The Exeter Trauma Stem: Early results of a new cemented Hemiarthroplasy for femoral neck fracture
|
|
|
- Leslie Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BJMP 2010;3(1):303 Research Article The Exeter Trauma Stem: Early results of a new cemented Hemiarthroplasy for femoral neck fracture David Cash, Jens Bayer, Karl Logan and James Wimhurst ABSTRACT Introduction: The Exeter Trauma Stem (ETS) is a new monoblock unipolar prosthesis with no independent published series using this implant. This study prospectively evaluates the first 50 ETS hemiarthroplasties performed as a primary treatment for fractured neck of femur at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital. Methods: Patient demographics and operative details were recorded from the patient notes. Radiographic evaluation involved the Barrack cementation grading system, Dorr s criteria and leg length measurement. All patients were sent an Oxford Hip Score questionnaire between two and four months postoperatively with 100% response rate. Results: Two thirds of cement mantles were Barrack grade A and B. Twenty-eight patients had lengthening of the operated limb with a mean of 12mm (5-30) including one irreducible prosthesis. Further complications included three deaths and one deep infection. The average Oxford Hip Score was Discussion: Patient demographics were similar to previous studies. There was no statistical difference between the cement mantles and those of another published study using the Exeter stem. The major difficulty evident from this study was correct positioning of the prosthesis with regards to leg-length. Post-operative hip scores were similar to other studies as was the mortality rate. Conclusion: Post-operative functional and radiographic scoring of the ETS prosthesis were encouraging but care is needed with regards to correct positioning of this prosthesis to attain equal leg lengths. Subsequent to the results of this study, a trialling system has been added to the instrumentation which the authors recommend in conjunction with pre-operative templating. KEYWORDS Exeter Trauma Stem, Cemented hemiarthroplasty, Hip fractures, Leg length inequality, Barrack Grading, Oxford Hip Score. INTRODUCTION The Western world is experiencing a rapid increase in the incidence of femoral neck fractures, from fractures in 1990 to a projected in as the age of the population increases. Hip fractures account for approximately 20 percent of orthopaedic bed occupancies in Britain at a total cost of up to per patient 1.Around half of these fractures are intracapsular in nature of which two thirds are displaced. The ideal surgical treatment for displaced intracapsular femoral neck fractures remains controversial with studies indicating a lack of consensus among treatment centres 2,3. Options include reduction with internal fixation, cemented or cementless hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement. Internal fixation is less traumatic than arthroplasty but has a higher re-operation rate 4,5 whilst cemented femoral prostheses are associated with a lower rate of revision compared to cementless implants. In addition there are statistically significant improvements in pain scores, walking ability, use of walking aids and activities of daily living within the cemented group 6,7. The cementation process may however be associated with increased morbidity due to fat embolisation and increased length of operation 8. Treatment planning for intracapsular fractures, therefore, needs to take into account the patient s medical fitness and activity level as well as the cost-effectiveness of the procedure. Figure 1: Exeter Trauma Stem (ETS) Implant
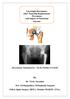
2 The Exeter Trauma Stem is a new monoblock unipolar implant using an intermediate size 1.5, forty millimetre offset Exeter stem with a large head sized to match the patient s anatomy (Figure 1, 2). All fifty procedures were performed with the patient in the lateral position via the modified lateral approach with the glutei incised at the musculotendinous junction. Cefuroxime was given on induction in each instance followed by two post operative doses at eight and sixteen hours after the procedure. Patients were scored by the hospital protocol for risk of thrombosis and were administered aspirin or subcutaneous lowmolecular weight heparin as appropriate. All drains were removed between twenty-four and forty-eight hours and patients were mobilised within one day of operation as pain allowed. Patient demographics and operative details were gathered both from the patients notes and from the ORSOS computerised theatre system. Figure 2: X-ray of ETS with correct length. Neck cut has been made 1cm above lesser trochanter with shoulder of prosthesis sunk below greater trochanter to ensure equal leg length As yet there are no independent published series of the results of using this implant. Purported advantages of the ETS include the use of a tried and tested polished, tapered stainless steel stem with which many primary hip surgeons are familiar, ease of cement-in-cement revision to a total hip replacement should the patient develop acetabular erosion and the relatively low cost of 240 compared to many contemporary cemented implants. This study prospectively evaluates the first 50 ETS hemiarthroplasties performed at the Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital, UK over a six month period providing an indication of early outcomes and complications involved with the use of this prosthesis. METHOD Patients presenting to our unit with a displaced intracapsular femoral neck fracture who were sufficiently active to get out of their home independently, had an ASA grade of 1 or 2 and were not significantly cognitively impaired were treated with a cemented ETS prosthesis. In addition, patients with displaced intracapsular fractures associated with significant comminution of the medial femoral neck precluding the use of our standard calcar-bearing Austin Moore (Stryker Howmedica Osteonics Ltd) hemiarthroplasty were also treated with an ETS regardless of functional capability and medical condition. The first fifty patients who underwent ETS hemiarthroplasty as a primary treatment for fractured neck of femur were included in the study. Four patients were excluded. Two of these patients had an ETS performed due to failure of cancellous screw fixation and two as part of a two stage revision for infected uncemented prosthesis. Radiographic evaluation involved the Barrack 9 cementation grading system, Dorr s criteria 10,11 including varus/valgus alignment of the prosthesis and leg length measurement.. Measurements of length and varus/valgus were performed using the PACS (GE Medical Systems 2005) digital imaging system by two orthopaedic registrars independent of one another. Finally all fifty patients were sent an Oxford Hip Score 12 at between two and four months postoperatively. Three patients died before the questionnaires were sent and of the remaining forty seven, there was a 98% response rate with 44 questionnaires completed solely by the patient and a further two completed with the aid of a carer. RESULTS 1. Patient Demographics and operative details Of the fifty patients in the study, thirty six were female and fourteen male. The mean age was 78 (range 38 to 99). Forty four ETS hemiarthroplasties were performed due to patient fitness and activity levels (Type 1 patients) with six undertaken in frail patients due to fracture extension into the calcar (Type 2). All type 1 patients were ASA grade 1 or 2 with all type 2 patients ASA grade 2-4. All type 1 patients had a mini-mental test score of 10/10 with type 2 patients ranging from 0-7. The mean delay to surgery was 26 hours (9-58). Eight procedures were performed by consultants, thirty eight by registrars (training years three to six) and four by the trauma fellow under supervision by a senior. The mean operative time was sixty four minutes and the mean haemoglobin drop was 2.6 g/dl 3. Seven patients required post operative transfusion of either two or three units of packed cells. Thirty four of the patients mobilised unaided pre-injury with eight using one stick, four using two sticks and four using a frame. Using the four categories above, the average drop in mobility from injury to discharge was 1.6 levels.
3 The average hospital stay was 8.6 days (range 5-69) with thirty five patients discharged to their own house, four to their own residential home and eleven to a rehabilitation ward. 2. Radiographic Evaluation The cement mantle was firstly evaluated using Barrack s grading:- grade A: medullary canal completely filled w/ cement (white out). grade B: a slight radiolucency exists at the bone cement interface. grade C: a radiolucency of more than 50% at the bone cement interface. grade D: radiolucency involving more than 100% of the interface between bone and cement in any projection, including absence of cement distal to the stem tip Post-operative radiographic evaluation according to this system showed that 54% of cement mantles were Barrack grade B (27 cases) with the majority of the remainder grade C (12 cases) and grade A (eight cases). Two were graded as D. Dorr s criteria were employed firstly to assess whether there was an adequate cement thickness of 3mm in Gruen zones 3 and 7 and of one centimetre distal to the tip of the prosthesis. Thirtyfour prosthesis scored 3/3, nine scored two, four scored one and two scored none. Dorr s criteria also assess position of the prosthesis using the AP radiograph. Ten prostheses were placed in a neutral position related to the femoral shaft. Seven were placed in 1-2 degrees of varus, twenty-seven were placed in 1-2 degrees of valgus and five were placed in 3-6 degrees of valgus. There were equal leg length measurements in nineteen patients post-operatively with two patients left 5-10mm short on the operated side. Twenty-eight patients were left long with a mean lengthening of 12mm (5-30) and of these five were left between 20 and 30mm long one of which was irreducible and needed to be revised on the table. 3. Post-operative operative Scoring The Oxford Hip Score contains 6 questions relating to pain and six relating to function and mobility which are scored 1 point for the best outcome and five for the poorest (Score 12-60). The average pain score was 12.0 and the average functional score was 15.2 giving an overall score of The type 1 patients fared better with an average score of 25.3, the average score for type 2 patients was 44.3 There was one superficial wound infection requiring antibiotic therapy and one early deep infection requiring open washout in theatre which resolved the infection in combination with antibiotic therapy. There were three deaths (one CVA, one MI and one from pneumonia) all of which occurred between days from the operative procedure. DISCUSSION The cohort of patients included in this study was similar to other studies with regards to male:female ratio, age and cognitive function 4,5. The patients also experienced a delay to surgery and length of operation similar to previous studies 4,7. The length of inpatient stay, however, was markedly better at 8.6 days compared to approximately fourteen to twenty-one days cited in the literature 13,14. The length of operation, post-operative mobility and transfusion requirements were also similar to studies evaluating hemiarthroplasty outcomes 4,5. Post-operative radiographic evaluation showed greater than 50% of cement mantles were Barrack grade B with the majority of the remainder grade C (24%) and A (16%). There was no statistical difference between our findings and those of an 8-12 year study of the Exeter stem in total hip replacement 15. The two Barrack D grade cement mantles were in patients who became unwell intra-operatively and the decision was taken not to pressurise during cementation. Figure 3: Original ETS broach with squared off handle, not allowing intra-operative trialling The major difficulty evident from this study is the correct positioning of the ETS prosthesis with regards to restoration of accurate leg length which the authors believe was due to two reasons. Firstly, the original set for the Exeter Trauma Stem comes with one femoral broach (Fig 3) which does not allow trial reduction. Therefore positioning of the prosthesis required intra-operative estimation of the correct leg length which can be difficult with hip fractures as the leg length is abnormal at the commencement of surgery. Therefore the centre of rotation of the femoral head on the injured side was approximated by comparison with the contralateral side on the pelvic AP radiograph and referenced against the level of the greater trochanter during the procedure. 4. Complications The one immediate complication was the need for an on-table revision due to an irreducible prosthesis. Secondly, because the large monoblock head of the ETS is matched to the patient s own femoral head anatomy, the
4 diameter of the ETS head is generally around 15-30mm wider than the 28mm heads commonly used with the Exeter stem in elective hip arthroplasty. Therefore care must be taken to sink the stem by a corresponding amount if a similar neck cut is used or the femoral neck osteotomy should be made at a more distal level. This often involves positioning the shoulder of the ETS stem below the level of the greater trochanter. This can mislead surgeons who are familiar with the Exeter stem as placing the ETS stem in a similar position to that employed with smaller head elective arthroplasty results in limb lengthening. Figure 4 shows a leg length discrepancy of 15mm despite a low neck cut as the stem has not been sunk sufficiently. This led to 56% of patients being left with true lengthening of the operated limb and one prosthesis irreducible. It is difficult to assess whether this is a common problem in the literature with other hemiarthroplasties used for femoral neck fractures as none of the comparable studies comment on clinical or radiographic assessment of leg length. Figure 4: X-ray of ETS with limb lengthening. Although the neck cut has been made relatively low in relation to the lesser trochanter, the shoulder of the prosthesis slopes marginally above the greater trochanter, inadvertently lengthening the operated limb. One major advantage to the tapered Exeter stem is the ease with which conversion to a total hip replacement can be performed using an in-cement technique 16. Many of the patients included in this study were below the age of 70 and a proportion could be expected to outlive the prosthesis especially with regards to acetabular erosion 4. Whilst none of this cohort has required revision for loosening, the irreducible Exeter implant was revised on-table using this technique without further complication. Post operative Oxford Hip Scores were encouraging with no difference between our mean score of 27.2 and other studies evaluating both cemented hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement following femoral neck fracture 12,17,18. The mortality rate was 6% six to twelve months post surgery with all three deaths more than one month post surgery and apparently unrelated to the surgery itself. Overall mortality rates following neck of femur fracture are approximately thirty percent at one year however studies specifically looking at outcomes following cemented hemiarthroplasty in the fit and active patient have found mortality rates similar to this study 5,19. Costing around 240, the ETS is a relatively cheap prosthesis in comparison to cemented bipolar prosthesis depite the additional expense of a cement restrictor, bone cement, cement gun and cement pressurisers. In conclusion, the Exeter Trauma Stem (ETS) is an effective method of treating displaced intracapsular neck of femur fractures with encouraging post-operative functional, pain and radiographic scoring outcomes. The message highlighted by this study is that additional care is needed with regards to the correct positioning of the prosthesis to ensure the restoration of limb length. Subsequent to discussion with the Stryker representative regarding the results of this study, a second generation trialling system has been added to the set with a modular broach. The authors suggest that not only should these modular broaches be used, but also accurate pre-operative planning is needed to ensure equal leg lengths post-operatively. Competing Interests Author would like to state that none of the authors involved with this paper have any financial or personal relationship with Stryker or any other companies that could inappropriately influence this study. Author Details DAVID CASH, JENS BAYER, KARL LOGAN: Specialist Registrars, Orthopaedic Department, Norfolk and Norwich Hospital JAMES WIMHURST, Consultant orthopaedic Surgeon, Orthopaedic Department, Norfolk and Norwich Hospital CORRESSPONDENCE: Mr. D Cash, Specialist Registrar, Orthopaedic Dept, Addenbrooke s Hospital, Long Road, Cambridge CB2 0QH davecash@doctors.org.uk REFERENCES 1. Parrott S : The economic cost of hip fracture in the UK (2000) 2. Crossman PT, Khan RJK, MacDowell A, Gardner AC, Reddy NS, Keene GS A survey of the treatment of displaced intracapsular femoral neck fractures in the UK. Injury, 33(2002): Anderson GH, Harper WM, Gregg PJ: Management of the intracapsular fractures of the proximal femur in 1990 : a cause for concern? J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 73B(Suppl 1) (1991) : Parker MJ, Khan RJK, Crawford J, Pryor GA: Hemiarthroplasty versus internal fixation for displaced intracapsular hip fractures in the elderly. J Bone Joint Surg (Br), 84(8) (2002): Davison JNS, Calder SJ, Anderson GH, Ward G, Jagger C, Harper WM, Gregg PJ: Treatment for displaced intracapsular fracture of the proximal femur. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 83 (2001) : Khan RJK, MacDowell A, Crossman PT, Keene GS: Cemented or uncemented hemiarthroplasty for displaced intracapsular fractures of the hip a systematic review. Injury 33 (2002) : Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, Scott NW and Forbes JF: Randomized comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty, and total hip arthroplasty. Treatment of displaced intracapsular hip fractures in healthy older patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 88(2) (2006): , 8. Parker MJ: The management of intracapsular fractures of the proximal femur. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 82 (2000) :
5 9. Barrack RL, Mulroy, RD Jr and Harris WH: Improved cementing techniques and femoral component loosening in young patients with hip arthroplasty. A 12-year radiographic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 74(3) (1992.): Dorr LD, Luckett M and Conaty JP: Total hip arthroplasties in patients younger than 45 years. A nine to ten-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res, (260) (1990.): Dorr LD, Takei GK and Conaty JP: Total hip arthroplasties in patients less than forty-five years old. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 65(4) (1983): Dawson J, Fitzpatrick R, Carr A, and Murray D: Questionnaire on the perceptions of patients about total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 78(2) (1996.): Department of Health. Hospital episode statistics, England: Financial year ; volume 1. London: HMSO, Hay D, Parker MJ: Hip fracture in the immobile patient. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 85 (2003) : Williams HDW, Browne G, Gie GA, Ling RSM, Timperley AJ, Wendover NA: The Exeter universal cemented femoral component at eight to twelve years J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 84 (2002) W W Duncan, M J W Hubble, A J Timperley and G A Gie: Cement in cement femoral revision with the Exeter hip. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 88 (Suppl 2) (2006) : Mishra V, Thomas G, Sibley TF: Results of displaced subcapital fractures treated by primary total hip replacement. Injury 35(2) (2004) : Wazir NN, Mukundala VV, Choon DSK: Early results of prosthetic hip replacement for femoral neck fractures in active elderly patients. J Orthop Surg 14 (2006) Keating JF, Grant A, Massom M, Scott NW, Forbes JF: Displaced intracapsular hip fractures in fit, older people: a randomised comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty. Health Technol Assess 9 (2005) 1-65
Cemented Thompson versus cemented bipolar prostheses for femoral neck fractures
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(2):166-71 Cemented Thompson versus cemented bipolar prostheses for femoral neck fractures Stefan Bauer, 1 Patrick Isenegger, 1 Oliver P Gautschi, 1 Kwok M Ho, 2 Piers
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(2):166-71 Cemented Thompson versus cemented bipolar prostheses for femoral neck fractures Stefan Bauer, 1 Patrick Isenegger, 1 Oliver P Gautschi, 1 Kwok M Ho, 2 Piers
21st Century Fracture Management ETS. Surgical Protocol
 21st Century Fracture Management ETS Surgical Protocol ETS Operative Technique Step 1 Confirm that a cemented hemiarthroplasty is indicated. An X-ray template of the ETS is provided. This should be used
21st Century Fracture Management ETS Surgical Protocol ETS Operative Technique Step 1 Confirm that a cemented hemiarthroplasty is indicated. An X-ray template of the ETS is provided. This should be used
Hip Fracture Management. Product overview
 Hip Fracture Management Product overview Hip Fracture Management Intracapsular fractures Total hip replacement (THR) can offer clinical benefits over traditional internal fixation or hemiarthroplasty solutions
Hip Fracture Management Product overview Hip Fracture Management Intracapsular fractures Total hip replacement (THR) can offer clinical benefits over traditional internal fixation or hemiarthroplasty solutions
Outcome of Replacement Hemi-arthroplasty by Non-Cemented Bipolar Prosthesis of Femoral Component of Hip
 Outcome of Replacement Hemi-arthroplasty by Non-Cemented Bipolar Prosthesis of Femoral Component of Hip *Hossain SN, 1 Hoque E, 2 Islam MM, 3 Rahman M, 4 Alam MS 5 Most femoral neck fractures are osteoporotic
Outcome of Replacement Hemi-arthroplasty by Non-Cemented Bipolar Prosthesis of Femoral Component of Hip *Hossain SN, 1 Hoque E, 2 Islam MM, 3 Rahman M, 4 Alam MS 5 Most femoral neck fractures are osteoporotic
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
 M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists
 : 31 35 doi 10.1308/1478708051450 Audit Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists Jac Ciampolini, Matthew JW Hubble Princess Elizabeth Orthopaedic Centre,
: 31 35 doi 10.1308/1478708051450 Audit Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists Jac Ciampolini, Matthew JW Hubble Princess Elizabeth Orthopaedic Centre,
PRIMARY BIPOLAR ARTHROPLASTY IN TREATMENT OF UNSTABLE INTERTROCHANTERIC FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
 PRIMARY BIPOLAR ARTHROPLASTY IN TREATMENT OF UNSTABLE INTERTROCHANTERIC FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS *Ibrahim M., Shah Sachin and Kothadia Pradeep Department of Orthopaedics, KBNIMS, Gulbarga, Karnataka,
PRIMARY BIPOLAR ARTHROPLASTY IN TREATMENT OF UNSTABLE INTERTROCHANTERIC FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS *Ibrahim M., Shah Sachin and Kothadia Pradeep Department of Orthopaedics, KBNIMS, Gulbarga, Karnataka,
TaperFit. Cemented Total Hip Replacement Surgical technique
 TaperFit Cemented Total Hip Replacement Surgical technique TaperFit Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative templating 5 Surgical exposure 5 Femoral neck resection 5 Acetabular preparation 5 Cenator
TaperFit Cemented Total Hip Replacement Surgical technique TaperFit Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative templating 5 Surgical exposure 5 Femoral neck resection 5 Acetabular preparation 5 Cenator
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.49 Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.49 Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2011 Vol 5 No 1 doi: /MOJ
 doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 22/ Mar 16, 2015 Page 3785
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
76 F: Plays tennis, lives independently, told she has weak bone
 Femoral Neck Fractures In the ELDERLY What to do, when and why Frank Liporace, MD Chairman & VP, Dept of Orthopaedics Chief of Trauma & Adult Reconstruction Jersey City Medical Center / RWJ Barnabas Health
Femoral Neck Fractures In the ELDERLY What to do, when and why Frank Liporace, MD Chairman & VP, Dept of Orthopaedics Chief of Trauma & Adult Reconstruction Jersey City Medical Center / RWJ Barnabas Health
BJMP. British Journal of Medical Practitioners. Volume 3 Number 1 March ISSN:
 BJMP Volume 3 Number 1 March 2010 British Journal of Medical Practitioners www.bjmp.org ISSN: 1757-8515 1 British Journal of Medical Practitioners Volume 3 Number 1 (March 2010) http://www.bjmp.org Editorial
BJMP Volume 3 Number 1 March 2010 British Journal of Medical Practitioners www.bjmp.org ISSN: 1757-8515 1 British Journal of Medical Practitioners Volume 3 Number 1 (March 2010) http://www.bjmp.org Editorial
Absolut TM Cemented Stem. Surgical Technique
 Absolut TM Cemented Stem Surgical Technique Contents ABSOLUT Cemented Stem 2 Absolut Confidence 2 Absolut Reproducibility 2 Absolut Choice 2 Pre-Operative Planning 3 Suggested Templating Method 3 Surgical
Absolut TM Cemented Stem Surgical Technique Contents ABSOLUT Cemented Stem 2 Absolut Confidence 2 Absolut Reproducibility 2 Absolut Choice 2 Pre-Operative Planning 3 Suggested Templating Method 3 Surgical
Bone Preservation Stem
 TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
DISCLOSURE FNFX ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? 11/21/2016 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET
 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? GEORGE HAIDUKEWYCH, MD ORLANDO, FLORIDA DISCLOSURE ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET CONSULTING DEPUY, SYNTHES, BIOMET, RESPONSIVE ORTHOPEDICS STOCK OWNERSHIP ORTHOPEDIATRICS
FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? GEORGE HAIDUKEWYCH, MD ORLANDO, FLORIDA DISCLOSURE ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET CONSULTING DEPUY, SYNTHES, BIOMET, RESPONSIVE ORTHOPEDICS STOCK OWNERSHIP ORTHOPEDIATRICS
Approach Patients with Confidence
 Approach Patients with Confidence The is the first stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior approach, as well as traditional approaches. The implant
Approach Patients with Confidence The is the first stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior approach, as well as traditional approaches. The implant
AUTOBLOQUANTE AUTOBLOQUANTE. Product Rationale Surgical Technique
 AUTOBLOQUANTE AUTOBLOQUANTE Product Rationale Surgical Technique AUTOBLOQUANTE The Product of Long-Term Clinical Experience The AUTOBLOQUANTE femoral component is a direct descendant of the original straight
AUTOBLOQUANTE AUTOBLOQUANTE Product Rationale Surgical Technique AUTOBLOQUANTE The Product of Long-Term Clinical Experience The AUTOBLOQUANTE femoral component is a direct descendant of the original straight
Optimizing function Maximizing survivorship Accelerating recovery
 Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Management of Hip Fractures
 Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
Bi-Polar 22.2mm & 28mm System - Operative technique
 Disclaimer Biomet UK Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend any particular surgical technique for use on a specific patient. The surgeon who performs
Disclaimer Biomet UK Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend any particular surgical technique for use on a specific patient. The surgeon who performs
HELIOS h i p s y s t e m
 HELIOS h i p s y s t e m Design The Helios stem is a highly polished, High Nitrogen Stainless Steel (ISO5832-9) dual tapered cemented stem. The design of the stem is based on the clinically lly successful
HELIOS h i p s y s t e m Design The Helios stem is a highly polished, High Nitrogen Stainless Steel (ISO5832-9) dual tapered cemented stem. The design of the stem is based on the clinically lly successful
VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses. Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME. Versatile solutions for total and partial hip replacement
 VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Versatile solutions for total and partial hip replacement VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses VerSys
VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Versatile solutions for total and partial hip replacement VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses VerSys
Segmental Fracture Of A Cemented Femoral Stem - A Case Report And Review Of Litrature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 13 Number 1 Segmental Fracture Of A Cemented Femoral Stem - A Case Report And Review Of Litrature R Sen, A Mootha, R Saini, V Kumar Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 13 Number 1 Segmental Fracture Of A Cemented Femoral Stem - A Case Report And Review Of Litrature R Sen, A Mootha, R Saini, V Kumar Citation
Introduction. Femoral neck fracture in the elderly
 Fll Fellow: 姜智偉 Introduction Femoral neck fracture in the elderly 14 50 % mortality tlit rate in the first year Highest in the first 6 months, then gradually reduced Affect mortality: Age, gender, comitant
Fll Fellow: 姜智偉 Introduction Femoral neck fracture in the elderly 14 50 % mortality tlit rate in the first year Highest in the first 6 months, then gradually reduced Affect mortality: Age, gender, comitant
Early Complications Following Cemented Modular Hip Hemiarthroplasty
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2015, 9, 15-19 15 Open Access Early Complications Following Cemented Modular Hip Hemiarthroplasty Niall P.T. Sullivan
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2015, 9, 15-19 15 Open Access Early Complications Following Cemented Modular Hip Hemiarthroplasty Niall P.T. Sullivan
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 12, December ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 12, December-2015 1186 Title : A comparative study of outcomes of unipolar versus bipolar hemi-arthroplasty in geriatric age
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 12, December-2015 1186 Title : A comparative study of outcomes of unipolar versus bipolar hemi-arthroplasty in geriatric age
Encina Taper Stem. Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA
 Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement
 Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
operative technique Kent Hip
 operative technique Kent Hip The Kent Hip Operative Technique The Kent Hip was developed by Mr Cliff Stossel, FRCS in Maidstone, Kent, UK and first implanted in 1986. It was designed to deal with problems
operative technique Kent Hip The Kent Hip Operative Technique The Kent Hip was developed by Mr Cliff Stossel, FRCS in Maidstone, Kent, UK and first implanted in 1986. It was designed to deal with problems
Approach Patients with Confidence
 Surgical Technique Approach Patients with Confidence The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
Surgical Technique Approach Patients with Confidence The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
9800 Metric Blvd. Austin, Texas
 rev. A Encore Orthopedics, Inc. 1998 www.encoremed.com 9800 Metric Blvd. Austin, Texas 78758 512-832-9500 1 contents How to use the Foundation Hip 1 2 Plan your approach Select your hardware Preparing
rev. A Encore Orthopedics, Inc. 1998 www.encoremed.com 9800 Metric Blvd. Austin, Texas 78758 512-832-9500 1 contents How to use the Foundation Hip 1 2 Plan your approach Select your hardware Preparing
Zimmer M/L Taper Hip Prosthesis. Surgical Technique
 Zimmer M/L Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Zimmer M/L Taper Hip Prosthesis 1 Zimmer M/L Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Table of Contents Preoperative Planning 2 Determination of Leg Length
Zimmer M/L Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Zimmer M/L Taper Hip Prosthesis 1 Zimmer M/L Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Table of Contents Preoperative Planning 2 Determination of Leg Length
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Preoperative Planning. The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to:
 Preoperative Planning The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to: - Determine preoperative leg length discrepancy. - Assess acetabular component size and placement. - Determine femoral component
Preoperative Planning The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to: - Determine preoperative leg length discrepancy. - Assess acetabular component size and placement. - Determine femoral component
5A* ODEP. Conserving bone. Preserving soft tissue. Restoring biomechanics. rating
 MiniHip is designed to give patients the advantages of a traditional hip replacement whilst also preserving the natural anatomy. MiniHip potentially allows for future revisions and so provides a pre-primary
MiniHip is designed to give patients the advantages of a traditional hip replacement whilst also preserving the natural anatomy. MiniHip potentially allows for future revisions and so provides a pre-primary
Surgical Technique. Hip System
 Surgical Technique Hip System INDICATIONS FOR USE The TaperSet Hip System is designed for total or partial hip arthroplasty and is intended to be used with compatible components of the Consensus Hip System.
Surgical Technique Hip System INDICATIONS FOR USE The TaperSet Hip System is designed for total or partial hip arthroplasty and is intended to be used with compatible components of the Consensus Hip System.
Exeter. Technical Guide
 Exeter Technical Guide Exeter Hip System Anatomic Restoration The Exeter hip system allows interoperative changes in offset, leg length and version, all independent of one another. This flexibility facilitates
Exeter Technical Guide Exeter Hip System Anatomic Restoration The Exeter hip system allows interoperative changes in offset, leg length and version, all independent of one another. This flexibility facilitates
Progeny Hip Stem. Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications
 Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Effect of surgical approach on the early outcome of total hip replacement for femoral neck fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 23, 79, 667-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Effect of surgical approach on the early outcome of total hip replacement for femoral neck fractures Ahmed M. Mohamed, Daoud Makki, James Gibbs From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 23, 79, 667-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Effect of surgical approach on the early outcome of total hip replacement for femoral neck fractures Ahmed M. Mohamed, Daoud Makki, James Gibbs From the
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
Continuing the Tradition. VerSys Heritage Hip System
 Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
Aesculap Targon FN. Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures. Aesculap Orthopaedics
 Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures. Martyn Parker Peterborough UK
 The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures Martyn Parker Peterborough UK PETERBOROUGH HIP FRACTURE PROJECT Avoid delays to surgery Minimally invasive surgery by experienced staff Unrestricted
The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures Martyn Parker Peterborough UK PETERBOROUGH HIP FRACTURE PROJECT Avoid delays to surgery Minimally invasive surgery by experienced staff Unrestricted
Efficacy Innovation ABG II. Brochure. Surgical Protocol. Cemented Stem
 Efficacy Innovation ABG II Cemented Stem Brochure Surgical Protocol 2 The ABG Hip System The ABG hip implant range has been progressively extended and enhanced over the past years, harnessing extensive
Efficacy Innovation ABG II Cemented Stem Brochure Surgical Protocol 2 The ABG Hip System The ABG hip implant range has been progressively extended and enhanced over the past years, harnessing extensive
CPCS. Training Manual. Collarless Polished Cemented Stem
 SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS ~ TRUST. INNOVATION. PERFORMANCE. CPCS Collarless Polished Cemented Stem Training Manual This document is for internal use by Smith & Nephew and sales force only and is not
SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS ~ TRUST. INNOVATION. PERFORMANCE. CPCS Collarless Polished Cemented Stem Training Manual This document is for internal use by Smith & Nephew and sales force only and is not
TaperFit. Cemented Femoral Stem Product rationale
 TaperFit Cemented Femoral Stem Product rationale TaperFit Design History Function TaperFit cemented femoral stems have been in use for over 17 years and are clinically proven to produce excellent results
TaperFit Cemented Femoral Stem Product rationale TaperFit Design History Function TaperFit cemented femoral stems have been in use for over 17 years and are clinically proven to produce excellent results
Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric
 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (5): 493 498 493 Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures A cohort study with 5 11 year follow-up of 88 consecutive patients Anders
Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (5): 493 498 493 Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures A cohort study with 5 11 year follow-up of 88 consecutive patients Anders
Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients
 Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Arthroplasties (with and without bone cement) for proximal femoral fractures in adults (Review)
 Arthroplasties (with and without bone cement) for proximal femoral fractures in adults (Review) Parker MJ, Gurusamy KS This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration
Arthroplasties (with and without bone cement) for proximal femoral fractures in adults (Review) Parker MJ, Gurusamy KS This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration
IMPROVED CEMENTING TECHNIQUES AND FEMORAL COMPONENT LOOSENING IN YOUNG PATIENTS WITH HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 IMPROVED CEMENTING TECHNIQUES AND FEMORAL COMPONENT LOOSENING IN YOUNG PATIENTS WITH HIP ARTHROPLASTY A 12-YEAR RADIOGRAPHIC REVIEW ROBERT L. BARRACK, RICHARD D. MULROY JR, WILLIAM H. HARRIS From the Massachusetts
IMPROVED CEMENTING TECHNIQUES AND FEMORAL COMPONENT LOOSENING IN YOUNG PATIENTS WITH HIP ARTHROPLASTY A 12-YEAR RADIOGRAPHIC REVIEW ROBERT L. BARRACK, RICHARD D. MULROY JR, WILLIAM H. HARRIS From the Massachusetts
AVANTEON. Operative Technique & Catalogue Information AVANTEON
 AVANTEON Operative Technique & Catalogue Information AVANTEON H I P S Y S T E M Pre-operative Planning The overall aim of pre-operative planning is to establish anatomical data from the patient to guide
AVANTEON Operative Technique & Catalogue Information AVANTEON H I P S Y S T E M Pre-operative Planning The overall aim of pre-operative planning is to establish anatomical data from the patient to guide
Exeter V40 Femoral Stem
 Exeter V40 Femoral Stem Table of Contents Indications and Contraindications... IFC Surgical Protocol Step 1 - Pre-Operative Planning and X-ray Evaluation... 1 Step 2 - Surgical Exposure... 2 Step 3 - Femoral
Exeter V40 Femoral Stem Table of Contents Indications and Contraindications... IFC Surgical Protocol Step 1 - Pre-Operative Planning and X-ray Evaluation... 1 Step 2 - Surgical Exposure... 2 Step 3 - Femoral
THE NATURAL FIT. Surgical Technique. Hip Knee Spine Navigation
 THE NATURAL FIT Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation MiniMAX Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation INTRODUCTION The MiniMAX TM is a cementless anatomic stem available in 9 right sizes and
THE NATURAL FIT Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation MiniMAX Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation INTRODUCTION The MiniMAX TM is a cementless anatomic stem available in 9 right sizes and
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
28 Surgical Technique
 Surgical Technique 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 28 26 Technique described by James L. Guyton, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee James W. Harkess, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee David G. LaVelle,
Surgical Technique 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 28 26 Technique described by James L. Guyton, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee James W. Harkess, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee David G. LaVelle,
Surgical Technique r5.indd 1 12/8/10 10:36 AM
 Surgical Technique The science of simplicity With more than 700,000 implantations and two and a half decades of clinical success, the Corail Total Hip System now has the most extensive experience with
Surgical Technique The science of simplicity With more than 700,000 implantations and two and a half decades of clinical success, the Corail Total Hip System now has the most extensive experience with
Aesculap Trilliance Triple Tapered Polished Hip Stem
 Aesculap Trilliance Triple Tapered Polished Hip Stem Aesculap Orthopaedics Trilliance Triple Tapered Polished Hip Stem CONTENTS 2 Contents Page Trilliance Philosophy 4 Trilliance Design 6 Trilliance Implants
Aesculap Trilliance Triple Tapered Polished Hip Stem Aesculap Orthopaedics Trilliance Triple Tapered Polished Hip Stem CONTENTS 2 Contents Page Trilliance Philosophy 4 Trilliance Design 6 Trilliance Implants
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of minimally invasive two-incision surgery for total hip replacement Introduction This
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of minimally invasive two-incision surgery for total hip replacement Introduction This
Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
Anterior Approach Surgical Technique. Paragon Stem System. enabling people to enjoy life
 Anterior Approach Surgical Technique Paragon Stem System enabling people to enjoy life Contents Pre-Operative Planning... 2 Suggested Templating Method... 2 Surgical Technique... 3 Surgical Approach...
Anterior Approach Surgical Technique Paragon Stem System enabling people to enjoy life Contents Pre-Operative Planning... 2 Suggested Templating Method... 2 Surgical Technique... 3 Surgical Approach...
Is there a significant difference in surgery and outcomes between unipolar and bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty? - A Prospective Study
 Mohammad Faisal and Prithviraj Nistane / International Journal of Biomedical Research 2016; 7(10): 708-712. 708 International Journal of Biomedical Research ISSN: 0976-9633 (Online); 2455-0566 (Print)
Mohammad Faisal and Prithviraj Nistane / International Journal of Biomedical Research 2016; 7(10): 708-712. 708 International Journal of Biomedical Research ISSN: 0976-9633 (Online); 2455-0566 (Print)
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Alpine Cementless Hip Stem
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Alpine Cementless Hip Stem The following technique is a general guide for the instrumentation of the Alpine Cementless Hip Stem. It is expected that the surgeon is already familiar with
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Alpine Cementless Hip Stem The following technique is a general guide for the instrumentation of the Alpine Cementless Hip Stem. It is expected that the surgeon is already familiar with
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to total hip replacement that places equal importance on recovery, function and survivorship. The DePuy PROXIMA Hip System
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to total hip replacement that places equal importance on recovery, function and survivorship. The DePuy PROXIMA Hip System
Clinical Evaluation Surgical Technique
 Clinical Evaluation Surgical Technique Table of Contents EMPERION Specifications 3 EMPERION Surgical Technique 9 EMPERION Catalog 18 Nota Bene: This technique description herein is made available to the
Clinical Evaluation Surgical Technique Table of Contents EMPERION Specifications 3 EMPERION Surgical Technique 9 EMPERION Catalog 18 Nota Bene: This technique description herein is made available to the
Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Scan Bi-Polar 22/28. Operative Technique
 Scan Bi-Polar 22/28 Operative Technique Disclaimer This publication and all content, artwork, photographs, names, logos and marks contained in it are protected by copyright, trademarks and other intellectual
Scan Bi-Polar 22/28 Operative Technique Disclaimer This publication and all content, artwork, photographs, names, logos and marks contained in it are protected by copyright, trademarks and other intellectual
The proven, simple solution. CPT 12/14 Hip System
 The proven, simple solution CPT 12/14 Hip System Primary CPT Hip The proven, simple solution 5mm The collarless, polished, doubletaper design concept used in the CPT 12/14 Hip System has proven itself
The proven, simple solution CPT 12/14 Hip System Primary CPT Hip The proven, simple solution 5mm The collarless, polished, doubletaper design concept used in the CPT 12/14 Hip System has proven itself
Surgical Technique. *smith&nephew POLARSTEM Cementless Stem System
 Surgical Technique *smith&nephew POLARSTEM Cementless Stem System POLARSTEM Cementless Stem System Contents Introduction... 3 Indications... 4 Contraindications... 4 Case Studies... 5 Preoperative Planning...
Surgical Technique *smith&nephew POLARSTEM Cementless Stem System POLARSTEM Cementless Stem System Contents Introduction... 3 Indications... 4 Contraindications... 4 Case Studies... 5 Preoperative Planning...
TaperFill. Surgical Technique
 TaperFill Surgical Technique Table of Contents Indications and Contraindications 3 TaperFill Hip Size Charts 4-5 DJO Surgical 9800 Metric Boulevard Austin, TX (800) 456-8696 www.djosurgical.com Preoperative
TaperFill Surgical Technique Table of Contents Indications and Contraindications 3 TaperFill Hip Size Charts 4-5 DJO Surgical 9800 Metric Boulevard Austin, TX (800) 456-8696 www.djosurgical.com Preoperative
AO Debate Controversies in Management
 46 AODIALOGUE 2 07 Jan Tidermark and Hans Törnqvist AO Debate Controversies in Management Case 1 A 72-year-old active lady (Fig 1). Sustained a displaced femoral neck fracture (Fig 2) after a simple fall.
46 AODIALOGUE 2 07 Jan Tidermark and Hans Törnqvist AO Debate Controversies in Management Case 1 A 72-year-old active lady (Fig 1). Sustained a displaced femoral neck fracture (Fig 2) after a simple fall.
Do Independent Sector Treatment Centres (ISTC) impact on specialist registrar training in primary hip and knee arthroplasty?
 The Royal College of Surgeons of England ORTHOPAEDICS doi 10.1308/003588408X301073 Do Independent Sector Treatment Centres (ISTC) impact on specialist registrar training in primary hip and knee arthroplasty?
The Royal College of Surgeons of England ORTHOPAEDICS doi 10.1308/003588408X301073 Do Independent Sector Treatment Centres (ISTC) impact on specialist registrar training in primary hip and knee arthroplasty?
Initial Evaluation on Subsidence of Cemented Collarless Polished Tapered Stem Applied to the Patients with Narrow Femoral Medullar Canal
 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2010, 4, 147-151 147 Open Access Initial Evaluation on Subsidence of Cemented Collarless Polished Tapered Stem Applied to the Patients with Narrow Femoral Medullar Canal
The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2010, 4, 147-151 147 Open Access Initial Evaluation on Subsidence of Cemented Collarless Polished Tapered Stem Applied to the Patients with Narrow Femoral Medullar Canal
Featuring. Technology. Product Rationale
 Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
AML Hip System. Design Rationale/ Surgical Technique
 AML Hip System Design Rationale/ Surgical Technique Design Rationale Evolution In 1977, DePuy Synthes Companies introduced the original cementless total hip. The AML Hip launched in order to solve one
AML Hip System Design Rationale/ Surgical Technique Design Rationale Evolution In 1977, DePuy Synthes Companies introduced the original cementless total hip. The AML Hip launched in order to solve one
R. Blomfeldt, H. Törnkvist, K. Eriksson, A. Söderqvist, S. Ponzer, J. Tidermark
 A randomised controlled trial comparing bipolar hemiarthroplasty with total hip replacement for displaced intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck in elderly patients R. Blomfeldt, H. Törnkvist, K.
A randomised controlled trial comparing bipolar hemiarthroplasty with total hip replacement for displaced intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck in elderly patients R. Blomfeldt, H. Törnkvist, K.
ACTIS. TOTAL HIP SYSTEM Approach Active Patients with Confidence DESIGN RATIONALE
 ACTIS TOTAL HIP SYSTEM Approach Active Patients with Confidence DESIGN RATIONALE APPROACH ACTIVE PATIENTS WITH CONFIDENCE The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes Companies of Johnson & Johnson
ACTIS TOTAL HIP SYSTEM Approach Active Patients with Confidence DESIGN RATIONALE APPROACH ACTIVE PATIENTS WITH CONFIDENCE The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes Companies of Johnson & Johnson
Tradition Hip Primary Surgical Technique
 Design Rationale Many total hip designs in today s marketplace do not take advantage of the known forces present in the femur. Long term stability of a total hip prosthesis requires an implant design and
Design Rationale Many total hip designs in today s marketplace do not take advantage of the known forces present in the femur. Long term stability of a total hip prosthesis requires an implant design and
VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis. Surgical Technique
 VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique 1 VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Table of Contents Preoperative
VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique 1 VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Table of Contents Preoperative
Leg length discrepancy After Total Hip Replacement: Prevalence And impact on functional outcome
 Leg length discrepancy After Total Hip Replacement: Prevalence And impact on functional outcome Dissertation Submitted for - M.ch, (Ortho) (USAIM) By; Dr. Vivek Savaskar M.S. {Orthopaedics}, Orthopaedic
Leg length discrepancy After Total Hip Replacement: Prevalence And impact on functional outcome Dissertation Submitted for - M.ch, (Ortho) (USAIM) By; Dr. Vivek Savaskar M.S. {Orthopaedics}, Orthopaedic
Mid Term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty for Various Hip Disorders
 ORIGINALARTICLE Mid Term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty for Various Hip Disorders Sanjeev Gupta, Rashid Anjum, Omeshwar Singh, Anil Gupta, Abdul Ghani, Mohammad Azhar ud din Darokhan Abstract The curent
ORIGINALARTICLE Mid Term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty for Various Hip Disorders Sanjeev Gupta, Rashid Anjum, Omeshwar Singh, Anil Gupta, Abdul Ghani, Mohammad Azhar ud din Darokhan Abstract The curent
ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER. undisplaced, but as a consequence of the delay in diagnosis displacement occurred SUMMARY
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 23-27 Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER Peterborough District Hospital, SUMMARY Thorpe Road, Peterborough From a series of 825 consecutive admissions with a hip
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 23-27 Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER Peterborough District Hospital, SUMMARY Thorpe Road, Peterborough From a series of 825 consecutive admissions with a hip
Bipolar versus fixed-head hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2011) 6:1 6 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0100-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bipolar versus fixed-head hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients Mostafa Abdelkhalek Mohamed
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2011) 6:1 6 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0100-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bipolar versus fixed-head hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients Mostafa Abdelkhalek Mohamed
Conversion total hip arthroplasty Functional outcome in Egyptian population
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 549-554 ORIGINAL STUDY Conversion total hip arthroplasty Functional outcome in Egyptian population Akram HAMMAD, Ahmed ABDEL-AAL From Mansoura and Assiut University Hospitals,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 549-554 ORIGINAL STUDY Conversion total hip arthroplasty Functional outcome in Egyptian population Akram HAMMAD, Ahmed ABDEL-AAL From Mansoura and Assiut University Hospitals,
EMPERION Modular Hip System Surgical Technique
 Surgical Technique Introduction The EMPERION Modular Hip System is a versatile system that can be used for primary and revision hip surgeries. Using modular proximal bodies, this system addresses the proximal
Surgical Technique Introduction The EMPERION Modular Hip System is a versatile system that can be used for primary and revision hip surgeries. Using modular proximal bodies, this system addresses the proximal
HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Introduction...2 Preoperative Planning...3 Preoperative Planning...3 Templating and Radiographs...4 Determination of Leg Length Discrepancy...5 Determining Acetabular Cup
HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Introduction...2 Preoperative Planning...3 Preoperative Planning...3 Templating and Radiographs...4 Determination of Leg Length Discrepancy...5 Determining Acetabular Cup
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Clinical guideline: Hip Fracture PRE-PUBLICATION CHECK ERROR TABLE
 National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical guideline: Hip Fracture PRE-PUBLICATION CHECK ERROR TABLE Organisation Order number Section number in FULL guideline Page number ERROR REPORT
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical guideline: Hip Fracture PRE-PUBLICATION CHECK ERROR TABLE Organisation Order number Section number in FULL guideline Page number ERROR REPORT
Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Alpine Cemented Hip Stem
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Alpine Cemented Hip Stem The following technique is a general guide for the instrumentation of the Alpine Cemented Hip Stem. It is expected that the surgeon is already familiar with
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Alpine Cemented Hip Stem The following technique is a general guide for the instrumentation of the Alpine Cemented Hip Stem. It is expected that the surgeon is already familiar with
Unipolar Versus Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly
 HIP THE HEMIARTHROPLASTY IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL Unipolar Versus Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly Ali A. Ali, Saad M. Rashed, Mushtaq T.
HIP THE HEMIARTHROPLASTY IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL Unipolar Versus Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly Ali A. Ali, Saad M. Rashed, Mushtaq T.
Digital Templating of the Non-Affected Hip as a Means of Minimizing Leg-Length Discrepancy after Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty
 Digital Templating of the Non-Affected Hip as a Means of Minimizing Leg-Length Discrepancy after Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Todd V. Swanson, MD 1 Jonathon M. Brown, BS 1 Siva K. Mamillapalli, MBBS,
Digital Templating of the Non-Affected Hip as a Means of Minimizing Leg-Length Discrepancy after Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Todd V. Swanson, MD 1 Jonathon M. Brown, BS 1 Siva K. Mamillapalli, MBBS,
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
FIRST STEM SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR AMIS. Surgical Technique
 FIRST STEM SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR AMIS Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med AMIStem Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med INTRODUCTION This document describes the Surgical Technique for the
FIRST STEM SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR AMIS Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med AMIStem Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med INTRODUCTION This document describes the Surgical Technique for the
