8. The function of the transverse abdominus is to: a. Flex the trunk b. Extend the trunk c. Compress the abdomen d. Rotate the abdomen
|
|
|
- Lorraine Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AMANDA. Muscle motor unit refers to: a. the ability of the muscle to grow b. the ability of the muscle to contract c. The basic stimulation of the muscle d. The interaction with muscles together as a unit 2. These muscles display striation a. Smooth b. Cardiac c. Skeletal d. B and C 3. Arm curls are a form of what kind of contraction a. Isometric b. Concentric contraction c. Eccentric contraction 4. This makes sure that protagonist and antagonist do not conflict. a. Recipital intervention b. Radical innervention c. Reciprocal innervention d. Recipital innitiation 5. Which two muscles both abduct the scapula? a. Splenius and sternocleidomastoid b. Splenius and serratus anterior c. Splenius and pectoralis minor d. Pectoralis minor and serratus anterior 6. What is the function of the latissimus Dorsi? a. Adduct humerus b. Medially rotate humerus c. Laterally rotate humerus d. A and b e. A and c 7. Which muscle blends with the seratus anterior? a. External oblique b. Internal oblique c. Rectus abdominus e. All of the above 8. The function of the transverse abdominus is to: a. Flex the trunk b. Extend the trunk c. Compress the abdomen d. Rotate the abdomen 9. Which of the following muscles insert at the coracoid process? a. Brachialis b. Biceps c. Triceps d. Brachioradialis 0. The brachialis are deep to the: a. Triceps b. Biceps c. Brachioradialis. The deep six all insert where? a. Greater trochantor b. Lesser trochantor c. Pubic crest d. Iliac crest 2. What is the function of the TFL? a. Inward rotation of the hip b. Hip flexion c. Hip abduction d. All of the above 3. What is the function of the Quadricep muscles? a. Knee flexion b. Knee extension c. Extend hip d. Outwardly rotate hip 4. What is the origine of the Hamstring muscles? a. Ischial tuberosity b. Tibia c. Fibula d. Iliotibial tract 5. What is the function of the popliteus a. Knee flexion b. Medial rotation of the tibia c. Unlocks knee d. A and b e. All of the above 6. Wich adductor extends the hip? a. Magnus b. Longus c. Brevis d. Garcilis e. None they all flex the hip 7. Which muscle crosses both the knee and the ankle? a. Flexor digitorum longus b. Gastrocnemius c. Soleus d. Tibialis anterior 8. Which muscles do work only on digit one? a. Extensor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus b. Extensor digitorum longus, flexor digitorum longus c. Extensor hallucis longus, flexor hallucis longus d. Extensor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus c d b c d d e c a b a d b a c a b c ERIC. When origin and insertion of the muscle move closer together this is called? a. Concentric contraction b. Eccentric contraction c. Isometric contraction d. Power stroke 2. Which muscle(s) is/are along the medial border of the scapula? a. Rhomboid b. Levator scapula c. All of the above
2 3. The mastoid process is the insertion of which muscles? a. Spinalis b. Splenius c. Sternocleidomastoid d. A and C e. B and C 4. Which member of the erector spinae group affects the neck? a. Spinalis b. Sternocleidomastoid c. Longizsimus d. Iliocostalic 5. Which muscle runs from T7 to L5? a. Pec. Major b. Deltoid c. Lat. Dorsi d. Teres Major 6. Which muscle originates on the lateral border of the scapula? a. Lat. Dorsi b. Deltoid c. Pec. Major d. Teres Major 7. Which abdominal muscles insert on the xyphoid process? a. Transverse abdominis and external oblique b. Rectus abdominis and internal oblique c. External oblique and internal oblique d. Internal oblique and transverse abdominis 8. The muscle that flexes the trunk laterally is called the a. Rectus abdominis b. Transverse abdominis c. Internal oblique d. External oblique 9. Which muscle s function is elbow extension? a. Triceps brachii b. Biceps brachii c. Brachialis d. Brachioradialis 0. Which muscle s function is shoulder flexion? a. Biceps brachii b. Brachialis c. Brachioradialis d. Triceps brachii. Which muscles cause inward rotation of the hip? a. TFL and gluteus medius b. Gluteus minimus and gluteus maximus c. Iliopsoas and pectineus d. TFL and gluteus minimus 2. Which muscle leads to sciatic pain? a. Piriformis b. Quadratus femoris c. Gluteus maximus d. Biceps brachii 3. Which muscle is known as the tailor muscle? a. Rectus femoris b. Sartorius c. Popliteus d. Biceps femoris 4. Which two muscles are on the front of the leg? a. Semimembranous and sartorius b. Sartorius and popliteus c. Semitendenous and sartorius d. Biceps femoris and rectus femoris 5. Which adductor of the hip crosses the knee? a. Adductor brevis b. Adductor longus c. Adductor magnus d. Gracilis 6. Which adductor of the hip originates at the ischiopubic ramus? a. Adductor brevis b. Adductor longus c. Adductor magnus d. Gracilis 7. What is the function of the soleus? a. Flex toes b. Plantar flexion c. Knee flexion d. Flex digit 8. Which muscle everts the foot? a. Tibialis anterior b. Flexor digitorum longus c. Extensor hallucis longus d. Extensor digitorum GEORGINA. What is the function of the lavator scapula? a. Abducts scapula b. Upward rotation of scapula c. Elevates scapula d. Downward rotation of scapula 2. The insertion of the lavator scapulae is? a. Lower medial boarder of scapula b. Upper medial boarder of scapula c. Upper scapular spine 3. The function of the pectoralis minor is: a. Upward elevation of scapula b. Downward rotation of humerus c. Upward rotation of shoulders d. Downward rotation of scapula 4. The most medial muscle of the errector spinae group is: a. Splenius b. Longissimus c. Illiocostalis d. Spinalus 5. The origin of both the teres major and teres minor is: a. The anterior superior iliac spine b. Sternum c. Lateral boarder of scapula d. Medial boarder of scapula
3 6. All three portions of the deltoid muscle act together to: a. Medially rotate scapula b. Laterally rotate hip c. Abduction of the humerus 7. What two muscles have their insertion on the xiphoid process? a. Transverse abdominus, rectus abdominus b. External oblique, rectus abdominus c. Internal oblique, transvers abdominus d. Rectus abdominus, internal oblique 8. What muscle of the abdominal wall blends with the serratus anterior? a. External oblique b. Rectus abdominus c. Internal oblique d. Transverse abdominus 9. What muscle has its insertion on the olecranon process? a. Brachioradialis b. Biceps brachii c. Brachialis d. Triceps brachii 0. The insertion of the brachialis is: a. Acromium process b. Radial tuberosity c. Coracoid process d. Coranoid process. What muscle has its general location on the lateral side of the radius and ulna ( upper back side)? a. Pronator teres b. Supinator c. Pronator quadratus 2. The muscle that has its origin on the back of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus is: a. Annconeus b. Supinator c. Pronator teres d. Pronator quadratus 3. The muscle that is the soccer muscle is called the : a. Pectineus b. Tensor fasciae latae c. Illiopsoas d. Gluteus maximus 4. What muscle adducts the hip and does outward rotation? a. Gluteus minimus b. Gluteus maximus c. Pectineuw d. None of the a bove 5. What is the function of the quadriceps? a. Knee rotation b. Hip extension c. Knee flexion d. Knee extension 6. What muscle is known as the tailor muscle? a. Biceps femoris b. Rectus femoris c. Semitendonosus d. Sartorius 7. What muscle flexs hip and does inward rotation of the hip? a. gracilis b. Adductor longus c. Adductor magnus d. Adductor brevis 8. What muscles have their insertion on the linea aspera? a. Gracilis, adductor magnus b. Adductor longus, gracilis c. Adductor brevis, adductor magnus d. Adductor longus, adductor brevis JEN. What is the insertion of the Levator Scapula? a. Lateral Border of Scapula b. Acromium Process c. Upper, Medial Border of Scapula d. Anterior surface of medial Border 2. What is the one function that the Trapezius does NOT do? a. Elevates scapula b. Upwards rotation c. Adduction d. Extends Neck 3. What is the function that the Serratus Anterior and Pectoralis Minor share? a. Abducts scapula b. Adduction of scapula c. Upward rotation d. Downward rotation 4. Which muslce of the Erector Spinae Group inserts on the neck? a. Iliocostalis b. Spinalis c. Longissimus d. Thoraicic 5. Where is the origin of the Teres Minor? a. Subscapular Fossa b. Lateral Border of Scapula c. Medial Border of Scapula d. Anterior Surface of Scapula 6. Which muscle does NOT adduct? a. Pectoralis Major b. Teres Major c. Latissimus Dorsi d. Deltoid 7. What is the only abdominal muscle that does not flex the trunk? a. Internal Oblique b. Transverse Abdominus c. Rectus Abdominus d. External Oblique 8. Where does the Rectus Abdominus originate? a. Pubic Crest b. Inguinal Ligament c. Iliac Crest d. Pubis Ramus
4 9. What is the function the Pronator Teres does besides pronation? a. Shoulder Flexion b. Elbow Flexion c. Shoulder Extension d. Elbow Extension 0. What muscle abducts the ulna in pronation? a. Biceps Brachii b. Brachioradialis c. Triceps Brachii d. Annconeus. What is the function that the Tensor Fasciae Latae and the Gluteus Minimus share? a. Outward Rotation b. Extend Hip c. Inward Rotation d. Hip Flexion 2. The Gluteus Minimus and Medius are both inserted where? a. Gluteal Line b. Greater Trochanter c. Iliotibia Tract d. Pectineal Line of Femur 3. What muscle is called the tailor muscle? a. Popliteus b. Biceps Femoris c. Sartorius d. Semitendinosous 4. What is the insertion for all the quadriceps? a. Condyle of Tibia b. Tibial Tuberosity c. Posterior of Tibia d. Head of Fibula 5. What is the origin that both the Adductor Longus and Adductor Brevis share? a. Pubic Crest b. Pubic Ramus c. Ishiopubic Crest d. Ishiopubic Ramus 6. What is the muscle that does NOT inwardly rotate the hip? a. Adductor Magnus b. Adductor Brevis c. Gracillis d. Adductor Longus 7. What is the function of the Flexor Hallucis Longus? a. Flex toes b. Extends Digit c. Plantar Flexion d. Flex Digit 8. Where is the insertion of the Soleus? a. Posterior Calcaneus b. Base of Distal Phalanx c. Anterior Calcaneus d. Dorsal Surface of distal Phalanges JONNY. This is the only muscle of the scapula that originates at the base of the skull a. rhomboid b. levator scapula c. trapezius d. serratus anterior 2. The rhomboid inserts on the: a. coracoid process b. medial boarder of scapula c. ribs surface -9 d. lateral /3 of clavic 3. This muscle is used to extend the neck: a. Slenius b. Longissimus c. Sternocleidomastoid d. Pectoralis Minor 4. The Iliocostalis originates here: a. Costal cartilage b. Scapula c. Cervical vertebrae d. Sacrum 5. This muscle is also known as the Wings : a. Teres major b. Latissimus dorsi c. Spinalis d. Trapezius 6. The Pectoralis major does this function: a. Adducts and medial rotates humerus b. Extends shoulder c. Abducts the humerus d. Elevates scapula 7. The subscapularis inserts here: a. Clavical b. Bicep groove c. Deltoid tuberosity d. Lesser tuberosity 8. This muscle laterally rotates humerus while originating from the scapula boarder: a. Infraspinatus b. Serratus anterior c. Teres minor d. Spinalis 9. This muscle twists trunk to the same side: a. Rectus Abdominis b. Internal oblique c. Longissimus d. Bicep brachii 0. The transverse abdominus inserts in these places: a. Costal cartilage, ribs 8-0, sacrum b. Greater tuberosity, xiphoid, lessser tuberosity c. Lumbar fascia, linea alba, xiphoid process d. Pubis, linea aspera, tibial tuberosity. I am the main muscle on the top of the humerus that is most recognized: a. Bicep brachii b. Triceps brachii c. Annconeus d. Brachiolis
5 2. The brachioradialis originates here: a. Styloid process of radius b. Lower 2/3 anterior humerus c. Lower front of tibia d. Above lateral epicondyle of humerus 3. Which muscle does not belong in the deep six: a. Gemullus Superior b. Obturator Externus c. Quadriceps d. Piriformis 4. Gluteus medius originates on the outer ilium and inserts greater trochanter which allows it do move the hip this way: a. Extend hip, outward rotation b. Outward rotation abducts c. Flex hip, outward rotation d. Inward rotate hip, abduct 5. The biceps femoris allows the hip to extend, rotate knee and flex knee, so the best origin and insertion locations are: a. Tuberosity of ischium, lateral condyle of tibia b. Ischial tuberosity, posterior medial condyle of tibia c. Iliac spine, tibia tuberosity d. Pubic crest, linea alba 6. What functions does the Sartorius perform: a. Flex hip, inward rotation b. Abduct, extend hip c. Adduct, rotate hip d. Flex hip, outward rotate hip, flex leg 7. The adductor magnus inserts here: a. Linea aspera, adductor tubercle b. Posterior tibia c. Patella ligament d. Linea aspera (upper) 8. The gracilis does this function: a. Adducts hip, inward rotates hip b. Knee flex, extend hip c. Adducts hip, knee flex d. Outward rotates hip, abducts JULIA. The Trapesius muscle is used in this action: a. Pitching b. Shrugging c. Abducting scapula d. All of the above 2. The pectoralis major s origin is: a. C-C4 b. Rasheal c. Ribs 3-5 d. Ribs The muscles of the Erector Spinae Group are: a. Spinalus, Longissimus, Iliocostalis b. Spinalus, longer, Iliolonger c. Longissimus, Illinois, spinae d. Splenius, Levator spinatus, Iliospinatus 4. Where does the Erector Spinae Group all have in common: a. All extend spine b. All extend neck c. All look nice d. A and B 5. The origin of the Latissimus Dorsi (muscle acting on the humerus) is: a. Posterior illium, sacrum, vertebral spines of T7-L5 b. Medial ½ of clavicle c. Lateral bicipital groove d. Latis Dorsis fossa 6. The deltoid muscle has how many portions: a. 5 b. 2 c The origin of the rectus Abdominus is: a. Pubic Crest b. Ishial tuberosity c. Costal Cartillages d. All of the above 8. The transverse abdominus: a. Lifts up ribs b. Helps your lungs contract c. Compresses abdomen d. Both B and C 9. If someone was to try to be all HUGE and say which was it was to the beach they would be using and showing their: a. Biceps Brachii b. Brachialis c. Brachioradialis d. All of the above 0. The primary function of the Bracioradialis is: a. Elbow extension b. Elbow flexion c. Elbow greestick d. Abducts ulna in rotation. The Iliopsoas function is to: a. Flex Hip b. Shift body weight c. Abduct hip d. Adduct hip 2. The Pectineus is inserted at the: a. Pectineal line of femur b. Pubic crest c. Inner illium d. Lesser trochanter 3. What are the muscles on the front of the tibia: a. Sartorius b. Semiteninosus c. Semimembranosus d. All of the above 4. The quadriceps is: a. Rectus femorus, vastus (lateralis, intermedius, medialis) b. Rectum, vastus (lateralis, intermedius, medialis) c. Vas deferens, receter
6 5. What is the function of the popliteus? a. Knee flexion b. Medially rotates the tibia c. Laterally roatates tibia d. Both A and B 6. What is the muscles that only crosses the knee? a. Popliteus b. Semiteninosus c. Semimembranosus d. Gluteus Minimus 7. These two posterior muscles have the same insertion on the posterior calcanius: a. Flexor Digitorum longus, Flexor Hallucis longus b. Extendor D L, Extender H L c. Extensor digits, extensor Hercules d. Gastrocnemius, Soleus 8. The extensor Digitorum: a. Flexes toes b. Extends toes c. Cramps toes MATT Muscle Review Questions. The Trapezius has which funtion? a. Downward Rotation and adduction of scapulas b. Elevates Scapula c. Upward Rotation and adduction of scapulas d. Abduction of scapulas 2. Which muscle has the origin of C-C4? a. Trapezius b. Rhomboid c. Levator Scapula d. Splenius 3. What is the function of the Serratus Anterior? a. Abduction of scapulas and downward rotation b. Abduction of scapulas and upward rotation c. Adduction of scapulas and upward rotation d. Adduction of scapulas and downward rotation 4. What is the insertion point of the Longissimus? a. Ribs and clavicle b. Mastoid process c. Mastoid process and C and T vertebrae d. C and T vertebra 5. If you adduct, medially rotate and flex your humerus which muscle are you using? a. Latissimus Dorsi b. Pectoralis Major c. Teres Major d. Teres Minor 6. Which two muscles laterally rotate the humerus? a. Teres Minor b. Supraspinatous c. Deltoid d. Infraspinatous. A and B 2.B and C 3.B and D 4.A and D 7. Which of the abdominal muscles is the most medial? a. Rectus Abdomis b. Internal Oblique c. External Oblique d. Transverse abdominis 8. What is the origin of the Transverse abdominis? a. Pubic crest b. Inguinal ligament, linea alba, pubis c. iliac crest lumbar fascia d. Inguinal ligament, iliac crest, costal cartilages What is the insertion of the Biceps Brachii? a. Coronoid process of ulna b. Styloid process on radius c. Radial tuberosity d. Olecranon process 0. Which muscle has the function of elbow flexion, primarily when arm is between supination and pronation? a. Biceps Brachii b. Brachialis c. Brachioradialis d. Triceps Brachii. What is the insertion point of the Illiopsoas? a. Pectineal line of femur b. Greater trochanter c. Lesser trochanter d. Iliotibia tract 2. If you wish to outwardly rotate your hip while abducting it, which muscle will you use? a. Iliopsoas b. Tensor Fascia Latae c. Gluteus medius d. Gluteus Minimus 3. What is the insertion of the Sartorius? a. Medial Condyle of Tibia b. Tibial Tuberosity c. Lateral condyle of Tibia d. Linea Aspera 4. If you wish to extend your hip, flex your knee and rotate knee outward, which muscle must you use? a. Rectus Femoris b. Biceps Femoris c. Semitendinosus d. Gluteus Maximus 5. Which is the adducter that does not inwardly rotate the hip? a. Adducter Magnus b. Pectineus c. Adducter Brevis d. Gracilis
7 6. What is the origin of the Flexor Digitorum Longus? a. Posterior Tibia b. Lateral condyle tibia and andterior fibula c. Base of 4 distal phalanx of 4 toes d. Posterior upper tibia and fibula 7. What muscle has the funtion of plantar flexion? a. Extensor Digitorum Longus b. Flexor Digitorum Longus c. Gastrocnemius d. Soleus 8. What is the funtion of the Extensor Digitorum Longus? a. Extend toes and evert toes b. Extends digit c. Plantar flexion d. Flex digit MEL. Which two muscles adducts the scapula? a. Pectoralis Minor and Levator Scapula b. Pectoralis Minor and Serratus Anterior c. Rhomboid and Trapezius d. Rhomboid and Serratus Anterior 2. What is the origin of the Pectoralis Minor? a. Lateral surface of ribs -9 b. Anterior surface of ribs 3-5 c. Vertebral spines C7-T5 d. Spines of C7-T2 3. How many muscles are in the Erector Spinae Group? a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d Which muscles s origin is the medial clavicle? a. Splenius b. Spinalis c. Sternocleidomastoid d. Longissimus 5. Which two muscles acting on the humerus are attached to the scapula? a. Latissimus Dorsi and Teres Major b. Deltoid and Pectoralis Major c. Teres Major and Pectoralis Major d. Teres Major and Deltoid 6. Which muscle is not a muscle of the rotator cuff? a. Teres Minor b. Teres Major c. Infraspinatus d. Subscapularis 7. Which of the abdomen muscles does not flex the trunk? a. Transverse Abdominus b. Internal Oblique c. Rectus Abdominus d. External Oblique 8. The External Oblique has an insertion of the outer surface ribs. What is the blank? a. 5-7 b. 5-9 c. 5-2 d Which muscle of the arm is not an elbow flexor and extensor? a. Biceps Brachii b. Brachioradialis c. Pronator Quadratus d. Anconeus 0. How many muscles of the arm are supinators and pronators of the forearm? a. 3 b. 4 c. 2 d. 5. Which muscles of the hip joint does not flex the hip? a. Tensor Fasciae Latae b. Pectineus c. Gluteus Medius d. Iliopsoas 2. Which muscle of the hip joint has a function of abducting the hip and outward rotation hip? a. Pectineus b. Gluteus Medius c. Gluteus Minimus d. Gluteus Maximus 3. Which hamstring has an origin of linea aspera and tuberosity of ischium? a. Semitendinosus b. Biceps Femoris c. Semimembranosus d. Sartorius 4. Which muscles of the hip joint unlocks the knee? a. Popliteus b. Quadriceps c. Sartorius d. Biceps Femoris 5. What is the insertion of the Adductor Brevis? a. Adductor Tubercle b. Medial Condyle c. Pectineal Line of Femur d. Linea Aspera 6. Which adductor muscle of the hip joint does not have an origin of the pubic crest? a. Adductor Brevis b. Adductor Longus c. Adductor Magnus d. Pectineus 7. Which muscle of the ankle and foot is deep? a. Flexor Digitorum Longus b. Gastrocnemius c. Soleus d. Extensor Digitorum Longus 8. Which muscle of the ankle and foot is not posterior? a. Extensor Digitorum Longus b. Flexor Digitorum Longus c. Gastrocnemius d. Soleus
8 TRISHA. What is the function of the Rhomboid? a. Upward rotation b. Abducts scapula c. Adducts scapula d. Both and 3 2. Which muscles adduct? a. Trapezius b. Levator Scapula c. Rhomboid d. Both and 3 3. Which muscle is NOT a part of the Erector Spinae group? a. Spinalis b. Longissimus c. Splenius d. Iliocostalis 4. What muscle has the origin of the lateral surface of ribs -9? a. Rhomboid b. Splenius c. Serratus Anterior d. Pectoralis Minor 5. Which 2 muscles insert in the lip of the bicipital groove? a. Teres Major and Teres Minor b. Pectoralis Major and Teres Major c. Pectoralis Major and Pectoralis Minor d. Latissimus Dorsi and Pectoralis Major 6. Which is a muscle of the rotator cuff that abducts the humerus? a. Supraspinatus b. Subscapularis c. Infraspinatus d. Teres Minor e. None of the above 7. What is the function of the Transverse Abdominus? a. Compresses abdomen b. Flexes trunk laterally c. Flexes trunk (one side flexes to the same side) d. Trunk extension 8. Which muscle(s) insert in the Linea alba? a. Rectus Abdominus & Transverse Abdominus b. External Oblique & Internal Oblique c. Transverse Abdominus & Internal Oblique d. Transverse Abdominus 9. Which muscles extend the elbow? a. Biceps Brachii & Triceps Brachii b. Brachialis & Brachioradialis c. Biceps Brachii & Annconeus d. Triceps Brachii & Annconeus 0. Which muscle abducts the ulna? a. Biceps Brachii b. Brachioradialis c. Triceps Brachii d. Annconeus. Which muscles inwardly rotate? a. Iliopsoas & Pectineus b. Obturator Internus & Obturator Externus c. Tensor Fasciae Latae & Gluteus Maximus d. Tensor Fasciae Latae & Gluteus Minimus 2. What is the function of the Deep 6" muscles? a. Flex leg b. Inward rotation of the hip c. Outward rotation of the hip d. Adduction 3. What is the common origin of Vastus Lateralis and Vastus Medialis? a. Linea aspera b. Iliac Spine c. Patella d. Femur 4. Which hamstring outwardly rotates the knee? a. Semitendinosus b. Biceps Femoris c. Popliteus d. Semimembranosus 5. Which two adductors share a common origin? a. Adductor Magnus & Adductor Longus b. Adductor Magnus & Adductor Brevis c. Adductor Longus & Gracilis d. Adductor Longus & Adductor Brevis 6. Which muscle extends the hip? a. Popliteus b. Adductor Magnus c. Adductor Longus d. Adductor Brevis e. Gracilis 7. Which muscle is responsible for plantar flexion and knee flexion? a. Tibialis Posterior b. Gastrocnemius c. Soleus d. Peroneus Longus 8. Which muscle originates in the posterior tibia? a. Tibialis Posterior b. Gastrocnemius c. Flexor Digitorum Longus d. Flexor Hallucis Longus JUSTINE. One of the origins of this muscle is found at the base of the skull. a. Ear b. Levator scapula c. Trapezius d. Rhomboid 2. A muscle must cross a joint to act on that joint. a. Painfully b. Antagonistly c. Inversly d. Directly
9 3. This large muscle is known as the boxer s muscle. a. Serratus posterior b. Rhomboid c. Pectoralis minor d. Serratus anterior 4. The splenius is used in extension. a. Neck b. Tricep c. Abdominal d. Quadracept 5. The Deltoid muscle is divided into how many parts? a. 4 b. 2 c. 3 d All of the muscles of the rotater cuff insert at the... a. Deltoid tuberosity b. Bicipital groove c. Greater tubercle of humerus d. Lesser tubercle of humerus 7. The external oblique, internal oblique and transverse abdominus all originate at the... a. Costal cartilage b. Outer surface of ribs 5-2 c. Pubic crest d. Inguinal ligament 8. This muscle enables forced expiration a. Transverse abdominus b. Rectus abdominus c. External oblique d. Internal oblique 9. The elbow flexor & extensor originates at the coracoid process and the top of the glenoid fossa and tuberosity of radius. a. Brachioradialis b. Biceps brachii c. Brachialis d. Triceps brachii 0. The Brachialis is to the biceps brachii. a. Medial b. Superficial c. Deep d. Lateral. Which of the following statements is true, regarding the gluteus muscles? a. The medius is superficial to the maximus b. The maximus is deep to the minimus c. The minimus is deep to the medius d. The medius is deep to the minimus 2. Which of these muscles originates at the outer ilium? a. Gluteus mimimus b. Gluteus medius c. Neither d. Both a & b 3. Which muscle is not a quadracep muscle? a. Vastus medialis b. Vastus lateralis c. Rectus femoris d. Vastus sartorius 4. Which muscle is not a hip extendor? a. Semitendinosus b. Semimembranosus c. Biceps femoris d. Sartorius 5. Where does the Gracilis insert? a. Adductor tubercle b. Middle of linea aspera c. Front of medial condyle d. Upper linea aspera 6. Not only does this muscle adduct the hip, but it inwardly rotates the hip AND flexes the hip. a. Adductor longus b. Adductor brevis c. Gracilis d. Adductor magnus 7. The action of the flexor hallucis longus is... a. Plantar flexion b. Dorsiflexion c. Extend digit one d. Flex digit one 8. What is the origin of the extensor digitorum longus? a. Posterior tibia & fibula b. Lateral condyle tibia anterior fibula c. Upper outer fibula d. Lower outer fibula VICKI. Both of these adduct the scapula a. Levator Scapula, Trapezius b. Rhomboid, Levetation Muscle c. Supraspinezous, Trapezed d. Trapezius, Rhomboid 2. The is used in an activity such as. a. Trapezius, hand stands b. Rhomboid, weight lifting c. Levator Scapula, shrugging d. Sternum, breathing 3. These muscles are responsible for rotation of the neck a. Rectoralis Minor, Splenius b. Sternocleidomastoid, Splenius c. Sternum, Splezious d. Longissimus, Splenius 4. This muscle inserts at the ribs and clavicle a. Iliocostalis b. Spinalis c. Longissimus d. Iliocosimus
10 5. The infraspinatus inserts on what and originates where? a. Lesser tuberosity, Supraspinus fossa b. Greater trochanter, Infraspinus fossa of the scapula c. Greater tuberosity, Supraspinus fossa d. Greater tuberosity, Infraspinus fossa of the scapula 6. These muscles act on the humerus and assist in rotation, pick the best answer a. Latissimus Dorsi, Infraspinatus b. Teres Major, Latissimus Dorsi c. Supraspinatus, Teres Minor d. a and b 7. What are two muscles of the abdomen that have an origin on the pubic crest, what are they? a. Rectus Abdominus, External Oblique b. Internal Oblique, Transverse Abdominus c. Oblique Abdominus, Rectus External d. Rectus Abdominus, Internal Oblique 8. This muscle has an origin of the Inguinal Ligament and an insertion of the xiphoid process and linea alba. What Muscle is this? a. External Oblique b. Internal Oblique c. Rectus Abdominus d. Transverse Abdominus 9. These muscles of the arm all flex the elbow a. Biceps Brachii, Brachioradialis, Brachialis b. Biceps Brachii, Triceps Brachii c. Brachialis, Triceps Brachii d. Deltoid, Brachioradialis 0. The Pronator Teres is involved with the function of and is located to the wrist a. Supination, Distal b. Pronation, Distal c. Pronation, Proximal d. Supination, Proximal. What do the deep six muscles, the Gluteus Medius and Gluteus Minimus all have in common? a. They all cross the hip joint b. They all have an origin of the ilium c. They all have an insertion on the greater trochanter d. a and c 2. What best describes the ilopsoas muscle? a. Origin: sides of lumbar vertebrae. Insertion: Greater Trochanter b. Origin: Sides of the sacrum. Insertion: Lesser Trochanter c. Origin: Anterior Sacrum. Insertion: Lesser Trochanter d. Origin: Sides of Lumbar Vertebrae. Insertion: Pubic Crest 3. What is the difference between the Semitendinosus and Semimembranosus? a. One assists Knee Flexion b. One origins on the Ischial Tuberosity c. One extends the hip d. One inserts on the anterior medial condyle 4. The Rectus Femoris has an origin on: a. Medial lip of the linea aspera b. Lateral lip of the linea aspera c. Anterior inferior iliac spine d. Anterior shaft of the femur. 5. What muscle has an origin of the pubic ramus, an insertion of the front medial condyle and flexes the knee. a. Gracilis b. Adductor Longus c. Adductor Magnus d. Adductor Brevis 6. What muscles promote inward rotation of the hip? a. Adductor Longus, Magnus, Brevis, and Gracilis b. Popliteus, Adductor Magnus, and Gracilis c. Adductor Magnus and Longus, Brevis d. Gracilis and Popliteus 7. What muscle has an origin of the later condyle of the tibia and anterior of the fibula. This muscle is used to extend the toes. What muscle is it? a. Extensor Digitorum Longus b. Flexor Digitorum Longus c. Gastrocnemius 8. These two muscles have the action of plantar flexionof the foot. What two muscles are they of the following: a. Gastrocnemius and Extensor Digitorum Longus b. Flexor Digitorum Longus and Soleus c. Extensor Digitorum Longus and Soleus d. Gastrocnemius and Soleus
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles. Muscles of the Head and Neck. Masseter. Orbicularis occuli. Orbicularis oris. Sternocleidomastoid
 Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY
 SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
Lab 9: Learn origin and insertion for each of the listed muscles. For Exercise 15, do Activities 1-6 in 9 th edition, Activities 1-4 in 10 th edition
 The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
Anatomy & Physiology. Muscles of the Lower Limbs.
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Lab Exercise #5 The Muscular System Student Performance Objectives
 Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back
 Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED
 Anatomy and Physiology Workbook LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED Label The Skeletal System Fibula Lumbar vertebrae Patella Sternum Ilium Femur Scapula Phalanges Sacrum Ischium Tarsals Cranium Clavicle Pubis Ribs
Anatomy and Physiology Workbook LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED Label The Skeletal System Fibula Lumbar vertebrae Patella Sternum Ilium Femur Scapula Phalanges Sacrum Ischium Tarsals Cranium Clavicle Pubis Ribs
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions
 BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1 and answer the following: Name the covering labeled Name the tubular portion labeled Name the hollow part labeled Name the material labeled Name
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1 and answer the following: Name the covering labeled Name the tubular portion labeled Name the hollow part labeled Name the material labeled Name
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES
 ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS
 TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Masseter- in front of ear Temporalis Mandible
 Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Appendix. Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance
 Appendix Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance Appendix Outline Respiratory System 426 Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426 Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426 Musculoskeletal
Appendix Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance Appendix Outline Respiratory System 426 Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426 Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426 Musculoskeletal
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
Internship Questions. PP 1 Anatomical Planes & Directions
 Internship Questions PP 1 Anatomical Planes & Directions 1. Which of the following is not a plane of motion a. Sagittal b. Vertical c. Frontal d. Transverse 2. Which of the following terms are related
Internship Questions PP 1 Anatomical Planes & Directions 1. Which of the following is not a plane of motion a. Sagittal b. Vertical c. Frontal d. Transverse 2. Which of the following terms are related
Healing Hands School of Holistic Health. Advanced Circulatory & Sports Massage Class Handouts
 Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
Human Anatomy Biology 255
 Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Sports Medicine Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX
 Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan & A. Eastlake, 2008 Muscles of the Upper Limbs In this
Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan & A. Eastlake, 2008 Muscles of the Upper Limbs In this
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS
 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
 Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Thigh. 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group
 Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Muscles Built on the Maniken
 Muscles Built on the Maniken Facial Muscle Group 1. Temporalis O temporal fossa I anterior border of the ramus of the mandible A elevates the mandible (bite muscle) and holds jaw while at rest 2. Procerus
Muscles Built on the Maniken Facial Muscle Group 1. Temporalis O temporal fossa I anterior border of the ramus of the mandible A elevates the mandible (bite muscle) and holds jaw while at rest 2. Procerus
Anatomy and Physiology 2016
 Anatomy and Physiology 2016 O = Temporal line I = coronoid process (Mandible) A = elevates mandible (chewing) O = galea aponeurotica (layer of dense fibrous tissue which covers the upper part of the cranium)
Anatomy and Physiology 2016 O = Temporal line I = coronoid process (Mandible) A = elevates mandible (chewing) O = galea aponeurotica (layer of dense fibrous tissue which covers the upper part of the cranium)
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Location Terms. Anterior and posterior. Proximal and Distal The term proximal (Latin proximus; nearest) describes where the appendage joins the body.
 HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy
 Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm
 Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb
 The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
Hip joint and pelvic girdle. Lower Extremity. Pelvic Girdle 6/5/2017
 Hip joint and pelvic girdle Lower Extremity The relationship between the pelvic girdle and hip is similar to that between the shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The lower limbs are attached to the axial
Hip joint and pelvic girdle Lower Extremity The relationship between the pelvic girdle and hip is similar to that between the shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The lower limbs are attached to the axial
this makes sense, however this is lower order thinking and does not solve the lower leg
 Functional Knee Valgus in a Barbell Squat 1 One of the most common lower leg dysfunction we see in athletes, particularly general population is functional knee valgus, or better referred to as the knees
Functional Knee Valgus in a Barbell Squat 1 One of the most common lower leg dysfunction we see in athletes, particularly general population is functional knee valgus, or better referred to as the knees
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY WEEKLY NOTES:
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY WEEKLY NOTES: Pages 2-11 Week 1 Head and Neck Pages 12-39 Week 2 Trunk Pages 40-52 Week 3 Hip Joint Pages 53-60 Week 4 Knee Joint Pages 61-70 Week 5 Ankle Joint Pages 71-82 Week 6 Foot
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY WEEKLY NOTES: Pages 2-11 Week 1 Head and Neck Pages 12-39 Week 2 Trunk Pages 40-52 Week 3 Hip Joint Pages 53-60 Week 4 Knee Joint Pages 61-70 Week 5 Ankle Joint Pages 71-82 Week 6 Foot
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis. Parts of the hip. Parts of the femur
 Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only. Side lye or prone.25 x 30-50mm Inferior to ilium
 LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp ) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a
 The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp. 321 322) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a muscle shortens, the insertion is pulled toward the
The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp. 321 322) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a muscle shortens, the insertion is pulled toward the
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Skeleton. The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation.
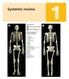 S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
Chiropractic Technician Class
 Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
The thigh. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
Practical 1 Worksheet
 Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking
 1 p.177 2 3 The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking and running. The iliopsoas and adductor
1 p.177 2 3 The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking and running. The iliopsoas and adductor
Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض. Ahmad Salman. 1 P a g e
 4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS
 Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
The Hip Joint. Shenequia Howard David Rivera
 The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
OVERVIEW OF THE SIX FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAYS
 A P P E N D I X O N E OVERVIEW OF THE SIX FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAYS THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 PHOTO A1.1A AND B STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY
A P P E N D I X O N E OVERVIEW OF THE SIX FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAYS THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 PHOTO A1.1A AND B STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints. Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint
 Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Muscles of the Cat Review Sheet
 MUSCLES F THE CHEST 1. Pectoralis major clavicle, sternum, costal cartilages greater tubercle of humerus Flexes, adducts and medially rotates arm (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES F
MUSCLES F THE CHEST 1. Pectoralis major clavicle, sternum, costal cartilages greater tubercle of humerus Flexes, adducts and medially rotates arm (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES F
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
Anatomy and Physiology 141 Exam II November 6, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology 141 Exam II November 6, 2014 Name Student Number 1. In regards to the gross anatomy of muscle, which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. Perimysium is more superficial than the epimysium
Anatomy and Physiology 141 Exam II November 6, 2014 Name Student Number 1. In regards to the gross anatomy of muscle, which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. Perimysium is more superficial than the epimysium
Lowe w r e r B ody Resistance Training
 Lower Body Resistance Training Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Proneus Tertius AROM 25-40 degrees Extensor active-insufficiency Flexion & Eversion (Pronation) Flexion
Lower Body Resistance Training Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Proneus Tertius AROM 25-40 degrees Extensor active-insufficiency Flexion & Eversion (Pronation) Flexion
Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles.
 L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
Lesson 24. A & P Hip
 Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Compiled and Designed by: Sport Dimensions - 2 -
 SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
3/27/2012. Muscle Classification: Functional Groups. Interactions of Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
