Understanding Anxiety & Panic Attacks
|
|
|
- Aubrie Willis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Understanding Anxiety & Panic Attacks Dr Kwame McKenzie Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association
2 IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute for personal medical advice but as a supplement to that advice for the patient who wishes to understand more about his or her condition. Before taking any form of treatment YOU SHOULD ALWAYS CONSULT YOUR MEDICAL PRACTITIONER. In particular (without limit) you should note that advances in medical science occur rapidly and some information about drugs and treatment contained in this booklet may very soon be out of date. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, or stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording and/or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publishers. The right of Dr Kwame McKenzie to be identified as the author of this work has been asserted in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988, Sections 77 and 78. Family Doctor Publications 2005 Family Doctor Publications, PO Box 4664, Poole, Dorset BH15 1NN ISBN: Contents Introduction...1 Causes of anxiety and fear...6 Symptoms of anxiety...12 Theories of anxiety...22 Types of anxiety problems Dealing with anxiety...54 Management of anxiety disorders using self-help techniques...58 Psychological treatments for anxiety disorders Drug treatment of anxiety...89 Seeking professional help Case studies for specific conditions Family and friends Useful information Index Your pages...
3 About the author Introduction Dr Kwame McKenzie is a Senior Lecturer and Consultant Psychiatrist at the Royal Free Hospital and University College Medical School in London. He is committed to improving the understanding of mental illness and has written over 200 articles, hosted a TV series and conducted numerous radio interviews on the subject. What is anxiety? It is almost impossible to live without anxiety or fear. It is widespread. We feel anxious regularly, although for each of us different events, situations or relationships will make us feel anxious. Lots of things make us anxious or fearful, from everyday events such as crossing the road or meeting new people to bigger decisions such as which school our children should go to or whether or not we should visit the doctor because we develop a pain. Anxiety affects everybody at times. Anxiety and fear There is a subtle difference between anxiety and fear. Fear is the feeling that you have when you see or experience something that frightens you. Anxiety can be regarded as a type of fear that you experience when you are thinking or worrying about something rather than actually experiencing it. I may fear for my life if a car speeds towards me when I am in the middle of the road but if I am sitting in my house, thinking about and becoming concerned 1
4 ANXIETY AND PANIC ATTACKS about safety on the roads, I could be described as being anxious about it. Anxiety and fear lead to similar feelings in the body. Fear is an important defence mechanism that has always been with us. People who do not feel fear can be dangerous to themselves and it can be dangerous to be with them. Some scientists believe that fear has an evolutionary basis. There are some objects that we are programmed to be scared of. These basic fears include certain animals such as snakes and spiders. As we were evolving, individuals with well-honed fear responses to these animals would have been more likely to survive and they would have been more likely to have had children and passed their genes on to the next generation. It takes millions of years for evolution to catch up and so some of our current fears may be linked to survival mechanisms from a long time ago. Fear is both physical and psychological. Situations that provoke fear cause a release of hormones and chemicals that change our body functions. These responses were set up for past times when life was less sophisticated and our challenges were more obvious. The hormones and chemicals cause changes in the body that keep us alert, make us steel ourselves perhaps to fight or prepare us to run away. We saw a predator, we recognised that it could be a danger to us and so we needed to prepare ourselves to fight it or to run away. Alternatively, we saw a possible source of food, perhaps a gazelle, which we did not want to miss the chance of catching because we needed to eat. We needed to think quickly, we needed to be ready to run and catch it, we needed to change our body state so that our performance was optimal. INTRODUCTION Catching prey or fighting for our lives requires only short-lived changes in our body physiology. After we have escaped or after the kill there is no need for our bodies to burn excess energy and so it returns to normal. Our fear responses work well for these sorts of short-lived situations. Our bodies at this time are focused on one thing that is more important than anything else we need to do. When the problem has passed we return to normal and continue with everyday life. Our fear response is set up to deal with severe short-lived physical problems with which our bodies need to deal. Fear and anxiety in the modern world The world has changed, however. Our worries and anxieties now are often not about physical threats or short-term problems. For instance, they may be about the future and how we are going to cope with problems or about situations that may arise but have not yet done so. Anxiety comes from the Latin anxius, which means to worry about an uncertain event. Our bodies use the same set of responses for anxiety as they use for fear. The problem is that our fear response is built to deal with sudden obvious danger but it does not work well for uncertain events. It does not know when best to switch on or turn off. If our fear response is maintained for too long, we feel panicky and uncomfortable. We find it difficult to continue with our day-to-day lives. We are set up to deal with short-lived physical challenges but the threats we come across are often diffuse, may last some time and are psychological rather than physical. The threats are not in front of us. They are often situations that we cannot necessarily 2 3
5 ANXIETY AND PANIC ATTACKS control. You cannot run away from rising debts, for example. It is impossible to fight job uncertainty physically. Nevertheless, these situations are important threats to our way of life. We are left with a prehistoric defence mechanism in the twenty-first century. Our bodies are built to deal with short-lived fears, but our world produces longerterm worries. The two are not a good match and, not surprisingly, the mismatch makes us prone to anxiety problems. The fact that more people do not suffer from such problems is the result of the fact that humans have an amazing ability to adapt. We all find ways of dealing with the stresses of our complex lives, but stresses and coping are finely balanced. This book should help you to understand anxiety problems. You can think of an anxiety problem as fear or anxiety that either lasts too long or is too great compared with the threat. As a result, it causes problems in everyday life. Challenging or threatening situations produce anxiety and sometimes fear. This is a normal reaction that is vital for survival. But if the fear or anxiety is severe, persistent or out of proportion to the threat, or if it impairs your everyday life and your work, you probably have an anxiety disorder. The good news is that anxiety disorders can usually be treated effectively, often without medication. This book helps you understand what is happening to you and what treatments are on offer. It is not a therapy book that you can use by itself, but it will be a useful reference before and during the treatment that you receive from your GP, therapist or specialist. KEY POINTS INTRODUCTION It is almost impossible to live without anxiety or fear Anxiety can be regarded as a type of fear that you experience when you are thinking or worrying about something rather than actually experiencing it Our bodies are built to deal with shortlived fears, but our world produces longer-term worries An anxiety problem is a fear or anxiety that either lasts too long or is out of proportion compared with the threat Anxiety disorders can usually be treated effectively, often without medication 4 5
6 ANXIETY AND PANIC ATTACKS Causes of anxiety and fear What causes anxiety and fear? Anxiety and fear are often caused by stress. Anxiety and fear are the feelings that we experience when we are cornered and we feel threatened. However, we do not always know exactly why we feel threatened. We all have minor fears. We are taught some of them; others seem to be innate (instinctive). Babies start off being happy to be held by anyone, but after a few months they become afraid of strangers and often cry if they are picked up by people who are unfamiliar to them. You can understand how this could work to their benefit. Childbirth used to be dangerous and mothers often died. A baby who was not happy to be picked up by any adult soon after birth would find it difficult to attract someone to look after him or her if the mother died or was sick. However, after a few months of being well looked after, it would be important to stay with and be protected by the person who was familiar and trusted. Strangers would be a threat to the baby s existence and because of this they call out when strangers come near them. Other fears also seem to be genetic, such as our fears of animals that scurry about, or fears of snakes or of heights. We can all think of plausible explanations why we may be scared of them, for instance, they may pass on germs that could kill us, they could bite us, or we may fear falling and hurting ourselves. Some facts, however, just do not fit. There are very few people who are afraid of cars although they are one of the most important causes of accidents in the UK. And there are lots of people who are afraid of flying in planes, although they are very safe indeed. This is what makes people think that we are predisposed to fearing some situations but not others. Anxiety and performance It is normal to be fearful. A little fear is good for us. A little bit of anxiety sharpens up our game. It puts us a bit on edge and improves our performance. A little bit of fear helps us to think quickly, and it makes us work better physically. Students who are not anxious do less well in exams and people who are not appropriately anxious in interviews do not do as well. In extreme situations, those who are fearful think and act quicker and so are more likely to survive than those who are fearless. Fear responses have their place. However, extreme fear and anxiety are not at all good for us. They impede our performance. Some people become so worried before public speaking that they sweat and stutter over their lines. Some students become so anxious over their exams that they cannot prepare properly for them; every time they sit down they worry about how they will do. Some people do badly in interviews because they are too nervous and some people become so fearful in extreme situations that they totally freeze. 6 7
7 Improving performance There is a trade-off between a person s level of anxiety and his or her performance. Mental and physical performance increases as the level of anxiety increases but gradually reaches a point where for every increase in level of anxiety performance decreases and decreases quickly. We all need some fear, but too much and we just cannot perform. If you are too relaxed you may not perform well. If you are over-anxious or over-stressed your performance deteriorates. Anxiety can cause further anxiety There is a further problem: anxiety and stress can produce a vicious circle. For instance, exam students who have become too anxious and cannot revise because they are worrying about how well they are going to do may soon realise that they have not been working. Better ANXIETY AND PANIC ATTACKS CAUSES OF ANXIETY AND FEAR This will make them more worried and produce more anxiety and more time wasted about how they are going to fare. The more they worry, the less time they spend working and the more they worry. There are other forms of anxiety that are not helpful. Later in the book forms of anxiety are described that seem to have no reason and are unrelated to any event. In addition fears and anxieties are described that are extreme compared with the threat. These forms of anxiety have no useful function at all and can be distressing. Sometimes the timing of our anxiety goes awry. During a traumatic event some people seem to cope very well but hours or even days later their anxiety kicks in. This sort of delayed fear and anxiety response is, again, very distressing and not useful. How common are anxiety problems? Anxiety is an everyday event for many people. Anxiety that causes problems with our enjoyment of life affects a lot of people. It is estimated that 14 per cent of the population (14 in every 100) have a problem that could benefit from treatment. Anxiety problems are very common and they are the most common psychological problem in the UK. They are more common than depression. Anxiety can become an escalating vicious circle, whereby the existence of anxiety produces other effects in the body, such as physical symptoms, that cause even more anxiety. Worse Less Increasing anxiety Anxiety and performance. More Does my anxiety need treatment? The simple answer is that, if your anxiety affects the way in which you live and if it affects your enjoyment of life, you may benefit from treatment. But, beware, 8 9
8 ANXIETY AND PANIC ATTACKS Anxiety can become a vicious circle CAUSES OF ANXIETY AND FEAR KEY POINTS Physical symptoms produce more anxious thoughts Stress Anxiety Anxious thoughts produce physical symptoms of anxiety Anxiety and fear are normal reactions that we need so that we can respond properly to threats Too much anxiety stops us performing properly Anxiety disorders are the result of too much or inappropriate anxiety the drive that some people have to succeed is based on their anxieties about themselves. So, if you were to try to get rid of anxiety altogether, you could feel more relaxed but you could diminish your drive to succeed. Fourteen per cent of the population at some time suffer from anxiety problems that could be treated If your anxiety affects the way that you live your life, consider getting treatment How common is anxiety? Type of anxiety Percentage of adults (aged 16 64) with anxiety problems Mixed anxiety and depression 8 per cent (8 in 100) Generalised anxiety 3 per cent (2 in 100) Obsessive compulsive 1 per cent (1 in 100) Panic disorder 1 per cent (1 in 100) Phobias 1 per cent (1 in 100) Total 14 per cent (14 in 100) 10 11
9 SYMPTOMS OF ANXIETY Symptoms of anxiety The fight, flight or fright response Our fear response is set up for dealing with a physical threat or opportunity. Some people call it a fight, flight or fright response because those seem to be the options that our body is giving us we freeze, fight our foe or run away. Our body gets ready for action in a number of ways. A number of hormones are released into our bloodstream from the glands in which they are stored. They have effects on our nerves and other organs, preparing us for action. The chief hormone is adrenaline (also known as epinephrine). It causes our heart to beat quicker, makes our blood pressure go up and gets us to breathe quicker. These actions make sure that we have lots of blood full of oxygen so that the muscles can work effectively. Adrenaline helps to make sure that our body uses this blood efficiently. It makes some blood vessels bigger and others smaller, and in this way causes blood to be diverted to the parts of the body that most need it. The muscles in our legs and arms are needed for fighting or running away and so they receive preferential treatment. The brain is provided with extra blood so that we stay alert and can think about what we need to do. Less important functions, such as digesting food, are put on the back burner, so blood to the stomach is decreased. Blood to the skin is also decreased. If we need to run, however, we need to run fast. Hence we need to be as light as we can. Adrenaline affects the muscles in our bladder and bowel. Being as light as we can be could be the difference between getting away and being caught. Adrenaline makes us feel like urinating and defecating so that we can get rid of excess water and solids. If we are running and using extra energy we do not want to overheat. Hence our bodies sweat. The water cools us off. Adrenaline also gives our sensory organs a pep up. We become tense so that everything can act and react more quickly. These bodily changes correspond to the symptoms that we feel when we are anxious, for instance: We feel our heart pounding or feel like we have palpitations because adrenaline has pushed our heart rate up. We feel dizzy because adrenaline has changed our blood pressure. We may feel a little short of breath because we are breathing faster. We get butterflies in the stomach because the blood is diverted from here and we may feel like going to the toilet because the muscles to the bladder are affected
10 ANXIETY AND PANIC ATTACKS Adrenaline and the fear response Adrenaline is released in the body in response to a physical threat or opportunity. It has a variety of effects within the body to ensure that we are ready to deal with the situation. SYMPTOMS OF ANXIETY What are the symptoms of anxiety? There are many symptoms of anxiety. They can be broadly categorised as either physical or psychological. Brain Physical Palpitations Sweating Tremor Dry mouth Difficulty breathing Choking Hypothalamus and pituitary gland Physical threat Nerve impulse Secretion of adrenaline (epinephrine) Chest tightness Abdominal pain/ discomfort/nausea Hot flushes Tingling in fingers Psychological Dizziness Fear of losing control Fear of dying Feeling out of it Loss of appetite Nerve impulse to adrenal glands Adrenal glands Poor sleep Tiredness Feeling on edge Restlessness Difficulty concentrating Depression We sweat; this happens in order to cool us down but at the same time we may feel cold because adrenaline has caused the blood to drain away from the skin. We feel on edge and tense because all our senses and muscles have been pepped up. Kidney Dispersion of adrenaline into the blood Kidney None of these symptoms will cause a problem to us. The body has it all under control. We do not even notice them when we experience them in the appropriate situation a threatening situation. We do notice them, however, if we experience them when we are not 14 15
Panic. Information booklet. RDaSH leading the way with care
 Panic Information booklet RDaSH leading the way with care It is common to feel panicky from time to time. It could be because you think there is someone following you, you can t remember your words in
Panic Information booklet RDaSH leading the way with care It is common to feel panicky from time to time. It could be because you think there is someone following you, you can t remember your words in
Your Safety System - a User s Guide.
 1 Your Safety System - a User s Guide. Human beings are designed for safety SO: You have 2 settings: 1. An ordinary everyday setting And 2. An emergency threat setting. This gets the body ready for immediate
1 Your Safety System - a User s Guide. Human beings are designed for safety SO: You have 2 settings: 1. An ordinary everyday setting And 2. An emergency threat setting. This gets the body ready for immediate
Your Safety System - a User s Guide.
 THE WOODHAVEN ANXIETY/STRESS MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME. Your Safety System - a User s Guide. Isabel Clarke and Becky Mallery. Woodhaven Psychological Therapies Service. 1 Your Safety System - a User s Guide.
THE WOODHAVEN ANXIETY/STRESS MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME. Your Safety System - a User s Guide. Isabel Clarke and Becky Mallery. Woodhaven Psychological Therapies Service. 1 Your Safety System - a User s Guide.
Anxiety. Everybody and normal reaction the organism to. you. from. your major muscle groups. escape. the dog. of both of these. Now. head.
 Anxiety Everybody and anybody will becomee anxious at some point in their lives. Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress and danger and it serves a very important purpose in protecting the organism to which
Anxiety Everybody and anybody will becomee anxious at some point in their lives. Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress and danger and it serves a very important purpose in protecting the organism to which
Needle Phobia: Overcoming your fear of injections
 NHS Fife Department of Psychology Needle Phobia: Overcoming your fear of injections Help Yourself @ moodcafe.co.u Needle Phobia: Overcoming your fear of injections This leaflet aims to give you information
NHS Fife Department of Psychology Needle Phobia: Overcoming your fear of injections Help Yourself @ moodcafe.co.u Needle Phobia: Overcoming your fear of injections This leaflet aims to give you information
Anxiety. A self help guide. East Cheshire Hospice Millbank Drive Macclesfield Cheshire SK10 3DR
 Anxiety A self help guide East Cheshire Hospice Millbank Drive Macclesfield Cheshire SK10 3DR Main reception: 01625 610364 Physiotherapy / OT 01625 665689 Fax: 01625 666995 www.eastcheshirehospice.org.uk
Anxiety A self help guide East Cheshire Hospice Millbank Drive Macclesfield Cheshire SK10 3DR Main reception: 01625 610364 Physiotherapy / OT 01625 665689 Fax: 01625 666995 www.eastcheshirehospice.org.uk
TeensHealth.org A safe, private place to get doctor-approved information on health, emotions, and life. Anxiety Disorders. What Is Anxiety?
 TeensHealth.org A safe, private place to get doctor-approved information on health, emotions, and life. What Is Anxiety? Anxiety Disorders Liam had always looked out for his younger brother Sam. But whenever
TeensHealth.org A safe, private place to get doctor-approved information on health, emotions, and life. What Is Anxiety? Anxiety Disorders Liam had always looked out for his younger brother Sam. But whenever
Anxiety. Learn, think, do
 Anxiety Learn, think, do Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health problem in Australia. The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports that anxiety affects over 2 million people aged 16 85 years,
Anxiety Learn, think, do Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health problem in Australia. The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports that anxiety affects over 2 million people aged 16 85 years,
Assessment of anxiety. 5Ws What When Where Why With whom. Impact Occupational/financial Domestic/self-care Social Personal interests Relationships
 Assessment of anxiety 5Ws What When Where Why With whom Impact Occupational/financial Domestic/self-care Social Personal interests Relationships FIDO Frequency Intensity Duration Onset Features Physiological
Assessment of anxiety 5Ws What When Where Why With whom Impact Occupational/financial Domestic/self-care Social Personal interests Relationships FIDO Frequency Intensity Duration Onset Features Physiological
Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide
 Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide Anxiety Anxiety can be a very normal and healthy response to stressful situations, such as paying bills or sitting an exam. However, it becomes a problem when
Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide Anxiety Anxiety can be a very normal and healthy response to stressful situations, such as paying bills or sitting an exam. However, it becomes a problem when
A fact sheet produced by the Mental Health Information Service
 Anxiety what is it? A fact sheet produced by the Mental Health Information Service Anxiety is a natural reaction that everyone experiences - part of our fight or flight response - which helps us to be
Anxiety what is it? A fact sheet produced by the Mental Health Information Service Anxiety is a natural reaction that everyone experiences - part of our fight or flight response - which helps us to be
How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Patient information leaflet Follow us on
 Coping with Anxiety How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in
Coping with Anxiety How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in
University Staff Counselling Service
 University Staff Counselling Service Anxiety and Panic What is anxiety? Anxiety is a normal emotional and physiological response to feeling threatened, ranging from mild uneasiness and worry to severe
University Staff Counselling Service Anxiety and Panic What is anxiety? Anxiety is a normal emotional and physiological response to feeling threatened, ranging from mild uneasiness and worry to severe
After an Accident or Trauma. A leaflet for patients who have been involved in an accident or traumatic event.
 After an Accident or Trauma A leaflet for patients who have been involved in an accident or traumatic event. Traumatic experiences such as accidents are, of course, very distressing to those involved.
After an Accident or Trauma A leaflet for patients who have been involved in an accident or traumatic event. Traumatic experiences such as accidents are, of course, very distressing to those involved.
Anxiety and panic attacks
 Anxiety and panic attacks Information for individuals, partners and families NCMH National Centre for Mental Health Anxiety and panic attacks It is normal to feel anxious or worried in situations that
Anxiety and panic attacks Information for individuals, partners and families NCMH National Centre for Mental Health Anxiety and panic attacks It is normal to feel anxious or worried in situations that
LIFE MENTAL HEALTH ANXIETY DISORDERS TREATMENT GUIDE
 ANXIETY DISORDERS TREATMENT GUIDE Anxiety Disorders Treatment Guide What is Panic Disorder? What is Agoraphobia? What is Generalised Anxiety Disorder? What is Social Phobia? What is Obsessive-Compulsive
ANXIETY DISORDERS TREATMENT GUIDE Anxiety Disorders Treatment Guide What is Panic Disorder? What is Agoraphobia? What is Generalised Anxiety Disorder? What is Social Phobia? What is Obsessive-Compulsive
Anxiety Attacks and Anxiety Disorders
 Anxiety Attacks and Anxiety Disorders Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment We all know what anxiety feels like. Your heart pounds before a big presentation or a tough exam. You get butterflies in your stomach
Anxiety Attacks and Anxiety Disorders Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment We all know what anxiety feels like. Your heart pounds before a big presentation or a tough exam. You get butterflies in your stomach
Anxiety and Worries. How common is it?
 Anxiety and Worries We all get frightened or worried from time to time. Fear can be a good thing as it keeps us from getting too close to danger. Sometimes, we can feel frightened or worry about things
Anxiety and Worries We all get frightened or worried from time to time. Fear can be a good thing as it keeps us from getting too close to danger. Sometimes, we can feel frightened or worry about things
did you feel sad or depressed? did you feel sad or depressed for most of the day, nearly every day?
 Name: Age: Date: PDSQ This form asks you about emotions, moods, thoughts, and behaviors. For each question, circle YES in the column next to that question, if it describes how you have been acting, feeling,
Name: Age: Date: PDSQ This form asks you about emotions, moods, thoughts, and behaviors. For each question, circle YES in the column next to that question, if it describes how you have been acting, feeling,
Beat. Adrenal Fatigue Naturally!
 Beat Adrenal Fatigue Naturally! What is Adrenal Fatigue? Before we dive into adrenal fatigue, let s first start with the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are glands that sit on top of the kidneys. They
Beat Adrenal Fatigue Naturally! What is Adrenal Fatigue? Before we dive into adrenal fatigue, let s first start with the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are glands that sit on top of the kidneys. They
Understanding and Managing Change
 www.working-minds.org.uk Understanding and Managing Change Understanding and Managing Change This leaflet is designed to assist you in understanding some of the normal emotions that we feel when we are
www.working-minds.org.uk Understanding and Managing Change Understanding and Managing Change This leaflet is designed to assist you in understanding some of the normal emotions that we feel when we are
WHAT IS STRESS? increased muscle tension increased heart rate increased breathing rate increase in alertness to the slightest touch or sound
 EXAM STRESS WHAT IS STRESS? Stress is part of the body s natural response to a perceived threat. We all experience it from time to time. When we feel under threat, our bodies go into fight or flight response,
EXAM STRESS WHAT IS STRESS? Stress is part of the body s natural response to a perceived threat. We all experience it from time to time. When we feel under threat, our bodies go into fight or flight response,
Managing Stress. pressure, fear, confusion, anger and sweating.
 Managing Stress Introduction Stress is a physical and emotional reaction that everyone experiences as they encounter changes in life. These reactions can have positive or negative effects. Stress has positive
Managing Stress Introduction Stress is a physical and emotional reaction that everyone experiences as they encounter changes in life. These reactions can have positive or negative effects. Stress has positive
The scientific discovery that changed our perception of anxiety
 The scientific discovery that changed our perception of anxiety For many years I have suffered with a very severe form of OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Disorder), anxiety, and clinical depression. I had no
The scientific discovery that changed our perception of anxiety For many years I have suffered with a very severe form of OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Disorder), anxiety, and clinical depression. I had no
Module 3 - How Pain Affects You
 Module 3 - How Pain Affects You You have learned that pain is produced as a result of all of the incoming electrical or danger signals which reach your brain. Example: Mum Watching Her Son Play Footy Think
Module 3 - How Pain Affects You You have learned that pain is produced as a result of all of the incoming electrical or danger signals which reach your brain. Example: Mum Watching Her Son Play Footy Think
ALLIANCE COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SLEEP DISORDERS CENTER PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE/HISTORY PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING WITH YOU ON THE NIGHT OF YOUR TEST.
 ALLIANCE COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SLEEP DISORDERS CENTER PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE/HISTORY PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING WITH YOU ON THE NIGHT OF YOUR TEST. NAME DATE: HEIGHT: WEIGHT: DOB: SEX: HOME PHONE #: REFERRING
ALLIANCE COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SLEEP DISORDERS CENTER PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE/HISTORY PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING WITH YOU ON THE NIGHT OF YOUR TEST. NAME DATE: HEIGHT: WEIGHT: DOB: SEX: HOME PHONE #: REFERRING
Me, My Heart and Anxiety
 Me, My Heart and Anxiety (Adapted for GUCH News from my talk at the Somerville Foundation Annual Conference September 2017.) One of the topics people most often I get most calls about is anxiety. My focus
Me, My Heart and Anxiety (Adapted for GUCH News from my talk at the Somerville Foundation Annual Conference September 2017.) One of the topics people most often I get most calls about is anxiety. My focus
Does anxiety cause some difficulty for a young person you know well? What challenges does this cause for the young person in the family or school?
 John Walker, Ph.D. Department of Clinical Health Psychology University of Manitoba Everyone has the emotions at times. Signal us to be careful. Help us to stay safe. Most children and adults have mild
John Walker, Ph.D. Department of Clinical Health Psychology University of Manitoba Everyone has the emotions at times. Signal us to be careful. Help us to stay safe. Most children and adults have mild
Non-epileptic attacks
 Non-epileptic attacks A short guide for patients and families Information for patients Neurology Psychotherapy Service What are non-epileptic attacks? Non-epileptic attacks are episodes in which people
Non-epileptic attacks A short guide for patients and families Information for patients Neurology Psychotherapy Service What are non-epileptic attacks? Non-epileptic attacks are episodes in which people
Welcome to Pine Street Family Practice s Podcasts!!
 Welcome to Pine Street Family Practice s Podcasts!! New Series of Podcasts A Few Topics Anxiety Diabetes Hypertension Dementia Obesity Nutrition What will the podcast review? Brief information on a health
Welcome to Pine Street Family Practice s Podcasts!! New Series of Podcasts A Few Topics Anxiety Diabetes Hypertension Dementia Obesity Nutrition What will the podcast review? Brief information on a health
Anxiety: what employers need to know
 Swindon Mindful Employer Network Anxiety: what employers need to know Tuesday 6 March DoubleTree by Hilton Swindon Swindon Mindful Employer Network ANXIETY WHAT EMPLOYERS NEED TO KNOW MELANIE RICHENS THE
Swindon Mindful Employer Network Anxiety: what employers need to know Tuesday 6 March DoubleTree by Hilton Swindon Swindon Mindful Employer Network ANXIETY WHAT EMPLOYERS NEED TO KNOW MELANIE RICHENS THE
Counselling Service. Understanding Anxiety & Panic Attacks
 Counselling Service Understanding Anxiety & Panic Attacks What is anxiety? All of us experience some anxiety from time to time. This is normal and may help us cope with a difficult or stressful situation.
Counselling Service Understanding Anxiety & Panic Attacks What is anxiety? All of us experience some anxiety from time to time. This is normal and may help us cope with a difficult or stressful situation.
P A N A N X I E T Y C
 P A N A N X I E T Y C The terms panic attack and anxiety attack are used interchangeably, but they are not the same. Key characteristics distinguish one from the other, though they have several symptoms
P A N A N X I E T Y C The terms panic attack and anxiety attack are used interchangeably, but they are not the same. Key characteristics distinguish one from the other, though they have several symptoms
Problem Summary. * 1. Name
 Problem Summary This questionnaire is an important part of providing you with the best health care possible. Your answers will help in understanding problems that you may have. Please answer every question
Problem Summary This questionnaire is an important part of providing you with the best health care possible. Your answers will help in understanding problems that you may have. Please answer every question
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Teena Jain 2017 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder What is post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD? PTSD is a disorder that some people develop after experiencing a shocking,
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Teena Jain 2017 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder What is post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD? PTSD is a disorder that some people develop after experiencing a shocking,
A report about. Anxiety. Easy Read summary
 A report about Anxiety Easy Read summary Mental Health Awareness Week 2014 This is an Easy Read summary of the Living with Anxiety report (2014). This report was written by the Mental Health Foundation.
A report about Anxiety Easy Read summary Mental Health Awareness Week 2014 This is an Easy Read summary of the Living with Anxiety report (2014). This report was written by the Mental Health Foundation.
Feeling low or anxious
 BRAIN INJURY SERIES Feeling low or anxious IN THIS BOOKLET What is depression? Anxiety explained Ways to overcome anxiety or depression Positive tips and advice Brain Injury Series This booklet was written
BRAIN INJURY SERIES Feeling low or anxious IN THIS BOOKLET What is depression? Anxiety explained Ways to overcome anxiety or depression Positive tips and advice Brain Injury Series This booklet was written
A VIDEO SERIES. living WELL. with kidney failure KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
 A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure KIDNEY TRANSPLANT Contents 2 Introduction 3 What will I learn? 5 Who is on my healthcare team? 6 What is kidney failure? 6 What treatments are available
A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure KIDNEY TRANSPLANT Contents 2 Introduction 3 What will I learn? 5 Who is on my healthcare team? 6 What is kidney failure? 6 What treatments are available
Anxiety and problem solving
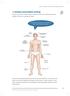 Anxiety and problem solving Anxiety is very common in ADHD, because it is diffi cult to relax with a restless body and racing thoughts. At night, worry may keep you awake. What physical sensations do you
Anxiety and problem solving Anxiety is very common in ADHD, because it is diffi cult to relax with a restless body and racing thoughts. At night, worry may keep you awake. What physical sensations do you
Explaining. pain. Understanding more about your persistent pain and how it affects your life
 Explaining pain Understanding more about your persistent pain and how it affects your life Persistent pain (sometimes called chronic or long-term pain) is described as pain that continues for three months
Explaining pain Understanding more about your persistent pain and how it affects your life Persistent pain (sometimes called chronic or long-term pain) is described as pain that continues for three months
Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Vulnerable Populations: Data Harmonization Measure
 Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Vulnerable Populations: Measure MENTAL HEALTH Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) Reference: Radloff, L.S. (1977). The CES-D Scale: a self-report
Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Vulnerable Populations: Measure MENTAL HEALTH Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) Reference: Radloff, L.S. (1977). The CES-D Scale: a self-report
July 2018 Coping with anxiety
 July 2018 Coping with anxiety This document is for parents and carers who have a child who is suffering with feelings of anxiety. We hope that this will enable you to respond effectively to your child
July 2018 Coping with anxiety This document is for parents and carers who have a child who is suffering with feelings of anxiety. We hope that this will enable you to respond effectively to your child
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Baby Blues and More. Postpartum mood disorders DRAFT. Emotional Changes After Giving Birth
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Postpartum mood disorders Some new mothers have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. This chapter gives ideas for things you can do to
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Postpartum mood disorders Some new mothers have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. This chapter gives ideas for things you can do to
Stress. Weller Health Education Center. What Is Stress? Good Stress and Bad Stress. 325 Northampton Street. Easton, Pennsylvania
 Weller Health Education Center 325 Northampton Street Easton, Pennsylvania 18042 610-258-8500 www.wellercenter.org Stress Feeling like there are too many pressures and demands on you? Losing sleep worrying
Weller Health Education Center 325 Northampton Street Easton, Pennsylvania 18042 610-258-8500 www.wellercenter.org Stress Feeling like there are too many pressures and demands on you? Losing sleep worrying
Panic. Easy read information
 Panic Easy read information 2 A member of staff or a carer can support you to read this booklet. They will be able to answer any questions that you have. How can this guide help me? This guide will help
Panic Easy read information 2 A member of staff or a carer can support you to read this booklet. They will be able to answer any questions that you have. How can this guide help me? This guide will help
NHS Fife Department of Psychology. Postnatal Anxiety. Help moodcafe.co.uk
 NHS Fife Department of Psychology Postnatal Anxiety Help Yourself @ moodcafe.co.uk Postnatal Anxiety This leaflet aims to give you information about postnatal anxiety (anxiety following pregnancy). If
NHS Fife Department of Psychology Postnatal Anxiety Help Yourself @ moodcafe.co.uk Postnatal Anxiety This leaflet aims to give you information about postnatal anxiety (anxiety following pregnancy). If
Section 4 - Dealing with Anxious Thinking
 Section 4 - Dealing with Anxious Thinking How do we challenge our unhelpful thoughts? Anxiety may decrease if we closely examine how realistic and true our unhelpful/negative thoughts are. We may find
Section 4 - Dealing with Anxious Thinking How do we challenge our unhelpful thoughts? Anxiety may decrease if we closely examine how realistic and true our unhelpful/negative thoughts are. We may find
ANXIETY ALERT WORKSHOP. Yvonne Tone RPN, RGN, M.Sc Student Counsellor Trinity College Dublin
 ANXIETY ALERT WORKSHOP Yvonne Tone RPN, RGN, M.Sc Student Counsellor Trinity College Dublin WELCOME!... Aims & Objectives: This workshop is designed to help you to: Explore how anxiety affects us Identify
ANXIETY ALERT WORKSHOP Yvonne Tone RPN, RGN, M.Sc Student Counsellor Trinity College Dublin WELCOME!... Aims & Objectives: This workshop is designed to help you to: Explore how anxiety affects us Identify
CBT Intake Form. Patient Name: Preferred Name: Last. First. Best contact phone number: address: Address:
 Patient Information CBT Intake Form Patient Name: Preferred Name: Last Date of Birth: _// Age: _ First MM DD YYYY Gender: Best contact phone number: Email address: _ Address: _ Primary Care Physician:
Patient Information CBT Intake Form Patient Name: Preferred Name: Last Date of Birth: _// Age: _ First MM DD YYYY Gender: Best contact phone number: Email address: _ Address: _ Primary Care Physician:
Social Anxiety Disorder
 Social Anxiety Disorder More than Just Shyness Teena Social Anxiety Disorder: More than Just Shyness Introduction Are you extremely afraid of being judged by others? Are you very self-conscious in everyday
Social Anxiety Disorder More than Just Shyness Teena Social Anxiety Disorder: More than Just Shyness Introduction Are you extremely afraid of being judged by others? Are you very self-conscious in everyday
Psychiatry. Anxiety Begone!
 Psychiatry Anxiety Begone! The Department of Psychiatry helps patients cope with psychological problems, behavioural disorders and life s stressors. We assess psychiatric and psychological conditions ranging
Psychiatry Anxiety Begone! The Department of Psychiatry helps patients cope with psychological problems, behavioural disorders and life s stressors. We assess psychiatric and psychological conditions ranging
Fear UNIT 7. Discussion point. It makes me feel 2 What are you afraid of? Why? I m scared of because 3 What do you think causes peoples fears?
 UNIT 7 Fear Discussion point Discuss these questions with a partner. 1 Look at the picture. How does it make you feel? It makes me feel 2 What are you afraid of? Why? I m scared of because 3 What do you
UNIT 7 Fear Discussion point Discuss these questions with a partner. 1 Look at the picture. How does it make you feel? It makes me feel 2 What are you afraid of? Why? I m scared of because 3 What do you
STEPS primary care mental health team, Glasgow. Height phobia. STEPS (2008). All rights reserved. Do not amend in any way.
 STEPS primary care mental health team, Glasgow Height phobia STEPS (2008). All rights reserved. Do not amend in any way. 1 Height Phobia Self-Help Strategies Step 1 Becoming more aware Keep a diary It
STEPS primary care mental health team, Glasgow Height phobia STEPS (2008). All rights reserved. Do not amend in any way. 1 Height Phobia Self-Help Strategies Step 1 Becoming more aware Keep a diary It
COUNSELLING WITH PLYMOUTH UNIVERSITY
 Understanding panic attacks and finding ways to cope Student Counselling www.plymouth.ac.uk/counselling COUNSELLING WITH PLYMOUTH UNIVERSITY What is happening to me? Panic attacks often start without warning
Understanding panic attacks and finding ways to cope Student Counselling www.plymouth.ac.uk/counselling COUNSELLING WITH PLYMOUTH UNIVERSITY What is happening to me? Panic attacks often start without warning
Panic Stations Module 2
 PANIC STATIONS Panic Stations Module 2 More about Panic Introduction 2 How do panic attacks happen? 2 How does panic disorder develop? 3 How is panic disorder maintained? 4 What can be done about panic
PANIC STATIONS Panic Stations Module 2 More about Panic Introduction 2 How do panic attacks happen? 2 How does panic disorder develop? 3 How is panic disorder maintained? 4 What can be done about panic
Psychological preparation for natural disasters
 Disaster Preparedness Psychological preparation for natural disasters Being psychologically prepared when a disaster is threatening can help people feel more confident, more in control and better able
Disaster Preparedness Psychological preparation for natural disasters Being psychologically prepared when a disaster is threatening can help people feel more confident, more in control and better able
FATIGUE ASSESSMENT SCALE
 WORKSHEET #1 FATIGUE ASSESSMENT SCALE Please indicate how true each statement has been for you during the past 7 days Not at all A little bit Some what Quite a lot Very much I feel fatigued I feel weak
WORKSHEET #1 FATIGUE ASSESSMENT SCALE Please indicate how true each statement has been for you during the past 7 days Not at all A little bit Some what Quite a lot Very much I feel fatigued I feel weak
Managing Mental Health (at Work)
 Managing Mental Health (at Work) So what do you hope to get from this session? Can you name some types of Mental Health Conditions? Depression Eating problems Phobias Anxiety Schizophrenia Stress Post-traumatic
Managing Mental Health (at Work) So what do you hope to get from this session? Can you name some types of Mental Health Conditions? Depression Eating problems Phobias Anxiety Schizophrenia Stress Post-traumatic
Managing parenting stress
 Managing parenting stress Emma Heaney-Yeatts Lead Counsellor and Extension Manager, Post and Antenatal Distress Support Wellington (PND Wellington). The pressures of being a parent With the New Year underway
Managing parenting stress Emma Heaney-Yeatts Lead Counsellor and Extension Manager, Post and Antenatal Distress Support Wellington (PND Wellington). The pressures of being a parent With the New Year underway
Anxiety Disorders. Dr Simon Christopherson Dr Alison Macrae
 Anxiety Disorders Dr Simon Christopherson Dr Alison Macrae 1 What is anxiety? Universal fight or flight experience Nerves / fearfulness can boost performance Worries keep you alert & prevent you missing
Anxiety Disorders Dr Simon Christopherson Dr Alison Macrae 1 What is anxiety? Universal fight or flight experience Nerves / fearfulness can boost performance Worries keep you alert & prevent you missing
What is anxiety? What does it look like? Why is my child anxious? What can I do to help my child?
 What is anxiety? What does it look like? Why is my child anxious? What can I do to help my child? Group Activity: How do you know when your child is anxious? What is anxiety? Anxiety is a feeling of unease,
What is anxiety? What does it look like? Why is my child anxious? What can I do to help my child? Group Activity: How do you know when your child is anxious? What is anxiety? Anxiety is a feeling of unease,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Baby Blues and More DRAFT. Knowing About This in Advance Can Help
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Recognizing and coping with postpartum mood disorders Some women have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. It helps to know about these
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Recognizing and coping with postpartum mood disorders Some women have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. It helps to know about these
A NEW MOTHER S. emotions. Your guide to understanding maternal mental health
 A NEW MOTHER S emotions Your guide to understanding maternal mental health It is not your fault It is treatable Understanding Maternal Mental Health Life with a new baby is not always easy and the adjustment
A NEW MOTHER S emotions Your guide to understanding maternal mental health It is not your fault It is treatable Understanding Maternal Mental Health Life with a new baby is not always easy and the adjustment
Phobias what, who, why and how to help
 Phobias what, who, why and how to help St. Andrews House, 48 Princess Road East, Leicester LE1 7DR, UK Telephone 0116 254 9568 Facsimile 0116 247 0787 E-mail mail@bps.org.uk Website www.bps.org.uk What
Phobias what, who, why and how to help St. Andrews House, 48 Princess Road East, Leicester LE1 7DR, UK Telephone 0116 254 9568 Facsimile 0116 247 0787 E-mail mail@bps.org.uk Website www.bps.org.uk What
Understanding and Coping with Stress
 Understanding and Coping with Stress Learning Intentions 1. Understand the stress response 2. Understand the positive and negative effects of stress 3. Identify the what causes stress 4. Understand the
Understanding and Coping with Stress Learning Intentions 1. Understand the stress response 2. Understand the positive and negative effects of stress 3. Identify the what causes stress 4. Understand the
Health Anxiety A booklet to help people who worry too much about health
 Health Anxiety A booklet to help people who worry too much about health I am always at the doctor's surgery. That is because I often worry about having something wrong with me. Last week it was tingling
Health Anxiety A booklet to help people who worry too much about health I am always at the doctor's surgery. That is because I often worry about having something wrong with me. Last week it was tingling
How can I explain anxiety to my child?
 How can I explain anxiety to my child? Alexandra Koster 2 January 2018 More and more people are suffering from anxiety due to many different factors relating to our modern lifestyle among other things
How can I explain anxiety to my child? Alexandra Koster 2 January 2018 More and more people are suffering from anxiety due to many different factors relating to our modern lifestyle among other things
Help is at hand. Lambeth. Problems at work? Depressed? Stressed? Phobias? Anxious? Can t find work? Lambeth Psychological Therapies
 South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust Problems at work? Lambeth Stressed? Depressed? Anxious? Phobias? Can t find work? Lambeth Psychological Therapies 020 3228 6747 Help is at hand Page 1 Are
South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust Problems at work? Lambeth Stressed? Depressed? Anxious? Phobias? Can t find work? Lambeth Psychological Therapies 020 3228 6747 Help is at hand Page 1 Are
understand the causes and effects of stress
 A guide for patients to help understand the causes and effects of stress What is stress? Stress is unavoidable. It can be described as the pressure we all encounter in our daily lives. It is a normal physical
A guide for patients to help understand the causes and effects of stress What is stress? Stress is unavoidable. It can be described as the pressure we all encounter in our daily lives. It is a normal physical
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Relaxation Training
 A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Relaxation Training 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Relaxation Training 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
MOODJUICE - Panic - Self-help Guide
 Page 1 of 28 Page 2 of 28 Self Help for Panic and Agoraphobia Do you often experience uncomfortable physical symptoms such as a rapid heart beat, breathlessness, shaking, dizziness and sweating? Do you
Page 1 of 28 Page 2 of 28 Self Help for Panic and Agoraphobia Do you often experience uncomfortable physical symptoms such as a rapid heart beat, breathlessness, shaking, dizziness and sweating? Do you
What is Stress? What causes stress?
 What is Stress? Stress is the physical and mental response of the body to demands made upon it by everyday life, especially if we are struggling to cope with pressured or difficult tasks or circumstances.
What is Stress? Stress is the physical and mental response of the body to demands made upon it by everyday life, especially if we are struggling to cope with pressured or difficult tasks or circumstances.
Stress & Mood Management. Managing Anxiety and Panic. Course Slides. Keeping Yourself Safe
 Course Slides Stress & Mood Management Managing Anxiety and Panic To obtain a copy of the course slides, log on to: www.inclusionthurrock.org Alternatively, email smm@sssft.nhs.uk. Please do not send any
Course Slides Stress & Mood Management Managing Anxiety and Panic To obtain a copy of the course slides, log on to: www.inclusionthurrock.org Alternatively, email smm@sssft.nhs.uk. Please do not send any
Treatment Advice for Dissociative Attacks (non-epileptic attacks) from
 Treatment Advice for Dissociative Attacks (non-epileptic attacks) from www.neurosymptoms.org 1 Treatment advice for Dissociative Attacks (Non-epileptic attacks/seizures) This document is reproduced from
Treatment Advice for Dissociative Attacks (non-epileptic attacks) from www.neurosymptoms.org 1 Treatment advice for Dissociative Attacks (Non-epileptic attacks/seizures) This document is reproduced from
Depression: what you should know
 Depression: what you should know If you think you, or someone you know, might be suffering from depression, read on. What is depression? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness and
Depression: what you should know If you think you, or someone you know, might be suffering from depression, read on. What is depression? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness and
These questionnaires are used by psychology services to help us understand how people feel. One questionnaire measures how sad people feel.
 ADAPTED PHQ-9 & GAD-7 QUESTIONNAIRES How to fill in these questionnaires: These questionnaires are used by psychology services to help us understand how people feel. One questionnaire measures how sad
ADAPTED PHQ-9 & GAD-7 QUESTIONNAIRES How to fill in these questionnaires: These questionnaires are used by psychology services to help us understand how people feel. One questionnaire measures how sad
Do you have sudden bursts of fear for no reason? Panic Disorder A R E A L I L L N E S S. Panic Disorcer NIH Publication No.
 Do you have sudden bursts of fear for no reason? A R E A L I L L N E S S Panic Disorder Panic Disorcer NIH Publication No. 00-4679 Does This Sound Like You? Do you have sudden bursts of fear for no reason?
Do you have sudden bursts of fear for no reason? A R E A L I L L N E S S Panic Disorder Panic Disorcer NIH Publication No. 00-4679 Does This Sound Like You? Do you have sudden bursts of fear for no reason?
Understanding Migraine & other headaches
 Understanding Migraine & other headaches Dr Anne MacGregor Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not
Understanding Migraine & other headaches Dr Anne MacGregor Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not
Problem Situation Form for Parents
 Problem Situation Form for Parents Please complete a form for each situation you notice causes your child social anxiety. 1. WHAT WAS THE SITUATION? Please describe what happened. Provide enough information
Problem Situation Form for Parents Please complete a form for each situation you notice causes your child social anxiety. 1. WHAT WAS THE SITUATION? Please describe what happened. Provide enough information
Controlling Worries and Habits
 THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
Sigmund Freud
 Sigmund Freud Expression of intrapsychic anxiety due to unresolved emotional conflict from childhood Unacceptable desires, strangulated affect after past trauma, displacement, avoidance Psychoneurosis
Sigmund Freud Expression of intrapsychic anxiety due to unresolved emotional conflict from childhood Unacceptable desires, strangulated affect after past trauma, displacement, avoidance Psychoneurosis
Recovering from a difficult birth
 Fife Clinical Psychology Department Recovering from a difficult birth Reviewed: June 2010 1 Recovering from a difficult birth This leaflet aims to give you information about recovering from a difficult
Fife Clinical Psychology Department Recovering from a difficult birth Reviewed: June 2010 1 Recovering from a difficult birth This leaflet aims to give you information about recovering from a difficult
Children and Young People with Anxiety. Young Person s Guide
 Children and Young People with Anxiety Young Person s Guide 1 Contents Introduction 4 What is Anxiety? 4 Types of Anxiety 7 Getting help and support 11 2 3 When anxiety gets really strong, you might experience
Children and Young People with Anxiety Young Person s Guide 1 Contents Introduction 4 What is Anxiety? 4 Types of Anxiety 7 Getting help and support 11 2 3 When anxiety gets really strong, you might experience
Specific Phobias. Symptoms
 ffl Specific Phobias Panic Disorder in Children and Adolescents Panic disorder is a common and treatable disorder. Children and adolescents with panic disorder Specific phobias are an overwhelming and
ffl Specific Phobias Panic Disorder in Children and Adolescents Panic disorder is a common and treatable disorder. Children and adolescents with panic disorder Specific phobias are an overwhelming and
MAXIMIZING PERFORMANCE BY MINIMIZING ANXIETY RICHARD BOGIELSKI
 MAXIMIZING PERFORMANCE BY MINIMIZING ANXIETY RICHARD BOGIELSKI August 7, 2017 Anxiety Anxiety is a normal human experience Anxiety which interferes with functionality is the definition of dysfunction What
MAXIMIZING PERFORMANCE BY MINIMIZING ANXIETY RICHARD BOGIELSKI August 7, 2017 Anxiety Anxiety is a normal human experience Anxiety which interferes with functionality is the definition of dysfunction What
COPYRIGHT NOTICE. Caroline Stewart & Robin Hall Overcome Panic Attacks & Agoraphobia Blank Worksheets ebook
 BLANK WORKSHEETS COPYRIGHT NOTICE Caroline Stewart & Robin Hall Overcome Panic Attacks & Agoraphobia Blank Worksheets ebook 2010 Caroline Stewart & Robin Hall website: www.cognitivetherapyonline.com email:
BLANK WORKSHEETS COPYRIGHT NOTICE Caroline Stewart & Robin Hall Overcome Panic Attacks & Agoraphobia Blank Worksheets ebook 2010 Caroline Stewart & Robin Hall website: www.cognitivetherapyonline.com email:
Panic Stations Module 1
 PANIC PANIC STATIONS STATIONS Panic Stations Module 1 Overview of Panic Introduction 2 Understanding Panic and Fear 2 Panic and Anxiety 3 Anxiety Symptoms Worksheet 7 Module Summary 8 About This Module
PANIC PANIC STATIONS STATIONS Panic Stations Module 1 Overview of Panic Introduction 2 Understanding Panic and Fear 2 Panic and Anxiety 3 Anxiety Symptoms Worksheet 7 Module Summary 8 About This Module
A-Z of Mental Health Problems
 Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Recovering from a difficult birth.
 NHS Fife Department of Psychology Recovering from a difficult birth. Help Yourself @ moodcafe.co.uk Recovering from a difficult birth This leaflet aims to give you information about recovering from a difficult
NHS Fife Department of Psychology Recovering from a difficult birth. Help Yourself @ moodcafe.co.uk Recovering from a difficult birth This leaflet aims to give you information about recovering from a difficult
Understanding Emotional TRIGGER. What are triggers?
 What are triggers? We all have emotional triggers. Perhaps someone makes an off-hand comment about how you look, your new project at work, how you seem a little tired lately, or a comment about someone
What are triggers? We all have emotional triggers. Perhaps someone makes an off-hand comment about how you look, your new project at work, how you seem a little tired lately, or a comment about someone
Lambeth Psychological Therapies
 Complaints procedure: If you are not happy about your experience with our service, you can speak to a member of staff directly; alternatively, you can contact the PALS Office. To make a formal complaint,
Complaints procedure: If you are not happy about your experience with our service, you can speak to a member of staff directly; alternatively, you can contact the PALS Office. To make a formal complaint,
CBT and Anxiety. Marjorie Rabiau, Ph.D. Pearl Lebovitch Clinical Day November 18, 2014
 CBT and Anxiety Marjorie Rabiau, Ph.D. Pearl Lebovitch Clinical Day November 18, 2014 Objectives Discuss effectiveness of CBT to treat anxiety Explain different CBT strategies to treat anxiety How to adapt
CBT and Anxiety Marjorie Rabiau, Ph.D. Pearl Lebovitch Clinical Day November 18, 2014 Objectives Discuss effectiveness of CBT to treat anxiety Explain different CBT strategies to treat anxiety How to adapt
Mr. Stanley Kuna High School
 Mr. Stanley Kuna High School Stress What is Stress? Stress is - The mental, emotional, and physiological response of the body to any situation that is new, threatening, frightening, or exciting. Stress
Mr. Stanley Kuna High School Stress What is Stress? Stress is - The mental, emotional, and physiological response of the body to any situation that is new, threatening, frightening, or exciting. Stress
STRESS MANAGEMENT FOR WOMEN
 STRESS MANAGEMENT FOR WOMEN 800-556-3009 www.careertrack.com DISCLAIMER: The principles and suggestions in this handout and the STRESS MANAGEMENT FOR WOMEN webinar are presented to apply to diverse personal
STRESS MANAGEMENT FOR WOMEN 800-556-3009 www.careertrack.com DISCLAIMER: The principles and suggestions in this handout and the STRESS MANAGEMENT FOR WOMEN webinar are presented to apply to diverse personal
ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE. Date of Birth: Briefly describe the history and development of this issue from onset to present.
 ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Address: Preferred phone number to reach you: Is it okay to leave a message? Yes No (Please check one) Date of Birth: Reason(s) for seeking treatment at this time? Briefly describe
ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Address: Preferred phone number to reach you: Is it okay to leave a message? Yes No (Please check one) Date of Birth: Reason(s) for seeking treatment at this time? Briefly describe
What? Me Worry!?! Module 1 Overview of Generalised Anxiety
 Module 1 Overview of Generalised Anxiety ntroduction 2 Understanding Anxiety 2 Understanding Generalised Anxiety 3 What Causes Generalised Anxiety? 5 Module Summary 6 Page 1 ntroduction What? Me worry?
Module 1 Overview of Generalised Anxiety ntroduction 2 Understanding Anxiety 2 Understanding Generalised Anxiety 3 What Causes Generalised Anxiety? 5 Module Summary 6 Page 1 ntroduction What? Me worry?
Fibromyalgia summary. Patient leaflets from the BMJ Group. What is fibromyalgia? What are the symptoms?
 Patient leaflets from the BMJ Group Fibromyalgia summary We all get aches and pains from time to time. But if you have long-term widespread pain across your whole body, you may have a condition called
Patient leaflets from the BMJ Group Fibromyalgia summary We all get aches and pains from time to time. But if you have long-term widespread pain across your whole body, you may have a condition called
Anxiety and relaxation
 Anxiety and relaxation Anxiety Anxiety can be described as a feeling of worry, nervousness or unease about something with an uncertain outcome. It occurs when someone s reaction to something is out of
Anxiety and relaxation Anxiety Anxiety can be described as a feeling of worry, nervousness or unease about something with an uncertain outcome. It occurs when someone s reaction to something is out of
Coping with Phobias. Dr Brenda Hogan, Clinical Psychologist Dr Charles Young, Counselling Psychologist
 Coping with Phobias Dr Brenda Hogan, Clinical Psychologist Dr Charles Young, Counselling Psychologist 2004 CONTENTS Section 1: Phobias What is a phobia? 3 Where do phobias come from? 4 Symptoms 4 Why won
Coping with Phobias Dr Brenda Hogan, Clinical Psychologist Dr Charles Young, Counselling Psychologist 2004 CONTENTS Section 1: Phobias What is a phobia? 3 Where do phobias come from? 4 Symptoms 4 Why won
Stress Management. Presented by: Jennifer Yuen. Campus Wellness Counselling Services. Strategies and Resources
 Stress Management Strategies and Resources Presented by: Jennifer Yuen Campus Wellness Counselling Services Reflection Take a few moments now to reflect on and write down: 1. Which situations do you find
Stress Management Strategies and Resources Presented by: Jennifer Yuen Campus Wellness Counselling Services Reflection Take a few moments now to reflect on and write down: 1. Which situations do you find
