THE MECONIUM PLUG SYNDROME* ROENTGEN EVALUATION AND DIFFERENTIATION FROM HIRSCHSPRUNG S DISEASE AND OTHER
|
|
|
- Sheila Harper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FEBRUARY, 1974 THE MECONIUM PLUG SYNDROME* ROENTGEN EVALUATION AND DIFFERENTIATION FROM HIRSCHSPRUNG S DISEASE AND OTHER PATHOLOGIC STATES By RUBEM POCHACZEVSKY, M.D., and JOHN C. LEONIDAS, M.D. Trn HE meconium plug syndrome is a relatively frequent cause of colonic mechanical obstruction in the newborn and is related to the failure to pass meconium in the first days of life. Many theories as to its etiology have been proposed including temporary inhibition of colonic peristalsis, alteration of the meconium composition, pancreatic enzyme de- 71 0, l.24,25,27 and neonatal hypermagnesemia. The retained meconium is hardened, with an increase in its surface tension and viscosity, causing it to become impacted i1:; the colon in the form ofa plug. The meconium plug syndrome usually follows a benign course and responds readily to conservative treatment. #{176} 24 Its recognition is, therefore, important in order that unnecessary operative treatment be avoided. The condition which most often mimics meconium plug syndrome is that of Hirschsprung s disease The latter s distinction is of equal importance since immediate surgical intervention is required. Other major pathologic conditions which may roentgenographically simulate the meconium plug syndrome are necrotizing enterocolitis of infancy, 9 20 meconium ileus, 8 ileal atresia, and, occasionally, midgut volvulus.2 In an attempt to evaluate criteria for their radiologic diagnoses and distinction, the authors reviewed the literature and their own case material of meconium plug syndrome, Hirschsprung s disease, necrotizing enterocoli tis of in fancy 9 2#{176} and meconium ileus. 8 NEW YORK, NEW YORK CASE MATERIAL MECONIUM PLUG SYNDROME Current case material consisted of 14 mi fants with meconium plug syndrome all o- whom were observed for periods of at least 2 years with no clinical evidence of Hirschsprung s disease or other gastrointestinal abnormality (Table I). All 14 cases of meconium plug syndrome had evidence of abdominal distention both clinically and roentgenographically (Fig. 1-4; and io). Accompanying mottled densities or bulky intraluminal colonic masses, which had the typical appearance of meconium (Fig. 1-4; and io), were noted on the plain film roentgenograms of the abdomen in 9 of these 14 cases. No meconium could be identified on the plain film roentgenograms of the other. Erect roentgeno- [ ABLE MECONIUM PLUG SYNDROME (14 Current Cases) Roentgen Abnormality Present Absent Total Plain Film Roentgenogram of the Abdomen Bowel distention Fluid levels (erect roentgenograms) Meconium identified Contrast Enema Roentgenogram Significant amounts of meconium Transition or collapsed colonic segment Stasis of contrast medium I * From the Department of Radiology, Mount Sinai Hospital Services, The City Hospital Center at Elmhurst and Mount Sinai School of Medicine, City University of New York, New York. 342
2 VOL. 120, No. 2 The Meconium Plug Syndrome 343 grams of the abdomen were obtained in 12 cases. No air-fluid levels were observed within the bowel in 7 of the 12 cases (Fig. 1-3), while air-fluid levels in the bowel were present in the remaining (Table i). Colonic contrast studies were performed on 8 patients. All showed an abnormally large amount of intraluminal meconium (Fig. 54; and 6-8) with a largely uninterrupted tape-like configuration threading through the major portion of the lumen of the colon (Fig. 54; 6-8; and iob). A collapsed or empty segment was noted distal to the meconium plug in 2 cases (Fig. 8). This pseudo transition simulated the appearance of Hirschsprung s disease. Delayed roentgenograms of the abdomen taken I day after the contrast study of the colon FIG. i. Case 1. Meconium plug syndrome. Erect roentgenogram of the abdomen. One day old female with a history of poor feedings and abdominal distention. Note retained colonic meconium giving the bowel a bubbly appearance. l ollowing this examination, a large meconium plug was passed. FIG. 2. Case II. Meconium plug syndrome. Twelve hour old male with abdominal distention and failure to pass meconium. Roentgenogram of the abdomen shows large meconium mass within cecum (arrows). Following this study a large meconium plug was passed. L 4! FIG.. Case iii. Meconium plug syndrome. One day old female. Erect roentgenogram of the abdomen. Note air-fluid level in the stomach, but no airfluid levels in the bowel. Note diffuse mottled densities due to meconium within the colon. A large meconium plug was subsequently passed. 1*
3 344 Rubem Pochaczevsky and John C. Leonidas FEBRUARY, 1974 FIG.. Case IV. Meconium plug syndrome. Four day old, premature, male twin with a history of sepsis and failure to pass meconium. Roentgenogram of the abdomen shows considerable amount of mewere available in 5 cases. Two of these showed no significant retention of contrast material after 24 hours, i had retention after 24 hours, while 2 demonstrated contrast material retention 72 hours post examination (Fig. 9) (Table i). Meconium plugs were passed by all 14 patients (Fig. 5B) with immediate clinical improvement in 13. The sole patient who did not improve (Case iv), was a premature twin who had associated sepsis, unrelated to the colon, and expired at 5 days of age. The other twin included among the 14 improved dramatically and continued to do well. HIRSCHSPRUNG S DISEASE Our case material consisted of 13 instances of biopsy proven Hirschsprung s disease diagnosed during Me first days of life (Table ii). All exhibited bowel distenconium in the region of the right colon (arrows). A cm. long meconium plug was passed after a rectal swab was inserted for stool culture. The infant had several subsequent apneic episodes, and died at days of age due to unrelated sepsis. FIG.. Case v. Meconium plug syndrome. Premature, i8 hour old male, with abdominal distention and failure to pziss meconium. (A) Barium enema examination shows large intracolonic meconium masses. (B) A large meconium plug was passed following completion of the barium enema study.
4 VOL. 120, No. 2 The Meconium Plug Syndrome 345 FIG. 6. Case VI. Meconium plug syndrome. Infant, 48 hours old, with a history of abdominal distention and vomiting. Barium enema examination accentuates long uninterrupted, intracolonic ribbon-like filling defects due to inspissated meconium. Following the barium enema studs a large oblong meconium plug was passed with immediate amelioration of the infant s symptoms. FIG.. Case VII. Meconium plug syndrome. One day old infant with abdominal distention and failure to pass meconium. Contrast enema examination shows undulating cylindrical meconium mass, extending from the rectum to the terminal ileum. lig. 8. Case VIII. Meconium plug syndrome. Newborn. Contrast enema examination shows an uninterrupted, snake-like mass of meconium occupying the entire transverse colon. Note collapsed colon distal to the splenic flexure. FIG. 9. Case ix. Meconium plug syndrome. Newborn. Previous contrast enema examination outlined considerable amounts of intraluminal meconium. Seventy-two hours following the enema study there is retained contrast medium within the colon. Retention of contrast medium is, therefore, not always a reliable point of differential distinction between the meconium plug syndrome and Hirschsprung s disease.
5 346 Rubem Pochaczevsky and John C. Leonidas FEBRUARY, 1974 TABLE II HIRSCHSPRUNG S DISEASE IN INFANTS FIG. io. Case xiv. Meconium plug syndrome. Newborn male with abdominal distention and mild respiratory distress. Roentgenogram of the abdomen shows marked bowel distention. Note sausage shaped oblong density within distal lumen of transverse colon (arrows). 4 DAYS OF AGE OR YOUNGER (13 Current Cases) Roentgen Abnormality Present Absent Total Plain Film Roentgenogram of the Abdomen Bowel distention,, Fluid levels (erect roentgenograms) 10 1 II Meconium identified 2 II 13 Contrast Enema Roentgenogram Excessive meconium identified Transition segment in rectosigmoid Stasis of contrast medium tion on the plain film roentgenograms of the abdomen. Ten of the 13 cases showed no mottled or bulky densities in the colon suggestive of meconium (Fig. i i4; 124; 134; and 14). Eleven of the 3 cases had ;.u. ; s disease. Two day old female with a history of L. to pass meconium and regurgitation of bile-stained material. (A) Abdominal roentgenogram shows marked bowel distention with no evidence of retained meconium. (B) Contrast enema roentgenogram demonstrates transitional segment in rectosigmoid. The lucency in the transverse colon is due to air. No significant amount of meconium is seen. A rectal biopsy confirmed the presence of Hirschsprung s disease.
6 VOL. 120, No. 2 The Meconium Plug Syndrome 347 FIG. 12. Hirschsprung s disease. Two day old infant with a history of abdominil distention. (A) Erect roentgenogram of the abdomen shows distention of bowel with air-fluid levels, but no evidence of meconium. (B) Contrast enema study shows no evidence of transitional segments and no significant meconium. G.I3.Lirschsprung s disease. One day old male with a history of vomiting and abdominal stention. (, Erect roentgenogram of the abdomen shows marked colonic distention with air-fluid levels (arrows). (B) Barium enema study demonstrates transitional segment in rectosigmoid. No significant meconium was noted. A rectal biopsy confirmed the roentgen diagnosis of aganglionosis.
7 348 Rubem Pochaczevsky and John C. Leonidas FEBRUARY, 1974 FIG. 14. Hirschsprung s disease. One day old male with a history of vomiting bile-stained material and feeding poorly. He had not passed any meconium since birth. Erect roentgenogram of the abdomen shows distention of bowel with air-fluid levels and no evidence of meconium. A barium enema study revealed a relative decrease in the caliber of the left colon. A diagnosis of Hirschsprung s disease was confirmed by rectal biopsy. erect roentgenograms of the abdomen and io exhibited air-fluid levels within the bowel (Fig. 124; 134; and (Table ii). Contrast studies of the colon were performed on 10 patients during the first days of life. Insignificant or only minimal amounts of colonic meconium were detected in 8 (Fig. IiB; I2B; and 13B) with significant amounts of meconium present in the remaining 2 cases. A transition segment in the rectosigmoid was seen in of the 10 cases (Fig. i ib; and i3b) and not seen in the others (Fig. i 2B). Delayed roentgenograms of the abdomen were obtained in 6 cases with significant contrast material retention seen in. The remaining case showed no significant contrast material retention on a 24 hour roentgenogram of the abdomen. DISCUSSION AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Analysis of our 14 cases of meconium plug syndrome (Table i) and review of the Ii ,27 showed that several pertinent roentgen findings were almost always present. The meconium plug syndrome usually presents with a picture of mechanical obstruction due to the presence of inspissated intraluminal meconium. The latter is often identifiable on the plain film roentgenograms of the abdomen by telltale mottled densities or bulky intraluminal colonic masses (Fig. -4; and io). If not readily recognizable on the plain film roentgenograms, contrast colonic enema examinations may demonstrate the typical tape or ribbon-like or sausage shaped defects occupying most of the colonic lumen (Fig. 4; and 6-8). Large amounts of meconium may, however, occasionally be appreciated as incidental findings on roentgenograms of newborns without clinical evidence of intestinal obstruction. In the meconium plug syndrome, a long con tracted pseudo transi tion segment may be present extending from the splenic flexure down to the rectum (Fig. 8). This is due to collapse of the colon distal to the plug and should not be confused with the true transition segment of Hirschsprung s disease which is most commonly located in the rectosigmoid (Fig. i ib; and i3b). A transition segment in the vicinity of the splenic tlexure was not seen in any of our patients with Hirschsprung s disease and appeared to be extremely rare in our review of published cases Roentgenographically, Hi rschsprung s disease is the entity which may most closely mimic the meconium plug syndrome (Tables II and iii). Hirschsprung s disease frequently presents with signs of mechanical large bowel obstruction in the immediate neonatal period with the plain film roentgenogram of the abdomen showing marked bowel distention (Fig. ii 4; 124; 134; and i). The diagnosis is usually confir#{241}ied with the demonstration of a transi-
8 VOL. 120, No. 2 The Meconium Plug Syndrome 349 TABLE III ROENTGEN COMPARISONS IN MECONIUM PLUG AND HIRSCHSPRUNG S DISEASE Meconium Syndrome Plug Hirschsprung s Disease in 4 day old or younger infant Bowel Distention Plain Film Roentgenogram of the Abdomen Fluid Levels. Meconium. Meconium Frequent Uncommon Frequent Large amount prior to the passage of plug tional segment in the colon (Fig. i ib; and I 3B). Untreated Hirschsprung s disease, particularly in older infants, is further characterized by considerable retention of fecal material. However, in a majority of our cases (Table II) of Hirschsprung s disease studied in the first days of life, as well as in a majority of those abdominal film roentgenograms and barium enema studies reviewed from the literature including total aganglionosis of the colon and terminal 4522 no roentgen evidence of excessive meconium retention was observed in the first days of life. It is during this period, however, that the meconium plug syndrome is evident. To date, no abnormal composition of the meconium has been described in Hirschsprung s disease with the basic abnormality related to an aganglionic bowel segment. Additionally, air-fluid levels were absent in more than half of the meconium plug syndrome cases (Fig. 1-3) (Table I), while they were almost always present in the large and small bowel on erect roentgenograms of the abdomen obtained in cases of Hirschsprung s disease (Fig. 114; 124; 134; and 14) (Tables i and III). This may be related to the fact that meconium dry and harden in the meconium plug syndrome with an associated paucity of fluid in the bowel possibly precluding the formation of air-fluid levels. Contrast Enema Roentgenogram Transition Segment Long contracted segment may occur distal to the plug Frequent Frequent Uncommon Absent or modcrate amount only Frequent; usually located in rectosigmoid May. Stasis Frequent occur Hirschsprung s disease, however, may simulate the meconium plug syndrome in several respects (Table III). Furthermore, the typical transitional segments or prolonged retention of contrast medium may not be apparent in the first days oflife in many cases of Hirschsprung s disease3 5 8 (Fig. I2B). It is, therefore, essential that these difficulties in differential diagnosis be kept in mind in the individual case and that all infants in whom a diagnosis of meconium plug syndrome has been made be followed for an adequate period of time to ensure the absence of recurrent intestinal obstruction. If any gastrointestinal signs or symptoms recur, a repeat contrast enema examination should be performed for possible detection of a transition zone which may have become more apparent in the interim. Rectal biopsy may be necessary in doubtful cases. Necrotizing enterocolitis of infancy may also present with abdominal distention in the newborn and may, occasionally, resemble the meconium plug syndrome. A recent review of our experience with 20 cases of necrotizing enterocolitis of infancy as well as an extensive review of the literature revealed that the most commonly associated major roentgen findings consisted of pneumoperi toneum, pneumatosis intestinalis, portal venous gas and small bowel distention. 9 2#{176}
9 350 Rubem Pochaczevsky and John C. Leonidas FEBRUARY, 1974 FIG. 15. Necrotizing enterocolitis of infancy. Erect abdominal roentgenogram, first day of life. History of bile emesis, rectal bleeding and respiratory distress. Note frothy appearance in distal transverse and descending colon, as well as curvilinear stripes of gas at the splenic flexure indicative of pneumatosis intestinalis. Note similarity to Case (Fig. ) and Case III (Fig. 3). Pneumatosis intestinalis may lend a frothy appearance to the colon (Fig. ii), simulating retained meconium (Fig. 1-3). However, the diagnosis is aided by the identification of su bserosal extralum inal bowel gas (gas stripes in the bowel) in necrotizing enterocolitis. Gas in the portal hepatic venous system and pneumoperitoneum are usually absent in meconium plug syndrome. Actually, the clinical presentation of the 2 entities is different in the overwhelming majority of cases.2#{176} Meconium ileus may also be associated with a bubbly appearance of retained meconium. However, this is usually limited to the distal small bowel,5 since the colon rarely contains appreciable amounts of meconium. 4 If a colonic contrast study is performed, it will frequently reveal an unused type of colon or microcolon. The obstruction is caused by tenacious, viscous meconium in the small bowel producing great variation in the size of the bowel loops and few or no air-fluid levels.6 25 Meconium ileus is associated with pancreatic cystic fibrosis and with an abnormal chloride sweat test Infants with meconium plug syndrome only rarely show evidence of cystic fibrosis of the pancreas,24 but because of this possibility careful follow-up of all patients with a history of meconium plug, including a sweat test is advisable. A bubbly appearance within distended loops may also be seen in cases of intestinal atresia unassociated with meconium ileus 8 22 (Fig. 16). Barium enema examination shows a microcolon as in meconium ileus and the differential diagnosis between the 2 may be impossible without appropriate laboratory studies, such as the sweat test. SUMMARY The authors experience with 14 cases of the meconium plug syndrome and 13 cases l IG. i6. Lower jejunal atresia. Note markedly distended small bowel loops in right upper quadrant containing large amounts of meconium. A colon study demonstrated a microcolon.
10 VOL. 120, No. 2 The Meconium Plug Syndrome 35 of Hirschsprung s disease is presented and the roentgenographic findings reviewed. Criteria for differentiation of meconium plug syndrome from Hirschsprung s disease as well as from other pathologic processes, such as necrotizing enterocolitis of infancy and meconium ileus, are formulated and illustrated. The following roentgen findings were almost always present in the meconium plug syndrome: small and large bowel distention, mottled or bulky intraluminal colonic masses reflecting excessive meconium retention and producing ribbon-like or sausage shaped defects on contrast enema roentgenograms. Air-fluid levels in the bowel were uncommon. Long contracted colonic segments simulating the transition segments of Hirschsprung s disease, and due to collapse of the colon distal to the plug, may be seen involving the descending colon down to the sigmoid and/or rectum. In distinction, excessive meconium was infrequently seen on plain film roentgenograms or contrast enema studies in 13 current cases of Hirschsprung s disease in infants days of age or younger. Additionally, air-fluid levels in the bowel were almost always present. If transition segments were identified in these young patients, they were localized to the rectosigmoid in most cases. Hirschsprung s disease remains, however, the most difficult problem in the differential diagnosis since it may occasionally present with clinical and roentgen findings almost identical with the meconium plug syndrome. Follow-up of all cases with the diagnosis of meconium plug syndrome is, therefore, recommended to exclude recurrence of symptoms in which event careful re-evaluation should be undertaken. Rubem Pochaczevsky, M.D. Department of Radiology City Hospital Center at Elmhurst Broadway Elmhurst, New York The authors wish to express their appreciation to Drs. David Bryk and E. George Kassner for case material contribution from The Jewish Hospital and Medical Center of Brooklyn. REFERENCES I. ASCH, M. J., WEITZMAN, J. J., HAYS, D. M., and BRENNAN, P. I otal colon aganglionoses. A.M.A. Arch. Surg., 1972, 105, BENSON, C. D., and LLOYD, J. R. Meconium plug syndrome. In: Pediatric Surgery. Edited by Orwar Seenson. Year Book Medical Publishers, Inc., Chicago, 1969, 2, BERDON, W. E., and BAKER, D. H. Roentgenographic diagnosis of Hirschsprung s disease in infancy. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1965, 93, BERDON, W. E., KOONTZ, P., and BAKER, D. H. Diagnosis ofcolonic and terminal ileal aganglionosis. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1964, 9!, BERMAN, C. Z. Roentgenographic manifestations of congenital megacolon (Hirschsprung s disease) in early infancy. Pediatrics, 1965, i8, BRYK, D. Meconium ileus: demonstration of meconium mass on barium enema study. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1965, 95, CLATWORTHY, H. W., JR., HOWARD, W. H. R., and LLOYD, J. Meconium plug syndrome. Surgery, 1956,39, DAVIs, W. S., and PARKER, A. Conditioning value of plain film examination in diagnosis of neonatal Hi rschsprung s disease. Radiology, 1969, 93, EHRENPREIS, T. H. Megacolon in the newborn: clinical and roentgenological study with special regard to pathogenesis. Acta paediat., 1945, 32, ELLIS, D. G., and CLATWORTHY, H. W., JR. Meconium plug syndrome revisited. 7. Pediat. Surg., 1966, 1, u. EMERY, J. L. Abnormalities in meconium of foetus and newborn. Arch. Dis. Childhood, 1957,32, EVANS, W. A., and WILLIS, R. Hirschsprung s disease: roentgen diagnosis in infants. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1957, 78, GILLI5, D. A., and GRANTYMYRE, E. B. Meconium plug syndrome and Hirschsprung s disease. Canad. M.A.7., 1965, 92, GROSSMAN, H., BERDON, W. E., and BAKER, D. H. Gastrointestinal findings in cystic fibrosis. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1966, 97, i. HILLER, H. G., and MCDONALD, P. Neonatal Hirschsprung s disease. Prog. Pediat. Radiol., 1969, 2,
11 352 Rubem Pochaczevsky and John C. Leonidas FEBRUARY, 1974 i6. HOPE, J. W., BORNS, P. F., and BERG, P. K. Roentgenologic manifestations of Hirschsprung s disease in infancy. AM. J. ROENT- GENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1965, 95, KOTTMEIER, P. K., and CLATWORTHY, H. W., JR. Aganglionic and functional megacolori in children: diagnostic dilemma. Pediatrics, 1965, 36, i8. LEONIDAS, J. C., BERDON, W. E., BAKER, D. H., and SANTULLI, T. V. Meconium ileus and its complications: reappraisal of plain film roentgen diagnostic criteria. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1970, io8, POCHACZEVSKY, R., and BRYK, D. New roentgenographic signs of neonatal gastric perforation. Radiology, 1972, 102, POCHACZEVSKY, R., and KA55NER, G. E. Necrotizing enterocolitis of infancy. AM. J. ROENT- GENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1971, 113, POCHACZEVSKY, R., RATNER, H., LEONIDAS, J. C., NAYSAN, P., and FERARU, F. Unusual forms of volvulus after neonatal period. AM. J. ROENTOENOL., RD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1972, 114, SINGLETON, E. R. Radiologic evaluation of intestinal obstruction in newborn. Radiol. Clin. North America, 1963, 1, i. 23. SOKAL, M. M., KOENIGSBERGER, M. R., RosE, J. S., BERDON, W. E., and SANTULLI, T. V. Neonatal hypermagnesemia and meconium plug syndrome. New England 7. Med., 1972, 286, SWISCHUK, L. E. Meconium plug syndrome: cause of neonatal intestinal obstruction. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1968, 103, TUCKER, A. S., and IZANAT, R. J., JR. Problems with meconium. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. 1HERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1971, 112, VAN LEEUWEN, G., GLENN, L., and WOODRUFF, C. Meconium plug syndrome with aganglionosis. Pediatrics, 1967, 40, ZACHARY, R. B. Meconium and faecal plugs in newborn. Arch. Dis. Childhood, 1957, 32,
12 This article has been cited by: 1. Lakshmana Das Narla, Elizabeth A. Hingsbergen Case 22: Total Colonic Aganglionosis Long-Segment Hirschsprung Disease. Radiology 215:2, [CrossRef] 2. S. M. Hussain, M. Meradji, S. G. F. Robben, W. C. J. Hop Plain film diagnosis in meconium plug syndrome, meconium ileus and neonatal Hirschsprung's disease. Pediatric Radiology 21:8, [CrossRef] 3. Catherine A. Poole, Marc I. Rowe Distal neonatal intestinal obstruction: The choice of contrast material. Journal of Pediatric Surgery 11:6, [CrossRef] 4. Paul R. White An Approach to Pediatric Gastrointestinal Radiology. Pediatric Clinics of North America 22:4, [CrossRef]
Hirschprung s. Meconium plug R/S >1 R/S <1
 NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
Sonography-guided Gastrografin Enema for Meconium Plug Syndrome in Premature Newborns: Preliminary Results 1
 Sonography-guided Gastrografin Enema for Meconium Plug Syndrome in Premature Newborns: Preliminary Results 1 Hyun Woo Goo, M.D., Ki Soo Kim, M.D. 2, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim, M.D. 2, Soo Young Pi, M.D. 2, Chong
Sonography-guided Gastrografin Enema for Meconium Plug Syndrome in Premature Newborns: Preliminary Results 1 Hyun Woo Goo, M.D., Ki Soo Kim, M.D. 2, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim, M.D. 2, Soo Young Pi, M.D. 2, Chong
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success
 Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis?
 Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis?
 Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. MNARI, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. MAATOUK, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. MNARI, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. MAATOUK, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Microcolon in Neonates: Clinical and Radiographic Appearance
 icrocolon in Neonates: Clinical and Radiographic Appearance Wan-Chak Lo, Chao-Ran Wang and Kun-Eng Lim icrocolon (unused colon) is not a common problem in neonates. Radiographic contrast medium enema shows
icrocolon in Neonates: Clinical and Radiographic Appearance Wan-Chak Lo, Chao-Ran Wang and Kun-Eng Lim icrocolon (unused colon) is not a common problem in neonates. Radiographic contrast medium enema shows
Daniel Hirsch, MD Director of Neonatology Somerset Medical Center Assistant Professor of Pediatrics UMDNJ RWJMS
 Daniel Hirsch, MD Director of Neonatology Somerset Medical Center Assistant Professor of Pediatrics UMDNJ RWJMS Daniel Hirsch, MD Director of Neonatology Somerset Medical Center Assistant Professor of
Daniel Hirsch, MD Director of Neonatology Somerset Medical Center Assistant Professor of Pediatrics UMDNJ RWJMS Daniel Hirsch, MD Director of Neonatology Somerset Medical Center Assistant Professor of
FACE THE EXAMINER. Hirschsprung s Disease in Newborns. (This section is meant for residents to check their understanding regarding a particular topic)
 Journal of Neonatal Surgery 2013;2(4):51 FACE THE EXAMINER Hirschsprung s Disease in Newborns (This section is meant for residents to check their understanding regarding a particular topic) QUESTIONS 1.
Journal of Neonatal Surgery 2013;2(4):51 FACE THE EXAMINER Hirschsprung s Disease in Newborns (This section is meant for residents to check their understanding regarding a particular topic) QUESTIONS 1.
Hirschsprung Disease and Contrast Enema: Diagnostic Value of Simplified Contrast Enema and Twenty-Four-Hour-Delayed Abdominal Radiographs
 J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 159-164 Hirschsprung Disease and Contrast Enema: Diagnostic Value of Simplified Contrast Enema and Twenty-Four-Hour-Delayed Abdominal Radiographs Chun-Chao Huang 1,2 Shin-Lin Shih
J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 159-164 Hirschsprung Disease and Contrast Enema: Diagnostic Value of Simplified Contrast Enema and Twenty-Four-Hour-Delayed Abdominal Radiographs Chun-Chao Huang 1,2 Shin-Lin Shih
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
ISSN East Cent. Afr. J. surg. (Online)
 143 Barium enema with reference to rectal biopsy for the diagnosis and exclusion of Hirschsprung disease W. Esayias 1, Y. Hawaz 1, B. Dejene 2, W. Ergete 3 Department of Radiology, School of Medicine,
143 Barium enema with reference to rectal biopsy for the diagnosis and exclusion of Hirschsprung disease W. Esayias 1, Y. Hawaz 1, B. Dejene 2, W. Ergete 3 Department of Radiology, School of Medicine,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
Introduction and Definitions
 Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients).
 Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION ESCAPED SURGERY: MECONIUM PLUG
 7 INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION ESCAPED SURGERY: MECONIUM PLUG Oluwayemi IO 1 *, Ade-Ojo IP 2, Olofinbiyi BA 2 1. Department of Paediatrics, Ekiti State University Teaching Hospital, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria
7 INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION ESCAPED SURGERY: MECONIUM PLUG Oluwayemi IO 1 *, Ade-Ojo IP 2, Olofinbiyi BA 2 1. Department of Paediatrics, Ekiti State University Teaching Hospital, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria
HREE Questions. Setting 3: Inpatient Facilities. Block
 Block HREE Questions Setting 3: Inpatient Facilities You have general admitting privileges to the hospital. You may see patients in the critical care unit, the pediatrics unit, the maternity unit, or recovery
Block HREE Questions Setting 3: Inpatient Facilities You have general admitting privileges to the hospital. You may see patients in the critical care unit, the pediatrics unit, the maternity unit, or recovery
Pediatric Bowel Obstruction
 Pediatric Bowel Obstruction Matt Zerden, Harvard Medical School III Patient 1 16 year old presents with severe, episodic abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Questionable abdominal mass in RLQ Previous
Pediatric Bowel Obstruction Matt Zerden, Harvard Medical School III Patient 1 16 year old presents with severe, episodic abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Questionable abdominal mass in RLQ Previous
Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help. Print this Page Add to my Bookmarks Page 3 of 10
 Welcome Kristin Ingstrup [ Logout ] SEARCH Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help Overview Editorial Board My Learning Plan January February March May June July August
Welcome Kristin Ingstrup [ Logout ] SEARCH Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help Overview Editorial Board My Learning Plan January February March May June July August
Suspected Hirschsprung's Disease in Infants: The Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast Enema
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2016;21:74-78 Suspected Hirschsprung's Disease in Infants: The Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast Enema PMY TANG, MWY LEUNG, NSY CHAO, KKW LIU, TW FAN Abstract Key words Objective:
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2016;21:74-78 Suspected Hirschsprung's Disease in Infants: The Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast Enema PMY TANG, MWY LEUNG, NSY CHAO, KKW LIU, TW FAN Abstract Key words Objective:
Total Colonic Aganglionosis: Reappraisal of Contrast Enema Study
 J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 11-19 Total Colonic Aganglionosis: Reappraisal of Contrast Enema Study Ting-Wen Sheng 1 Chao-Jan Wang 1,4 Wan-Chak Lo 1,4 Rey-In Lien 2,4 Jin-Yao Lai 3,4 Pei-Yeh Chang 3,4 Department
J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 11-19 Total Colonic Aganglionosis: Reappraisal of Contrast Enema Study Ting-Wen Sheng 1 Chao-Jan Wang 1,4 Wan-Chak Lo 1,4 Rey-In Lien 2,4 Jin-Yao Lai 3,4 Pei-Yeh Chang 3,4 Department
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus
 A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
Functional Intestinal Obstruction in the Neonate
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 800. J. M. HOWAT and A. W. WILKINSON From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, and Institute of Child Health, University of London Howat, J.
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 800. J. M. HOWAT and A. W. WILKINSON From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, and Institute of Child Health, University of London Howat, J.
GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 1071-1076, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM JAMES A. NELSON,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 1071-1076, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM JAMES A. NELSON,
GIANT DUODENAL DIVERTICULA*
 JUNE, 1974 GIANT DUODENAL DIVERTICULA* By JACK R. MILLARD, M.D., FRED M. H. ZITER, JR., M.D., and WILLIAM P. SLOVER, M.D. HARTFORD, D UODENAL diverticula are common incidental findings on barium examinations
JUNE, 1974 GIANT DUODENAL DIVERTICULA* By JACK R. MILLARD, M.D., FRED M. H. ZITER, JR., M.D., and WILLIAM P. SLOVER, M.D. HARTFORD, D UODENAL diverticula are common incidental findings on barium examinations
Strangulating Obstruction of the Bowel: A Reevaluation of Radiographic Criteria
 Strangulating Obstruction of the Bowel: A Reevaluation of Radiographic Criteria DAVID BRYK1 Fifty consecutive cases of strangulating obstruction were compared with 100 consecutive cases of surgically proven
Strangulating Obstruction of the Bowel: A Reevaluation of Radiographic Criteria DAVID BRYK1 Fifty consecutive cases of strangulating obstruction were compared with 100 consecutive cases of surgically proven
Abdominal Plain Radiograph in Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction. G Raghavendra Prasad*, Amtul Aziz
 Journal of Neonatal Surgery 2017; 6(1):6 Doi:10.21699/jns.v6i1.483 REVIEW ARTICLE Abdominal Plain Radiograph in Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction G Raghavendra Prasad*, Amtul Aziz Deccan College of Medical
Journal of Neonatal Surgery 2017; 6(1):6 Doi:10.21699/jns.v6i1.483 REVIEW ARTICLE Abdominal Plain Radiograph in Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction G Raghavendra Prasad*, Amtul Aziz Deccan College of Medical
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
Abdominal Assessment
 Abdominal Assessment Mary Marian, MS,RD,CSO University of AZ, Tucson, AZ Neha Parekh, MS,RD,LD,CNSC Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Objectives: 1. Outline the steps in performing an abdominal examination.
Abdominal Assessment Mary Marian, MS,RD,CSO University of AZ, Tucson, AZ Neha Parekh, MS,RD,LD,CNSC Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Objectives: 1. Outline the steps in performing an abdominal examination.
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management
 Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency
 Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency Poster No.: C-2233 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Vanhoutte, M. Lefere, R. Vanslembrouck, D. Bielen, G. De 1 1 2 1 1
Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency Poster No.: C-2233 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Vanhoutte, M. Lefere, R. Vanslembrouck, D. Bielen, G. De 1 1 2 1 1
Small-Bowel and colon Transit. Mahsa Sh.Nezami October 2016
 Small-Bowel and colon Transit Mahsa Sh.Nezami October 2016 Dyspeptic symptoms related to dysmotility originating from the small bowel or colon usually include : Abdominal pain Diarrhea Constipation However,
Small-Bowel and colon Transit Mahsa Sh.Nezami October 2016 Dyspeptic symptoms related to dysmotility originating from the small bowel or colon usually include : Abdominal pain Diarrhea Constipation However,
Diagnostic Imaging of Pediatric Gastrointestinal Abnormalities. Learning Objectives
 Diagnostic Imaging of Pediatric Gastrointestinal Abnormalities Tess Chapman, MD Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Washington School of Medicine Staff Radiologist, Seattle Children s Hospital
Diagnostic Imaging of Pediatric Gastrointestinal Abnormalities Tess Chapman, MD Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Washington School of Medicine Staff Radiologist, Seattle Children s Hospital
PNEUMATOSIS INTESTINALIS IN THE NEONATE*
 VOL. 120, No. 2 PNEUMATOSIS INTESTINALIS IN THE NEONATE* By ARVIN E. ROBINSON, M.D.,t HERMAN GROSSMAN, M.D., and GEORGE W. BRUMLEY, M.D. \ ATHILE recent emphasis has been on V V the association of pneumatosis
VOL. 120, No. 2 PNEUMATOSIS INTESTINALIS IN THE NEONATE* By ARVIN E. ROBINSON, M.D.,t HERMAN GROSSMAN, M.D., and GEORGE W. BRUMLEY, M.D. \ ATHILE recent emphasis has been on V V the association of pneumatosis
INTESTINAL STRICTURES IN THE NEONATE* A COMPLICATION OF JSCHEMIC BOWEL DISEASE
 APRIL, 1975 INTESTINAL STRICTURES IN THE NEONATE* A COMPLICATION OF JSCHEMIC BOWEL DISEASE By HOWARD COCKRILL, M.D., MICHAEL OLIPHANT, M.D., and HERMAN GROSSMAN, M.D. DURHAM, NORTH CAROLINA O VER the past
APRIL, 1975 INTESTINAL STRICTURES IN THE NEONATE* A COMPLICATION OF JSCHEMIC BOWEL DISEASE By HOWARD COCKRILL, M.D., MICHAEL OLIPHANT, M.D., and HERMAN GROSSMAN, M.D. DURHAM, NORTH CAROLINA O VER the past
Neonatal Perforated Gut: Etiology and Risk Factors
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Research Article Mostafa Kotb 1 * and Marwa Beyaly 2 1 Pediatric Surgery Department, Alexandria Faculty of Medicine, Egypt. 2 Human Genetics Department, Medical Research
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Research Article Mostafa Kotb 1 * and Marwa Beyaly 2 1 Pediatric Surgery Department, Alexandria Faculty of Medicine, Egypt. 2 Human Genetics Department, Medical Research
Pediatric abdominal emergencies In the first year of life
 Common Pediatric abdominal emergencies In the first year of life Kristian Stien Thomassen Section of Pediatric Radiology Dept. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Understand the
Common Pediatric abdominal emergencies In the first year of life Kristian Stien Thomassen Section of Pediatric Radiology Dept. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Understand the
Case Report The Combination of Gastroschisis, Jejunal Atresia, and Colonic Atresia in a Newborn
 Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2015, Article ID 129098, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/129098 Case Report The Combination of Gastroschisis, Jejunal Atresia, and Colonic Atresia in a Newborn
Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2015, Article ID 129098, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/129098 Case Report The Combination of Gastroschisis, Jejunal Atresia, and Colonic Atresia in a Newborn
The Anorectal Myenteric Plexus: Its Relation to Hypoganglionosis of the Colon
 The Anorectal Myenteric Plexus: Its Relation to Hypoganglionosis of the Colon ARTHUR G. WEINBERG, M.D. The Children's Hospital of Akron and Case-Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Akron, Ohio
The Anorectal Myenteric Plexus: Its Relation to Hypoganglionosis of the Colon ARTHUR G. WEINBERG, M.D. The Children's Hospital of Akron and Case-Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Akron, Ohio
PAEDIATRIC GASTROINTESTINAL RADIOLOGY
 Objective Guide to Radiology of the Paediatric Intestinal Tract Responsibility / Registrar Frequency As required Associated Documents : RADFLPAEPR003 Contrast mixes RADFLPAEPR001 Paediatric Barium swallow
Objective Guide to Radiology of the Paediatric Intestinal Tract Responsibility / Registrar Frequency As required Associated Documents : RADFLPAEPR003 Contrast mixes RADFLPAEPR001 Paediatric Barium swallow
Objectives. Pediatric Mortality. Another belly pain. Gastroenteritis. Spewing & Pooing Child 4/18/16
 Gastro-tastrophies A Review of Pediatric GI Emergencies Objectives Discuss common presentations of Pediatric Abdominal Pain complaints Discuss work up and physical exam findings Discuss care, management
Gastro-tastrophies A Review of Pediatric GI Emergencies Objectives Discuss common presentations of Pediatric Abdominal Pain complaints Discuss work up and physical exam findings Discuss care, management
Radiological Findings in Total Colon Aganglionosis and Allied Disorders
 CASE REPORT Radiation Medicine: Vol. 21 No. 3, 128 134 p.p., 2003 Radiological Findings in Total Colon Aganglionosis and Allied Disorders Katsumi Hayakawa, 1 Yasuyo Hamanaka, 1 Minoru Suzuki, 1 Masashi
CASE REPORT Radiation Medicine: Vol. 21 No. 3, 128 134 p.p., 2003 Radiological Findings in Total Colon Aganglionosis and Allied Disorders Katsumi Hayakawa, 1 Yasuyo Hamanaka, 1 Minoru Suzuki, 1 Masashi
DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS
 DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS YASHODAMMAL 70 YRS OD LADY had C/o diffuse lower abdominal pain 20 days h/o blood in stools 4 days h/o vomiting 2 days h/o burning micturation
DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS YASHODAMMAL 70 YRS OD LADY had C/o diffuse lower abdominal pain 20 days h/o blood in stools 4 days h/o vomiting 2 days h/o burning micturation
Intestinal obstruction due to dual gastrointestinal atresia in infants: diagnosis and management of 3 cases
 Chen et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2014, 14:108 CASE REPORT Open Access Intestinal obstruction due to dual gastrointestinal atresia in infants: diagnosis and management of 3 cases Hua-dong Chen 1, Hong Jiang
Chen et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2014, 14:108 CASE REPORT Open Access Intestinal obstruction due to dual gastrointestinal atresia in infants: diagnosis and management of 3 cases Hua-dong Chen 1, Hong Jiang
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
The Value of Urgent Barium Enema and Computed Tomography in Acute Malignant Colonic Obstruction: Is Urgent Barium Enema Still Necessary?
 J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 105-110 The Value of Urgent Barium Enema and Computed Tomography in Acute Malignant Colonic Obstruction: Is Urgent Barium Enema Still Necessary? Chun-Chao Huang 1,2 Fei-Shih Yang
J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 105-110 The Value of Urgent Barium Enema and Computed Tomography in Acute Malignant Colonic Obstruction: Is Urgent Barium Enema Still Necessary? Chun-Chao Huang 1,2 Fei-Shih Yang
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: the role of ultrasound in the assessment of bowel viability
 Necrotizing Enterocolitis: the role of ultrasound in the assessment of bowel viability Ricardo Faingold, MD. Department of Medical Imaging The Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University SPR Vancouver
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: the role of ultrasound in the assessment of bowel viability Ricardo Faingold, MD. Department of Medical Imaging The Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University SPR Vancouver
lschemic Colitis Associated with Sigmoid Volvulus: New Observations
 lschemic Colitis Associated with Sigmoid Volvulus: New Observations MORTON A. MEYERS, GARY G. GHAHREMANI,2 AND ANTONIO F. GOVONI Ischemic colitis following conservative management of sigmoid volvulus is
lschemic Colitis Associated with Sigmoid Volvulus: New Observations MORTON A. MEYERS, GARY G. GHAHREMANI,2 AND ANTONIO F. GOVONI Ischemic colitis following conservative management of sigmoid volvulus is
INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC
 INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 16 S. Amjad Hussain, Chinda Suriyapa, Karl Grubaugh ( Depts. of Surger and
INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 16 S. Amjad Hussain, Chinda Suriyapa, Karl Grubaugh ( Depts. of Surger and
Bowel perforation is seen in 12 to 31% of neonates
 Use of Ultrasound in the Detection of Occult owel Perforation in Neonates Stephen F. Miller, MD, Joanna J. Seibert, MD, David L. Kinder, SRT, ROMS, lyson R. Wilson, SRT, ROMS Intestinal perforation is
Use of Ultrasound in the Detection of Occult owel Perforation in Neonates Stephen F. Miller, MD, Joanna J. Seibert, MD, David L. Kinder, SRT, ROMS, lyson R. Wilson, SRT, ROMS Intestinal perforation is
Kyoko Mochizuki *, Masato Shinkai, Norihiko Kitagawa, Hiroshi Take, Hidehito Usui, Takashi Hosokawa and Kaori Yamoto
 Mochizuki et al. Surgical Case Reports (2017) 3:42 DOI 10.1186/s40792-017-0318-y CASE REPORT Open Access Continuous transanal decompression for infants with long- and total-type Hirschsprung s diseases
Mochizuki et al. Surgical Case Reports (2017) 3:42 DOI 10.1186/s40792-017-0318-y CASE REPORT Open Access Continuous transanal decompression for infants with long- and total-type Hirschsprung s diseases
Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University.
 Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University. Chronic transmural inflammatory process of the bowel & affects any part of the gastro -intestinal tract from the mouth to the
Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University. Chronic transmural inflammatory process of the bowel & affects any part of the gastro -intestinal tract from the mouth to the
THE mainstay of the radiographic study of the upper gastrointestinal tract has
 BARIUM-SPRAY EXAMINATION OF THE STOMACH- PRELIMINARY REPORT OF A NEW ROENTGENOGRAPHIC TECHNIC EDWARD BUONOCORE, M.D., and THOMAS F. MEANEY, M.D. Department of Hospital Radiology THE mainstay of the radiographic
BARIUM-SPRAY EXAMINATION OF THE STOMACH- PRELIMINARY REPORT OF A NEW ROENTGENOGRAPHIC TECHNIC EDWARD BUONOCORE, M.D., and THOMAS F. MEANEY, M.D. Department of Hospital Radiology THE mainstay of the radiographic
Congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract: A radiological review
 Congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract: A radiological review Poster No.: C-1669 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: S. P. Ramachandra, M. Bydder, N. Gurjar,
Congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract: A radiological review Poster No.: C-1669 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: S. P. Ramachandra, M. Bydder, N. Gurjar,
이희정. Plain Abdominal Radiography in Infants and Children. Hee Jung Lee, M.D.
 대한소아소화기영양학회지 : 제 14 권제 2 호 2011 DOI: 10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.2.130 종설 영유아및소아의단순복부 X- 선사진 계명대학교의과대학영상의학교실 이희정 Plain Abdominal Radiography in Infants and Children Hee Jung Lee, M.D. Department of Radiology,
대한소아소화기영양학회지 : 제 14 권제 2 호 2011 DOI: 10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.2.130 종설 영유아및소아의단순복부 X- 선사진 계명대학교의과대학영상의학교실 이희정 Plain Abdominal Radiography in Infants and Children Hee Jung Lee, M.D. Department of Radiology,
LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL
 SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
Human Anatomy rectum
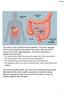 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
NEC- What Lies Under the Big Umbrella?
 NEC- What Lies Under the Big Umbrella? Instructor in Surgery Associate Surgical Director, Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation Department of Surgery, Boston Children's Hospital Harvard Medical
NEC- What Lies Under the Big Umbrella? Instructor in Surgery Associate Surgical Director, Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation Department of Surgery, Boston Children's Hospital Harvard Medical
Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
ONE of the most severe complications of diverticulitis of the sigmoid
 CLEVELAND CLINIC QUARTERLY Copyright 1970 by The Cleveland Clinic Foundation Volume 37, July 1970 Printed in U.S.A. Colonic diverticulitis with perforation to region of left hip: a rare complication Report
CLEVELAND CLINIC QUARTERLY Copyright 1970 by The Cleveland Clinic Foundation Volume 37, July 1970 Printed in U.S.A. Colonic diverticulitis with perforation to region of left hip: a rare complication Report
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal pneumatosis coli a mild form of classical necrotizing enterocolitis?
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal pneumatosis coli a mild form of classical necrotizing enterocolitis? August 2008 2 Steurer M, Stocker M, Caduff JH, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (SM,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal pneumatosis coli a mild form of classical necrotizing enterocolitis? August 2008 2 Steurer M, Stocker M, Caduff JH, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (SM,
... Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment.
 Definition Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment. " Epidemiology Humans represent the main reservoir of Clostridium difficile, which is not part of the
Definition Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment. " Epidemiology Humans represent the main reservoir of Clostridium difficile, which is not part of the
No Disclosures. Approach to Abdominal Radiographs
 Approach to Abdominal Radiographs Tapas K. Tejura, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology Keck Medical Center of USC tapas.tejura@med.usc.edu No Disclosures 34-year-old male with acute abdominal
Approach to Abdominal Radiographs Tapas K. Tejura, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology Keck Medical Center of USC tapas.tejura@med.usc.edu No Disclosures 34-year-old male with acute abdominal
This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus).
 THE COLON This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus). 3 4 5 This part is responsible for formation of stool. The large intestine (colon- coloured
THE COLON This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus). 3 4 5 This part is responsible for formation of stool. The large intestine (colon- coloured
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis?
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis? June 2004 2 Stocker M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis? June 2004 2 Stocker M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology. Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update
 Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
National Museum of Health and Medicine
 National Museum of Health and Medicine Otis Historical Archives Bower Photograph Collection Date of Records: 1910s-1920s Size: 1 box Finding Aid: by Eric W. Boyle (2012) Biographical Note: Col. Morris
National Museum of Health and Medicine Otis Historical Archives Bower Photograph Collection Date of Records: 1910s-1920s Size: 1 box Finding Aid: by Eric W. Boyle (2012) Biographical Note: Col. Morris
Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases
 Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases Hsiu-Po Wang Department of Emergency Medicine National Taiwan University Hospital Real-time ultrasound has become a standard
Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases Hsiu-Po Wang Department of Emergency Medicine National Taiwan University Hospital Real-time ultrasound has become a standard
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions
 Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions Miah MAY Introduction In our day to day practice we have to face many of the acute abdominal conditions. As we know acute abdomen
Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions Miah MAY Introduction In our day to day practice we have to face many of the acute abdominal conditions. As we know acute abdomen
LONG TERM FOLLOW-UP OF HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE: REVIEW OF EARLY AND LATE COMPLICATIONS. S. Agarwala, V. Bhatnagar and D.K. Mitra
 Original Articles LONG TERM FOLLOW-UP OF HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE: REVIEW OF EARLY AND LATE COMPLICATIONS S. Agarwala, V. Bhatnagar and D.K. Mitra From the Department of Pediatric Surgery, All India Institute
Original Articles LONG TERM FOLLOW-UP OF HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE: REVIEW OF EARLY AND LATE COMPLICATIONS S. Agarwala, V. Bhatnagar and D.K. Mitra From the Department of Pediatric Surgery, All India Institute
Hirschsprung's disease
 Postgrad. med. J. (March 1967) 43, 135-140. Hirschsprung's disease REGINALD CARPENTER F.R.C.S. Department of Surgery, University College Hospital of the West Indies, Jamaica Introduction The first description
Postgrad. med. J. (March 1967) 43, 135-140. Hirschsprung's disease REGINALD CARPENTER F.R.C.S. Department of Surgery, University College Hospital of the West Indies, Jamaica Introduction The first description
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM SURGICAL PROCEDURES December 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 2016) INTESTINES (EXCEPT RECTUM) Asst Surg Anae
 December 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) INTESTINES (EXCEPT RECTUM) Z513 Hydrostatic - Pneumatic dilatation of colon stricture(s) through colonoscope... 10.50 Z50 Fulguration of first polyp through colonoscope...
December 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) INTESTINES (EXCEPT RECTUM) Z513 Hydrostatic - Pneumatic dilatation of colon stricture(s) through colonoscope... 10.50 Z50 Fulguration of first polyp through colonoscope...
Radiology. Gastrointestinal. Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact. Farooq P. Agha
 Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE*
 RESULTS WITH ABDOMINAL RESECTION IN HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE* BY F. REHBEIN and H. VON ZIMMERMANN From the Surgical Department of the Children's Hospital, Bremen For six years we have been practising abdominal
RESULTS WITH ABDOMINAL RESECTION IN HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE* BY F. REHBEIN and H. VON ZIMMERMANN From the Surgical Department of the Children's Hospital, Bremen For six years we have been practising abdominal
Adult Intussusception
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 3, September 2005 Adult Intussusception Suhair Alsaad, MBCHB, CABS, FRCSI* Mariam Al-Muftah, MBCHB** Objectives: Adult intussusception is a rare entity. We present
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 3, September 2005 Adult Intussusception Suhair Alsaad, MBCHB, CABS, FRCSI* Mariam Al-Muftah, MBCHB** Objectives: Adult intussusception is a rare entity. We present
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Residents Section Pattern of the Month
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Krajewski et al. olonic Dilation Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Katherine Krajewski 1 ettina Siewert Ronald L. Eisenberg Krajewski K,
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Krajewski et al. olonic Dilation Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Katherine Krajewski 1 ettina Siewert Ronald L. Eisenberg Krajewski K,
Wessex Care Pathway for Term Infants Referred with Bilious Vomiting for Exclusion of Malrotation
 Wessex Care Pathway for Term Infants Referred with Bilious Vomiting for Exclusion of Malrotation Version: 1.3 Issued: Review date: Author: Melanie Drewett The procedural aspects of this guideline can be
Wessex Care Pathway for Term Infants Referred with Bilious Vomiting for Exclusion of Malrotation Version: 1.3 Issued: Review date: Author: Melanie Drewett The procedural aspects of this guideline can be
Hepatic Portal Venous Gas: An Ominous Sign Of Abdominal Catastrophe In A Blunt Abdominal Trauma Scenario. A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 25 Number 1 Hepatic Portal Venous Gas: An Ominous Sign Of Abdominal Catastrophe In A Blunt Abdominal Trauma D BV, B P., S P., S BP., S B. Citation D BV,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 25 Number 1 Hepatic Portal Venous Gas: An Ominous Sign Of Abdominal Catastrophe In A Blunt Abdominal Trauma D BV, B P., S P., S BP., S B. Citation D BV,
Gastrointestinal Pathology. August 2007
 Gastrointestinal Pathology August 2007 Case 1 Dysphagia and halitosis Case 1 Dilatation of the oesophagus with a smooth narrowing of its lower end. The large volume of contained fluid indicates delayed
Gastrointestinal Pathology August 2007 Case 1 Dysphagia and halitosis Case 1 Dilatation of the oesophagus with a smooth narrowing of its lower end. The large volume of contained fluid indicates delayed
Abdominal Manifestations of Cystic Fibrosis in Children: Report of 50 cases
 Abdominal Manifestations of Cystic Fibrosis in Children: Report of 50 cases Poster No.: C-2070 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: B. Iturre Salinas 1, A. Gozalo García 2, N. Martinez
Abdominal Manifestations of Cystic Fibrosis in Children: Report of 50 cases Poster No.: C-2070 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: B. Iturre Salinas 1, A. Gozalo García 2, N. Martinez
Different Surgical Techniques in Management of Small Intestinal Atresia in High Risk Neonates
 Annals of Pediatric Surgery Vol 5, No 1, January 2009, PP 31-35 Original Article Different Surgical Techniques in Management of Small Intestinal Atresia in High Risk Neonates Almoutaz A. Eltayeb Pediatric
Annals of Pediatric Surgery Vol 5, No 1, January 2009, PP 31-35 Original Article Different Surgical Techniques in Management of Small Intestinal Atresia in High Risk Neonates Almoutaz A. Eltayeb Pediatric
Roundtable Presentation Hirschsprung s Disease
 Roundtable Presentation Hirschsprung s Disease Disclosure Information There were no financial interests or relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose for any of the Hirschsprung s Disease roundtable
Roundtable Presentation Hirschsprung s Disease Disclosure Information There were no financial interests or relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose for any of the Hirschsprung s Disease roundtable
MORTALITY RISK FACTORS FOR NEONATAL INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION
 Basrah Journal Of Surgery MORTALITY RISK FACTORS FOR NEONATAL INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION Haithem Hussein Ali Almoamin MB, ChB, FIBMS Pediatric Surgery, Lecturer, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine,
Basrah Journal Of Surgery MORTALITY RISK FACTORS FOR NEONATAL INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION Haithem Hussein Ali Almoamin MB, ChB, FIBMS Pediatric Surgery, Lecturer, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine,
SOUTHERN WEST MIDLANDS NEWBORN NETWORK
 SOUTHERN WEST MIDLANDS NEWBORN NETWORK Hereford, Worcester, Birmingham, Sandwell & Solihull Title : Person Responsible for Review : Management of Gastro-Intestinal Stomata In Neonates R. Wragg & G.Jawaheer
SOUTHERN WEST MIDLANDS NEWBORN NETWORK Hereford, Worcester, Birmingham, Sandwell & Solihull Title : Person Responsible for Review : Management of Gastro-Intestinal Stomata In Neonates R. Wragg & G.Jawaheer
Hirschsprung's Disease: a Comparison of Swenson's and Soave's Pull-through Methods
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: Iraqi_jms_alnahrain@yahoo.com http://www. colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Hirschsprung's Disease: a Comparison of Swenson's and Soave's
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: Iraqi_jms_alnahrain@yahoo.com http://www. colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Hirschsprung's Disease: a Comparison of Swenson's and Soave's
Clinical Characteristics and Management of Benign Transient Non-Organic Ileus of Neonates: A Single-Center Experience
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.157 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 55(1):157-161, 2014 Clinical Characteristics and Management of Benign Transient Non-Organic
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.157 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 55(1):157-161, 2014 Clinical Characteristics and Management of Benign Transient Non-Organic
Topics for discussion. Pediatric General Surgery. Physiology. Surgical Newborns. Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction
 Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Nursing Principles & Skills II. Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction
 Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學
 Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
CEA (CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN)
 (CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN) 428 C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus C15.5 Malignant neoplasm of lower third of esophagus C15.8 Malignant
(CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN) 428 C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus C15.5 Malignant neoplasm of lower third of esophagus C15.8 Malignant
Gastrointestinal obstruction Dr Iain Lawrie
 Gastrointestinal obstruction Dr Iain Lawrie Consultant and Honorary Clinical Senior Lecturer in Palliative Medicine The Pennine Acute Hospitals NHS Trust / The University of Manchester iain.lawrie@pat.nhs.uk
Gastrointestinal obstruction Dr Iain Lawrie Consultant and Honorary Clinical Senior Lecturer in Palliative Medicine The Pennine Acute Hospitals NHS Trust / The University of Manchester iain.lawrie@pat.nhs.uk
Imaging Children with Acute Abdominal Pain -- Role/Protocols of US, CT, MR
 Imaging Children with Acute Abdominal Pain -- Role/Protocols of US, CT, MR Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Emory University Financial disclosures: AIM (American Imaging Management) radiation protection advisory
Imaging Children with Acute Abdominal Pain -- Role/Protocols of US, CT, MR Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Emory University Financial disclosures: AIM (American Imaging Management) radiation protection advisory
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases. Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT)
 Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Technetium-99m pertechnetate imaging in diagnosis
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 21. Technetium-99m pertechnetate imaging in diagnosis of Meckel's diverticulum JOHN C. LEONIDAS and DONALD R. GERMANN From the Departments of Radiology, Children's
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 21. Technetium-99m pertechnetate imaging in diagnosis of Meckel's diverticulum JOHN C. LEONIDAS and DONALD R. GERMANN From the Departments of Radiology, Children's
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
Two Lesser Known but Useful Signs of Neonatal Pneumothorax
 Two Lesser Known but Useful Signs of Neonatal Pneumothorax LEONARD E. SWISCHUK1 Two lesser known signs of neonatal pneumothorax are presented : the large, hyperlucent hemithorax sign and the medial stripe
Two Lesser Known but Useful Signs of Neonatal Pneumothorax LEONARD E. SWISCHUK1 Two lesser known signs of neonatal pneumothorax are presented : the large, hyperlucent hemithorax sign and the medial stripe
The Case Begins. The case continued. Necrotizing Enterocolitis
 Bugs, Drugs and Things that go Bump in the Night From ghoulies to ghosties and long leggety beasties & things that go bump in the night, good lord deliver us Old Cornish Prayer Caring for premature infant
Bugs, Drugs and Things that go Bump in the Night From ghoulies to ghosties and long leggety beasties & things that go bump in the night, good lord deliver us Old Cornish Prayer Caring for premature infant
NEC. cathy e. shin childrens hospital los angeles department of surgery university of southern california keck school of medicine
 NEC cathy e. shin childrens hospital los angeles department of surgery university of southern california keck school of medicine Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) the most common and most lethal disease
NEC cathy e. shin childrens hospital los angeles department of surgery university of southern california keck school of medicine Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) the most common and most lethal disease
The Alimentary System
 The Alimentary System Contrast Medium: 1. Barium Examinations of different parts of the GI tract require different densities of Barium suspension. The escape of Barium into the peritoneal cavity is extremely
The Alimentary System Contrast Medium: 1. Barium Examinations of different parts of the GI tract require different densities of Barium suspension. The escape of Barium into the peritoneal cavity is extremely
