Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services. Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual
|
|
|
- Lucy Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014
2 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1 10/30/13 4/01/14 Respiratory Arrest P 2 10/30/13 4/01/14 Obstructed Airway P 3 10/30/13 4/01/14 Respiratory Distress / Failure (Croup/Epiglottitis) P 4 10/30/13 4/01/14 Non-Traumatic Cardiac Arrest P 5 10/30/13 4/01/14 Asthma/Wheezing P 6 10/30/13 4/01/14 Anaphylactic Reaction P 7 10/30/13 4/01/14 Altered Mental Status P 8 10/30/13 4/01/14 Status Eilepticus P 9 10/30/13 4/01/14 Decompensated Shock P 10 10/30/13 4/01/14 Traumatic Cardiac Arrest P 11 10/30/13 4/01/14 For Nassau County protocols, pediatric patients are as defined by the AHA, children without secondary signs of puberty. A "length/weight based" dosing device should be used on all pediatric patients to assure the correct administration of medications.
3 Pediatric ALS Protocols NEWBORN RESUSCITATION Protocol P1 Suction immediately after birth ONLY if there is an obvious obstruction to spontaneous breathing or positive-pressure ventilation is necessary. o BLS Newborn Resuscitation procedures. o If newborn is depressed and meconium staining is present, delay drying and stimulation. Suction airway before taking other resuscitative measures. o Begin Newborn Resuscitation procedures only after the airway has been cleared of thick meconium, as follows: Perform endotracheal intubation and directly suction the endotracheal tube via a meconium aspirator/adapter while slowly withdrawing the endotracheal tube. Note: Do not exceed 100-mmHg suction vacuum Repeat this procedure until little or no meconium is acquired or until the heart rate indicates resuscitation must begin immediately. Do not replace the endotracheal tube once the airway has been cleared of thick meconium unless the newborn remains limp, apneic, or pulseless. For all newborns requiring resuscitation once BLS Newborn Resuscitation procedures have begun: During transport, or if transport is delayed: o If the newborn appears to be in respiratory distress and the heart rate is below 120 BPM, administer oxygen in as high a concentration as possible. o If the newborn appears to be in respiratory distress and the heart rate is below 100 BPM, ventilate via BVM or mouth-to-mask with oxygen attached. o If the newborn appears to be in respiratory distress and the heart rate is below 60 BPM, ventilate via BVM or mouth to mask, begin CPR, administer: o Epinephrine 1:10, mg/kg via IV / IO MEDICAL CONTROL OPTIONS o Repeat Epinephrine every 3-5 minutes o Endotracheal Intubation o Epinephrine 1: mg/kg via Endotracheal tube o Check for Blood Glucose - if < 60 mg/dl - Dextrose D10 IV / IO - (0.5 gm/kg) o IV / IO infusion of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) 10 ml/kg. Reassess & document after each bolus. Attempt IV or IO only once each.
4 Pediatric ALS Protocols PEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY ARREST Protocol P2 For pediatric patients in actual or impending respiratory arrest, or who are unconscious and cannot be adequately ventilated: o Open airway and begin ventilation as per BLS Pediatric Respiratory Distress/Failure procedures. If narcotic overdose is suspected, refer AMS protocol (P8) o If an obstructed airway is suspected, refer obstructed airway protocol. (P3) o Perform endotracheal intubation if BLS measures are not adequate. Consider a supraglottic airway o I.V. of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) KVO or a saline lock Paramedic During transport or if transport is delayed o Administer Naloxone, Patients 2 years old - titrate in increments of 0.1mg/kg- until effective (max 2 mg) Patients < 2 years old - titrate to (max 1 mg) o o IO infusion of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl). Naloxone IV/ IO / ET / IN / IM as directed. (No more than 2 attempts at vascular access) Paramedic - If a tension pneumothorax is suspected consider orders to perform needle decompression, using an gauge catheter
5 Pediatric ALS Protocols PEDIATRIC OBSTRUCTED AIRWAY Protocol P3 For pediatric patients who are unconscious or present with signs & symptoms of inadequate air exchange: o Begin BLS Pediatric Obstructed Airway procedures. o Perform direct laryngoscopy - attempt to remove the foreign body with appropriate size Magill Forceps. NOTE: IF AN ENLARGED EPIGLOTTIS IS VISUALIZED - DO NOT ATTEMPT ENDOTRACHEAL INTUBATION. USE BAG-VALVE-MASK (w/ pop-off disabled) o Perform endotracheal intubation, if BLS measures are not adequate. Consider a supraglottic airway Paramedic If unable to ventilate despite confirmed intubation by direct visualization: Note the endotracheal tube depth Deflate cuff (if cuffed tube is used) Advance tube to its deepest depth - and return to original depth Re-inflate tube cuff and attempt ventilation If unable to ventilate effectively - immediately initiate transport Paramedic - If a tension pneumothorax is suspected consider orders to perform needle decompression, using an gauge catheter
6 Pediatric ALS Protocols PEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY DISTRESS or Suspected Croup / Epiglottitis Protocol P4 o Begin BLS Pediatric Respiratory Distress / Failure procedures. o If child is alert and oriented, transport in position of comfort with parent. Offer cool mist 100% Oxygen if child will allow. o If child presents with signs & symptoms of inadequate air exchange, refer to protocol (P3) NOTE: DO NOT ATTEMPT ENDOTRACHEAL INTUBATION. USE BAG-VALVE-MASK o Racemic Epinephrine, 0.05 mg/kg in 3cc 0.9% saline (Max. 5 ml) via Nebulizer (if unavailable, Epinephrine may be used at the same nebulizer dose) o Consider Endotracheal Intubation in acute epiglottitis with an ET tube one mm smaller than calculated. o Dexamethasone (Decadron) 0.6 mg/kg IV / IO o Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) 2 mg/kg IV / IO (max 60 mg) Paramedic - If child is in respiratory arrest, perform needle cricothyrotomy.
7 Pediatric ALS Protocols NON TRAUMATIC CARDIAC ARREST Protocol P5 o Begin BLS Pediatric Cardiac Arrest procedures. Initiate CPR Perform endotracheal intubation, if BLS airway measures are not adequate. o Cardiac Monitoring. If in ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, immediately defibrillate at 2 joules/kg. Resume CPR immediately. - (2 min.) If still in ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, immediately repeat defibrillation at 4 joules/kg. Resume CPR immediately - (2 min.) Epinephrine 1:10, mg/kg via IV or IO (Repeat every 3-5 minutes) OR Epinephrine 1:1, mg/kg via ET (only if no IV/IO) (Repeat every 3-5 minutes) If still in ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, immediately repeat defibrillation at 4 joules/kg. Resume CPR immediately - (2 min.) o Begin transport o IV or IO infusion of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) KVO. o Contact Medical Control for additional medication orders. Increase energy settings up to 10 joules / Kg Amiodarone 5mg/kg IV/ IO if V-Tach or V-Fib (max. 300mg) OR Lidocaine 1 mg/kg rapid IV/IO push if Amiodarone is not available. Dextrose D10 IV / IO - (0.5 gm/kg) Sodium Bicarbonate 1 meq/kg IV/IO/saline lock. Magnesium Sulfate mg/kg (max. 2g) - for Torsades
8 Pediatric ALS Protocols PEDIATRIC ASTHMA/WHEEZING Protocol P6 For pediatric patients with acute asthma and/or active wheezing: o Begin BLS Pediatric Respiratory Distress/Failure procedures. o Administer Albuterol Sulfate 0.083% -one unit dose of 3 ml - via nebulizer. patients < 6 months - ½ unit dose If no response, 2nd unit dose to follow immediately. If still no response, contact medical control immediately. o Administer Ipratropium Bromide 0.02% (one unit dose of 2.5 ml for children 6 years) (1/2 unit dose of 2.5 ml for children under 6), via nebulizer in conjunction with each Albuterol Sulfate dose. Patients 1 year, with severe respiratory distress, respiratory failure, and/or decreased breath sounds o Epinephrine 1: mg/kg IM (max. 0.3 mg) o Intubation o Consider IV/IO and rapid transport - if Patient unstable. o IV infusion of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) KVO, IV/ IO o Repeat Albuterol Sulfate via nebulizer. o Repeat Ipratropium Bromide 0.02% by nebulizer. o Repeat Epinephrine 1:1, mg/kg IM (max 0.3 mg) o Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) 2 mg/kg IV/IO (max 60 mg)
9 Pediatric ALS Protocols PEDIATRIC ANAPHYLACTIC REACTION Protocol P7 o Begin BLS Anaphylactic Reaction procedures. o Epinephrine 1: mg/kg IM (max. 0.3 mg) or o Epinephrine Autoinjector JR mg IM o Administer Albuterol Sulfate 0.083% one unit dose of 3 ml - via nebulizer. patients < 6 months - ½ unit dose - if wheezing If patient develops signs of respiratory failure or airway obstruction: o Endotracheal intubation o Initiate rapid transport. Paramedic o Diphenhydramine 1mg/kg IV/ IO / IM During transport, or if transport is delayed: o IV infusion of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) via a large bore IV (18-22 gauge) to keep the vein open, or a saline lock. o IF PATIENT IS IN ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK and IV cannot be established, IO infusion of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) at KVO rate. o Repeat any of the above standing orders. o Begin rapid IV or IO infusion of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl), 20 ml/kg. Repeat as necessary. o Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) 2 mg/kg IV/IO (max 60 mg)
10 Pediatric ALS Protocols PEDIATRIC ALTERED MENTAL STATUS Protocol P8 For pediatric patients in coma, with evolving neurological deficit, or with altered mental status of unknown etiology: NOTE: MAINTENANCE OF NORMAL RESPIRATORY AND CIRCULATORY FUNCTION IS ALWAYS THE FIRST PRIORITY. PATIENTS WITH ALTERED MENTAL STATUS DUE TO RESPIRATORY FAILURE OR ARREST, OBSTRUCTED AIRWAY, SHOCK, TRAUMA, NEAR DROWNING OR OTHER ANOXIC INJURY SHOULD BE TREATED UNDER OTHER PROTOCOLS. o Assess respiratory and circulatory status. o Begin BLS Altered Mental Status procedures. o IV of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) KVO, or a saline lock. Attempt IV only once. Perform a glucometer test for blood sugar level. If less than 60 mg/dl administer dextrose or glucagon and continue to monitor as needed after administration. o Dextrose D10 IV / IO - (0.5 gm/kg) OR o Glucagon 0.1 mg/kg IM (if no IV established). o Repeat any of the above orders. o IO infusion of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl). o Naloxone 0.1mg/kg IV / IO / IM / IN - if there is no change in mental status o Transport to a Pediatric specialty receiving facility
11 Pediatric ALS Protocols PEDIATRIC STATUS EPILEPTICUS Protocol P9 For pediatric patients in Status Epilepticus: o Begin BLS Seizures procedure - cardiac monitor, pulse oximetry, waveform capnography. Perform a glucometer test for blood sugar level. If 60 mg/dl: o IV / IO infusion of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) KVO o Dextrose D10 IV / IO - (0.5 gm/kg) OR o Glucagon 0.1 mg/kg IM (if no IV established). Paramedic If patient is still seizing or blood sugar is normal: o Midazolam 0.2 mg/kg IM / IN (max. 5 mg) Note: IN route is preferred If seizures persist - contact Medical control of options. o IO infusion of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl). o Midazolam 0.2 mg/kg IM / IN (max. 5 mg) - Note: IN route is preferred o Lorazepam 0.05 mg/kg IV/ IN/ IO (slowly over 2 minutes) Repeat doses may be given if seizures persist o Diazepam 0.1 mg/kg IV/ IO (slowly over 2 minutes) Repeat doses may be given if seizures persist If NO IV / IO: o Repeat Midazolam 0.2 mg/kg IM / IN (max. 5 mg) o Diazepam 0.1 mg/kg per rectum NOTE: DO NOT ADMINISTER DIAZEPAM or MIDAZOLAM IF THE SEIZURES HAVE STOPPED. FLUSH IV LINE BETWEEN GLUCOSE AND DIAZEPAM or MIDAZOLAM
12 Pediatric ALS Protocols PEDIATRIC DECOMPENSATED SHOCK Protocol P10 o Begin BLS Pediatric Shock procedures. o If signs of hemorrhage or dehydration are not present, begin Cardiac Monitoring. If adrenal cortical insufficiency (Addison's) / hyperplasia is confirmed * o Hydrocortisone Sodium Succinate (Solu-Cortef) 2mg/kg IV/IO (max.100mg) NOTE: FOR PATIENTS IN SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA OR VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA WITH A PULSE, AND WITH EVIDENCE OF LOW CARDIAC OUTPUT, CONTACT MEDICAL CONTROL FOR OPTIONS. During transport, or if transport is delayed: o Begin rapid IV Bolus of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) 20 ml/kg, via a large-bore IV (18-22 gauge) or IO catheter. Attempt IV or IO only once each. o If signs of hemorrhage or dehydration are present, and the patient remains in decompensated shock, begin second large bore IV and repeat bolus up to an additional 20 ml/kg, (total of 40 ml/kg), Attempt second IV only once. Begin IO infusion Continue rapid IV or IO bolus of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) up to an additional 20 ml/kg (total of 60 ml/kg). Hydrocortisone Sodium Succinate (Solu-Cortef) 2mg/kg IV/IO (max.100mg) If transport is delayed or extended, and the patient presents with: 1. Supraventricular tachycardia or ventricular tachycardia with a pulse, with evidence of low cardiac output, perform synchronized cardioversion at joules/kg, using pediatric pads. If necessary, repeat at 1-2 joules/kg. 2. Supraventricular tachycardia with evidence of low cardiac output, if the Defibrillator is not able to deliver a calculated dose, administer Adenosine 0.1 mg/kg, rapid IV or IO bolus (not to exceed 6 mg), followed immediately by 5-10 ml of Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) flush. If necessary, Adenosine may be repeated at 0.2 mg/kg, rapid IV or IO bolus (not to exceed 12 mg), followed immediately by 5-10 ml Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) flush.
13 Pediatric ALS Protocols PEDIATRIC TRAUMATIC CARDIAC ARREST Protocol P11 : o Initiate BLS stabilization procedures o Perform ETI - if BLS measures not adequate (use caution with possible C-spine injury) o Begin rapid transport o Establish IV or IO access, administer bolus Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) - 20 ml/kg o Monitor ECG o If continued signs of inadequate perfusion persist repeat a second IV bolus of 20 ml/kg (total of 40 ml/kg) Medical Control Options: o Continue Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl) up to an additional 20 ml/kg (total of 60 ml/kg). o Hospital Diversion o Epinephrine 1:10, mg/kg IV/IO Paramedic - If a tension pneumothorax is suspected consider orders to perform needle decompression, using an gauge catheter
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS
 THE REGIONAL EMERGENCY MEDICAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE NEW YORK CITY PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS Effective September 1, 2017 Version ALS09012017C The Regional
THE REGIONAL EMERGENCY MEDICAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE NEW YORK CITY PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS Effective September 1, 2017 Version ALS09012017C The Regional
Pediatric Resuscitation
 Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02
 PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL
 CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION. 1. Safe scene, standard precautions. 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness. 3. Quick look (monitor)
 LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
MICHIGAN. State Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. Adult Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
PROTOCOL 1 Endotracheal Intubation (Adult and Pediatric) REQUEST EMT-P RESPONSE DO NOT DELAY TRANSPORT
 PROTOCOL 1 Endotracheal Intubation (Adult and Pediatric) 1. Basic Life Support airway management procedures are initiated. 2. Endotracheal Intubation is indicated under any of the following conditions:
PROTOCOL 1 Endotracheal Intubation (Adult and Pediatric) 1. Basic Life Support airway management procedures are initiated. 2. Endotracheal Intubation is indicated under any of the following conditions:
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8061.19 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Decreased Sensorium Last Approved Date: 05/01/17 Effective Date: 05/01/19 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8061.19 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Decreased Sensorium Last Approved Date: 05/01/17 Effective Date: 05/01/19 Next Review
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
PALS Case Scenario Testing Checklist Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction
 Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update What s New for 2010? 3 CPR. 4 4 Steps of BLS Survey 5 CPR 6 CPR.
 1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies)
 SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES
 EMS Agency SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Pediatric Advanced Life Support Policies Emergency Medical Services TITLE: Pediatric Routine Medical Care EMS Policy No. 5800 Pediatric Routine
EMS Agency SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Pediatric Advanced Life Support Policies Emergency Medical Services TITLE: Pediatric Routine Medical Care EMS Policy No. 5800 Pediatric Routine
MASTER SYLLABUS
 A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Respiratory Care MASTER SYLLABUS 2018-2019 C. Course Number and Title: RESP 2330 Advanced Life Support Procedures D. Course Coordinator: Tricia Winters,
A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Respiratory Care MASTER SYLLABUS 2018-2019 C. Course Number and Title: RESP 2330 Advanced Life Support Procedures D. Course Coordinator: Tricia Winters,
table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines
 table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines P1 PEDIATRIC PATIENT CARE...70 P2 APPARENT LIFE-THREATENING EVENT (ALTE)...71 P3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...72 73 P4 NEONATAL CARE AND RESUSCITATION...74
table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines P1 PEDIATRIC PATIENT CARE...70 P2 APPARENT LIFE-THREATENING EVENT (ALTE)...71 P3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...72 73 P4 NEONATAL CARE AND RESUSCITATION...74
In accordance with protocols, this patient should be transported to which medical facility?
 NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
Preparing for your upcoming PALS course
 IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
PALS PRETEST. PALS Pretest
 PALS PRETEST 1. A child with a fever, immune system compromise, poor perfusion and hypotension is most likely to be experiencing which type of shock A. cardiogenic B. Neurogenic C. Septic D. Hypovolemic
PALS PRETEST 1. A child with a fever, immune system compromise, poor perfusion and hypotension is most likely to be experiencing which type of shock A. cardiogenic B. Neurogenic C. Septic D. Hypovolemic
SUBCHAPTER 7. STANDING ORDERS FOR ADULT PATIENT Adopted 08/2011 Update 03/2013
 8:41-7.1 Scope SUBCHAPTER 7. STANDING ORDERS FOR ADULT PATIENT Adopted 08/2011 Update 03/2013 The following treatment protocols shall be considered standing orders when treating adult patients. For the
8:41-7.1 Scope SUBCHAPTER 7. STANDING ORDERS FOR ADULT PATIENT Adopted 08/2011 Update 03/2013 The following treatment protocols shall be considered standing orders when treating adult patients. For the
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
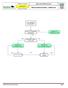 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
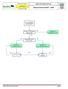 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
HEALTH PROFESSIONS COUNCIL OF SOUTH AFRICA PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR EMERGENCY CARE CAPABILITIES OF EMERGENCY CARE PROVIDERS: JUNE 2016
 HEALTH PROFESSIONS COUNCIL OF SOUTH AFRICA PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR EMERGENCY CARE CAPABILITIES OF EMERGENCY CARE PROVIDERS: JUNE 2016 CAPABILITIES Airway Management Finger sweep Head-tilt-chin lift Jaw-thrust
HEALTH PROFESSIONS COUNCIL OF SOUTH AFRICA PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR EMERGENCY CARE CAPABILITIES OF EMERGENCY CARE PROVIDERS: JUNE 2016 CAPABILITIES Airway Management Finger sweep Head-tilt-chin lift Jaw-thrust
EMS Region Medication List 2010
 EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
Learning Station Competency Checklists
 Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
NYC REMAC PUBLIC NOTICE PROPOSED REVISIONS PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS THE REGIONAL EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES COUNCIL OF NEW YORK CITY, INC.
 NYC REMAC PUBLIC NOTICE PROPOSED REVISIONS PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS The Regional Emergency Medical Advisory Committee (REMAC) of New York City Prehospital Treatment Protocols define the minimum
NYC REMAC PUBLIC NOTICE PROPOSED REVISIONS PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS The Regional Emergency Medical Advisory Committee (REMAC) of New York City Prehospital Treatment Protocols define the minimum
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Number Protocol Name 1.1 General Pre-hospital Care: Regional Protocol 1.2 Abdominal Pain 1.3 Nausea and Vomiting: Regional
MICHIGAN State Protocols General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Number Protocol Name 1.1 General Pre-hospital Care: Regional Protocol 1.2 Abdominal Pain 1.3 Nausea and Vomiting: Regional
Summary of 2018 Protocol Changes PROTOCOL TITLE PAGE # LINE # ORIGINAL TEXT NEW TEXT
 Important Numbers 3 Regional Programs telephone and fax numbers have been updated. Health Care Facility 5, 14 Calvert Memorial Hospital CalvertHealth Medical Center Health Care Facility 6 Code 239 Frederick
Important Numbers 3 Regional Programs telephone and fax numbers have been updated. Health Care Facility 5, 14 Calvert Memorial Hospital CalvertHealth Medical Center Health Care Facility 6 Code 239 Frederick
Michigan Adult Cardiac Protocols TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Contra Costa County Emergency Medical Services Drug Reference. Indication Dosing Cautions Comments
 Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES. -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P
 PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
Johnson County Emergency Medical Services Page 23
 Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
PALS Pulseless Arrest Algorithm.
 PALS Pulseless Arrest Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Bradycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Tachycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M
PALS Pulseless Arrest Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Bradycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Tachycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult
 Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
San Benito County EMS Agency Section 700: Patient Care Procedures
 Purpose: To outline the steps EMTs & paramedics will take to manage possible life threats in any child or adult patient they encounter. This policy is in effect for all treatment protocols & is to be referred
Purpose: To outline the steps EMTs & paramedics will take to manage possible life threats in any child or adult patient they encounter. This policy is in effect for all treatment protocols & is to be referred
PALS Review 2015 Guidelines
 PALS Review 2015 Guidelines BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. 1. Scene Safety 2. Establish Unresponsiveness 3. Check for breathing if absent or agonal (No
PALS Review 2015 Guidelines BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. 1. Scene Safety 2. Establish Unresponsiveness 3. Check for breathing if absent or agonal (No
ACLS Review. Pulse Oximetry to be between 94 99% to avoid hyperoxia (high oxygen tension can lead to tissue death
 ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
Z19.2 Cross Reference to Patient Care Maps & Clinical Care Procedures
 2017-04-07 Old version G1 Code of Ethics G2 Scope and Function G3 Scene Assessment G4 Triage G5 Primary Survey G6 Shock G7 Load and Go G8 Secondary Survey G9 Unconscious Patient G10A Obstructed Airway
2017-04-07 Old version G1 Code of Ethics G2 Scope and Function G3 Scene Assessment G4 Triage G5 Primary Survey G6 Shock G7 Load and Go G8 Secondary Survey G9 Unconscious Patient G10A Obstructed Airway
Pediatric Advanced Life Support Overview Judy Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Overview 2006 Judy Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P General Our Database is lacking in pediatrics Pediatrics are DIFFERENT than Adults not just smaller The same procedure may require
Pediatric Advanced Life Support Overview 2006 Judy Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P General Our Database is lacking in pediatrics Pediatrics are DIFFERENT than Adults not just smaller The same procedure may require
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac
 Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Other Cardiac Dysrhythmias C9
 CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Other Cardiac Dysrhythmias C9 ATRIAL FLUTTER Variable rate depending on block. Atrial rate between 250-350, saw-tooth pattern. (see Appendix B for energy settings for bi-phasic low
CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Other Cardiac Dysrhythmias C9 ATRIAL FLUTTER Variable rate depending on block. Atrial rate between 250-350, saw-tooth pattern. (see Appendix B for energy settings for bi-phasic low
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013
 NUMBERS Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013 Weight in kg = 8 + (age in yrs X 2) Neonate (less than 1 month)
NUMBERS Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013 Weight in kg = 8 + (age in yrs X 2) Neonate (less than 1 month)
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
 Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Pediatric Prehospital Treatment Protocols
 Pediatric Prehospital Treatment Protocols COUNTY EMS AGENCY Updated: July 17, 20 18 Pediatric Primary Survey 1 Pediatric PEA 2 Pediatric Asystole 3 Pediatric V-Fib/Pulseless V-Tach 4 Neonatal Resuscitation
Pediatric Prehospital Treatment Protocols COUNTY EMS AGENCY Updated: July 17, 20 18 Pediatric Primary Survey 1 Pediatric PEA 2 Pediatric Asystole 3 Pediatric V-Fib/Pulseless V-Tach 4 Neonatal Resuscitation
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES
 EMS Agency SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Pediatric Advanced Life Support Policies Emergency Medical Services TITLE: Pediatric Routine Medical Care EMS Policy No. 5800 Pediatric Routine
EMS Agency SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Pediatric Advanced Life Support Policies Emergency Medical Services TITLE: Pediatric Routine Medical Care EMS Policy No. 5800 Pediatric Routine
Pediatric advanced life support. Management of decreased conscious level in children. Virgi ija Žili skaitė 2017
 Pediatric advanced life support. Management of decreased conscious level in children Virgi ija Žili skaitė 2017 Life threatening conditions: primary assessment, differential diagnostics and emergency care.
Pediatric advanced life support. Management of decreased conscious level in children Virgi ija Žili skaitė 2017 Life threatening conditions: primary assessment, differential diagnostics and emergency care.
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION
 CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION A. Age delineation: Infant CPR guidelines apply to victims less than one year of age; Child CPR guidelines apply to victims one year of age to the onset of adolescence
CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION A. Age delineation: Infant CPR guidelines apply to victims less than one year of age; Child CPR guidelines apply to victims one year of age to the onset of adolescence
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES
 EMS Agency SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Pediatric Advanced Life Support Policies Emergency Medical Services TITLE: Pediatric Routine Medical Care EMS Policy No. 5800 Pediatric Routine
EMS Agency SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Pediatric Advanced Life Support Policies Emergency Medical Services TITLE: Pediatric Routine Medical Care EMS Policy No. 5800 Pediatric Routine
Requirements to successfully complete PALS:
 The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains these 2010 Guidelines.The 2010
The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains these 2010 Guidelines.The 2010
European Resuscitation Council
 European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
DYSRHYTHMIAS. D. Assess whether or not it is the arrhythmia that is making the patient unstable or symptomatic
 DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
North Carolina College of Emergency Physicians Standards for EMS Medications and Skills Use
 . The baseline medications and skills required in all systems and Specialty Care Transport Programs) with EMS personnel credentialed at the specified level. S. The equipment required in all Specialty Care
. The baseline medications and skills required in all systems and Specialty Care Transport Programs) with EMS personnel credentialed at the specified level. S. The equipment required in all Specialty Care
Resuscitation Checklist
 Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS
 EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS Effective: July 1, 2017 Reviewed: November 9, 2016 Revised: November 9, 2016 EMS Agency Medical Director ALLERGIC REACTION/ANAPHYLAXIS ADULT BLS TREATMENT
EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS Effective: July 1, 2017 Reviewed: November 9, 2016 Revised: November 9, 2016 EMS Agency Medical Director ALLERGIC REACTION/ANAPHYLAXIS ADULT BLS TREATMENT
Name: Level of license: Date: Agency(ies):
 Schoolcraft County Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, October 2013 version 1.0 Name: Level of license: Date: Agency(ies): 1. EMS agencies within the Medical Control Authority
Schoolcraft County Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, October 2013 version 1.0 Name: Level of license: Date: Agency(ies): 1. EMS agencies within the Medical Control Authority
Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines. Cardiac Arrest
 Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines Cardiac Arrest Note: These guidelines are based on (or adapted from) the current American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency
Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines Cardiac Arrest Note: These guidelines are based on (or adapted from) the current American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency
ADULT TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
Head Trauma Protocol
 Injuries to the head may cause underlying brain tissue damage. Increased intracranial pressure from bleeding or swelling tissue is a common threat after head trauma. Common signs and symptoms of increased
Injuries to the head may cause underlying brain tissue damage. Increased intracranial pressure from bleeding or swelling tissue is a common threat after head trauma. Common signs and symptoms of increased
Pediatric Advanced Life Support Treatment Protocol Important: Use Broselow tape for all pediatric and neonatal drug dosages and for equipment sizes.
 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Treatment Protocol Important: Use Broselow tape for all pediatric and neonatal drug dosages and for equipment sizes. John P. Mulligan, M.D, Kathryn Bell, DO, Dan Kowalzyk,
Pediatric Advanced Life Support Treatment Protocol Important: Use Broselow tape for all pediatric and neonatal drug dosages and for equipment sizes. John P. Mulligan, M.D, Kathryn Bell, DO, Dan Kowalzyk,
Manual Defibrillation. CPR AGE: 18 years LOA: Altered HR: N/A RR: N/A SBP: N/A Other: N/A
 ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
SREMS Minimum Equipment Standards
 Ambulance AEMT EMT-CC EMT-P Standard Description Opt Req Opt Req Opt Req Opt Req Unit meets NYS minimum BLS equipment standards for X certification, per latest Part 800. Portable monitor-defibrillator
Ambulance AEMT EMT-CC EMT-P Standard Description Opt Req Opt Req Opt Req Opt Req Unit meets NYS minimum BLS equipment standards for X certification, per latest Part 800. Portable monitor-defibrillator
STATE OF OHIO EMS BOARD
 0 STATE OF OHIO EMS BOARD Emergency Medical Services Pediatric Guidelines and Procedures Manual INTRODUCTION On behalf of the State Board of Emergency Medical Services, the Ohio Emergency Medical Services
0 STATE OF OHIO EMS BOARD Emergency Medical Services Pediatric Guidelines and Procedures Manual INTRODUCTION On behalf of the State Board of Emergency Medical Services, the Ohio Emergency Medical Services
SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC
 SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC The following is a summary of the key issues and changes in the AHA 2010 Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiac
SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC The following is a summary of the key issues and changes in the AHA 2010 Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiac
PALS PROVIDER Course Study Guide/Pre-Test
 PALS PROVIDER Course Study Guide/Pre-Test *PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING THIS DOCUMENT WITH YOU TO CLASS* Heartland CPR, llc 8101 NW 10 th St, Suite #C3 Oklahoma City, OK 73127 405-603-6666 contact@heartlandcpr.com
PALS PROVIDER Course Study Guide/Pre-Test *PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING THIS DOCUMENT WITH YOU TO CLASS* Heartland CPR, llc 8101 NW 10 th St, Suite #C3 Oklahoma City, OK 73127 405-603-6666 contact@heartlandcpr.com
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes
 Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health
 CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health Manual Subject Emergency Medical Services Administrative Policies and Procedures Table of Contents
CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health Manual Subject Emergency Medical Services Administrative Policies and Procedures Table of Contents
A silent chest is. Pediatrics II Asthma, seizures and cardiac arrest. Children are different. Cough variant asthma. Symptoms of severe distress
 Asthma ~21% of all asthma cases are school aged Pediatrics II Asthma, seizures and cardiac arrest Identify 3 symptoms of an asthma exacerbation Bronchospasm Edema of the bronchi Increased mucus production
Asthma ~21% of all asthma cases are school aged Pediatrics II Asthma, seizures and cardiac arrest Identify 3 symptoms of an asthma exacerbation Bronchospasm Edema of the bronchi Increased mucus production
PALS Study Guide 2016
 Mandatory Precourse Self-Assessment at least 70% pass. Bring proof of completion to class. The PALS Provider exam is 50 multiple-choice questions. Passing score is 84%. Student may miss 8 questions. All
Mandatory Precourse Self-Assessment at least 70% pass. Bring proof of completion to class. The PALS Provider exam is 50 multiple-choice questions. Passing score is 84%. Student may miss 8 questions. All
Adult Intubation Skill Sheet
 Adult Intubation 2. Opens the airway manually and inserts an oral airway *** 3. Ventilates the patient with BVM attached to oxygen at 15 lpm *** 4. Directs assistant to oxygenate the patient 5. Selects
Adult Intubation 2. Opens the airway manually and inserts an oral airway *** 3. Ventilates the patient with BVM attached to oxygen at 15 lpm *** 4. Directs assistant to oxygenate the patient 5. Selects
Pediatric Treatment Protocols Date: January 1, 2015 Page 1 of 1
 Date: January 1, 2015 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Altered Mental Status Section 3-1 Pediatric Anaphylaxis/Allergic Reaction Section 3-2 Pediatric Assessment & Treatment Section 3-3 Pediatric
Date: January 1, 2015 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Altered Mental Status Section 3-1 Pediatric Anaphylaxis/Allergic Reaction Section 3-2 Pediatric Assessment & Treatment Section 3-3 Pediatric
yregion I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Airway Management
 yregion I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Airway Management Overview: Managing a patient s airway may be necessitated due to upper or lower airway obstruction, inadequate
yregion I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Airway Management Overview: Managing a patient s airway may be necessitated due to upper or lower airway obstruction, inadequate
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults
 Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults Fatma Özdemir, MD Emergency Deparment of Uludag University Faculty of Medicine OVERVIEW Introduction Pathophysiology BLS algorithm ALS algorithm Post resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults Fatma Özdemir, MD Emergency Deparment of Uludag University Faculty of Medicine OVERVIEW Introduction Pathophysiology BLS algorithm ALS algorithm Post resuscitation
INTUBATION/RSI. PURPOSE: A. To facilitate secure, definitive control of the airway by endotracheal intubation in an expeditious and safe manner
 Manual: LifeLine Patient Care Protocols Section: Adult/Pediatrics Protocol #: AP1-009 Approval Date: 03/01/2018 Effective Date: 03/05/2018 Revision Due Date: 12/01/2018 INTUBATION/RSI PURPOSE: A. To facilitate
Manual: LifeLine Patient Care Protocols Section: Adult/Pediatrics Protocol #: AP1-009 Approval Date: 03/01/2018 Effective Date: 03/05/2018 Revision Due Date: 12/01/2018 INTUBATION/RSI PURPOSE: A. To facilitate
HealthCare Training Service
 HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
Providing Evidence- Based Care for Children on Ambulances
 Providing Evidence- Based Care for Children on Ambulances Manish I. Shah, MD, MS Prehospital Domain Lead EMS for Children Innovation and Improvement Center Associate Professor Department of Pediatrics
Providing Evidence- Based Care for Children on Ambulances Manish I. Shah, MD, MS Prehospital Domain Lead EMS for Children Innovation and Improvement Center Associate Professor Department of Pediatrics
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016
 Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016 1. Which of the following is incorrect? a. Each EMS and Fire agency should have protocols in place for evaluation of personnel involved in fire suppression operations
Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016 1. Which of the following is incorrect? a. Each EMS and Fire agency should have protocols in place for evaluation of personnel involved in fire suppression operations
Final Written Exam ASHI ACLS
 Final Written Exam ASHI ACLS Instructions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Questions 1 and 2 pertain to the following scenario: A 54-year-old man has experienced
Final Written Exam ASHI ACLS Instructions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Questions 1 and 2 pertain to the following scenario: A 54-year-old man has experienced
Pediatric Medical Care
 2013 Standard Medical Care Procedures (Pediatric) Pediatric emergencies make up a small percentage of our call volume. Children very seldom suffer a life threatening medical emergency, but when it does
2013 Standard Medical Care Procedures (Pediatric) Pediatric emergencies make up a small percentage of our call volume. Children very seldom suffer a life threatening medical emergency, but when it does
MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS
 MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS Page 2 : BRONCHOSPASM / ASTHMA Page 3 : TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX Page 4 : Page 5 : Page 6 : CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE/ PULMONARY EDEMA ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK / ALLERGIC REACTION ANGINA
MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS Page 2 : BRONCHOSPASM / ASTHMA Page 3 : TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX Page 4 : Page 5 : Page 6 : CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE/ PULMONARY EDEMA ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK / ALLERGIC REACTION ANGINA
Pediatric Shock. Hypovolemia. Sepsis. Most common cause of pediatric shock Small blood volumes (80cc/kg)
 Critical Concepts: Shock Inadequate peripheral perfusion where oxygen delivery does not meet metabolic demand Adult vs Pediatric Shock - Same causes/different frequencies Pediatric Shock Hypovolemia Most
Critical Concepts: Shock Inadequate peripheral perfusion where oxygen delivery does not meet metabolic demand Adult vs Pediatric Shock - Same causes/different frequencies Pediatric Shock Hypovolemia Most
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY CARE GUIDE Child 70mm. Child 70mm
 PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY CARE GUIDE Pediatric Parameters & Equipment Age Neonate 3mo 6mo 1 yr 2 yr 3 yr 4 yr 6 yr 8 yr 12 yr 14 yr Wt (kg) 3.5 6 8 10 12 14 16 20 25 40 50 ~ BSA (m 2 ) 0.24 0.34 0.42 0.49 0.56
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY CARE GUIDE Pediatric Parameters & Equipment Age Neonate 3mo 6mo 1 yr 2 yr 3 yr 4 yr 6 yr 8 yr 12 yr 14 yr Wt (kg) 3.5 6 8 10 12 14 16 20 25 40 50 ~ BSA (m 2 ) 0.24 0.34 0.42 0.49 0.56
Asystole / PEA (PEDIATRIC)
 FRRCKSBURG MS Asystole / A (ATRC) 1 Check for Responsiveness Check for Breathing Check for Carotid ulse nitiate CR o As soon as a mechanical external compression device (i.e. Lucas 2) (rocedure 11) becomes
FRRCKSBURG MS Asystole / A (ATRC) 1 Check for Responsiveness Check for Breathing Check for Carotid ulse nitiate CR o As soon as a mechanical external compression device (i.e. Lucas 2) (rocedure 11) becomes
Cleveland Clinic Regional Hospitals EMS Protocol DRAFT Release Notes. Global Changes
 Cleveland Clinic Regional Hospitals EMS Protocol 2014 DRAFT Release Notes Global Changes Added cautions and stops with selected high risk medications / procedures on protocol tree page for safety Individual
Cleveland Clinic Regional Hospitals EMS Protocol 2014 DRAFT Release Notes Global Changes Added cautions and stops with selected high risk medications / procedures on protocol tree page for safety Individual
Pennsylvania Statewide. Advanced Life Support Protocols. Pennsylvania Department of Health Bureau of Emergency Medical Services
 Pennsylvania Statewide Advanced Life Support Protocols Pennsylvania Department of Health Bureau of Emergency Medical Services Effective July 1, 2011 (717) 787-8740 March 1, 2011 Dear EMS Provider: The
Pennsylvania Statewide Advanced Life Support Protocols Pennsylvania Department of Health Bureau of Emergency Medical Services Effective July 1, 2011 (717) 787-8740 March 1, 2011 Dear EMS Provider: The
Pediatric (BP, weight conversion) Information
 Pediatric (BP, weight conversion) Information Reference Reviewed: Updated: Blood pressure Minimal systolic BP = 70 + (2 x age) Normal systolic BP = 90 + (2 x age) Estimation of Pediatric Weight (2 x age)
Pediatric (BP, weight conversion) Information Reference Reviewed: Updated: Blood pressure Minimal systolic BP = 70 + (2 x age) Normal systolic BP = 90 + (2 x age) Estimation of Pediatric Weight (2 x age)
PEDIATRIC MEDICAL EMERGENCIES
 PEDIATRIC MEDICAL EMERGENCIES Last Revised: October 2016 Pediatric Medical Emergencies Section D 1 INITIAL PEDIATRIC CARE NOTE: The pediatric patient is determined by the weight as well as the age. On
PEDIATRIC MEDICAL EMERGENCIES Last Revised: October 2016 Pediatric Medical Emergencies Section D 1 INITIAL PEDIATRIC CARE NOTE: The pediatric patient is determined by the weight as well as the age. On
