An efficient framework for estimation of muscle fiber orientation using ultrasonography
|
|
|
- Hilary Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 RESEARCH Open Access An efficient framework for estimation of muscle fiber orientation using ultrasonography Shan Ling 1,2,3, Bin Chen 2,3,4, Yongjin Zhou 2,3,5*, Wan-Zhang Yang 6, Yu-Qian Zhao 1, Lei Wang 2,3 and Yong-Ping Zheng 5 *Correspondence:yj.zhou@siat.ac.cn Equal contributors 2 The Shenzhen Key Laboratory for Low-cost Healthcare, Shenzhen, China 3 Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China Full list of author information is available at the end of the article Abstract Background: Muscle fiber orientation (MFO) is an important parameter related to musculoskeletal functions. The traditional manual method for MFO estimation in sonograms was labor-intensive. The automatic methods proposed in recent years also involved voting procedures which were computationally expensive. Methods: In this paper, we proposed a new framework to efficiently estimate MFO in sonograms. We firstly employed Multi-scale Vessel Enhancement Filtering (MVEF) to enhance fascicles in the sonograms and then the enhanced images were binarized. Finally, line-shaped patterns in the binary map were detected one by one, according to their shape properties. Specifically speaking, for the long-and-thinner regions, the orientation of the targeted muscle fibre was directly computed, without voting procedures, as the orientation of the ellipse that had the same normalized second central moments as the region. For other cases, the Hough voting procedure might be employed for orientation estimation. The performance of the algorithm was evaluated using four various group of sonograms, which are a dataset used in previous reports, 33 sonograms of gastrocnemius from 11 young healthy subjects, one sonogram sequence including 200 frames from a subject and 256 frames from an aged subject with cerebral infarction respectively. Results: It was demonstrated in the experiments that measurements of the proposed method agreed well with those of the manual method and achieved much more efficiency than the previous Re-voting Hough Transform (RVHT) algorithm. Conclusions: Results of the experiments suggested that, without compromising the accuracy, in the proposed framework the previous orientation estimation algorithm was accelerated by reduction of its dependence on voting procedures. Keywords: Ultrasound, Muscle, Hough transform, Orientation, Line detection, Image segmentation Background Ultrasonography is being widely used as a clinical and research tool for dynamic studies of the muscle during contraction and relaxation, since it s real-time, widely available, radiation-free and low-cost. Muscle architectural characteristics, such as pennation angle or fiber orientation [1-8], fascicle length [1,2,9-12], fascicle curvature [13-16] and muscle thickness [9,17-21], can be extracted from ultrasonography to evaluate the muscle 2013 Ling et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 2 of 17 function and activity. And changes of these architectural parameters over the time can form quantitative observations of muscle behavior under contraction. Since orientation of muscle fiber or aponeuroses is often computed first and then acted as basis of the estimation of muscle fiber length during morphological studies of skeletal muscles [22-24], an efficient realization of automatic measurement of muscle fiber orientation (MFO) would also contribute to the estimation of muscle fiber length which is a significant measure of muscle properties. Traditionally, the fibers and their orientations in musculoskeletal sonograms were detected manually by drawing lines using NIH image software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) (for example, [9,25,26]). Being labor-intensive, the manual method affected the real-time and quantitative observations on muscle behaviors. Therefore, recently the method for automatic estimation of fiber orientation in musculoskeletal sonograms had drawn some attentions [3-8]. Although some methods have been developed to extract curve features of muscle fiber [12,27], the detection of lineshaped patterns in musculoskeletal sonograms, as key step of pennation angle estimation, is still of great interests to the field [9,28-30]. However, automatic methods previously reported were all build on the voting procedures using either Hough [3,5] or Radon [6,7] transform which are computationally expensive. For example, in a previous study, we proposed the Re-voting Hough Transform (RVHT) algorithm to realize the automatic estimation of MFO in muscular sonograms [3]. Because of its sensitivity to noises, we later complemented RVHT by employing Gabor Filtering as a pre-processing procedure to enhance the longitudinal sonograms of fiber [5]. Recently, after the evaluation of Gabor Filtering and another enhancement method, namely multiscale vessel enhancement filtering (MVEF), we found MVEF a better choice with comparable enhancement performance but less computation than Gabor Filtering [20]. Certainly, the involvement of the image enhancement procedures would cost more computation. In the current study, we propose a new framework for MFO estimation in sonograms by skipping the voting step as much as possible. Instead, the shape properties of the interested regions will be used to output the orientation in most cases, detailed in the method section. Compared with the single RVHT method, this framework is expected to achieve higher efficiency at line angle estimation without compromising the accuracy. Methods The efficient framework for estimation of MFO includes three steps: 1) image enhancement, 2) extraction of object regions, and 3) estimation of MFO. Image enhancement using MVEF algorithm Sonograms are usually affected by speckle noises, which hinder the analysis of musculoskeletal geometry. Taking into account the fact that the fiber in sonograms are tubular and include coherent orientation tendencies, we apply MVEF to enhance the sonograms before the line angle detection. The MVEF method is based on the second order local structure, with excellent noise and background suppression performance [31]. The method includes three steps: the Hessian matrix estimation (including the
3 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 3 of 17 choice of Gaussian kernels), computation of eigenvector for each scale and processing for the maximum vesselness response. More details can be found in [31]. Extraction of object regions In this study, objects to be extracted from sonograms are regions which may represent long and thin muscle fibers. Since fibers, both aponeuroses and other fascia structures, have higher intensity than the background in a sonogram, a straightforward approach to find the potential regions of fibers is to apply a threshold on the enhanced image, so that the pixels whose value is greater than the threshold are regarded as the pixels located in the potential object regions. In this paper, the Otsu s method is employed to get the optimal threshold [32]. This will result in a binary map, I map, where the white components represent the candidate regions for muscle fibers. Estimation of MFO According to our observations, shapes of the interested object regions could vary and be divided into three different patterns. RA: regions which are long and thin, where each of them represents one major muscle fiber. RB: regions which are long but have branches because of adherence of two or several muscle fibers. RC: regions which are short and possibly from a broken line caused by partial imaging one singlemusclefiber. Orientations of RA and RC would be calculated as the angle between the y-axis and major axis of ellipse that has the same normalized second central moments as the region. Angles of RB would be calculated using Hough transform (HT). Specifically speaking, 3 shape measures for the region, aspect ratio Ar, widthω and length L, will be used for classification of RA, RB and RC. In this study, L and ω are calculated respectively as the length of the major and minor axis of the ellipse that has the same normalized second central moments as the region, and the aspect ratio is defined as L/ω. The procedures of the proposed framework for MFO estimation on the binary map are shown in Figure 1. The proposed framework detects lines one by one in I map, starting with the longest region and detailed steps are: Step 1. Setting parameters T 1, T 2, T 3 and N; n=1; I n map ¼ I map. (T 1, T 2 are thresholds for shape measurements Ar and ω respectively. T 3 is the ratio of the length of the last and first detected lines. N is the upper limit of line number for each image). Step 2. Extracting the longest region and calculating its aspect ratio Ar n, width ω n and length L n. Step 3. If Ar n > T 1 and ω n < T 2, the orientation of the region is estimated as the angle between the y-axis and major axis of ellipse that has the same normalized second central moments as the region; Otherwise, applying HT on the region, and the line that with global maximum in the accumulator array is detected. Step 4. Removing pixels close to the line detected in step #3 and getting the updated map I nþ1 map. (This step can remove noises near the line and avoid the duplication in the angle measurement of RC). Step 5. Check whether n =NorL n < L 1 T 3. If not, n=n+1and repeat from step #2.
4 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 4 of 17 Binary Map Selecting the Longest region Check if the region is : RA/RC RB Computing the orientation of the ellipse that has the same secondcentral-moments as the region Applying HT Stop condition? Yes End No Removing pixels near the detected line to update the binary map Figure 1 The diagram of the efficient framework for estimating MFO. Experiments Experiment setup for normal subjects The proposed framework is first evaluated using the dataset from previous reports [3,5], which were acquired on biceps and forearm muscles during various typical exercise tasks, from three healthy adult male volunteers, and the detailed experiment setup can be found in [3,5]. Then to further evaluate the proposed framework on same muscle but from different subjects, we designed an experiment example on the sonograms of gastrocnemius. Eleven healthy male subjects (mean ± SD, age = 29.4 ± 1.8 years; body weight 65.9 ± 9.3 kg; height = ± 5.1 cm) volunteered to participate in this experiment. No participant had a history of neuromuscular disorders, and all were aware of experimental purposes and procedures. The human subject ethical approval was obtained from the relevant committee in the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hum, Hong Kong and informed consents were obtained from subjects prior to the experiment. The testing position of the subject was in accordance with the Users Guide of a Norm dynamometer (Humac/Norm Testing and Rehabilitation System, Computer
5 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 5 of 17 Sports Medicine, Inc., Massachusetts, USA). Each subject was required to put forth his maximal effort of isometric plantar flexion for a period of 3 seconds with verbal encouragement provided. The maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) was defined as the highest value of torque recorded during the entire isometric contraction. A rest of 5 min was allowed before the subject performing another MVC test. The MVC torque was then calculated by averaging the two recorded highest torque values from the two tests. The subject was instructed to generate a torque waveform in rough sinusoid shape, up to 90% of his MVC, using ankle plantar flexion movements in prone position. The torque was measured by the aforementioned dynamometer and the reason for choosing 90% MVC as the highest value was to avoid muscle fatigue. A real-time B-mode ultrasonic scanner (EUB-8500, Hitachi Medical Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) with a 10 MHz electronic linear array probe (L53L, Hitachi Medical Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) was used to obtain ultrasound images of muscles. The long axis of the ultrasound probe was arranged parallel to the long axis of the gastrocnemius and on its muscle belly. The ultrasound probe was fixed by a custom-designed foam container with fixing straps, and a very generous amount of ultrasound gel was applied to secure acoustic coupling between the probe and skin during muscle contractions, as shown in Figure 2. The probe was adjusted to optimize the contrast of muscle fascicles in ultrasound images. Then the B-mode ultrasound images were digitized by a video card (NI PCI-1411, National Instruments, Austin, USA) at a rate of 25 frame/s for later analysis. Surface electromyography (EMG) signals were collected from the gastrocnemius muscle using bipolar Ag-AgCl electrodes (Axon System, Inc., NY, USA), amplified by a multiple channel amplifier (RM6280 Multi-Channel Biosignal Collection and Processing System, Chengdu Instrument Company, Chengdu, China), with a gain of 2000, filtered separately by Hz, Hz band-pass analog filters within the amplifier, and then digitized by a 12-bit data acquisition card (NI-DAQ 6024E, National Instruments Corporation, Austin, TX, USA) with a sampling rate of 1 khz. Figure 2 Experimental setup for collecting the torque, EMG and sonograms from the subject s gastrocnemius during isometric knee extension.
6 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 6 of 17 Ultrasound image sequences, surface EMG and torque signals were simultaneously collected and stored by a custom-made program for ultrasonic measurement of motion and elasticity (UMME, Totally eleven sequences of gastrocnemius ultrasound images were acquired and each includes 200 images. For each sequence, 3 frames corresponding to the torque at 0%, 45% and 90% MVC were used to evaluate the proposed framework. Furthermore, one sequence including all 200 frames from one representative subject is used to evaluate the performance of MFO tracking, following the practice of [4,7]. Experiment setup for an aged subject with cerebral infarction We also tried to preliminarily evaluate the performance of the proposed framework on sonograms from other than healthy or young subjects. One male subject with unilateral limb dysfunction caused by cerebral infarction (age = 68 years; body weight = 71 kg; height = 1.72 m; right leg dysfunctional) volunteered to participate in this study. The human subject ethical approval was obtained from the relevant committee in Zhujiang Hospital, Guangzhou, China before carrying out the experiment. The subject was briefed about the procedure of experiment and written consents were collected prior to the experiment. The subject was seated with both right hip and knee angles of 90. During measurement, the subject was asked to perform plantar flextion both in left leg (normal) and in right leg (dysfunctional) with his best efforts, and the rough contraction time is about.4 seconds in one exercise. A laptop ultrasound system (SS-10, Sonostar Technologies Co., Limited, Guangzhou, China), with a 7.5 MHz electronic linear array probe, was used to obtain the ultrasonic image sequences. The long axis of the probe was arranged parallel to the long axis of the gastrocnemius muscle (as shown in Figure 3) and during the muscle contraction the probe was managed to keep on well coupled to the muscle belly with a luxury usage of gel by an experienced operator. 128 consecutive frames from each leg were captured. The caregiver of the patient had the The long axis of the probe The long axis of the gastrocnemius Figure 3 Experimental setup for collecting gastrocnemius sonograms from an aged subject with cerebral infarction.
7 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 7 of 17 SonoStar scanner available only, and they allowed no third-party scanner used inside their medical facilities. Data processing All images were cropped to remove the imaging tags and retained only the image content, and then processed using the procedures described above. All codes were written in Matlab R2010a. Five parameters could be controlled by the users. In our experiment, T 1, T 2 were set to 5, 30 pixels respectively. The removal width, which indicated the number of neighboring pixels to be removed along the line after a line was detected, was set to 17 pixels. Last-to-first ratio T 3 was set to 10%. This ratio together with N (the number of lines to be detected for each image) was used as iteration termination conditions. For evaluation purpose in this article, we supposed there would be at most seven representative and interesting linear patterns visible per sonogram from the normal subjects, i.e., patterns corresponding to the skin, bone, superficial aponeurosis, deep aponeurosis and fascicles in between them. Therefore, for normal subjects in this study, we set N, the maximum line per sonogram, to 7. Results Results on the dataset from previous reports Totally 314 lines were detected in the 45 sonograms from previous reports [3,5], among which 313 were regarded as being valid according to visual verification and 8 lines were detected using HT. A typical original sonogram of biceps and the corresponding results obtained using the proposed method, are shown in Figure 4. The lines and their angle values were marked with the order in which they got detected. MFO here was computed as the angle between the detected line and the vector pointing from the up-left to bottom-left corner of the image, which was the same as the definition of the NIH Image (National Institutes of Health, USA) software. In order to verify the validity of the method, two operators who were experienced in ultrasound imaging of muscles, were employed to draw lines manually on the original images at locations where lines were detected using the proposed framework, and read the drawn angles using NIH Image software. As a result, 313 lines were marked out manually, all included in the 314 lines detected by the proposed framework. The angles estimated by our method, operator #1 and operator #2 were defined as ap, aa1 and aa2 respectively and displayed in Figure 5. To investigate how well our results fit the manually drawn values, the mean of aa1 and aa2, named as Op, was compared with the corresponding value of ap. The correlation analysis of Op and ap is shown in Figure 6. Further Bland-Altman plot [33] illustrated in Figure 7 presents the details of the angle measurements statistics. The angle differences between the manual and automatic measurements is 0.11 ± 1.80 at the 95% confidence level. The general detection performances of the proposed method and RVHT are shown in Table 1, where RVHT with enhancement represents RVHT using Gabor filtering as a preprocessing procedure. Comparison of computation cost between the proposed
8 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 8 of 17 (a) (b) (c) (d) line #1 : 90 line #4 92 line #7 : 92 line #6 : 81 line #3 : 88 line #2 : 82 line #5 : 85 Figure 4 A representative image of biceps from the previous reports [3,5] and corresponding MFO results. (a) The original image. (b) The image after MVEF. (c) The image after binarization, where red, blue and green regions denote the typical RA, RB and RC respectively. (d) MFO detection results, where the angle of red line was detected using HT and the angle of yellow line was estimated as the orientation of the ellipse that has the same second-moments as the region. framework and RVHT is displayed in Table 2. We also tested the computing cost of a single Hough Transform and a single procedure of computing the orientation of the ellipse in C (Microsoft Visual Studio 2010, Microsoft Corporation, Seattle, USA), and for a typical edge map with size and 2055 white pixels in the region of interest, the cost is 149 and 4 seconds respectively for iterations. Results on sonograms of gastrocnemius from 11 subjects Totally 231 lines were detected in the 33 sonograms of gastrocnemius from 11 normal subjects, among which 217 were regarded as being valid according to visual verification and only 1 line was detected using HT. Blamd-Altman plot of angle detection results
9 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 9 of 17 Figure 5 Comparison of angle estimation results obtained using the proposed and manual methods on the dataset from previous reports [3,5] where aa1 aa2 and ap stand for the results from operator #1, #2 and those using the proposed method. for these data, obtained by the proposed framework and the 2 operators, is displayed in Figure 8. The angle differences between the manual and automatic measurements is 0.03 ± 2.72 at the 95% confidence level. Results on MFO tracking from 200 frames of one representative subject We also tracked the orientation changes of a selected dominant fascicle and the deep aponeurosis in a sequence. Comparisons of these two orientations estimated using the proposed and manual methods were shown in Figure 9. It was observed that there were good correlations among the results obtained by the two operators and the proposed framework. Angles of the selected fasicle and the deep aponeurosis were also shown in Figure 10(a-b) together with the corresponding normalized torque signal and the normalized root mean square (RMS, 256-points) values of EMG signal in Figure 10(c-d). Results on sonograms from the aged subject with cerebral infarction Two typical frames from left and right legs of the aged subject and their line detection results estimated using the proposed method are shown in Figure 11. Based on the triceps 120 Angles Detected by the Proposed Method: ap (degree) y = x R² = Mean of Angles Measured by the Two Operators: Op (degree) Figure 6 The correlation between angle estimation results obtained using the proposed and manual methods on the dataset from previous reports [3,5]. R is the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient.
10 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 10 of 17 Obtained the Angles between Differences by the Proposed Method and the Mean of Those by 2 Operators: ap-op, (degree) Mean + 2SD Mean Mean 2SD Overall Mean of the Angles Obtained by the Proposed Method and 2 Operators: (Op+ap)/2, (degree) Figure 7 The Bland-Altman plot of angle estimation results on the dataset from previous reports [3,5]. The units for both x-axis and y-axis are in degrees, where Op and ap stand for the mean results of the two operators and the results obtained using the proposed method respectively. surae architecture, the maximum line per sonogram N was set to 4 for the data from aged subject. 440 and 452 lines were detected for frames for normal and dysfunctional limbs respectively, and among which 3 was invalid according to visual verification. However, totally 67 interested muscle fibers were not detected by the proposed method. Discussion The effects of the parameters on the line detection Results of the method are affected by at least 4 parameters, i.e., T 1, T 2, T 3 and N. The total number of detected lines in a sonogram could be determined by T 3 and N. The maximum line per sonogram N could be easily tuned up, if necessary, to accommodate the detection of more localized linear patterns. Taking 45 sonograms of biceps and forearm as examples, if we set N to 9 instead of 7, the number of total detected Table 1 The comparison of the differences of the angle estimation results (degree) ap-op** Proposed method RVHT* without enhancement RVHT with enhancement Mean Standard error Median Standard deviation Kurtosis Skewness Range Minimum Maximum Sum Count (total line detected) False line detected *RVHT = revoting Hough transform. **ap and op stand for the results of the proposed methods and the mean of the results from two operators.
11 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 11 of 17 Table 2 Comparison of computation cost Methods Time per-line (s/line) Line detected using HT Total line detected Proposed a RVHT b RVHT2 c a Proposed: the proposed framework. b RVHT: revoting Hough transform. c RVHT2: RVHT using MVEF as a preprocessing procedure. lines would increase from 314 to 378, while the number of false lines not actually corresponding to any one single muscle fiber increased from 1 to 4. The last-to-first ratio T 3 was set to exclude very short regions which may be noises, artefacts or the shorter regions of the broken fiber (whose angles could be the duplications of the longest segment from the same broken fiber). It is clear that the larger T 3 is, the less possible that a false line would be wrongly detected. While on the other hand, if this ratio is too large, less lines could be detected especially if the longest line in the image are very long. For 45 sonograms of biceps and forearm, when we tune T 3 from 10% up to 50%, all detected lines were valid but the number of total detected lines decreased from 314 to 118. As for T 1 and T 2, which are thresholds for aspect ratio Ar and width ω respectively, taking an incoming region as an example, the larger its Ar and the smaller its ω is, themorepossibleitwillfallsintoragroup.simplyspeaking,t 1 and T 2 affect the number of lines detected using HT. The larger T 1 and the smaller T 2 is, the more lines will be detected using HT, and the slower the algorithm will be. However, smaller T 1 or larger T 2 could cause higher risks to mis-classify a RB as a RA, which may lead to a wrong angle estimation. Therefore, one has to compromise between the computation efficiency and correctness and tune the parameters based on the specific image contents. Differences Between the Angles Obtained by the Proposed Method and the Mean of Those by 2 Operators: ap-op, (degree) Mean + 2SD Mean Mean - 2SD Overall Mean of the Angles Obtained by the Proposed Method and 2 Operators: (Op+ap)/2, (degree) Figure 8 The Bland-Altman plot of angle estimation results of 33 gastrocnemius sonograms from 11 normal subjects. The units for both x-axis and y-axis are in degrees, where Op and ap stand for the mean results of the two operators and the results obtained using the proposed method respectively.
12 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 12 of 17 (a) Fascide angle(degree) aa1 aa2 ap Frame Number (b) Angle of Deep Aponeurosis(degree) aa1 aa2 ap Frame Number Figure 9 Comparison of orientations estimated for a dominant fascicle and the deep aponeurosis using manual and proposed methods respectively, where aa1, aa2 and ap stand for the results from operator #1, #2 and the proposed method. (a) Fascicle orientation estimated by the proposed framework and the two operators. (b) Orientation of deep aponeurosis estimated by the proposed framework and the two operators. Evaluation of the validity and accuracy of the proposed method As for the quantitative performance of our method, taking the result on the dataset used in previous study [3,5] as an example, a very good linear correlation between the results of the manual and proposed methods was obtained (shown in Figure 6, R 2 =0.987). Meanwhile, Bland-Altman plots in Figure 7 and Figure 8 also echoed the good agreement between the results of the manual and proposed methods both in the previous dataset and sonograms of gastrocnemius from normal subjects. As shown in Table 1, the angle differences between the manual and automatic measurements, 0.11 ± 1.80 at the 95% confidence level, are comparable to the previous results of 0.13 ± 1.79 obtained using RVHT with Gabor filtering [5]. Results of the proposed method for interested MFO tracking agreed well with those of the manual method, as shown in Figure 9. It can be observed in Figure 10 that the
13 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 13 of 17 (a) Fascicle Angle (degree) (b) Angle of the Deep Aponeurosis (degree) (c) Torque (d) EMG-RMS Frame Number Frame Number Frame Number Frame Number Figure 10 Orientations of the fascicle and the deep aponeurosis along with the torque and EMG signals. (a) The signal about the fascicle orientation estimated using the proposed framework, (b) the signal about the orientation of the deep aponeurosis estimated using the proposed framework, (c) the normalized torque signal, and (c) the normalized EMG RMS signal. interested MFOs detected were not as smooth as the torque signal, but followed the general cyclic changes along with the torque output. The results from the aged subject with cerebral infarction have given us some preliminary confidence on the proposed framework. However, the proposed method failed to detect all valid major muscle fibers (about 7.5% missed). This could be related to the fact that the images from this subject are quite different from young or healthy subjects in terms of both echo intensity and image texture [34].
14 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 14 of 17 (a) (b) (c) line #2 : 90 line #1 : 93 line #3 : 97 (d) (e) (f) line #2 : 91 line #1 : 93 line #3 : 99 Figure 11 Results on a patient with unilateral limb dysfunction caused by cerebral infarction. (a)-(c) are a typical frame, its MVEF result and line detection result for left leg respectively. (d)-(f) are a typical frame, the enhanced image using MVEF and line detection result for right leg (dysfunctional). Evaluation of the efficiency of the proposed method Because MVEF has less computation than Gabor Filtering [20], we compared speed of our framework with that of RVHT both with and without MVEF procedure. It can be seen from Table 2, that in general, the speed of the proposed framework is much faster than that of RVHT, which makes significant difference in terms of massive data. Two major reasons contributed to the higher efficiency of the proposed method: Firstly, the new framework skipped the voting step as much as possible. Instead, the shape properties of muscle fibers were used to output the MFO in most cases. The time complexity for computing the orientation of the ellipse that has the same normalized second central moments of the region is O(n 2 ), which is smaller than Hough/
15 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 15 of 17 Radon transform for line detection in an image with the time complexity O(n 3 ). Subsequently, the time complexity of the whole framework is related to the shape of fibers. Taking the result on the dataset used in previous study [3,5] as an example, only a very few regions are branch-structured and therefore detected using HT in sonograms. Experiments showed that the number of lines detected using HT was only 2.5% of the total number of detected lines for the 45 sonograms. As for the 230 (30 from 10 subjects and a sequence of 200 frames from the representative subject) sonograms of gastrocnemius from normal subjects, only one line was detected using HT. In other words, in most cases our framework detects lines without the voting procedures, and HT remains only a complementary operation for branch-structured fiber. Secondly, in our framework, candidates in each voting step were pixels of a subregion, which is different from the previous RVHT where all pixels in the image would be involved in a voting step. Improving computation efficiency contributes a lot to the real-time application of ultrasonic diagnosis. The benefit of improved computation speed will grow much larger when we are shifting today from dealing with individual scans to several stream of video captured during the scan procedures. The high efficiency of the method is crucial for applications in the evaluation of the muscle dynamic behavior using sonograms where massive data are involved (such as [4,6-12]). Conclusions In this paper we proposed a new framework for the efficient estimation of MFO using ultrasonography. The framework aimed to output angles using the shape properties of muscle fibers in sonograms with as less as possible Hough/Radon voting procedures. Results of the experiments suggest that, without compromising the accuracy, the proposed framework achieved higher efficiency than previous RVHT algorithm at line angle estimation, which is much more outstanding when massive data would be involved.therefore,ournewmethodwouldfacilitate image-guided ultrasound musculoskeletal analysis better, from automatic estimation of MFO to subsequent muscle fiber length and thickness. Abbreviations MFO: Muscle fiber orientation; HT: Hough transform; RVHT: Revoting hough transform; MVEF: Multiscale vessel enhancement filtering; MVC: Maximal voluntary contraction; EMG: Electromyography; RMS: Root mean square. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions SL: composed the manuscript together with BC and YJZ, YJZ: proposed the idea, BC: analyzed the data with SL, YQZ, LW, WZY and YPZ: performed experiments together with YJZ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgements The project is supported partially by the next generation communication technology Major project of National S&T (2013ZX ), the Guangdong Innovative Research Team Program (2011S013,GIRTF-LCHT), International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of Guangdong Province (2012B ) and the Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Commission (GHP/047/09). Author details 1 School of Geosciences and Info-Physics, Central South University, Changsha, China. 2 The Shenzhen Key Laboratory for Low-cost Healthcare, Shenzhen, China. 3 Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China. 4 Harbin Institute of Technology Shenzhen Graduate School, Shenzhen, China. 5 Interdisciplinary
16 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 16 of 17 Division of Biomedical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China. 6 Affiliated Nanshan Hospital of Guangdong Medical College, Shenzhen, China. Received: 18 July 2013 Accepted: 26 September 2013 Published: 30 September 2013 References 1. Chleboun GS, France AR, Crill MT,BraddockHK,HowellJN:In vivo measurement of fascicle length and pennation angle of the human biceps femoris muscle. Cells Tissues Organ 2001, 169(4): Maganaris CN, Baltzopoulos V, Sargeant AJ: Repeated contractions alter the geometry of human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 2002, 93(6): Zhou Y, Zheng Y-P: Estimation of muscle fiber orientation in ultrasound images using revoting hough transform (RVHT). Ultrasound Med Biol 2008, 34(9): Zhou Y, Li J-Z, Zhou G, Zheng Y-P: Dynamic measurement of pennation angle of gastrocnemius muscles during contractions based on ultrasound imaging. Biomed Eng Online 2012, 11. doi: / x Zhou Y, Zheng Y-P: Longitudinal enhancement of the hyperechoic regions in ultrasonography of muscles using a gabor filter bank approach: a preparation for semi-automatic muscle fiber orientation estimation. Ultrasound Med Biol 2011, 37(4): Rana M, Hamarneh G, Wakeling JM: Automated tracking of muscle fascicle orientation in B-mode ultrasound images. J Biomech 2009, 42(13): Zhao H, Zhang L-Q: Automatic tracking of muscle fascicles in ultrasound images using localized radon transform. Biomed Eng, IEEE Transactions on 2011, 58(7): MiyoshiT,KiharaT,KoyamaH,YamamotoS-I,KomedaT:Automatic detection method of muscle fiber movement as revealed by ultrasound images. Med Eng Phys 2009, 31(5): Randhawa A, Wakeling JM: Associations between muscle structure and contractile performance in seniors. Clin Biomech 2013, 28(6): Loram ID, Maganaris CN, Lakie M: Use of ultrasound to make noninvasive in vivo measurement of continuous changes in human muscle contractile length. J Appl Physiol 2006, 100(4): Mademli L, Arampatzis A: Behaviour of the human gastrocnemius muscle architecture during submaximal isometric fatigue. Eur J Appl Physiol 2005, 94(5 6): Cronin NJ, Carty CP, Barrett RS, Lichtwark G: Automatic tracking of medial gastrocnemius fascicle length during human locomotion. J Appl Physiol 2011, 111(5): Muramatsu T, Muraoka T, Kawakami Y, Shibayama A, Fukunaga T: In vivo determination of fascicle curvature in contracting human skeletal muscles. J Appl Physiol 2002, 92(1): Wang H-K, Wu Y-K, Lin K-H, Shiang T-Y: Noninvasive analysis of fascicle curvature and mechanical hardness in calf muscle during contraction and relaxation. Manual Ther 2009, 14(3): Namburete AI, Rana M, Wakeling JM: Computational methods for quantifying in vivo muscle fascicle curvature from ultrasound images. J Biomech 2011, 44(14): Darby J, Li B, Costen N, Loram I, Hodson-Tole E: Estimating skeletal muscle fascicle curvature from b-mode ultrasound image sequences. IEEE Transac Biomed Eng 2013, 60(7): Hodges P, Pengel L, Herbert R, Gandevia S: Measurement of muscle contraction with ultrasound imaging. Muscle Nerve 2003, 27(6): Shi J, Zheng Y-P, Chen X, Huang Q-H: Assessment of muscle fatigue using sonomyography: muscle thickness change detected from ultrasound images. Med Eng Phys 2007, 29(4): Thoirs K, English C: Ultrasound measures of muscle thickness: intra examiner reliability and influence of body position. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 2009, 29(6): HanP,ChenY,AoL,XieG,LiH,WangL,ZhouY:Automatic thickness estimation for skeletal muscle in ultrasonography: evaluation of two enhancement methods. Biomed Eng Online 2013, 12. doi: / x Ling S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Wang L, Zheng Y: Automatic Tracking of Aponeuroses and Estimation of Muscle Thickness in Ultrasonography: A Feasibility Study. IEEE J Biomed Health Info doi: /jbhi Kumagai K, Abe T, Brechue WF, Ryushi T, Takano S, Mizuno M: Sprint performance is related to muscle fascicle length in male 100-m sprinters. J Appl Physiol 2000, 88(3): Blazevich AJ, Gill ND, Zhou S: Intra and intermuscular variation in human quadriceps femoris architecture assessed in vivo. J Anat 2006, 209(3): Kubo K, Kanehisa H, Azuma K, Ishizu M, Kuno SY, Okada M, Fukunaga T: Muscle architectural characteristics in women aged years. Med Sci Sport Exer 2003, 35(1): Reeves ND, Narici MV, Maganaris CN: In vivo human muscle structure and function: adaptations to resistance training in old age. Exp Physiol 2004, 89(6): Itoi E, Sashi R, Minagawa H, Shimizu T, Wakabayashi I, Sato K: Position of Immobilization After Dislocation of the Glenohumeral Joint A Study with Use of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J of Bone & Joint Surgery 2001, 83(5): Darby J, Hodson-Tole EF, Costen N, Loram ID: Automated regional analysis of B-mode ultrasound images of skeletal muscle movement. J Appl Physiol 2012, 112(2): Strasser EM, Draskovits T, Praschak M, Quittan M, Graf A: Association between ultrasound measurements of muscle thickness, pennation angle, echogenicity and skeletal muscle strength in the elderly. AGE doi: /s z. 29. Brancaccio P, Somma F, Provenzano F, Rastrelli L: Changes in muscular pennation angle after crenotherapy. Muscles, Ligaments and Tendons J 2013, 3(2): Kwah LK, Pinto RZ, Diong J, Herbert RD: Reliability and validity of ultrasound measurements of muscle fascicle length and pennation in humans: a systematic review. J Appl Physiol 2013, 114(6):
17 Ling et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:98 Page 17 of Frangi AF, Niessen WJ, Vincken KL, Viergever MA: Multiscale vessel enhancement filtering. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Interventation MICCAI 98. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 1998: Otsu N: A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. Automatica 1975, 11( ): Martin Bland J, Altman D: Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. The Lancet 1986, 327(8476): Watanabe Y, Yamada Y, Fukumoto Y, Ishihara T, Yokoyama K, Yoshida T, Miyake M, Yamagata E, Kimura M: Echo intensity obtained from ultrasonography images reflecting muscle strength in elderly men. Clin Interv Aging 2013, 8:993. doi: / x Cite this article as: Ling et al.: An efficient framework for estimation of muscle fiber orientation using ultrasonography. BioMedical Engineering OnLine :98. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Automatic thickness estimation for skeletal muscle in ultrasonography: evaluation of two enhancement methods
 Han et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:6 RESEARCH Open Access Automatic thickness estimation for skeletal muscle in ultrasonography: evaluation of two enhancement methods Pan Han 1,2, Ye Chen
Han et al. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2013, 12:6 RESEARCH Open Access Automatic thickness estimation for skeletal muscle in ultrasonography: evaluation of two enhancement methods Pan Han 1,2, Ye Chen
A System for the Synchronized Recording of Sonomyography, Electromyography
 The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 2007, 1, 77-84 77 A System for the Synchronized Recording of Sonomyography, Electromyography and Joint Angle Q.H. Huang a,b, Y.P. Zheng*,a, X. Chen a, J.F. He a
The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 2007, 1, 77-84 77 A System for the Synchronized Recording of Sonomyography, Electromyography and Joint Angle Q.H. Huang a,b, Y.P. Zheng*,a, X. Chen a, J.F. He a
APONEUROSIS LENGTH AND FASCICLE INSERTION ANGLES OF THE BICEPS BRACHII
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 2, Nos. 3 & 4 (2002) 1 7 c World Scientific Publishing Company APONEUROSIS LENGTH AND FASCICLE INSERTION ANGLES OF THE BICEPS BRACHII DEANNA S. ASAKAWA,,GEORGEP.PAPPAS,,
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 2, Nos. 3 & 4 (2002) 1 7 c World Scientific Publishing Company APONEUROSIS LENGTH AND FASCICLE INSERTION ANGLES OF THE BICEPS BRACHII DEANNA S. ASAKAWA,,GEORGEP.PAPPAS,,
ULTRASOUND and surface electromyography (EMG) are
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 55, NO. 3, MARCH 2008 1191 Continuous Monitoring of Sonomyography, Electromyography and Torque Generated by Normal Upper Arm Muscles During Isometric Contraction:
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 55, NO. 3, MARCH 2008 1191 Continuous Monitoring of Sonomyography, Electromyography and Torque Generated by Normal Upper Arm Muscles During Isometric Contraction:
Optimal Pennation Angle of the Primary Ankle Plantar and Dorsiflexors: Variations With Sex, Contraction Intensity, and Limb
 Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2006; 22:255-263. 2006 Human Kinetics, Inc. Optimal Pennation Angle of the Primary Ankle Plantar and Dorsiflexors: Variations With Sex, Contraction Intensity, and Limb
Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2006; 22:255-263. 2006 Human Kinetics, Inc. Optimal Pennation Angle of the Primary Ankle Plantar and Dorsiflexors: Variations With Sex, Contraction Intensity, and Limb
Can pennation angles be predicted from EMGs for the primary ankle plantar and dorsiflexors during isometric contractions?
 Journal of Biomechanics 41 (8) 2492 2497 www.elsevier.com/locate/jbiomech www.jbiomech.com Can pennation angles be predicted from EMGs for the primary ankle plantar and dorsiflexors during isometric contractions?
Journal of Biomechanics 41 (8) 2492 2497 www.elsevier.com/locate/jbiomech www.jbiomech.com Can pennation angles be predicted from EMGs for the primary ankle plantar and dorsiflexors during isometric contractions?
APONEUROSIS LENGTH AND FASCICLE INSERTION ANGLES OF THE BICEPS BRACHII
 APONEUROSIS LENGTH AND FASCICLE INSERTION ANGLES OF THE BICEPS BRACHII Deanna S. Asakawa 1, 2, George P. Pappas 1, 2, John E. Drace 2 and Scott L. Delp 1 1 Biomechanical Engineering Division, Mechanical
APONEUROSIS LENGTH AND FASCICLE INSERTION ANGLES OF THE BICEPS BRACHII Deanna S. Asakawa 1, 2, George P. Pappas 1, 2, John E. Drace 2 and Scott L. Delp 1 1 Biomechanical Engineering Division, Mechanical
Feasibility Evaluation of a Novel Ultrasonic Method for Prosthetic Control ECE-492/3 Senior Design Project Fall 2011
 Feasibility Evaluation of a Novel Ultrasonic Method for Prosthetic Control ECE-492/3 Senior Design Project Fall 2011 Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Volgenau School of Engineering George
Feasibility Evaluation of a Novel Ultrasonic Method for Prosthetic Control ECE-492/3 Senior Design Project Fall 2011 Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Volgenau School of Engineering George
In vivo determination of fascicle curvature in contracting human skeletal muscles
 J Appl Physiol 92: 129 134, 2002. In vivo determination of fascicle curvature in contracting human skeletal muscles TADASHI MURAMATSU, 1 TETSURO MURAOKA, 2 YASUO KAWAKAMI, 2 AKIRA SHIBAYAMA, 2 AND TETSUO
J Appl Physiol 92: 129 134, 2002. In vivo determination of fascicle curvature in contracting human skeletal muscles TADASHI MURAMATSU, 1 TETSURO MURAOKA, 2 YASUO KAWAKAMI, 2 AKIRA SHIBAYAMA, 2 AND TETSUO
IMPROVEMENT OF MUSCLE STRENGTH IN REHABILITATION BY THE USE OF SURFACE ELECTROMYOGRAPHY
 IMPROVEMENT OF MUSCLE STRENGTH IN REHABILITATION BY THE USE OF SURFACE ELECTROMYOGRAPHY Rainbow-K.Y. Law, Kevin-S.C. Kwong, Christina-W.Y. Hui-Chan Department of Rehabilitation Sciences, The Hong Kong
IMPROVEMENT OF MUSCLE STRENGTH IN REHABILITATION BY THE USE OF SURFACE ELECTROMYOGRAPHY Rainbow-K.Y. Law, Kevin-S.C. Kwong, Christina-W.Y. Hui-Chan Department of Rehabilitation Sciences, The Hong Kong
AUTOMATIC MEASUREMENT ON CT IMAGES FOR PATELLA DISLOCATION DIAGNOSIS
 AUTOMATIC MEASUREMENT ON CT IMAGES FOR PATELLA DISLOCATION DIAGNOSIS Qi Kong 1, Shaoshan Wang 2, Jiushan Yang 2,Ruiqi Zou 3, Yan Huang 1, Yilong Yin 1, Jingliang Peng 1 1 School of Computer Science and
AUTOMATIC MEASUREMENT ON CT IMAGES FOR PATELLA DISLOCATION DIAGNOSIS Qi Kong 1, Shaoshan Wang 2, Jiushan Yang 2,Ruiqi Zou 3, Yan Huang 1, Yilong Yin 1, Jingliang Peng 1 1 School of Computer Science and
A new method for gravity correction of dynamometer data and determining passive elastic moments at the joint
 A new method for gravity correction of dynamometer data and determining passive elastic moments at the joint The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
A new method for gravity correction of dynamometer data and determining passive elastic moments at the joint The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Effect of electrode position of low intensity neuromuscular electrical stimulation on the evoked force in the quadriceps femoris muscle
 DOI 10.1186/s13104-017-2630-9 BMC Research Notes RESEARCH NOTE Open Access Effect of electrode position of low intensity neuromuscular electrical stimulation on the evoked force in the quadriceps femoris
DOI 10.1186/s13104-017-2630-9 BMC Research Notes RESEARCH NOTE Open Access Effect of electrode position of low intensity neuromuscular electrical stimulation on the evoked force in the quadriceps femoris
AUTOMATIC DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING GABOR FILTER WITH LOCAL ENTROPY THRESHOLDING
 AUTOMATIC DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING GABOR FILTER WITH LOCAL ENTROPY THRESHOLDING MAHABOOB.SHAIK, Research scholar, Dept of ECE, JJT University, Jhunjhunu, Rajasthan, India Abstract: The major
AUTOMATIC DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING GABOR FILTER WITH LOCAL ENTROPY THRESHOLDING MAHABOOB.SHAIK, Research scholar, Dept of ECE, JJT University, Jhunjhunu, Rajasthan, India Abstract: The major
Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected?
 FAQs ABOUT OPENSIM Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected? A: Muscle models in OpenSim generate force based on three parameters: activation, muscle fiber
FAQs ABOUT OPENSIM Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected? A: Muscle models in OpenSim generate force based on three parameters: activation, muscle fiber
NAILFOLD CAPILLAROSCOPY USING USB DIGITAL MICROSCOPE IN THE ASSESSMENT OF MICROCIRCULATION IN DIABETES MELLITUS
 NAILFOLD CAPILLAROSCOPY USING USB DIGITAL MICROSCOPE IN THE ASSESSMENT OF MICROCIRCULATION IN DIABETES MELLITUS PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0841 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDE : DR.AMBEDKAR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
NAILFOLD CAPILLAROSCOPY USING USB DIGITAL MICROSCOPE IN THE ASSESSMENT OF MICROCIRCULATION IN DIABETES MELLITUS PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0841 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDE : DR.AMBEDKAR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
Myofascial Pain Syndrome Trigger Point Detection based on Ultrasound Image
 Myofascial Pain Syndrome Trigger Point Detection based on Ultrasound Image EKO SUPRIYANTO, JOANNE SOH ZI EN, SYED MOHD NOOH OMAR Advanced Diagnostics and Progressive Human Care Research Group Research
Myofascial Pain Syndrome Trigger Point Detection based on Ultrasound Image EKO SUPRIYANTO, JOANNE SOH ZI EN, SYED MOHD NOOH OMAR Advanced Diagnostics and Progressive Human Care Research Group Research
EXTRACT THE BREAST CANCER IN MAMMOGRAM IMAGES
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 96-105, Article ID: IJCIET_10_02_012 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=10&itype=02
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 96-105, Article ID: IJCIET_10_02_012 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=10&itype=02
Doctoral School on Engineering Sciences Università Politecnica delle Marche
 Doctoral School on Engineering Sciences Università Politecnica delle Marche Extended summary Muscle Fatigue Assessment during Flexion Extension Movements Curriculum: Electromagnetism and Bioengineering
Doctoral School on Engineering Sciences Università Politecnica delle Marche Extended summary Muscle Fatigue Assessment during Flexion Extension Movements Curriculum: Electromagnetism and Bioengineering
Research on Digital Testing System of Evaluating Characteristics for Ultrasonic Transducer
 Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Research on Digital Testing System of Evaluating Characteristics for Ultrasonic Transducer Qin Yin, * Liang Heng, Peng-Fei
Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Research on Digital Testing System of Evaluating Characteristics for Ultrasonic Transducer Qin Yin, * Liang Heng, Peng-Fei
A New Approach For an Improved Multiple Brain Lesion Segmentation
 A New Approach For an Improved Multiple Brain Lesion Segmentation Prof. Shanthi Mahesh 1, Karthik Bharadwaj N 2, Suhas A Bhyratae 3, Karthik Raju V 4, Karthik M N 5 Department of ISE, Atria Institute of
A New Approach For an Improved Multiple Brain Lesion Segmentation Prof. Shanthi Mahesh 1, Karthik Bharadwaj N 2, Suhas A Bhyratae 3, Karthik Raju V 4, Karthik M N 5 Department of ISE, Atria Institute of
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment
 Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416)
 Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Fiber Geometry Muscle fibers are linked together by collagenous connective tissue. Endomysium surrounds individual fibers, perimysium collects bundles
Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Fiber Geometry Muscle fibers are linked together by collagenous connective tissue. Endomysium surrounds individual fibers, perimysium collects bundles
EXTRACTION OF RETINAL BLOOD VESSELS USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES
 EXTRACTION OF RETINAL BLOOD VESSELS USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES T.HARI BABU 1, Y.RATNA KUMAR 2 1 (PG Scholar, Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering, College of Engineering(A), Andhra
EXTRACTION OF RETINAL BLOOD VESSELS USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES T.HARI BABU 1, Y.RATNA KUMAR 2 1 (PG Scholar, Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering, College of Engineering(A), Andhra
Estimation of the Upper Limb Lifting Movement Under Varying Weight and Movement Speed
 1 Sungyoon Lee, 1 Jaesung Oh, 1 Youngwon Kim, 1 Minsuk Kwon * Jaehyo Kim 1 Department of mechanical & control engineering, Handong University, qlfhlxhl@nate.com * Department of mechanical & control engineering,
1 Sungyoon Lee, 1 Jaesung Oh, 1 Youngwon Kim, 1 Minsuk Kwon * Jaehyo Kim 1 Department of mechanical & control engineering, Handong University, qlfhlxhl@nate.com * Department of mechanical & control engineering,
Detection of Glaucoma and Diabetic Retinopathy from Fundus Images by Bloodvessel Segmentation
 International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 2249 8958, Volume-5, Issue-5, June 2016 Detection of Glaucoma and Diabetic Retinopathy from Fundus Images by Bloodvessel Segmentation
International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 2249 8958, Volume-5, Issue-5, June 2016 Detection of Glaucoma and Diabetic Retinopathy from Fundus Images by Bloodvessel Segmentation
THE EFFECT OF THE ACHILLES TENDON MOMENT ARM ON KNEE JOINT CONTACT FORCE. Ashley E. Warren. A Senior Honors Project Presented to the.
 THE EFFECT OF THE ACHILLES TENDON MOMENT ARM ON KNEE JOINT CONTACT FORCE by Ashley E. Warren A Senior Honors Project Presented to the Honors College East Carolina University In Partial Fulfillment of the
THE EFFECT OF THE ACHILLES TENDON MOMENT ARM ON KNEE JOINT CONTACT FORCE by Ashley E. Warren A Senior Honors Project Presented to the Honors College East Carolina University In Partial Fulfillment of the
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System
 Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 3) Nordin & Frankel (Ch 5), or Hall (Ch. 6) Muscle Properties Ø Irritability Ø Muscle has the capability of receiving
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 3) Nordin & Frankel (Ch 5), or Hall (Ch. 6) Muscle Properties Ø Irritability Ø Muscle has the capability of receiving
SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE
 of 4 SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE Li-Qun Zhang -4 and William Z. Rymer,2,4 Sensory Motor Performance Program, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago Departments of 2 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,
of 4 SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE Li-Qun Zhang -4 and William Z. Rymer,2,4 Sensory Motor Performance Program, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago Departments of 2 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,
Development of an ergonomic musculoskeletal model to estimate muscle forces during vertical jumping
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 13 (2011) 338 343 5 th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology (APCST) Development of an ergonomic musculoskeletal model to estimate muscle
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 13 (2011) 338 343 5 th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology (APCST) Development of an ergonomic musculoskeletal model to estimate muscle
Cancer Cells Detection using OTSU Threshold Algorithm
 Cancer Cells Detection using OTSU Threshold Algorithm Nalluri Sunny 1 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Mithinti Srikanth 2 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Kodali
Cancer Cells Detection using OTSU Threshold Algorithm Nalluri Sunny 1 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Mithinti Srikanth 2 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Kodali
EARLY STAGE DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER USING CT-SCAN IMAGES BASED ON CELLULAR LEARNING AUTOMATE
 EARLY STAGE DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER USING CT-SCAN IMAGES BASED ON CELLULAR LEARNING AUTOMATE SAKTHI NEELA.P.K Department of M.E (Medical electronics) Sengunthar College of engineering Namakkal, Tamilnadu,
EARLY STAGE DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER USING CT-SCAN IMAGES BASED ON CELLULAR LEARNING AUTOMATE SAKTHI NEELA.P.K Department of M.E (Medical electronics) Sengunthar College of engineering Namakkal, Tamilnadu,
FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals
 FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals Musfirah Abd Aziz and Nur Azah Hamzaid Abstract Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals Musfirah Abd Aziz and Nur Azah Hamzaid Abstract Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
Computer-Aided Quantitative Analysis of Liver using Ultrasound Images
 6 JEST-M, Vol 3, Issue 1, 2014 Computer-Aided Quantitative Analysis of Liver using Ultrasound Images Email: poojaanandram @gmail.com P.G. Student, Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering,
6 JEST-M, Vol 3, Issue 1, 2014 Computer-Aided Quantitative Analysis of Liver using Ultrasound Images Email: poojaanandram @gmail.com P.G. Student, Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering,
Bracing Effects of the Flexpine in Scoliosis Patients
 American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (ASRJETS) ISSN (Print) 2313-4410, ISSN (Online) 2313-4402 Global Society of Scientific Research and Researchers http://asrjetsjournal.org/
American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (ASRJETS) ISSN (Print) 2313-4410, ISSN (Online) 2313-4402 Global Society of Scientific Research and Researchers http://asrjetsjournal.org/
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail.
 This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Finni Juutinen, Taija; Peltonen, Jussi; Stenroth, Lauri;
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Finni Juutinen, Taija; Peltonen, Jussi; Stenroth, Lauri;
ANALYSIS AND DETECTION OF BRAIN TUMOUR USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES
 ANALYSIS AND DETECTION OF BRAIN TUMOUR USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES P.V.Rohini 1, Dr.M.Pushparani 2 1 M.Phil Scholar, Department of Computer Science, Mother Teresa women s university, (India) 2 Professor
ANALYSIS AND DETECTION OF BRAIN TUMOUR USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES P.V.Rohini 1, Dr.M.Pushparani 2 1 M.Phil Scholar, Department of Computer Science, Mother Teresa women s university, (India) 2 Professor
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory
 CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory 1 Basic Anatomy Key Concepts: 3.23-3.25 3.25 2 Force & Levers 1 st class» seesaw» muscles that extend neck R F AF
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory 1 Basic Anatomy Key Concepts: 3.23-3.25 3.25 2 Force & Levers 1 st class» seesaw» muscles that extend neck R F AF
Assessment of Reliability of Hamilton-Tompkins Algorithm to ECG Parameter Detection
 Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management Istanbul, Turkey, July 3 6, 2012 Assessment of Reliability of Hamilton-Tompkins Algorithm to ECG Parameter
Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management Istanbul, Turkey, July 3 6, 2012 Assessment of Reliability of Hamilton-Tompkins Algorithm to ECG Parameter
1 Introduction. Fig. 1 Examples of microaneurysms
 3rd International Conference on Multimedia Technology(ICMT 2013) Detection of Microaneurysms in Color Retinal Images Using Multi-orientation Sum of Matched Filter Qin Li, Ruixiang Lu, Shaoguang Miao, Jane
3rd International Conference on Multimedia Technology(ICMT 2013) Detection of Microaneurysms in Color Retinal Images Using Multi-orientation Sum of Matched Filter Qin Li, Ruixiang Lu, Shaoguang Miao, Jane
performance in young jumpers
 BIOLOGY OF EXERCISE VOLUME 5.2, 2009 Isokinetic muscle strength and running long jump performance in young jumpers D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2009.0030 YIANNIS KOUTSIORAS, ATHANASIOS TSIOKANOS, DIMITRIOS
BIOLOGY OF EXERCISE VOLUME 5.2, 2009 Isokinetic muscle strength and running long jump performance in young jumpers D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2009.0030 YIANNIS KOUTSIORAS, ATHANASIOS TSIOKANOS, DIMITRIOS
ROI DETECTION AND VESSEL SEGMENTATION IN RETINAL IMAGE
 ROI DETECTION AND VESSEL SEGMENTATION IN RETINAL IMAGE F. Sabaz a, *, U. Atila a a Karabuk University, Dept. of Computer Engineering, 78050, Karabuk, Turkey - (furkansabaz, umitatila)@karabuk.edu.tr KEY
ROI DETECTION AND VESSEL SEGMENTATION IN RETINAL IMAGE F. Sabaz a, *, U. Atila a a Karabuk University, Dept. of Computer Engineering, 78050, Karabuk, Turkey - (furkansabaz, umitatila)@karabuk.edu.tr KEY
Automatic Hemorrhage Classification System Based On Svm Classifier
 Automatic Hemorrhage Classification System Based On Svm Classifier Abstract - Brain hemorrhage is a bleeding in or around the brain which are caused by head trauma, high blood pressure and intracranial
Automatic Hemorrhage Classification System Based On Svm Classifier Abstract - Brain hemorrhage is a bleeding in or around the brain which are caused by head trauma, high blood pressure and intracranial
Analysis of EMG Signal to Evaluate Muscle Strength and Classification
 Analysis of EMG Signal to Evaluate Muscle Strength and Classification Kiran K. 1, Uma Rani K. 2 1MTech Student, Biomedical Signal Processing and Instrumentation, Dept. of IT, SJCE, Mysuru, Karnataka, India
Analysis of EMG Signal to Evaluate Muscle Strength and Classification Kiran K. 1, Uma Rani K. 2 1MTech Student, Biomedical Signal Processing and Instrumentation, Dept. of IT, SJCE, Mysuru, Karnataka, India
Extraction of Blood Vessels and Recognition of Bifurcation Points in Retinal Fundus Image
 International Journal of Research Studies in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 1, Issue 5, August 2014, PP 1-7 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) Extraction of Blood Vessels and
International Journal of Research Studies in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 1, Issue 5, August 2014, PP 1-7 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) Extraction of Blood Vessels and
Comparison of the Achilles tendon moment arms determined using the tendon excursion and threedimensional
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiological Reports ISSN 2051-817X Comparison of the Achilles tendon moment arms determined using the tendon excursion and threedimensional methods Satoru Hashizume 1,2,3, Atsuki Fukutani
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiological Reports ISSN 2051-817X Comparison of the Achilles tendon moment arms determined using the tendon excursion and threedimensional methods Satoru Hashizume 1,2,3, Atsuki Fukutani
SINGLE- AND TWO-JOINT MOVEMENTS IN HUMANS
 SINGLE- AND TWO-JOINT MOVEMENTS IN HUMANS BASIC PRINCIPLES OF THE MOVEMENT ANALYSIS METHODS OF THE MOVEMENT ANALYSIS EMGs are recorded by pairs of the surface electrodes with center to center distance
SINGLE- AND TWO-JOINT MOVEMENTS IN HUMANS BASIC PRINCIPLES OF THE MOVEMENT ANALYSIS METHODS OF THE MOVEMENT ANALYSIS EMGs are recorded by pairs of the surface electrodes with center to center distance
MRI Image Processing Operations for Brain Tumor Detection
 MRI Image Processing Operations for Brain Tumor Detection Prof. M.M. Bulhe 1, Shubhashini Pathak 2, Karan Parekh 3, Abhishek Jha 4 1Assistant Professor, Dept. of Electronics and Telecommunications Engineering,
MRI Image Processing Operations for Brain Tumor Detection Prof. M.M. Bulhe 1, Shubhashini Pathak 2, Karan Parekh 3, Abhishek Jha 4 1Assistant Professor, Dept. of Electronics and Telecommunications Engineering,
Semi-automatic Thyroid Area Measurement Based on Ultrasound Image
 Semi-automatic Thyroid Area Measurement Based on Ultrasound Image Eko Supriyanto, Nik M Arif, Akmal Hayati Rusli, Nasrul Humaimi Advanced Diagnostics and Progressive Human Care Research Group Research
Semi-automatic Thyroid Area Measurement Based on Ultrasound Image Eko Supriyanto, Nik M Arif, Akmal Hayati Rusli, Nasrul Humaimi Advanced Diagnostics and Progressive Human Care Research Group Research
On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding
 Title On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding Author(s) Guo, Y; Lee, W Citation The 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS 2014), Chicago, IL.,
Title On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding Author(s) Guo, Y; Lee, W Citation The 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS 2014), Chicago, IL.,
The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011
 DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
A new Method on Brain MRI Image Preprocessing for Tumor Detection
 2015 IJSRSET Volume 1 Issue 1 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology A new Method on Brain MRI Preprocessing for Tumor Detection ABSTRACT D. Arun Kumar
2015 IJSRSET Volume 1 Issue 1 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology A new Method on Brain MRI Preprocessing for Tumor Detection ABSTRACT D. Arun Kumar
Architectural and functional features of human triceps surae muscles during contraction
 Architectural and functional features of human triceps surae muscles during contraction YASUO KAWAKAMI, YOSHIHO ICHINOSE, AND TETSUO FUKUNAGA Department of Life Sciences (Sports Sciences), The University
Architectural and functional features of human triceps surae muscles during contraction YASUO KAWAKAMI, YOSHIHO ICHINOSE, AND TETSUO FUKUNAGA Department of Life Sciences (Sports Sciences), The University
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System
 Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 3) Nordin & Frankel (Ch 5), or Hall (Ch. 6) Muscle Properties 1 Muscle Properties (cont.) Functions of Muscle Produce
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 3) Nordin & Frankel (Ch 5), or Hall (Ch. 6) Muscle Properties 1 Muscle Properties (cont.) Functions of Muscle Produce
ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function. Skeletal muscles act on bones to produce movement of the limb and to move (lift and carry) objects.
 ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function The primary function of a skeletal muscle is to generate forces, by contracting; these forces allow us to move through and interact with our environment Skeletal
ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function The primary function of a skeletal muscle is to generate forces, by contracting; these forces allow us to move through and interact with our environment Skeletal
Skeletal Muscles and Functions
 Skeletal Muscles and Functions Huei-Ming Chai, PT, Ph.D. School of Physical Therapy National Taiwan University Classification of Muscles striated muscles skeletal muscles: voluntary contraction cardiac
Skeletal Muscles and Functions Huei-Ming Chai, PT, Ph.D. School of Physical Therapy National Taiwan University Classification of Muscles striated muscles skeletal muscles: voluntary contraction cardiac
Influence of Inward Pressure Applied by the Transducer on Trunk Muscle Thickness during Ultrasound Imaging
 Kawasaki Journal of Medical Welfare Vol. 19, No. 2, 2014 32-37 Original Paper Influence of Inward Pressure Applied by the Transducer on Trunk Muscle Thickness during Ultrasound Imaging Hiroshi ISHIDA *
Kawasaki Journal of Medical Welfare Vol. 19, No. 2, 2014 32-37 Original Paper Influence of Inward Pressure Applied by the Transducer on Trunk Muscle Thickness during Ultrasound Imaging Hiroshi ISHIDA *
Tight sportswear and physiological function
 The Research Journal of the Costume Culture pissn: 6- eissn: 66- Vol., No. pp.66~6, August http://dx.doi.org/.77/rjcc...66 Tight sportswear and physiological function - Effect on muscle strength and EMG
The Research Journal of the Costume Culture pissn: 6- eissn: 66- Vol., No. pp.66~6, August http://dx.doi.org/.77/rjcc...66 Tight sportswear and physiological function - Effect on muscle strength and EMG
EMG-Driven Human Model for Orthosis Control
 EMG-Driven Human Model for Orthosis Control Christian Fleischer, Günter Hommel Institute for Computer Engineering and Microelectronics Berlin University of Technology, Germany {fleischer, hommel}@cs.tu-berlin.de
EMG-Driven Human Model for Orthosis Control Christian Fleischer, Günter Hommel Institute for Computer Engineering and Microelectronics Berlin University of Technology, Germany {fleischer, hommel}@cs.tu-berlin.de
D.O.I: GEORGIOS DASTERIDIS, THEOPHILOS PILIANIDIS, NIKOLAOS MANTZOURANIS, NIKOLAOS AGGELOUSIS
 BIOLOGY OF EXERCISE VOLUME 8.1, 2012 The effects of athletics training on isometric strength and EMG activity in adolescent athletes D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2012.0053 GEORGIOS DASTERIDIS, THEOPHILOS
BIOLOGY OF EXERCISE VOLUME 8.1, 2012 The effects of athletics training on isometric strength and EMG activity in adolescent athletes D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2012.0053 GEORGIOS DASTERIDIS, THEOPHILOS
The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database
 Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
South Asian Journal of Engineering and Technology Vol.3, No.9 (2017) 17 22
 South Asian Journal of Engineering and Technology Vol.3, No.9 (07) 7 Detection of malignant and benign Tumors by ANN Classification Method K. Gandhimathi, Abirami.K, Nandhini.B Idhaya Engineering College
South Asian Journal of Engineering and Technology Vol.3, No.9 (07) 7 Detection of malignant and benign Tumors by ANN Classification Method K. Gandhimathi, Abirami.K, Nandhini.B Idhaya Engineering College
Technological development for applying MR Elastography to shoulder muscles
 Technological development for applying MR Elastography to shoulder muscles Poster No.: C-1003 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Ito 1, T. Numano 1, T. Onishi 1, K. Mizuhara 1, K.
Technological development for applying MR Elastography to shoulder muscles Poster No.: C-1003 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Ito 1, T. Numano 1, T. Onishi 1, K. Mizuhara 1, K.
Routine Quality Assurance Cookbook
 This Cookbook is a companion guide to the AIUM Routine Quality Assurance (QA) for Diagnostic Ultrasound Equipment document, which outlines the basic QA requirements for AIUM-accredited practices. The Guide
This Cookbook is a companion guide to the AIUM Routine Quality Assurance (QA) for Diagnostic Ultrasound Equipment document, which outlines the basic QA requirements for AIUM-accredited practices. The Guide
Improved Intelligent Classification Technique Based On Support Vector Machines
 Improved Intelligent Classification Technique Based On Support Vector Machines V.Vani Asst.Professor,Department of Computer Science,JJ College of Arts and Science,Pudukkottai. Abstract:An abnormal growth
Improved Intelligent Classification Technique Based On Support Vector Machines V.Vani Asst.Professor,Department of Computer Science,JJ College of Arts and Science,Pudukkottai. Abstract:An abnormal growth
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 593.2 (2015) pp 441 455 441 Changes in the length and three-dimensional orientation of muscle fascicles and aponeuroses with passive length changes in human gastrocnemius muscles R. D. Herbert
J Physiol 593.2 (2015) pp 441 455 441 Changes in the length and three-dimensional orientation of muscle fascicles and aponeuroses with passive length changes in human gastrocnemius muscles R. D. Herbert
COMPARATIVE STUDY ON FEATURE EXTRACTION METHOD FOR BREAST CANCER CLASSIFICATION
 COMPARATIVE STUDY ON FEATURE EXTRACTION METHOD FOR BREAST CANCER CLASSIFICATION 1 R.NITHYA, 2 B.SANTHI 1 Asstt Prof., School of Computing, SASTRA University, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu, India-613402 2 Prof.,
COMPARATIVE STUDY ON FEATURE EXTRACTION METHOD FOR BREAST CANCER CLASSIFICATION 1 R.NITHYA, 2 B.SANTHI 1 Asstt Prof., School of Computing, SASTRA University, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu, India-613402 2 Prof.,
Design of Palm Acupuncture Points Indicator
 Design of Palm Acupuncture Points Indicator Wen-Yuan Chen, Shih-Yen Huang and Jian-Shie Lin Abstract The acupuncture points are given acupuncture or acupressure so to stimulate the meridians on each corresponding
Design of Palm Acupuncture Points Indicator Wen-Yuan Chen, Shih-Yen Huang and Jian-Shie Lin Abstract The acupuncture points are given acupuncture or acupressure so to stimulate the meridians on each corresponding
Research on a Transmit-Receive Method of Ultrasonic Array for Planar Defects
 7 th Asia-Pacific Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring November 12-15, 2018 Hong Kong SAR, P.R. China Research on a Transmit-Receive Method of Ultrasonic Array for Planar Defects Zhenggan Zhou 1,2,3
7 th Asia-Pacific Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring November 12-15, 2018 Hong Kong SAR, P.R. China Research on a Transmit-Receive Method of Ultrasonic Array for Planar Defects Zhenggan Zhou 1,2,3
Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function
 Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function Unit 2: Chapter 5 Part A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about skeletal muscle is true: A) Skeletal muscles are usually linked
Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function Unit 2: Chapter 5 Part A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about skeletal muscle is true: A) Skeletal muscles are usually linked
The Human Machine: Biomechanics in Daily Life.
 The Human Machine: Biomechanics in Daily Life www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Biomechanics The study or application of mechanics to biological systems. The study of the forces that act on the body and their
The Human Machine: Biomechanics in Daily Life www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Biomechanics The study or application of mechanics to biological systems. The study of the forces that act on the body and their
Clinically Available Optical Topography System
 Clinically Available Optical Topography System Clinically Available Optical Topography System 18 Fumio Kawaguchi Noriyoshi Ichikawa Noriyuki Fujiwara Yûichi Yamashita Shingo Kawasaki OVERVIEW: Progress
Clinically Available Optical Topography System Clinically Available Optical Topography System 18 Fumio Kawaguchi Noriyoshi Ichikawa Noriyuki Fujiwara Yûichi Yamashita Shingo Kawasaki OVERVIEW: Progress
Novel single trial movement classification based on temporal dynamics of EEG
 Novel single trial movement classification based on temporal dynamics of EEG Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Wairagkar, M., Daly, I., Hayashi, Y. and Nasuto, S. (2014) Novel single trial movement
Novel single trial movement classification based on temporal dynamics of EEG Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Wairagkar, M., Daly, I., Hayashi, Y. and Nasuto, S. (2014) Novel single trial movement
International Journal of Research (IJR) Vol-1, Issue-6, July 2014 ISSN
 Developing an Approach to Brain MRI Image Preprocessing for Tumor Detection Mr. B.Venkateswara Reddy 1, Dr. P. Bhaskara Reddy 2, Dr P. Satish Kumar 3, Dr. S. Siva Reddy 4 1. Associate Professor, ECE Dept,
Developing an Approach to Brain MRI Image Preprocessing for Tumor Detection Mr. B.Venkateswara Reddy 1, Dr. P. Bhaskara Reddy 2, Dr P. Satish Kumar 3, Dr. S. Siva Reddy 4 1. Associate Professor, ECE Dept,
Gabor Wavelet Approach for Automatic Brain Tumor Detection
 Gabor Wavelet Approach for Automatic Brain Tumor Detection Akshay M. Malviya 1, Prof. Atul S. Joshi 2 1 M.E. Student, 2 Associate Professor, Department of Electronics and Tele-communication, Sipna college
Gabor Wavelet Approach for Automatic Brain Tumor Detection Akshay M. Malviya 1, Prof. Atul S. Joshi 2 1 M.E. Student, 2 Associate Professor, Department of Electronics and Tele-communication, Sipna college
Automated Detection of Vascular Abnormalities in Diabetic Retinopathy using Morphological Entropic Thresholding with Preprocessing Median Fitter
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 3 September 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-784X Automated Detection of Vascular Abnormalities in Diabetic Retinopathy using Morphological
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 3 September 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-784X Automated Detection of Vascular Abnormalities in Diabetic Retinopathy using Morphological
TWO HANDED SIGN LANGUAGE RECOGNITION SYSTEM USING IMAGE PROCESSING
 134 TWO HANDED SIGN LANGUAGE RECOGNITION SYSTEM USING IMAGE PROCESSING H.F.S.M.Fonseka 1, J.T.Jonathan 2, P.Sabeshan 3 and M.B.Dissanayaka 4 1 Department of Electrical And Electronic Engineering, Faculty
134 TWO HANDED SIGN LANGUAGE RECOGNITION SYSTEM USING IMAGE PROCESSING H.F.S.M.Fonseka 1, J.T.Jonathan 2, P.Sabeshan 3 and M.B.Dissanayaka 4 1 Department of Electrical And Electronic Engineering, Faculty
Erigo User Script 1. Erigo Background Information. 2. Intended use and indications
 Erigo User Script 1. Erigo Background Information The Erigo was developed in collaboration with the Spinal Cord Injury Center at the Balgrist University Hospital in Zurich, Switzerland and the Orthopaedic
Erigo User Script 1. Erigo Background Information The Erigo was developed in collaboration with the Spinal Cord Injury Center at the Balgrist University Hospital in Zurich, Switzerland and the Orthopaedic
The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle
 AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation Day 03B The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session the delegate would have understood
AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation Day 03B The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session the delegate would have understood
발목관절의각도가무릎관절폄근의근활성도에미치는영향
 1) 발목관절의각도가무릎관절폄근의근활성도에미치는영향 1 The Effects of Ankle Joint Angle on Knee Extensor Electromyographic Activity Sang-seok Yeo PT Jung-won Kwon PT Chung-sun Kim PT PhD 1 Department of Physical Therapy Graduate
1) 발목관절의각도가무릎관절폄근의근활성도에미치는영향 1 The Effects of Ankle Joint Angle on Knee Extensor Electromyographic Activity Sang-seok Yeo PT Jung-won Kwon PT Chung-sun Kim PT PhD 1 Department of Physical Therapy Graduate
The role of ultrasound in the early assessment of sarcopenia Stany Perkisas, MD EUGMS, Nice, 21/09/2017
 The role of ultrasound in the early assessment of sarcopenia Stany Perkisas, MD EUGMS, Nice, 21/09/2017 Disclosure I have nothing to disclose. There are no relevant financial relations interfering with
The role of ultrasound in the early assessment of sarcopenia Stany Perkisas, MD EUGMS, Nice, 21/09/2017 Disclosure I have nothing to disclose. There are no relevant financial relations interfering with
QUANTIFICATION OF PROGRESSION OF RETINAL NERVE FIBER LAYER ATROPHY IN FUNDUS PHOTOGRAPH
 QUANTIFICATION OF PROGRESSION OF RETINAL NERVE FIBER LAYER ATROPHY IN FUNDUS PHOTOGRAPH Hyoun-Joong Kong *, Jong-Mo Seo **, Seung-Yeop Lee *, Hum Chung **, Dong Myung Kim **, Jeong Min Hwang **, Kwang
QUANTIFICATION OF PROGRESSION OF RETINAL NERVE FIBER LAYER ATROPHY IN FUNDUS PHOTOGRAPH Hyoun-Joong Kong *, Jong-Mo Seo **, Seung-Yeop Lee *, Hum Chung **, Dong Myung Kim **, Jeong Min Hwang **, Kwang
Automated Assessment of Diabetic Retinal Image Quality Based on Blood Vessel Detection
 Y.-H. Wen, A. Bainbridge-Smith, A. B. Morris, Automated Assessment of Diabetic Retinal Image Quality Based on Blood Vessel Detection, Proceedings of Image and Vision Computing New Zealand 2007, pp. 132
Y.-H. Wen, A. Bainbridge-Smith, A. B. Morris, Automated Assessment of Diabetic Retinal Image Quality Based on Blood Vessel Detection, Proceedings of Image and Vision Computing New Zealand 2007, pp. 132
MUSCLE BEHAVIOR IN ARTIFICIALLY ACTIVATED MUSCLE - MEASUREMENTS ON NEUROLOGICALLY INTACT AND PARAPLEGIC SUBJECTS METHODS
 MUSCLE BEHAVIOR IN ARTIFICIALLY ACTIVATED MUSCLE - MEASUREMENTS ON NEUROLOGICALLY INTACT AND PARAPLEGIC SUBJECTS Margit Gföhler, Johann Wassermann 2, Prisca Eser 3, Tanja Kakebeeke 3, Helga E. Lechner
MUSCLE BEHAVIOR IN ARTIFICIALLY ACTIVATED MUSCLE - MEASUREMENTS ON NEUROLOGICALLY INTACT AND PARAPLEGIC SUBJECTS Margit Gföhler, Johann Wassermann 2, Prisca Eser 3, Tanja Kakebeeke 3, Helga E. Lechner
Automatic Definition of Planning Target Volume in Computer-Assisted Radiotherapy
 Automatic Definition of Planning Target Volume in Computer-Assisted Radiotherapy Angelo Zizzari Department of Cybernetics, School of Systems Engineering The University of Reading, Whiteknights, PO Box
Automatic Definition of Planning Target Volume in Computer-Assisted Radiotherapy Angelo Zizzari Department of Cybernetics, School of Systems Engineering The University of Reading, Whiteknights, PO Box
A quality control program for MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 3, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2002 A quality control program for MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy Tao Wu* and Joel P. Felmlee Department of Radiology,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 3, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2002 A quality control program for MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy Tao Wu* and Joel P. Felmlee Department of Radiology,
Coast Campus, Queensland, 4222, Australia Version of record first published: 22 Mar 2013.
 This article was downloaded by: [Griffith University] On: 24 March 2013, At: 14:28 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
This article was downloaded by: [Griffith University] On: 24 March 2013, At: 14:28 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
Application of Phased Array Radar Theory to Ultrasonic Linear Array Medical Imaging System
 Application of Phased Array Radar Theory to Ultrasonic Linear Array Medical Imaging System R. K. Saha, S. Karmakar, S. Saha, M. Roy, S. Sarkar and S.K. Sen Microelectronics Division, Saha Institute of
Application of Phased Array Radar Theory to Ultrasonic Linear Array Medical Imaging System R. K. Saha, S. Karmakar, S. Saha, M. Roy, S. Sarkar and S.K. Sen Microelectronics Division, Saha Institute of
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion
 Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
EMG Signals for Co-Activations of Major Lower Limb Muscles in Knee Joint Dynamics
 Biomedical Science and Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 1, 9-14 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/bse/3/1/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/bse-3-1-3 EMG Signals for Co-Activations
Biomedical Science and Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 1, 9-14 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/bse/3/1/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/bse-3-1-3 EMG Signals for Co-Activations
Chapter 6. Results. 6.1 Introduction
 Chapter 6 Results 6.1 Introduction This chapter presents results of both optimization and characterization approaches. In the optimization case, we report results of an experimental study done with persons.
Chapter 6 Results 6.1 Introduction This chapter presents results of both optimization and characterization approaches. In the optimization case, we report results of an experimental study done with persons.
Comparison of N-K Table Offset Angles with the Human Knee Flexor Torque Curve
 Comparison of N-K Table Offset Angles with the Human Knee Flexor Torque Curve By: Daniel J. LaPlaca *, Douglas R. Keskula, Kristinn I. Heinrichs, and David H. Perrin LaPlaca, D.J., Keskula, D., Heinrichs,
Comparison of N-K Table Offset Angles with the Human Knee Flexor Torque Curve By: Daniel J. LaPlaca *, Douglas R. Keskula, Kristinn I. Heinrichs, and David H. Perrin LaPlaca, D.J., Keskula, D., Heinrichs,
ECG Beat Recognition using Principal Components Analysis and Artificial Neural Network
 International Journal of Electronics Engineering, 3 (1), 2011, pp. 55 58 ECG Beat Recognition using Principal Components Analysis and Artificial Neural Network Amitabh Sharma 1, and Tanushree Sharma 2
International Journal of Electronics Engineering, 3 (1), 2011, pp. 55 58 ECG Beat Recognition using Principal Components Analysis and Artificial Neural Network Amitabh Sharma 1, and Tanushree Sharma 2
Muscle architecture and optimum angle of the knee flexors and extensors: A comparison between cyclists and Australian Rules Football players
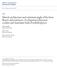 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Pre. 2011 2010 Muscle architecture and optimum angle of the knee flexors and extensors: A comparison between cyclists and Australian Rules Football
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Pre. 2011 2010 Muscle architecture and optimum angle of the knee flexors and extensors: A comparison between cyclists and Australian Rules Football
(which was not peer-reviewed) is the author/funder, who has granted biorxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity.
 Title: Functional Deficits are Explained by Plantarflexor Remodeling Following Achilles Tendon Rupture Repair: Preliminary Findings Authors: Josh R. Baxter, PhD 1, Todd J. Hullfish, BSME 1, and Wen Chao,
Title: Functional Deficits are Explained by Plantarflexor Remodeling Following Achilles Tendon Rupture Repair: Preliminary Findings Authors: Josh R. Baxter, PhD 1, Todd J. Hullfish, BSME 1, and Wen Chao,
Concurrent deficits of soleus and gastrocnemius muscle fascicles and Achilles tendon post stroke
 J Appl Physiol 118: 863 871, 2015. First published February 6, 2015; doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00226.2014. Concurrent deficits of soleus and gastrocnemius muscle fascicles and Achilles tendon post stroke
J Appl Physiol 118: 863 871, 2015. First published February 6, 2015; doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00226.2014. Concurrent deficits of soleus and gastrocnemius muscle fascicles and Achilles tendon post stroke
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
In che modo le griglie bidimensionali di elettrodi ci aiutano nell interpretazione del segnale EMG di superficie?
 Nuove evidenze per l'acquisizione ed interpretazione del segnale EMG: dal bipolare al multicanale e ritorno In che modo le griglie bidimensionali di elettrodi ci aiutano nell interpretazione del segnale
Nuove evidenze per l'acquisizione ed interpretazione del segnale EMG: dal bipolare al multicanale e ritorno In che modo le griglie bidimensionali di elettrodi ci aiutano nell interpretazione del segnale
Research Article Parkinsonian Rigidity Shows Variable Properties Depending on the Elbow Joint Angle
 Parkinson s Disease Volume, Article ID 587, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55//587 Research Article Parkinsonian Rigidity Shows Variable Properties Depending on the Elbow Joint Angle Takuyuki Endo, Toshimitsu
Parkinson s Disease Volume, Article ID 587, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55//587 Research Article Parkinsonian Rigidity Shows Variable Properties Depending on the Elbow Joint Angle Takuyuki Endo, Toshimitsu
Advertisement Evaluation Based On Visual Attention Mechanism
 2nd International Conference on Economics, Management Engineering and Education Technology (ICEMEET 2016) Advertisement Evaluation Based On Visual Attention Mechanism Yu Xiao1, 2, Peng Gan1, 2, Yuling
2nd International Conference on Economics, Management Engineering and Education Technology (ICEMEET 2016) Advertisement Evaluation Based On Visual Attention Mechanism Yu Xiao1, 2, Peng Gan1, 2, Yuling
