Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are epithelial invaginations in the gallbladder wall that from as a result of increased gallbladder pressures.
|
|
|
- Ashlynn Dickerson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy The complexity of the biliary tree can be broken down into much simpler segments. The intrahepatic ducts converge to form the right and left hepatic ducts which exit the liver and join to become the common hepatic duct. The cystic duct branches off the common hepatic duct and drains into the gallbladder. The common hepatic duct continues towards the duodenum, but it is called the common bile duct (CBD) after the take-off of the cystic duct. The CBD then joins the pancreatic duct prior to draining into the second portion of the duodenum. Obstruction, inflammation, or infection of the biliary tract changes the baseline anatomy and size of the various ducts. The normal calibers of the CBD and pancreatic duct are < 8mm and < 4mm, respectively. The gallbladder wall is typically < 4mm in thickness. Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are epithelial invaginations in the gallbladder wall that from as a result of increased gallbladder pressures. Ducts of Luschka are biliary ducts that lie in gallbladder fossa and connect directly between liver and the gallbladder. These can result in bile leak after cholecystectomy. Pathophysiology is the yellowing of the skin and sclera due to abnormally elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood. It can be characterized into three different categories including pre-hepatic, intra-hepatic, or post-hepatic. Pre-hepatic and intra-hepatic causes are known as medical jaundice, while post-hepatic (or obstructive jaundice) is considered surgical jaundice. PRE-HEPATIC In pre-hepatic jaundice, there is excess production of bilirubin that overtakes the ability of liver to conjugate the bilirubin and excrete into the gut. This is predominantly unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. The most common cause of pre-hepatic jaundice is hemolytic anemia which causes excess heme breakdown. INTRA-HEPATIC Intra-hepatic causes are due to parenchymal liver disease with inability to either conjugate or excrete bilirubin. In this case, the fraction of bilirubin that is elevated varies. Viral hepatitis often has a predominantly unconjugated bilirubinemia. A conjugated hyperbilirubinemia is seen with cholestasis from drugs or primary biliary cholangitis. American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 1 of 11
2 POST-HEPATIC In post-hepatic jaundice or obstructive jaundice, there is an impediment to the flow of bile due to a partial or complete obstruction of the extrahepatic biliary passage between the liver and duodenum. Obstruction can occur within the biliary ducts themselves or more distal within the pancreas. This is predominantly a conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Table 1 PRE-HEPATIC INTRA-HEPATIC POST-HEPATIC PHYSIOLOGY Excessive hemolysis leading to increased bilirubin delivered to the liver Defective conjugation Impaired cellular uptake Abnormal secretion Mechanical obstruction of bile flow causing impaired excretion ELEVATED BILIRUBIN Unconjugated Conjugated and unconjugated is possible Conjugated URINE COLOR Normal Dark Dark STOOL COLOR Normal Normal Acholic PRURITUS No No Yes Obstructive (Surgical) Surgical jaundice is suspected over medical jaundice in the following scenarios: - History of abdominal pain and fevers - Painless jaundice with weight loss, pruritus, and clay colored stools - Conjugated bilirubinemia with elevation of alkaline phosphatase and GGT - An enlarged gallbladder, abdominal mass, and/or lymph node in left supraclavicular area is considered advanced disease American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 2 of 11
3 Distinguishing surgical jaundice from medical jaundice is just the first step in the diagnosis and treatment. Post-hepatic obstruction can be located in several different areas of the biliary tree and can be due to a variety of benign and malignant pathologies outlined below. Benign: Choledocholithiasis Mirizzi syndrome Bile duct stricture Chronic pancreatitis Primary sclerosing cholangitis Choledochal cyst Malignant: Pancreatic Solid Cystic Cholangiocarcinoma Klatskin tumor Ampulla of Vater Pediatric: Biliary atresia Iatrogenic: CBD injury following laparoscopic cholecystectomy Ischemic stricture from cautery or hepatic artery injury Diagnosis of Medical vs Surgical Distinguishing between medical jaundice (pre- and intra-hepatic) and surgical jaundice (posthepatic or obstructive) can be difficult. It is extremely important to obtain a thorough history and physical to help distinguish the underlying pathophysiology of the jaundice. HISTORY The history of present illness should elicit a wide range of possible symptoms associated with jaundice. Obstructive jaundice often produces pruritus, pale stools, and dark colored urine. Abdominal pain along with fevers and jaundice is suggestive of obstruction with an associated infection known as cholangitis. A malignant source of obstruction more often presents with painless jaundice and weight loss. Intrahepatic cholestasis can be due to intrahepatic sources of jaundice or post-hepatic mechanical obstruction making the diagnosis difficult to make on the history of present illness alone. Therefore, a detailed past medical history and social history are warranted. Risk American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 3 of 11
4 factors for gallstones and possible choledocholithiasis are important to obtain. This includes obesity, female gender, and age more than 40 years. Prior intraabdominal pathology should be identified, including a history of inflammatory bowel disease, which can have associated hepatic steatosis, cholelithiasis, or primary sclerosing cholangitis. A history of pancreatitis should be noted as this can lead to biliary strictures. Any iatrogenic interventions such as surgery or endoscopy are critical to obtain. A social history should include current and past alcohol consumption as well as risk factors for transmission of viral hepatitis such as intravenous drug abuse and tattoos. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION A thorough but focused physical exam can also help narrow the possible causes of jaundice. This should include a general, abdominal, and rectal exam. The overall general exam allows the clinician to determine the severity of the illness, and the urgency of intervention and level of care required. Also noted on the general exam is jaundice (or icterus) itself. This is defined as the yellowing of skin and whites of the eye (scleral icterus) that accompanies high levels of bilirubin and is typically seen when the levels are greater than 2-3 mg/dl. A palpable gallbladder, mass in the abdomen or lymph nodes in the supraclavicular area (Virchow s node) are suggestive of a malignancy causing obstructive jaundice. Stigmata of liver failure or portal hypertension such as caput medusa, spider nevi, and ascites are suggestive of a chronic parenchymal liver disease and an intra-hepatic cause of jaundice. The following terminology is important to know when diagnosing jaundice: Charcot s triad - Right upper quadrant pain - - Fever Reynold s Pentad - Right upper quadrant pain - - Fever - Hypotension - Altered mental status Courvoisier s sign/law - Enlarged, non-tender, and palpable gallbladder in patients with obstructive jaundice due to tumors of the biliary tree or pancreatic head Murphy s sign - Positive if patient experiences RUQ tenderness and stops breathing upon inspiration as the gallbladder moves down in contact with the examiner s hand - Suggestive of acute cholecystitis American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 4 of 11
5 Scleral icterus - Yellowing of the white of the eye due to excessive bilirubin in the bloodstream Caput medusae - Distended and engorged superficial epigastric veins which appear to be radiating from the umbilicus across the abdomen due to portal hypertension Rectal varices - Dilation of submucosal vessels and backflow in the veins of the rectum as the blood shunts from the portal system to the systemic venous system due to portal hypertension LABORATORY TESTS Following history and physical exam, laboratory tests should be the next step in proper diagnosis of jaundice. Obstructive jaundice has hallmark findings on the biochemistry profile. It is primarily a conjugated hyperbilirubinemia with the direct bilirubin > 50% of the total bilirubin. There is also an associated elevation of alkaline phosphatase. Depending on the duration of symptoms and severity of obstruction, coagulation can be altered in addition to renal dysfunction. Leukocytosis is more likely seen in infectious and inflammatory causes of obstruction such as cholangitis or cholecystitis. IMAGING STUDIES Ultrasound Ultrasound is the gold standard imaging study for evaluation of the gallbladder. It is able to identify dilated intrahepatic and proximal extrahepatic bile ducts (including CBD) in addition to gallstones. Unfortunately, ultrasound is not optimal for visualization of the distal extrahepatic biliary tree and pancreas due to overlying gas in the duodenum. Therefore, further imaging needs to be obtained for evaluation of the pancreatic head, pancreatic duct, and distal common bile duct. Cholangiography Cholangiography is defined as specific imaging of the biliary tree. This is crucial to visualize the entire biliary system and helps delineate the level and possibly the cause of obstruction. Varying techniques include: MRCP - Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography - Utilizes T2-weighted MRI which shows static or slow moving fluids as high signal and surrounding tissue as low signal - Allows for evaluation of the ducts and surrounding liver parenchyma American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 5 of 11
6 ERCP - Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography - Upper endoscopic camera is placed through the mouth down into stomach and subsequently the duodenum - Cannula is placed through ampulla of Vater - Contrast is injected and x-rays taken to evaluate patency of the ducts PTC - Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography - Under ultrasound guidance the intrahepatic biliary tree is punctured utilizing a needle with subsequent guidewire placement (L hepatic duct via subcostal location is most common) - After catheter placement, contrast can be injected for visualization of the biliary tree - Interventions can be performed after crossing the obstruction with a guide wire including dilation, biopsy, and stent placement - If the obstruction cannot be passed, a drain can be left in place for drainage/decompression ** The following are considered advanced imaging for suspected malignancy: Contrast enhanced CT abdomen ** This allows for a global assessment of the abdomen. Attention should be focused towards mass lesions in the liver, biliary tract, and/or pancreas. CT also allows for staging of a malignancy by identifying lymph nodes and metastasis. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) ** EUS is sensitive for detecting small lesions in the head of pancreas and surrounding lymphadenopathy. It also allows for a needle biopsy of the lesion when appropriate. Management of Obstructive The first step in management of obstructive jaundice is based on the acuity of the disease and clinical status of the patient. Patients with hemodynamic instability, coagulopathy, and/or renal dysfunction need to be quickly resuscitated prior to managing the specific etiology of the obstruction. In the presence of cholangitis, often it is difficult to stabilize the patient until the obstruction is relieved and source control of the infection achieved. The following algorithms should be considered. American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 6 of 11
7 RESUSCITATION Presents with cholangitis Goal = resuscitation 1) Intravenous fluids to correct dehydration and pre-renal failure 2) Broad spectrum antibiotics - Gram negative coverage is essential 3) Correct coagulopathy, if present 4) Upon stabilization, decompress biliary obstruction without surgical intervention (ERCP or PTC as described above) 5) Further treatment of obstruction based on etiology Presents with jaundice in the absence of cholangitis Goal = diagnosis and management of obstruction 1) US and blood work to confirm biliary obstruction 2) Advanced imaging to identify site and etiology of obstruction if remains unclear MANAGEMENT OF SPECIFIC ETIOLOGY Choledocholithiasis 1) ERCP with stone extraction from CBD 2) Elective cholecystectomy to prevent recurrence (ideally during same admission) Benign biliary stricture 1) ERCP or PTC with balloon dilatation of the stricture with stent placement 2) If fails, surgery with biliary-enteric anastomosis Pancreatic cancer 1) Full staging to determine resectability - 95% tumors are unsuitable for surgical resection - Contraindications for surgery include distant metastases, encasement of SMA or celiac artery vessels 2) Neoadjuvant chemoradiation pending staging 3) Pancreatoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure) for resectable cases 4) Unresectable cases are treated with palliation including biliary stent placement, chemotherapy, and adequate analgesia Hilar cholangiocarcinoma 1) Full staging to determine resectability - Contraindications for surgery o Involvement of both right and left hepatic ducts into the liver o Invasion of portal vein and hepatic artery branches to both lobes of liver o Distant metastases American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 7 of 11
8 2) Bile duct resection with hepatectomy and hepaticojejunostomy to residual lobe is procedure of choice 3) Unresectable cases treated with biliary drainage via stent and palliation Choledochal cysts 1) Types I, II, and IV are typically resected due to risk of malignancy 2) Types I and IV are completely resected with Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy 3) Type II cysts are resected with simple cyst excision 4) Type III cysts are only treated if symptomatic which consists of sphincterotomy or endoscopic resection 5) Type V cysts are difficult to manage and can require liver transplantation Questions 1. The common bile duct is: A. The segment of biliary passage from the confluence of the right and left hepatic ducts to the ampulla of Vater. B. The segment of biliary passage from the right hepatic duct to the cystic duct insertion. C. The segment of the biliary passage from the insertion of the cystic duct to the ampulla of Vater. D. The segment of biliary passage from the junction of the right and left hepatic ducts to the ampulla of Vater. 2. A 35-year-old obese and previously healthy woman presents with first episode of right upper quadrant pain and fever. Which of the following is the most appropriate first imaging modality? A. Percutaneous cholangiography and external biliary decompression B. CT abdomen and pelvis C. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography and stent insertion D. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography and internal biliary drainage with stent E. Ultrasound 3. In jaundice caused by choledocholithiasis, the following biochemical abnormalities are most likely to be seen: A. Increase in GGT and liver transaminases B. Increase in conjugated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase C. Increase in liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase D. Increase in GGT and alkaline phosphatase E. Elevated prothrombin time and GGT American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 8 of 11
9 4. A 60-year-old man presents with history of pruritus and acholic stools. He has high fever and tenderness in the upper abdomen. Biochemistry shows direct hyperbilirubinemia and elevated CA 19-9 level. Ultrasound exam shows intrahepatic biliary duct dilatation and dilatation of extrahepatic duct to the region of the pancreas. The patient is resuscitated and started on antibiotics. The next best investigation to provide relief is: A. CT abdomen and pelvis B. Percutaneous cholangiography and external biliary decompression C. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography and stent insertion D. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography and internal biliary drainage with stent E. Surgical exploration and biliary drainage 5. All of the following cytokines are mediators of the initial proinflammatory response to infection and injury EXCEPT: A. Interleukin 10 B. Tumor necrosis factor α C. Interleukin 1 D. Interleukin 6 E. Interleukin 8 Answers 1. The common bile duct is: C. The common bile duct is the portion of the biliary tree where the common hepatic duct joins the cystic duct. The common bile duct reaches from this confluence to the duodenum. Its function is to carry bile from the biliary system to the small intestine. 2. A 35-year-old obese and previously healthy woman presents with first episode of right upper quadrant pain and fever. Which of the following is the most appropriate first imaging modality? E. Ultrasound is first line imaging technique for right upper quadrant pathology. It is non-invasive, quick, and cost effective. Ultrasound can identify intra and extrahepatic biliary abnormalities. However, it is less sensitive for the distal biliary tree due to the pancreas and gas in the small bowel. 3. In jaundice caused by choledocholithiasis, the following biochemical abnormalities are most likely to be seen: B. Choledocholithiasis causes post-hepatic biliary obstruction. This results in elevated conjugated bilirubin and elevated alkaline phosphatase on laboratory tests. American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 9 of 11
10 4. A 60-year-old man presents with history of pruritus and acholic stools. He has high fever and tenderness in the upper abdomen. Biochemistry shows direct hyper-bilirubinemia and elevated CA 19-9 level. Ultrasound exam shows intrahepatic biliary duct dilatation and dilatation of extrahepatic duct to the region of the pancreas. The patient is resuscitated and started on antibiotics. The next best investigation to provide relief is: D. This patient likely has a malignant pancreatic head mass given the diffuse biliary tree dilation and elevated CA After resuscitation and treatment for cholangitis, invasive measures should be taken to decompress the biliary tree. The appropriate next step is ERCP which allows for internal biliary drainage via stent as well as biopsy brushings to help confirm the diagnosis. 5. All of the following cytokines are mediators of the initial proinflammatory response to infection and injury EXCEPT: Problems A. Proinflammatory cytokines include TNF- α, IL-1, IL-6, and IL-8. These factors induce fever, inflammation, and tissue injury. With time, the cytokines can cause shock and subsequently death. IL-10 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine. For each of the problems, answer the following questions: - What further data should be obtained from the patient s history that gives clues about etiology? - What findings would you look for on physical exam? - What is your differential diagnosis? - What work-up would you recommend (include laboratory tests and diagnostic interventions)? - What therapy or treatment would you recommend? 1) A 35-year-old woman presents with onset of acute abdominal pain, fever and high colored urine. 2) A 65-year-old man presents with itching, anorexia, weight loss, and yellowish discoloration of eyes. References 1. Chavez YH, Kalloo AN. In; Cameron J, Cameron A eds. Obstructive : Endoscopic Therapy. Current Surgical Therapy. 12e. p Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 10 of 11
11 2. Chockalingam A, Georgiades C, Hong K. In; Cameron J, Cameron A eds. Transhepatic interventions for obstructive jaundice. Current Surgical Therapy. 12e. p Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; Jackson PG, Evans SRT. In; Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL eds. Biliary System. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 20e. p Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; Authors/Contributors Ranjan Sudan, MD, FACS, (Section Editor and Goals and Objectives Author) Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC Kadiyala V. Ravindra, MBBS, FACS (Content Author) Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC Morgan L. Cox, MD (Content Author) Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC Romeo C. Ignacio, Jr., MD, FACS (Assessment Consultant) Naval Medical Center, San Diego, CA American College of Surgeons Division of Education Page 11 of 11
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Cholangiocarcinoma: Radiologic evaluation and interventions
 November 2014 Cholangiocarcinoma: Radiologic evaluation and interventions Colin Nevins, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Initial course and work-up Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
November 2014 Cholangiocarcinoma: Radiologic evaluation and interventions Colin Nevins, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Initial course and work-up Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Imaging of liver and pancreas
 Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Personal Profile. Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history. Hepatitis B carrier
 Personal Profile Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history Hepatitis B carrier Chief complaint Fever on and off for 2 days Present illness 94.10.14 Sudden onset of epigastric pain 94.10.15 Fever
Personal Profile Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history Hepatitis B carrier Chief complaint Fever on and off for 2 days Present illness 94.10.14 Sudden onset of epigastric pain 94.10.15 Fever
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE
 ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE Dr. Sohan kumar sah *, Dr. Liu Sibin, Dr. sumendra raj pandey, Dr. Prakashmaan shah, Dr. Gaurishankar pandit, Dr. Suraj kurmi and Dr. Sanjay kumar jaiswal
ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE Dr. Sohan kumar sah *, Dr. Liu Sibin, Dr. sumendra raj pandey, Dr. Prakashmaan shah, Dr. Gaurishankar pandit, Dr. Suraj kurmi and Dr. Sanjay kumar jaiswal
JAUNDICE. Zdeněk Fryšák 3rd Clinic of Internal Medicine Nephrology-Rheumatology-Endocrinology Faculty Hospital Olomouc
 JAUNDICE Zdeněk Fryšák 3rd Clinic of Internal Medicine Nephrology-Rheumatology-Endocrinology Faculty Hospital Olomouc Definition of Jaundice Icterus A yellowish staining of the skin, sclerae and deeper
JAUNDICE Zdeněk Fryšák 3rd Clinic of Internal Medicine Nephrology-Rheumatology-Endocrinology Faculty Hospital Olomouc Definition of Jaundice Icterus A yellowish staining of the skin, sclerae and deeper
Management of Gallbladder Disease
 Management of Gallbladder Disease Steven B. Johnson, MD, FACS, FCCM Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery Program Director, Phoenix Integrated Surgical Residency University of Arizona College of
Management of Gallbladder Disease Steven B. Johnson, MD, FACS, FCCM Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery Program Director, Phoenix Integrated Surgical Residency University of Arizona College of
Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
Management of Cholangiocarcinoma. Roseanna Lee, MD PGY-5 Kings County Hospital
 Management of Cholangiocarcinoma Roseanna Lee, MD PGY-5 Kings County Hospital Case Presentation 37 year old male from Yemen presented with 2 week history of epigastric pain, anorexia, jaundice and puritis.
Management of Cholangiocarcinoma Roseanna Lee, MD PGY-5 Kings County Hospital Case Presentation 37 year old male from Yemen presented with 2 week history of epigastric pain, anorexia, jaundice and puritis.
Biliary Tract Disease. Emmet Andrews Cork University Hospital 6 th September 2010
 Biliary Tract Disease Emmet Andrews Cork University Hospital 6 th September 2010 Overview Gallstones Biliary tract tumours Other conditions Acute acalculous cholecystitis Mirizzi s syndrome Primary Biliary
Biliary Tract Disease Emmet Andrews Cork University Hospital 6 th September 2010 Overview Gallstones Biliary tract tumours Other conditions Acute acalculous cholecystitis Mirizzi s syndrome Primary Biliary
BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II
 CME Pretest BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II VOLUME 41 1 2015 A pretest is mandatory to earn CME credit on the posttest. The pretest should be completed BEFORE reading the overview. Both tests must be
CME Pretest BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II VOLUME 41 1 2015 A pretest is mandatory to earn CME credit on the posttest. The pretest should be completed BEFORE reading the overview. Both tests must be
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
CBD stones & strictures (Obstructive jaundice)
 1 CBD stones & strictures (Obstructive jaundice) Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA), MHPE (Nl & Eg) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz
1 CBD stones & strictures (Obstructive jaundice) Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA), MHPE (Nl & Eg) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz
Postoperative jaundice
 Postoperative jaundice Principles of Surgery Ehren Eksteen 17/3/2010 Abri Bezuidenhout 28/3/2012 Intro Jaundice is defined as yellow discolouration of the skin,sclera and heavily perfused areas in a patient
Postoperative jaundice Principles of Surgery Ehren Eksteen 17/3/2010 Abri Bezuidenhout 28/3/2012 Intro Jaundice is defined as yellow discolouration of the skin,sclera and heavily perfused areas in a patient
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree
 A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation
 Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Bile Duct Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Bile Duct Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Bile Duct Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Biliary MRI w Eovist
 Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
4/9/2018 OBJECTIVES PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS
 PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics
 Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland in the body; it has many functions, including production of bile (a fluid
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland in the body; it has many functions, including production of bile (a fluid
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction
 Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Vesalius SCALpel : Biliary (see also: biliary/pancreatic folios) Physiology
 Vesalius SCALpel : Biliary (see also: biliary/pancreatic folios) Physiology 95% of bile acids reabsorbed; colic and chenodeoxycolic primary bile acids cholecystokinin (CCK) major stimulus of gallbladder
Vesalius SCALpel : Biliary (see also: biliary/pancreatic folios) Physiology 95% of bile acids reabsorbed; colic and chenodeoxycolic primary bile acids cholecystokinin (CCK) major stimulus of gallbladder
Case Scenario 1. Discharge Summary
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
What Are Gallstones? GALLSTONES. Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in. the gallbladder of some people.
 What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons
 General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: UPPER GI & HPB - HEPATIC, PANCREATIC & BILIARY
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: UPPER GI & HPB - HEPATIC, PANCREATIC & BILIARY
ERCP / PTC Surgical Laparoscopic vs open Timing and order of approach
 Choledocholithiasis Which Approach and When? Lygia Stewart, MD University of California, San Francisco 2010 Naffziger Post-Graduate Course Clinical Manifestations of Choledocholithiasis Asymptomatic (no
Choledocholithiasis Which Approach and When? Lygia Stewart, MD University of California, San Francisco 2010 Naffziger Post-Graduate Course Clinical Manifestations of Choledocholithiasis Asymptomatic (no
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease
 Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease The Liver The liver is located in the right upper portion of the abdominal cavity just beneath the right side of the rib cage. The liver has many functions that
Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease The Liver The liver is located in the right upper portion of the abdominal cavity just beneath the right side of the rib cage. The liver has many functions that
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons
 General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: UPPER GI & HPB - HEPATIC, PANCREATIC & BILIARY
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: UPPER GI & HPB - HEPATIC, PANCREATIC & BILIARY
Imaging Guided Biopsy. Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer
 Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
A LEADER IN ADVANCED ENDOSCOPY AND HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY
 A LEADER IN ADVANCED ENDOSCOPY AND HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center Welcome The St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center is a leader
A LEADER IN ADVANCED ENDOSCOPY AND HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center Welcome The St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center is a leader
PANCREATIC CANCER GUIDELINES
 PANCREATIC CANCER GUIDELINES North-East London Cancer Network & Barts and the London HPB Centre PROTOCOL FOR MANAGEMENT OF PANCREATIC CANCER (SEPTEMBER 2010) I. PRE-REFERRAL GUIDELINES Screening 1. Offer
PANCREATIC CANCER GUIDELINES North-East London Cancer Network & Barts and the London HPB Centre PROTOCOL FOR MANAGEMENT OF PANCREATIC CANCER (SEPTEMBER 2010) I. PRE-REFERRAL GUIDELINES Screening 1. Offer
Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds
 Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds Imaging in jaundice and 2ww pathway Image protocol Staging Limitations Pancreatic cancer 1.2.4 Refer people using a suspected
Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds Imaging in jaundice and 2ww pathway Image protocol Staging Limitations Pancreatic cancer 1.2.4 Refer people using a suspected
Bile Duct Injuries. Dr. Bennet Rajmohan, MRCS (Eng), MRCS Ed Consultant General & Laparoscopic Surgeon Apollo Speciality Hospitals Madurai, India
 Bile Duct Injuries Dr. Bennet Rajmohan, MRCS (Eng), MRCS Ed Consultant General & Laparoscopic Surgeon Apollo Speciality Hospitals Madurai, India Introduction Bile duct injury (BDI) rare but potentially
Bile Duct Injuries Dr. Bennet Rajmohan, MRCS (Eng), MRCS Ed Consultant General & Laparoscopic Surgeon Apollo Speciality Hospitals Madurai, India Introduction Bile duct injury (BDI) rare but potentially
Multiple Primary Quiz
 Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Malignant Obstructive Jaundice has dismal
 Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.L vol: 22(2}: pp. 79-83, 2008. Anatomic Level of Biliary Obstruction and Outcome of Pre-Operative Biliary Stenting in Malignant Obstructive Jaundice -A Shaikh Zayed Hospital Experience
Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.L vol: 22(2}: pp. 79-83, 2008. Anatomic Level of Biliary Obstruction and Outcome of Pre-Operative Biliary Stenting in Malignant Obstructive Jaundice -A Shaikh Zayed Hospital Experience
3/28/2012. Periampullary Tumors. Postgraduate Course in General Surgery CASE 1: CASE 1: Overview. Eric K. Nakakura Ko Olina, HI
 Overview Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Case presentation Differential diagnosis Diagnosis and therapy Outcomes Principles of palliative care Eric K. Nakakura Ko Olina, HI March 27, 2012 CASE 1:
Overview Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Case presentation Differential diagnosis Diagnosis and therapy Outcomes Principles of palliative care Eric K. Nakakura Ko Olina, HI March 27, 2012 CASE 1:
MAKING CONNECTIONS. Los Angeles Medical Center
 MAKING CONNECTIONS Los Angeles Medical Center Resident: Chris Molloy, MD Fellow: Christian Coroian, MD, MBA Attending: Tina Hardley, MD Program/Dept(s): Los Angeles Medical Center CHIEF COMPLAINT & HPI
MAKING CONNECTIONS Los Angeles Medical Center Resident: Chris Molloy, MD Fellow: Christian Coroian, MD, MBA Attending: Tina Hardley, MD Program/Dept(s): Los Angeles Medical Center CHIEF COMPLAINT & HPI
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain
 Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Pancreatic Cancer. What is pancreatic cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst?
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Together, putting patients first
 The Role of a Gastroenterologist in the Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cancer Sarah Jowett, Consultant Gastroenterologist Bradford Teaching Hospitals Trust Leeds Regional Study Day, 12 September
The Role of a Gastroenterologist in the Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cancer Sarah Jowett, Consultant Gastroenterologist Bradford Teaching Hospitals Trust Leeds Regional Study Day, 12 September
Frank Burton Memorial Update on Pancreato-biliary Cancers
 Frank Burton Memorial Update on Pancreato-biliary Cancers Diagnosis and management of pancreatic cancer: common dilemmas Moderators: Banke Agarwal, MD Paul Buse, MD Evaluation of patients with obstructive
Frank Burton Memorial Update on Pancreato-biliary Cancers Diagnosis and management of pancreatic cancer: common dilemmas Moderators: Banke Agarwal, MD Paul Buse, MD Evaluation of patients with obstructive
Gall bladder cancer. Information for patients Hepatobiliary
 Gall bladder cancer Information for patients Hepatobiliary page 2 of 12 Who will provide my care? You will be cared for by a number of professionals who work together. These professionals will be specialist
Gall bladder cancer Information for patients Hepatobiliary page 2 of 12 Who will provide my care? You will be cared for by a number of professionals who work together. These professionals will be specialist
LIVER CIRRHOSIS. The liver extracts nutrients from the blood and processes them for later use.
 LIVER CIRRHOSIS William Sanchez, M.D. & Jayant A. Talwalkar, M.D., M.P.H. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group Miles and Shirley Fiterman Center for Digestive Diseases Mayo College of Medicine Rochester,
LIVER CIRRHOSIS William Sanchez, M.D. & Jayant A. Talwalkar, M.D., M.P.H. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group Miles and Shirley Fiterman Center for Digestive Diseases Mayo College of Medicine Rochester,
5/17/2013. Pancreatic Cancer. Postgraduate Course in General Surgery CASE 1: CASE 1: Overview. Case presentation. Differential diagnosis
 Overview Case presentation Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Differential diagnosis Diagnosis and therapy Eric K. Nakakura Koloa, HI March 26, 2013 Outcomes CASE 1: CASE 1: A 78-year-old man developed
Overview Case presentation Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Differential diagnosis Diagnosis and therapy Eric K. Nakakura Koloa, HI March 26, 2013 Outcomes CASE 1: CASE 1: A 78-year-old man developed
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA (CCA)
 CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA (CCA) Deepak Hariharan MD (Research), FRCS, Locum Consultant HPB Surgeon AIM Outline essential facts & principles Present 4 cases Discuss Challenges /Controversies INTRODUCTION Most
CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA (CCA) Deepak Hariharan MD (Research), FRCS, Locum Consultant HPB Surgeon AIM Outline essential facts & principles Present 4 cases Discuss Challenges /Controversies INTRODUCTION Most
The Bile Duct (and Pancreas) and the Physician
 The Bile Duct (and Pancreas) and the Physician Javaid Iqbal Consultant in Gastroenterology and Pancreato-biliary Medicine University Hospital South Manchester Not so common?! Two weeks 38 ERCP s 20 15
The Bile Duct (and Pancreas) and the Physician Javaid Iqbal Consultant in Gastroenterology and Pancreato-biliary Medicine University Hospital South Manchester Not so common?! Two weeks 38 ERCP s 20 15
Chapter 45 3/2/2017. Care of the Patient with a Gallbladder, Liver, Biliary Tract, or Exocrine Pancreatic Disorder
 Chapter 45 Care of the Patient with a Gallbladder, Liver, Biliary Tract, or Exocrine Pancreatic Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights
Chapter 45 Care of the Patient with a Gallbladder, Liver, Biliary Tract, or Exocrine Pancreatic Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights
6 th August 2018 Day 1 - Gallbladder & Bile duct Topic
 Venue: Sterling Hospital Auditorium, Sterling Hospitals, Gurukul Road Ahmedabad, Gujarat 6 th August 2018 Day 1 - Gallbladder & Bile duct Registration(8:00am-8:15am) Inauguration(8:15am-8:30am) Welcome
Venue: Sterling Hospital Auditorium, Sterling Hospitals, Gurukul Road Ahmedabad, Gujarat 6 th August 2018 Day 1 - Gallbladder & Bile duct Registration(8:00am-8:15am) Inauguration(8:15am-8:30am) Welcome
Lutheran Medical Center. Daniel H. Hunt, M.D. June 10 th, 2005
 Lutheran Medical Center Daniel H. Hunt, M.D. June 10 th, 2005 History xx y.o. pt with primary CBD stones s/p ERCP xx months earlier for attempted stone extraction resulting in post ERCP pancreatitis. Patient
Lutheran Medical Center Daniel H. Hunt, M.D. June 10 th, 2005 History xx y.o. pt with primary CBD stones s/p ERCP xx months earlier for attempted stone extraction resulting in post ERCP pancreatitis. Patient
CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice
 CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice Episode overview: 1) Describe heme metabolism 2) List common pre-hepatic/hepatic/post-hepatic causes of jaundice Wisecracks: 1) What are clinical signs of liver disease? 2)
CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice Episode overview: 1) Describe heme metabolism 2) List common pre-hepatic/hepatic/post-hepatic causes of jaundice Wisecracks: 1) What are clinical signs of liver disease? 2)
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell. Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer
 Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent
 A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando?
 Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases
 GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht
 Hilar cholangiocarcinoma Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht Content Anatomy Biliary strictures (Hilar) Cholangiocarcinoom Staging Biliary tract 1 st order Ductus hepatica dextra Ductus hepaticus
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht Content Anatomy Biliary strictures (Hilar) Cholangiocarcinoom Staging Biliary tract 1 st order Ductus hepatica dextra Ductus hepaticus
R.Sotoudehmanesh, MD Professor of Gastroenterology Digestive Disease Research Institute Tehran University of Medical Sciences Pancreatobiliary
 R.Sotoudehmanesh, MD Professor of Gastroenterology Digestive Disease Research Institute Tehran University of Medical Sciences Pancreatobiliary /Advanced Endoscopy group Most common biliary malignancy and
R.Sotoudehmanesh, MD Professor of Gastroenterology Digestive Disease Research Institute Tehran University of Medical Sciences Pancreatobiliary /Advanced Endoscopy group Most common biliary malignancy and
Surgical Management of CBD Injury Jin Seok Heo
 Surgical Management of CBD Injury Jin Seok Heo Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea Bile duct injury (BDI) Introduction Incidence
Surgical Management of CBD Injury Jin Seok Heo Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea Bile duct injury (BDI) Introduction Incidence
Approach to the Biliary Stricture
 Approach to the Biliary Stricture ACG Eastern Postgraduate Course Washington DC June 8, 2014 Steven A. Edmundowicz MD FASGE Chief of Endoscopy Division of Gastroenterology Professor of Medicine Disclosures
Approach to the Biliary Stricture ACG Eastern Postgraduate Course Washington DC June 8, 2014 Steven A. Edmundowicz MD FASGE Chief of Endoscopy Division of Gastroenterology Professor of Medicine Disclosures
Clinical Spectrum of Presentation of Obstructive Jaundice in Inflammation, Stone Disease, and Malignancy
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/326 Clinical Spectrum of Presentation of Obstructive Jaundice in Inflammation, Stone Disease, and Malignancy R Selvasekaran
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/326 Clinical Spectrum of Presentation of Obstructive Jaundice in Inflammation, Stone Disease, and Malignancy R Selvasekaran
Pancreas Case Scenario #1
 Pancreas Case Scenario #1 An 85 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with increasing abdominal pain. On 8/19 she had a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. This showed a 4.6 cm mass
Pancreas Case Scenario #1 An 85 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with increasing abdominal pain. On 8/19 she had a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. This showed a 4.6 cm mass
Jaundice , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. syf80102 Last reviewed: 05/05/2017 1
 Jaundice Introduction Jaundice causes your skin and the whites of your eyes to turn yellow. Too much bilirubin causes jaundice. Bilirubin is a yellow chemical in hemoglobin, the substance that carries
Jaundice Introduction Jaundice causes your skin and the whites of your eyes to turn yellow. Too much bilirubin causes jaundice. Bilirubin is a yellow chemical in hemoglobin, the substance that carries
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
A CASE REPORT OF SPONTANEOUS BILOMA - AN ENIGMATIC SURGICAL PROBLEM
 A CASE REPORT OF SPONTANEOUS BILOMA - AN ENIGMATIC SURGICAL PROBLEM *Sumanta Kumar Ghosh and Biswajit Mukherjee ESIC Medical College, Joka, Kolkata, India *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Occurrence
A CASE REPORT OF SPONTANEOUS BILOMA - AN ENIGMATIC SURGICAL PROBLEM *Sumanta Kumar Ghosh and Biswajit Mukherjee ESIC Medical College, Joka, Kolkata, India *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Occurrence
Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options
 Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options Poster No.: C-1501 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hadjivassiliou,
Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options Poster No.: C-1501 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hadjivassiliou,
Endoscopic Management of Biliary Strictures. Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center
 Endoscopic Management of Biliary Strictures Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Malignant Biliary Strictures Etiologies: Pancreatic
Endoscopic Management of Biliary Strictures Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Malignant Biliary Strictures Etiologies: Pancreatic
LIVER. Question 1 ~ Anatomy. Answer 1 ~ Anatomy 1/5/2018. SEMCME Board Review January 11-12, 2017
 SEMCME Board Review January 11-12, 2017 Surgical Treatment of Hepatobiliary and Splenic Disorders Michael J. Jacobs, MD, FACS, FICS Clinical Professor of Surgery- MSU CHM Associate Chair of Surgery Director
SEMCME Board Review January 11-12, 2017 Surgical Treatment of Hepatobiliary and Splenic Disorders Michael J. Jacobs, MD, FACS, FICS Clinical Professor of Surgery- MSU CHM Associate Chair of Surgery Director
Surgical Treatment of Hepatobiliary and Splenic Disorders
 SEMCME Board Review January 10-11, 2019 Surgical Treatment of Hepatobiliary and Splenic Disorders Michael J. Jacobs, MD, FACS, FICS Clinical Professor of Surgery- MSU CHM Associate Chair of Surgery Director
SEMCME Board Review January 10-11, 2019 Surgical Treatment of Hepatobiliary and Splenic Disorders Michael J. Jacobs, MD, FACS, FICS Clinical Professor of Surgery- MSU CHM Associate Chair of Surgery Director
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
HEPATIC METASTASES. We can state 3 types of metastases depending on their treatment options:
 HEPATIC METASTASES 1. Definition Metastasis means the spread of cancer. Cancerous cells can separate from the primary tumor and enter the bloodstream or the lymphatic system (the one that produces, stores,
HEPATIC METASTASES 1. Definition Metastasis means the spread of cancer. Cancerous cells can separate from the primary tumor and enter the bloodstream or the lymphatic system (the one that produces, stores,
Tata Memorial Centre s opinion is summarized as follows: 1. Given the type 1 stricture (as mentioned in the structured summary), assessment
 March 5 th 2016 Dear Ms. Malti Sinha, Thank you for reaching out to Tata Memorial Centre for an expert opinion in regard to assessing your treatment options. Navya Network is pleased to offer this online
March 5 th 2016 Dear Ms. Malti Sinha, Thank you for reaching out to Tata Memorial Centre for an expert opinion in regard to assessing your treatment options. Navya Network is pleased to offer this online
Disclosures. Extra-hepatic Biliary Disease and the Pancreas. Objectives. Pancreatitis 10/3/2018. No relevant financial disclosures to report
 Extra-hepatic Biliary Disease and the Pancreas Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures to report Jeffrey Coughenour MD FACS Clinical Associate Professor of Surgery and Emergency Medicine Division
Extra-hepatic Biliary Disease and the Pancreas Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures to report Jeffrey Coughenour MD FACS Clinical Associate Professor of Surgery and Emergency Medicine Division
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids. Cholestasis
 Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do?
 ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do? Rajesh N. Keswani, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine EUS/ERCP in 2015 THE
ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do? Rajesh N. Keswani, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine EUS/ERCP in 2015 THE
Management of Pancreatic Fistulae
 Management of Pancreatic Fistulae Jose Ramos University of the Witwatersrand Donald Gordon Medical Centre Fistula definition A Fistula is a permanent abnormal passageway between two organs (epithelial
Management of Pancreatic Fistulae Jose Ramos University of the Witwatersrand Donald Gordon Medical Centre Fistula definition A Fistula is a permanent abnormal passageway between two organs (epithelial
PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST DRAINAGE: ENDOSCOPIC APPROACHES & THE NURSING ROLE. PRESENTED BY: Susan DePasquale, CGRN, MSN
 PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST DRAINAGE: ENDOSCOPIC APPROACHES & THE NURSING ROLE PRESENTED BY: Susan DePasquale, CGRN, MSN Pancreatic Fluid Collection (PFC) A result of pancreatic duct (PD) and side branch disruption,
PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST DRAINAGE: ENDOSCOPIC APPROACHES & THE NURSING ROLE PRESENTED BY: Susan DePasquale, CGRN, MSN Pancreatic Fluid Collection (PFC) A result of pancreatic duct (PD) and side branch disruption,
Resident Teaching Conference:
 Resident Teaching Conference: Evaluation of the Dreaded Liver Mass May 6, 2011 Sunil Geevarghese, MD, HS 00 Matt Landman, MD Anatomy Overview Couinaud anatomy Resection nomenclature Functional Assessment
Resident Teaching Conference: Evaluation of the Dreaded Liver Mass May 6, 2011 Sunil Geevarghese, MD, HS 00 Matt Landman, MD Anatomy Overview Couinaud anatomy Resection nomenclature Functional Assessment
Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico
 Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques Associate Professor
Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques Associate Professor
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY
 LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY Treating Gallbladder Problems with Laparoscopy A Common Problem If you ve had an attack of painful gallbladder symptoms, you re not alone. Gallbladder disease is very common.
LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY Treating Gallbladder Problems with Laparoscopy A Common Problem If you ve had an attack of painful gallbladder symptoms, you re not alone. Gallbladder disease is very common.
Case Reports. Intraductal Papillary Cholangiocarcinoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 Case Reports Kongkam K, Rerknimitr R 45 Case Report and Review of the Literature Pradermchai Kongkam, M.D. Rungsun Rerknimitr, M.D. ABSTRACT A case of papillary cholangiocarcinoma is presented. A 64-year-old
Case Reports Kongkam K, Rerknimitr R 45 Case Report and Review of the Literature Pradermchai Kongkam, M.D. Rungsun Rerknimitr, M.D. ABSTRACT A case of papillary cholangiocarcinoma is presented. A 64-year-old
The campaign on laboratory: focus on Gallstone Disease and ERCP
 The campaign on laboratory: focus on Gallstone Disease and ERCP Mauro Giuliani, MD, Specialist in Visceral Surgery, Vice Head Physician, Surgical Ward, Ospedale Regionale di Locarno Alberto Fasoli, MD,
The campaign on laboratory: focus on Gallstone Disease and ERCP Mauro Giuliani, MD, Specialist in Visceral Surgery, Vice Head Physician, Surgical Ward, Ospedale Regionale di Locarno Alberto Fasoli, MD,
Biliary Tract Disease HPB Division, Surgery Department of Ramathibodi. Paramin Muangkaew MD.
 Biliary Tract Disease HPB Division, Surgery Department of Ramathibodi Paramin Muangkaew MD. Anatomy Proximal Intrahepatic bile duct IHD Primary Secondary Extrahepatic bile duct Rt & Lt HD CHD Cystic duct
Biliary Tract Disease HPB Division, Surgery Department of Ramathibodi Paramin Muangkaew MD. Anatomy Proximal Intrahepatic bile duct IHD Primary Secondary Extrahepatic bile duct Rt & Lt HD CHD Cystic duct
Case Study: #3: Gallbladder Carcinoma?
 Case Study: #3: Gallbladder Carcinoma? By: Megan Wyatt K. SON Wyatt 225 2B1 RDMS, RVT Patient: Male 85 YOA Caucasian Indication: Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase History Annual physical showed elevated alkaline
Case Study: #3: Gallbladder Carcinoma? By: Megan Wyatt K. SON Wyatt 225 2B1 RDMS, RVT Patient: Male 85 YOA Caucasian Indication: Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase History Annual physical showed elevated alkaline
Endoscopic Ultrasonography Assessment for Ampullary and Bile Duct Malignancy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 Pancreatic Cancer- Case #1. Endoscopic management of GI malignancy. Endoscopic approaches in GI malignancy- Agenda
 Slide 1 A teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School Endoscopic management of GI malignancy Tyler Berzin MD, MS Center for Advanced Endoscopy Division of Gastroenterology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical
Slide 1 A teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School Endoscopic management of GI malignancy Tyler Berzin MD, MS Center for Advanced Endoscopy Division of Gastroenterology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical
ERCP in altered anatomy. Lars Aabakken Oslo University Hospital - Rikshospitalet Oslo, Norway
 ERCP in altered anatomy Lars Aabakken Oslo University Hospital - Rikshospitalet Oslo, Norway CO2 as insufflation gas Reduces post-procedure pain Reduces in-procedure bowel distension Improves the intubation
ERCP in altered anatomy Lars Aabakken Oslo University Hospital - Rikshospitalet Oslo, Norway CO2 as insufflation gas Reduces post-procedure pain Reduces in-procedure bowel distension Improves the intubation
CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (115) Wai C T, Seto K Y, Sutedja D S
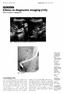 Medical Education Singapore Med.1 2007, 48 (4) : 361 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (115) Wai C T, Seto K Y, Sutedja D S fit. B CD - -0 o -5 r t -10 Fig. I US images of the upper right abdomen
Medical Education Singapore Med.1 2007, 48 (4) : 361 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (115) Wai C T, Seto K Y, Sutedja D S fit. B CD - -0 o -5 r t -10 Fig. I US images of the upper right abdomen
Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks. Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD
 Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD Evolution of ERCP 1968. 1970s ECPG Endoscopic CholangioPancreatoGraphy Japan 1974 Biliary
Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD Evolution of ERCP 1968. 1970s ECPG Endoscopic CholangioPancreatoGraphy Japan 1974 Biliary
Biliary Atresia. Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s
 Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Cholangiocellular carcinoma. Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD
 Cholangiocellular carcinoma Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD Acalculous biliary diseases April 12, 2017 2 Cholangiocarcinoma A slow growing malignancy of the biliary tract which tend - to infiltrate locally
Cholangiocellular carcinoma Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD Acalculous biliary diseases April 12, 2017 2 Cholangiocarcinoma A slow growing malignancy of the biliary tract which tend - to infiltrate locally
What can you expect after your ERCP?
 ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
Endoscopic treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: Is there something new?
 Endoscopic treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: Is there something new? Arnaud Lemmers, MD, PhD Gastroenterology Department, Erasme Hospital, ULB, Brussels BASL December 1st 2017 AGENDA Introduction
Endoscopic treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: Is there something new? Arnaud Lemmers, MD, PhD Gastroenterology Department, Erasme Hospital, ULB, Brussels BASL December 1st 2017 AGENDA Introduction
This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated.
 A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
