Functional Electrical Stimulation
|
|
|
- Jason Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Functional Electrical Stimulation Mr. Deon Bührs 22/04/2002
2 What is Functional Electrical Stimulation 4 The Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator 4 Development 4 Approvals and recommendations 5 Current use and findings 5 What does using the system involve? 5 Future developments 6 The Odstock Two-Channel Stimulator 6 Development 6 Current use 6 What does using the system involve? 7 Future developments 7 The Microstim 2 7 Development 7 Current use 8 What does using the system involve? 8 Future developments 8 The Four-Channel Exercise Stimulator 9 Development 9 Current use 9 What does using the system involve? 9 Functional Electrical Stimulation & Stroke Rehabilitation 10 Functional Electrical Stimulation & Multiple Sclerosis 11 Functional Electrical Stimulation & Spinal Cord Injuries 11 Incomplete injuries 11 Tetraplegics 12 2
3 Where can I go for Treatment? 13 How is the Treatment Funded? 13 Clinical Evidence & Reports 14 Abstracts on Stroke and Multiple Sclerosis 14 Abstracts on Tetraplegia 14 Publications 15 3
4 What is Functional Electrical Stimulation? Functional Electrical Stimulation is the clinical application of a small electric current to the intact nerves of the body, in order to trigger a muscle contraction. This contraction is then incorporated into a functional activity, for example walking. A clear distinction needs to be made between Therapeutic Stimulation and Functional Stimulation. The former being of an exercise orientation, where one would relax whilst the stimulation works on its own. Functional Electrical Stimulation on the other hand, incorporates this elicited muscle movement into an everyday activity, like standing, walking, reaching out etc. Much work has been done in the field of FES world wide, but one of the largest clinical applications of FES is found in Salisbury District Hospital, Department of Medical Physics, England. They have up to now seen more than 1100 patients, trained more than 300 clinicians, and employ an active Research and Development programme. Their clinical service began in 1994, and they currently employ Clinical Engineers, Physiotherapists, Occupational therapists and technicians to this end. The following is a list of the Stimulators designed in Salisbury, under the Department of Medical Physics, together with their applications. All systems are CE marked, and are BSI (British Standards Institution) Registered. The Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator Development The Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator (ODFS) was developed at the Medical Physics Department of Salisbury District Hospital in Wiltshire, England over a period of several years under the support of the National Health Service (NHS) and additional grants. The development culminated in a Randomised Control Trial being conducted from , after which the Development and Evaluation Committee (DEC) recommended its use for the treatment of Dropped-foot in the NHS. 4
5 The development and research was conducted by a multi-disciplinary group of Clinical and Electronic Engineers and Physiotherapists. This culture of teamwork and continual research and development continues to today. The team now comprises of 3 Physiotherapists, 2 Occupational Therapists, a Medical Physicist, 4 Clinical Engineers and technical and secretarial staff headed by Professor Ian D. Swain. The team is affiliated to the University of Bournemouth. Use of the ODFS has extended to other countries, due to its success as an active orthosis in assisting patients into the final stage of gait re-education and rehabilitation. These countries include Belgium, Hong Kong, Denmark, Italy, Spain and Switzerland. It is now that the possibility of patients in South Africa receiving this treatment is a reality. This is currently offered on a private patient basis, pending further funding agreements. Approvals and recommendations Approval for this treatment has been granted on an individual basis by many Health Authorities in the United Kingdom, on the recommendation of several independent bodies. These are: 1. The Development and Evaluation Committee Report, The Royal College of Physicians, CE mark classification. Further findings reveal the potential cost saving benefits of reducing the occurrence of falls. These when expressed in monetary value, outweigh the initial expense of the equipment. This will be worked out in savings benefit in the South African market soon. Current use and findings Over 1000 patients have currently used the stimulator system, of which approximately 75% are Stroke victims, 15% Multiple Sclerosis sufferers, and the remaining 10% being comprised of patients with incomplete Spinal Cord Injuries, Traumatic Brain Injuries, and Cerebral Palsy. The center in Salisbury has trained over 300 clinicians in the use of the single-channel stimulation system, and has now set up 5 independently run clinics across the UK. The Medical Physics Department in Salisbury has been fully supportive of the initiative in establishing an FES clinic in South Africa, and will continue to supply support and back-up service to this end. A service is currently available in Pretoria East, under the care of a Physiotherapist, and Neurosurgeon. What does using the system involve? The single-channel Dropped Foot system is the size of a pack of cards, easily attached to the waistband or belt, or even carried concealed in a pocket. Electrical stimulation is passed through the skin via a lead to self-adhesive electrode pads, which are placed over the lower leg. The impulses then stimulate the muscles needed to lift the foot upward via the nerve fibers. The timing of stimulation is controlled internally by the stimulator, relying on a foot switch, which is placed inside the shoe. This then synchronizes the stimulation cycles with each individual walking pattern. If a satisfactory response is found at the initial assessment, two appointments on consecutive days are needed in order to train the patient and/or carers in setting up the system correctly. This is then followed up with appointments 6 weeks later, then 3 months, and 6 months apart. Once the system becomes part of daily life, the follow-up appointments will be carried out 6 monthly. The system is ideally used on a daily basis, for the whole day, for as long as it is required. Other possibilities involve adding therapeutic exercise stimulation to the daily program, or a two-channel device, stimulating an additional muscle group. 5
6 Future developments Current trials are underway exploring the possible use of an implanted stimulation unit. This involves the implantation of the electrodes around the nerve fibers, but still employs an external control unit and footswitch. A policy of continual upgrading and improvement is employed. The Odstock Two-Channel Stimulator Development The 2-channel stimulator developed as a logical progression on the single-channel Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator. It was found that in some clinical cases it was necessary to stimulate another group of muscles to improve the global gait pattern. Current use The 2-channel stimulator is currently used in a variety of cases, coordinating another group of muscles to the walking cycle. The following algorithms have been developed: Bilateral dropped foot stimulation (especially in MS and incomplete Spinal Cord Injuries) Dropped foot with Calf stimulation Dropped foot with Hamstring stimulation Dropped foot with Quadriceps stimulation Dropped foot with Gluteal stimulation Dropped foot with Triceps stimulation Bilateral Quadriceps stimulation 6
7 By using these, we can for example improve the initiation of swing-phase by stimulating the hamstrings, or improve hip protraction in the stance-phase of walking by stimulating the gluteal muscles. What does using the system involve? This stimulator is only prescribed in some cases, and only after regular use of the single channel system. It may however be set-up as the primary intervention of bilateral dropped foot, for example in Spinal Cord Injured patients, or Multiple Sclerosis sufferers. The size of this stimulator is slightly larger than the ODFS. The user will be waring 2 sets of electrodes, with 2 leads. In some cases it may also be necessary to use two foot-switches. Furthermore, there is no difference from the ODFS as to frequency of use and follow-up appointments required. This stimulator would then replace the initial unit. Future developments This system is currently being redesigned at Salisbury District Hospital, and is being used in a multicenter trial looking at the potential benefits of this system over the conventional use of a dropped foot splint (ankle-foot orthosis). The Microstim 2 Development This stimulator was also developed by the Salisbury team, as the need for therapeutic exercise stimulation arose in the clinical environment, to augment the functional stimulation work. It has two channels of stimulation, able to deliver various frequencies and independent intensities via surface electrodes. 7
8 Current use The applications of the Microstim 2 vary, but in essence remain of therapeutic input. The current uses of exercise stimulation include: 1) Shoulder pain and subluxation ( gapping of the shoulder joint) 2) Arm stimulation including the hand and forearm. 3) Leg stimulation to improve the affectivity of the Dropped Foot Stimulator 4) Facial stimulation 5) General control of spasticity, and resting tone. These applications are often used in Stroke patients, but also Multiple Sclerosis and Facial Palsy s like Bell s Palsy. What does using the system involve? Exercises are usually prescribed twice a day, slowly increasing the time of stimulation until stimulating for approximately 30 minutes twice daily. The electrodes will be applied only for this period, during which functional activities can be carried out as prescribed by a Physiotherapist. The mode setting on the stimulator allows for the integration of stimulating muscle groups, or individual alternating stimulation. Future developments This stimulator is also currently being redesigned, although there will be no technical changes to the current device. 8
9 The Four-Channel Exercise Stimulator Development In essence, just a 4-channel version of the Microstim 2, although it does allow for parameter changes by the clinician allowing more versatility. It also allows for variable integration of the separate channels, thereby lending itself to more functional integration of various muscle groups. Current use Uses include facilitating a reaching movement of the arm, shoulder stimulation, and in some incomplete Spinal injured patients, for muscle retraining. It is also a useful aid to Physiotherapy reeducation of movements, when using a Wow-pedal. This enables the therapist to bring on the stimulation using a foot pedal, to encourage synergistic muscle activation in conventional physiotherapy treatments. What does using the system involve? Similar application is utilized as the Microstim 2, but this can be used in conjunction with Physiotherapy. 9
10 Functional Electrical Stimulation & Stroke Rehabilitation Conventional therapy in improving mobility in Stroke patients involve the use of a wheelchair or walking aids like a walking frame, stick or crutches. If a patient is able to walk about, this ability is often hampered by a dropped foot. This occurs when the muscles of the lower leg are not strong enough to lift the foot upwards when bringing the foot forwards off the ground. As a result, the foot catches resulting in stumbling and even falling. To avoid this patients often compensate by either hitching the hip, or swinging the leg outward. The conventional treatment might include the use of a dropped foot splint, or Ankle-Foot Orthosis (AFO), which is a plastic support worn inside the shoe. FES offers an alternative to this treatment, encouraging active movement of the foot, and by constantly taking the foot through full range of movement with walking, avoids stiffening up of the ankle. Improvements are reflected in objective tests, recording the speed of walking and the effort of walking by measuring the heart rate. Common reports are of walking being made easier, quicker, and safer, with patients feeling a lot more confident in walking about. The problem of having to wear larger shoes in order to fit the splint in is also solved. Carry-over of these improvements is often found when looking at unstimulated walking too, indicating a training effect of stimulation. Other improvements are also found in decreasing spasticity and improving range of movement, and peripheral circulation. Improved symmetry is also encouraged due to the nature of the foot switch-stimulation relationship. Two channels of stimulation are also used at times, in order to integrate another set of muscles into the walking pattern. This might include the hamstring muscles to improve the knee bending when bringing the foot forwards, or to the gluteal muscles to bring the body over the effected leg when standing. Exercise stimulation may also be applied to the leg in order to improve the effect of the abovementioned systems. This could be done using the 2- or 4-channel stimulator. Improvements have been found using exercise stimulation to the shoulder, easing shoulder pain, and reducing subluxation. This is when a gap appears in the shoulder joint, as the muscles are unable to keep the arm in place. There have also been reports of improved sensation following electrical stimulation. 10
11 Functional Electrical Stimulation & Multiple Sclerosis The application of FES to Multiple Sclerosis induced weakness is possible, as the nerve fibers are still intact, making it an upper motor neuron disease. The applications are focussed on the clinical presentation of the patient, and are often in the form of a single channel of stimulation to improve a dropped foot. A dropped foot is brought on by the inability of the muscles of the foot to lift it up during the swing phase of walking. This often results in tripping and even falling. A conventional approach might include Physiotherapy rehabilitation, the use of walking aids, and at times, an ankle-foot orthosis is used to keep the foot in a lifted position. FES offers an alternative to this treatment, encouraging active movement of the foot, and by constantly taking the foot through the full range of movement with walking, avoids stiffening up of the ankle. Improvements are reflected in objective tests, recording the speed of walking and the effort of walking by measuring the heart rate. Common reports are of walking being made easier, quicker, and safer, with patients feeling a lot more confident in walking about. Carry-over of these improvements may be found when looking at unstimulated walking too, although due to the progressive nature of this disease, are not as pronounced as in Stroke patients. Other improvements are also found in decreasing calf tone and improving range of movement, and peripheral circulation. Improved standing symmetry is also encouraged due to the nature of the foot switch-stimulation relationship. Two channels of stimulation are also used at times, in order to integrate another set of muscles into the walking pattern. This might include the hamstring muscles to improve knee bending when bringing the foot forwards, or to the gluteal muscles to bring the body over the effected leg when standing. Bilateral dropped foot stimulation is not uncommon in MS patients. Exercise stimulation may also be applied to the leg in order to improve the effect of the above-mentioned systems, or to the upper limb. This could be done using the 2- or 4-chnnel stimulator. Functional Electrical Stimulation & Spinal Cord Injuries Incomplete injuries. The electrical stimulation parameters used in the Odstock range of stimulators allows for nerve stimulation only, and is therefore unable to induce any movement in denervated muscles. This denervation would occur as a result of a lower motor neuron injury. As a rough guideline, this occurs in patients with a spinal cord injury of the level of L1 (Lumber 1) and lower. When being used in patients with a lesion higher than this, in order to achieve any sort of functional improvement, there needs to be some element of incompleteness to the clinical picture. In other words there needs to be some specific element absent from an already moderately functioning lower limb, or arm. The patients usually seen are those mobile using some form of walking aid already, and are perhaps using an Ankle foot orthosis to improve the walking by keeping the foot in a semi lifted position. 11
12 FES offers an alternative to conventional treatment, encouraging active movement of the foot, and by constantly taking the foot through full range of movement with walking, avoids stiffening up of the ankle. Improvements are reflected in objective tests, recording the speed of walking and the effort of walking by measuring the heart rate. Common reports are of walking being made easier, quicker, and safer, with patients feeling a lot more confident in walking about. Carry-over of these improvements is often found when looking at unstimulated walking too, indicating a training effect of stimulation. Other improvements are also found in decreasing calf tone and improving range of movement, and peripheral circulation. Improved standing symmetry is also encouraged due to the nature of the foot switchstimulation relationship. Two channels of stimulation are also used at times, in order to integrate another set of muscles into the walking pattern. This might include the hamstring muscles to improve the knee bending when bringing the foot forwards, or to the gluteal muscles to bring the body over the effected leg when standing. The quadriceps muscles may also be stimulated to improve standing stability. Exercise stimulation may also be applied to the leg in order to improve the effect of the abovementioned systems, or to the upper limb for therapeutic stimulation. This could be done using the 2- or 4-chnnel stimulator. Tetraplegics Patients who have suffered from a cervical cord injury usually have limited upper limb function, and are wheelchair dependent for mobility. Conventional treatment involves physiotherapy and occupational rehabilitation, and tendon transfers may be done to improve hand function. NeuroControl, a company based in the USA has now developed the Freehand System", which involves the implantation of 8 electrodes into the muscles of the hand and forearm. These are stimulated via an external system by transmitting radio frequencies to an implanted receiver unit. This is often done together with tendon transfers, and enables the patient to perform tasks using a shoulder control to bring on different movements of the hand. The patient is then able to grasp objects, and manipulate them spatially. Selection criterion is strict, as some patients may benefit from tendon transfers alone. Usual candidates are C5/6/7 injured patients. Currently this surgery is not being performed in South Africa, but the Salisbury unit in the UK, others in Europe, Japan, Australia, Canada and the USA do. For more information, go to the NeuroControl website. Other possibilities include abdominal stimulation to improve respiratory function by improve coughing, and decreasing the occurrence of orthostatic hypotention (a lowering of the blood pressure in response to body position, resulting in dizziness/fainting). 12
13 Where can I go for Treatment? Treatment is currently available in Garsfontein East, Pretoria and at the Netcare Rehabilitation Hospital in Auckland Park, Johannesburg. Plans are underway to set up other clinics in Cape Town and Durban. Address: Bührs Physiotherapists 51 Carstens Crescent Garsfontein East Pretoria South Africa Cell number: Telephone/fax: address: d.buhrs@proffessa.co.za How is the Treatment Funded? We are currently busy with negotiations with the Private medical aid schemes, in order to secure funding for this treatment. Until this is finalised, patients will need to pay upfront for the cost of the equipment, and try to claim this back from their medical aid schemes themselves. We can advise you in this and assist in the application for an Ex Gracia payment, should this be nessesary. Initial assessments will be carried out in the usual way of a Complex Physiotherapeutic evaluation, which is funded by most medical schemes. The follow-up clinic appointments with the Physiotherapist should be covered in the usual way by those medical aids with Physiotherapy benefits. These followups are on average 5 in the first year, totaling 6; and then 2 per year from then onwards. The equipment costs are currently the responsibility of the patient. 13
14 Clinical Evidence & Reports 1. Abstracts on Stroke and Multiple Sclerosis Patients' Perceptions of the Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator (ODFS) Clinical use of the Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator. Its effect on the Speed and Effort of walking The effects of common peroneal stimulation on the effort and speed of walking. A randomised controlled trial with chronic hemiplegic patients The effect of common peroneal nerve stimulation on quadriceps spasticity in hemiplegia Correction of Bi-lateral Dropped Foot using the Odstock 2-Channel Stimulator (O2CHS) The Relationship between abnormal patterns of muscle activation and response to Common Peroneal nerve stimulation in Hemiplegia Different muscle activation patterns, identified during walking, in people with spastic Dropped Foot Electrical stimulation exercise to improve hand function and sensation following chronic stroke. Pilot trial to determine Control algorithms and patient selection criteria for Two- Channel Stimulation following Stroke The efficacy of Functional Electrical Stimulation in improving walking ability for people with Multiple Sclerosis Development and Evaluation Committee Report: Common Peroneal Stimulation for the Correction of Drop-foot United Kingdom Clinical guidelines for Stroke-The Royal College of Physicians 2. Abstracts on Tetraplegia Clinical experience of the NeuroControl Free Hand Neuro Prosthesis for Tetraplegic hand function Deltoid Triceps Transfer and functional independence of people with Tetraplegia A portable system for closed loop control of the paralysed hand using functional electrical stimulation Clinical Experience of the NeuroControl Freehand System Electrical stimulation of abdominal muscles for control of blood pressure and assisted cough in a C4 level tetraplegic 14
15 Publications 1. Taylor PN, Ewins DJ, Fox B, Grundy D, Swain ID. Limb blood flow, cardiac output and quadriceps muscle bulk following spinal cord injury and the effects of training for the Odstock Functional Electrical Standing System. Paraplegia 31 (1993) Taylor PN, Burridge JH. Development and experience in use of an electronic stimulator for correction of dropped foot in early gait re-education of subjects following CVA. Therapy weekly Taylor PN, Fox BA, Ewins DJ, Swain ID, Exercise procedure and treatment routine for preparation of paraplegics prior to standing using FES. Ed. Cliford-Rose F, Jones R, Vrbova G. Neuromuscular Stimulation: Basic Concepts and Clinical Practice. Demos 1989 USA 4. Ewins DJ, Taylor PN, Crook SE, Lipcyznski RT, Swain ID. Practical low cost stands/sit system for mid-thoracic paraplegics. J.Biomed. Eng (2): Burridge J, Taylor P, Hagan SA, Wood DE, Swain ID. The effect on the spasticity of the quadriceps muscles of stimulation of the Common Peroneal nerve of chronic hemiplegic subjects during walking. Physiotherapy vol. 83, no 2, pp Burridge, J. Taylor, P. Swain, I. (1997) Clinical Experience of the Odstock Drop Foot Stimulator. Artificial Organs 21 (3): Burridge, J. Taylor, P. Hagan, S. Swain, I (1997) The effect of Common peroneal stimulation on the effort and speed of walking. A randomised controlled trial with chronic hemiplegic subjects. Clinical Rehabilitation 11: Rushton DN, Barr FMD, Donaldson N de N, Harper VJ, Perkins TA, Taylor PN, Tromans AM. Selecting candidates for a lower limb stimulator implant programme: a patient-centred method. Spinal Cord (1998) Burridge JH, Swain ID, Taylor PN Functional electrical Stimulation: a review of the literature published on common peroneal nerve stimulation for the correction of dropped foot. Reviews in Clinical Gerontology : Taylor PN, Burridge JH, Dunkerley AL, Lamb A, Wood DE, Norton JA, Swain ID. Patient's Perceptions of the Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator (ODFS). Clin. Rehab. 1999; 13: Paul Taylor, Jane Burridge, Anna Dunkerley, Duncan Wood, Jonathan Norton, Christine Singleton, Ian Swain. Clinical audit of 5 years provision of the Odstock Dropped Foot stimulator (ODFS). Artif Organs Vol.23, No. 5, May AH Woodcock, PN Taylor, DJ Ewins, Long Pulse Biphasic Electrical Stimulation of Denervated Muscle. Artif Organs Vol.23, No. 5, May Taylor PN, Burridge JH, Dunkerley AL, Wood DE, Norton JA, Singleton C and Swain ID Clinical Use of the Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator. It s Effect on the Speed and Effort of Walking. Arch Phys Med Rehab.1999; 80: SE Crook, PH Chappell. A portable system for closed loop control of the paralysed hand using functional electrical stimulation. Medical Engineering and Physics 20 (1998) Swain ID, Bader DL. The measurement and effects of interface pressure on soft tissues. Journal of Engineering in Medicine. In press,
16 16. Burridge JH, McLellan DL. Relation between abnormal patterns of muscle activation and response to common peroneal nerve stimulation in paraplegia. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, In press, Dunkerley AL, Ashburn A, Stack EL. (2000) Deltoid triceps transfer and functional independence of people with tetraplegia. Spinal Cord 38, Published Abstracts 1. Ewins DJ, Taylor PN, Swain ID, A functional closed loop stand/sit system for mid-low thoracic paraplegics. Advances in the control of human extremities 10. ed. Popovic D Belgrade: Nauka Taylor PN, Ewins DJ, Swain ID. The Odstock closed loop FES standing system. Experience in clinical use. The Ljubljana FES Conference, Ljubljana, Slovenia ISBN pp Taylor PN, Burridge JH, Hagan SA, Swain IDS. Electrical stimulation exercises to improve hand function and sensation following chronic stroke. Pro. 5th Vienna International Workshop on Functional Electrostimulation 1995 ISBN pp Burridge J, Taylor P, Hagan SA, Swain ID. Experience and clinical use of the Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator. (ODFS) Pro. 5th Vienna International Workshop on Functional Electrostimulation 1995 ISBN pp Barr FMD, Harper VJ, Rushton DN, Taylor PN, Phillips GF, Hagan SA, Wood D. Screening and assessments for a lumbosacral anterior root stimulator implant program. Pro. 5th Vienna International Workshop on Functional Electrostimulation 1995 ISBN pp Taylor. PN Burridge JH, Dunkerley A, Wood D, Norton J, Singleton C, Swain ID Long term follow up of 160 users of the Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator. Pro. 6th Vienna International Workshop on Functional Electrostimulation 1998 ISBN Perkins TA, Donaldson N de N, Dunkerley AL, Hatcher, Tromans AM, Wood DE. Development of paraplegic leg powered cycling with the Lumbo-sacral Anterior Root Stimulator Implant. 1999, 4th annual IFESS conference pp ISBN Wright PA, Burridge JH, Ewins DJ, Mann GE, Mclellan DL, Swain ID, Taylor PN, wood DE. The Compustim 10B in stroke: Control algorithms and patient selection criteria th annual IFESS conference pp ISBN Burridge JH, Wood DJ, Taylor PN, McLellan DL The relationship between abnormal patterns of muscle activity and response to common peroneal nerve stimulation. 4th annual IFESS conference pp ISBN Ewins DJ, Write PA, Burridge JH, Mann GE, Swain ID, Taylor PN, Wood DE. The compustim 10B Programming interface. 4th annual IFESS conference pp ISBN Taylor PN, Wright PA, Burridge JH, Mann GE, Swain ID. Correction of Dropped Foot using the Odstock 2 Channel Stimulator (O2CHS). 4th annual IFESS conference pp ISBN Swain ID, Burridge JH, Johnson CA, Mann GE, Taylor PN, Wright PA. The efficacy of functional electrical stimulation in improving walking ability for people with multiple sclerosis. 5th Annual Conference of the International Electrical Stimulation Society, (ISBN ), pp , Aalborg, Denmark, June
17 13. Taylor PN, Esnouf JE, Hobby J. Clinical experience of the NeuroControl Freehand system. 5th Annual Conference of the International Electrical Stimulation Society, (ISBN ), p , Aalborg, Denmark, June Mann GE, Swain ID, Cole R. Initial experience in the use of functional electrical stimulation in a variety of neurological conditions resulting in facial palsy. 5th Annual Conference of the International Electrical Stimulation Society, (ISBN ), pp , Aalborg, Denmark, June Taylor PN, Tromans A, Swain ID. Electrical stimulation of abdominal muscles for control of blood pressure and assisted cough in a C4 level tetraplegic. 5th Annual Conference of the International Electrical Stimulation Society, (ISBN ), pp , Aalborg, Denmark, June Mann GE, Burridge JH, Ewins DJ, McLellan DL, Swain ID, Taylor PN, Wood DE, Wright PA. Optimising two-channel stimulation to improve walking following stroke. 5th Annual Conference of the International Electrical Stimulation Society, (ISBN ), pp , Aalborg, Denmark, June Norton JA, Donaldson N de N, Day BL, Dekker L, Perkins TA, Wood DE, McFadden C, Tromans A. The determinants of posture in paraplegics standing using lumbar anterior root stimulation. 5th Annual Conference of the International Electrical Stimulation Society, (ISBN ), pp , Aalborg, Denmark, June
FES courses from Salisbury District Hospital
 FES courses from Salisbury District Hospital The purpose of the course is to give an introduction to practical clinical FES as practised in the clinical service at Salisbury District Hospital. The techniques
FES courses from Salisbury District Hospital The purpose of the course is to give an introduction to practical clinical FES as practised in the clinical service at Salisbury District Hospital. The techniques
Medical Coverage Policy Functional Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation EFFECTIVE DATE: 10/16/212 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 09/11/2014
 Medical Coverage Policy Functional Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation EFFECTIVE DATE: 10/16/212 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 09/11/2014 OVERVIEW Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation, (NMES), involves the use
Medical Coverage Policy Functional Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation EFFECTIVE DATE: 10/16/212 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 09/11/2014 OVERVIEW Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation, (NMES), involves the use
Sunshine Prosthetics & Orthotics, LLC 1700 Rt. 23 N Ste 180 Wayne NJ Functional electrical stimulation (FES)
 Functional electrical stimulation (FES) We hope you find the information in this factsheet helpful. If you would like to speak with someone about any aspect of MS, contact the MS Trust information team
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) We hope you find the information in this factsheet helpful. If you would like to speak with someone about any aspect of MS, contact the MS Trust information team
Lack of muscle control (Stroke, bladder control, neurological disorders) Mechanical movement therapist assisted
 By Lisa Rosenberg Electrical Current Stimulates muscles and nerves Produces movement Helps Individuals with Disabilities Lack of muscle control (Stroke, bladder control, neurological disorders) Passive
By Lisa Rosenberg Electrical Current Stimulates muscles and nerves Produces movement Helps Individuals with Disabilities Lack of muscle control (Stroke, bladder control, neurological disorders) Passive
Protocol. Functional Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
 Protocol Functional Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (80301) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/10 Next Review Date: 01/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 03/07, 05/08, 05/09, 01/10, 01/11,
Protocol Functional Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (80301) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/10 Next Review Date: 01/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 03/07, 05/08, 05/09, 01/10, 01/11,
Patient Details Front Sheet
 Name DOB/ PID ODSTOCK MEDICAL LIMITED National Clinical FES Centre - Salisbury Quality Form QF/020 Clinical Care Pathway; ODFS Patient Details Front Sheet Address Contact telephone numbers; Home Work Mobile..
Name DOB/ PID ODSTOCK MEDICAL LIMITED National Clinical FES Centre - Salisbury Quality Form QF/020 Clinical Care Pathway; ODFS Patient Details Front Sheet Address Contact telephone numbers; Home Work Mobile..
2 Gait Laboratory, Queen Mary's Hospital, London, UK. 3 One Small Step Gait Laboratory, Guy's Hospital London, UK
 Upper and Lower Limb Electrical Stimulation in Paediatrics Held at Queen Mary's Hospital, Roehampton, London Thursday, 13th June 2002 The aim of the workshop was to promote discussion and the exchange
Upper and Lower Limb Electrical Stimulation in Paediatrics Held at Queen Mary's Hospital, Roehampton, London Thursday, 13th June 2002 The aim of the workshop was to promote discussion and the exchange
Precise Pulses Optimised Support
 Precise Pulses Optimised Support The Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) MyGait system for drop foot and gait rehabilitation Information for clinical specialists MyGait Ottobock 1 2 Ottobock MyGait
Precise Pulses Optimised Support The Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) MyGait system for drop foot and gait rehabilitation Information for clinical specialists MyGait Ottobock 1 2 Ottobock MyGait
Restoration of Reaching and Grasping Functions in Hemiplegic Patients with Severe Arm Paralysis
 Restoration of Reaching and Grasping Functions in Hemiplegic Patients with Severe Arm Paralysis Milos R. Popovic* 1,2, Vlasta Hajek 2, Jenifer Takaki 2, AbdulKadir Bulsen 2 and Vera Zivanovic 1,2 1 Institute
Restoration of Reaching and Grasping Functions in Hemiplegic Patients with Severe Arm Paralysis Milos R. Popovic* 1,2, Vlasta Hajek 2, Jenifer Takaki 2, AbdulKadir Bulsen 2 and Vera Zivanovic 1,2 1 Institute
Physical effects of stroke
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Physical effects of stroke A stroke can cause problems with physical activities like walking, writing and dressing, due to muscle weakness,
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Physical effects of stroke A stroke can cause problems with physical activities like walking, writing and dressing, due to muscle weakness,
A new model of plastic ankle foot orthosis (FAFO (II)) against spastic foot and genu recurvatum
 Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1992,16,104-108 A new model of plastic ankle foot orthosis (FAFO (II)) against spastic foot and genu recurvatum *S. OHSAWA, S. IKEDA, S. TANAKA, T. TAKAHASHI, +
Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1992,16,104-108 A new model of plastic ankle foot orthosis (FAFO (II)) against spastic foot and genu recurvatum *S. OHSAWA, S. IKEDA, S. TANAKA, T. TAKAHASHI, +
AN ANALYTICAL MODEL OF A SPINAL ROOT STIMULATED NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM
 1 of 4 AN ANALYTICAL MODEL OF A SPINAL ROOT STIMULATED NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM N.A.C.Hatcher 1, R.Allen 1, S.J.Elliott 1 and T.A.Perkins 2 1 Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, University of Southampton,
1 of 4 AN ANALYTICAL MODEL OF A SPINAL ROOT STIMULATED NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM N.A.C.Hatcher 1, R.Allen 1, S.J.Elliott 1 and T.A.Perkins 2 1 Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, University of Southampton,
Clinical Use of the Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator: Its Effect ion the Speed and Effort of Walking
 1577 Clinical Use of the Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator: Its Effect ion the Speed and Effort of Walking Paul N. Taylor, MSc, Jane H. Burridge, Phi), Anna L. Dunkerley, MSc, Duncan E. Wood, PhD, Jonathan
1577 Clinical Use of the Odstock Dropped Foot Stimulator: Its Effect ion the Speed and Effort of Walking Paul N. Taylor, MSc, Jane H. Burridge, Phi), Anna L. Dunkerley, MSc, Duncan E. Wood, PhD, Jonathan
A preliminary non-randomised study to evaluate the safety and performance of the ActiGait implanted drop-foot stimulator in established hemiplegia
 A preliminary non-randomised study to evaluate the safety and performance of the ActiGait implanted drop-foot stimulator in established hemiplegia Haugland M, Larsen B, Burridge J, Svaneborg N, Iversen
A preliminary non-randomised study to evaluate the safety and performance of the ActiGait implanted drop-foot stimulator in established hemiplegia Haugland M, Larsen B, Burridge J, Svaneborg N, Iversen
BACKGROUND. Paul Taylor. The National Clinical FES Centre Salisbury UK. Reciprocal Inhibition. Sensory Input Boosted by Electrical Stimulation
 The REAcH project. A Randomised Controlled Trial of an Accelerometer Triggered Functional Electrica Stimulation Device For Recovery of Upper Limb Function in Chronic Stroke Patients. Paul Taylor The National
The REAcH project. A Randomised Controlled Trial of an Accelerometer Triggered Functional Electrica Stimulation Device For Recovery of Upper Limb Function in Chronic Stroke Patients. Paul Taylor The National
Salisbury FES User Day Friday, 22 nd February 2013
 Salisbury FES User Day Friday, 22 nd February 2013 RCP Guidelines The fourth addition of the Royal College of Physicians National Clinical Guideline for Stroke has been published. The guidelines have been
Salisbury FES User Day Friday, 22 nd February 2013 RCP Guidelines The fourth addition of the Royal College of Physicians National Clinical Guideline for Stroke has been published. The guidelines have been
24 Hour Positioning, Passive Movements, Shoulder pain, Splinting, Use of Assistive Technology, Early Mobilisation, and the Home Environment.
 24 Hour Positioning, Passive Movements, Shoulder pain, Splinting, Use of Assistive Technology, Early Mobilisation, and the Home Environment. Christine Hogg Physiotherapy Team Leader and Vicky Thomas Senior
24 Hour Positioning, Passive Movements, Shoulder pain, Splinting, Use of Assistive Technology, Early Mobilisation, and the Home Environment. Christine Hogg Physiotherapy Team Leader and Vicky Thomas Senior
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulator (NMES) Corporate Medical Policy
 Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulator (NMES) Corporate Medical Policy File name: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulator (NMES) File Code: UM.NS.04 Origination: 05/01/2007 Last Review: 06/2018 Next Review: 06/2019
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulator (NMES) Corporate Medical Policy File name: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulator (NMES) File Code: UM.NS.04 Origination: 05/01/2007 Last Review: 06/2018 Next Review: 06/2019
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System Reviewed & ratified by: o o o o Dr D Smith Consultant Neurologist Dr R Davies Consultant Neurologist Dr B Michael Neurology Clinical
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System Reviewed & ratified by: o o o o Dr D Smith Consultant Neurologist Dr R Davies Consultant Neurologist Dr B Michael Neurology Clinical
Functional electrical stimulation. FES applications
 Functional electrical stimulation FES applications For all therapeutic areas The functional electrical stimulation (FES) is highly important for the therapy and rehabilitation of paralytic illnesses. If
Functional electrical stimulation FES applications For all therapeutic areas The functional electrical stimulation (FES) is highly important for the therapy and rehabilitation of paralytic illnesses. If
Erigo User Script 1. Erigo Background Information. 2. Intended use and indications
 Erigo User Script 1. Erigo Background Information The Erigo was developed in collaboration with the Spinal Cord Injury Center at the Balgrist University Hospital in Zurich, Switzerland and the Orthopaedic
Erigo User Script 1. Erigo Background Information The Erigo was developed in collaboration with the Spinal Cord Injury Center at the Balgrist University Hospital in Zurich, Switzerland and the Orthopaedic
Neurexa product line. Actively promoting movement. Information for specialist dealers. Neurexa product line Ottobock 1
 Neurexa product line Actively promoting movement Information for specialist dealers Neurexa product line Ottobock 1 Neurexa product line Neurexa is a product line designed for the treatment of patients
Neurexa product line Actively promoting movement Information for specialist dealers Neurexa product line Ottobock 1 Neurexa product line Neurexa is a product line designed for the treatment of patients
Cape Cod Ski Club. * Use this exercise program at your own risk. Seek medical guidance before beginning this or any other exercise program.
 Cape Cod Ski Club * Use this exercise program at your own risk. Seek medical guidance before beginning this or any other exercise program. Cape Cod Ski Club - Strength Standing Wall Sit This exercise strengthens
Cape Cod Ski Club * Use this exercise program at your own risk. Seek medical guidance before beginning this or any other exercise program. Cape Cod Ski Club - Strength Standing Wall Sit This exercise strengthens
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers. Workbook 3 Balance re-education
 NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 3 Balance re-education Contents Workbook 3 Balance re-education 1 3.1 Aim 3 3.2 Learning outcomes 3 3.3 What is balance? 4 3.4 Adapting our base
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 3 Balance re-education Contents Workbook 3 Balance re-education 1 3.1 Aim 3 3.2 Learning outcomes 3 3.3 What is balance? 4 3.4 Adapting our base
What to expect following spinal cord injury. Information for patients Therapy Services
 What to expect following spinal cord injury Information for patients Therapy Services Introduction This leaflet aims to explain what spinal cord injury is and what to expect over the next few months. What
What to expect following spinal cord injury Information for patients Therapy Services Introduction This leaflet aims to explain what spinal cord injury is and what to expect over the next few months. What
The Police Treatment Centres
 Foam Roller Exercises The exercises provided here are for general information only and should not be treated as a substitute for professional supervision or advice. By following these exercises you agree
Foam Roller Exercises The exercises provided here are for general information only and should not be treated as a substitute for professional supervision or advice. By following these exercises you agree
Treating the New Normal: Electrical Stimulation. Timothy Devlin, OT
 Treating the New Normal: Electrical Stimulation Timothy Devlin, OT Electrical Stimulation When normal communication between the brain and upper extremities is interrupted secondary to injury or disease,
Treating the New Normal: Electrical Stimulation Timothy Devlin, OT Electrical Stimulation When normal communication between the brain and upper extremities is interrupted secondary to injury or disease,
PHYSIOTHERAPY IN SSPE
 PHYSIOTHERAPY IN SSPE Published by: Physiotherapist RUKIYE KORUCU Istanbul, Turkey Sep 2007 English translation by R.Schoenbohm WHY PHYSIOTHERAPY? Preserve the breathing capacity Strengthen the chewing
PHYSIOTHERAPY IN SSPE Published by: Physiotherapist RUKIYE KORUCU Istanbul, Turkey Sep 2007 English translation by R.Schoenbohm WHY PHYSIOTHERAPY? Preserve the breathing capacity Strengthen the chewing
APPLICATION OF MICROPROCESSOR CONTROLLED MULTICHANNEL STIMULATOR TO
 Original Paper APPLICATION OF MICROPROCESSOR CONTROLLED MULTICHANNEL STIMULATOR TO THE REHABILITATION OF SCI SUBJECTS T. Karcnik, 1 DSc; R. Erzin, MSc; M. Munih, 2 DSc; A. Kralj, 3 DSc; T. Bajd, 3 DSc
Original Paper APPLICATION OF MICROPROCESSOR CONTROLLED MULTICHANNEL STIMULATOR TO THE REHABILITATION OF SCI SUBJECTS T. Karcnik, 1 DSc; R. Erzin, MSc; M. Munih, 2 DSc; A. Kralj, 3 DSc; T. Bajd, 3 DSc
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
Ratified by: Care and Clinical Policies Date: 17 th February 2016
 Clinical Guideline Reference Number: 0803 Version 5 Title: Physiotherapy guidelines for the Management of People with Multiple Sclerosis Document Author: Henrieke Dimmendaal / Laura Shenton Date February
Clinical Guideline Reference Number: 0803 Version 5 Title: Physiotherapy guidelines for the Management of People with Multiple Sclerosis Document Author: Henrieke Dimmendaal / Laura Shenton Date February
Exoskeletons: Insights into the Future of Robotic Ambulation
 Exoskeletons: Insights into the Future of Robotic Ambulation Clare Hartigan, PT, MPT Laurie Anderson, VP Clinical Operations Shepherd Center Paradigm First, a Few Housekeeping Points Slides will advance
Exoskeletons: Insights into the Future of Robotic Ambulation Clare Hartigan, PT, MPT Laurie Anderson, VP Clinical Operations Shepherd Center Paradigm First, a Few Housekeeping Points Slides will advance
FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals
 FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals Musfirah Abd Aziz and Nur Azah Hamzaid Abstract Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals Musfirah Abd Aziz and Nur Azah Hamzaid Abstract Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
Information and Exercise Booklet
 FACULTY OF HEALTH SCIENCES School of Allied Health Department of Physiotherapy Appendix E Information and Exercise Booklet Project: Does oestrogen, exercise or a combination of both, improve pain and function
FACULTY OF HEALTH SCIENCES School of Allied Health Department of Physiotherapy Appendix E Information and Exercise Booklet Project: Does oestrogen, exercise or a combination of both, improve pain and function
1-Apley scratch test.
 1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
Vibramoov NEUROREHABILITATION OF THE LOCOMOTOR SYSTEM THROUGH FUNCTIONAL PROPRIOCEPTIVE STIMULATION
 Vibramoov NEUROREHABILITATION OF THE LOCOMOTOR SYSTEM THROUGH FUNCTIONAL PROPRIOCEPTIVE STIMULATION Principe of action BRAIN ACTIVATION VIBRAMOOV REVOLUTIONIZES FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT THERAPY One of the main
Vibramoov NEUROREHABILITATION OF THE LOCOMOTOR SYSTEM THROUGH FUNCTIONAL PROPRIOCEPTIVE STIMULATION Principe of action BRAIN ACTIVATION VIBRAMOOV REVOLUTIONIZES FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT THERAPY One of the main
Exoskeleton. Information for patients Spinal Injuries
 Exoskeleton Information for patients Spinal Injuries What is Ekso GT? Ekso GT is a robotic human-assisted exoskeleton that is designed as an assisted walking device for individuals with impaired walking
Exoskeleton Information for patients Spinal Injuries What is Ekso GT? Ekso GT is a robotic human-assisted exoskeleton that is designed as an assisted walking device for individuals with impaired walking
NeuroOrthopaedics upper extremities
 NeuroOrthopaedics upper extremities Medical devices for deficiencies in the arm-shoulder-hand region Information for practitioners Effectively supporting rehabilitation of the hand and shoulder Strokes
NeuroOrthopaedics upper extremities Medical devices for deficiencies in the arm-shoulder-hand region Information for practitioners Effectively supporting rehabilitation of the hand and shoulder Strokes
Configure for Diverse
 Configure for Diverse Clinical Needs Foot Drop Lower Cuff Foot Drop & Knee Instability Lower & Thigh Cuffs Pediatric Foot Drop Small Lower Cuff Foot Sensor: required for gait Knee Instability & Thigh Weakness
Configure for Diverse Clinical Needs Foot Drop Lower Cuff Foot Drop & Knee Instability Lower & Thigh Cuffs Pediatric Foot Drop Small Lower Cuff Foot Sensor: required for gait Knee Instability & Thigh Weakness
3/5/2014. Rehabilitation Technology versus Research Technology: Where/What is the Value?
 Technology Applied to SCI: The Value of Assistive Devices During SCI Recovery and While Living with SCI Mark S. Nash, Ph.D., FACSM Departments of Neurological Surgery and Rehabilitation Medicine Principal
Technology Applied to SCI: The Value of Assistive Devices During SCI Recovery and While Living with SCI Mark S. Nash, Ph.D., FACSM Departments of Neurological Surgery and Rehabilitation Medicine Principal
The Handmaster NMS1 surface FES neuroprosthesis in hemiplegic patients
 The Handmaster NMS1 surface FES neuroprosthesis in hemiplegic patients R. H. Nathan 1,2, H. P. Weingarden 1,3, A. Dar 1,2, A. Prager 1 1 NESS Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Systems Ltd. 2 Biomedical
The Handmaster NMS1 surface FES neuroprosthesis in hemiplegic patients R. H. Nathan 1,2, H. P. Weingarden 1,3, A. Dar 1,2, A. Prager 1 1 NESS Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Systems Ltd. 2 Biomedical
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders
 Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders These guidelines were drawn following a workshop held in Newcastle 2002. Several experts from different disciplines including
Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders These guidelines were drawn following a workshop held in Newcastle 2002. Several experts from different disciplines including
Muscle Weakness Or Paralysis With Compromise Of Peripheral Nerve
 Muscle Weakness Or Paralysis With Compromise Of Peripheral Nerve Muscle weakness or complete paralysis may be secondary to an interruption in the communication between the brain and nerve cells in the
Muscle Weakness Or Paralysis With Compromise Of Peripheral Nerve Muscle weakness or complete paralysis may be secondary to an interruption in the communication between the brain and nerve cells in the
General Principles of Stretching. To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently.
 General Principles of Stretching To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently. Slowly means that while the exercise is being done the muscle being stretched must be moved slowly
General Principles of Stretching To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently. Slowly means that while the exercise is being done the muscle being stretched must be moved slowly
III. Based upon our criteria and review of the peer-reviewed literature, NMES has not been proven to be effective and is
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
The Police Treatment Centres
 Resistance Band Exercises The exercises provided here are for general information only and should not be treated as a substitute for professional supervision or advice. By following these exercises you
Resistance Band Exercises The exercises provided here are for general information only and should not be treated as a substitute for professional supervision or advice. By following these exercises you
The use of Acupuncture in the treatment of incomplete spinal cord injury. Janice Champion Clinical Specialist Colin Waldock Clinical Specialist
 The use of Acupuncture in the treatment of incomplete spinal cord injury Janice Champion Clinical Specialist Colin Waldock Clinical Specialist Learning Outcomes To enhance understanding of the use of acupuncture
The use of Acupuncture in the treatment of incomplete spinal cord injury Janice Champion Clinical Specialist Colin Waldock Clinical Specialist Learning Outcomes To enhance understanding of the use of acupuncture
Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
 For enquiries and appointments, please contact us at: 物理醫學及復康科部 Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 5/F, Li Shu Pui Block, Hong Kong Sanatorium
For enquiries and appointments, please contact us at: 物理醫學及復康科部 Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 5/F, Li Shu Pui Block, Hong Kong Sanatorium
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): Neurorehabilitation of the Upper Limb and Trunk
 Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): Neurorehabilitation of the Presented by the Occupational Therapy Department - Health Sciences Centre Winnipeg Dr. Kristin Musselman Sunday, June 3, 2018 Winnipeg,
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): Neurorehabilitation of the Presented by the Occupational Therapy Department - Health Sciences Centre Winnipeg Dr. Kristin Musselman Sunday, June 3, 2018 Winnipeg,
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
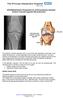 GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
are: Standard of care are: are:
 Protocol Functional Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (80301) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/16 Next Review Date: 05/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/07, 05/08, 05/09, 01/10, 01/11, 01/12,
Protocol Functional Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (80301) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/16 Next Review Date: 05/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/07, 05/08, 05/09, 01/10, 01/11, 01/12,
Subject: Functional Neuromuscular Stimulation
 09-E0000-54 Original Effective Date: 04/15/02 Reviewed: 08/23/18 Revised: 09/15/18 Subject: Functional Neuromuscular Stimulation THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION,
09-E0000-54 Original Effective Date: 04/15/02 Reviewed: 08/23/18 Revised: 09/15/18 Subject: Functional Neuromuscular Stimulation THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION,
To date, most of the clinical work in the functional
 Functional Electrical Stimulation Therapy for Grasping in Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview Naaz Kapadia, MSc (Rehab), 1 and Milos R. Popovic, PhD 1,2 1 Rehabilitation Engineering Laboratory, Toronto Rehabilitation
Functional Electrical Stimulation Therapy for Grasping in Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview Naaz Kapadia, MSc (Rehab), 1 and Milos R. Popovic, PhD 1,2 1 Rehabilitation Engineering Laboratory, Toronto Rehabilitation
A Measurement of Lower Limb Angles Using Wireless Inertial Sensors during FES Assisted Foot Drop Correction with and without Voluntary Effort
 A Measurement of Lower Limb Angles Using Wireless Inertial Sensors during FES Assisted Foot Drop Correction with and without Voluntary Effort Takashi Watanabe, Shun Endo, Katsunori Murakami, Yoshimi Kumagai,
A Measurement of Lower Limb Angles Using Wireless Inertial Sensors during FES Assisted Foot Drop Correction with and without Voluntary Effort Takashi Watanabe, Shun Endo, Katsunori Murakami, Yoshimi Kumagai,
Rehabilitation programme after internal fixation surgery
 Rehabilitation programme after internal fixation surgery Information for patients at Princess Royal University Hospital This leaflet gives you advice about the things you can do after your operation both
Rehabilitation programme after internal fixation surgery Information for patients at Princess Royal University Hospital This leaflet gives you advice about the things you can do after your operation both
Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE)
 Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE) We offer individualized treatment plans based on your physician's recommendations, our evaluations, and your feedback. Most post-operative and preoperative rehabilitation
Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE) We offer individualized treatment plans based on your physician's recommendations, our evaluations, and your feedback. Most post-operative and preoperative rehabilitation
ICU: Rehabilitation Programme
 Information and exercises ICU: Rehabilitation Programme Introduction During an ICU stay, maintaining a patient s stamina, muscle strength and general movement is very important to their prolonged recovery.
Information and exercises ICU: Rehabilitation Programme Introduction During an ICU stay, maintaining a patient s stamina, muscle strength and general movement is very important to their prolonged recovery.
Redefining Neurorehab. Improve Function. Maximize Independence. Enhance Quality of Life.
 Redefining Neurorehab Improve Function. Maximize Independence. Enhance Quality of Life. What is MyndMove? MyndMove is the first therapy to deliver significant lasting voluntary upper extremity function
Redefining Neurorehab Improve Function. Maximize Independence. Enhance Quality of Life. What is MyndMove? MyndMove is the first therapy to deliver significant lasting voluntary upper extremity function
Hand of Hope. For hand rehabilitation. Member of Vincent Medical Holdings Limited
 Hand of Hope For hand rehabilitation Member of Vincent Medical Holdings Limited Over 17 Million people worldwide suffer a stroke each year A stroke is the largest cause of a disability with half of all
Hand of Hope For hand rehabilitation Member of Vincent Medical Holdings Limited Over 17 Million people worldwide suffer a stroke each year A stroke is the largest cause of a disability with half of all
Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders
 Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders These guidelines were drawn following a workshop held in Newcastle 2002. Several experts from different disciplines including
Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders These guidelines were drawn following a workshop held in Newcastle 2002. Several experts from different disciplines including
BACK SPASM. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
Rehabilitation programme after hemiarthroplasty surgery
 Rehabilitation programme after hemiarthroplasty surgery Information for patients at Princess Royal University Hospital This leaflet gives you advice about the things you can do after your operation both
Rehabilitation programme after hemiarthroplasty surgery Information for patients at Princess Royal University Hospital This leaflet gives you advice about the things you can do after your operation both
Rehabilitation programme after cannulated hip screw surgery
 Rehabilitation programme after cannulated hip screw surgery Information for patients at Princess Royal University Hospital This leaflet gives you advice about the things you can do after your operation
Rehabilitation programme after cannulated hip screw surgery Information for patients at Princess Royal University Hospital This leaflet gives you advice about the things you can do after your operation
Disclosure. Esquenazi
 Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this activity, the participant will be able to: A. Understand the purpose and function of the ReWalk exoskeletal orthotic device. B. Understand the variation in
Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this activity, the participant will be able to: A. Understand the purpose and function of the ReWalk exoskeletal orthotic device. B. Understand the variation in
Guidelines for patients having. Achilles Tendon Repair. Achilles Tendon Repair
 Guidelines for patients having ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Achilles Tendon Repair Please stick addressograph
Guidelines for patients having ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Achilles Tendon Repair Please stick addressograph
Functional Electrical Stimulation-Assisted Walking: Enhancement of Voluntary Walking Function Among Persons with Severe Hemiplegia Post Stroke
 Functional Electrical Stimulation-Assisted Walking: Enhancement of Voluntary Walking Function Among Persons with Severe Hemiplegia Post Stroke Naaz Kapadia Date: May 10, 2010 Research Coordinator-Physiotherapist
Functional Electrical Stimulation-Assisted Walking: Enhancement of Voluntary Walking Function Among Persons with Severe Hemiplegia Post Stroke Naaz Kapadia Date: May 10, 2010 Research Coordinator-Physiotherapist
Overview Functional Training
 Overview Functional Training Exercises with Therapist 1. Sitting 2. Standing up vs. Sitting down 3. Standing 4. Stance phase ( Static and dynamic ) 5. Swing phase 6. Gait Evaluation 7. Walking level ground
Overview Functional Training Exercises with Therapist 1. Sitting 2. Standing up vs. Sitting down 3. Standing 4. Stance phase ( Static and dynamic ) 5. Swing phase 6. Gait Evaluation 7. Walking level ground
Paraplegics standing up using multichannel FES and arm support
 Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology, Volume 26, Number 3, (May/June 2002), pages 106 110 Paraplegics standing up using multichannel FES and arm support J. KuzÏ elicï ki{*, R. Kamnik{, T. Bajd{,
Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology, Volume 26, Number 3, (May/June 2002), pages 106 110 Paraplegics standing up using multichannel FES and arm support J. KuzÏ elicï ki{*, R. Kamnik{, T. Bajd{,
Botulinum Toxin Treatment for children
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Botulinum Toxin Treatment for children Physiotherapy This patient information leaflet is designed to answer frequently asked
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Botulinum Toxin Treatment for children Physiotherapy This patient information leaflet is designed to answer frequently asked
DRIVE CLEAR OF PAIN A COMFORTABLE RIDE WITH ERGONOMIC ADVICE THE KEY TO YOU WILL BE SITTING PRETTY SIMPLE TIPS FOR
 DRIVE CLEAR OF PAIN THE KEY TO SIMPLE TIPS FOR DRIVING WELL STAYING FIT YOU WILL BE SITTING PRETTY A COMFORTABLE RIDE WITH ERGONOMIC ADVICE BROUGHT TO YOU BY THE CHARTERED SOCIETY OF PHYSIOTHERAPY induc
DRIVE CLEAR OF PAIN THE KEY TO SIMPLE TIPS FOR DRIVING WELL STAYING FIT YOU WILL BE SITTING PRETTY A COMFORTABLE RIDE WITH ERGONOMIC ADVICE BROUGHT TO YOU BY THE CHARTERED SOCIETY OF PHYSIOTHERAPY induc
Otago strength and balance training exercise programme
 Otago strength and balance training exercise programme An information guide for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please
Otago strength and balance training exercise programme An information guide for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please
RECOMMENDED STRETCHES
 RECOMMENDED STRETCHES Stretching prescribed below is always best done either after a session while your muscles are warm or after a short warm up such as 5mins of running, skipping, cycling, rowing etc.
RECOMMENDED STRETCHES Stretching prescribed below is always best done either after a session while your muscles are warm or after a short warm up such as 5mins of running, skipping, cycling, rowing etc.
Omo and Manu Neurexa plus
 Omo and Manu Neurexa plus Promote movement. Stay independent. Information for specialists Omo and Manu Neurexa plus Effectively supporting rehabilitation of the hand and shoulder The devices in the Neurexa
Omo and Manu Neurexa plus Promote movement. Stay independent. Information for specialists Omo and Manu Neurexa plus Effectively supporting rehabilitation of the hand and shoulder The devices in the Neurexa
RETURN TO SPORT PROTOCOL CO.RE
 RETURN TO SPORT PROTOCOL CO.RE WHO CAN USE THIS PROGRAM This protocol is designed as a return to sport program following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction but applies equally well to rehabilitation
RETURN TO SPORT PROTOCOL CO.RE WHO CAN USE THIS PROGRAM This protocol is designed as a return to sport program following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction but applies equally well to rehabilitation
FES-UPP: A novel functional electrical stimulation system to support upper limb functional task practice following stroke.
 FES-UPP: A novel functional electrical stimulation system to support upper limb functional task practice following stroke Paul Taylor The upper limb following stroke Around 85% of people with stroke have
FES-UPP: A novel functional electrical stimulation system to support upper limb functional task practice following stroke Paul Taylor The upper limb following stroke Around 85% of people with stroke have
STROKE POSITIONING, TRANSFERRING & SHOULDER MANAGEMENT IN ACUTE AND REHAB
 STROKE POSITIONING, TRANSFERRING & SHOULDER MANAGEMENT IN ACUTE AND REHAB PRESENTED BY: Francine Carrier-Stevens, PT. Natasha Uens, PT. Chelsea Foster, RN. OVERVIEW Objectives Factors affecting mobility
STROKE POSITIONING, TRANSFERRING & SHOULDER MANAGEMENT IN ACUTE AND REHAB PRESENTED BY: Francine Carrier-Stevens, PT. Natasha Uens, PT. Chelsea Foster, RN. OVERVIEW Objectives Factors affecting mobility
Instructions for Ilizarov and Taylor Spatial Frame Foot Drop Splints and Shoes
 Instructions for Ilizarov and Taylor Spatial Frame Foot Drop Splints and Shoes Irving Building Occupational Therapy, Rehabilitation Services 0161 206 519 G1809190W. Design Services, Salford Royal NHS Foundation
Instructions for Ilizarov and Taylor Spatial Frame Foot Drop Splints and Shoes Irving Building Occupational Therapy, Rehabilitation Services 0161 206 519 G1809190W. Design Services, Salford Royal NHS Foundation
High Tibial Osteotomy (HTO) Rehabilitation Protocols
 High Tibial Osteotomy (HTO) Rehabilitation Protocols Targets Upon Discharge from Hospital Protected weight-bearing (feather-weight -bearing) Ambulating with crutches Rehab brace without range of motion
High Tibial Osteotomy (HTO) Rehabilitation Protocols Targets Upon Discharge from Hospital Protected weight-bearing (feather-weight -bearing) Ambulating with crutches Rehab brace without range of motion
HEALTH PROFESSIONS ACT 56 OF 1974
 HEALTH PROFESSIONS ACT 56 OF 1974 REGULATIONS DEFINING THE SCOPE OF THE PROFESSION OF PHYSIOTHERAPY Published under Government Notice R2301 in Government Gazette 5349 of 3 December 1976. The Minister of
HEALTH PROFESSIONS ACT 56 OF 1974 REGULATIONS DEFINING THE SCOPE OF THE PROFESSION OF PHYSIOTHERAPY Published under Government Notice R2301 in Government Gazette 5349 of 3 December 1976. The Minister of
Original Article. The functional impact of the Freehand System on tetraplegic hand function. Clinical Results. Introduction.
 (2002) 40, 560 ± 566 ã 2002 International Society All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/sc Original Article The functional impact of the Freehand System on tetraplegic hand function.
(2002) 40, 560 ± 566 ã 2002 International Society All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/sc Original Article The functional impact of the Freehand System on tetraplegic hand function.
Peripheral Nerve Problems
 Patient Education Peripheral Nerve Problems How they develop and ways to treat them This handout provides general information about how nerves work, what happens when they are injured, and how peripheral
Patient Education Peripheral Nerve Problems How they develop and ways to treat them This handout provides general information about how nerves work, what happens when they are injured, and how peripheral
Rehabilitation. Walking after Total Knee Replacement. Continuous Passive Motion Device
 Walking after Total Knee Replacement After your TKR, continue using your walker or crutches until your surgeons tells you it is okay to stop using them. When turning with a walker or crutches DO NOT PIVOT
Walking after Total Knee Replacement After your TKR, continue using your walker or crutches until your surgeons tells you it is okay to stop using them. When turning with a walker or crutches DO NOT PIVOT
Brunel balance assessment (BBA)
 Brunel balance assessment (BBA) Tyson, S Title Authors Type URL Brunel balance assessment (BBA) Tyson, S Published Date 2004 Monograph This version is available at: http://usir.salford.ac.uk/4886/ USIR
Brunel balance assessment (BBA) Tyson, S Title Authors Type URL Brunel balance assessment (BBA) Tyson, S Published Date 2004 Monograph This version is available at: http://usir.salford.ac.uk/4886/ USIR
Does your spasticity...
 QUESTIONS Does your spasticity... help or limit your walking? make it difficult to breathe or take a deep breath? help or hinder your ability to get in and out of bed? cause pain? Affect your posture in
QUESTIONS Does your spasticity... help or limit your walking? make it difficult to breathe or take a deep breath? help or hinder your ability to get in and out of bed? cause pain? Affect your posture in
Gait analysis in children and adolescents with spinal cord injuries.
 gfedcb 1: J Spinal Cord Med. 2004;27 Suppl 1:S44-9. Gait analysis in children and adolescents with spinal cord injuries. Smith PA, Hassani S, Reiners K, Vogel LC, Harris GF. Motion Analysis Laboratory,
gfedcb 1: J Spinal Cord Med. 2004;27 Suppl 1:S44-9. Gait analysis in children and adolescents with spinal cord injuries. Smith PA, Hassani S, Reiners K, Vogel LC, Harris GF. Motion Analysis Laboratory,
Peripheral Nerve Problems
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peripheral Nerve Problems How they develop and ways to treat them This handout explains how nerves work, what happens when they are injured, and how peripheral nerve problems
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peripheral Nerve Problems How they develop and ways to treat them This handout explains how nerves work, what happens when they are injured, and how peripheral nerve problems
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: neurostimulation_electrical 4/2004 10/2017 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Neuromuscular
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: neurostimulation_electrical 4/2004 10/2017 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Neuromuscular
Why You (and Your Insurance Company) Need to Get Your Child Standing by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Why You (and Your Insurance Company) Need to Get Your Child Standing by Susan Agrawal Fractures. Constipation. Hips out of their sockets. Tight hamstrings. Orthopedic surgery. Casts
www.complexchild.com Why You (and Your Insurance Company) Need to Get Your Child Standing by Susan Agrawal Fractures. Constipation. Hips out of their sockets. Tight hamstrings. Orthopedic surgery. Casts
Building Better Balance
 Building Better Balance The Effects of MS on Balance Individuals with MS experience a decline in their balance due to various MS related impairments. Some of these impairments can be improved with exercise
Building Better Balance The Effects of MS on Balance Individuals with MS experience a decline in their balance due to various MS related impairments. Some of these impairments can be improved with exercise
CORE STABILITY & LOW BACK PAIN. Tim Ellis, Physiotherapist BA(Hons) BSc(Hons) MHlthSc(Hons) APA
 CORE STABILITY & LOW BACK PAIN Tim Ellis, Physiotherapist BA(Hons) BSc(Hons) MHlthSc(Hons) APA 1 Core Stability & Low Back Pain In this 8 page ebook, our Principal Physiotherapist, Tim Ellis, explains
CORE STABILITY & LOW BACK PAIN Tim Ellis, Physiotherapist BA(Hons) BSc(Hons) MHlthSc(Hons) APA 1 Core Stability & Low Back Pain In this 8 page ebook, our Principal Physiotherapist, Tim Ellis, explains
Total knee replacement
 Total knee replacement Inpatient and home exercises Information for patients MSK Orthopaedic Inpatients (Therapy) When you go home from hospital following your knee replacement, a referral will be made
Total knee replacement Inpatient and home exercises Information for patients MSK Orthopaedic Inpatients (Therapy) When you go home from hospital following your knee replacement, a referral will be made
Static Flexibility/Stretching
 Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Do the same as above, but turn your head TOWARDS the side that you re holding on to the chair.
 Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
This Manual is copyright under the Berne Convention. In terms of the Copyright Act 98 of 1978 no part of this leaflet may be reproduced or
 Basic Ball Exercise Manual Train your Core This Manual is copyright under the Berne Convention. In terms of the Copyright Act 98 of 1978 no part of this leaflet may be reproduced or transmitted in any
Basic Ball Exercise Manual Train your Core This Manual is copyright under the Berne Convention. In terms of the Copyright Act 98 of 1978 no part of this leaflet may be reproduced or transmitted in any
Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Exercise programme
 Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Pulmonary Rehabilitation Exercise programme Introduction to exercises Wear sensible shoes and loose clothing. When performing
Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Pulmonary Rehabilitation Exercise programme Introduction to exercises Wear sensible shoes and loose clothing. When performing
Physical & Occupational Therapy
 In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
Appendix 1: Description of the Ossébo fall and injury prevention exercise programme [posted as supplied by author]
![Appendix 1: Description of the Ossébo fall and injury prevention exercise programme [posted as supplied by author] Appendix 1: Description of the Ossébo fall and injury prevention exercise programme [posted as supplied by author]](/thumbs/89/101009847.jpg) Appendix 1: Description of the Ossébo fall and injury prevention exercise programme [posted as supplied by author] Overall description Programme duration: 2 years/8 quarters Weekly frequency: 1 group session
Appendix 1: Description of the Ossébo fall and injury prevention exercise programme [posted as supplied by author] Overall description Programme duration: 2 years/8 quarters Weekly frequency: 1 group session
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
 What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
