Diagnostic Aspects of Neonatal Ascites: Report of 27 Cases
|
|
|
- Alexandrina Gilmore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diagnostic Aspects of Neonatal Ascites: Report of 27 Cases N. THORNE GRISCOM, ARNOLD H. COLODNY,2 HENRIETTA K. ROSENBERG, CHRISTIAN P. FLIEGEL, BRIAN E. HARDY2 Review of 27 cases of massive ascites found in the first month of life. usually immediately after delivery. revealed a broad spectrum of causes. Seven newborns had urinary ascites. five had bowel disease. three had cardiac arrhythmias, two had liver disease. and one each had toxoplasmosis, ovarian cyst, and chylous ascites. In seven cases the cause was never established. Physical examination. a planned sequence of radiologic examinations, and paracentesis for fluid analysis when necessary are the major steps in differential diagnosis. A systematic approach to the problem is proposed. The discovery of ascites in a newborn startles obstetrician, pediatrician. radiologist, and surgeon alike. The causes are many, although nearly all reports on the subject are based on only one or two cases. This review of 27 live-born neonates with massive ascites suggests the approximate frequency and characteristics of the various causes. A systematic diagnostic approach to a newborn in whom ascites is suspected is proposed. Case Material and Findings The salient features of the 27 cases are presented in table 1. The cases are divided into urinary gastrointestinal [9, 101. cardiac 11 1, 121. hepatic systemic infectious , chylous , and ovarian [2] categories, plus a group of cases of indeterminate cause [26]. The infants were referred for care to Children s Hospital Medical Center. (24 patients), were born at the Boston Hospital for Women (10 patients), or both. Abdominal distension was discovered at birth in 24 cases, and later in the first month in the three others. The two newborns with posterior urethral valves were boys, but four of the other five cases of urinary ascites occurred in girls. The children with cardiac and hepatic ascites were all boys. Five of the seven cases of ascites of unknown cause occurred in girls. Except in the child with familial cirrhosis, the family histories were not helpful. The five examples of gastrointestinal ascites were selected from a far larger group of newborns with peritonitis due to clear-cut or suspected perforation of the bowel, mostly with obstruction [9, 271. In these five, however, the initial presentation was that of ascites without good preoperative clinical or radiologic evidence of obstruction (figs. 1 and 2); thus they are included as part of the spectrum of neonatal ascites. None had a pneumoperitoneum, distinct gaseous distension of bowel, or an intestinal or peritoneal pseudocyst [271. Seven of these 27 infants had some degree of edema of the extremities or abdominal wall, including two of the three cases of cardiogenic ascites. In each case ascites was the dominant finding, and in no case was it clear on presentation that the ascites was of circulatory etiology; these cases are therefore also included in the description of neonatal ascites. Infants with erythroblastosis fetalis and other types of hydrops fetalis 1281 were excluded. The peritoneal fluid was readily displayed by radiographs. In eight of the 23 patients with available plain films of the abdomen, the liver was visible (at least in retrospect) within the slightly more lucent abdominal fluid, and this excellent sign of ascites was questionably present on the plain films of three others (fig. 3) 129, 531. Thin, clear ascitic fluid tended to be lucent by x-ray, whereas the cloudy or bloody collections were not. Our fragmentary data do not show a correlation between lucency and low specific gravity; however, it is evident that lucency of peritoneal fluid is far from pathognomonic of chylous ascites Most of the cases showed the other plain film signs of ascites 130, 31 1, often with striking clarity (figs. 1-3). During the total body opacification phase of intravenous urography 1321, the fluid contrasted with the denser liver in 13 of 17 cases (figs. 4-6). Although the presence of ascites was thus easily confirmed, finding its cause was often more difficult. Cystography and intravenous urography were quite useful in defining urinary ascites and its pathogenesis (figs. 7-10). Two children showed contrast leakage from one or both kidneys (figs. 8 and 9) [341, and one girl displayed leakage through a bladder perforation (fig. 10) 15, Total body opacification showed the avascular nature of the ovarian cyst (fig. 6). Chest films demonstrated cardiomegaly in all three cases of cardiogenic ascites but also in three of the seven cases of ascites of unknown cause. Other imaging techniques were not used systematically. A barium enema easily showed the one instance of malrotation. In another patient, a peritoneogram (fig. 7A) provided excellent demonstration of the ascites but otherwise advanced the diagnostic process only slightly. Cardiac catheterization and angiocardiography were used to show the disordered physiology in two of the three infants with arrhythmias. An aortogram via the umbilical artery 1371 Received November 17, 1976; accepted after revision February Department of Radiology. Children s Hospital Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts Address reprint requests to N T. Griscom 2 Department of Surgery. Children s Hospital Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts Present address: Department of Radiology. Children s Hospital of Philadelphia. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Present address: Department of Radiology. Children s Hospital. CH-4000 Basel 5. Switzerland Am J Roentgeno/ 128: June
2 962 GRISCOM ET AL. TABLE 1 Summary of Cases Differences of Peritoneal Fluid from Category and Case No. Delivery vomiting Edema Mass Tissue Fluid #{149} Cause of Ascites Follow.up Data Urinary: 1 (fig.7) Dystocia 2(fig.8) 3 Oligohydramnios; dystocia 4(fig. 10) 5 7(fig.5) Gastrointestinal: (fig.9) 9(fig. 1) 11 12(fig.2) Cardiac: 13(fig.3) Polyhydramnios Polyhydramnios 14 Polyhydramnios 15 Hepatic: (fig.4) Systemic 18 Chylous: 19 Ovarian: 20 (fig. 6) infectious: - - Enlarged kidneys and bladder Enlarged bladder ?Central Brown abdominal mass - - Hepato- Serosanguinous and splenomegaly Polyhydramnios, dystocia Indeterminate: Dystocia Bowel contents Ileal atresia, perforation - - Thin meconium Ileal perforation,?cause Dark brown Cloudy yellow - ++ Hepatomegaly - ++ Hepatomegaly Hepatoand splenomegaly Milky - Left upper quadrant mass - Posterior urethral valves - Posterior urethral valves - Urethral, anal atresia, perforated bladder - Bladder perforation,?cause - Bladder perforation,?cause -.. Neurogenic bladder, myelocele, reflux - Reflux,?neurogenic bladder Ileal volvulus, perforation ?Infectious,??rubella Serosanguinous?Infectious Ileal duplication, perforation Well, age 26 months Malrotation, volvulus, ischemia Well, age 8 - Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Wolff-Parkinson-White phenomenon -.. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia -.. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia - Familial cirrhosis - Probable hepatitis Toxoplasmosis Lymphatic leak, base of mesentery Light brown Ovarian cyst, torsion, local rupture?infectious Doing well, age 6 Renal failure, age 1 3 Died Well, age 10 Died at 7 days Died at 3 months Microcephaly, age 8 Died at 10 weeks Well, age 4 Cystic fibrosis; died at 9 days Negative laparotomy; well, age 1 5 months Well, age 3 Well, age 1 Died at 8 days; small liver Borderline liver tests, age 7 Died at 1 days Well, age 11 months Well, age S Squint, retarded, age 4 Nonspecific autopsy at 4 weeks Ascites disappeared; tuberous sclerosis. age 3
3 NEONATAL ASCITES 963 TABLE 1 (Continued) Category and Case No Delivery Vomitin g Edema Mass Differences Peritoneal Fluid Tissue Fluid of from #{149} Cause of Ascites Follow-up Data 24 Polyhydramnios Unknown Nonspecific autopsy at 1 day Unknown Nonspecific autopsy at 1 day 26 Dystocia Unknown Ascites disappeared; well, age 2 months Unknown Ascites disappeared; well, age 4 Note.-Ascites was found at birth in all cases except from the authors. Case 3 [1]; case 20 [2] Minus sign indicates no differences found k... :Fg. 1..T-: Case. Upright anteroposteriof age showing no indication of intestinal obstruction. Plaques and lumps of peritoneal calcification are present (arrows). Laparotomy showed large quantity of thin green peritoneal fluid, collapse of small bowel, and ileal perforation of unknown cause, leading to meconium peritonitis. Cystic fibrosis was never tested for, but child was well at age 4. and 12 where it was found at 23. 7, and 4 days. respectively. Further details on all cases available Fig. 2.-Case 12. Upright anteroposterior film of abdomen in 4-dayold child with abdominal distension and a few hours of vomiting. Film suggests that bowel, though abnormal, does not account for abdominal dis tension and that ascites is present. Malrotation of midgut. a 7200 volvulus. ischemia of bowel without perforation or appreciable dilatation, and large quantity of cloudy yellow culturenegative fluid were found at laparotomy. showed a small liver and copious ascites in the child with intestines in the case of hepatitis. cirrhosis, but ultrasonography would probably have been However, radiologic techniques often gave only a a better method. Ultrasound was useful in excluding a partial answer to the question of etiology. Most of the mesenteric cyst or some other gross lymphatic abnor- infants had some type of chemical, bacteriologic, or cytomality in the child with chylous ascites and would probably logic examination of the ascitic fluid, sometimes quite have been informative in other cases. A 131l,rose bengal extensive. Table 1 lists only those characteristics of diagliver scan showed failure of passage of bile into the nostic usefulness. The most worthwhile determinations
4 964 GRISCOM ET AL. Fig. 3 -Case 13. Plain film of abdomen showing contrast of liver (arrows) with ascitic fluid Gas-containing bowel has risen to center of distended abdomen Child had episodes of supraventricular tachycardia in first few weeks of life, ascites attributed to intrauterine paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia Fig 5 -Case 7 Anteroposterior film of abdomen several minutes after injection for urography. Right lobe of liver (arrows) contrasts with.,:-. peritoneal fluid by total body opacification effect as well as by its inherent radiodensity.; Fig 4 -Case 17. Recumbent anterioposterior view of abdomen on first day of life 10 mm after intravenous injection of 15 ml Renografin 60. Arrows mark interface between liver. opacified by circulating iodine Liver biopsy suggested hepatitis..41c -. Fig. 6.-Case 20. Left posterior oblique film of abdomen at several hours of age 2 mm after intravenous injection for urography, 400 ml of peritoneal fluid already removed. Open arrows indicate left lobe of liver, opaque against avascular ascitic fluid Laparotomy showed more fluid (50 ml) and twisted left ovarian cyst (giant corpus luteum, closed arrows). Lucency in center of mass indicates avascularity: specimen showed central hemorrhage and necrosis and apparently had ruptured locally Other films published in [2]
5 NEONATAL ASCITES 965 F I I, C.. were the gross appearance of the fluid and the presence or absence of white and red blood cells. In the four children with intestinal perforation (fig. 1), the peritoneal fluid was highly abnormal and quite unlike tissue fluid. As the bleeding disorder of the girl with toxoplasmosis became more severe, the fluid became bloody. The fluid of the child with chylous ascites became milky after feedings were begun. However, peritoneal fluid tends to reach obstruction. Our series also fails to show the expected predominance of posterior urethral valves among causes of urinary ascites. Only two of the seven cases of urinary ascites were shown to be caused by valves. Furthermore, these two children were the only two cases of ascites among 27 neonates with hydronephrosis due to valves seen at this hospital Although ureteropelvic obstruction appears to be the leading cause of neonatal hydronephrosis no case of, I
6 966 GRISCOM ET AL. urinary ascites due to this type of obstruction occurred in our series or was found in an incomplete review of the literature. The obstructions leading to ascites all occurred in the urethra, bladder, or distal ureter, even though the actual leak may have been in the kidney (figs. 8 and 9). In seven of the 27 newborns the cause of the ascites was never established despite many diagnostic tests, nor did we know which organ system was at fault. In the three fatal cases, autopsies were unrevealing; in the other four the ascites spontaneously disappeared. Perhaps in some the ascites was caused by systemic infection present at birth, but this was not verified by culture, serologic studies, or convincing findings at autopsy. One of the four survivors is mentally slow and may have had congenital rubella; another recovered completely from her abdominal problems but was later found to have tuberous sclerosis, presumably an unrelated illness. The third and fourth seemed quite well at the age of 2 months and 4 years, respectively. Two other cases of spontaneously remitting benign neonatal ascites of unknown cause have recently been reported [26]. Presumably these 27 cases are reasonably representative of ascites as it is found in live-born infants on active delivery and newborn referral services. Causes of neonatal ascites not found in the present series are listed in table 2. A thorough review of the related subject of hydrops
7 TABLE 2 Causes of Neonatal Ascites Not Found in This Series 1 Fig Case 6 Cystogram of girl born with myelomeningocele (small arrow) and ascites. Intravenous urography performed earlier in day showed bilateral hydronephrosis and passage of contrast material into right subcapsular space. Note bilateral reflux (worse on left) nd passage of contrast material into right s.bcapsular space (large arrows) Artifact above left kidney is opaque pact protecting myelomeningocele. which caused hydrocephalus and death at 3 months of age - _ - I Cause Reference Urinary: Ureterocele [3, 42] Bladder neck obstruction [6] Urethral stricture [3. 34] Pelvic neuroblastoma, bladder perforation [6. 36] Congenital nephrosis [43] Ureteric stenosis [44] Renal vein thrombosis [ ]t Gastrointestinal: Appendicitis, perforation [10] Perforation of Meckel s diverticulum [45] Imperforate anus [46] Cardiac and circulatory: Hypoplastic left heart syndrome [12] Hypoproteinemia [4O]t Many other cardiac and circulatory diseases, #{149} especially including erythroblastosis fetalis [ ]t Portohepatic: Polycystic disease of the liver [14] Meckel-Gruber syndrome, liver cysts [47] Biliary atresia [48] Common duct perforation [49] Portal vein obstruction, hypoplasia [4O.t 48.t SO] Galactosemia Systemic infectious: [4O]t Cytomegalovirus infection [21] Syphilis [17] Sepsis [3] Leptospirosis Chagas s disease [28]t Chylous: Constricting peritoneal band [23] Occlusion or stenosis of thoracic duct [22]t Genital: Hydrometrocolpos, imperforate anus [SO] Others. some of indeterminate cause [1 2, 28]t #{149} Coexisting with hydrops fetalis. t Listings only fetalis (fluid accumulation throughout the tissues and body cavities of a fetus or newborn infant) is given by Driscoll [28]. A diagnostic approach to a newborn suspected of having ascites is outlined in figure 1 1. Plain films will usually distinguish ascites from ordinary intestinal obstruction and from undetected tumors. If the plain films indicate ascites and the child is critically ill, paracentesis should probably be performed next rather than cystography and intravenous urography, both for relief of respiratory cornpromise and for diagnosis. If the peritoneal fluid resembles intestinal contents, laparotomy for repair of bowel perforation is urgently necessary. If the fluid is hemorrhagic. consideration should be given to rupture of a solid viscus [51, 521, to toxoplasmosis or some other hemorrhagic disorder, or to rupture of an ovarian cyst. If the fluid resembles serum, cystography and intravenous urography should be performed. [28]t
8 968 GRISCOM ET AL. NEWBORN, ABDOMINAL DISTENSION, NO PALPABLE MASS, NOT VOMiTING, DISTENSION MORE IMPRESSWE THAN ANY FLUID ACCUMULATION ELSEWHERE recumbent AP, upright AP, and lateral films of abdomen gaseous dilatation of bowel or solid mass, shown by tumor distension accounted for by neither pneumoperitoneum (intestinal calcification or bowel of those, apparently representing obstruction or perforation) displacement ascites yes laparotomy, for bowel perforation consider ovarian cyst, ruptured solid viscus, hemorrhagic disorder as in toxoplasmosis peritoneal /\ calcification? yes no / meconium peritonitis cystography intravenous sweat test normal urinary tract abnormal electrocardiogram, cardiomegaly by chest film, or both no abnormal (urinary appropriate urography consider systemic infectious and paracentesis for fluid inspection, hematocrit, white cell count, presence cardiac causes of ascites of chyle if baby has been given milk, culture fluid resembles bowel contents hemorrhagic but not chylous resembles serum resembling bowel contents A few differential diagnostic points follow which are not conveniently presented in flow chart form. (1 ) If a large bladder or a myelomeningocele is present, the ascites is probably urinary. (2) If vomiting occurs or if bowel loops are abnormal even though not distended, gastrointestinal causes are likely. (3) If there is impressive peripheral or body wall edema, consider infection, heart disease, liver disease, erythroblastosis, and other causes of hydrops fetalis [281. (4) If hepatomegaly is present, infectious, cardiac, and hepatic causes of ascites become more likely. Ultrasonography has yet to define its place in this diagnostic scheme; presumably it will be found very useful. Circumstances will frequently demand modification of the approach suggested in figure 1 1. However, passage of the data from the present series through the proposed system indicates that it is a reasonably efficient diagnostic plan. The use of such an approach will occasionally prevent needless laparotomy. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thank Drs. Shirley Driscoll, John Kirkpatrick, Robert Lebowitz, and Michael Oxman for comments on this report and Ms. Andrea Kelton for superlative secretarial assistance. Fig Flow chart illustrating proposed diagnostic approach. ascites) surgery barium studies, liver function tests; ultrasound for acute phase titers; mesenteric cyst, review entire situation; lymphangioma, consider hepatogenic malrotation; ascites, infectious consider ascttes, benign ascites exploration REFERENCES 1. Syrnonds DA, Driscoll SG: Massive fetal ascites, urethral atresia, and cytomegalic inclusion disease. Am J Dis Child 127: , Carlson DH, Griscom NT: Ovarian cysts in the newborn. Am J Roentgenol 1 16: , Cremin BJ: Urinary ascites and obstructive uropathy. Br J Radiol48: , Dockray KT: Preferred treatment for urinary ascites in newborns. J Urol 1 1 2: Howat JM: Urinary ascites complicating spina bifida. Arch Dis Child46:1O3-1OS, Mann CM, Leape LL, Holder TM: Neonatal urinary ascites: a report of two cases of unusual etiology and a review of the literature. J Urol : , McDonald J. Murphy AV: Neonatal ascites from spontaneous rupture of the bladder. Arch Dis Child 50: , 197S 8. Parker AM: Neonatal urinary ascites: a potentially favorable sign in bladder outlet obstruction. Urology 3: , Birtch AG, Coran AG, Gross RE: Neonatal peritonitis. Surgery 61 : , Nilforoushan MA: Fever and ascites in a newborn. Cl/n
9 NEONATAL ASCITES 969 Ped/atr(Phila) 14:878, Cowan RH, Waldo AL, Harris HB, Cassady G. Brans YW: Neonatal paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia with hydrops. Ped/atr/cs 55: , 197S 12. Leake RD. Strimling B, Emmanouilides GC: Intrauterine cardiac failure with hydrops fetalis. Clln Pediatr (Phila) 12: , Bellin LB. Bailit 1W: Congenital cirrhosis of the liver associated with infectious hepatitis of pregnancy. J Ped/atr 40:60-63, Ehrlich JC, Goodfriend MJ, Shinohara Y, Seki M: Fetal ascites and portal dysplasia of the liver (polycystic disease without cysts). Ped/atrics 33: , Fletcher CB, Eakin EL, Rothman PE: Fetal ascites-liver giant-cell transformation. Am J D/s Child 108: , Thaler MM: Fatal neonatal cirrhosis, entity or end result? Pediatrics 33: , Aziz EM: Fetal ascites secondary to congenital syphilis. South MedJ67:81-84, Bain AD, Bowie JH, Flint WF, Beverley JKA, Beattie CP: Congenital toxoplasmosis simulating hemolytic disease of the newborn. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 63: Couvreur J, Desmonts G: Congenital and maternal toxoplasmosis, a review of 300 congenital cases. Dev Med Child Neurol4: , Embil JA, Krause VW, Haldane EV, Easterbrook KB, Crosby JM: Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: clinical, pathological, and virological studies of two fatal cases. Can Med AssocJ 101: , Frank DJ, DeVaux WD, Perkins JR. Perrin EV: Fetal ascites and cytomegalic inclusion disease. Am J Dis Child 112: , Gribetz D, Kanof A: Chylous ascites in infancy. Pediatrics 7: , GrossJl, Goldenberg ye, Humphreys EM: Venous remnants producing neonatal chylous ascites. Pediatrics 27: , Sanchez RE, Mahour GH, Brennan LP, Woolley MM: Chylous ascites in children. Surgery 69: , Wyatt GM, Gross RE: Chylous ascites: roentgenological observations from a case in infancy. Am J Roentgenol 45: , Bryan EM: Benign fetal ascites associated with maternal hydramnios. Cl/n Pediatr (Phila) 14:88-91, 197S 27. Effmann EL, Griscom NT, Colodny AH, Vawter G: Pseudocysts of bowel and peritoneum associated with neonatal intestinal obstruction. In preparation 28. Driscoll SG: Current concepts: hydrops fetalis. N Engl J Med 275: , Proto AV, Lane EJ: Visualization of differences in softtissue densities: the liver in ascites. Radiology 121:19-23, Franken EA Jr: Ascites in infants and children, roentgen diagnosis. Radiology 102: , Proto AV, Lane EJ. Marangola JP: A new concept of ascitic fluid distribution. Am J Roentgenol 126: , Martin DJ, Griscom NT, Neuhauser EBD: A further look at the total body opacification effect. Br J Radiol 4:18-192, Griscom NT, Cochran WC, Harris GBC. Easterday CL, Umansky I, Frigoletto FD: The processus vaginalis of the third trimester fetus. Radiology 96: , Moncada R, Wang JJ, Love L. Bush I: Neonatal ascites associated with urinary outlet obstruction (urine ascites). Radiology 90: , Leonidas JC, Leiter E, Gribetz D: Congenital urinary tract obstruction presenting with ascites at birth. Radiology 96: Weller MH. Miller K: Unusual aspects of urine ascites. Radiology 109: , Lindstrom A, Gyepes MT: Aortography through the umbilical artery in the newborn, Angiography in Infants and Children, edited by Gyepes MT. New York. Grune & Stratton, 1974, pp Winestock D, Macpherson RI: Neonatal ascites, a case for diagnosis. J Can Assoc Radiol 22: , Cywes S. Wynne JM, Louw JH: Urinary ascites in the newborn, with a report of two cases. J Pediatr Surg 3: , Mustard WT. Aavitch MM, Snyder WH, Welch KJ, Benson CD: Pediatric Surgery, 2d ed. Chicago. Year Book Medical Publishers, Lebowitz AL. Griscom NT: Neonatal hydronephrosis. 146 cases. Radiol Clin North Am. In press, North AF Jr. Eldridge DM. Talpey WB: Abdominal distention at birth due to ascites associated with obstructive uropathy. AmJDis Child 111: , Hallman N, Norio A, Rapola J: Congenital nephrotic syndrome. Nephron 11: , Linde NC: Neonatal ascites and urinary tract obstruction. Acta Paediatr Scand 55: , Abt IA: Fetal peritonitis. Med Cl/n North Am 15: , Clayton JW, Ford AM: A case of foetal ascites. MedJ Aust 1:537, Dorland WAN: Watery accumulations in the fetal abdomen obstructing labor. Am J Obstet 79: Baghdassarian OM, Koehler PR, Schultze G: Massive neonatal ascites. Radiology 76: , Aavitch MM: Neonatal ascites. Med Times 96: , Fordyce W: Intrauterine ascites. its obstetrical significance and pathology. Teratologia 1 : Cywes S. Cremin BJ: Roentgenologic features of hemoperitoneum in the newborn. Am J Roentgenol 106: , Marquis JR. Sun SC, Verasestakul S: Rupture of the spleen in a newborn infant. Radiology 119: , Love L, Demos TC, Aeynes CJ, Williams V. Shkolnik A, Gandhi V. Zerofos N: Visualization of the lateral edge of the liver in ascites. Radiology 122: , 1977
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Urinary Ascites in Newborn A Rare Case Report
 ISSN 2231-4261 CASE REPORT Urinary Ascites in Newborn A Rare Case Report Suryakant Y. Ingale 1*, Sudhakar Jadhav 2, Kant Shah 2 1 Department of Paediatrics, Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Karad
ISSN 2231-4261 CASE REPORT Urinary Ascites in Newborn A Rare Case Report Suryakant Y. Ingale 1*, Sudhakar Jadhav 2, Kant Shah 2 1 Department of Paediatrics, Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Karad
Case MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve
 Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis?
 Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Pediatric Ure-Radiology*
 Pediatric Ure-Radiology* HERMAN GROSSMAN, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina "Routine" radiologic studies do not, often enough, concentrate
Pediatric Ure-Radiology* HERMAN GROSSMAN, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina "Routine" radiologic studies do not, often enough, concentrate
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis?
 Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. MNARI, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. MAATOUK, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. MNARI, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. MAATOUK, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success
 Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management
 Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Gastrointestinal tract
 Chapter 7 Gastrointestinal tract NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY Sonographically, the fetal stomach is visible from 9 weeks of gestation as a sonolucent cystic structure in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen.
Chapter 7 Gastrointestinal tract NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY Sonographically, the fetal stomach is visible from 9 weeks of gestation as a sonolucent cystic structure in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen.
Urinary Tract Abnormalities
 Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Case Whirlpool sign in midgut volvulus
 Case 11454 Whirlpool sign in midgut volvulus Emad El-din Althamer 1, Shagufta Jabeen 2, Nada Al-Assaf 1, Akram Jawad 1, Muhammad Hassan 1, Muhammad Fatani 1, Rumayan Al-Rumyan 1, A Aziz Mosabihi 1, Ahmeduddin
Case 11454 Whirlpool sign in midgut volvulus Emad El-din Althamer 1, Shagufta Jabeen 2, Nada Al-Assaf 1, Akram Jawad 1, Muhammad Hassan 1, Muhammad Fatani 1, Rumayan Al-Rumyan 1, A Aziz Mosabihi 1, Ahmeduddin
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students
 Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students Lesson 3: Cystography & Urethrography Part 1 American Urological Association Introduction Conventional radiography of the urinary tract includes several diagnostic
Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students Lesson 3: Cystography & Urethrography Part 1 American Urological Association Introduction Conventional radiography of the urinary tract includes several diagnostic
A STUDY ON LONGTERM OUTCOMES OF POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES
 3 Original article A STUDY ON LONGTERM OUTCOMES OF POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES Dr. Urvish R. Parikh [1], Dr Sudhir B. Chandana [], Dr Vinay M. Rohra [3],, Dr Jay B. Pandya [5], Dr Ankit B. Kothari [4] Assistant
3 Original article A STUDY ON LONGTERM OUTCOMES OF POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES Dr. Urvish R. Parikh [1], Dr Sudhir B. Chandana [], Dr Vinay M. Rohra [3],, Dr Jay B. Pandya [5], Dr Ankit B. Kothari [4] Assistant
Urinary ascites from spontaneous bladder perforation in female neonate
 Ped Urol Case Rep 2015;2(6):27-32 DOI:10.14534/PUCR.2015614087 Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Urinary ascites
Ped Urol Case Rep 2015;2(6):27-32 DOI:10.14534/PUCR.2015614087 Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Urinary ascites
Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017
 Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017 Richard I. Markowitz, MD, FACR Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania No Disclosures Cognitive Perceptual
Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017 Richard I. Markowitz, MD, FACR Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania No Disclosures Cognitive Perceptual
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus
 A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
Uroradiology For Medical Students
 Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients).
 Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. A paraurethral cyst or the mandatory peek into the diapers of newborn girls
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY A paraurethral cyst or the mandatory peek into the diapers of newborn girls November 2008 2 Minocchieri S, Kaczala GW, Messer AM, Dingeldein I, Nelle MN, Department of Pediatrics,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY A paraurethral cyst or the mandatory peek into the diapers of newborn girls November 2008 2 Minocchieri S, Kaczala GW, Messer AM, Dingeldein I, Nelle MN, Department of Pediatrics,
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION ESCAPED SURGERY: MECONIUM PLUG
 7 INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION ESCAPED SURGERY: MECONIUM PLUG Oluwayemi IO 1 *, Ade-Ojo IP 2, Olofinbiyi BA 2 1. Department of Paediatrics, Ekiti State University Teaching Hospital, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria
7 INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION ESCAPED SURGERY: MECONIUM PLUG Oluwayemi IO 1 *, Ade-Ojo IP 2, Olofinbiyi BA 2 1. Department of Paediatrics, Ekiti State University Teaching Hospital, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria
Small bowel atresia. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families
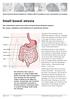 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Small bowel atresia This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the causes, symptoms and treatment
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Small bowel atresia This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the causes, symptoms and treatment
GU Ultrasound in First Trimester
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Ascites, a New Cause for Bilateral Hydronephrosis: Case Report
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 1035 1039 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.112 Ascites, a New Cause for Bilateral Hydronephrosis: Case Report D. Jain*, S. Dorairajan, and
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 1035 1039 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.112 Ascites, a New Cause for Bilateral Hydronephrosis: Case Report D. Jain*, S. Dorairajan, and
Hirschprung s. Meconium plug R/S >1 R/S <1
 NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
An Unexpected Cause Of Spontaneous Perinephric Urinoma: A Case Report. L Chandrasekharan, T Abdl Ghaffar, M Venkatramana, K Mammigatty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 An Unexpected Cause Of Spontaneous Perinephric Urinoma: A Case Report L Chandrasekharan, T Abdl Ghaffar, M Venkatramana, K Mammigatty Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 An Unexpected Cause Of Spontaneous Perinephric Urinoma: A Case Report L Chandrasekharan, T Abdl Ghaffar, M Venkatramana, K Mammigatty Citation
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Torsion of a Wandering Spleen Presenting as a Painful Pelvic Mass Post Pregnancy: Imaging Diagnosis
 CASE REPORT Torsion of a Wandering Spleen Presenting as a Painful Pelvic Mass Post Pregnancy: Imaging Diagnosis Abbey P 1, Aarushi A 1, Andley M 2, Anand R 1 1 Department of Radio-Diagnosis, 2 Department
CASE REPORT Torsion of a Wandering Spleen Presenting as a Painful Pelvic Mass Post Pregnancy: Imaging Diagnosis Abbey P 1, Aarushi A 1, Andley M 2, Anand R 1 1 Department of Radio-Diagnosis, 2 Department
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen. Jonathan Swanson, MD
 Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR) New
 Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR) New What is vesicoureteral reflux? Vesicoureteral reflux is the abnormal backflow of urine from the bladder into the ureter and up to the kidney. The majority of the time this
Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR) New What is vesicoureteral reflux? Vesicoureteral reflux is the abnormal backflow of urine from the bladder into the ureter and up to the kidney. The majority of the time this
Information for Patients
 Information for Patients Congenital Malformation in the Urinary Tract: Ureteral Duplication, Ureterocele, and Ectopic Ureter English Table of contents Ureteral Duplication... 3 Symptoms and Diagnosis...
Information for Patients Congenital Malformation in the Urinary Tract: Ureteral Duplication, Ureterocele, and Ectopic Ureter English Table of contents Ureteral Duplication... 3 Symptoms and Diagnosis...
Ultrasound Anomaly Details
 Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學
 Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Question 1 History. Likely Diagnosis Differential. Further Investigation or Management. Requires Paediatric Surgical referral for laparotomy
 Question 1 Male newborn spilling green tinged vomit day 1 of life Imaging Abdominal X-Rays performed on 03/05/2012 Upper and lower gastrointestinal contrast studies performed on 03/05/2012 Abdominal X-Rays
Question 1 Male newborn spilling green tinged vomit day 1 of life Imaging Abdominal X-Rays performed on 03/05/2012 Upper and lower gastrointestinal contrast studies performed on 03/05/2012 Abdominal X-Rays
Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help. Print this Page Add to my Bookmarks Page 3 of 10
 Welcome Kristin Ingstrup [ Logout ] SEARCH Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help Overview Editorial Board My Learning Plan January February March May June July August
Welcome Kristin Ingstrup [ Logout ] SEARCH Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help Overview Editorial Board My Learning Plan January February March May June July August
Pediatric Surgery MUHC MCH Siste. Objectives of Training
 Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Urine Blockage in Newborns
 Urine Blockage in Newborns National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract is the body s drainage system for removing wastes and extra fluid.
Urine Blockage in Newborns National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract is the body s drainage system for removing wastes and extra fluid.
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine
 The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System
 A5 Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System Erin Parilla, MD Neonatologist Pediatrix Medical Group, Tampa, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated she has no significant
A5 Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System Erin Parilla, MD Neonatologist Pediatrix Medical Group, Tampa, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated she has no significant
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis?
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis? June 2004 2 Stocker M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis? June 2004 2 Stocker M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
Obstructive Uropathy. PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO. Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta
 Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Case: Spontaneous bladder rupture presenting as sudden-onset abdominal pain in a child after many years in remission from bladder rhabdomyosarcoma
 Case: Spontaneous bladder rupture presenting as sudden-onset abdominal pain in a child after many years in remission from bladder rhabdomyosarcoma Cyrus Chehroudi; Kourosh Afshar, MD University of British
Case: Spontaneous bladder rupture presenting as sudden-onset abdominal pain in a child after many years in remission from bladder rhabdomyosarcoma Cyrus Chehroudi; Kourosh Afshar, MD University of British
Case 1307 Mesothelial cysts
 Case 1307 Mesothelial cysts Vinhais S, Monteiro M, Cunha TM INSTITUTO PORTUGUÊS DE ONCOLOGIA de Francisco Gentil de LISBOA Section: Gastro-Intestinal Imaging Published: 2001, Nov. 23 Patient: 44 year(s),
Case 1307 Mesothelial cysts Vinhais S, Monteiro M, Cunha TM INSTITUTO PORTUGUÊS DE ONCOLOGIA de Francisco Gentil de LISBOA Section: Gastro-Intestinal Imaging Published: 2001, Nov. 23 Patient: 44 year(s),
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review
 Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
PREAMBLE GENERAL DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY
 PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
Paediatric surgical emergencies. Mani Thyagarajan BWCH
 Paediatric surgical emergencies Mani Thyagarajan BWCH General points Always discuss Call consultant for help ASAP CT scan is a bad modality in paediatrics Ultrasound? Intussusception? Renal colic? UTI
Paediatric surgical emergencies Mani Thyagarajan BWCH General points Always discuss Call consultant for help ASAP CT scan is a bad modality in paediatrics Ultrasound? Intussusception? Renal colic? UTI
Hydronephrosis. Nephrosis. Refers to the kidney
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
Intrarenal reflux and the scarred kidney
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 531. Intrarenal reflux and the scarred kidney G. L. ROLLESTON, T. M. J. MALING, and C. J. HODSON* From the Department of Radiology, Christchurch Hospital and
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 531. Intrarenal reflux and the scarred kidney G. L. ROLLESTON, T. M. J. MALING, and C. J. HODSON* From the Department of Radiology, Christchurch Hospital and
Radiology. Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions
 Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US
 Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
Interpret clinical and laboratory tests to identify conditions that require surgical intervention, including:
 Pediatric Surgery Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Pediatric Surgery Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
R adio logical investigations of urinary system
 R adio logical investigations of urinary system There are 4 main radiological Ix: 1 IVU: Intravenous urography. 2- U/S 3-CT scan 4-Radioisotope scan. Others (not frequently used): MRI, arteriography, antegrade
R adio logical investigations of urinary system There are 4 main radiological Ix: 1 IVU: Intravenous urography. 2- U/S 3-CT scan 4-Radioisotope scan. Others (not frequently used): MRI, arteriography, antegrade
Body MRI from the Liver to the Bladder
 Body MRI from the Liver to the Bladder I Want You! Audience Participation Methodist Hospital Continuing Education Seminar Jordan Swensson, MD November 7, 2015 Objectives Observe the uses of MRI for organs
Body MRI from the Liver to the Bladder I Want You! Audience Participation Methodist Hospital Continuing Education Seminar Jordan Swensson, MD November 7, 2015 Objectives Observe the uses of MRI for organs
APPROACH TO ABDOMINAL MASS
 Thomas Hong APPROACH TO ABDOMINAL MASS General Presentation An abdominal mass in a neonate, young child, or adolescent patient is something that every pediatrician needs to be wary of as these masses can
Thomas Hong APPROACH TO ABDOMINAL MASS General Presentation An abdominal mass in a neonate, young child, or adolescent patient is something that every pediatrician needs to be wary of as these masses can
Perineal Sonography in Diagnosis of an Ectopic Ureteric Opening Into the Urethra
 Case Series Perineal Sonography in Diagnosis of an Ectopic Ureteric Opening Into the Urethra S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD Objective. To study the role of perineal sonography in the diagnosis of
Case Series Perineal Sonography in Diagnosis of an Ectopic Ureteric Opening Into the Urethra S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD Objective. To study the role of perineal sonography in the diagnosis of
D URING the past i8 months at this institution, infusion urography has been
 SEPTEMBER, 1975 ABSTRACT: EVALUATION OF PELVIC MASSES DURING INFUSION EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY* By THOMAS J. IMRAY, M.D. MILWAUKEE, WISCONSIN Infusion excretory urography not only clearly delineates the urinary
SEPTEMBER, 1975 ABSTRACT: EVALUATION OF PELVIC MASSES DURING INFUSION EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY* By THOMAS J. IMRAY, M.D. MILWAUKEE, WISCONSIN Infusion excretory urography not only clearly delineates the urinary
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice
 Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice Ahmed Laving KPA Annual Scientific Conference 2018 Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Case Presentation
Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice Ahmed Laving KPA Annual Scientific Conference 2018 Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Case Presentation
Non-Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction in children: 3 Years Experience and review of literature.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 52-57 www.iosrjournals.org Non-Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction in
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 52-57 www.iosrjournals.org Non-Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction in
Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings
 August 2011 Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings Omar Pardesi, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient LD: History & Physical HPI: 28 y.o. female presents with diffuse abdominal
August 2011 Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings Omar Pardesi, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient LD: History & Physical HPI: 28 y.o. female presents with diffuse abdominal
Objectives. Pediatric Mortality. Another belly pain. Gastroenteritis. Spewing & Pooing Child 4/18/16
 Gastro-tastrophies A Review of Pediatric GI Emergencies Objectives Discuss common presentations of Pediatric Abdominal Pain complaints Discuss work up and physical exam findings Discuss care, management
Gastro-tastrophies A Review of Pediatric GI Emergencies Objectives Discuss common presentations of Pediatric Abdominal Pain complaints Discuss work up and physical exam findings Discuss care, management
Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis
 27 Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis Toru Hasegawa a Koichi Yoshida b Kazuhiro Matsui c a Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toyama,
27 Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis Toru Hasegawa a Koichi Yoshida b Kazuhiro Matsui c a Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toyama,
Case Report Imperforate Hymen Causing Bilateral Hydroureteronephrosis in an Infant with Bicornuate Uterus
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 102683, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/102683 Case Report Imperforate Hymen Causing Bilateral Hydroureteronephrosis in an Infant with Bicornuate Uterus Ayse Secil
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 102683, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/102683 Case Report Imperforate Hymen Causing Bilateral Hydroureteronephrosis in an Infant with Bicornuate Uterus Ayse Secil
Wessex Care Pathway for Term Infants Referred with Bilious Vomiting for Exclusion of Malrotation
 Wessex Care Pathway for Term Infants Referred with Bilious Vomiting for Exclusion of Malrotation Version: 1.3 Issued: Review date: Author: Melanie Drewett The procedural aspects of this guideline can be
Wessex Care Pathway for Term Infants Referred with Bilious Vomiting for Exclusion of Malrotation Version: 1.3 Issued: Review date: Author: Melanie Drewett The procedural aspects of this guideline can be
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect October 2004 2 Cevey-Macherel MN, Meijboom EJ, Di Bernardo S, Truttmann AC, Division of Neonatology and Division of Pediatric
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect October 2004 2 Cevey-Macherel MN, Meijboom EJ, Di Bernardo S, Truttmann AC, Division of Neonatology and Division of Pediatric
Pelvic Pain in the Pediatric Patient Susan D. John, M.D.
 Pelvic Pain in the Pediatric Patient Susan D. John, M.D. RSNA 2012 Patients First Objectives After attending this presentation, participants will be able to: Understand the common congenital and acquired
Pelvic Pain in the Pediatric Patient Susan D. John, M.D. RSNA 2012 Patients First Objectives After attending this presentation, participants will be able to: Understand the common congenital and acquired
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE: GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING
 GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING PYLORIC STENOSIS Population: Infants: onset between 2-5 weeks of age 1 in 250 births Male: female ratio 4:1 Familial incidence History: No vomiting in the first few weeks
GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING PYLORIC STENOSIS Population: Infants: onset between 2-5 weeks of age 1 in 250 births Male: female ratio 4:1 Familial incidence History: No vomiting in the first few weeks
Fetal Urologic Anomalies
 Fetal Urologic Anomalies Kathryn Drennan, MD Elizabeth McKinney, MD MultiCare Regional Maternal-Fetal Medicine What you should know They are common Account for 15%-20% of all congenital anomalies Associated
Fetal Urologic Anomalies Kathryn Drennan, MD Elizabeth McKinney, MD MultiCare Regional Maternal-Fetal Medicine What you should know They are common Account for 15%-20% of all congenital anomalies Associated
1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive abdominal distension 3 months Failure
 Dr Rajasree S Dr Srinivas S, Dr Bagdi RK, Dr Satheesh C Apollo Childrens Hospital, Chennai 1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive
Dr Rajasree S Dr Srinivas S, Dr Bagdi RK, Dr Satheesh C Apollo Childrens Hospital, Chennai 1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Congenital omphalo-mesenteric fistula in a newborn
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Congenital omphalo-mesenteric fistula in a newborn NOVEMBER 2011 2 Dommange SJ, Lhermitte B, de Buys Roessingh A, Cachat F, Panchard MA, Department of Pediatrics (DSJ, CF,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Congenital omphalo-mesenteric fistula in a newborn NOVEMBER 2011 2 Dommange SJ, Lhermitte B, de Buys Roessingh A, Cachat F, Panchard MA, Department of Pediatrics (DSJ, CF,
The Case Begins. The case continued. Necrotizing Enterocolitis
 Bugs, Drugs and Things that go Bump in the Night From ghoulies to ghosties and long leggety beasties & things that go bump in the night, good lord deliver us Old Cornish Prayer Caring for premature infant
Bugs, Drugs and Things that go Bump in the Night From ghoulies to ghosties and long leggety beasties & things that go bump in the night, good lord deliver us Old Cornish Prayer Caring for premature infant
Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst?
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Bladder exstrophy and epispadias
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Bladder exstrophy and epispadias This leaflet explains about bladder exstrophy and epispadias and what to expect
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Bladder exstrophy and epispadias This leaflet explains about bladder exstrophy and epispadias and what to expect
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
Clinical, Diagnostic, and Operative Correlation of Acute Abdomen
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/163 Clinical, Diagnostic, and Operative Correlation of Acute Abdomen Madipeddi Venkanna 1, Doolam Srinivas 2, Budida
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/163 Clinical, Diagnostic, and Operative Correlation of Acute Abdomen Madipeddi Venkanna 1, Doolam Srinivas 2, Budida
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
Abdominal Cystic Lymphangioma in Children
 Annals of Pediatric Surgery Vol 5, No 2, April 2009, PP 132-136 Original Article Abdominal Cystic Lymphangioma in Children Hisham Fayad Aly Department of Pediatric Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University,
Annals of Pediatric Surgery Vol 5, No 2, April 2009, PP 132-136 Original Article Abdominal Cystic Lymphangioma in Children Hisham Fayad Aly Department of Pediatric Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University,
Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic
 Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic Mikael Hellström Professor Department of Radiology Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg University 0.9-1.8/1.000 inhabitants
Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic Mikael Hellström Professor Department of Radiology Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg University 0.9-1.8/1.000 inhabitants
Summary and conclusions
 Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum. Elective Student S. C.
 Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
 International Journal of Health Sciences, Qassim University, Vol. 8, No. 1 (January-March 2014) Case Report Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
International Journal of Health Sciences, Qassim University, Vol. 8, No. 1 (January-March 2014) Case Report Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
CONGENITAL ANTERIOR URETHRAL DIVERTICULUM
 CONGENITAL ANTERIOR URETHRAL DIVERTICULUM W Y Cheong, H K Cheng, K P Tan SYNOPSIS We report the first documented case in Singapore of a congenital saccular anterior urethral diverticulum causing bladder
CONGENITAL ANTERIOR URETHRAL DIVERTICULUM W Y Cheong, H K Cheng, K P Tan SYNOPSIS We report the first documented case in Singapore of a congenital saccular anterior urethral diverticulum causing bladder
Bits and Bobs secondary causes of heart problems. Dr Angela McBrien 9 th September 2017
 Bits and Bobs secondary causes of heart problems Dr Angela McBrien 9 th September 2017 Not the heart Dextroposition Heart in the right chest with the apex to the left Often caused by left sided chest mass
Bits and Bobs secondary causes of heart problems Dr Angela McBrien 9 th September 2017 Not the heart Dextroposition Heart in the right chest with the apex to the left Often caused by left sided chest mass
UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series. Urological Trauma
 UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series Urological Trauma Disclaimer: This is a lot of information to cover and we are unlikely to cover it all today These slides are to be utilized for your
UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series Urological Trauma Disclaimer: This is a lot of information to cover and we are unlikely to cover it all today These slides are to be utilized for your
West Yorkshire Major Trauma Network Clinical Guidelines 2015
 WYMTN: Pelvic fracture with urogenital trauma KEY RECOMMENDATIONS 1. During the initial exploratory survey / secondary survey, a. The external urethral meatus and the transurethral bladder catheter (if
WYMTN: Pelvic fracture with urogenital trauma KEY RECOMMENDATIONS 1. During the initial exploratory survey / secondary survey, a. The external urethral meatus and the transurethral bladder catheter (if
THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN*
 THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN* BY FRANK G. DELUCA, ORVAR SWENSONt, JOHN H. FISHER and ADEL H. LOUTFI From the Boston Floating Hospital for Infants and Children, Boston, Massachusetts
THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN* BY FRANK G. DELUCA, ORVAR SWENSONt, JOHN H. FISHER and ADEL H. LOUTFI From the Boston Floating Hospital for Infants and Children, Boston, Massachusetts
Choledochal cyst in infancy and childhood Analysis of 16 cases
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1977, 52, 121-128 Choledochal cyst in infancy and childhood Analysis of 16 cases AKIO KOBAYASH1 AND YOSHIRO OHBE From the Section of Gastroenterology, Department of Paediatrics,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1977, 52, 121-128 Choledochal cyst in infancy and childhood Analysis of 16 cases AKIO KOBAYASH1 AND YOSHIRO OHBE From the Section of Gastroenterology, Department of Paediatrics,
이희정. Plain Abdominal Radiography in Infants and Children. Hee Jung Lee, M.D.
 대한소아소화기영양학회지 : 제 14 권제 2 호 2011 DOI: 10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.2.130 종설 영유아및소아의단순복부 X- 선사진 계명대학교의과대학영상의학교실 이희정 Plain Abdominal Radiography in Infants and Children Hee Jung Lee, M.D. Department of Radiology,
대한소아소화기영양학회지 : 제 14 권제 2 호 2011 DOI: 10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.2.130 종설 영유아및소아의단순복부 X- 선사진 계명대학교의과대학영상의학교실 이희정 Plain Abdominal Radiography in Infants and Children Hee Jung Lee, M.D. Department of Radiology,
RADPrimer Curriculum Breast Topics Covered Basic Intermediate 225
 Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
