paul, Minnesota Disclosures
Is Meniscectomy such a bad thing compared to meniscal repair? Jack M. Bert, MD Adjunct Clinical Professor University of Minnesota Minnesota Bone & Joint Specialists, Ltd St. Paul, Minnesota Disclosures
Bone patellar tendon bone autograft versus LARS artificial ligament for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
 Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2013) 23:819 823 DOI 10.1007/s00590-012-1073-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bone patellar tendon bone autograft versus LARS artificial ligament for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2013) 23:819 823 DOI 10.1007/s00590-012-1073-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bone patellar tendon bone autograft versus LARS artificial ligament for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
STATE OF THE ART OF ACL SURGERY (Advancements that have had an impact)
 STATE OF THE ART OF ACL SURGERY (Advancements that have had an impact) David Drez, Jr., M.D. Clinical Professor of Orthopaedics LSU School of Medicine Financial Disclosure Dr. David Drez has no relevant
STATE OF THE ART OF ACL SURGERY (Advancements that have had an impact) David Drez, Jr., M.D. Clinical Professor of Orthopaedics LSU School of Medicine Financial Disclosure Dr. David Drez has no relevant
Tensioning a Soft Tissue ACL Graft
 Tensioning a Soft Tissue ACL Graft By Stephen M. Howell, MD Maury L. Hull, PhD. Sacramento, CA The method of tensioning a soft tissue ACL graft is controversial, because surgeons do not agree on how much
Tensioning a Soft Tissue ACL Graft By Stephen M. Howell, MD Maury L. Hull, PhD. Sacramento, CA The method of tensioning a soft tissue ACL graft is controversial, because surgeons do not agree on how much
Anterolateral Ligament. Bradd G. Burkhart, MD Orlando Orthopaedic Center Sports Medicine
 Anterolateral Ligament Bradd G. Burkhart, MD Orlando Orthopaedic Center Sports Medicine What in the world? TIME magazine in November 2013 stated: In an age filled with advanced medical techniques like
Anterolateral Ligament Bradd G. Burkhart, MD Orlando Orthopaedic Center Sports Medicine What in the world? TIME magazine in November 2013 stated: In an age filled with advanced medical techniques like
Investigation of the factors to affect the duration to return sports after the surgery of anterior talofibular ligament repair with arthroscopy
 Investigation of the factors to affect the duration to return sports after the surgery of anterior talofibular ligament repair with arthroscopy Hamamatsu University School of Medicine Mitsuru Hanada, Shoichi
Investigation of the factors to affect the duration to return sports after the surgery of anterior talofibular ligament repair with arthroscopy Hamamatsu University School of Medicine Mitsuru Hanada, Shoichi
KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE Irving Raphael, MD June 13, 2014 RSM Medical Associates Head Team Physician Syracuse University Outline Meniscal Injuries anatomy Exam Treatment ACL Injuries Etiology Physical
KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE Irving Raphael, MD June 13, 2014 RSM Medical Associates Head Team Physician Syracuse University Outline Meniscal Injuries anatomy Exam Treatment ACL Injuries Etiology Physical
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics
 Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Differential Diagnosis
 Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
Minimally Invasive ACL Surgery
 Minimally Invasive ACL Surgery KOCO EATON, M.D. T A M P A B A Y R A Y S ( 1 9 9 5 P R E S E N T ) T A M P A B A Y B U C C A N E E R S ( 2 0 1 5 2 0 1 6 ) T A M P A B A Y R O W D I E S ( 2 0 1 4 2 0 1 7
Minimally Invasive ACL Surgery KOCO EATON, M.D. T A M P A B A Y R A Y S ( 1 9 9 5 P R E S E N T ) T A M P A B A Y B U C C A N E E R S ( 2 0 1 5 2 0 1 6 ) T A M P A B A Y R O W D I E S ( 2 0 1 4 2 0 1 7
MENISCAL INJURIES. (copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION
 (copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL INJURIES Menisci are important for weight bearing, load distribution, joint stability and proprioception. Figure 1: A normal medial meniscus Any load
(copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL INJURIES Menisci are important for weight bearing, load distribution, joint stability and proprioception. Figure 1: A normal medial meniscus Any load
