and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
|
|
|
- Charlene Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 K n e e J o i n t
2 K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia and
3 B- a gliding joint between the patella and the patellar surface of the femur Note that the fibula is not directly involved in the joint. Patellar surface OF THE FEMUR
4 2-Type OF JOINT The joint between the femur and tibia is a synovial joint of the hinge variety, but some degree of rotatory movement is possible. The joint between the patella and femur is a synovial joint of the plane gliding variety. MEDIAL AND LATERAL ROTATION
5 3 - C a p s u l e The capsule is attached to the margins of the articularsurfaces surrounds the sides and posterior aspect of the joint. On the front of the joint, the capsule is absent permitting the synovial membrane to pouch upward beneath the quadriceps tendon, forming the suprapatellar bursa
6 On each side of the patella, the capsule is strengthened by expansions from the tendons of vastus lateralis and medialis.
7 po Behind the joint, the capsule is strengthened by an expansion of the semimembranous muscle called the oblique popliteal ligament Posterior view of the knee joint An opening in the capsule behind the lateral tibial condyle permits the tendon of the popliteus toemerge
8 Ligaments of the knee Extracapsular 1. Tibial collateral ligament 2. Fibular collateral ligament 3. Ligamentum patellae 4. The oblique popliteal ligament Intracapsular 1-Medial and lateral menisci 2-Anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments
9
10 4-Ligame n t s o f the k n ee joint The ligaments may be divided into A-Extracapsular Ligaments The ligamentum patellae is attached above to the lower border of the patella and below to the tuberosity of the tibia.
11
12 The lateral collateral ligament is cordlike and is attached above to the lateral condyle of the femur and below to the head of the fibula. What does this mean?
13 The medial collateral ligament is a flat band and is attached above to the medial condyle of the femur and below to the medial surface of the shaft of the tibia. It is firmly attached to the edge of the medial meniscus?!
14 po The oblique popliteal ligament Is a tendinous expansion derived from the semimembranosus muscle. It strengthens the posterior aspect of the capsule
15 B- I n t r a c a p s u l a r L i g a m e n t s The cruciate ligaments They are named anterior and posterior, according to their tibial attachments The cruciate ligaments are the main bond between the femur and the tibia during the joint's range of movement.
16 Posterior Cruciate Ligament Anterior Cruciate Ligament Is attached to the anterior intercondylar area of the tibia and passes upward, backward, and laterally, to be attached to the posterior part of the medial surface of the lateral femoral condyle Prevents posterior displacement of the femur on the tibia. With the knee joint flexed, the anterior cruciate ligament prevents the tibia from being pulled anteriorly.
17 Posterior Cruciate Ligament Is attached to the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia and passes upward, forward, and medially to be attached to the anterior part of the lateral surface of the medial femoral condyle Prevents anterior displacement of the femur onthe tibia. With the knee joint flexed, the posterior cruciate ligament prevents the tibia from being pulled posteriorly. Anterior cruciate lig Posterior view of the knee
18
19 2/15/2016 LELLI'S TEST FOR ACL LESION Dr.Shataratد. ةيلك ةيندرالا ةعماجال تارطشال دجما بطال
20
21 5-Menisci Medial and lateral menisci are C- shaped sheets of fibrocartilage. (composed of fibrous connective tissue and NOT of cartilage. Anterior Their function is to deepen the articular surfaces of the tibial condyles to receive the convex femoral condyles; They also serve as cushions between the two bones Each meniscus is attached to the upper surface of the tibia by anterior and posterior horns. Posterior
22 A. Complete bucket handle tear. B. The meniscus is torn from its peripheral attachment. The most common type of meniscus tear that causes locking is known as a bucket-handle tear. This is where part of the cartilage gets torn, but remains partially attached producing a moveable flap. As the knee moves around, if the flap is large enough it can get wedged in the wrong position, blocking the joint and causing knee locking. C. Tear of the posterior portion of the meniscus D. Tear of the anterior portion of the meniscus
23 Notice that the lateral condyle of femur is a bit longer than the medial why?! Lateral condyle of femur (OUTR) THE OUTER IS STOUTER prevents lateral dislocation of the patella Longer than the medial Medial condyle of femur (INNER) THE INNER IS THINER
24 Locking mechanism When standing, the knee joint is 'locked' which reduces the amount of muscle work needed to maintain the standing position The locking mechanism is achieved by medial rotation of the femur on the tibia during extension. Medial rotation and full extension tighten all the associated ligaments Tight ligaments during standing Locked joint Another feature that keeps the knee extended when standing is that the body's center of gravity is positioned along a vertical line that passes anterior to the knee joint. The extended knee is said to be inthe locked position
25 Before flexion of the knee joint can occur, it is essential that the major ligaments be untwisted to permit movements between the joint surfaces. untight ligaments during flextion unlocked joint This unlocking or untwisting process is accomplished by the popliteus muscle, which laterally rotates the femur on the tibia
26 Popliteus Muscle plays a key role in the movements of the knee joint Origin: From the lateral surface of the lateral condyle of the femur by a rounded tendon and by a few fibers from the lateral semilunar cartilage
27 Insertion: The fibers pass downward and medially and are attached to the posterior surface of the tibia, above the soleal line. Action: Medial rotation of the tibia on the femur or, if the foot is on the ground, lateral rotation of the femur on the tibia The latter action occurs at the commencement of flexion of the extended knee, and its rotatory action slackens the ligaments of the knee joint; this action is sometimes referred to as unlocking the knee joint.
28 The muscle arises within the capsule of the knee joint its tendon separates the lateral meniscus from the lateral ligament of the joint. It emerges through the lower part of the posterior surface of the capsule of the joint to pass to its insertion.
29
30 7-Bursae Related to the Knee Joint Numerous bursae are related to the knee joint. They are found wherever skin, muscle, or tendon rubs against bone. Four are situated in front of the joint and six are found behind the joint. The suprapatellar bursa lies beneath the quadriceps muscle and communicates with the joint cavity consequently, abrasions or penetrating wounds (e.g., a stab wound) superior to the patella may result in suprapatellar bursitis caused by bacteria entering the bursa from the torn skin. The infection may spread to the knee joint.
31 The prepatellar bursa lies in the subcutaneous tissue between the skin and the front of the lower half of the patella and the upper part of the ligamentum patellae Prepatellar bursitis ( housemaid's knee ) is usually a friction bursitis caused by friction between the skin and the patella
32 Subcutaneous superficial infrapatellar bursitis results from excessive friction between the skin and the tibial tuberosity Deep infrapatellar bursitis results in edema between the patellar ligament and the tibia, superior to the tibial tuberosity
33 The popliteal bursa is found in association with the tendon of the popliteus and communicates with the joint cavity The semimembranosus bursa
34 The remaining four bursae are found related to the tendon of insertion of the biceps femoris; related to the tendons of the sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus muscles as they pass to their insertion on the tibia;
35
36 9-movements of the knee joint Flexion The biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus muscles, assisted by the gracilis, and sartorius, produce flexion. Flexion is limited by the contact of the back of the leg with the thigh. Extension The quadriceps femoris. Extension is limited by the tension of all the major ligaments of the joint. Medial Rotation The sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus Lateral Rotation The biceps femoris Note: The stability of the knee joint depends on the tone of the strong muscles acting on the joint and the strength of the ligaments.
37 10- blood supply From the popliteal artery Branch of the femoral artery in the adductor canal From the popliteal artery
38 11-MRI of the knee: sagittal view QUADRICEPS TENDON SUPRAPATELLAR BURSA FEMUR LATERAL MENISCUS PATELLA PATELLAR TENDON FIBULA TIBIA
39 MRI of the Knee Joint (Frontal Section) NOTE: This MRI frontal section cuts through the intercondylar eminence of the tibia (not labeled) and the intercondylar fossa of the femur. Observe the menisci, which in this frontal section, have a triangular shape.
40 Epiphysial line Medial collateral ligament Posterior cruciate ligament. Medial meniscus Lateral collateral ligament. Anterior cruciate ligament. Lateral meniscus Head of fi bula. Fig Coronal T1-weighted magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the knee in an adult male. (By courtesy of Dr Justin Lee, Chelsea and Westminster Hospital, London.)
41 MRI of the knee: coronal plane FEMUR LATERAL MENISCUS POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT TIBIA MEDIAL MENISCUS
42
43 12- clinical applications 2/15/2016 Dr.Shataratد. ةيلك ةيندرالا ةعماجال تارطشال دجما بطال
44 2/15/2016 Dr.Shataratد. ةيلك ةيندرالا ةعماجال تارطشال دجما بطال
45
Joints of the Lower Limb II
 Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
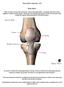
 The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
UNIT 7 JOINTS. Knee and Ankle Joints DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY
 UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
In the name of god. Knee. By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions. Heat: Dr. Babakhani. Nov.
 In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
The Knee. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Knee 7/28/2013. The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint
 The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL
 CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
Muscles of the Thigh. 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group
 Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Sports Medicine 15. Unit I: Anatomy. The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin. Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs
 Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
1-Muscles: 2-Blood supply: Branches of the profunda femoris artery. 3-Nerve supply: Sciatic nerve
 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t r i n g p a r t o r i s c h i a l p a r t ) 2-Blood supply:
1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t r i n g p a r t o r i s c h i a l p a r t ) 2-Blood supply:
Hip joint Type: Articulating bones:
 Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888
 The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management
 Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. Anatomy. Anatomy. Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy MCL, Medial Collateral Ligament LCL, Lateral Collateral Ligament PCL, Posterior Cruciate Ligament ACL,
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy MCL, Medial Collateral Ligament LCL, Lateral Collateral Ligament PCL, Posterior Cruciate Ligament ACL,
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh
 Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
Exercise Science Section 4: Joint Mechanics and Joint Injuries
 Exercise Science Section 4: Joint Mechanics and Joint Injuries An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Types of Joints Fibrous joint Cartilaginous
Exercise Science Section 4: Joint Mechanics and Joint Injuries An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Types of Joints Fibrous joint Cartilaginous
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
Joints: Part B 10/30/14. Classification of Synovial Joints. Six types, based on shape of articular surfaces: Plane Joints
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part B Classification of Synovial Joints Six types, based on shape of articular surfaces: Plane Hinge Pivot
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part B Classification of Synovial Joints Six types, based on shape of articular surfaces: Plane Hinge Pivot
Chapter 10. The Knee Joint. The Knee Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones. Bones. Knee joint. Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS
 The Knee Joint Chapter 10 The Knee Joint Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 10-1 Knee joint largest joint in body very complex
The Knee Joint Chapter 10 The Knee Joint Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 10-1 Knee joint largest joint in body very complex
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Myology of the Knee. PTA 105 Kinesiology
 Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
The Knee. Two Joints: Tibiofemoral. Patellofemoral
 Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
rotation of the hip Flexion of the knee Iliac fossa of iliac Lesser trochanter Femoral nerve Flexion of the thigh at the hip shaft of tibia
 Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Posterior compartment of the thigh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Posterior compartment of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Posterior compartment of the thigh 1-Muscles: Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Adductor magnus
Posterior compartment of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Posterior compartment of the thigh 1-Muscles: Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Adductor magnus
Ultrasound of the Knee Joint. Jun Sung Park,M.D. Bundang General Hospital Dept. of Rehabilitation Medicine
 Ultrasound of the Knee Joint Jun Sung Park,M.D. Bundang General Hospital Dept. of Rehabilitation Medicine Clinical History and P/E Chronic or Acute Symptoms Chronic Sx. : possible of systemic articular
Ultrasound of the Knee Joint Jun Sung Park,M.D. Bundang General Hospital Dept. of Rehabilitation Medicine Clinical History and P/E Chronic or Acute Symptoms Chronic Sx. : possible of systemic articular
Leg. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction
 Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #6: Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction 1 Webinar Goals Explore the assessment and treatment of other culprits in knee dysfunction. 2 Time: 60 minutes Schedule: Logistics
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #6: Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction 1 Webinar Goals Explore the assessment and treatment of other culprits in knee dysfunction. 2 Time: 60 minutes Schedule: Logistics
Articulations. Articulation. Joint between bones. Does not mean movement! Some joints are immovable; sutures.
 Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone).
 It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
8.2: Fibrous Joints. There are three (3) types of fibrous joints (synarthroses): Syndesmosis Suture Gomphosis. Interosseus membrane of leg.
 8.1: Introduction Are known as articulations Functional junctions between bones Bind parts of skeletal system together Make bone growth possible Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth
8.1: Introduction Are known as articulations Functional junctions between bones Bind parts of skeletal system together Make bone growth possible Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth
Acland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy. Transcript for Volume Robert D Acland
 Acland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Transcript for Volume 2 2007 Robert D Acland This free downloadable pdf file is to be used for individual study only. It is not to be reproduced in any form without
Acland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Transcript for Volume 2 2007 Robert D Acland This free downloadable pdf file is to be used for individual study only. It is not to be reproduced in any form without
DISSECTION SCHEDULE. Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial)
 DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB
 BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB LOWER LIMB: BONES LOWER LIMB GLUTEAL REGION consists of 6 major segments: FEMORAL REGION (THIGH) KNEE REGION LEG REGION TALOCRURAL REGION (ANKLE) FOOT REGION LOWER
BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB LOWER LIMB: BONES LOWER LIMB GLUTEAL REGION consists of 6 major segments: FEMORAL REGION (THIGH) KNEE REGION LEG REGION TALOCRURAL REGION (ANKLE) FOOT REGION LOWER
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
Knee Injury Assessment
 Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
Mohammad Ashraf. Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali. Ahmad Salman. 1 P a g e
 - 7 Mohammad Ashraf Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Structures under the cover of Gluteus Maximus: 1-Bones: Ileum, Femur (Head, greater trochanter and gluteal tuberosity), Ischium (ischial
- 7 Mohammad Ashraf Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Structures under the cover of Gluteus Maximus: 1-Bones: Ileum, Femur (Head, greater trochanter and gluteal tuberosity), Ischium (ischial
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
Imaging the Knee 17/10/2017. Friction syndrome Common in runners or cyclists Fluid between ITB and Lateral femoral condyle
 17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB
 MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
Lecture 09. Popliteal Fossa. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai
 Lecture 09 Popliteal Fossa BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 14.02.2018 What is popliteus? Introduction Anything relating to, or near the part of the leg behind the knee. From New Latin popliteus the muscle
Lecture 09 Popliteal Fossa BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 14.02.2018 What is popliteus? Introduction Anything relating to, or near the part of the leg behind the knee. From New Latin popliteus the muscle
Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling
 KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Practical 1 Worksheet
 Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Hip and Knee Approaches
 Hip and Knee Approaches Professor VLADIMIR STAVREV, MD, PhD, DMSc GEORGI MINEV MD DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY, MEDICAL UNIVERSITY -PLOVDIV Anterior View Hip Joint Posterior View - Hip Joint
Hip and Knee Approaches Professor VLADIMIR STAVREV, MD, PhD, DMSc GEORGI MINEV MD DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY, MEDICAL UNIVERSITY -PLOVDIV Anterior View Hip Joint Posterior View - Hip Joint
Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض. Ahmad Salman. 1 P a g e
 4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
The thigh. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
Exercise 13. Articulations and Body Movements
 Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Standardised. knee. scanning of the. Basic pathology. Nemanja Damjanov. University of Belgrade Institute of Rheumatology
 Standardised scanning of the Nemanja Damjanov University of Belgrade Institute of Rheumatology knee Basic pathology Disclosure Lecturer: Pfizer, Abbvie, Roche, MSD, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Gedeon Richter,
Standardised scanning of the Nemanja Damjanov University of Belgrade Institute of Rheumatology knee Basic pathology Disclosure Lecturer: Pfizer, Abbvie, Roche, MSD, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Gedeon Richter,
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis. Parts of the hip. Parts of the femur
 Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Pelvic Girdle
 ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL
 Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Function of Joints 1. Serve as functional junctions between bones. 2. Bind bones, strokes, and other related tissues together. 3. Allow bone growth to occur. 4. Permit certain
Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Function of Joints 1. Serve as functional junctions between bones. 2. Bind bones, strokes, and other related tissues together. 3. Allow bone growth to occur. 4. Permit certain
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy. Stephanie E. Siegrist, MD, LLC
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee
 Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 1 Webinar Goals Understand the significance of
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 1 Webinar Goals Understand the significance of
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee
 Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. Webinar Goals Understand the significance of
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. Webinar Goals Understand the significance of
Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb
 The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 9 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 9 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Joints can be classified structurally as A) bony. B) fibrous. C) cartilaginous. D) synovial. E) All of the answers are correct. 2)
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 9 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Joints can be classified structurally as A) bony. B) fibrous. C) cartilaginous. D) synovial. E) All of the answers are correct. 2)
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
ABSTRACT 2 Key Words: meniscus, tibiofemoral joint, osteoarthritis
 ABSTRACT In the United States, meniscal lesions represent the most common intra-articular knee injury. 1 In fact, the mean annual incidence of meniscal tears is approximately 60 to 70 per 100,000 patients.
ABSTRACT In the United States, meniscal lesions represent the most common intra-articular knee injury. 1 In fact, the mean annual incidence of meniscal tears is approximately 60 to 70 per 100,000 patients.
Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by
 Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by structure and by function: Structural classification focuses
Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by structure and by function: Structural classification focuses
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect. Two classification methods are used to categorize joints:
 Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect Two classification methods are used to categorize joints: Functional classification Structural classification Functional classification
Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect Two classification methods are used to categorize joints: Functional classification Structural classification Functional classification
LOWER LIMB. As we know the bony part of the body is divided into Axial and Appendicular (upper and lower Limbs)
 LOWER LIMB As we know the bony part of the body is divided into Axial and Appendicular (upper and lower Limbs) Bones of the Lower limb: 1-Pelvic Girdle: composed of: 1. Right hip bone : is formed by 3
LOWER LIMB As we know the bony part of the body is divided into Axial and Appendicular (upper and lower Limbs) Bones of the Lower limb: 1-Pelvic Girdle: composed of: 1. Right hip bone : is formed by 3
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Introduction 1. List the functions of joints. 2. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Introduction 1. List the functions of joints. 2. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity
 Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Types of Joints 1. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible at the joint. (p. 268) 2.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Types of Joints 1. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible at the joint. (p. 268) 2.
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh:
 5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
KNEE INJURIES IN FEMALE SOCCER PLAYERS: A FOCUS ON THE ACL
 KNEE INJURIES IN FEMALE SOCCER PLAYERS: A FOCUS ON THE ACL Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors PEÑA, VANESSA NICOLE Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital
KNEE INJURIES IN FEMALE SOCCER PLAYERS: A FOCUS ON THE ACL Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors PEÑA, VANESSA NICOLE Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
Joints. Agenda. Joints. Structural and Functional Classification of Articulations
 Joints Structural and Functional Classification of Articulations Agenda Joint Basics Classification Structural Joint Details Joint Stability Movements of Synovial Joints Shape Classification of Synovial
Joints Structural and Functional Classification of Articulations Agenda Joint Basics Classification Structural Joint Details Joint Stability Movements of Synovial Joints Shape Classification of Synovial
Bones of Lower Limb. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT ARTICULATION Articulation is between: The rounded head of the Glenoid cavity humerus and The shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula. 2 The articular surfaces
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT ARTICULATION Articulation is between: The rounded head of the Glenoid cavity humerus and The shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula. 2 The articular surfaces
I. Introduction. Unit Two. of the Skeletal System. II. Classification of Joints. URLs for this chapter:
 8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Knee Ultrasonography step by step
 Knee Ultrasonography step by step Poster No.: C-2809 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. A. Torres de Abreu Macedo, N. Pereira da Silva, A. I. Aguiar, F. Alves, F. Caseiro Alves; Coimbra/PT
Knee Ultrasonography step by step Poster No.: C-2809 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. A. Torres de Abreu Macedo, N. Pereira da Silva, A. I. Aguiar, F. Alves, F. Caseiro Alves; Coimbra/PT
Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT. Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Dated:
 Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 11.02.2017 INTRODUCTION to the thigh Muscles. The musculature of the thigh can be split into three sections by intermuscular
Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 11.02.2017 INTRODUCTION to the thigh Muscles. The musculature of the thigh can be split into three sections by intermuscular
DIAGNOSIS AND EARLY MANAGEMENT OF KNEE INJURIES
 DIAGNOSIS AND EARLY MANAGEMENT OF KNEE INJURIES INTRODUCTION: The knee is a common site of athletic injury. The knee injuries can be classified either into traumatic or acute and chronic, with overuse
DIAGNOSIS AND EARLY MANAGEMENT OF KNEE INJURIES INTRODUCTION: The knee is a common site of athletic injury. The knee injuries can be classified either into traumatic or acute and chronic, with overuse
The Leg. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The hip joint is a multiaxial synovial ball-and-socket joint between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the
 NfW Hip Joint The hip joint is a multiaxial synovial ball-and-socket joint between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvic bone. Unlike the ball-and-socket shoulder joint, the hip joint
NfW Hip Joint The hip joint is a multiaxial synovial ball-and-socket joint between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvic bone. Unlike the ball-and-socket shoulder joint, the hip joint
Distal Femoral Resection
 Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA
 Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
