PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation **
|
|
|
- Edith Scott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3 PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation ** I. RECOGNITION A. History 1. Unexplained or un-witnessed injury 2. Conflicting, inconsistent or developmentally inappropriate 3. Delay in seeking care B. Physical 1. Altered mental status 2. Closed head injury 3. Fractures: skull, rib, long bone, multiple fractures, differing ages 4. Oral injuries 5. Bruising in a non-mobile infant, regardless of location 6. Burns: circumferential, scalds, patterns, or diaper area 7. Subdural hematomas 8. Abdominal injury: liver lacerations, ruptured viscus II. II.A.1.References 9,11,16,19,20,27 II.A.2.References: 1,3,19,20,25, 29,32 II.A.3.References: 20,25,31 II.A.4.References: 19,23 II.A.5.References: 2,8,9,18,25, 26, 27,30 II.B.1.References: 7,10,14,16,24,28 II.B.2.References: 9,11,16,19,20,27 EVALUATION A. Children 0-12 months old [see Appendix 1] 1. Skeletal survey (2 cranial views, AP and lateral CXR, oblique views of the ribs, KUB, AP Pelvis, all long bones, hands and feet) 2. Head CT (non-contrast) a) If abnormal, ophthalmology consult for dilated funduscopic exam. b)if abnormal, consider neurosurgical consult 3. General Pediatric Surgery Consult in any case with exam or lab findings concerning for abdominal trauma[see Appendix 3] 4. Laboratory Collection a) Chem-10 b)non-accidental Trauma panel (CBC, PT, PTT, AST, ALT, ferritin) c) Amylase & lipase d)urinalysis e) If altered or seizing, order urine tox screen B. Children months old [see Appendix 2] 1. Occult abdominal injury screening (AST/ALT) [see Appendix 3] 2. Skeletal survey based on chief complaint III. IV. 3. If there is a concern for inflicted neurotrauma based on H&P, proceed as above in #2-5 C. Children > 24 months old 1. Occult abdominal injury screening (AST/ALT) [see Appendix 3] 2. X-ray as indicated 3. Complete skeletal survey is recommended for specific patients: a) Burn victims or disabled children who are non-mobile b)multiple fractures suspected REPORTING A. Notify attending physician on duty of concern for inflicted injury B. Social worker on call is to be notified of any and all cases of suspected inflicted injury C. Ensure Child Protective Services is notified DOCUMENTATION A. HPI: Timing and mechanism of injury. Source of history; if differing information, delineate different authors B. PMH: Screen for alternate medical explanations for injury C. PE: specifically describe appearance, location, and size of injury D. Reporting: Document agencies notified, note case numbers 1. Complete Physician s Report of Injury to a Child 2. Photodocumentation as needed V. DISPOSITION AND FOLLOW-UP A. Social work and CPS, once notified, will assist in disposition B. If fracture present on skeletal survey, or if patient age < 12 months, repeat skeletal survey in 2 weeks 1. Follow-up films will NOT include skull views 2. Indicate that follow-up film results should be reported to Child Protection MDs (Dr. Isaac or Dr. Donaruma) if the patient s PMD is not involved with case C. Sibling/cohort evaluation of all other children who share environment of the injured child is needed D. Follow-up appointment at Children s Protective Health Clinic if repeat assessment needed II.C.1. References: 7,10,14,16,24,28 V.B. References: 5,17,19 Created by: Marcella Donaruma, M.D
4 Laboratory Evaluation Child 0-12 months Concern for inflicted injury Skeletal survey Appendix 1 Child Protection Physician consult available by pager! 9,11,16,19, 20, 27, 32 Chem-10, NAT Panel (Includes: CBC, PT, PTT, AST, ALT, Ferritin), Amylase, Lipase, Urinalysis Bicarbonate < 15 mmol/l 2,25,26,30 Age<12 months with: Developmental delay, Abnormal OFC Abnormal findings including: signs of abdominal injury on physical exam or laboratory evaluation +Head or facial trauma Head CT + Abnormal findings including: acute/chronic bleed, cerebral edema, cortical contusion, infarct 1,3,19,20,25, 29,32 + Abnormal findings including: acute fractures, callous formation, periosteal reaction Multiple fractures of long bones Follow-Up Will require follow-up study in 2 weeks. Indicate to send results to Dr. Isaac or Dr. Donaruma on order request Blood gas Surgical Consult Laboratory evaluation 5,17,19 Altered mental status or seizures Toxicology Screen 8,9,18,26 Ammonia, urine amino acids, urine organic acids serum amino acids 27 Ophthalmologic exam 20,25,31 Consider Neurosurgical consult Ca, Phos, Alk Phos, PTH, 1, 25-OH Vit D, 25 OH-Vit D 13,32 If needed, may schedule f/u appointment at Children s Protective Health Clinic Created by: Marcella Donaruma, MD
5 AST/ALT Screen for occult abdominal injury. [See Appendix 3 ] Child months Concern for inflicted injury If clinically indicated: Patient is not yet ambulatory, visible swelling/deformity, refusal to move limb, refusal to bear weight Appendix 2 If physical exam abnormalities present (i.e., altered mental status, bruising) Abnormal findings including: signs of abdominal injury on physical exam or laboratory evaluation If clinically indicated: Altered mental status, seizures, abnormal neurological exam, developmental delay Skeletal survey 9,11,16,19, 20, 27, 32 Laboratory evaluation 2,25,26,30 Chem-10, Non-Accidental Trauma Panel (Includes: CBC, PT, PTT, AST, ALT, Ferritin), Amylase, Lipase, Urinalysis Altered mental status or seizures noted Toxicology Screen 8,9,18,26 Surgical Consult 19,23 Child Protection Physician consult available by pager! + Head or facial trauma Ophthalmology consult 20,25,31 Head CT + Abnormal findings including: acute/ chronic bleed, cerebral edema, cortical contusion, infarct 1,3,19,20,25,29,32 Consider Neurosurgical consult + Skull fracture or C-spine injury Will require follow-up study in 2 weeks. Indicate to send results to Dr. Isaac or Dr. Donaruma on order request 5,17,19 Created by: Marcella Donaruma, MD Abnormal findings including: acute fractures, callous formation, periosteal reaction Follow-Up If needed, may schedule f/u appointment at Children s Protective Health Clinic
6 Guidelines for the Use of Elevated Liver Transaminases in Detecting Occult Liver Injury in Child Abuse Age 0-60 months with concerns for acute inflicted injury Findings may include but are not limited to unexplained bruising, burns, bleeding, fractures Appendix 3 7,10,14,16,24,28 Hemodynamically stable and GCS > 13 Hemodynamically stable and GCS > 13 Hemodynamically unstable or GCS < 13 Proceed with trauma protocol Measure AST and ALT (fingerstick) Unreliable/ changing abdominal exam Axial bruising AST < 200 and ALT < 100 AST > 200 and/or ALT >100 Thoracic injury of any type No further intervention recommended CT scan Abdomen with contrast Created by: Marcella Donaruma, MD Consult pediatric surgery
7 References for Appendix 1, Appendix 2, and Appendix 3 (PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT) 1. Child abuse and the eye. The Ophthalmology Child Abuse Working Party. Eye, ( Pt 1): p Diagnostic imaging of child abuse. Pediatrics, (6): p Agran, P.F., et al., Rates of pediatric injuries by 3-month intervals for children 0 to 3 years of age. Pediatrics, (6 Pt 1): p. e Bays, J., Feldman, Kenneth W., ed. Child Abuse by Posioning. Child Abuse: Medical Diagnosis and Treatment, ed. R. Block, Ludwig, Stephen. 2001, Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia. 5. Belfer, R.A., B.L. Klein, and L. Orr, Use of the skeletal survey in the evaluation of child maltreatment. Am J Emerg Med, (2): p Case, M.E., et al., Position paper on fatal abusive head injuries in infants and young children. Am J Forensic Med Pathol, (2): p Coant, P.N., et al., Markers for occult liver injury in cases of physical abuse in children. Pediatrics, (2): p Dias, M.S., et al., Serial radiography in the infant shaken impact syndrome. Pediatr Neurosurg, (2): p Duhaime, A.C. and M.D. Partington, Overview and clinical presentation of inflicted head injury in infants. Neurosurg Clin N Am, (2): p , v. 10. Gross, M., et al., Management of pediatric liver injuries: a 13-year experience at a pediatric trauma center. J Pediatr Surg, (5): p ; discussion Helfer, R.E., T.L. Slovis, and M. Black, Injuries resulting when small children fall out of bed. Pediatrics, (4): p Hennes, H.M., et al., Elevated liver transaminase levels in children with blunt abdominal trauma: a predictor of liver injury. Pediatrics, (1): p Hoffman, R.J. and L. Nelson, Rational use of toxicology testing in children. Curr Opin Pediatr, (2): p Holmes, J.F., et al., Identification of children with intra-abdominal injuries after blunt trauma. Ann Emerg Med, (5): p Hymel, K.P., et al., Comparison of intracranial computed tomographic (CT) findings in pediatric abusive and accidental head trauma. Pediatr Radiol, (9): p Jenny, C., Evaluating infants and young children with multiple fractures. Pediatrics, (3): p Kemp, A.M., et al., Which radiological investigations should be performed to identify fractures in suspected child abuse? Clin Radiol, (9): p Kempe, C.H., et al., The battered-child syndrome. Jama, : p
8 19. Kleinman, P.K., Diagnostic Imaging of Child Abuse. 2nd ed. 1998, Saint Louis: Mosby, Inc. 20. Liesner, R., I. Hann, and K. Khair, Non-accidental injury and the haematologist: the causes and investigation of easy bruising. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis, Suppl 1: p. S Maguire, S., Mann, M.K., Sibert, J., Kemp, A., Are there patterns of bruising in childhood which are diagnostic or suggestive of abuse? A systematic review. Arch Dis Child, (2): p Minns, R.A., Brown, J. Keith, ed. Shaking & Other Non-accidental Head Injuries in Children. 2005, MacKeith Press: London. 23. Murphy, J., et al., Accidental poisoning preceding nonaccidental injury. Arch Dis Child, (1): p Oldham, K.T., et al., Blunt hepatic injury and elevated hepatic enzymes: a clinical correlation in children. J Pediatr Surg, (4): p O'Neill, J.A., Jr., et al., Patterns of injury in the battered child syndrome. J Trauma, (4): p Paschall, R., ed. The Chemically Abused Child. Child Maltreatment, ed. A.P. Giardino. Vol , GW Medical Publishing. 27. Reece, R., Nicholson, Carol E., ed. Inflicted Childhood Neurotrauma. 2003, American Academy of Pediatrics: Bethesda. 28. Roaten, J.B., et al., Visceral injuries in nonaccidental trauma: spectrum of injury and outcomes. Am J Surg, (6): p Sugar, N.F., J.A. Taylor, and K.W. Feldman, Bruises in infants and toddlers: those who don't cruise rarely bruise. Puget Sound Pediatric Research Network. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, (4): p Thomas, A.E., The bleeding child; is it NAI? Arch Dis Child, (12): p Woodcock, R.J., P.C. Davis, and K.L. Hopkins, Imaging of head trauma in infancy and childhood. Semin Ultrasound CT MR, (2): p Zimmerman, S., et al., Utility of follow-up skeletal surveys in suspected child physical abuse evaluations. Child Abuse Negl, (10): p
Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline
 Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline WHEN TO CONSIDER ABUSE Consider abuse on the differential Injuries to multiple organ systems Injuries in different stages of healing Patterned injuries
Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline WHEN TO CONSIDER ABUSE Consider abuse on the differential Injuries to multiple organ systems Injuries in different stages of healing Patterned injuries
CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May Leslie M. Quinn M.D.
 CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May 2012 - Leslie M. Quinn M.D. PHYSICAL ABUSE: For any child presenting with signs and or symptoms of an injury consider
CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May 2012 - Leslie M. Quinn M.D. PHYSICAL ABUSE: For any child presenting with signs and or symptoms of an injury consider
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines
 Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) PEDIATRIC Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma Center Medical Director/ Trauma
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) PEDIATRIC Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma Center Medical Director/ Trauma
Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient
 September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
Radiological investigations
 Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Disclosure. Physical Abuse. Objectives. What is the Mechanism of the Injury?
 Disclosure Abuse or Not Abuse: What is the Answer? Natalie Kissoon, MD Assistant Professor Division of Child Abuse Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science Natalie Kissoon, MD has no relationships
Disclosure Abuse or Not Abuse: What is the Answer? Natalie Kissoon, MD Assistant Professor Division of Child Abuse Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science Natalie Kissoon, MD has no relationships
Bilateral rib fractures 2 on right and 1 on left In different stages of healing, with left fracture older than right fractures
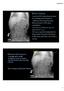 More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
Pediatric head trauma: the evidence regarding indications for emergent neuroimaging
 DOI 10.1007/s00247-008-0996-5 ALARA: BUILDING BRIDGES BETWEEN RADIOLOGY AND EMERGENCY MEDICINE Pediatric head trauma: the evidence regarding indications for emergent neuroimaging Nathan Kuppermann Received:
DOI 10.1007/s00247-008-0996-5 ALARA: BUILDING BRIDGES BETWEEN RADIOLOGY AND EMERGENCY MEDICINE Pediatric head trauma: the evidence regarding indications for emergent neuroimaging Nathan Kuppermann Received:
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know. 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012
 Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
2/13/13. Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University
 Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University 3 month old, previously healthy infant, brought to the primary care physician due to a fall He was being carried by the father, who tripped over the family
Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University 3 month old, previously healthy infant, brought to the primary care physician due to a fall He was being carried by the father, who tripped over the family
OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE
 2011 MFMER slide-1 OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Mark S. Mannenbach, MD Mayo Medical Center Rochester, MN 2011 MFMER slide-2 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, the participant will be able
2011 MFMER slide-1 OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Mark S. Mannenbach, MD Mayo Medical Center Rochester, MN 2011 MFMER slide-2 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, the participant will be able
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type.
 Neurosurg Clin N Am 13 (2002) 259 264 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Abdominal injuries, in child abuse, 150, 159 Abrasions, in child abuse, 157 Abuse, child. See Child
Neurosurg Clin N Am 13 (2002) 259 264 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Abdominal injuries, in child abuse, 150, 159 Abrasions, in child abuse, 157 Abuse, child. See Child
Child Protection Guidelines in Suspected Non-Accidental Head Injury (NAHI) in Children Under 2 years of age. DRAFT REVIEW May 2008
 Child Protection Guidelines in Suspected Non-Accidental Head Injury (NAHI) in Children Under 2 years of age DRAFT REVIEW May 2008 Responsibility for monitoring Review and update CPU Dr. Jean Herbison Current
Child Protection Guidelines in Suspected Non-Accidental Head Injury (NAHI) in Children Under 2 years of age DRAFT REVIEW May 2008 Responsibility for monitoring Review and update CPU Dr. Jean Herbison Current
Analysis of pediatric head injury from falls
 Neurosurg Focus 8 (1):Article 3, 2000 Analysis of pediatric head injury from falls K. ANTHONY KIM, MICHAEL Y. WANG, M.D., PAMELA M. GRIFFITH, R.N.C., SUSAN SUMMERS, R.N., AND MICHAEL L. LEVY, M.D. Division
Neurosurg Focus 8 (1):Article 3, 2000 Analysis of pediatric head injury from falls K. ANTHONY KIM, MICHAEL Y. WANG, M.D., PAMELA M. GRIFFITH, R.N.C., SUSAN SUMMERS, R.N., AND MICHAEL L. LEVY, M.D. Division
Evaluation of Children with Blunt Abdominal Trauma. James F. Holmes, MD, MPH UC Davis School of Medicine
 Evaluation of Children with Blunt Abdominal Trauma James F. Holmes, MD, MPH UC Davis School of Medicine Objectives Epidemiology of intra-abdominal injury (IAI) Physical examination findings with IAI Laboratory
Evaluation of Children with Blunt Abdominal Trauma James F. Holmes, MD, MPH UC Davis School of Medicine Objectives Epidemiology of intra-abdominal injury (IAI) Physical examination findings with IAI Laboratory
10/8/17. I have no disclosures. What are they? Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma
 I have no disclosures Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma What are they? Fractures of the radius, ulna and/or humerus Who gets them? Active children usually after
I have no disclosures Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma What are they? Fractures of the radius, ulna and/or humerus Who gets them? Active children usually after
of Trauma Assembly 27 th Page 1
 Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 27 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 08 To Scan or Not To Scan Thatt is the Question January 16, 2014 Waldorf Astoria Naples Naples, Floridaa Page
Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 27 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 08 To Scan or Not To Scan Thatt is the Question January 16, 2014 Waldorf Astoria Naples Naples, Floridaa Page
Imaging in the Trauma Patient
 Imaging in the Trauma Patient David A. Spain, MD Department of Surgery Stanford University Pan Scan Instead of Clinical Exam? 1 Granted, some patients don t need CT scan Platinum Package Stanford Special
Imaging in the Trauma Patient David A. Spain, MD Department of Surgery Stanford University Pan Scan Instead of Clinical Exam? 1 Granted, some patients don t need CT scan Platinum Package Stanford Special
Annotation. Outcomes of infants and children with inflicted traumatic brain injury
 Outcomes of infants and children with inflicted traumatic brain injury Kathi L Makaroff* MD, Research Instructor of Pediatrics; Frank W Putnam MD, Director, Mayerson Center for Safe and Healthy Children,
Outcomes of infants and children with inflicted traumatic brain injury Kathi L Makaroff* MD, Research Instructor of Pediatrics; Frank W Putnam MD, Director, Mayerson Center for Safe and Healthy Children,
5 B s of Child Physical Abuse: Bruises, Burns, Bones, Bellies, and Brains
 5 B s of Child Physical Abuse: Bruises, Burns, Bones, Bellies, and Brains Kristen Reeder, MD Child Abuse Pediatrician, REACH Program Children s Health SM Children s Medical Center Dallas Assistant Professor
5 B s of Child Physical Abuse: Bruises, Burns, Bones, Bellies, and Brains Kristen Reeder, MD Child Abuse Pediatrician, REACH Program Children s Health SM Children s Medical Center Dallas Assistant Professor
CLINICAL PRACTICE RESOURCE FOR HOSPITALS AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS: Evaluation and Management of Suspected Child Abuse or Neglect
 CLINICAL PRACTICE RESOURCE FOR HOSPITALS AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS: Evaluation and Management of Suspected Child Abuse or Neglect I. IDENTIFY THE CHILD WHO MAY BE A VICTIM OF ABUSE OR NEGLECT. A. Injuries
CLINICAL PRACTICE RESOURCE FOR HOSPITALS AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS: Evaluation and Management of Suspected Child Abuse or Neglect I. IDENTIFY THE CHILD WHO MAY BE A VICTIM OF ABUSE OR NEGLECT. A. Injuries
Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures
 July 2006 Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures Denise De Las Nueces, Harvard Medical School Year IV General Overview Introduction
July 2006 Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures Denise De Las Nueces, Harvard Medical School Year IV General Overview Introduction
ARTICLE. Intracranial Hemorrhage in Children Younger Than 3 Years
 Intracranial Hemorrhage in Children Younger Than 3 Years Prediction of Intent ARTICLE Robert G. Wells, MD; Christine Vetter, MD; Prakash Laud, PhD Objective: To determine whether certain computed tomographic
Intracranial Hemorrhage in Children Younger Than 3 Years Prediction of Intent ARTICLE Robert G. Wells, MD; Christine Vetter, MD; Prakash Laud, PhD Objective: To determine whether certain computed tomographic
Pan Scan Instead of Clinical Exam? David A. Spain, MD
 Pan Scan Instead of Clinical Exam? David A. Spain, MD Granted, some patients don t t need CT scan Platinum Package Stanford Special CT Scan Head Neck Chest Abdomen Pelvis Takes about 20 minutes to do
Pan Scan Instead of Clinical Exam? David A. Spain, MD Granted, some patients don t t need CT scan Platinum Package Stanford Special CT Scan Head Neck Chest Abdomen Pelvis Takes about 20 minutes to do
Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries
 Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries Paul Kleinman, M.D. Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, Ma. Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Kemp AM et. Al.
Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries Paul Kleinman, M.D. Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, Ma. Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Kemp AM et. Al.
Sasha Dubrovsky, MSc MD FRCPC Pediatric Emergency Medicine Montreal Children s Hospital - MUHC October 2010
 Sasha Dubrovsky, MSc MD FRCPC Pediatric Emergency Medicine Montreal Children s Hospital - MUHC October 2010 Learning objectives 1. Discuss diagnostic goals in pediatric trauma Diagnose All vs. Severe Injuries
Sasha Dubrovsky, MSc MD FRCPC Pediatric Emergency Medicine Montreal Children s Hospital - MUHC October 2010 Learning objectives 1. Discuss diagnostic goals in pediatric trauma Diagnose All vs. Severe Injuries
Injuries in Non Mobile Infants Protocol
 Injuries in Non Mobile Infants Protocol Contents 1. Introduction 2. Definition 3. Recommended Action 4. Specific considerations for disabled children 5. Accidental / non-accidental / inconclusive categories
Injuries in Non Mobile Infants Protocol Contents 1. Introduction 2. Definition 3. Recommended Action 4. Specific considerations for disabled children 5. Accidental / non-accidental / inconclusive categories
Pattern of Fractures in Non-Accidental Injuries in the Pediatric Population in Singapore
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:432-438 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.432 Pattern of Fractures in Non-Accidental Injuries in the Pediatric Population in Singapore Sumanth
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:432-438 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.432 Pattern of Fractures in Non-Accidental Injuries in the Pediatric Population in Singapore Sumanth
Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma
 Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma Rebecca Girardet Associate Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Child Protection Pediatrics McGovern Medical School at The University of Texas Health Science Center
Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma Rebecca Girardet Associate Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Child Protection Pediatrics McGovern Medical School at The University of Texas Health Science Center
Guide to the Medical Evaluation in Suspected Physical Abuse
 Guide to the Medical Evaluation in Suspected Physical Abuse Introduction Every year more than 3 million referrals are made to child protective services for concerns of child abuse and neglect with almost
Guide to the Medical Evaluation in Suspected Physical Abuse Introduction Every year more than 3 million referrals are made to child protective services for concerns of child abuse and neglect with almost
Pediatric Abdomen Trauma
 Pediatric Abdomen Trauma Susan D. John, MD, FACR Pediatric Trauma Trauma is leading cause of death and disability in children and adolescents Causes and effects vary between age groups Blunt trauma predominates
Pediatric Abdomen Trauma Susan D. John, MD, FACR Pediatric Trauma Trauma is leading cause of death and disability in children and adolescents Causes and effects vary between age groups Blunt trauma predominates
Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C)
 Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C) Cutaneous Injuries Bruise : injury to soft tissues in which skin is not broken, characterized
Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C) Cutaneous Injuries Bruise : injury to soft tissues in which skin is not broken, characterized
Brain and Cervico-Medullary Injury : Patterns and Mechanisms
 Brain and Cervico-Medullary Injury : Patterns and Mechanisms P. Ellen Grant MD Associate Professor of Radiology, HMS Director, Center for Fetal-Neonatal Neuroimaging & Developmental Science Children s
Brain and Cervico-Medullary Injury : Patterns and Mechanisms P. Ellen Grant MD Associate Professor of Radiology, HMS Director, Center for Fetal-Neonatal Neuroimaging & Developmental Science Children s
The Evaluation of Suspected Child Physical Abuse
 CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care The Evaluation of Suspected Child Physical Abuse Cindy W. Christian, MD, FAAP, COMMITTEE ON CHILD ABUSE AND NEGLECT Child physical
CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care The Evaluation of Suspected Child Physical Abuse Cindy W. Christian, MD, FAAP, COMMITTEE ON CHILD ABUSE AND NEGLECT Child physical
17. Imaging and interventional radiology
 17. Imaging and interventional radiology These guidelines have been adapted from the Leeds Major Trauma Centre Imaging in Paediatric Major Trauma guidelines Written by Dr Annmarie Jeanes (Consultant Paediatric
17. Imaging and interventional radiology These guidelines have been adapted from the Leeds Major Trauma Centre Imaging in Paediatric Major Trauma guidelines Written by Dr Annmarie Jeanes (Consultant Paediatric
Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures
 Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures SPR Sunrise Session May 17, 2018 Megan B. Marine, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology, Pediatric Division Co-Director, Pediatric Radiology Fellowship
Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures SPR Sunrise Session May 17, 2018 Megan B. Marine, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology, Pediatric Division Co-Director, Pediatric Radiology Fellowship
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS. December 19, 2012
 PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS Niel F. Miele,, M.D. December 19, 2012 EPIDEMIOLOGY Major Trauma responsible for
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS Niel F. Miele,, M.D. December 19, 2012 EPIDEMIOLOGY Major Trauma responsible for
CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE
 CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Kansas Association of Osteopathic Medicine April 13 th, 2018 Jami Jackson DO, FAAP, MPH Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor
CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Kansas Association of Osteopathic Medicine April 13 th, 2018 Jami Jackson DO, FAAP, MPH Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor
Recognizing and Responding to Child Abuse & Neglect
 Recognizing and Responding to Child Abuse & Neglect Maria D. McColgan, MD Associate Professor Drexel University College of Medicine Director, Child Protection Program St. Christopher s Hospital for Children
Recognizing and Responding to Child Abuse & Neglect Maria D. McColgan, MD Associate Professor Drexel University College of Medicine Director, Child Protection Program St. Christopher s Hospital for Children
CEDR 2018 QCDR Measures for CMS 2018 MIPS Performance Year Reporting
 ACEP19 Emergency Department Utilization of CT for Minor Blunt Head Trauma for Aged 18 Years and Older Percentage of visits for aged 18 years and older who presented with a minor blunt head trauma who had
ACEP19 Emergency Department Utilization of CT for Minor Blunt Head Trauma for Aged 18 Years and Older Percentage of visits for aged 18 years and older who presented with a minor blunt head trauma who had
O ne million patients are treated annually in United
 859 ORIGIAL ARTICLE Can we abolish skull x rays for head injury? M J Reed, J G Browning, A G Wilkinson, T Beattie... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Matthew J Reed, Accident
859 ORIGIAL ARTICLE Can we abolish skull x rays for head injury? M J Reed, J G Browning, A G Wilkinson, T Beattie... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Matthew J Reed, Accident
The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast
 The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast September 27, 2018 Introduction: Hello everyone, my name is Dominique Piché
The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast September 27, 2018 Introduction: Hello everyone, my name is Dominique Piché
Non-accidental Trauma: An unresponsive infant with bilateral retinal hemorrhages.
 Non-accidental Trauma: An unresponsive infant with bilateral retinal hemorrhages. Lucas J. A. Wendel, MD, Susannah Q. Longmuir, MD, and Nasreen A. Syed, MD February 12, 2009 Chief Complaint: 7 month old
Non-accidental Trauma: An unresponsive infant with bilateral retinal hemorrhages. Lucas J. A. Wendel, MD, Susannah Q. Longmuir, MD, and Nasreen A. Syed, MD February 12, 2009 Chief Complaint: 7 month old
Can we abolish skull x-rays for head injury?
 ADC Online First, published on April 25, 2005 as 10.1136/adc.2004.053603 Can we abolish skull x-rays for head injury? Matthew J Reed, Jen G Browning, A. Graham Wilkinson & Tom Beattie Corresponding author:
ADC Online First, published on April 25, 2005 as 10.1136/adc.2004.053603 Can we abolish skull x-rays for head injury? Matthew J Reed, Jen G Browning, A. Graham Wilkinson & Tom Beattie Corresponding author:
Abuse Or Not? Interactive Visual Clues in Child Abuse
 Abuse Or Not? Interactive Visual Clues in Child Abuse Amy Baxter MD FAAP FACEP Associate Clinical Professor Medical College of Georgia 4 month old sleepy vomiting Mom works nights Wouldn t feed well Shivering
Abuse Or Not? Interactive Visual Clues in Child Abuse Amy Baxter MD FAAP FACEP Associate Clinical Professor Medical College of Georgia 4 month old sleepy vomiting Mom works nights Wouldn t feed well Shivering
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT GUIDELINE PAGE 1 NO REVISION NO. 1 EFFECTIVE DATE: 03/01/2015 SUPERSEDES: 9/26/12
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT GUIDELINE PAGE 1 REVISION NO. 1 EFFECTIVE DATE: 03/01/2015 SUPERSEDES: 9/26/12 DEPARTMENT (DIVISION): Trauma TITLE: Management of Abdominal Solid Organ Injuries PURPOSE The vast majority
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT GUIDELINE PAGE 1 REVISION NO. 1 EFFECTIVE DATE: 03/01/2015 SUPERSEDES: 9/26/12 DEPARTMENT (DIVISION): Trauma TITLE: Management of Abdominal Solid Organ Injuries PURPOSE The vast majority
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 17 Orthopedic Techniques Key Points 2 17.1 Traction Use an appropriate method of traction to treat fractures of the extremities and cervical spine Apply extremity
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 17 Orthopedic Techniques Key Points 2 17.1 Traction Use an appropriate method of traction to treat fractures of the extremities and cervical spine Apply extremity
Child as a victim of injury. Maciej Dudkiewicz M.D. Ph.D. Dpt of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medical University of Lodz
 Child as a victim of injury Maciej Dudkiewicz M.D. Ph.D. Dpt of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medical University of Lodz Epidemiology Trauma is most common cause of mortality and morbidity in the US pediatric
Child as a victim of injury Maciej Dudkiewicz M.D. Ph.D. Dpt of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medical University of Lodz Epidemiology Trauma is most common cause of mortality and morbidity in the US pediatric
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION PATIENTS AND METHODS. Total no. of cases
 AN INTERNATIONAL QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCES 3(4):802-806 ISSN (online): 2320-4257 www.biolifejournal.com B I O L I F E R E S E A R C H A R T I C L E Predictors of the selective use of
AN INTERNATIONAL QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCES 3(4):802-806 ISSN (online): 2320-4257 www.biolifejournal.com B I O L I F E R E S E A R C H A R T I C L E Predictors of the selective use of
Thicker than Water. Alisa McQueen MD, FAAP, FACEP Associate Professor of Pediatrics The University of Chicago
 Thicker than Water Alisa McQueen MD, FAAP, FACEP Associate Professor of Pediatrics The University of Chicago I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Who is bleeding? How much and what kind
Thicker than Water Alisa McQueen MD, FAAP, FACEP Associate Professor of Pediatrics The University of Chicago I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Who is bleeding? How much and what kind
Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) Protocol
 Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) Protocol All children suspected of non-accidental trauma will have a complete work-up including a complete history and physical exam with a focus on injuries and explanation
Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) Protocol All children suspected of non-accidental trauma will have a complete work-up including a complete history and physical exam with a focus on injuries and explanation
High Specificity Features on Plain Film of Non-Accidental Injury
 High Specificity Features on Plain Film of Non-Accidental Injury Adam A Dmytriw 1,2, Kota Talla 1, Munire Gündogan 2 1 Department of Medical Imaging, University of Toronto 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology,
High Specificity Features on Plain Film of Non-Accidental Injury Adam A Dmytriw 1,2, Kota Talla 1, Munire Gündogan 2 1 Department of Medical Imaging, University of Toronto 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology,
I have no financial disclosures.
 In the Belly of the Whale: Surviving Thoracoabdominal Trauma Debra Esernio Jenssen, MD, FAAP I have no financial disclosures. Objectives Review epidemiology of abusive chest and abdominal trauma. Identify
In the Belly of the Whale: Surviving Thoracoabdominal Trauma Debra Esernio Jenssen, MD, FAAP I have no financial disclosures. Objectives Review epidemiology of abusive chest and abdominal trauma. Identify
The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides
 The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides Adapted From The Visual Diagnosis of Non-Accidental Trauma and Failure to Thrive A Study Guide By Barton D. Schmitt, M.D. in Cooperation with The American
The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides Adapted From The Visual Diagnosis of Non-Accidental Trauma and Failure to Thrive A Study Guide By Barton D. Schmitt, M.D. in Cooperation with The American
Date of Admission: [DATE]. Date of Discharge:
![Date of Admission: [DATE]. Date of Discharge: Date of Admission: [DATE]. Date of Discharge:](/thumbs/74/71277118.jpg) Date of Admission: [DATE]. Date of Discharge: History of Present Illness: Mr. [NAME] AKA [NAME] is a 31-year-old male who presents to the [PLACE] Trauma Surgery Service as a moderate trauma on [DATE] following
Date of Admission: [DATE]. Date of Discharge: History of Present Illness: Mr. [NAME] AKA [NAME] is a 31-year-old male who presents to the [PLACE] Trauma Surgery Service as a moderate trauma on [DATE] following
Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous structures - Significant thoracic inj
 PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
Abdominal Trauma. Nat Krairojananan M.D., FRCST Department of Trauma and Emergency Medicine Phramongkutklao Hospital
 Abdominal Trauma Nat Krairojananan M.D., FRCST Department of Trauma and Emergency Medicine Phramongkutklao Hospital overview Quick review abdominal anatomy Review of mechanism of injury Review of investigation
Abdominal Trauma Nat Krairojananan M.D., FRCST Department of Trauma and Emergency Medicine Phramongkutklao Hospital overview Quick review abdominal anatomy Review of mechanism of injury Review of investigation
Medical Aspects of Child Physical Abuse the approach to physically abused kids. Objectives
 Center for Safe & Healthy Children Medical Aspects of Child Physical Abuse the approach to physically abused kids Nancy S. Harper, MD FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Associate Professor of Pediatrics, University
Center for Safe & Healthy Children Medical Aspects of Child Physical Abuse the approach to physically abused kids Nancy S. Harper, MD FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Associate Professor of Pediatrics, University
SPECIAL DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES IN BLUNT TRAUMA OLEH : Prof.DR.Dr Abdul Rasyid SpRad (K),Ph.D Dr.Evo Elidar Sp.Rad
 SPECIAL DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES IN BLUNT TRAUMA OLEH : Prof.DR.Dr Abdul Rasyid SpRad (K),Ph.D Dr.Evo Elidar Sp.Rad Trauma Emergency Room layout Ideally the trauma emergency room is centrally located to provide
SPECIAL DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES IN BLUNT TRAUMA OLEH : Prof.DR.Dr Abdul Rasyid SpRad (K),Ph.D Dr.Evo Elidar Sp.Rad Trauma Emergency Room layout Ideally the trauma emergency room is centrally located to provide
Reviewing the recent literature to answer clinical questions: Should I change my practice?
 Reviewing the recent literature to answer clinical questions: Should I change my practice? JILL MILLER, MD PEM ATTENDING CHKD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PEDIATRICS, EVMS Objectives Review the literature to answer
Reviewing the recent literature to answer clinical questions: Should I change my practice? JILL MILLER, MD PEM ATTENDING CHKD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PEDIATRICS, EVMS Objectives Review the literature to answer
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Iowa Methodist Medical Center Des Moines
 Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Iowa Methodist Medical Center Des Moines Blunt Abdominal Trauma Evaluation and Management Guideline PEDIATRIC Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma Center
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Iowa Methodist Medical Center Des Moines Blunt Abdominal Trauma Evaluation and Management Guideline PEDIATRIC Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma Center
Recurrent Subdural Hematomas in Benign Macrocrania of Infancy
 Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Medical & Clinical DOI: 10.21767/2471-299X.100032 Recurrent Subdural Hematomas in Benign Macrocrania of Infancy Ademar Lucas Junior São Camilo Diagnostic
Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Medical & Clinical DOI: 10.21767/2471-299X.100032 Recurrent Subdural Hematomas in Benign Macrocrania of Infancy Ademar Lucas Junior São Camilo Diagnostic
PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY
 PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY October 2011 Quality Improvement Resources Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children is a collaborative program between the Illinois Department of Public Health
PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY October 2011 Quality Improvement Resources Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children is a collaborative program between the Illinois Department of Public Health
Restore adequate respiratory and circulatory conditions. Reduce pain
 Pre-hospital management of the trauma patient is best performed by an integrated team focused on minimizing the time from injury to definitive care at an appropriate trauma center. Dispatchers, first responders,
Pre-hospital management of the trauma patient is best performed by an integrated team focused on minimizing the time from injury to definitive care at an appropriate trauma center. Dispatchers, first responders,
Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries. Chapter 28
 Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Chapter 28 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Signs of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Tenderness Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting Distention Solid Organs
Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Chapter 28 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Signs of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Tenderness Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting Distention Solid Organs
CORE STANDARDS STANDARDS USED IN TARN REPORTS
 CORE STANDARDS Time to CT Scan BEST PRACTICE TARIFF SECTION 4.10 MAJOR TRAUMA 7 If the patient is admitted directly to the MTC or transferred as an emergency, the patient must be received by a trauma team
CORE STANDARDS Time to CT Scan BEST PRACTICE TARIFF SECTION 4.10 MAJOR TRAUMA 7 If the patient is admitted directly to the MTC or transferred as an emergency, the patient must be received by a trauma team
Head injury in children
 Head injury in children Michael Kim, MD Department of Emergency Medicine University of Wisconsin- Madison #1 cause of death and disability Bimodal distribution 62,000 hospitalization 564,000 ED visits
Head injury in children Michael Kim, MD Department of Emergency Medicine University of Wisconsin- Madison #1 cause of death and disability Bimodal distribution 62,000 hospitalization 564,000 ED visits
Validity of Caregivers Reports on Head Trauma Due to Falls in Young Children Aged Less than 2 Years
 Clinical Medicine Insights: Pediatrics Original Research Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Validity of Caregivers Reports on Head Trauma Due
Clinical Medicine Insights: Pediatrics Original Research Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Validity of Caregivers Reports on Head Trauma Due
CORE-INFO: fractures in children
 CORE-INFO: fractures in children This leaflet summarises what is currently known about the relationship between fractures and physical abuse and will be of particular interest to paediatricians, general
CORE-INFO: fractures in children This leaflet summarises what is currently known about the relationship between fractures and physical abuse and will be of particular interest to paediatricians, general
Blunt abdominal trauma in children
 REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Blunt abdominal trauma in children Deborah Schonfeld and Lois K. Lee Purpose of review This review will examine the current evidence regarding pediatric blunt abdominal trauma and
REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Blunt abdominal trauma in children Deborah Schonfeld and Lois K. Lee Purpose of review This review will examine the current evidence regarding pediatric blunt abdominal trauma and
Guideline for the Management of Blunt Liver and Spleen Injuries
 Pediatric Trauma Practice Guideline Management of Blunt Liver and Spleen Guideline for the Management of Blunt Liver and Spleen Background: Children are more vulnerable to blunt abdominal injury than adults.
Pediatric Trauma Practice Guideline Management of Blunt Liver and Spleen Guideline for the Management of Blunt Liver and Spleen Background: Children are more vulnerable to blunt abdominal injury than adults.
Use of CT in minor traumatic brain injury. Lisa Ayoub-Rodriguez, MD Bert Johansson, MD Michael Lee, MD
 Use of CT in minor traumatic brain injury Lisa Ayoub-Rodriguez, MD Bert Johansson, MD Michael Lee, MD No financial or other conflicts of interest Epidemiology of traumatic brain injury (TBI) Risks associated
Use of CT in minor traumatic brain injury Lisa Ayoub-Rodriguez, MD Bert Johansson, MD Michael Lee, MD No financial or other conflicts of interest Epidemiology of traumatic brain injury (TBI) Risks associated
Request Card Task ANSWERS
 Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Children diagnosed with skull fractures are often. Transfer of children with isolated linear skull fractures: is it worth the cost?
 clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:602 606, 2016 Transfer of children with isolated linear skull fractures: is it worth the cost? Ian K. White, MD, 1 Ecaterina Pestereva, BS, 1 Kashif A. Shaikh, MD,
clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:602 606, 2016 Transfer of children with isolated linear skull fractures: is it worth the cost? Ian K. White, MD, 1 Ecaterina Pestereva, BS, 1 Kashif A. Shaikh, MD,
The ABC s of Chest Trauma
 The ABC s of Chest Trauma J Bradley Pickhardt MD, FACS Providence St Patrick Hospital What s the Problem? 2/3 of trauma patients have chest trauma Responsible for 25% of all trauma deaths Most injuries
The ABC s of Chest Trauma J Bradley Pickhardt MD, FACS Providence St Patrick Hospital What s the Problem? 2/3 of trauma patients have chest trauma Responsible for 25% of all trauma deaths Most injuries
Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
 Guideline for North Bristol Trust Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury This guideline describes the following: Initial assessment and management of the patient with head injury Indications for CT
Guideline for North Bristol Trust Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury This guideline describes the following: Initial assessment and management of the patient with head injury Indications for CT
Instructional Course #34. Review of Neuropharmacology in Pediatric Brain Injury. John Pelegano MD Jilda Vargus-Adams MD, MSc Micah Baird MD
 Instructional Course #34 Review of Neuropharmacology in Pediatric Brain Injury John Pelegano MD Jilda Vargus-Adams MD, MSc Micah Baird MD Outline of Course 1. Introduction John Pelegano MD 2. Neuropharmocologic
Instructional Course #34 Review of Neuropharmacology in Pediatric Brain Injury John Pelegano MD Jilda Vargus-Adams MD, MSc Micah Baird MD Outline of Course 1. Introduction John Pelegano MD 2. Neuropharmocologic
George M Wadie, MD Director Division of Pediatric Surgery Sacred Heart Medical Center. Springfield, OR Adjunct Assistant Professor of Surgery Oregon
 George M Wadie, MD Director Division of Pediatric Surgery Sacred Heart Medical Center. Springfield, OR Adjunct Assistant Professor of Surgery Oregon Health and Sciences University. Portland, OR Outline
George M Wadie, MD Director Division of Pediatric Surgery Sacred Heart Medical Center. Springfield, OR Adjunct Assistant Professor of Surgery Oregon Health and Sciences University. Portland, OR Outline
Which Blunt Trauma Patients Should Be Studied by Abdominal CT?
 MDCT of Bowel and Mesenteric Injury: How Findings Influence Management 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology
MDCT of Bowel and Mesenteric Injury: How Findings Influence Management 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HEAD INJURIES IN REMOTE AND RURAL ALASKA
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HEAD INJURIES IN REMOTE AND RURAL ALASKA Approximately 800 patients with head injuries die or are hospitalized in the state of Alaska each year 1. In addition, thousands
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HEAD INJURIES IN REMOTE AND RURAL ALASKA Approximately 800 patients with head injuries die or are hospitalized in the state of Alaska each year 1. In addition, thousands
Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue. Injuries to. and Spine. December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief
 Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue Injuries to the Head and Spine December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief C.E. Card Information BLS Providers 2 Cards / Provider Category 1 Course # Blank Topic#
Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue Injuries to the Head and Spine December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief C.E. Card Information BLS Providers 2 Cards / Provider Category 1 Course # Blank Topic#
Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics
 Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe common accidental injuries which can be confused with child abuse Describe
Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe common accidental injuries which can be confused with child abuse Describe
ATLS: Initial Assessment and Management. SAUSHEC Medical Student Lecture Series
 ATLS: Initial Assessment and Management SAUSHEC Medical Student Lecture Series Objectives Identify sequence of priorities in assessing the multiply injured patient Apply principles outlined in primary
ATLS: Initial Assessment and Management SAUSHEC Medical Student Lecture Series Objectives Identify sequence of priorities in assessing the multiply injured patient Apply principles outlined in primary
The Role of Skeletal Survey in Identifying Non- Accidental Trauma in Pediatric Trauma Patients
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms GSBS Dissertations and Theses Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 6-13-2017 The Role of Skeletal Survey in Identifying Non- Accidental Trauma
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms GSBS Dissertations and Theses Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 6-13-2017 The Role of Skeletal Survey in Identifying Non- Accidental Trauma
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 4/30/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 18 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 4/30/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 18 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Chapter 31. Objectives. Objectives 01/09/2013. Head Trauma
 Chapter 31 Head Trauma Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. Define key terms introduced
Chapter 31 Head Trauma Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. Define key terms introduced
Pediatric Blunt Abdominal Trauma: Solid Organs, Seatbelts, and Sieverts. 23 March. The Plan. Tucker Redfern Symposium Ramin Jamshidi, MD FACS
 Pediatric Blunt Abdominal Trauma: Solid Organs, Seatbelts, and Sieverts Tucker Redfern Symposium 2018 23 March 1965: Gemini 3 launch 2001: Mir scrapped The Plan Solid Organ Injuries Seat-Belt Trauma Abdominal
Pediatric Blunt Abdominal Trauma: Solid Organs, Seatbelts, and Sieverts Tucker Redfern Symposium 2018 23 March 1965: Gemini 3 launch 2001: Mir scrapped The Plan Solid Organ Injuries Seat-Belt Trauma Abdominal
Since the publication of The Battered-Child Syndrome in 1962,1
 The new england journal of medicine Clinical Practice Caren G. Solomon, M.D., M.P.H., Editor Physical Abuse of Children Carol D. Berkowitz, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette highlighting
The new england journal of medicine Clinical Practice Caren G. Solomon, M.D., M.P.H., Editor Physical Abuse of Children Carol D. Berkowitz, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette highlighting
Evaluation and Stabilization of the Athlete with Possible Spine Injury
 Evaluation and Stabilization of the Athlete with Possible Spine Injury Jeffrey H. Bohmer, MD, FACEP Emergency Physician Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital June 12, 2015 Introduction Goals: 1.
Evaluation and Stabilization of the Athlete with Possible Spine Injury Jeffrey H. Bohmer, MD, FACEP Emergency Physician Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital June 12, 2015 Introduction Goals: 1.
Michael Avant, M.D. The Children s Hospital of GHS
 Michael Avant, M.D. The Children s Hospital of GHS OVERVIEW ER to ICU Transition Early Management Priorities the First 48 hours Organ System Support Complications THE FIRST 48 HOURS Communication Damage
Michael Avant, M.D. The Children s Hospital of GHS OVERVIEW ER to ICU Transition Early Management Priorities the First 48 hours Organ System Support Complications THE FIRST 48 HOURS Communication Damage
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Original Article. Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction. Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH
 Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
2019 Patient Price Information List
 2019 Patient Price Information List In compliance with state law, Genesis Healthcare System is providing this price list containing our charges for room and board, emergency department, operating room,
2019 Patient Price Information List In compliance with state law, Genesis Healthcare System is providing this price list containing our charges for room and board, emergency department, operating room,
Avoidable Imaging Learning Collaborative: 2008 Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Clinical Policy Success Story BWH Head and PE CTs with Clinical Decision
 Avoidable Imaging Learning Collaborative: 2008 Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Clinical Policy Success Story BWH Head and PE CTs with Clinical Decision Support Using the Canadian CT Head Rule to Reduce Unnecessary
Avoidable Imaging Learning Collaborative: 2008 Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Clinical Policy Success Story BWH Head and PE CTs with Clinical Decision Support Using the Canadian CT Head Rule to Reduce Unnecessary
PEDIATRIC BLUNT TRAUMA WHAT S DIFFERENT? NORDIC TRAUMA COURSE 2016
 PEDIATRIC BLUNT TRAUMA WHAT S DIFFERENT? NORDIC TRAUMA COURSE 2016 Ken F. Linnau, MD, MS Emergency Radiology Harborview Medical Center University of Washington Seattle, WA Thanks to Nupur Verma, MD University
PEDIATRIC BLUNT TRAUMA WHAT S DIFFERENT? NORDIC TRAUMA COURSE 2016 Ken F. Linnau, MD, MS Emergency Radiology Harborview Medical Center University of Washington Seattle, WA Thanks to Nupur Verma, MD University
Bontrager, Kenneth: Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 8 th edition, C.V. Mosby, 2010, ISBN# #882 Scan-trons and pencils
 Basic Radiographic Procedures (RADR 1411) Credit: 3 semester credit hours (3 hours lecture, 2 hours lab) Pre-requisite: RADR 1309 Introduction to Radiography and Patient Care Course Description An introduction
Basic Radiographic Procedures (RADR 1411) Credit: 3 semester credit hours (3 hours lecture, 2 hours lab) Pre-requisite: RADR 1309 Introduction to Radiography and Patient Care Course Description An introduction
Original Date: February 2006 PLAIN FILM X-RAYS
 Magellan Healthcare Clinical guidelines Original Date: February 2006 PLAIN FILM X-RAYS Page 1 of 5 Adopted Date 1 : April 2016 Physical Medicine Clinical Decision Making Last Review Date: August 2015 Guideline
Magellan Healthcare Clinical guidelines Original Date: February 2006 PLAIN FILM X-RAYS Page 1 of 5 Adopted Date 1 : April 2016 Physical Medicine Clinical Decision Making Last Review Date: August 2015 Guideline
A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT IN CASES OF HEMOPERITONEUM IN SOLID ORGAN INJURIES AT TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN WESTERN INDIA
 RESEARCH ARTICLE A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT IN CASES OF HEMOPERITONEUM IN SOLID ORGAN INJURIES AT TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN WESTERN INDIA Chintan Patel 1, Isha Patel 2, Divyang Dave
RESEARCH ARTICLE A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT IN CASES OF HEMOPERITONEUM IN SOLID ORGAN INJURIES AT TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN WESTERN INDIA Chintan Patel 1, Isha Patel 2, Divyang Dave
Original Date: February 2006 PLAIN FILM X-RAYS
 Magellan Healthcare Clinical guidelines Original Date: February 2006 PLAIN FILM X-RAYS Page 1 of 5 Adopted Date 1 : April 2016 Physical Medicine Clinical Decision Making Last Review Date: August 2016 Guideline
Magellan Healthcare Clinical guidelines Original Date: February 2006 PLAIN FILM X-RAYS Page 1 of 5 Adopted Date 1 : April 2016 Physical Medicine Clinical Decision Making Last Review Date: August 2016 Guideline
LIVER INJURIES PROFF. S.FLORET
 LIVER INJURIES PROFF. S.FLORET Abdominal injuries For anatomical consideration: Abdomen can be divided in four areas Intra thoracic abdomen True abdomen Pelvic abdomen Retroperitoneal abdomen ETIOLOGY
LIVER INJURIES PROFF. S.FLORET Abdominal injuries For anatomical consideration: Abdomen can be divided in four areas Intra thoracic abdomen True abdomen Pelvic abdomen Retroperitoneal abdomen ETIOLOGY
