Waste Products & Kidney Function
|
|
|
- Sandra Harmon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
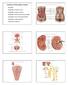
1 Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share adult anatomical relationship male urethra serves as a common passage for urine and sperm 23-1
2 Urinary System Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Diaphragm 11th and 12th ribs Adrenal gland Renal artery Renal vein Kidney Vertebra L2 Aorta Inferior vena cava Ureter Urinary bladder Urethra (a) Anterior view (b) Posterior view Figure 23.1a-b urinary system consists of 6 organs: 2 kidneys, 2 ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra 23-2
3 Kidney Location Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Anterior Small intestine Stomach Colon Pancreas Renal artery and vein Inferior vena cava Peritoneum L1 Ureter Aorta Spleen Kidney Hilum Fibrous capsule Perirenal fat capsule Lumbar muscles Renal fascia Posterior Figure 23.3 a-b 23-3
4 Functions of the Kidney filters blood plasma, separates waste from useful chemicals, returns useful substances to blood, eliminates wastes regulate blood volume and pressure by eliminating or conserving water regulate the osmolarity of the body fluids by controlling the relative amounts of water and solutes eliminated secretes enzyme, renin, which activates hormonal mechanisms that control blood pressure and electrolyte balance secretes the hormone, erythropoietin, which stimulates the production of red blood cells collaborate with the lungs to regulate the PCO2 and acid-base balance of body fluids final step in synthesizing hormone, calcitriol, which contributes to calcium homeostasis 23-4
5 metabolic waste waste substance produced by the body urea formation proteins amino acids NH2 removed forms ammonia, liver converts to urea uric acid Nitrogenous Wastes Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. product of nucleic acid catabolism H creatinine N indicates renal insufficiency uremia nitrogenous waste toxicity treatment hemodialysis or organ transplant H2 N H Ammonia blood urea nitrogen (BUN) expression of the level of nitrogenous waste in the blood C H product of creatine phosphate catabolism normal concentration of blood urea is mg/dl azotemia elevated BUN O NH2 Urea NH O H C HN C C N C C O N H C Uric acid N H HN O C N CH3 CH2 O Creatinine Figure
6 Anatomy of Kidney Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Fibrous capsule Renal cortex Renal medulla Renal papilla Renal sinus Renal pelvis Major calyx Minor calyx Renal column Renal pyramid Ureter Renal blood vessels (b) Figure 23.4b 23-6
7 Renal Circulation kidneys account for only 0.4% of body weight, they receive about 21% of the cardiac output (renal fraction) renal artery - branch into afferent arterioles - each supplying one nephron - leads to a ball of capillaries - glomerulus - blood is drained from the glomerulus by efferent arterioles - lead to either peritubular capillaries or vasa recta around portion of the renal tubule renal vein empties into inferior vena cava 23-7
8 Microcirculation of the Kidney in the cortex, peritubular capillaries branch off of the efferent arterioles supplying the tissue near the glomerulus, the proximal and distal convoluted tubules Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cortical nephron Afferent arteriole Glomerulus Juxtamedullary nephron Efferent arteriole C o r t e x PCT Interlobular artery DCT Interlobular vein Peritubular capillaries Corticomedullary junction Arcuate artery Arcuate vein Vasa recta in medulla, the efferent arterioles supply the nephron loop portion of the nephron. M e d u l l a Collecting duct Nephron loop Figure
9 The Nephron each kidney has about 1.2 million nephrons each composed of two principal parts: renal corpuscle filters the blood plasma renal tubule long coiled tube that converts the filtrate into urine renal corpuscle consists of the glomerulus and a two-layered glomerular (Bowman) capsule that encloses glomerulus 23-9
10 Renal Corpuscle Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Key Flow of blood Flow of filtrate Afferent arteriole Glomerulus Blood flow Figure 23.7a Efferent arteriole Blood flow (a) Glomerular capsule: Parietal layer Capsular space Podocytes of visceral layer Proximal convoluted tubule Glomerular capillaries (podocytes and capillary wall removed) glomerular filtrate collects in capsular space, flows into proximal convoluted tubule. Note the vascular and urinary poles. Note the afferent arteriole is larger than the efferent arteriole.
11 Renal Tubule renal tubule a duct that leads away from the glomerular capsule and ends at the tip of the medullary pyramid divided into four regions proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop, distal convoluted tubule parts of one nephron collecting duct receives fluid from many nephrons proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) arises from glomerular capsule longest and most coiled region simple cuboidal epithelium with prominent microvilli for majority of absorption nephron loop (loop of Henle) long U-shaped portion of renal tubule descending limb and ascending limb thick segments initial part of descending limb and part or all of the ascending limb heavily engaged in the active transport of salts thin segment forms lower part of descending limb cells very permeable to water 23-11
12 Renal Tubule distal convoluted tubule (DCT) begins shortly after the ascending limb reenters the cortex shorter and less coiled that PCT DCT is the end of the nephron collecting duct receives fluid from the DCTs of several nephrons as it passes back into the medulla numerous collecting ducts converge toward the tip of the medullary pyramid 23-12
13 The Nephron Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Renal capsule Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Renal medulla (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus Minor calyx Renal papilla Cortical nephron Efferent arteriole Convoluted tubules (PCT and DCT) Afferent arteriole Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) Nephron loop: Descending limb Ascending limb Juxtamedullary nephron Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Cortex Medulla Collecting duct (CD) Thick segment Thin segment Key Nephron loops Flow of blood Flow of tubular fluid (b) Collecting duct Papillary duct (c) Figure
14 Cortical and Juxtamedullary Nephrons cortical nephrons Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cortical nephron Afferent arteriole Glomerulus Juxtamedullary nephron Efferent arteriole C o r t e x PCT Interlobular artery DCT Interlobular vein 85% of all nephrons short nephron loops efferent arterioles branch into peritubular capillaries around PCT and DCT Peritubular capillaries juxtamedullary nephrons Corticomedullary junction Arcuate artery Arcuate vein Vasa recta M e d u l l a Collecting duct Nephron loop Figure % of all nephrons very long nephron loops, maintain salinity gradient in the medulla and helps conserve water efferent arterioles branch into vasa recta around long nephron loop
15 Overview of Urine Formation Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Blood flow 1 Glomerular filtration Creates a plasmalike filtrate of the blood kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages Rental Corpuscle Flow of filtrate glomerular filtrate 2 Tubular reabsorption Removes useful solutes from the filtrate, returns them to the blood and Peritubular Capillaries fluid in capsular space blood plasma without protein tubular fluid Tubular secretion Removes additional wastes from theblood, adds them to the filtrate Rental tubule 3 water conservation Removes water from the urine and returns it to blood; cincentrates wastes Figure 23.9 glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion water conservation H2O H2O H2O fluid in renal tubule similar to above except tubular cells have removed and added substances urine once it enters the collecting duct only remaining change is water content Urine
16 Filtration Pores and Slits Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Turned back: Blood cells Plasma proteins Large anions Protein-bound minerals and hormones Most molecules > 8 nm in diameter Bloodstream Endothelial cell of glomerular capillary Basement membrane Filtration slit Filtration pore Foot process of podocyte Passed through filter: Water Electrolytes Glucose Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Urea Uric acid Creatinine Capsular space Figure
17 Filtration Membrane glomerular filtration a special case of the capillary fluid exchange process in which water and some solutes in the blood plasma pass from the capillaries of the glomerulus into the capsular space of the nephron filtration membrane three barriers through which fluid passes 23-17
18 Filtration Membrane almost any molecule smaller than 3 nm can pass freely through the filtration membrane water, electrolytes, glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, nitrogenous wastes, and vitamins some substances of low molecular weight are bound to the plasma proteins and cannot get through the membrane most calcium, iron, and thyroid hormone unbound fraction passes freely into the filtrate kidney infections and trauma can damage the filtration membrane and allow albumin or blood cells to filter. proteinuria presence of protein in the urine hematuria presence of blood in the urine 23-18
19 Filtration Pressure blood hydrostatic pressure (BHP) much higher in glomerular capillaries (60 mm Hg compared to 10 to 15 in most other capillaries) because afferent arteriole is larger than efferent arteriole larger inlet and smaller outlet 23-19
20 Filtration Pressure Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. high BP in glomerulus makes kidneys vulnerable to hypertension BHP 60 out COP 32 in NFP 10 out CP 18 in Blood hydrostatic pressure (BHP) Colloid osmotic pressure (COP) Capsular pressure (CP) Net filtration pressure (NFP) Figure mm Hgout 32 mm Hgin 18 mm Hgin it can lead to rupture of glomerular capillaries, produce scarring of the kidneys (nephrosclerosis), and atherosclerosis of renal blood vessels, ultimately leading to renal failure 10 mm Hgout 23-20
21 Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) glomerular filtration rate (GFR) the amount of filtrate formed per minute by the 2 kidneys combined 99% of filtrate is reabsorbed since only 1 to 2 liters urine excreted / day 23-21
22 Regulation of Glomerular Filtration GFR too high fluid flows through the renal tubules too rapidly for them to reabsorb usual amount of water and solutes urine output rises chance of dehydration and electrolyte depletion the GFR too low wastes reabsorbed GFR controlled by adjusting glomerular blood pressure from moment to moment GFR control is achieved by three homeostatic mechanisms renal autoregulation sympathetic control hormonal control 23-22
23 Renal Autoregulation of GFR renal autoregulation the ability of the nephrons to adjust their own blood flow and GFR without external (nervous or hormonal) control enables them to maintain a relatively stable GFR in spite of changes in systemic arterial blood pressure two methods of autoregulation: myogenic mechanism and tubuloglomerular feedback myogenic mechanism based on the tendency of smooth muscle to contract when stretched increased arterial blood pressure stretches the afferent arteriole arteriole constricts and prevents blood flow into the glomerulus from changing much when blood pressure falls the afferent arteriole relaxes allows blood flow more easily into glomerulus filtration remains stable 23-23
24 Renal Autoregulation of GFR tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism by which glomerulus receives feedback on the status of the downstream tubular fluid and adjust filtration to regulate the composition of the fluid, stabilize its own performance, and compensate for fluctuation in systemic blood pressure juxtaglomerular apparatus complex structure found at the very end of the nephron loop where it has just reentered the renal cortex loop comes into contact with the afferent and efferent arterioles at the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle 23-24
25 Renal Autoregulation of GFR three special kind of cells occur in the juxtaglomerular apparatus: macula densa patch of slender, closely spaced epithelial cells at end of the nephron loop on the side of the tubules facing the arterioles senses variations in flow or fluid composition and secretes a paracrine that stimulates JG cells juxtaglomerular (JG) cells enlarged smooth muscle cells in the afferent arteriole directly across from macula densa when stimulated by the macula they dilate or constrict the arterioles they also contain granules of renin, which they secrete in response to drop in blood pressure mesangial cells in the cleft between the afferent and efferent arterioles and among the capillaries of the glomerulus connected to macula densa and JG cells by gap junctions and communicate by means of paracrines build supportive matrix for glomerulus, constrict or relax capillaries to regulate flow 23-25
26 Juxtaglomerular Apparatus if GFR rises the flow of tubular fluid increases and more NaCl is reabsorbed macula densa stimulates JG cells with a paracrine JG cells contract which constricts afferent arteriole, reducing GFR to normal OR mesangial cells may contract, constricting the capillaries and reducing filtration if GFR falls macula relaxes afferent arterioles and mesangial cells blood flow increases and GFR rises back to normal
27
28 Effectiveness of Autoregulation maintains a dynamic equilibrium - GFR fluctuates within narrow limits only blood pressure changes do affect GFR and urine output somewhat renal autoregulation can not compensate for extreme blood pressure variation 23-28
29 Negative Feedback Control of GFR Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. High GFR Reduced GFR Rapid flow of filtrate in renal tubules Constriction of afferent arteriole Sensed by macula densa Paracrine secretion Figure
30 Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Mechanism renin secreted by juxtaglomerular cells if BP drops dramatically renin converts angiotensinogen, a blood protein, into angiotensin I in the lungs and kidneys, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II, the active hormone works in several ways to restore fluid volume and BP 23-30
31
32 Urine Formation II: Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. conversion of glomerular filtrate to urine involves Rental Corpuscle the removal and addition of chemicals by tubular Flow of filtrate reabsorption and secretion Peritubular Blood flow 1 Glomerular filtration Creates a plasmalike filtrate of the blood 2 Tubular reabsorption Removes useful solutes from the filtrate, returns them to the blood and Capillaries occurs through PCT to DCT tubular fluid is modified Tubular secretion Removes additional wastes from theblood, adds them to the filtrate Rental tubule 3 water conservation Removes water from the urine and returns it to blood; cincentrates wastes steps involved include: tubular reabsorption tubular secretion water conservation H2O H2O H2O Figure 23.9 Urine 23-32
33 Summary of Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Glucose Amino acids Protein Vitamins Lactate Urea Uric acid Na+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl HCO3 H2 O PCT Na+ Cl HCO3 H2 O H2 O Urea H+ K+ NH4+ nephron loop reabsorbs another 25% of filtrate DCT reabsorbs Na+, Cl- and water under hormonal control, especially aldosterone and ANP the tubules also extract drugs, wastes, and some solutes from the blood and secrete them into the tubular fluid DCT completes the process of determining the chemical composition of urine Na+ K+ Cl Collecting duct H2 O Urea Key Tubular reabsorption Tubular secretion PCT reabsorbs 65% of glomerular filtrate and returns it to peritubular capillaries much reabsorption by osmosis & cotransport mechanisms linked to active transport of sodium DCT Urea H+ NH4+ Uric acid Creatinine Some drugs Nephron loop: Descending limb Ascending limb Figure collecting duct conserves water 23-33
34 Hormonal Control Blood Pressure High Blood Pressure ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide) secreted Increase water loss, decrease blood volume Decrease blood pressure Low Blood Pressure Renin leads to Angiotensin II activation Angiotensin II causes release of Aldosterone and ADH (antidiuretic hormone) Water retention, increased blood volume Increase blood pressure
35 Blood Pressure Homones ANP decrease blood volume decrease blood pressure Aldosterone and ADH increase blood volume increase blood pressure
36 Collecting Duct Concentrates Urine Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. collecting duct (CD) begins in the cortex where it receives tubular fluid from several nephrons Tubular fluid (300 mosm/l) Osmolarity of tissue fluid (mosm/l) 600 H2O H2O 900 as CD passes through the medulla, it reabsorbs water and concentrates urine up to four times Cortex Medulla 300 H2O H2O medullary portion of CD is Collecting more permeable to water duct than to NaCl Nephron loop 1,200 H2O Urine (up to 1,200 mosm/l) Figure as urine passes through the increasingly salty medulla, water leaves by osmosis concentrating urine 23-36
37 Maintenance of Osmolarity in Renal Medulla Figure Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Osmolarity of ECF (mosm/l) Cortex 400 Medulla 400 Urea Na+ K+ Cl 400 Na+ K+ Cl Urea Na K+ Cl Urea H2 O Active transport Diffusion through a membrane channel H2O NaCl NaCl Urea H2O H2 O Urea Key 1, H2O Na+ K+ Cl H2 O 900 Na+ K+ Cl Urea H2 O NaCl Urea 900 NaCl 1,200 1,200 1,200 Nephron loop Collecting duct Vasa recta 23-37
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Func%ons of the Urinary System
 Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Regula%on of blood volume Regula%on of blood pressure Regula%on of blood- solute concentra%on Regula%on of ph of extracellular fluid Regula%on of erythropoiesis
Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Regula%on of blood volume Regula%on of blood pressure Regula%on of blood- solute concentra%on Regula%on of ph of extracellular fluid Regula%on of erythropoiesis
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Func%ons of the Urinary System
 Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Diaphragm Regula%on of blood volume 11th and 12th ribs Adrenal gland Renal artery Renal vein Regula%on of blood pressure Kidney Vertebra L2 Aorta Inferior vena cava
Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Diaphragm Regula%on of blood volume 11th and 12th ribs Adrenal gland Renal artery Renal vein Regula%on of blood pressure Kidney Vertebra L2 Aorta Inferior vena cava
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology)
 Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran The Urinary System
Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran The Urinary System
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Chapter 25: Urinary System
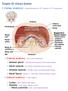 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Urinary System Review Questions:
 Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
Chapter 26 The Urinary System
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12. Urinary System INTRODUCTION. Main functions of the kidneys are
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 INTRODUCTION Main functions of the kidneys are regulate blood volume, water content regulate blood composition e..g. Na, Cl, K, ph
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 INTRODUCTION Main functions of the kidneys are regulate blood volume, water content regulate blood composition e..g. Na, Cl, K, ph
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Chapter 26 The Urinary System. Overview of Kidney Functions. External Anatomy of Kidney. External Anatomy of Kidney
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
Waste. Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8. Urinary System. Urinary System. Nitrogenous Wastes. Nitrogenous Wastes 4/22/2016
 Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Chapter 24: The Urinary System
 Chapter 24: The Urinary System Overview of kidney functions n Regulation of blood ionic composition n Regulation of blood ph n Regulation of blood volume n Regulation of blood pressure n Maintenance of
Chapter 24: The Urinary System Overview of kidney functions n Regulation of blood ionic composition n Regulation of blood ph n Regulation of blood volume n Regulation of blood pressure n Maintenance of
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Urinary System
 Urinary System What are the organs that comprise the urinary system? Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder Ureters Urethra Hepatic veins (cut) Esophagus (cut) Inferior vena cava Adrenal gland Aorta
Urinary System What are the organs that comprise the urinary system? Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder Ureters Urethra Hepatic veins (cut) Esophagus (cut) Inferior vena cava Adrenal gland Aorta
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Chapter 23 *Lecture PowerPoint
 Chapter 23 *Lecture PowerPoint The Urinary System *See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Chapter 23 *Lecture PowerPoint The Urinary System *See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste:
 I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
1. The Fibrous Capsule covers the outside of the kidney. It is made of fat and fibers.
 Slide 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is the excretion of toxic metabolic waste through urine production. The kidneys filter blood plasma and as a result of filtering blood, the kidneys help
Slide 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is the excretion of toxic metabolic waste through urine production. The kidneys filter blood plasma and as a result of filtering blood, the kidneys help
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
1.&Glomerular/Pressure&Filtration&
 Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C.
 Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C. I. Overview of fluids A. Normal volumes 1. fluid intake a. = 1500 ml b. = 750 ml c. = 250 ml (remember ETS) d. total = 2500 ml/day 2. fluid
Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C. I. Overview of fluids A. Normal volumes 1. fluid intake a. = 1500 ml b. = 750 ml c. = 250 ml (remember ETS) d. total = 2500 ml/day 2. fluid
Functions of the kidney
 Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Chapter 26. The Urinary System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD
 Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
URINARY SYSTEM. Primary functions. Major organs & structures
 URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
Basic Functions of the Kidneys
 Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms
 209 Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. collecting duct 2. distal convoluted tubule 3. glomerulus 4. nephron 5. nephron loop
209 Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. collecting duct 2. distal convoluted tubule 3. glomerulus 4. nephron 5. nephron loop
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/77/74887026.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
Urine Formation. Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages Urine Formation. Glomerular Filtration 4/24/2016
 Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily.
 1 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily. Next, the kidneys filter blood. As a result of filtering blood, the kidneys
1 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily. Next, the kidneys filter blood. As a result of filtering blood, the kidneys
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
