BDNF release from single cells elicits local dendritic growth in nearby neurons
|
|
|
- Ariel Greene
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
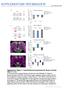
1 BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209, Durhm, North Crolin 27710, USA 2 Current ress: Deprtments of Biology n Neurosiene, Bowoin College, 6500 College Sttion, Brunswik, Mine 04011, USA Corresponene shoul e resse to H.W.H. (hhorh@owoin.eu) Pulishe online: 30 Septemer 2002, oi: /nn927 In ulture neurons, the exogenous pplition of neurotrophins (in homogenous onentrtions) lters mny fetures of xonl n enriti rors. In vivo, however, relese of enogenous neurotrophins from neuronl proesses retes sptilly heterogeneous neurotrophin istriutions. To proe the onsequenes of suh enogenous neurotrophin istriution, we proue onor neurons in ferret ortex rin slies tht o-expresse rin-erive neurotrophi ftor (BDNF) n re fluoresent protein (RFP). Using two-photon mirosopy, we nlyze their effets on reipient neurons tht expresse green fluoresent protein (GFP) lone. BDNF relese from enrites n ell oies te iretly on nery reipient neurons to inrese enriti rnhing in istne-epenent mnner. Three-imensionl nlysis of onor n reipient enrites inite tht the BDNF soure h to e within 4.5 µm to inue enriti growth in the reipient neuron. Thus, BDNF relese from n iniviul ell lters the struture of nery enrites on n exquisitely lol sle. The evelopment of enriti rors is influene y innte geneti progrms 1, tivity 2 4 n externl moleulr ues 5 7. As severl of these moleulr ues re themselves regulte y neuronl tivity, unerstning how moleulr ues influene enriti growth n revel how tivity is trnslte into struturl hnges in the eveloping rin. BDNF, memer of the neurotrophin fmily of growth ftors, is of speil interest in this regr, s its expression n relese re moulte y neuronl tivity 8 11 n its presene n lter the struture of enrites n spines in the mmmlin CNS By virtue of its omine tivity-epenent relese n morphogeni properties, BDNF my funtion s synpti morphogen 18. To ssess BDNF s role in regulting enriti growth, however, it is neessry to present neurons with ellulr soure of BDNF tht more losely mimis physiologil onitions. To this en, we use iniviul pyrmil neurons in ortil slies s neurotrophin onors to simulte in vivo neurotrophin elivery from enogenous soures. We foun (i) tht BDNF ts s sptilly restrite signl for enriti rnhing tht is psse etween neurons, n (ii) tht it inues fol enriti growth tht my influene the funtionl properties of neuronl iruitry. RESULTS Using prtile-meite gene trnsfer, we rete two popultions of pyrmil neurons within slies of ferret visul ortex. Re onor neurons were o-trnsfete with DNA for re fluoresent protein (RFP) n n epitope-tgge BDNF onstrut, n green reipient neurons were trnsfete with GFP lone. Thirty-six hours fter trnsfetion, pirs of onor n reipient neurons in lose proximity to one nother in the x y plne were simultneously imge using two-olor, two-photon mirosopy (Fig. 1). Two-photon mirosopy not only resolve the etile struture of the reipient neurons, ut the optil setioning inherent in this metho enle us to etermine the istne etween onor n reipient enrites. We were thus le to estimte the rnge of BDNF s influene. The t presente here re se on 79 ell pirs (23 BDNF onor/reipient pirs, 29 ontrol pirs, 21 nerve growth ftor (NGF) pirs n 6 trunte TrkB (T1) ell pirs). Lol inrese in enriti rnhing We previously foun tht BDNF overexpression inreses the numer of sl enrites on onor neurons 16 (lthough the fine proesses of the resulting hlo of enrites were not lerly seen uner 960 nm light the wvelength require to simultneously visulize oth GFP n RFP). Here we foun tht the enrites of reipient neurons were ffete very ifferently, epening on their proximity to the som or enrites of onor neuron. This proximity orrelte with fol inrese in the reipient neuron s enriti rnhing (Fig. 1 ). The reipient neuron s enriti rnhes tht were lote ner BDNF onor neurons frequently grew in norml iretions or emerge from the prent enrite t unusul ngles. None of these fetures were seen in reipient enrites tht were lote ner ontrol onor neuron ell oies or enrites (ells trnsfete with RFP lone, Fig. 1e n f). These ltertions in enriti rnhing were restrite to the enrites in the immeite viinity of the onor. In ontrst to BDNF overexpression 16 or th pplition of BDNF 12, oth of nture neurosiene volume 5 no 11 novemer
2 e whih n inrese the numer of sl enrites, proximity to BDNF onor neuron left the sl enrite numer unhnge. The numer of sl enrites on reipient neurons tht were lose to (<4.5 µm) BDNF-expressing onor neurons or RFP ontrol onors ws inistinguishle (4.23 ± 0.47, n = 13 versus 4.06 ± 0.30, n = 16, t-test, P = 0.755). The hlo of enrites hrteristi of ells overexpressing BDNF ws sent 16. Furthermore, lthough BDNF overexpression in iniviul neurons erese enriti stility 16, time-lpse imging showe tht the shortterm stility of reipient enrites ws unffete y proximity to BDNF onors (n = 10, 2-hour imging, t not shown). To exmine the effets of onor lotion on the rnhing of iniviul enrites, proesses were reonstrute n the threeimensionl (3D) reltionship to the onor ws quntifie Fig. 2. BDNF-inue enriti rnhing is highly restrite n orreltes with istne from the soure of BDNF. Color-oe reonstrutions of iniviul reipient neuron enrites revel effet of istne from the soure of BDNF. From the som to the first intersetion point, the reipient enrites re renere in green. Therefter, the olor of the enrite inites the istne etween the onor neuron n reipient enrite (olore r t the ottom). Fille green retngles represent the min pil enrite, n open irles represent soms of reipient neurons. Donor proesses re epite s smll re retngles n RFP soms re fille in re for BDNF onor neurons ( e) n outline in re for ontrol onor neurons (f j). Most yellow enrites (those <4.5 µm from onor proess) re highly rnhe ( ), wheres lue n turquoise enrites (>4.5 µm from onor proess) remine unrnhe ( n e). Reonstrutions lso show fol rnhing, with no effets on enrites evient proximl to the intersetion point ( n ). In ontrst, reipient neuron enrites ner RFP ontrol ells (f j) show no inrese enriti rnhing either when lose (f j) or fr (h n j). Green irles tht represent soms re pproximtely 10 µm in imeter. f Fig. 1. Lol growth of enrites of reipient neurons in res ner BDNF onor neurons. (, ) Simultneous two-photon imging of reipient (green) n BDNF onor neurons (re) revele lol res of inrese enriti omplexity (oxes enlrge in n ). Twophoton imges onsist of stks of multiple optil setions. Reipient neurons h norml numers of sl enrites n norml overll shpe n ensity of their enriti rors. However, norml ptterns of rnhing were oserve in enrites growing in lose proximity to BDNF onor neurons, s evient in higher-power imges (, ). In ontrst, ontrol neurons expressing only RFP h no influene on GFP reipient neurons (e), even in res where reipient enrites were lose to the ontrol neuron (f). Sle rs, 10 µm. (Fig. 2). Invrily, rnhing egn to inrese preisely where the reipient neuron s enrites intersete with those of the onor neuron. Inrese rnhing ontinue istlly, ut i not propgte retrogrely to the more proximl strethes of enrite (Fig. 2 e). The proximity of the BDNF soure to the reipient enrite in 3D spe strongly influene the extent of enriti rnhing (olor-oe in Fig. 2 e). For exmple, n pil enrite of reipient ell rossing onor neuron ell oy showe ense network of rnhes when the pil enrite rosse within 4.5 µm of the ell oy (s in Fig. 2). No suh inrese rnhing ws evient when n pil enrite ws more thn 4.5 µm ove or elow the BDNF onor ell oy (s in Fig. 2e). To ontrol for the remote possiility tht inrese rnhing in reipient neurons resulte from overexpression of RFP, rther thn BDNF, we exmine the effets of ontrol neurons expressing RFP lone on the rnhing of reipient neurons. Regrless of proximity, onor neurons trnsfete with RFP lone h no influene on the rnhing of iniviul reipient neurons (Fig. 2f j). Thus, the inrese enriti rnhing in reipient neurons results from BDNF overexpression, n not RFP overexpression. Moreover, this ontrol shows tht lose proximity of e f g h i j 1178 nture neurosiene volume 5 no 11 novemer 2002
3 Fig. 3. Lol enriti growth is not generl result of neurotrophin overexpression. NGF onor neurons were rete y o-trnsfeting neurons with NGF n RFP. Even when NGF onor proesses (re) were in the sme optil setion s reipient enrites (green, ) or in jent setions (), lol enriti morphology i not iffer from ontrols. High-power imges onfirm tht reipient enrites remine simple n showe no inrese enriti rnhing ( n ). Sle rs, 10 µm. enrite of one fluoresent ell to the ell oy or enrites of nother oes not in itself inue fol enriti rnhing. To etermine whether the oserve effets of BDNF on reipient neurons were speifi to BDNF, we rete NGF onor neurons y sustituting n epitope-tgge NGF onstrut for the BDNF DNA. Unlike BDNF onors, NGF onor neurons eliite no lol or glol growth of enrites reltive to ontrols, even when the NGF onor proess n the reipient proess were within the sme optil setion (11.82 ± 0.84 µm for 16 NGF intersetion points versus ± 0.46 µm for 39 ontrol intersetion points, ANOVA, P = 0.98, Fig. 3). This inites tht the effets of BDNF on lol enrite growth were not generl effet of neurotrophin overexpression. To etermine how lose BDNF onor neuron nees to e to signifintly ffet enriti rnhing in reipient neuron, we use the numer of intervening optil setions etween onor n reipient neurons t n intersetion point (Methos). Lol enriti rnhing ner this point ws ssesse y summing the liner length of enrites within 10-µm imeter yliner entere on the intersetion point n extening ove n elow it (Fig. 4 n e). When the soure of BDNF ws within the sme optil setion (<3 µm), the verge length of reipient enrites (16.2 ± 0.88 µm, n = 39 intersetion points) ws 40% greter thn tht of RFP ontrols (11.6 ± 0.46 µm, n = 39 intersetion points), ifferene tht ws sttistilly signifint (Fig. 4i, ANOVA, P < 0.05). No inrese in enriti length ws evient when the soure of BDNF ws more thn 4.5 µm wy (Fig. 4i). As further test of whether the presene of onor proess use lol enriti sprouting in reipient neurons, for eh e f g h i j neuron we lulte the rtio etween the solute length mesurements otine ove (Fig. 4i) to mesurements otine on equivlent enrites on the opposite sie of the ror n t n equl istne from the som (Fig. 4j). A rtio of unity (1:1) inites tht there ws no ifferene, on verge, in the mount of enrite in the two loles, wheres rtio greter thn one signifies inrese rnhing ner the site of intersetion with the onor neuron. Consistent with the results from the mesurements of solute enriti length, the rtio etween the enriti lengths ner the soure of BDNF n on the opposite sie of the som ws signifintly >1 only when the soure of BDNF ws within 3 µm (Fig. 4j). Fig. 4. Quntifition of lol enriti lengths revels istneepenent, lol effets of BDNF. ( h) Exmples of metho use to quntify enriti length t lose intersetion point () n fr intersetion point (e) etween onor (re) n reipient enrite (green). In oth ses, irle ws entere on n intersetion point ientifie in the 2-D imge. The z-xis lotion of the intersetion point ws lote ( n g), n irles were lso ple in the optil setion ove ( n f) n elow ( n h), reting yliner. Denriti length ws first mesure in the entrl setion, n ny itionl enrite present ove or elow ws e. RFP n GFP proesses were lerly ololize t lose intersetions () in ontrst to fr intersetions where only the GFP enrite ws visile in iniviul optil setions (g). White irles re 10 µm in imeter. (i) Histogrm of enriti lengths inne oring to the istne etween the intersetion of the reipient n BDNF onor proesses (lk rs) n ontrol proesses (gry rs). Asterisk enotes signifint ifferene within tht in s sertine y ANOVA n then Tukey multiple omprison post-test (P < 0.05) s ompre to ontrol in eh in. Brs re men + s.e.m. (j) The rtio of the mesure enriti lengths t the point of intersetion n on the opposite sie of the enriti ror inne oring to the istne etween the intersetion of the reipient n BDNF onor neurons (lk rs) n ontrol neurons (gry rs). Asterisk enotes signifint ifferenes s in (i) (P < 0.05). Brs re men ± s.e.m. nture neurosiene volume 5 no 11 novemer
4 This inites tht signifint inreses in enriti omplexity were restrite to lotions ner the soure of BDNF. BDNF ts iretly to inue fol enriti growth As we h previously shown tht BDNF is relese from BDNFoverexpressing ells 16, we were onfient tht the fol enriti growth ws onsequene of BDNF relese from onor neurons into the extrellulr spe. The fining tht BDNF expression in one neuron eliits growth in nother oes not neessrily men, however, tht relese BDNF is the signl responsile for the enhne enriti outgrowth. The relese BDNF oul t either iretly on reipient enrites or iniretly through nery ells. To etermine whether BDNF te iretly to eliit fol enriti growth, we rete reipient neurons tht expresse ominnt-negtive TrkB reeptor, thus renering them unresponsive to BDNF. Reipient neurons were otrnsfete with GFP n n epitope-tgge form of trunte TrkB (T1) 19 lking the intrellulr signling omin 20,21. Expression of oth T1 n BDNF ws onfirme vi post-ho immunohistohemistry for ll ells (s in Fig. 5 n ), n we use only pirs of neurons in whih BDNF n T1 were expresse, respetively, for nlysis. T1-trnsfete reipient neurons i not respon to BDNF from onor neuron enrites or ell oies (Fig. 5). Their enrites were no more omplex thn ontrols, regrless of their proximity to BDNF soure. Using the sme mesurement pproh esrie ove, the verge length of ontrol reipi- Fig. 5. Overexpression of ominnt negtive form of TrkB (T1) in reipient neurons loks BDNF-inue rnhing. Reipient neurons o-trnsfete with GFP n T1 o not show inrese enriti rnhing no mtter how lose the soure of BDNF ( ). Donor n reipient proesses re in the sme optil setion in the mjority of the intersetion points in these imges. (, ) Expression of T1 n BDNF were onfirme y post-ho immunohistohemistry. () Exmple of neurons in whih my-tgge BDNF (re rrow) is expresse in the re onor neuron n FLAG-tgge T1 (green rrow) is expresse in the green reipient neuron. Sle rs, 10 µm. ent enrites lote <4.5 µm from BDNF onor proesses (omining first two ins in Fig. 3, 16.0 ± 0.69 µm, n = 59 intersetion points) ws signifintly lrger thn the verge length of T1-expressing enrites (11.0 ± 0.66 µm, n = 10 intersetion points, P = 0.005, t-test). This result onfirms the qulittive impression from the imges in Fig. 5: T1 overexpression in the reipient neuron loke BDNF-inue inreses in lol enriti growth. Therefore, BDNF from onor neurons ts on reipient neuron enrites iretly, through intertions with the TrkB reeptor. Lol BDNF oes not ffet xons or spines The effets of interellulr BDNF were most ovious on enrites, ut s BDNF n inue xon outgrowth in the CNS 15,22, we exmine whether BDNF onor neurons influene sprouting of pyrmil ell xons in reipient neurons. The min xonl trunk of pyrmil neurons frequently forms severl ollterl rnhes within few hunre mirons of the ell oy 23. Reipient xons trversing lose to soures of BDNF i not show ny rnhing (Fig. 6). In ft, exmintion of 16 intersetion points (ll within severl hunre mirons of the reipient ell oy) where the soure of BDNF ws within 4.5 µm from reipient neuron xons showe no eviene of xonl ollterl sprouting. BDNF hs lso een implite s synpti morphogen 18, so we investigte whether fol BDNF ltere the stility or morphology of iniviul spines. Consistent with previous reports of spine instility uner norml onitions 24,25, we oserve hnges in the length n shpe of ontrol filopoi n spines Fig. 6. BDNF onor neurons o not influene ollterl rnhing of reipient neuron xons. () Multiple xons trverse the hlo of BDNF onor neuron ut remine unrnhe. Sle r, 10 µm. (, ) Highpower view of iniviul xons from () tht pss within 3 mirons vertilly of BDNF onor enriti rnhes. Optil setions equivlent to 6 µm of tissue re stke in (), n 10-µm equivlent is stke in (). Sle rs (, ) re 2.5 µm nture neurosiene volume 5 no 11 novemer 2002
5 Fig. 7. Spine n filopoi hrteristis re not influene y BDNF from onor neurons. () Imges of single ontrol enriti setion over time revels tht some spines i not hnge in length (green rrowhe) n other spines hnge length rmtilly (pink rrowhe). Likewise, some filopoi ynmilly ltere their length over time (lue rrowhe), while others were muh more stle (yellow rrowhe). Sle r, 5 µm. () A grph of the hnges in spine length over time of two spines in () (pink n green rrowhes) inites lrge vrition in the mount of motility from spine to spine. () Grph of the hnges in filopoil length over time of two filopoi in () (lue n yellow). () The ensity of protrusions ws mesure t eh intersetion point n groupe y the istne etween the reipient n onor proesses. Intersetion points were ollete from 23 reipient ells (117 intersetion points) ner BDNF onor ells (lk rs) n from 29 reipient ells (159 intersetion points) ner RFP ontrol onor neurons (gry rs). There ws no effet of tretment or istne on lol ensity of spines or filopoi (ANOVA, P = 0.089). Brs re men ± s.e.m. over time (Fig. 7 ). The verge ynmis of ll protrusions on ontrol GFP-trnsfete neurons (0.52 ± 0.05 µm/10 min, n = 40 protrusions) were unhnge in the presene of fol ellulr soure of BDNF (0.46 ± 0.02 µm/10 min, n =106 protrusions, P = 0.298, t-test). Even when mesurements were limite to the spines within 5-µm rius of onor proess, there ws no BDNF influene on ynmis s ompre to spines ner RFP ontrol onors (Tle 1). We lso seprtely nlyze the motility of enriti filopoi, whih re less stle thn fully ifferentite spines. However, these too were not ifferentilly influene y fol soure of BDNF (Tle 1). Likewise, neither the length of filopoi nor tht of spines iffere from ontrols, regrless of their proximity to BDNF soure (Tle 1). Finlly, in ontrst to the effet of overexpressing BDNF in single ells, whih les to ereses in spine ensity 16, fol soure of BDNF from onor neurons i not lter the lol ensity of protrusions on reipient enrites s ompre to ontrols (Fig. 7, P =0.089, ANOVA), even when the soure of BDNF ws in the sme optil setion. DISCUSSION These results emonstrte tht BDNF supplie y single neuron influene enriti rnhing of nery enrites, with little effet on xons or spines. The inrese in enriti rnhing ws restrite to fol res of enrites, n this effet ws more shrply restrite t frther istnes from the soure of BDNF. Lol effets of BDNF on enriti rnhing The morphologil response to fol BDNF ws restrite to lol portion of the enriti rnh. There ws no inrese in rnh ensity either t the ell oy or in prts of the enriti ror fr from the soure of BDNF (Fig. 4j). These effets re reminisent of the lol effets of NGF on neurite outgrowth s ssesse in segmente ultures 26. How neurotrophins inue highly lol morphologil ltertions is unknown, espeilly in light of the ft tht lign-oun Trk reeptors re retrogrely trnsporte to the som 27,28. Reent eviene inites tht sptilly istint pplition of NGF n result in ifferentil tivtion of ownstrem pthwys 29, implying tht the funtionl result of neurotrophin pplition n e epenent on ellulr lotion. In ition, mny of BDNF s reporte effets, suh s ltering reeptor tivity 30, iretly opening ion hnnels 31 or moulting Rho GTPses 32, oul hnge the enriti ytoskeleton lolly n ontriute to the morphologil ltertions foun here. The BDNF-inue enriti rnhing ws lmost entirely ue to BDNF relese from enrites. Although BDNF ws overexpresse in these onor ells, the presene of enriti BDNF my e relisti euse oth suellulr in situ hyriiztion 33 n immunoeletron mirosopy 34 stuies hve lolize BDNF to enrites. Furthermore, these stuies show tht TrkB ololizes with BDNF in enrites of pyrmil neurons 33,34, whih provies plusile sustrte for enro-enriti BDNF signling. Wht implitions o these experiments hve for norml enro-enriti intertions? Owing to the ensity of pyrmil neurons in the ortex, there re multiple points where iniviul enrites oul influene one nother. BDNF-meite enro-enriti intertions my e espeilly importnt in other res of the rin where enrites re highly enrihe, suh s in the rrels of the somtosensory ortex or in the glomeruli of the olftory ul. The glomeruli re prtiulrly interesting euse they re extremely enrite-rih, ontining the enrites of mitrl ells, tufte ells n periglomerulr ells 35. Although we hve not iretly teste the role of neuronl tivity in the experiments reporte here, the tivity-epenent relese n response properties of BDNF 8 11,36 suggest tht enrites my respon to sptil ptterns of orrelte tivity y inuing positive feek loop tht results in the enrihment of enriti rnhes in restrite portions of enriti rors. For exmple, lol enriti rnhing ptterns seen in the stripes of three-eye frogs 4 or the retin 37 oul rely on suh BDNF-meite enriti signling uring evelopment. Constrine iffusion of BDNF Fol BDNF relese y neurons into the three-imensionl ellulr mtrix of n orgnotypi slie, omine with two-photon mirosopy, provies onsierle insight into the sptil influenes of BDNF. Anlysis of seril optil setions revele strik- nture neurosiene volume 5 no 11 novemer
6 Tle 1. BDNF i not influene spine n filopoi length or ynmis. Control BDNF Ner (<4.5 µm) Fr (>4.5 µm) Ner (<4.5 µm) Fr (>4.5 µm) Signifine Dynmis (µm/10 min) Spines 0.50 ± ± ± ± 0.05 P = 0.15 (n =) (6) (20) (59) (21) Filopoi 0.66 ± ± ± ± 0.14 P = 0.38 (n =) (3) (7) (17) (9) Length (µm) Spines 0.76 ± ± ± ± 0.16 P = 0.14 (n =) (6) (20) (59) (21) Filopoi 3.51 ± ± ± ± 0.44 P = 0.79 (n =) (3) (7) (17) (9) The ynmis or length of reipient proesses lote ner or fr from ontrol onor neurons (left) n ner or fr from BDNF onor neurons (right) re isplye. The numer of protrusions for eh tegory is note elow within prentheses. ANOVAs one on eh row of t onfirm tht BDNF i not influene spine or filopoil prmeters (fr right olumn). ing restritions in the istne over whih BDNF from onor enrites oul influene reipient enriti morphology. These results inite tht BDNF either oes not iffuse very fr, or is highly iffusile ut only effetive t high onentrtions. Eviene supports the former onlusion. With reporte isoeletri point (pi) of greter thn ten, the iffusion of BDNF is proly highly restrite s result of its intertions with the surrouning extrellulr environment 38. The high ensity of TrkB reeptors n the evelopmentl upregultion of the intive T1 form of the BDNF reeptor 39 oul sequester n internlize BDNF, further reuing oth the onentrtion n the rte of iffusion 40,41. Together these results imply tht TrkB n T1 my impee the lrey limite iffusion of BDNF, resulting in the highly lol effets of BDNF seen here. BDNF elivery vi iniviul neurons BDNF hs pleiotropi effets on neuronl morphology 42. Most experimentl protools, however, rely on th pplition of homogenous onentrtion of BDNF, whih is likely to e very ifferent from the sptil pttern of BDNF present in the rin. Unlike the lol effets presente here, th pplition or overexpression of BDNF ffet enrites glolly 12,16 n hnge the ensity of spines 14,16,43. Prmeters suh s BDNF onentrtion, urtion of exposure n sptil ptterns of TrkB reeptor tivtion lerly iffer mong these vrious methos n my explin the iverse morphologil effets of BDNF. Moreover, the physiologil onsequenes of BDNF on network properties 44 my e quite ifferent with glol s oppose to lol pplition. Neurons overexpressing BDNF relese BDNF into the extrellulr mtrix uner ontrol of the ell s relese mehnisms 16. Even if levels or ptterns of BDNF re somewht ifferent from those proue y ompletely enogenous relese, reting efine ellulr soure of BDNF is likely to more losely mimi the enogenous sitution thn o th pplition, injetion, loe es or implnttion of BDNF-trnsfete nonneuronl ells. Furthermore, the tions of BDNF oserve here my e more relisti thn in issoite ultures euse relese BDNF interts with the enogenous ssortment of extrellulr mtrix omponents s it iffuses. Reent experiments hve iretly emonstrte the tivity-epenent interellulr trnsfer of BDNF in issoite ultures 11, n the finings presente here provie eviene tht interellulr trnsfer within 3D mtrix of ells hs iret effet on enriti growth. But how norml is BDNF relese from trnsfete neurons? Both the mount relese n the pthwys use for relese (onstitutive versus regulte) might e ifferent from untrnsfete neurons, lthough ville eviene suggests tht the ifferenes my not e tht gret. Wheres BDNF levels in trnsfete lyer 2/3 neurons re higher thn in untrnsfete neurons in tht lyer, these levels re similr to tht seen in untrnsfete lyer 5 ells 16. Experiments tht hve emonstrte regulte relese of BDNF rely on overexpression, strongly suggesting tht the trnsfete neurons in our experiments use the regulte pthwy for relese 45. Future experiments might ress the regulte relese of BDNF from onor neurons y mnipulting tivity levels in these ulture slies n etermining if the interellulr effets of BDNF on enriti rnhing n e moulte. We i not iretly ssess the role of neuronl tivity in the tions of BDNF. In previous work 36, we hve shown tht loke of neuronl tivity in younger slies prevents the enriteenhning effets of BDNF. Although the ge of the nimls use here s soure for slies (postntl y 27, P27) ws somewht oler thn in erlier work, it seems likely tht the sme requirement hols here s well. In these slies, neurons exhiit low levels of spontneous tivity 46. We hve lso foun tht long-term loke of tivity y phrmologil gents n result in profoun ell eth in neurons t these ges (H.W.H. n L.C.K., unpu. oserv.). Thus, we elieve tht the fol enriti growth reporte here most likely requires the presene of ongoing spontneous tivity. Lol effets of BDNF on xons n spines As BDNF regultes xonl form uring evelopment 15,22,42, we ske whether lol soures of BDNF woul inue xon ollterl sprouting. BDNF oul potentilly influene ll prts of neuron, s reful suellulr loliztion stuies hve esrie homogenous istriutions for oth TrkB n T1 reeptors throughout xons, enrites n soms 47. Severl experiments hve shown, however, tht the xon, sl n pil enrites of single neuron n isply ifferentil responses to neurotrophins 12,15. Exmintion of the onor n reeptor pirs here inites tht the presene of BDNF is unlikely to regulte interstitil rnhing of xons within lyer II/III. The vrition in xonl responses to BDNF my e ue to tissue-speifi ifferenes s well s ifferenes in BDNF elivery methos. Fol relese of BDNF lso i not lter the ensity, length or motility of enriti spines n filopoi. In other experimentl ontexts, however, BDNF lters spine ensity 14,16,43, n ifferent experimentl onitions hve yiele opposing effets. Comining the permissive effet of BDNF in LTP inution 48, the hnges in spine morphology ssoite with LTP 49 n the morphogeni properties of BDNF 12,15,16, it seems likely tht BDNF oul t s synpti morphogen 18. Although fol pplition y our onor-ell mehnism oes not lter the lol prop nture neurosiene volume 5 no 11 novemer 2002
7 erties of spines, it oes not rule out the possiility tht BDNF oul t s synpti morphogen euse the enriti relese of BDNF esrie here my e signifintly ifferent from synptilly relese BDNF. In ition, spine ensity is still inresing t this ge in the ferret 50, whih oul mke lol hnges in spine ensities iffiult to etet. METHODS Slie ulture n trnsfetion. Coronl slies (400 µm thik) of P25 28 ferret (Mrshll Frms, North Rose, New York) visul ortex were prepre, ulture n trnsfete s previously esrie 16 exept tht slies were inute t 37 C for the entire experiment. Approvl for niml experiments ws given y the Duke University Institutionl Animl Cre n Usge Committee. A Helios Gene Gun (Bio-R, Herules, Cliforni) ws use to trnsfet neurons with omintions of onstruts enoing BDNF-my, NGF-my or T1-FLAG, n the fluoresent proteins egfp n sred (Clonteh, Plo Alto, Cliforni). The BDNF-my onstrut (gift of Y.-A. Bre) is inistinguishle from ntive BDNF with regr to its ility to support the survivl of hik sensory neurons in vitro (J. Klose & Y.-A. Bre, pers. omm.). The NGF-my use ws s previously esrie 16. Rt DNAs enoing the trunte TrkB reeptor (T1) ws tgge with FLAG epitope n lone into the pef-bos vetor 19 (gift of E. Cstren). Gene gun ullets were prepre using Bio- R protools. Briefly, 8 mg of 1.6-µm gol prtiles (Bio-R) were ote with 3 µg totl DNA/mg gol in the following omintions: 1.6:1 rtio of BDNF-my to RFP, n these prtiles were mixe with n equl mount of gol prtiles ote with 2 µg egfp. For T1 ontrols, the BDNF/RFP gol ws mixe with gol ote with 16:1 rtio of T1 to egfp. Alterntively, gol ote with 10 µg of RFP lone ws omine with GFP gol for BDNF ontrols, n gol ote with rtio of 2:1 NGF to RFP ws mixe with GFP gol for NGF ontrols. Two-photon lser snning mirosopy n t quisition. Cell pirs were first ientifie t 10 mgnifition using fluoresene isseting mirosope (Lei Mirosystems, Bnnokurn, Illinois). They were then visulize with ustom uilt 2-photon mirosope equippe with ul, externl photomultipliers (Hmmtsu, Brigewter, New Jersey). The light soure ws Ti:Spphire lser (Tsunmi, Spetr-Physis, Mountin View, Cliforni) pumpe y 10-W soli stte lser (Milleni X, Spetr-Physis). A 40, 0.75 NA wter immersion lens (Zeiss, Thornwoo, New York) ws use to illuminte the smple with pproximtely 20 mw of 960-nm light yieling optil setions with n pproximte epth of 3 µm. Both low-zoom (zoom, 1.5; step size, 1.5 µm) n highzoom (zoom, 5; step size 0.5 or 0.7 µm) imges were ollete. When spine motility ws investigte, 3 10 high zoom imge stks were sequentilly ollete. As ontrol for the lol effets of BDNF, n re n equl istne from the ell oy on the opposite sie ws lso imge, n experimentl n ontrol sies were interleve. Exept for slight ontrst n rightness justments, no imge enhnement or filtering mnipultions ws one on these imges. Immunohistohemistry. For visuliztion of BDNF-my, NGF-my n T1-FLAG expression, slies were prepre for histohemistry s esrie 16. Slies were then inute with 1:1,000 mouse nti-my ntioy (PhrMingen, Sn Diego, Cliforni) or 1:750 iotinylte nti- FLAG (M2, Gio-BRL, Githersurg, Mryln) followe y 1:500 ntimouse Cy-5 (Chemion, Temeul, Cliforni) or 1:1,000 streptviin Cy-5 (Jkson ImmunoResrh Ls, West Grove, Pennsylvni). Dt nlysis. After olletion with the 2-photon mirosope, imges were poole, ssigne n lphnumeri oe n nlyze lin to onition using IPL softwre (Snlytis, Firfx, Virgini). Every existing intersetion point ws ientifie in 2-imensionl imges n nlyze. The z-xis istne etween the onor n reipient t n intersetion point ws etermine y ounting optil setion seprtion. For exmple, proesses within the sme optil setion were onsiere to e <3 µm prt, those in jent setions (fter 1.5- µm step) were µm prt, n so forth. For enriti reonstrutions, iniviul enrites (inluing ny proess longer thn 3 µm) were tre from 2- D imge stks. Reonstrutions were olore yellow for enrites in the sme or jent optil setions (<4.5 µm), turquoise for one or two intervening optil setions ( µm) or lue for three or more intervening optil setions (>7.5 µm). Lol enriti length ws quntifie s follows. The x,y oorintes of intersetion points etween re n green ells were note in 2-D imges. The optil setion ontining the green proess ws lote. A 10-µm imeter irle ws then entere on the x,y oorintes of the intersetion point in tht optil setion s well s the optil setion immeitely ove n elow, in effet reting yliner 10 µm wie n pproximtely 6 µm tll (s in Fig. 4, se on n estimte optil setion epth of 3 µm, 1.5-µm steps). The liner enrite length tht ws present in the enter irle ws mesure first, n then itionl enriti length present in the irles ove n elow were mesure n e. Any proess over 3 µm long ws inlue in this mesurement. Mesure lengths were verge n inne on the sis of z-xis istne etween onor n reipient (sertine s esrie ove). An ANOVA ws then one to exmine the effet of tretment n z-istne on enriti length. Rtiometri t ws ollete similrly on points n equl istne from the ell oy on the opposite sie. In ses where the opposite sie of the enriti ror ws lso lose to re onor neuron, or when no opposite sie ws ville, the verge length of ll mesure opposite sites ws use for the rtio lultion. ANOVA ws performe on the rtio mesurements to ssess ftor intertion. Spines n filopoi tht were within these yliners were further nlyze. The numer of protrusions ws ounte n the ensity per 10 µm of enrite lulte. IPL ws use to mesure protrusion length in 2D imges t eh time point ollete. Lengths in Tle 1 re the verge length over time. ANOVA ws use to proe the effets of tretment n z-istne on protrusion prmeters. Aknowlegments We thnk R. Irving for tehnil ssistne n D. Lo for inisive, helpful isussions. L.C.K. is n investigtor in the Howr Hughes Meil Institute. This work ws supporte y Ntionl Institutes of Helth grnt EY n the Humn Frontiers Siene Progrm. Competing interests sttement The uthors elre tht they hve no ompeting finnil interests. RECEIVED 15 JULY; ACCEPTED 9 SEPTEMBER Brtlett, W. P. & Bnker, G. A. An eletron mirosopi stuy of the evelopment of xons n enrites y hippompl neurons in ulture I. Cells whih evelop without interellulr ontts. J. Neurosi. 4, (1984). 2. Kossel, A., Lowel, S. & Bolz, J. Reltionships etween enriti fiels n funtionl rhiteture in strite ortex of norml n visully eprive ts. J. Neurosi. 15, (1995). 3. Ktz, L. C. Lol iruitry of ientifie projetion neurons in t visul ortex rin slies. J. Neurosi. 7, (1987). 4. Ktz, L. C. & Constntine-Pton, M. Reltionships etween segregte fferents n postsynpti neurons in the opti tetum of three-eye frogs. J. Neurosi. 8, (1988). 5. Whitfor, K. L. et l. Regultion of ortil enrite evelopment y Slit- Roo intertions. Neuron 33, (2002). 6. Neivi, E., Wu, G. Y. & Cline, H. T. Promotion of enriti growth y CPG15, n tivity-inue signling moleule. Siene 281, (1998). 7. Kossel, A. H., Willims, C. V., Shweizer, M. & Kter, S. B. Afferent innervtion influenes the evelopment of enriti rnhes n spines vi oth tivity-epenent n non-tivity-epenent mehnisms. J. Neurosi. 17, (1997). 8. Zfr, F., Hengerer, B., Leirok, J., Thoenen, H. & Linholm, D. Ativity epenent regultion of BDNF n NGF mrnas in the rt hippompus is meite y non-nmda glutmte reeptors. EMBO J. 9, (1990). 9. Ghosh, A., Crnhn, J. & Greenerg, M. E. Requirement for BDNF in tivityepenent survivl of ortil neurons. Siene 263, (1994). 10. Goomn, L. J. et l. Regulte relese n polrize loliztion of rinerive neurotrophi ftor in hippompl neurons. Mol.Cell. Neurosi. 7, (1996). 11. Kohr, K., Kitmur, A., Morishim, M. & Tsumoto, T. Ativity-epenent trnsfer of rin-erive neurotrophi ftor to post-synpti neurons. Siene 291, (2001). nture neurosiene volume 5 no 11 novemer
8 12. MAllister, A. K., Lo, D. C. & Ktz, L. C. Neurotrophins regulte enriti growth in eveloping visul ortex. Neuron 15, (1995). 13. MAllister, A. K., Ktz, L. C. & Lo, D. C. Opposing roles for enogenous BDNF n NT-3 in regulting ortil enriti growth. Neuron 18, (1997). 14. Shim, A., Mson, C. A. & Morrison, M. E. TrkB signling moultes spine ensity n morphology inepenent of enrite struture in ulture neontl purkinje ells. J. Neurosi. 18, (1998). 15. Lom, B. & Cohen-Cory, S. Brin-erive neurotrophi ftor ifferentilly regultes retinl gnglion ell enriti n xonl roriztion in vivo. J. Neurosi. 19, (1999). 16. Horh, H. W., Kruttgen, A., Portury, S. D. & Ktz, L. C. Destiliztion of ortil enrites n spines y BDNF. Neuron 23, (1999). 17. Youin, T. A. & Lo, D. C. Trunte n full-length trkb reeptors regulte istint moes of enriti growth. Nt. Neurosi. 3, (2000). 18. Poo, M.-M. Neurotrophins s synpti moultors. Nt. Rev. Neurosi. 2, 1 9 (2001). 19. Hpslo, A. et l. Expression of the nturlly ourring trunte trkb neurotrophin reeptor inues outgrowth of filopoi n proesses in neurolstom ells. Onogene 18, (1999). 20. Klein, R., Conwy, D., Pr, L. F. & Bri, M. The trkb tyrosine protein kinse gene oes for seon neurogeni reeptor tht lks the tlyti kinse omin. Cell 61, (1990). 21. Milems, D. S., Linerg, R. A. & Hunter, T. TrkB, neurl reeptor protein-tyrosine kinse: eviene for full-length n two trunte reeptors. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, (1991). 22. Cohen-Cory, S. & Frser, S. E. Effets of rin-erive neurotrophi ftor on opti xon rnhing n remoeling in vivo. Nture 378, (1995). 23. Ktz, L. C. Speifiity in the evelopment of vertil onnetions in t strite ortex. Eur. J. Neurosi. 3, 1 9 (1991). 24. Fisher, M., Keh, S., Knutti, D. & Mtus, A. Rpi tin-se plstiity in enriti spines. Neuron 20, (1998). 25. Dunevsky, A., Tshiro, A., Mjewsk, A., Mson, C. & Yuste, R. Developmentl regultion of spine motility in mmmlin entrl nervous system. Pro. Ntl. A. Si. USA 96, (1999). 26. Cmpenot, R. B. Development of symptheti neurons in omprtmentlize ultures. I. Lol ontrol of neurite growth y nerve growth ftor. Dev. Biol. 93, 1 12 (1982). 27. DiStefno, P. S. et l. The neurotrophins BDNF, NT-3, n NGF isply istint ptterns of retrogre xonl trnsport in peripherl n entrl neurons. Neuron 8, (1992). 28. Henry, I., Stoekel, K., Thoenen, H. & Iversen, L. The retrogre xonl trnsport of nerve growth ftor. Brin Res. 68, (1974). 29. Kuruvill, R., Ye, H. H. & Ginty, D. D. Sptilly n funtionlly istint roles of the PI3-K effetor pthwy uring NGF signling in symptheti neurons. Neuron 27, (2000). 30. Jrvis, C. R. et l. Neurotrophin moultion of NMDA reeptors in ulture murine n isolte rt neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 78, (1997). 31. Kfitz, K. W., Rose, C. R., Thoenen, H. & Konnerth, A. Neurotrophin-evoke rpi exittion through TrkB reeptors. Nture 401, (1999). 32. Ozinler, P. H. & Erzurumlu, R. S. Regultion of neurotrophin-inue xonl responses vi rho GTPses. J. Comp. Neurol. 438, (2001). 33. Tongiorgi, E., Righi, M. & Cttneo, A. Ativity-epenent enriti trgeting of BDNF n TrkB mrnas in hippompl neurons. J. Neurosi. 17, (1997). 34. Aoki, C. et l. Loliztion of rin-erive neurotrophi ftor n TrkB reeptors to postsynpti ensities of ult rt ererl ortex. J. Neurosi. Res. 59, (2000). 35. Shepher, G. & Greer, C. in The Synpti Orgniztion of the Brin (e. Shepher, G.) (Oxfor Univ. Press, New York, 1998). 36. MAllister, A. K., Ktz, L. C. & Lo, D. C. Neurotrophin regultion of ortil enriti growth requires tivity. Neuron 17, (1996). 37. Peihl, L. & Wssle, H. Size, stter n overge of gnglion-ell reeptivefiel enters in the t retin. J. Physiol. 291, (1979). 38. Bre, Y. A., Egr, D. & Thoenen, H. Purifition of new neurotrophi ftor from the mmmlin rin. EMBO 1, (1982). 39. Allenoerfer, K. L. et l. Regultion of neurotrophin reeptors uring the mturtion of the mmmlin visul system. J. Neurosi. 14, (1994). 40. Fryer, R. H. et l. Developmentl n mture expression of full-length n trunte TrkB reeptors in the rt forerin. J. Comp. Neurol. 374, (1996). 41. Biffo, S., Offenhuser, N., Crter, B. D. & Bre, Y. A. Seletive ining n internlistion y trunte reeptors restrit the vilility of BDNF uring evelopment. Development 121, (1995). 42. Gllo, G. & Letourneu, P. C. Neurotrophins n the ynmi regultion of the neuronl ytoskeleton. J. Neuroiol. 44, (2000). 43. Murphy, D. D., Cole, N. B. & Segl, M. Brin-erive neurotrophi ftor meites estriol-inue enriti spine formtion in hippompl neurons. Pro. Ntl. A. Si. USA 95, (1998). 44. Rutherfor, L. C., Nelson, S. B. & Turrigino, G. G. BDNF hs opposite effets on the quntl mplitue of pyrmil neuron n interneuron exittory synpses. Neuron 21, (1998). 45. Mowl, S. J. et l. Differentil sorting of nerve growth ftor n rinerive neurotrophi ftor in hippompl neurons. J. Neurosi. 19, (1999). 46. Dlv, M. B. & Ktz, L. C. Rerrngements of synpti onnetions in visul ortex revele y lser photostimultion. Siene 265, (1994). 47. Kryl, D. et l. Suellulr loliztion of full-length n trunte trk reeptor isoforms in polrize neurons n epithelil ells. J. Neurosi. 19, (1999). 48. Korte, M. et l. Virus-meite gene trnsfer into hippompl CA1 region restores long-term potentition in rin-erive neurotrophi ftor mutnt mie. Pro. Ntl. A. Si. USA 93, (1996). 49. Yuste, R. & Bonhoeffer, T. Morphologil hnges in enriti spines ssoite with long-term synpti plstiity. Annu. Rev. Neurosi. 24, (2001). 50. Zervs, M. & Wlkley, S. U. Ferret pyrmil ell enritogenesis: hnges in morphology n gngliosie expression uring ortil evelopment. J. Comp. Neurol. 413, (1999) nture neurosiene volume 5 no 11 novemer 2002
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
WesternBright Quantum
 WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
Neuroligin-1 dependent competition regulates cortical synaptogenesis and synapse number
 Neuroligin- epenent ompetition regultes ortil synptogenesis n synpse numer Hyung-Be Kwon,3, Yevgeni Kozorovitskiy, Won-Jong Oh 2, Rui T Peixoto, Nzi Akhtr, Jessi L Sulnier, Chenghu Gu 2 & Bernro L Stini
Neuroligin- epenent ompetition regultes ortil synptogenesis n synpse numer Hyung-Be Kwon,3, Yevgeni Kozorovitskiy, Won-Jong Oh 2, Rui T Peixoto, Nzi Akhtr, Jessi L Sulnier, Chenghu Gu 2 & Bernro L Stini
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Provider How To. Software Process Service Results
 Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
 nestin ironetin p75 s1 CNS SKPs Dermo-1 +ve SKPs CNS H2O SCGs Skin Di. SKPs TH SHOX2 GAPDH NCAM D H Figure S1, Immunoytohemil nlysis o SKP spheres ulture rom neontl mouse (nestin, ironetin, S-1) or rt
nestin ironetin p75 s1 CNS SKPs Dermo-1 +ve SKPs CNS H2O SCGs Skin Di. SKPs TH SHOX2 GAPDH NCAM D H Figure S1, Immunoytohemil nlysis o SKP spheres ulture rom neontl mouse (nestin, ironetin, S-1) or rt
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
Shear behaviour of regular and irregular rock joints under cyclic conditions
 Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Crossing the Line A GIS investigation
 GIS investigtion NAME rossing the Line A GIS investigtion Glol perspetive: rossing the Line DAE Answer ll questions on the stuent nswer sheet hnout Bounries re invisile lines on the erth s surfe. hey ivie
GIS investigtion NAME rossing the Line A GIS investigtion Glol perspetive: rossing the Line DAE Answer ll questions on the stuent nswer sheet hnout Bounries re invisile lines on the erth s surfe. hey ivie
Non-redundant odor coding by sister mitral cells revealed by light addressable glomeruli in the mouse
 Non-reunnt oor oing y sister mitrl ells revele y light ressle glomeruli in the mouse Ashesh K Dhwle,2, Akri Hgiwr 3, Upiner S Bhll 2, Venktesh N Murthy 3 & Dinu F Alenu 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve.
Non-reunnt oor oing y sister mitrl ells revele y light ressle glomeruli in the mouse Ashesh K Dhwle,2, Akri Hgiwr 3, Upiner S Bhll 2, Venktesh N Murthy 3 & Dinu F Alenu 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve.
Tonic excitation or inhibition is set by GABA A conductance in hippocampal interneurons
 Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Effects of Enzyme Inducers in Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone: An Antidiabetic Drug in Albino Rats
 Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
100 μm. Axon growth cones. Tubulin (red) + scr (green)
 Supplementary Figures mirorna-9 regulates axon extension an ranhing y targeting Map1 in mouse ortial neurons Dajas-Bailaor, F., Bonev, B., Garez, P., Stanley, P., Guillemot, F., Papalopulu, N. a 2 μm 1
Supplementary Figures mirorna-9 regulates axon extension an ranhing y targeting Map1 in mouse ortial neurons Dajas-Bailaor, F., Bonev, B., Garez, P., Stanley, P., Guillemot, F., Papalopulu, N. a 2 μm 1
Directional guidance of neuronal migration in the olfactory system by the protein Slit
 rtiles Diretionl guine of neuronl migrtion in the olftory system y the protein Wei Wu*, Kit Wong, Jin-hui Chen*, Zhi-hong Jing, Sophie Dupuis, Jne Y. Wu & Yi Ro * Lortory of Moleulr Neuroiology, Shnghi
rtiles Diretionl guine of neuronl migrtion in the olftory system y the protein Wei Wu*, Kit Wong, Jin-hui Chen*, Zhi-hong Jing, Sophie Dupuis, Jne Y. Wu & Yi Ro * Lortory of Moleulr Neuroiology, Shnghi
Targeting BIG3 PHB2 interaction to overcome tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells
 Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
Bistability of cerebellar Purkinje cells modulated by sensory stimulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
nature letters to nature ... Mechanism for the learning deficits in a mouse model of neurofibromatosis type 1 advance online publication
 vne online pulition... Mehnism for the lerning efiits in mouse moel of neurofiromtosis type 1 Rui M. Cost*, Nikoli B. Feerov*, Jeff H. Kogn*, Geoffrey G. Murphy*, Joel Stern*, Msuo Ohno*, Rju Kuherlpti,
vne online pulition... Mehnism for the lerning efiits in mouse moel of neurofiromtosis type 1 Rui M. Cost*, Nikoli B. Feerov*, Jeff H. Kogn*, Geoffrey G. Murphy*, Joel Stern*, Msuo Ohno*, Rju Kuherlpti,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
Abortion frequency (%) Ovary position on ear Ovary volume (mm 3 )
 ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Parathyroid hormone related peptide is a naturally occurring, protein kinase A dependent angiogenesis inhibitor
 Prthyroi hormone relte peptie is nturlly ourring, protein kinse A epenent ngiogenesis inhiitor MANJIRI M. BAKRE 1, YUHONG ZHU 1, HONG YIN 1, DOUG W. BURTON 2, ROBERT TERKELTAUB 2, LEONARD J. DEFTOS 2 &
Prthyroi hormone relte peptie is nturlly ourring, protein kinse A epenent ngiogenesis inhiitor MANJIRI M. BAKRE 1, YUHONG ZHU 1, HONG YIN 1, DOUG W. BURTON 2, ROBERT TERKELTAUB 2, LEONARD J. DEFTOS 2 &
SK channels and NMDA receptors form aca 2+ -mediated feedback loop in dendritic spines
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice
 rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
b-sitosterol activates Fas signaling in human breast cancer cells
 ARTICLE IN PRESS Phytomeiine 14 (2007) 747 754 www.elsevier.e/phyme -Sitosterol tivtes Fs signling in humn rest ner ells A.B. Aw,, M. Chinnm, C.S. Fink, P.G. Brfor Deprtment of Exerise n Nutrition Sienes
ARTICLE IN PRESS Phytomeiine 14 (2007) 747 754 www.elsevier.e/phyme -Sitosterol tivtes Fs signling in humn rest ner ells A.B. Aw,, M. Chinnm, C.S. Fink, P.G. Brfor Deprtment of Exerise n Nutrition Sienes
Diversity and wiring variability of olfactory local interneurons in the Drosophila antennal lobe
 Diversity n wiring vriility of olftory lol interneurons in the Drosophil ntennl loe Y-Hui Chou 1,3, Mri L Spletter 1,3, Emre Yksi 2,3, Jonthn C S Leong 1, Rhel I Wilson 2 & Liqun Luo 1 21 Nture Ameri,
Diversity n wiring vriility of olftory lol interneurons in the Drosophil ntennl loe Y-Hui Chou 1,3, Mri L Spletter 1,3, Emre Yksi 2,3, Jonthn C S Leong 1, Rhel I Wilson 2 & Liqun Luo 1 21 Nture Ameri,
A savings procedure based construction heuristic for the offshore wind cable layout optimization problem
 A svings proeure se onstrution heuristi for the offshore win le lyout optimiztion prolem Sunney Foter (B.Eng. Mehnil) MS. Cnite in Energy Deprtment of Informtis, University of Bergen, Norwy sunney.foter@stuent.ui.no
A svings proeure se onstrution heuristi for the offshore win le lyout optimiztion prolem Sunney Foter (B.Eng. Mehnil) MS. Cnite in Energy Deprtment of Informtis, University of Bergen, Norwy sunney.foter@stuent.ui.no
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:./n BJ RAS:ER Herrnz et l Supplementry Figure HFFF RAS:ER.. mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF + OHT Torin NVP-BEZ + OHT shmtor. shmtor.
DOI:./n BJ RAS:ER Herrnz et l Supplementry Figure HFFF RAS:ER.. mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF + OHT Torin NVP-BEZ + OHT shmtor. shmtor.
T e c h n i c a l R e p o r t s
 Noninvsive multiphoton fluoresene mirosopy resolves retinol n retinl onenstion prouts in mouse eyes Grzyn Plzewsk 1, To Me 2,3, Yoshikzu Imnishi 3, Wenyu Sun 1, Yu Chen 3, Dvi R Willims 4, Dvi W Piston
Noninvsive multiphoton fluoresene mirosopy resolves retinol n retinl onenstion prouts in mouse eyes Grzyn Plzewsk 1, To Me 2,3, Yoshikzu Imnishi 3, Wenyu Sun 1, Yu Chen 3, Dvi R Willims 4, Dvi W Piston
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Perception of Saudi dentists and lay people to altered smile esthetics
 The Sui Dentl Journl (2013) 25, 13 21 King Su University The Sui Dentl Journl www.ksu.eu.s www.sieneiret.om ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pereption of Sui entists n ly people to ltere smile esthetis Neel Tli, *, Smr
The Sui Dentl Journl (2013) 25, 13 21 King Su University The Sui Dentl Journl www.ksu.eu.s www.sieneiret.om ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pereption of Sui entists n ly people to ltere smile esthetis Neel Tli, *, Smr
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is involved in learning and neuroprotection
 Glugon-like peptie-1 reeptor is involve in lerning n neuroprotetion Mtthew J During 1,2,Lei Co 2,Dvi S Zuzg 2,Jeremy S Frnis 1,Helen L Fitzsimons 1,2,Xingyng Jio 2, Ross J Bln 2,Mtthis Klugmnn 1,Willim
Glugon-like peptie-1 reeptor is involve in lerning n neuroprotetion Mtthew J During 1,2,Lei Co 2,Dvi S Zuzg 2,Jeremy S Frnis 1,Helen L Fitzsimons 1,2,Xingyng Jio 2, Ross J Bln 2,Mtthis Klugmnn 1,Willim
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates energy balance downstream of melanocortin-4 receptor
 Brin-erive neurotrophi ftor regultes energy lne ownstrem of melnoortin-4 reeptor Boji Xu 1,5,Evn H Gouling 2,Keling Zng 1,Dvi Cepoi 3,Roger D Cone 3,Kevin R Jones 4,Lurene H Teott 2 & Louis F Reihrt 1
Brin-erive neurotrophi ftor regultes energy lne ownstrem of melnoortin-4 reeptor Boji Xu 1,5,Evn H Gouling 2,Keling Zng 1,Dvi Cepoi 3,Roger D Cone 3,Kevin R Jones 4,Lurene H Teott 2 & Louis F Reihrt 1
CSE 5311 Notes 2: Binary Search Trees
 S Notes : inry Ser Trees (Lst upte /7/ 8:7 M) ROTTIONS Single left rottion t (K rotting ege ) Single rigt rottion t (K rotting ege ) F oule rigt rottion t F G F G Wt two single rottions re equivlent? (OTTOM-UP)
S Notes : inry Ser Trees (Lst upte /7/ 8:7 M) ROTTIONS Single left rottion t (K rotting ege ) Single rigt rottion t (K rotting ege ) F oule rigt rottion t F G F G Wt two single rottions re equivlent? (OTTOM-UP)
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
N6-methyladenosine (m6a) is the most prevalent messenger
 https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Increasing the usage level of corn and distillers grains in market turkey diets through the use of supplemental amino acids
 Inresing the usge level of orn n istillers grins in mrket turkey iets through the use of supplementl mino is August 014 By: Sny Noll University of Minnesot Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... INTRODUCTION...
Inresing the usge level of orn n istillers grins in mrket turkey iets through the use of supplementl mino is August 014 By: Sny Noll University of Minnesot Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... INTRODUCTION...
Original article HIV-1 Tat protein impairs adipogenesis and induces the expression and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in human SGBS adipocytes
 Antivirl Therpy 2012; 17:529 540 (oi: 10.3851/IMP2021) Originl rtile HIV-1 Tt protein impirs ipogenesis n inues the expression n seretion of proinflmmtory ytokines in humn SGBS ipoytes Juliet Díz-Delfín
Antivirl Therpy 2012; 17:529 540 (oi: 10.3851/IMP2021) Originl rtile HIV-1 Tt protein impirs ipogenesis n inues the expression n seretion of proinflmmtory ytokines in humn SGBS ipoytes Juliet Díz-Delfín
Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha Therapy in Crohn s Disease: Clinical and Health Economic Aspects
 Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-α Therpy in Crohn s Disese Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-lph Therpy in Crohn s Disese: Clinil n Helth Eonomi Aspets Fion MGuire, 5th yer Meiine ABSTRACT Ojetives: Crohn s isese is hroni,
Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-α Therpy in Crohn s Disese Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-lph Therpy in Crohn s Disese: Clinil n Helth Eonomi Aspets Fion MGuire, 5th yer Meiine ABSTRACT Ojetives: Crohn s isese is hroni,
Letter. Autocrine BDNF TrkB signalling within a single dendritic spine
 Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
Operating Systems Principles. Page Replacement Algorithms
 Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
supplementary information
 DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
Early depolarizing GABA controls critical-period plasticity in the rat visual cortex
 Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
Regular Paper. Introduction
 Regulr Pper Serotonin, Tryptophn-Derive Signl Conserve in Plnts n Animls, Regultes Root System Arhiteture Proly Ating s Nturl Auxin Inhiitor in Ariopsis thlin Rmón Pelgio-Flores, Rny Ortíz-Cstro, Alfonso
Regulr Pper Serotonin, Tryptophn-Derive Signl Conserve in Plnts n Animls, Regultes Root System Arhiteture Proly Ating s Nturl Auxin Inhiitor in Ariopsis thlin Rmón Pelgio-Flores, Rny Ortíz-Cstro, Alfonso
Plzf regulates limb and axial skeletal patterning
 rtile Plzf regultes lim n xil skeletl ptterning Mri Brn 1, Niol Hwe 1, Lee Niswner 2 & Pier Polo Pnolfi 1 The promyeloyti leukemi zin finger (Plzf) protein (enoe y the gene Zfp145) elongs to the POZ/zin-finger
rtile Plzf regultes lim n xil skeletl ptterning Mri Brn 1, Niol Hwe 1, Lee Niswner 2 & Pier Polo Pnolfi 1 The promyeloyti leukemi zin finger (Plzf) protein (enoe y the gene Zfp145) elongs to the POZ/zin-finger
Using Contrapositives to Enhance the Implication Graphs of Logic Circuits
 Using Contrpositives to Enhne the Implition Grphs of Logi Ciruits Kunl K. Dve Vishwni D. Agrwl Mihel L. Bushnell Rutgers University, Dept. of ECE Auurn University, Dept. of ECE Rutgers University, Dept.
Using Contrpositives to Enhne the Implition Grphs of Logi Ciruits Kunl K. Dve Vishwni D. Agrwl Mihel L. Bushnell Rutgers University, Dept. of ECE Auurn University, Dept. of ECE Rutgers University, Dept.
ARTICLES. Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
 Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Regulation of neuronal morphology and function by the tumor suppressors Tsc1 and Tsc2
 Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor
Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
A p75 NTR and Nogo receptor complex mediates repulsive signaling by myelin-associated glycoprotein
 A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
SOME MECHANISTIC CONCEPTS IN ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION REACTIONS TO C=C BONDS
 SM MANISTI NPTS IN LTPILI AITIN ATINS T = BNS The = ond is considered to e wek se/nucleophile. The high concentrtion of electron density mkes the pi ond Lewis se, ut in order to donte electrons the pi
SM MANISTI NPTS IN LTPILI AITIN ATINS T = BNS The = ond is considered to e wek se/nucleophile. The high concentrtion of electron density mkes the pi ond Lewis se, ut in order to donte electrons the pi
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, demyelinating, degenerative
 Dign Intervent Riol 2005; 11:137-141 Turkish Soiety of Riology 2005?????????????????????? NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effetiveness of mgnetiztion trnsfer tehnique in the evlution of ute plques
Dign Intervent Riol 2005; 11:137-141 Turkish Soiety of Riology 2005?????????????????????? NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effetiveness of mgnetiztion trnsfer tehnique in the evlution of ute plques
Virus-mediated EpoR76E Therapy Slows Optic Nerve Axonopathy in Experimental Glaucoma
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy originl rtile Virus-meite EpoR76E Therpy Slows Opti Nerve Axonopthy in Experimentl Gluom Wesley S Bon 1,2, Jessi Hines-Ber 1,2, YPul L GolenMerry 1, Mr Dvis 1, Alm
The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy originl rtile Virus-meite EpoR76E Therpy Slows Opti Nerve Axonopthy in Experimentl Gluom Wesley S Bon 1,2, Jessi Hines-Ber 1,2, YPul L GolenMerry 1, Mr Dvis 1, Alm
Inhibition of Dexamethasone-induced Fatty Liver Development by Reducing mir-17-5p Levels
 originl rtile Inhiition of Dexmethsone-inue Ftty Liver Development y Reuing -5p Levels Willim W Du,, Fengqiong Liu 3, Sze Wn Shn,, Xini Ciny M,, Shn Gupt,, Tinru Jin 4, Dvi Spner, Sergey N Krylov 5, You
originl rtile Inhiition of Dexmethsone-inue Ftty Liver Development y Reuing -5p Levels Willim W Du,, Fengqiong Liu 3, Sze Wn Shn,, Xini Ciny M,, Shn Gupt,, Tinru Jin 4, Dvi Spner, Sergey N Krylov 5, You
Supplementary Figure S1_Cottini
 Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pathway sensitizes hepatic insulin signaling and is modulated by VEGF inhibition
 A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
Designer receptors show role for ventral pallidum input to ventral tegmental area in cocaine seeking
 Designer reeptors show role for ventrl pllium input to ventrl tegmentl re in oine seeking Stephen V Mhler 1, Elen M Vzey 1, Jo T Bekley 1, Coly R Keistler 1, Ellen M MGlinhey 1, Jennifer Kufling 1, Steven
Designer reeptors show role for ventrl pllium input to ventrl tegmentl re in oine seeking Stephen V Mhler 1, Elen M Vzey 1, Jo T Bekley 1, Coly R Keistler 1, Ellen M MGlinhey 1, Jennifer Kufling 1, Steven
Regulation of NKT cell-mediated immune responses to tumours and liver inflammation by mitochondrial PGAM5-Drp1 signalling
 Reeive Mr Aepte Aug Publishe 8 Sep DOI:.8/nomms97 Regultion of NKT ell-meite immune responses to tumours n liver inflmmtion by mitohonril PGAM-Drp signlling Young Jun Kng, Bo-Rm Bng, Kyung Ho Hn, Lixin
Reeive Mr Aepte Aug Publishe 8 Sep DOI:.8/nomms97 Regultion of NKT ell-meite immune responses to tumours n liver inflmmtion by mitohonril PGAM-Drp signlling Young Jun Kng, Bo-Rm Bng, Kyung Ho Hn, Lixin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
Rotoroll OK! User's Guide
 Rotoroll Pge Sfety preution. The user must never open Rotoroll to inspet it, reple prts or unertke repirs. The reeling mehnisms spring my pop out of its set n use mge n injury to persons, nimls n ojets
Rotoroll Pge Sfety preution. The user must never open Rotoroll to inspet it, reple prts or unertke repirs. The reeling mehnisms spring my pop out of its set n use mge n injury to persons, nimls n ojets
OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis
 OPGL is key regultor of osteolstogenesis, lymphoyte evelopment n lymph-noe orgnogenesis Young-Yun Kong*, Hiroki Yoshi*, Iliko Srosi², Hong-Lin Tn², Emm Timms³, Csey Cpprelli², Sen Morony², Antonio J. Oliveir-os-Sntos*,
OPGL is key regultor of osteolstogenesis, lymphoyte evelopment n lymph-noe orgnogenesis Young-Yun Kong*, Hiroki Yoshi*, Iliko Srosi², Hong-Lin Tn², Emm Timms³, Csey Cpprelli², Sen Morony², Antonio J. Oliveir-os-Sntos*,
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
Pellino3 targets the IRF7 pathway and facilitates autoregulation of TLR3- and viral-induced expression of type I interferons
 Pellino3 trgets the pthwy n filittes utoregultion of TLR3- n virl-inue expression of type I interferons Jku Sienienko 1,, Ruihri Jkson 1,, Mrk Mellett 1,, Nezir Delgi 1, Shuo Yng 1, Bingwei Wng 1, Lis
Pellino3 trgets the pthwy n filittes utoregultion of TLR3- n virl-inue expression of type I interferons Jku Sienienko 1,, Ruihri Jkson 1,, Mrk Mellett 1,, Nezir Delgi 1, Shuo Yng 1, Bingwei Wng 1, Lis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
LETTER. Aberrant light directly impairs mood and learning through melanopsin-expressing neurons
 oi:1.138/nture11673 Aerrnt light iretly impirs moo n lerning through melnopsin-expressing neurons Tr A. LeGtes 1 *, Cr M. Altimus 1 *,HuiWng 2, Hey-Kyoung Lee 2, Sunggu Yng 2, Hiqing Zho 1, Alfreo Kirkwoo
oi:1.138/nture11673 Aerrnt light iretly impirs moo n lerning through melnopsin-expressing neurons Tr A. LeGtes 1 *, Cr M. Altimus 1 *,HuiWng 2, Hey-Kyoung Lee 2, Sunggu Yng 2, Hiqing Zho 1, Alfreo Kirkwoo
Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters
 Len, ut not oese, ft is enrihe for unique popultion of regultory T ells tht ffet metoli prmeters Mrkus Feuerer,5, Lur Herrero 2,5, Dniel Cipollett,4,5, Afi Nz 2, Jmie Wong,5, Ali Nyer 2, Jongsoon Lee 2,
Len, ut not oese, ft is enrihe for unique popultion of regultory T ells tht ffet metoli prmeters Mrkus Feuerer,5, Lur Herrero 2,5, Dniel Cipollett,4,5, Afi Nz 2, Jmie Wong,5, Ali Nyer 2, Jongsoon Lee 2,
GSK-3 is a master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis
 GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
Roquin binds inducible costimulator mrna and effectors of mrna decay to induce micrornaindependent post-transcriptional repression
 ins inuile ostimultor mrna n effetors of mrna ey to inue mirornainepenent post-trnsriptionl repression Elke Glsmher 1, Ki P Hoefig 1,3, Kthrin U Vogel 1,3, Niol Rth 1, Lirui Du 1, Christine Wolf 1, Eliseth
ins inuile ostimultor mrna n effetors of mrna ey to inue mirornainepenent post-trnsriptionl repression Elke Glsmher 1, Ki P Hoefig 1,3, Kthrin U Vogel 1,3, Niol Rth 1, Lirui Du 1, Christine Wolf 1, Eliseth
FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration
 integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
