11/05/1431. Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate
|
|
|
- Natalie Beasley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate Chapter 27 pages
2 OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe: Absorptive Characteristics of different parts of nephrons Transport Mechanisms operating in nephrons Tubular Reabsoprtion and Secretion 2
3 URINE COMPOSITION ph Colour Specific Gravity Volume freshly voided urine is usually acidic (around ph 6), range=4.8 and 7.5 Bright Yellow & transparent to L per day Albumin 20 µg of albumin per minute (30 mg in 24 hours) Glucose None inulin urea gluc Creat Urinary Excretion Rate = Filtration Rate Reabsorption Rate + Secretion Rate 3
4 Glucose Urea Glucose (g/day) Bicarbonate (meq/day) Sodium (meq/day) Chloride (meq/day) Potassium (meq/day) Urea (g/day) Creatinine (g/day) Amount Filtered Amount Reabsorbed Amount Excreted % of Filtered Load Reabsorbed ,320 4,318 2 > ,560 25, ,440 19, Changes in Average Concentration of Different Substances at Different Points in Tubular System Relative to Glomerular Filtrate 4
5 CLASSIFICATION OF TRANSPORT MECHANISMS SIMPE DIFFUSION FACILITATED DIFFUSION PRIMARY ACTIVE TRANSPORT SECONDARY ACTIVE TRANSPORT PINOCYTOSIS BULK FLOW 5
6 PRIMARY ACTIVE TRANSPORTERS Sodium-potassium ATPpase Hydrogen ATPpase Hydrogen-potassium ATPpase Calcium ATPpase. REABSORTION PATHWAYS PARACELLULAR TRANSCELLULAR 6
7 Ultrafiltration PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE many mitochondria brush border multiplies the surface area about 20-fold. tight junctions lateral intercellular spaces. 7
8 PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE PCT SGLT 2 Na G H+ Na AA Na Cl- Iso osmotic 65% Na ATP K Org acids & bases bile salts,oxalate urate Ep,NE drugs toxins PAH 8
9 PCT PARACELLULAR PATHWAY Obligatory 80 % Hormonally Regulated 20 % 9
10 10
11 THIN DESCENDING SEGMENT OF LOOP OF HENLE few mitochondria flattened with few microvilli Solutes H 2 O THICK ASCENDING LOOP OF HANLE AND EARLY DCT Many mitochondria and microvilli, but fewer than in the proximal tubule 11
12 THICK ASCENDING LOOP OF HENLE AND EARLY DCT Many mitochondria and microvilli, but fewer than in the proximal tubule Solutes H 2 O 12
13 EARLY DISTAL TUBULE Mechanism of sodium chloride transport in the early distal tubule 13
14 LATE DCT AND CORTICAL COLLECTING DUCT I Cell P Cell Mitochondria and microvilli decrease Principal Cells (Na Abs and ADH related Water abs) Intercalated Cells (Acid Sec and HCO3 Transport) 14
15 Principal Cell intercalated cell 15
16 MEDULLARY COLLECTING DUCT 16
17 High Osmolality Low ECF Volume Osmoreceptors Pressure R ADH P Cell Aquaporins H2O H2O H2O H2O Neelam Valley 17
18 REABSORPTION OF WATER IN DIFFERENT SEGMENTS OF TUBULES PART OF NEPHRON PERCENTAGE REABSORBED Proximal tubules 65 Loop of Henle 15 Distal tubules 10 Collecting ducts 9.3 Passing into urine 0.7 REABSORPTION OF WATER IN DIFFERENT SEGMENTS OF TUBULES PART OF NEPHRON AMOUNT REABSORBED Glomerular Filtrate 125 Flowing into the loops of Henle 45 Flowing into the distal tubules 25 Flowing into the collecting tubules 12 Flowing into the urine 1 18
19 GLUCOSE REABSORPTION IN NEPHRON Lumen Epithelial Cells Peritubular Capillary Early PCT Na G G ATP Na K G SGLT 2 G GLUT 2 BLOOD Tm for Glucose is 375 mg/min GLUCOSE REABSORPTION IN GIT Lumen Epithelial Cells ECF G G Na G SGLT 1 F GLUT 5 G F Na ATP K GLUT 2 BLOOD 19
20 GLUCOSE REABSORPTION Tmax 375 mg/min FBG= FBG= mg/dl RBG= RBG= mg/dl Filtered Load 125 mg/min (GFRxPlasmaGlu) Renal Threshold 200mg/dl GLUCOSE REABSORPTION 20
21 AMINO ACIDS REABSORPTION IN NEPHRON Lumen Na aa Prot. Sodium Pinocytosis Epithelial Cells Early PCT aa Na ATP Peritubular Capillary K BLOOD Facilitated Diffusion Albumin Excretion in health and disease 21
22 TUBULAR TRANSPORT MAXIMUM The Maximum limit/rate at which a solute can be transported across the tubular cells of kidneys is called TUBULAR TRANSPORT MAXIMUM Tm for Glucose is 375 mg/min TUBULAR TRANSPORT MAXIMUM FOR DIFFERENT SUBSTANCES SUBSTANCE Glucose Phosphate Sulfate Amino Acids Urate Plasma Protein Hemoglobin Lactate Acetoacetate Tm 375 mg/min 0.1 mm/min 0.06 mm/min 1.5 mm/min 15 mg/min 30 mg/min 1 mg/min 75 mg/min variable 22
23 Transport Maximums for Substances That Are Actively Secreted Substance Creatinine Para-aminohippuric acid Transport Maximum 16 mg/min 80 mg/min GRADIENT-TIME TRANSPORT (1) the electrochemical gradient for diffusion of the substance across the membrane (2) the permeability of the membrane for the substance (3) the time that the fluid containing the substance remains within the tubule. 23
24 Sodium Reabsorption from tubular lumen into blood involves 3 steps: 1. Sodium diffuses across the luminal membrane into the cell down an electrochemical gradient established by the sodium-potassium ATPase pump on the basolateral side of the membrane. 2. Sodium is transported across the basolateral membrane against an electrochemical gradient by the sodium-potassium ATPase pump. 3. Sodium, water, and other substances are reabsorbed from the interstitial fluid into the peritubular capillaries by ultrafiltration, a passive process driven by the hydrostatic and colloid osmotic pressure gradients. SODIUM HANDLING Na+ moves by co transport or exchange from the tubular lumen into tubular epithelial cells downhill. From cells into interstitium it moves by primary active transport (Except thin portions of loop of Henle). In DCT and CT it is under hormonal control 24
25 SODIUM HANDLING SITE Proximal Tubule Thick Ascending Limb EarlyDCT Late DCTCollecting Duct APICAL TRANSPORTER Na/Gluc CT Na/Pi CT Na/Amino Acid Na/Lactate Na/H Exchanger Cl/Base Exchanger Na, 2 Cl,, K CT Na/H Exchanger K K Channels NaCl CT Na Channel (ENaC) FUNCTION Na & Gluc Uptake Na & Pi Uptake Na & AA Uptake Na & Lactate Uptake Na Uptake and H Extrusion Cl Uptake Na, 2 Cl,, K Uptake Na Uptake and H Extrusion K K Extrusion Na & Cl Uptake Na Uptake 25
26 Active reabsorption of sodium coupled to the passive reabsorption of chloride Na-H COUNTER TRANSPORT 26
27 HYDROGEN Na-H COUNTER TRANSPORT Luminal Membrane Secreted in Proximal Tubule and Thick ascending LOH by Counter Transport with Na Secreted in DCT by H ATP ase PCT & LOH I Cell intercalated cell 27
28 Effect Of Aldosterone On Cortical Collecting Duct Na Channel (ENaC) UREA Plasma concentration is mmol/l 50 % is reabsorbed in PCT passively with water It is the only waste to be reabsorbed Creatinine and Phenol are not reabsorbed. 28
29 POTASSIUM It is both reabasorbed and secreted 67% of filtered load is reabsorbed by PCT solvent drag secreted by Thick Asc LOH, early distal tubule / collecting duct correlated with dietary intake 80% of filtered load appears in urine if dietary content high 1% if dietary content low CALCIUM Ionized Calcium is freely filtered and reabsorbed in PCT It moves into tubular cells passively (downhill) It moves out of the cell by Ca/Na Counter Transport or Actively by Ca ATP ase Mechanism Its reabsorption is Hormonally controlled 29
30 PHOSPHATE It is reabsorbed by cotransport with Na in PCT in luminal border Its reabsorption is Hormonally controlled It is increased by Vit D and decreased by Parathyroid Hormone SULPHATE Like PHOSPHATE reabsorbed with Na PERITUBULAR CAPILLARY AND RENAL INTERSTITIAL FLUID PHYSICAL FORCES 30
31 31
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Functions of Proximal Convoluted Tubules
 1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
Identify and describe. mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption
 Define tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion, transcellular and paracellular transport. Identify and describe mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption Describe tubular secretion with PAH transport
Define tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion, transcellular and paracellular transport. Identify and describe mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption Describe tubular secretion with PAH transport
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
Renal Physiology II Tubular functions
 Renal Physiology II Tubular functions LO. 42, 43 Dr. Kékesi Gabriella Basic points of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration (GF) a) Ultrafiltration 2. Tubular functions active and passive a) Reabsorption
Renal Physiology II Tubular functions LO. 42, 43 Dr. Kékesi Gabriella Basic points of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration (GF) a) Ultrafiltration 2. Tubular functions active and passive a) Reabsorption
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (2) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 TUBULAR FUNCTIONS (Learning objectives 54-57) 1 Tubular Transport About 99% of filtrated water and more than 90% of the filtrated
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (2) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 TUBULAR FUNCTIONS (Learning objectives 54-57) 1 Tubular Transport About 99% of filtrated water and more than 90% of the filtrated
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology. Urinary System. Summary of Glomerular Filtrate
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System 1 Summary of Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins GFR ~ 125 ml per min If nothing else
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System 1 Summary of Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins GFR ~ 125 ml per min If nothing else
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 18 Urinary System 3 Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Principles of
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 18 Urinary System 3 Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Principles of
Sodium and chlorine transport
 Kidney physiology 2 Sodium and chlorine transport The kidneys help to maintain the body's extracellular fluid (ECF) volume by regulating the amount of Na+ in the urine. Sodium salts (predominantly NaCl)
Kidney physiology 2 Sodium and chlorine transport The kidneys help to maintain the body's extracellular fluid (ECF) volume by regulating the amount of Na+ in the urine. Sodium salts (predominantly NaCl)
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Urinary System. Dr. ZHANG Xiong. Dept. of Physiology. ZJU School of Medicine. QUESTION 6
 Urinary System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine http://10.71.121.158 Copyright@ Xiong Zhang QUESTION 6 How is the filtrate reabsorbed in tubular system? Copyright@ Xiong Zhang
Urinary System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine http://10.71.121.158 Copyright@ Xiong Zhang QUESTION 6 How is the filtrate reabsorbed in tubular system? Copyright@ Xiong Zhang
BLOCK REVIEW Renal Physiology. May 9, 2011 Koeppen & Stanton. EXAM May 12, Tubular Epithelium
 BLOCK REVIEW Renal Physiology Lisa M. HarrisonBernard, Ph.D. May 9, 2011 Koeppen & Stanton EXAM May 12, 2011 Tubular Epithelium Reabsorption Secretion 1 1. 20, 40, 60 rule for body fluid volumes 2. ECF
BLOCK REVIEW Renal Physiology Lisa M. HarrisonBernard, Ph.D. May 9, 2011 Koeppen & Stanton EXAM May 12, 2011 Tubular Epithelium Reabsorption Secretion 1 1. 20, 40, 60 rule for body fluid volumes 2. ECF
Kidney and urine formation
 Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance
 Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important
Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important
Early Filtrate Processing Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Early Filtrate Processing Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Once the filtrate is formed, the early
Early Filtrate Processing Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Once the filtrate is formed, the early
Other Factors Affecting GFR. Chapter 25. After Filtration. Reabsorption and Secretion. 5 Functions of the PCT
 Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Normal Renal Function
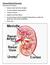 Normal Renal Function Functions of the Kidney: balances solute and water transport excretes metabolic waste products conserves nutrient regulates acid-base balance secretes hormones that help regulate
Normal Renal Function Functions of the Kidney: balances solute and water transport excretes metabolic waste products conserves nutrient regulates acid-base balance secretes hormones that help regulate
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Dept. of Physiology. ZJU School of Medicine.
 Urinary System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine Http://10.10.10.151/Able.Acc2.Web/Template/View.aspx?action =view&coursetype=0&courseid=26519 QUESTION 6 How is the filtrate reabsorbed
Urinary System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine Http://10.10.10.151/Able.Acc2.Web/Template/View.aspx?action =view&coursetype=0&courseid=26519 QUESTION 6 How is the filtrate reabsorbed
Urine Formation. Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages Urine Formation. Glomerular Filtration 4/24/2016
 Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE
 NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Renal Reabsorption & Secretion
 Renal Reabsorption & Secretion Topics for today: Nephron processing of filtrate Control of glomerular filtration Reabsorption and secretion Examples of solute clearance rates Hormones affecting kidney
Renal Reabsorption & Secretion Topics for today: Nephron processing of filtrate Control of glomerular filtration Reabsorption and secretion Examples of solute clearance rates Hormones affecting kidney
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED. Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics
 Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Hill et al. 2004, Fig. 27.6
 Lecture 25, 15 November 2005 Osmoregulation (Chapters 25-28) Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 1. Osmoregulation 2. Kidney Function Text: Chapters
Lecture 25, 15 November 2005 Osmoregulation (Chapters 25-28) Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 1. Osmoregulation 2. Kidney Function Text: Chapters
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
Homeostatic Regulation
 Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Renal physiology II. Basic renal processes. Dr Alida Koorts BMS
 Renal physiology II Basic renal processes Dr Alida Koorts BMS 7-12 012 319 2921 akoorts@medic.up.ac.za Basic renal processes 1. filtration 2. reabsorption 3. secretion Glomerular filtration The filtration
Renal physiology II Basic renal processes Dr Alida Koorts BMS 7-12 012 319 2921 akoorts@medic.up.ac.za Basic renal processes 1. filtration 2. reabsorption 3. secretion Glomerular filtration The filtration
Osmoregulation and the Excretory System
 Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
After studying this lecture, you should be able to...
 Reabsorption of Salt and Water After studying this lecture, you should be able to... 1. Define the obligatory water loss. 2. Describe the mechanism of Na ++ reabsorption in the distal tubule and explain
Reabsorption of Salt and Water After studying this lecture, you should be able to... 1. Define the obligatory water loss. 2. Describe the mechanism of Na ++ reabsorption in the distal tubule and explain
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Diagram of the inner portions of the kidney
 Excretory and Endocrine functions of the kidney The kidneys are the main excretory organs which eliminate in the urine, most metabolites primarily those containing nitrogen such as ammonia, urea and creatinine.
Excretory and Endocrine functions of the kidney The kidneys are the main excretory organs which eliminate in the urine, most metabolites primarily those containing nitrogen such as ammonia, urea and creatinine.
1. remove: waste products: urea, creatinine, and uric acid foreign chemicals: drugs, water soluble vitamins, and food additives, etc.
 Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
Tubular Reabsorption & Secretion Lecture 5, 6. Objectives: Editing file. by the end of this lecture you will be able to:
 Index: Important Extra information Doctor s notes Only in female slides Only in male slides Tubular Reabsorption & Secretion Lecture 5, 6 Editing file Objectives: by the end of this lecture you will be
Index: Important Extra information Doctor s notes Only in female slides Only in male slides Tubular Reabsorption & Secretion Lecture 5, 6 Editing file Objectives: by the end of this lecture you will be
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1)
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional roles of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional roles of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018. Rahmeh Alsukkar
 Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Physiology Lecture 2. What controls GFR?
 Physiology Lecture 2 Too much blood is received by the glomerular capillaries, this blood contains plasma, once this plasma enters the glomerular capillaries it will be filtered to bowman s space. The
Physiology Lecture 2 Too much blood is received by the glomerular capillaries, this blood contains plasma, once this plasma enters the glomerular capillaries it will be filtered to bowman s space. The
mid ihsan (Physiology ) GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B **
 (Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
(Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
DIURETICS-2. Dr. Shariq Syed. Shariq AIKC/TYB/2014
 DIURETICS-2 Dr. Syed Structure of Kidney Blood filtered by functional unit: Nephron Except for cells, proteins, other large molecules, rest gets filtered Structure of Kidney 3 major regions of nephron
DIURETICS-2 Dr. Syed Structure of Kidney Blood filtered by functional unit: Nephron Except for cells, proteins, other large molecules, rest gets filtered Structure of Kidney 3 major regions of nephron
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/80/80449526.jpg) 1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys
 Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Moayyad Al-Shafei. - Saad Hayek. - Yanal Shafaqoj. 1 P a g e
 - 5 - Moayyad Al-Shafei - Saad Hayek - Yanal Shafaqoj 1 P a g e In this lecture we are going to study the tubular reabsorption of Na+. We know that the body must maintain its homeostasis by keeping its
- 5 - Moayyad Al-Shafei - Saad Hayek - Yanal Shafaqoj 1 P a g e In this lecture we are going to study the tubular reabsorption of Na+. We know that the body must maintain its homeostasis by keeping its
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
MS1 Physiology Review of Na+, K+, H + /HCO 3. /Acid-base, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology
 MS1 Physiology Review of,, / /Acidbase, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology University of Florida College of Medicine Basic principles Proximal tubule Majority
MS1 Physiology Review of,, / /Acidbase, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology University of Florida College of Medicine Basic principles Proximal tubule Majority
Physiology (4) 2/4/2018. Wael abu-anzeh
 Physiology (4) 2/4/2018 Wael abu-anzeh In the previous lectures we have discussed the filtration and the reabsorption processes but in this lecture we will talk about the factor that will regulate or control
Physiology (4) 2/4/2018 Wael abu-anzeh In the previous lectures we have discussed the filtration and the reabsorption processes but in this lecture we will talk about the factor that will regulate or control
The kidneys are excretory and regulatory organs. By
 exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
RENAL. 6. Renal acid secretion is affected by all of the following except a. pco 2 b. K c. Carbonic anhydrase d. Aldosterone e. Ca
 RENAL 1. The reabsorption of Na in the proximal tubules a. Reabsorbs 80% of the filtered sodium load b. Causes increased hypertonicity c. Is powered by N/H ATPase d. Shares a common carrier with glucose
RENAL 1. The reabsorption of Na in the proximal tubules a. Reabsorbs 80% of the filtered sodium load b. Causes increased hypertonicity c. Is powered by N/H ATPase d. Shares a common carrier with glucose
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Chapter 26 The Urinary System. Overview of Kidney Functions. External Anatomy of Kidney. External Anatomy of Kidney
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
1.&Glomerular/Pressure&Filtration&
 Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Done By: Lulu Al-Obaid - Abdulrahman Al-Rashed Reviewed By: Mohammed Jameel Khulood Al-Raddadi
 Done By: Lulu Al-Obaid - Abdulrahman Al-Rashed Reviewed By: Mohammed Jameel Khulood Al-Raddadi At the end of this lecture student should be able to describe: The loop of Henle is referred to as countercurrent
Done By: Lulu Al-Obaid - Abdulrahman Al-Rashed Reviewed By: Mohammed Jameel Khulood Al-Raddadi At the end of this lecture student should be able to describe: The loop of Henle is referred to as countercurrent
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
RENAL FUNCTION An Overview
 RENAL FUNCTION An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ. Temple 1 Kidneys
RENAL FUNCTION An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ. Temple 1 Kidneys
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis.
 Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Faculty version with model answers
 Faculty version with model answers Urinary Dilution & Concentration Bruce M. Koeppen, M.D., Ph.D. University of Connecticut Health Center 1. Increased urine output (polyuria) can result in a number of
Faculty version with model answers Urinary Dilution & Concentration Bruce M. Koeppen, M.D., Ph.D. University of Connecticut Health Center 1. Increased urine output (polyuria) can result in a number of
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
Renal Clearance. Dr. Eman El Eter
 Renal Clearance Dr. Eman El Eter Concept of clearance Clearance is the volume of plasma that is completely cleared of a substance each minute. Example: Renal clearance of Substance X is defined as the
Renal Clearance Dr. Eman El Eter Concept of clearance Clearance is the volume of plasma that is completely cleared of a substance each minute. Example: Renal clearance of Substance X is defined as the
Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance
 Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance Body fluid The fluids are distributed throughout the body in various compartments. Body fluid is composed primarily of water Water is the solvent in which all solutes
Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance Body fluid The fluids are distributed throughout the body in various compartments. Body fluid is composed primarily of water Water is the solvent in which all solutes
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Overview of Kidney Function
 The Kidney Overview of Kidney Function osmolarity of the body fluids volume of ECF plasma ph waste products (urea, uric acid, creatinine, foreign compounds) synthesis of: - EPO, renin, kallikrein, prostaglandins,
The Kidney Overview of Kidney Function osmolarity of the body fluids volume of ECF plasma ph waste products (urea, uric acid, creatinine, foreign compounds) synthesis of: - EPO, renin, kallikrein, prostaglandins,
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
URINARY SYSTEM. Primary functions. Major organs & structures
 URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
