Oral administration of tannins and flavonoids in children with acute diarrhea: a pilot, randomized, control-case study
|
|
|
- Melvyn Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2018) 44:64 RESEARCH Open Access Oral administration of tannins and flavonoids in children with acute diarrhea: a pilot, randomized, control-case study Marina Russo, Vincenzo Coppola, Eleonora Giannetti, Roberta Buonavolontà, Antonio Piscitelli and Annamaria Staiano * Abstract Background: AG is the most common cause of pediatric consultations among children between 2 and 5 years of age and it still leads to high mortality and morbidity. Its management is based on rehydration therapy, but this treatment is not effective in reducing duration of diarrhea. For this reason, other safer and less expensive interventions, which could be added to oral rehydration therapy, are of great interest. Methods: A pilot, randomized, case-controlled trial was conducted in 60 children affected by AG (< 7 days) with mild-moderate dehydration, according to WHO recommendations, from1 year to 17 years old. Patients were divided into 2 Groups: Group 1 consisting of 30 children treated with Actitan F and standard oral rehydration (SOR); Group 2 consisting of 30 children who received only SOR. Both groups received treatment for seven days, respectively. Patients of Group 1 stopped for their own choice, SOR after the first 24 h and continued only with Actitan F. Results: After 24 h of treatment, the median number of stools was 3.5 for Group 1, and 4 for Group 2. In Group 1 the difference between the number of stools at baseline (n = 5) and after 24 h of treatment (n =3.5)wassignificant(p < ). At the end of treatment, the median duration of diarrhea in Group 1 was 5 days, compared with 4 days in the Group 2, this difference was not statically significant (p 0.48). Conclusions: Oral administration of Actitan F associated with SOR seems safe and effective treatment in shortening the duration of AG in children. Further studies confirming these data are needed. Trial registration: NCT (retrospectively registered). Keywords: Acute gastroenteritis, Treatment, Tannins, Flavonoids Background Acute gastroenteritis (AG) is the most common cause of pediatric consultations among children between 2 and 5 years of age [1]. AG in children still leads to high mortality and morbidity [2].According to current European guidelines, the main treatment for AG is the oral rehydration with anhypo-osmolar solution and regular feeding without dietary changes, including milk consumption. However, these treatment, does not reduce severity and duration of symptoms. Considering the burden of AG to children and the high cost for healthcare system, effective * Correspondence: staiano@unina.it Department of Translational Medical Science, Section of Pediatrics, Federico II University of Naples, Via S. Pansini, 5, Naples, Italy and less expensive interventions, that could be added to the effect of oral rehydration therapy, are of great interest [3]. According to the European Society of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (ESPGHAN) guidelines for diarrhoea [4], probiotics, with evidence of efficacy such as S. boulardii and L. rhamnosus GG, can be considered as a supplement to hypo-osmolar solution. It is known that probiotics reduce the mean duration of diarrhoea by about 24 h, but their efficacy on stool amount is not described [4]. Although the grade of recommendation is very strong, quality of evidences is still low [5]. Other preparations used for treatment of diarrhoea include oral administration of immunoglobulins, antiperistaltic and antisecretory agents, such as various preparations of bismuth subsalicylate, cholestyramine and loperamide [6 10]. Use of The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2018) 44:64 Page 2 of 6 antiperistaltic drugs is not effective and can cause serious side effects in children, including lethargy, seizures, Reye s syndrome, paralytic ileus and respiratory depression [11 13]. Use of loperamide, one of the most common antiperistaltic agents, is not recommended in young children and infants. In conclusion, an ideal antidiarrheal agent should have a high index of safety even when used without close professional supervisions, and should be compatible with oral rehydration solutions, treating effectively diarrhea of any etiology with moderate cost. During last years, several randomized and controlled studies showed the efficacy of tannin-rich carob pod for the treatment of acute-onset diarrhea [10]. In 2003,Subbotina et al. demonstrated that tormentil root extract, which has high content of tannins, reduces the duration of rotavirus diarrhea compared with the control group in a pediatric population (P < ) [5].They also demonstrated that in the group treated with tormentil root extract, 8 of 20 children (40%) were diarrhea-free 48 h after admission to the hospital, compared with 1 of 20 in control group (5%, P < ) [5]. In this pilot study we aimed to evaluate the efficacy and the compliance of a treatment with Actitan-F, a natural molecular complex of tannins (from Agrimony and Tormentil) and flavonoids (Chamomile), associated with SOR, in a pediatric population of children affected by AG. Methods We included 60 children (mean age: 3.1 yrs., range years) with a diagnosis of AG, referred between April and July 2017 to the Department of Translational Medicine, section of Pediatric, University of Naples Federico II. Patients enrolled were children from 3 months to 12 years old, with a diagnosis of acute diarrhoea appeared less than 7 days before the admission, capability to oral rehydration, mild to moderate dehydration. Patients with diarrhoea over 7 days, serious somatic pathology and severe dehydration were excluded. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Naples Federico II with the protocol number 25/17. At admission, written informed consent was obtained from participants parents and from all patients older than 10 years. At first visit, a medical history was collected by one of the authors and all patients underwent clinical evaluation, including body weight and body temperature. Frequency of bowel movements, stool consistency measured through the Bristol Stool Form Scale (BSFS) and other associated gastrointestinal symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and rectal bleeding, were accurately recorded. The BSFS is the most commonly standardized instrument used to rate stool consistency in children [14]. On admission, the degree of dehydration was clinically determined for each patient, based on WHO recommendations and data were recorded on a scale from 1 to 3 (1 for mild or < 5%; 2 for moderate or 5 to 10%; 3 for severe or 10% and more) [15]. All enrolled children were randomly divided into two groups: Group 1 was treated with Actitan F and standard oral rehydration (SOR) and Group 2 was treated with SOR only ad libitum for 7 days (Fig. 1) SOR is a reduced osmolarity oral solution (50/60 mmol/l Na), which is the first line therapy recommended by ESPGHAN guideline for Acute Diarrhea [16]. Actitan F, instead, was orally administrated at dose of 1 sack every 4 h, maximum 4 sacks/ day for 7 days. Caregivers were instructed to administer the daily dose after mixing the contents of the sachet with a small amount of water. The study products used in this trial were donated by Aboca Società Agricola SpA., Località Aboca, 20, 52,037 Sansepolcro (AR) Italy. At home, all parents had to fulfil a daily diary to record number and consistency of stools, presence of fever, vomiting and children compliance with the therapy. During the final visit, scheduled after 7 days, the interim history was assessed, daily diaries were reviewed and discussed, and a physical evaluation was performed. Outcomes The primary outcome was to evaluate the efficacy of a treatment with Actitan-F, a natural molecular complex of tannins (from Agrimony and Tormentil) and flavonoids (Chamomile) added to SOR compared to SOR in a paediatric population of children affected by AG. The secondary outcome was to assess safety, tolerability and compliance of the study products for short-term treatment. Endpoints The primary endpoint was the duration of diarrhoea, defined as the number of stools after 24 h of treatment or the time needed to normalize number and consistency of stools (compared with the period before the onset of diarrhoea). Secondary endpoint were the evaluation of vomiting, body weight, possible need of hospitalization, compliance to therapy. Statistical analysis Data were analysed using SPSS version 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA) for descriptive and frequency results and presented as median and range for quantitative variables and percentiles for categorical variables. Significance was defined as P value < Comparisons between the two groups used the Fisher s exact test for categorical variables and the Mann-Whitney U test for quantitative variables. χ2 test was used to
3 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2018) 44:64 Page 3 of 6 Fig. 1 Flow-chart of the study determine patients acceptance of the products (Actitan F and SOR) we tasted. Results All patients completed the study. Socio-demographic and clinical characteristics of the study population are showed in Table 1. At baseline, a mean of defecation/ daily was 5 in both groups (ranged from 3 to 8 in Group 1 and from 2 to 10 in Group 2) (p = 0.63). The median number of stools after 24 h was 3.5 in Group 1 and 4 in Group 2. The difference in the number of stools the first day of treatment between the two groups was not statistically significant (p = 0.4); however, the difference between the number of stools at baseline and after 24 h of treatment was significant (p = < ) in the group treated with Actitan F. After 24 h of treatment, we found that the most of children (23/30, 76%) in Group 1, by their own choice, interrupted the assumption of SOR and continued to take only Actitan F. At the end of treatment, in Group 1 the primary endpoint was reached after 5 days while in Group 2 after 4 days, this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.48) (Fig. 2). We also showed improved stool consistency from baseline to 24 h in the two groups, from liquid stools in 89.7 and 86.7% for Group 1 and Group 2, respectively, to 60 and 73.3% (p =0.34). In particular, regarding stool consistency, we found that at day 6 in Group % of patients reported formed stools compared with 50% in Group 2 (p =0.028). The presence of vomiting at baseline was 73.3% (22 children of 30) for Group 1 and 43.3% (13 children of 30) for the Group 2; at 24 h vomiting was present in 46.6% of the Group1 and 16% of the Group 2 with no statistical significant difference. Bloody diarrhoea was found in only 10 and 6% of patients at baseline for Group 1 and Group 2, respectively; at the end of treatment, no patient presented blood in the stool in both groups. As for weight and fever, we did not Table 1 Demographics and Clinical characteristics at baseline Overall (N=60) Group 1 (N=30) Group 2 (N=30) p-value Median age (range), years 3.1 ( ) 4.1 ( ) 2.7 ( ) 0.23 Starting date of diarrhea before consultation in days (range) 1 (1 4) 1 (1 4) 1 (1 3) 0.32 Median number of stools/day at baseline (range) 5 (2 10) 5 (3 8) 5 (2 10) 0.63 Consistency of stools at baseline (%) 0.35 Watery 81.4% 86.2% 76.7% Soft 18.6% 13.8% 23.3% Vomiting at baseline (median and range) 1.5 (0 23) 3 (0 23) 0.5 (0 7) Fever (%) 50.0% 50.0% 50.0% 1.0
4 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2018) 44:64 Page 4 of 6 Fig. 2 Primary Endpoint: Bowel movements/ day find any statistically significant difference between the groups. No one was hospitalized. Compliance and patient acceptance of treatment Concerning compliance with therapy, 8/30 children (26%) in Group 1 and 10/30 (30%) in Group 2 refused to take Actitan F and SOR, respectively (p = 0.77) (Fig. 3). Regarding the perception of the treatment efficacy, parents of children in Group 1 evaluated the Actitan F treatment very useful in 50% of cases, while parents of patients in Group 2 evaluated SOR quite effective in 68% of cases, this difference was statistically significant (p < ). Similar trend was present in the perception of improvement after 24 h, where we found a tendency to significance in Group 1withrespecttoGroup2(p = 0.07). No adverse events in both groups were reported during the study. Discussion In this pilot study, we investigated the therapeutic efficacy of a medical device made of natural complex Fig. 3 Percentage of patients who complained with flavor of MDSM (Group1) and Oral solution (Group2) (p = 0.77) substances in the treatment of children with AG. The positive clinical effect exerted by this new product on diarrhoea could be related to the tannins. Their action, indeed, is essentially focused on the intestinal mucosa, favouring its rapid recovery. More specifically, when tannins meet mucous membranes, they aspecifically interact with those membranes by making them more tight and less permeable; this process is called astringency. This feature increases protection to the subadjacent layers of mucosa from the microorganisms and irritant chemicals [17]. The efficacy and safety of a similar product in treatment of acute diarrhoea in pediatrics have been already demonstrated during the last years. In 2009 Carretero et al. observed a significant decrease in the number of stools and an improvement in stool consistency in patients treated with oral rehydration solution (SOR) and gelatin tannate vs. patients treated only with SOR [18]. Loeb et al. showed that patients receiving a product containing tannate had a normalization of bowel movements, body temperature, weight, and ceased to vomit much faster than those receiving placebo [10]. Plein and colleagues studied the effect of tannate on diarrhoea in patients with Crohn s disease [19]. The results obtained demonstrated that there was a significant reduction in bowel movement frequency at the end of treatment. Another clinical experience was reported by Ziegenhagen and colleagues, who showed the better efficacy and safety profile of tannin salts versus activated charcoal. Moreover, in the group receiving tannin salts, the frequency of abdominal pain was lower than in the activated charcoal group (50 versus 82%) [20]. Although our study protocol included the administration of Actitan F plus SOR for a week in Group 1 and SOR alone in Group 2, most of the patients in the first Group interrupted the assumption of oral rehydration
5 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2018) 44:64 Page 5 of 6 after the first day of treatment. We can explain this choice considering that after 24 h of combined treatment the reduction in number of stools in Group 1 was significantly different than at baseline (p < ) (5 vs. 3.5 stools/day). Due to the high perception of symptom improvement reported by parents of children in Group 1 after the first day of treatment, we can speculate that the rapid improvement of clinical condition may have induced parents to stop earlier the oral solution and continue only with Actitan F. As a matter of fact, our results showing that the mean duration of diarrhea in both groups after 7 days of therapy was not statistically significant, should be interpreted in the light of what we have just described. Regarding stool consistency, we showed no statistically significant differences between the two groups, however at day 6 of treatment we found that 76.9% of patients in Group 1 reported formed stools compared with 50% in Group 2, this data showed a tendency to significance with a p = 0,028, maybe do to the small number of patients enrolled. We can explain this better result on stool consistency comparing to SOR alone, knowing that it has already been demonstrated that tannins and flavonoids exerts their action by restoring the physiological function of the intestine barrier and have astringent properties [17]. Moreover, in our study any adverse event in children were observed in both groups, and this confirms the safety of tannins in the pediatric population. Compliance with administration of Actitan F was good; every patient received 75% of doses according to the patient s weight. This result confirms a good ease of administration. In contrast to other studies, we did not perform stool cultures at baseline [21, 22]. Nevertheless, ESPGHAN does not recommend performing stool cultures for acute gastroenteritis in primary healthcare, and we did not aim to evaluate the impact of tannins based on the different aetiologies of diarrhoea. Conclusion Therefore, we can conclude that Actitan F in association with SOR, may offer a safe and cost-effective approach to AG in infants and children. However, further studies and large trials are required. Because this study showed promising results, it would be worthwhile to perform a large randomized control trial to unravel the efficacy of the Actitan F plus SOR in children with AG. Abbreviations AG: Acute gastroenteritis; SOR: standard oral rehydration Funding Aboca Società Agricola SpA., Località Aboca, 20, Sansepolcro (AR) Italy. Availability of data and materials Data will not be shared in accordance to the Department s policy. Authors contributions MR performed data acquisition, analysed the data, wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and approved the final version of the paper. VC performed data acquisition, critically revised the manuscript and approved the final version of the paper. VC, RB and AP performed data acquisition, critically revised the manuscript and approved the final version of the paper. EG designed the research study, analyzed the data, and approved the final version of the paper. AS designed the research study, critically revised the manuscript and approved the final version and the submission. Ethics approval and consent to participate The study was approved by the Independent Ethics Committee of the Federico II University of Naples (reference number: 25/17). Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Received: 30 November 2017 Accepted: 9 May 2018 References 1. Van Damme P. Multicenter prospective study of the burden of rotavirus acute gastroenteritis in Europe, : the REVEAL study. J Infect Dis. 2007;195(Suppl 1):S Ogilvie I. Burden of community-acquired and nosocomial rotavirus gastroenteritis in the pediatric population of Western Europe: a scoping review. BMC Infect Dis. 2012;12: Szajewska H. Probiotics in gastrointestinal diseases in children: hard and not-so-hard evidence of efficacy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006;42: Guarino A. Probiotics as prevention and treatment for diarrhea. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009;25(1): Subbotina Maria D. Effect of oral administration of tormentil root extract (Potentilla tormentilla) on rotavirus diarrhea in children: a randomized, double blind, controlled trial. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22: Madkour AA. Cholestyramine in acute infantile diarrhea: a double-blind, placebo controlled clinical trial in hospitalized infants. Alexandria. J Pediatr. 1990;4: Madkour AA. Smectite in acute diarrhea of children: a double-blind placebocontrolled clinical trial. Gastroenterology. 1991;100:A Kaplan MA, Prior MJ, McKonly KI, et al. A multicenter randomized controlled trial of liquid loperamide product versus placebo in the treatment of acute diarrhea in children. Clin Pediatr. 1999;38: Ebina T. Prevention of rotavirus infection with cow colostrum containing antibody against human rotavirus. Lancet. 1983;2: Loeb H. Tannin-rich carob pod for the treatment of acute-onset diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1989;8: Elaraby II. The use of chlorpromazine as an antisecretory agent in acute diarrhea of childhood. Alexandria J Pediatr. 1989;3: Kassem AS. Loperamide in acute childhood diarrhoea: a double blind controlled trial. J Diarr Dis Res. 1983;1: Kassem AS. Effect of antibiotics on the duration of diarrhea and speed of rehydration. Gazette Egyptian Paediatr Assoc 1983;31: Lane MM. Reliability and validity of a modified Bristol stool form scale for children, J Pediatr. 2011;159: e World Health Organization. The treatment of diarrhea: A manual for physicians and other senior health workers; Guarino A. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition/european Society for Pediatric Infectious Diseases Evidence- Based Guidelines for the Management of Acute Gastroenteritis in children in Europe: update JPGN. 2014;59(Issue 1): Mills S, Bone K. The essential guide to herbal safety. UK: Churchil Livingstone; Esteban Carretero J. A comparative analysis of ORS (oral rehydration solution) vs. ORS + gelatin tannin in two cohorts of pediatric patients with acute diarrhea. REV ESP ENFERM DIG (Madrid). 2009;101(1):41 8.
6 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2018) 44:64 Page 6 of Plein K. Treatment of chronic diarrhea in Crohn disease. A pilot study of the clinical effect of tannin albuminate and ethacridine lactate. Fortschr Med. 1993;111: Ziegenhagen DJ. Traveler's diarrhea in Turkey. Prospective randomized therapeutic comparison of charcoal versus tannin albuminate/ethacridine lactate. Med Klin. 1992;87: Salazar-Lindo E. Racecadotril in the treatment of acute watery diarrhea in children. N Engl Med J. 2000;343: Cezard J. Efficacy and tolerability of Racecadotril in acute diarrhea in children. Gastroenterology. 2001;120( ):13.
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 11 Page November 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i11.186 Role of Saccharomyces Boulardii and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i11.186 Role of Saccharomyces Boulardii and
The therapeutic effect of gelatin tannate in acute diarrhea in children
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2017; 59: 531-536 DOI: 10.24953/turkjped.2017.05.005 The therapeutic effect of gelatin tannate in acute diarrhea in children Soner Sertan Kara 1, Burcu Volkan 2, İbrahim
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2017; 59: 531-536 DOI: 10.24953/turkjped.2017.05.005 The therapeutic effect of gelatin tannate in acute diarrhea in children Soner Sertan Kara 1, Burcu Volkan 2, İbrahim
Opinion 24 July 2013
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 24 July 2013 SMECTA, powder for oral solution in sachets 30 sachets of 3.76 g (CIP: 34009 319 230-7 7) 60 sachets
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 24 July 2013 SMECTA, powder for oral solution in sachets 30 sachets of 3.76 g (CIP: 34009 319 230-7 7) 60 sachets
ACUTE GASTROENTERITIS IN CHILDREN
 ACUTE GASTROENTERITIS IN CHILDREN Prof. Alok Kumar Professor of Pediatrics & Infectious Diseases Faculty of Medical Sciences The University of the West Indies (Cave Hill) 11/6/2017 1 DEFINITION Gastroenteritis
ACUTE GASTROENTERITIS IN CHILDREN Prof. Alok Kumar Professor of Pediatrics & Infectious Diseases Faculty of Medical Sciences The University of the West Indies (Cave Hill) 11/6/2017 1 DEFINITION Gastroenteritis
Algorithms & Information Sheets
 Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
racecadotril 10mg, 30mg granules for oral suspension (Hidrasec Infants, Hidrasec Children ) SMC No. (818/12) Abbott Healthcare Products Ltd
 racecadotril 10mg, 30mg granules for oral suspension (Hidrasec Infants, Hidrasec Children ) SMC No. (818/12) Abbott Healthcare Products Ltd 09 November 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has
racecadotril 10mg, 30mg granules for oral suspension (Hidrasec Infants, Hidrasec Children ) SMC No. (818/12) Abbott Healthcare Products Ltd 09 November 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has
Acute Gastroenteritis
 Acute Gastroenteritis Definitions Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnostics Therapy Erdélyi, Dániel 2018.04.10. Definitions Acute gastroenteritis (AGE): Loose or liquid stools 3 times daily (better:
Acute Gastroenteritis Definitions Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnostics Therapy Erdélyi, Dániel 2018.04.10. Definitions Acute gastroenteritis (AGE): Loose or liquid stools 3 times daily (better:
New Medicine Review. Racecadotril for the symptomatic treatment of acute diarrhoea (adults and children over 3 months)
 BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC) April 2013 Review date: April 2016 Bulletin 180: Racecadotril for the symptomatic treatment of acute diarrhoea in adults and children over 3 months
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC) April 2013 Review date: April 2016 Bulletin 180: Racecadotril for the symptomatic treatment of acute diarrhoea in adults and children over 3 months
Case Report Severe Diarrhea in a 4-Month-Old Baby Girl with Acute Gastroenteritis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 01, Article ID 90375, 4 pages doi:10.1155/01/90375 Case Report Severe Diarrhea in a 4-Month-Old Baby Girl with Acute Gastroenteritis: A Case Report and
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 01, Article ID 90375, 4 pages doi:10.1155/01/90375 Case Report Severe Diarrhea in a 4-Month-Old Baby Girl with Acute Gastroenteritis: A Case Report and
A Randomized Open Label Comparative Clinical Study of a Probiotic against a Symbiotic in the Treatment of Acute Diarrhoea in Children
 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(9): 96-100 I J M R
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(9): 96-100 I J M R
Comparative Evaluation of Efficacy of Antibiotic in Treating Bacterial Enteritis in Children: A Hospital Based Study
 Original article: Comparative Evaluation of Efficacy of Antibiotic in Treating Bacterial Enteritis in Children: A Hospital Based Study Radheshyam Shrotriya, Anju Kochar Principal Specialist (Pediatrics),
Original article: Comparative Evaluation of Efficacy of Antibiotic in Treating Bacterial Enteritis in Children: A Hospital Based Study Radheshyam Shrotriya, Anju Kochar Principal Specialist (Pediatrics),
*World Health Organization / United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund
 Logotype ORSALIT Drawing: little fish 1x Drawing: fruits 1x ORSALIT is an oral rehydration solution (ORS) with reduced osmolarity and composition in accordance with the recommendations of the European
Logotype ORSALIT Drawing: little fish 1x Drawing: fruits 1x ORSALIT is an oral rehydration solution (ORS) with reduced osmolarity and composition in accordance with the recommendations of the European
Pthaigastro.org. Drugs Used in Acute Diarrhea: Cons. Nipat Simakachorn, M.D. Department of Pediatrics Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital.
 Drugs Used in Acute Diarrhea: Cons Nipat Simakachorn, M.D. Department of Pediatrics Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital 27-Apr-2012 Optimistic Pessimistic Global percentage of children
Drugs Used in Acute Diarrhea: Cons Nipat Simakachorn, M.D. Department of Pediatrics Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital 27-Apr-2012 Optimistic Pessimistic Global percentage of children
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Common questions about treating diarrhoea with zinc and oral rehydration salts (ORS) SPACE FOR LOGO INTRODUCTION To treat childhood diarrhoea, the World Health Organization recommends
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Common questions about treating diarrhoea with zinc and oral rehydration salts (ORS) SPACE FOR LOGO INTRODUCTION To treat childhood diarrhoea, the World Health Organization recommends
Objectives. Introduction. Etiology of Acute Diarrhea 10/3/2012
 Update on acute diarrhea in developing countries: oral rehydration, refeeding, probiotics, and beyond Debora Duro MD, MS Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition Associate Professor of Pediatrics at Florida
Update on acute diarrhea in developing countries: oral rehydration, refeeding, probiotics, and beyond Debora Duro MD, MS Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition Associate Professor of Pediatrics at Florida
Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation in childhood
 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Nifuroxazide (Ercefuryl) Plus Oral rehydration solution Versus Oral Rehydration Alone in Hospitalized Pediatric Gastroenteritis
 Nifuroxazide (Ercefuryl) Plus Oral rehydration solution Versus Oral Rehydration Alone in Hospitalized Pediatric Gastroenteritis Lourdes T. Santiago, M.D.,* Catherine P. Ranoa, M.D.,** Edmond G. Chan, M.D.***
Nifuroxazide (Ercefuryl) Plus Oral rehydration solution Versus Oral Rehydration Alone in Hospitalized Pediatric Gastroenteritis Lourdes T. Santiago, M.D.,* Catherine P. Ranoa, M.D.,** Edmond G. Chan, M.D.***
Defining incidence of intussusception (IS) in Bangladesh in preparation for a phase III trial of a new Rotavirus vaccine
 Defining incidence of intussusception (IS) in Bangladesh in preparation for a phase III trial of a new Rotavirus vaccine Principal Investigator: Dr. K. Zaman Final Report June 1, 2007 1 This study was
Defining incidence of intussusception (IS) in Bangladesh in preparation for a phase III trial of a new Rotavirus vaccine Principal Investigator: Dr. K. Zaman Final Report June 1, 2007 1 This study was
Doppler Ultrasound findings in Children with Cow's Milk Allergy
 Doppler Ultrasound findings in Children with Cow's Milk Allergy Poster No.: C-0174 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Baldisserotto; Porto Alegre/BR Acceptance testing,
Doppler Ultrasound findings in Children with Cow's Milk Allergy Poster No.: C-0174 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Baldisserotto; Porto Alegre/BR Acceptance testing,
Primary Lactase Deficiency among Malnourished Children with Persistent Diarrhea in Tbilisi, Georgia
 THIEME Case Report e19 Primary Lactase Deficiency among Malnourished Children with Persistent Diarrhea in Tbilisi, Georgia Ketevan Nemsadze 1 Eka Liluashvili 1 N. Kikodze 1 T. Bakhtadze 1 1 Department
THIEME Case Report e19 Primary Lactase Deficiency among Malnourished Children with Persistent Diarrhea in Tbilisi, Georgia Ketevan Nemsadze 1 Eka Liluashvili 1 N. Kikodze 1 T. Bakhtadze 1 1 Department
Frequently Asked Questions on Zinc and Suggested Responses
 Last edited: September 27, 2012 Zinc Treatment of Childhood Diarrhea Frequently Asked Questions Diarrhoea still remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in developing countries. Every year more
Last edited: September 27, 2012 Zinc Treatment of Childhood Diarrhea Frequently Asked Questions Diarrhoea still remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in developing countries. Every year more
Homeopathic Products. Evidence??
 Homeopathic Products Principle of analogy or Law of Similars Small or infinitesimal doses (3X-30C) Avogadro s number=6x10 23 = ~23X Succussion and potentization (see http://www.boiron.com/en/htm/02_medi_hom
Homeopathic Products Principle of analogy or Law of Similars Small or infinitesimal doses (3X-30C) Avogadro s number=6x10 23 = ~23X Succussion and potentization (see http://www.boiron.com/en/htm/02_medi_hom
Does Bicarbonate Concentration Predict Hospitalization among Children with Gastroenteritis?
 Does Bicarbonate Concentration Predict Hospitalization among Children with Gastroenteritis? Muin Habashneh MD*, Mohammad Alrwalah MD* ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the relationship between bicarbonate
Does Bicarbonate Concentration Predict Hospitalization among Children with Gastroenteritis? Muin Habashneh MD*, Mohammad Alrwalah MD* ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the relationship between bicarbonate
by Ruchika Kumar, 1 Praveen Kumar, 1 S. Aneja, 1 Virendra Kumar, 1 and Harmeet S. Rehan 2
 Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 2015, 61, 435 441 doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmv054 Advance Access Publication Date: 27 August 2015 Original Paper Safety and Efficacy of Low-osmolarity ORS vs. Modified Rehydration
Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 2015, 61, 435 441 doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmv054 Advance Access Publication Date: 27 August 2015 Original Paper Safety and Efficacy of Low-osmolarity ORS vs. Modified Rehydration
Trends of kidney transplantation in Japan in 2018: data from the kidney transplant registry
 Yagisawa et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2019) 5:3 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-019-0199-6 POSITION STATEMENT Trends of kidney transplantation in Japan in 2018: data from the kidney transplant registry
Yagisawa et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2019) 5:3 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-019-0199-6 POSITION STATEMENT Trends of kidney transplantation in Japan in 2018: data from the kidney transplant registry
Probiotics for Primary Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infection
 Probiotics for Primary Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infection Objectives Review risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Describe guideline recommendations for CDI prevention Discuss
Probiotics for Primary Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infection Objectives Review risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Describe guideline recommendations for CDI prevention Discuss
THE EFFECT OF PROBIOTIC, OHHIRA OMX CAPSULES, IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE NON-BLOODY DIARRHEA IN INFANTS 3-24 MONTHS OF AGE
 THE EFFECT OF PROBIOTIC, OHHIRA OMX CAPSULES, IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE NON-BLOODY DIARRHEA IN INFANTS - MONTHS OF AGE Hazel T. Valdoria, MD., Felizardo N. Gatcheco, MD. INTRODUCTION Diarrheal diseases
THE EFFECT OF PROBIOTIC, OHHIRA OMX CAPSULES, IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE NON-BLOODY DIARRHEA IN INFANTS - MONTHS OF AGE Hazel T. Valdoria, MD., Felizardo N. Gatcheco, MD. INTRODUCTION Diarrheal diseases
Fecal shedding of rotavirus vaccine in premature babies in the neonatal unit
 Fecal shedding of rotavirus vaccine in premature babies in the neonatal unit Dr. Manish Sadarangani Director, Vaccine Evaluation Center, BC Children s Hospital Research Institute Assistant Professor, Division
Fecal shedding of rotavirus vaccine in premature babies in the neonatal unit Dr. Manish Sadarangani Director, Vaccine Evaluation Center, BC Children s Hospital Research Institute Assistant Professor, Division
Clinical Report: Probiotics and Prebiotics in Pediatrics
 www.medscape.com Authors and Disclosures Author(s) Dan W. Thomas, MD Professor of Pediatrics, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California; Head, Division of Gastroenterology
www.medscape.com Authors and Disclosures Author(s) Dan W. Thomas, MD Professor of Pediatrics, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California; Head, Division of Gastroenterology
Copyright ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN. All rights reserved.
 Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, Publish Ahead of Print DOI : 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002053 Universal recommendations for the management of acute diarrhea in non-malnourished children
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, Publish Ahead of Print DOI : 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002053 Universal recommendations for the management of acute diarrhea in non-malnourished children
Study on Incidence of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhoea in General Paediatric Ward
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2002;7:33-38 Study on Incidence of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhoea in General Paediatric Ward CM HUI, K TSE Abstract Objective: To estimate the incidence rate and risk factors
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2002;7:33-38 Study on Incidence of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhoea in General Paediatric Ward CM HUI, K TSE Abstract Objective: To estimate the incidence rate and risk factors
Resolution of acute gastroenteritis symptoms in children and adults treated with a novel polyphenol-based prebiotic
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12301 World J Gastroenterol 2014 September 14; 20(34): 12301-12307 ISSN 1007-9327
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12301 World J Gastroenterol 2014 September 14; 20(34): 12301-12307 ISSN 1007-9327
Classification of pediatric functional gastrointestinal disorders related to abdominal pain using Rome III vs. Rome IV criterions
 Edwards et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:41 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0769-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Classification of pediatric functional gastrointestinal disorders related to abdominal
Edwards et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:41 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0769-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Classification of pediatric functional gastrointestinal disorders related to abdominal
Saccharomyces boulardii in Acute Gastroenteritis in Children
 Article ID: WMC001627 ISSN 2046-1690 Saccharomyces boulardii in Acute Gastroenteritis in Children Corresponding Author: Dr. Yvan Vandenplas, Brussels, Pediatrics, UZ Brussel, Laarbeeklaan 101, 1090 - Belgium
Article ID: WMC001627 ISSN 2046-1690 Saccharomyces boulardii in Acute Gastroenteritis in Children Corresponding Author: Dr. Yvan Vandenplas, Brussels, Pediatrics, UZ Brussel, Laarbeeklaan 101, 1090 - Belgium
The Cow s Milk-related Symptom Score. CoMiSS TM. An awareness tool. to recognize cow s milk-related symptoms in infants and young children
 The Cow s Milk-related Symptom Score CoMiSS TM An awareness tool to recognize cow s milk-related symptoms in infants and young children Background SYMPTOMS RELATED TO INTAKE OF COW S MILK Many infants
The Cow s Milk-related Symptom Score CoMiSS TM An awareness tool to recognize cow s milk-related symptoms in infants and young children Background SYMPTOMS RELATED TO INTAKE OF COW S MILK Many infants
Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration. May 16/17
 Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration May 16/17 Volume Depletion (hypovolemia): refers to any condition in which the effective circulating volume is reduced. It can be produced by salt and water loss
Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration May 16/17 Volume Depletion (hypovolemia): refers to any condition in which the effective circulating volume is reduced. It can be produced by salt and water loss
Travellers Diarrhea Update: From Prevention to Self-Treatment. Michael Payne November 4 th, 2016
 Travellers Diarrhea Update: From Prevention to Self-Treatment Michael Payne November 4 th, 2016 Outline 1. Epidemiology of travellers diarrhea 2. Prevention Behavioral Vaccination Medications 3. Self-treatment
Travellers Diarrhea Update: From Prevention to Self-Treatment Michael Payne November 4 th, 2016 Outline 1. Epidemiology of travellers diarrhea 2. Prevention Behavioral Vaccination Medications 3. Self-treatment
Rifaximin for Travellers Diarrhoea
 New Medicines Profile April 2013 Issue No. 13.01 for Travellers Diarrhoea Concise evaluated information to support the managed entry of new medicines in the NHS Summary is a broad spectrum antibiotic licensed
New Medicines Profile April 2013 Issue No. 13.01 for Travellers Diarrhoea Concise evaluated information to support the managed entry of new medicines in the NHS Summary is a broad spectrum antibiotic licensed
Training in Infectious Diseases Modeling. A reflection on vaccination as a disease control measure
 Training in Infectious Diseases Modeling A reflection on vaccination as a disease control measure -Example of Rotavirus disease- Participant s Guide Adapted by Nathalie Elomeiri; Camelia Savulescu; Fernando
Training in Infectious Diseases Modeling A reflection on vaccination as a disease control measure -Example of Rotavirus disease- Participant s Guide Adapted by Nathalie Elomeiri; Camelia Savulescu; Fernando
Antibiotic use, gastroenteritis and respiratory illness in South Australian children
 Epidemiol. Infect. (2002), 129, 507 513. f 2002 Cambridge University Press DOI: 10.1017/S0950268802007628 Printed in the United Kingdom Antibiotic use, gastroenteritis and respiratory illness in South
Epidemiol. Infect. (2002), 129, 507 513. f 2002 Cambridge University Press DOI: 10.1017/S0950268802007628 Printed in the United Kingdom Antibiotic use, gastroenteritis and respiratory illness in South
APDW 2016 Poster No. a90312
 APDW 2016 Poster No. a90312 SYN-010, a Proprietary Modified-Release Formulation of Lovastatin Lactone, Lowered Breath Methane and Improved Stool Frequency in Patients with IBS-C Results of a multi-center,
APDW 2016 Poster No. a90312 SYN-010, a Proprietary Modified-Release Formulation of Lovastatin Lactone, Lowered Breath Methane and Improved Stool Frequency in Patients with IBS-C Results of a multi-center,
Meta-analysis: Lactobacillus GG for treating acute diarrhoea in children
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Meta-analysis: Lactobacillus GG for treating acute diarrhoea in children H.SZAJEWSKA,A.SKÓRKA, M. RUSZCZYŃSKI & D. GIERUSZCZAK-BIAŁEK The Second Department of Paediatrics
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Meta-analysis: Lactobacillus GG for treating acute diarrhoea in children H.SZAJEWSKA,A.SKÓRKA, M. RUSZCZYŃSKI & D. GIERUSZCZAK-BIAŁEK The Second Department of Paediatrics
Acute Gastroenteritis 2015
 Acute Gastroenteritis 2015 Disclosure Statement Joel S. Tieder, MD, MPH Clinical Advances in Pediatrics Symposium September 18, 2015 I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacture(s) of
Acute Gastroenteritis 2015 Disclosure Statement Joel S. Tieder, MD, MPH Clinical Advances in Pediatrics Symposium September 18, 2015 I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacture(s) of
Study summaries L. casei 431
 This binder provides you with summaries of selected publications on Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei L. casei 431. The publications are clinical studies performed in humans documenting the effects
This binder provides you with summaries of selected publications on Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei L. casei 431. The publications are clinical studies performed in humans documenting the effects
The role of nutrition in optimum gastrointestinal health
 The role of nutrition in optimum gastrointestinal health Kelly A. Tappenden, Ph.D., R.D., FASPEN Kraft Foods Human Nutrition Endowed Professor University Distinguished Teacher-Scholar University of Illinois
The role of nutrition in optimum gastrointestinal health Kelly A. Tappenden, Ph.D., R.D., FASPEN Kraft Foods Human Nutrition Endowed Professor University Distinguished Teacher-Scholar University of Illinois
Keywords acute diarrhea, probiotic, synbiotic, Prodefen, children, tolerability, efficacy
 679587GPHXXX10.1177/2333794X16679587Global Pediatric HealthGarcía-Menor et al research-article2016 Original Article A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Additional Benefit
679587GPHXXX10.1177/2333794X16679587Global Pediatric HealthGarcía-Menor et al research-article2016 Original Article A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Additional Benefit
Gastroenteritis in children Paediatric department
 Gastroenteritis in children Paediatric department 01935 475 122 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is Gastroenteritis? Gastroenteritis (stomach bug) is an infection in the gut (intestines). It is common in all
Gastroenteritis in children Paediatric department 01935 475 122 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is Gastroenteritis? Gastroenteritis (stomach bug) is an infection in the gut (intestines). It is common in all
You should call our office immediately if your child has any of the following symptoms: 1. Looks weak or is unresponsive
 Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines, often called the stomach flu (although it is not caused by the influenza virus.) The symptoms of gastroenteritis commonly
Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines, often called the stomach flu (although it is not caused by the influenza virus.) The symptoms of gastroenteritis commonly
Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating Probiotics in Children with Severe Acute Malnutrition.
 J O U R N A L C L U B Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating Probiotics in Children with Severe Acute Malnutrition. Source Citation: Grenov B, Namusoke H, Lanyero B, Nabukeera-Barungi N, Ritz C, Mølgaard
J O U R N A L C L U B Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating Probiotics in Children with Severe Acute Malnutrition. Source Citation: Grenov B, Namusoke H, Lanyero B, Nabukeera-Barungi N, Ritz C, Mølgaard
Safety and Efficacy of Saccharomyces boulardii for the management of Diarrhoea in Indian children
 International Journal of Scientific Research and Management (IJSRM) Volume 06 Issue 01 Pages MP-2018-01-05 2018 Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Index Copernicus value (2015): 57.47, (2016):93.67,
International Journal of Scientific Research and Management (IJSRM) Volume 06 Issue 01 Pages MP-2018-01-05 2018 Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Index Copernicus value (2015): 57.47, (2016):93.67,
Authors and Disclosures
 Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Review Article Role of Antidiarrhoeal Drugs as Adjunctive Therapies for Acute Diarrhoea in Children
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Pediatrics Volume 2013, Article ID 612403, 14 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/612403 Review Article Role of Antidiarrhoeal Drugs as Adjunctive
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Pediatrics Volume 2013, Article ID 612403, 14 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/612403 Review Article Role of Antidiarrhoeal Drugs as Adjunctive
Key Words: Cow s milk protein allergy, Cow s milk-related-symptom-score extensive hydrolysate
 pissn: -8 eissn: -880 https://doi.org/0.5/pghn.07.0.. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 07 March 0():- Original Article PGHN Pooled Analysis of the Cow s Milk-related-Symptom-Score (CoMiSS TM ) as a Predictor
pissn: -8 eissn: -880 https://doi.org/0.5/pghn.07.0.. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 07 March 0():- Original Article PGHN Pooled Analysis of the Cow s Milk-related-Symptom-Score (CoMiSS TM ) as a Predictor
Appendix 9B. Diagnosis and Management of Infants with Suspected Cow s Milk Protein Allergy.
 Appendix 9B Diagnosis and Management of Infants with Suspected Cow s Milk Protein Allergy. A guide for healthcare professionals working in primary care. This document aims to provide health professionals
Appendix 9B Diagnosis and Management of Infants with Suspected Cow s Milk Protein Allergy. A guide for healthcare professionals working in primary care. This document aims to provide health professionals
Developing the potential of prebiotics and probiotics as immune health ingredients
 Developing the potential of prebiotics and probiotics as immune health ingredients ARTHUR OUWEHAND ACTIVE NUTRITION DUPONT NUTRITION & HEALTH 20 th November 2014, The gut microbiome The gut microbiota
Developing the potential of prebiotics and probiotics as immune health ingredients ARTHUR OUWEHAND ACTIVE NUTRITION DUPONT NUTRITION & HEALTH 20 th November 2014, The gut microbiome The gut microbiota
Adherence to pediatric diabetic ketoacidosis guidelines by community emergency departments providers
 Zee-Cheng et al. International Journal of Emergency Medicine (2017) 10:11 DOI 10.1186/s12245-017-0137-8 International Journal of Emergency Medicine ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Adherence to pediatric
Zee-Cheng et al. International Journal of Emergency Medicine (2017) 10:11 DOI 10.1186/s12245-017-0137-8 International Journal of Emergency Medicine ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Adherence to pediatric
MOVICOL HALF PI December MOVICOL-Half. Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Potassium 5.4 mmol/l. Bicarbonate 17 mmol/l
 MOVICOL -Half Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: Product Description: MOVICOL-Half Each sachet of MOVICOL-Half contains: Macrogol 3350 6.563 g Sodium chloride 175.4 mg Sodium bicarbonate
MOVICOL -Half Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: Product Description: MOVICOL-Half Each sachet of MOVICOL-Half contains: Macrogol 3350 6.563 g Sodium chloride 175.4 mg Sodium bicarbonate
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews
 PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews The effect of probiotics on functional constipation: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials EIRINI DIMIDI, STEPHANOS CHRISTODOULIDES,
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews The effect of probiotics on functional constipation: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials EIRINI DIMIDI, STEPHANOS CHRISTODOULIDES,
Fonterra Probiotics: From guts to glory
 Fonterra Probiotics: From guts to glory James Dekker April 16, 2015 Host Institution Probiotic bacteria Live micro-organisms which, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the
Fonterra Probiotics: From guts to glory James Dekker April 16, 2015 Host Institution Probiotic bacteria Live micro-organisms which, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the
Handbook of Nonprescription Drugs: An Interactive Approach to Self Care, 18 th Edition Corrections and Revisions
 Handbook of Nonprescription Drugs: An Interactive Approach to Self Care, 18 th Edition Corrections and Revisions Note: All the corrections and revisions have been made on the e version of the book that
Handbook of Nonprescription Drugs: An Interactive Approach to Self Care, 18 th Edition Corrections and Revisions Note: All the corrections and revisions have been made on the e version of the book that
Viral gastroenteritis Gastrointestinal infections caused by viruses are the most common and the most contagious.3
 CMA Today Quick Clinic May/Jun 2017 (Issue 3/Volume 50) GI woes Gastroenteritis affects patients at home and abroad By Nancy Solomon We expect patients to come into the office a few times a year with that
CMA Today Quick Clinic May/Jun 2017 (Issue 3/Volume 50) GI woes Gastroenteritis affects patients at home and abroad By Nancy Solomon We expect patients to come into the office a few times a year with that
Upper extremity open fractures in hospitalized road traffic accident patients: adult versus pediatric cases
 Rubin et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:157 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0657-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Upper extremity in hospitalized road traffic accident : adult versus pediatric
Rubin et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:157 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0657-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Upper extremity in hospitalized road traffic accident : adult versus pediatric
RESEARCH. Probiotics for treatment of acute diarrhoea in children: randomised clinical trial of five different preparations
 Probiotics for treatment of acute diarrhoea in children: randomised clinical trial of five different preparations Roberto Berni Canani, assistant professor of paediatrics, 1 Pia Cirillo, paediatrician,
Probiotics for treatment of acute diarrhoea in children: randomised clinical trial of five different preparations Roberto Berni Canani, assistant professor of paediatrics, 1 Pia Cirillo, paediatrician,
Acute diarrhoea. What are the mechanisms of acute diarrhoea? What are the causes of acute diarrhoea?
 In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Acute diarrhoea www.corecharity.org.uk What are the mechanisms of acute diarrhoea? What are the causes of acute diarrhoea?
In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Acute diarrhoea www.corecharity.org.uk What are the mechanisms of acute diarrhoea? What are the causes of acute diarrhoea?
IBS: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria
 IBS: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria William D. Chey, MD Professor of Medicine University of Michigan What is the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptom based
IBS: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria William D. Chey, MD Professor of Medicine University of Michigan What is the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptom based
William Chey, MD University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI
 Lin Chang, MD David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, CA William Chey, MD University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI Mark Pimentel, MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Accredited by Jointly
Lin Chang, MD David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, CA William Chey, MD University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI Mark Pimentel, MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Accredited by Jointly
Emerging Treatments for IBS-C and Clinical Trial Endpoints
 Emerging Treatments for IBS-C and Clinical Trial Endpoints Lin Chang, M.D. Oppenheimer Family Center for Neurobiology of Stress David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Learning Objectives Describe current
Emerging Treatments for IBS-C and Clinical Trial Endpoints Lin Chang, M.D. Oppenheimer Family Center for Neurobiology of Stress David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Learning Objectives Describe current
Therapy of Viral Gastroenteritis
 Chapter 1.4 Therapy of Viral Gastroenteritis G. Kang The Wellcome Trust Research Laboratory, Division of Gastrointestinal Sciences, Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India 1 INTRODUCTION
Chapter 1.4 Therapy of Viral Gastroenteritis G. Kang The Wellcome Trust Research Laboratory, Division of Gastrointestinal Sciences, Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India 1 INTRODUCTION
Immodium / loprarmide
 Immodium / loprarmide IMODIUM (loperamide hydrochloride) is indicated for the control and symptomatic relief of acute nonspecific diarrhea and of chronic diarrhea associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
Immodium / loprarmide IMODIUM (loperamide hydrochloride) is indicated for the control and symptomatic relief of acute nonspecific diarrhea and of chronic diarrhea associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
Protectives and Adsorbents. Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry
 Protectives and Adsorbents Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year 2016-2017 Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry Protectives and Adsorbents This group of gastrointestinal agents
Protectives and Adsorbents Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year 2016-2017 Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry Protectives and Adsorbents This group of gastrointestinal agents
Under-five and infant mortality constitutes. Validation of IMNCI Algorithm for Young Infants (0-2 months) in India
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Validation of IMNCI Algorithm for Young Infants (0-2 months) in India SATNAM KAUR, V SINGH, AK DUTTA AND J CHANDRA From the Department of Pediatrics, Kalawati Saran Children s
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Validation of IMNCI Algorithm for Young Infants (0-2 months) in India SATNAM KAUR, V SINGH, AK DUTTA AND J CHANDRA From the Department of Pediatrics, Kalawati Saran Children s
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objective: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variables:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Translating the science into efficacy claims on probiotic or prebiotic products in the US market
 Translating the science into efficacy claims on probiotic or prebiotic products in the US market American Dairy Science Association Annual Meeting July 13, 2010 Dairy & Food Culture Technologies Consulting
Translating the science into efficacy claims on probiotic or prebiotic products in the US market American Dairy Science Association Annual Meeting July 13, 2010 Dairy & Food Culture Technologies Consulting
Human Anatomy rectum
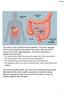 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
NUR 568: Critical Appraisal Topic Lactobacillus in the Management of Abdominal Pain in Children Christina A. Dahl, RN, FNP-s University of Mary
 Running Head: NUR 568 Critical Appraisal Topic 1 NUR 568: Critical Appraisal Topic Lactobacillus in the Management of Abdominal Pain in Children Christina A. Dahl, RN, FNP-s University of Mary Running
Running Head: NUR 568 Critical Appraisal Topic 1 NUR 568: Critical Appraisal Topic Lactobacillus in the Management of Abdominal Pain in Children Christina A. Dahl, RN, FNP-s University of Mary Running
Acute Diarrhea. Shajia Shelby, MD Anna Trauernicht, MD. Children s Hospital and Medical Center, University of Nebraska Medical Center
 Acute Diarrhea Shajia Shelby, MD Anna Trauernicht, MD Children s Hospital and Medical Center, University of Nebraska Medical Center 2013 Resident Education Series Reviewed by Edward Hoffenberg, MD of the
Acute Diarrhea Shajia Shelby, MD Anna Trauernicht, MD Children s Hospital and Medical Center, University of Nebraska Medical Center 2013 Resident Education Series Reviewed by Edward Hoffenberg, MD of the
GASTROENTERITIS. What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US
 GASTROENTERITIS What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Why should Gastroenteritis be treated Dehydration is an important sign of advanced and/or untreated gastroenteritis. Severe
GASTROENTERITIS What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Why should Gastroenteritis be treated Dehydration is an important sign of advanced and/or untreated gastroenteritis. Severe
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: rifaximin (Xifaxan) Reference Number: HIM.PA.68 Effective Date: 12/14 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Health Insurance Marketplace Coding Implications Revision Log See Important
Clinical Policy: rifaximin (Xifaxan) Reference Number: HIM.PA.68 Effective Date: 12/14 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Health Insurance Marketplace Coding Implications Revision Log See Important
Presented by Megan R. Sanctuary, MS University of California at Davis
 Effects of supplementation with Bifidobacterium infantis in combination with bioactive milk components on gastrointestinal symptoms in children with autism Presented by Megan R. Sanctuary, MS University
Effects of supplementation with Bifidobacterium infantis in combination with bioactive milk components on gastrointestinal symptoms in children with autism Presented by Megan R. Sanctuary, MS University
RACECADOTRIL IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE WATERY DIARRHEA IN CHILDREN RACECADOTRIL IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE WATERY DIARRHEA IN CHILDREN.
 RACECADOTRIL IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE WATERY DIARRHEA IN CHILDREN EDUARDO SALAZAR-LINDO, M.D., JAVIER SANTISTEBAN-PONCE, M.D., ELSA CHEA-WOO, M.D., AND MANUEL GUTIERREZ, M.D. ABSTRACT Background (acetorphan),
RACECADOTRIL IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE WATERY DIARRHEA IN CHILDREN EDUARDO SALAZAR-LINDO, M.D., JAVIER SANTISTEBAN-PONCE, M.D., ELSA CHEA-WOO, M.D., AND MANUEL GUTIERREZ, M.D. ABSTRACT Background (acetorphan),
Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders. TERRAGASTRO - Good health starts in the gut
 Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE Referred to as gastrointestinal diseases, they are common disorders which affect the esophagus,
Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE Referred to as gastrointestinal diseases, they are common disorders which affect the esophagus,
Guideline scope Diverticular disease: diagnosis and management
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Diverticular disease: diagnosis and management The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a clinical guideline on diverticular
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Diverticular disease: diagnosis and management The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a clinical guideline on diverticular
IBS - Definition. Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by:
 IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
Protocol for the management of acute severe ulcerative colitis in children
 Protocol for the management of acute severe ulcerative colitis in children Introduction: Paediatric UC is severe and more extensive than adult onset UC with 6-8% presenting as pancolitis (1,2) Within five
Protocol for the management of acute severe ulcerative colitis in children Introduction: Paediatric UC is severe and more extensive than adult onset UC with 6-8% presenting as pancolitis (1,2) Within five
Racecadotril in the treatment of acute diarrhea in children: a systematic, comprehensive review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
 Eberlin et al. BMC Pediatrics (2018) 18:124 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1095-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Racecadotril in the treatment of acute diarrhea in children: a systematic, comprehensive
Eberlin et al. BMC Pediatrics (2018) 18:124 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1095-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Racecadotril in the treatment of acute diarrhea in children: a systematic, comprehensive
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2011) ewsletter Jambulingappa et al.
 PRESCRIBI G PATTER I ACUTE GASTROE TERITIS AMO G PEDIATRIC I PATIE TS I A TEACHI G HOSPITAL 1. Kiran Lakkol Jambulingappa Assistant Professor, E-mail: drkiranlakkol@gmail.com, drkiranphar06@yahoo.com 2.
PRESCRIBI G PATTER I ACUTE GASTROE TERITIS AMO G PEDIATRIC I PATIE TS I A TEACHI G HOSPITAL 1. Kiran Lakkol Jambulingappa Assistant Professor, E-mail: drkiranlakkol@gmail.com, drkiranphar06@yahoo.com 2.
Perceptions and practices of oral rehydration therapy among caregivers in Cork, Ireland
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Maduemem KE et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Oct;4(10):3536-3541 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Maduemem KE et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Oct;4(10):3536-3541 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
Studies on inflammatory bowel disease and functional gastrointestinal disorders in children and adults Hoekman, D.R.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Studies on inflammatory bowel disease and functional gastrointestinal disorders in children and adults Hoekman, D.R. Link to publication Citation for published version
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Studies on inflammatory bowel disease and functional gastrointestinal disorders in children and adults Hoekman, D.R. Link to publication Citation for published version
The importance of early complementary feeding in the development of oral tolerance: Concerns and controversies
 The importance of early complementary feeding in the development of oral tolerance: Concerns and controversies Prescott SL, Smith P, Tang M, Palmer DJ, Sinn J, Huntley SJ, Cormack B. Heine RG. Gibson RA,
The importance of early complementary feeding in the development of oral tolerance: Concerns and controversies Prescott SL, Smith P, Tang M, Palmer DJ, Sinn J, Huntley SJ, Cormack B. Heine RG. Gibson RA,
Surviving Norovirus. Not Just a Cruise Ship Issue. Maria Wellisch, RN, LFNA Vice President of Corporate Education Morningside Ministries
 Surviving Norovirus Not Just a Cruise Ship Issue Maria Wellisch, RN, LFNA Vice President of Corporate Education Morningside Ministries How Prevalent is Norovirus 21 million cases 71,000 individuals hospitalized
Surviving Norovirus Not Just a Cruise Ship Issue Maria Wellisch, RN, LFNA Vice President of Corporate Education Morningside Ministries How Prevalent is Norovirus 21 million cases 71,000 individuals hospitalized
Detecting Undernutrition on Hospital Admission - Screening Tool Versus WHO Criteria
 Clinical Medicine Research 2017; 6(3): 74-79 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/cmr doi: 10.11648/j.cmr.20170603.13 ISSN: 2326-9049 (Print); ISSN: 2326-9057 (Online) Detecting Undernutrition on Hospital
Clinical Medicine Research 2017; 6(3): 74-79 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/cmr doi: 10.11648/j.cmr.20170603.13 ISSN: 2326-9049 (Print); ISSN: 2326-9057 (Online) Detecting Undernutrition on Hospital
Developed September Revised May 2018; June 2017; June 2015; October 2013; December 2011; April 2010; December 2006.
 Texas Vendor Drug Program Drug Use Criteria: Rifaximin (Xifaxan ) Publication History Developed September 2006. Revised May 2018; June 2017; June 2015; October 2013; December 2011; April 2010; December
Texas Vendor Drug Program Drug Use Criteria: Rifaximin (Xifaxan ) Publication History Developed September 2006. Revised May 2018; June 2017; June 2015; October 2013; December 2011; April 2010; December
FDA s GREAT Workshop. Industry Perspective: Development Activities Towards Phase 3 Endpoints. September 19, 2012
 FDA s GREAT Workshop Industry Perspective: Development Activities Towards Phase 3 Endpoints Malcolm Hill, Pharm.D. Meritage Pharma, Inc. San Diego, CA 09/19/12 1 September 19, 2012 Presentation Overview
FDA s GREAT Workshop Industry Perspective: Development Activities Towards Phase 3 Endpoints Malcolm Hill, Pharm.D. Meritage Pharma, Inc. San Diego, CA 09/19/12 1 September 19, 2012 Presentation Overview
Title: Aerophagia due to abdomino-phrenic dyssynergia in a 2-year-old child. Authors: Pablo Ercoli, Belinda García, Enrique del Campo, Sergio Pinillos
 Title: Aerophagia due to abdomino-phrenic dyssynergia in a 2-year-old child Authors: Pablo Ercoli, Belinda García, Enrique del Campo, Sergio Pinillos DOI: 10.17235/reed.2018.5444/2017 Link: PubMed (Epub
Title: Aerophagia due to abdomino-phrenic dyssynergia in a 2-year-old child Authors: Pablo Ercoli, Belinda García, Enrique del Campo, Sergio Pinillos DOI: 10.17235/reed.2018.5444/2017 Link: PubMed (Epub
What can we learn from the clinical studies in infants (on thickeners)?
 What can we learn from the clinical studies in infants (on thickeners)? Dominique Turck Member of the FAF WG Re-evaluation of FA in foods for infants below 16 weeks of age FA Stakeholders Workshop 30 November
What can we learn from the clinical studies in infants (on thickeners)? Dominique Turck Member of the FAF WG Re-evaluation of FA in foods for infants below 16 weeks of age FA Stakeholders Workshop 30 November
WHICH BOWEL PREPARATION WORKS BEST? A RANDOMISED CONTROL TRIAL. Nicole Weston Senior Oncology and Palliative Care Dietitian 18 th May 2017
 WHICH BOWEL PREPARATION WORKS BEST? A RANDOMISED CONTROL TRIAL Nicole Weston Senior Oncology and Palliative Care Dietitian 18 th May 2017 Background Lack of prospective, adequately powered trials to identify
WHICH BOWEL PREPARATION WORKS BEST? A RANDOMISED CONTROL TRIAL Nicole Weston Senior Oncology and Palliative Care Dietitian 18 th May 2017 Background Lack of prospective, adequately powered trials to identify
Outcomes from treating bile acid malabsorption (BAM) using a multidisciplinary approach
 Outcomes from treating bile acid malabsorption (BAM) using a multidisciplinary approach Gupta A et al. Support Care Cancer. 2015 Oct;23(10):2881-90 Prescribing information can be found at the end of this
Outcomes from treating bile acid malabsorption (BAM) using a multidisciplinary approach Gupta A et al. Support Care Cancer. 2015 Oct;23(10):2881-90 Prescribing information can be found at the end of this
As A Biotherapeutic Agent B-CROBES MARKETING (M) SDN BHD
 As A Biotherapeutic Agent B-CROBES MARKETING (M) SDN BHD Hexbio Hexbio for Diarrhea Hexbio for Constipation Hexbio for Nutrient Absorption, Immunity & Recovery Dosage & Administration Stool Assessment
As A Biotherapeutic Agent B-CROBES MARKETING (M) SDN BHD Hexbio Hexbio for Diarrhea Hexbio for Constipation Hexbio for Nutrient Absorption, Immunity & Recovery Dosage & Administration Stool Assessment
Diarrhoea on the AMU. Dr Chris Roseveare
 Diarrhoea on the AMU Dr Chris Roseveare The Society for Acute Medicine, Spring Meeting, Radisson Blu Hotel, Dublin 3-4 May 2012 Acute diarrhoea in developed countries adult populations Mainly a primary
Diarrhoea on the AMU Dr Chris Roseveare The Society for Acute Medicine, Spring Meeting, Radisson Blu Hotel, Dublin 3-4 May 2012 Acute diarrhoea in developed countries adult populations Mainly a primary
Paediatric Directorate
 Paediatric Directorate Dehydration Guidelines Primary cause of dehydration diarrhoea +/- vomiting. Approximately 10%Children < 5yrs present with gastroenteritis each year Diagnosis History - sudden change
Paediatric Directorate Dehydration Guidelines Primary cause of dehydration diarrhoea +/- vomiting. Approximately 10%Children < 5yrs present with gastroenteritis each year Diagnosis History - sudden change
