Section 1 1 What Is Science? (pages 3 7)
|
|
|
- Marilynn Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Section 1 1 What Is Science? (pages 3 7) This section explains what the goal of science is and describes a scientific view of the world. What Science Is and Is Not (page 3) 1. What is the goal of science? The goal of science is to investigate and understand nature, to explain events in nature, and to use those explanations to make useful predictions. 2. What is science? Science is an organized way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Thinking Like a Scientist (page 4) 3. What is observation? Observation is the process of gathering information about events or processes in a careful, orderly way. 4. The information gathered from observation is called data. 5. Complete the table about types of data. TYPES OF DATA Type Data Involves... Example Quantitative Numbers The manatee has one scar on its back. Qualitative Characteristics that cannot be The scar appears old. easily measured or counted 6. What is an inference? experience. An inference is a logical interpretation based on prior knowledge and Explaining and Interpreting Evidence (page 5) 7. What is a hypothesis? A hypothesis is a proposed scientific explanation for a set of observations.
2 Name Class Date 8. In science, a hypothesis is useful only if it can be tested. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? A hypothesis should be stated in such a way that it can never be proved wrong. false 10. What are three ways from which hypotheses may arise? a. From prior knowledge b. From logical inferences c. From informed, creative imagination 11. Circle the letter of each of the following that may be an outcome of testing a hypothesis. a. The hypothesis is partly true but needs to be revised. b. The hypothesis is wrong. c. The hypothesis is supported. d. The hypothesis is of no value. Science as a Way of Knowing (page 6) 12. What do scientists assume about the universe? They assume that the universe is a system in which basic natural laws apply. 13. What are some qualities that are desirable in a scientist? skepticism, and a recognition that science has limits. Qualities include openness, Science and Human Values (page 7) 14. Is the following sentence true or false? A community must use its shared values to make decisions about scientific issues. true
3 Section 1 2 How Scientists Work (pages 8 15) This section explains how scientists test hypotheses. It also describes how a scientific theory develops. Designing an Experiment (pages 8 10) 1. The idea that life can arise from nonliving matter is called spontaneous generation. 2. What was Francesco Redi s hypothesis about the appearance of maggots? Flies produce maggots. 3. What are variables in an experiment? They are factors that can change. 4. Ideally, how many variables should an experiment test at a time? It should test only one variable at a time. 5. When a variable is kept unchanged in an experiment, it is said to be controlled. 6. What is a controlled experiment? A controlled experiment is an experiment in which one variable is changed while the other variables are controlled. 7. The illustration below shows the beginning of Redi s experiment. Complete the illustration by showing the outcome. Redi s Experiment on Spontaneous Generation Uncovered jars Covered jars Several days pass. Maggots appear No maggots appear
4 Name Class Date 8. Complete the table about variables. VARIABLES Type of Variable Definition Manipulated variable The variable that is deliberately changed in an experiment Responding variable The variable that is observed and changes in response to the manipulated variable 9. In Redi s experiment, what were the manipulated variable and the responding variable? The manipulated variable was the presence or absence of the gauze covering, and the responding variable was whether maggots appear. 10. For what do scientists use the data from a controlled experiment? the hypothesis and draw a conclusion. They use it to evaluate 11. When scientists look for explanations for specific observations, what do they assume about nature? They assume that the patterns in nature are consistent. Publishing and Repeating Investigations (pages 10 13) 12. Why do scientists assume that experimental results can be reproduced? A key assumption in science is that nature behaves in a consistent manner. 13. What did Anton van Leeuwenhoek discover? in rainwater, pond water, and dust that he called animalcules. He discovered a world of tiny moving objects 14. What did John Needham conclude from his test of Redi s findings? little animals in a bottle of gravy could only have come from the juice of the gravy. He concluded that the 15. What did Spallanzani do to improve upon Redi s and Needham s work? He boiled two containers of gravy, assuming that the boiling would kill any microorganisms that were present. 16. How did Pasteur settle the spontaneous generation argument? He designed a special flask that showed as long as broth was protected from microorganisms, it remained free of living things.
5 When Experiments Are Not Possible (page 14) 17. In animal field studies, why do scientists usually try to work without making the animals aware that humans are present? To learn how animals in the wild interact, it is necessary to observe the animals without disturbing them. 18. When a controlled experiment is not possible, why do scientists try to identify as many relevant variables as possible? They identify as many as possible so that most variables are controlled. How a Theory Develops (pages 14 15) 19. The theory that new organisms come from existing organisms is called biogenesis. 20. In science, what is a theory? A theory is a well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations. 21. Is the following sentence true or false? A theory may be revised or replaced by a more useful explanation. true Reading Skill Practice A flowchart can help you remember the order in which a set of events has occurred or should occur. On a separate sheet of paper, create a flowchart that represents the process that Redi carried out in his investigation of spontaneous generation. This process is explained under the heading Designing an Experiment on pages For more information about flowcharts, see Organizing Information in Appendix A of your textbook. Students flowcharts should begin with Redi s proposal of a hypothesis and end with his drawing a conclusion about how maggots are produced.
6 Name Class Date Section 1 3 Studying Life (pages 16 22) This section describes the characteristics of living things. It also explains how life can be studied at different levels. Introduction (page 16) 1. What is biology? Biology is the science that seeks to understand the living world. Characteristics of Living Things (pages 16 20) 2. What is a cell? A cell is a collection of living matter enclosed by a barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings. 3. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about cells. a. A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive. b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. What are two types of asexual reproduction? a. A single-celled organism divides in half to form two new organisms. b. A portion of an organism splits off to form a new organism. 5. Living things are based on a universal genetic code. 6. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about living things. a. The life cycle of many organisms involves development. b. For bacteria, growth is mostly a simple increase in size. c. Each type of organism has a distinctive life cycle. d. Cells may change in number but never differentiate. 7. Why does an organism need energy and a constant supply of materials? An organism uses energy and materials to grow, develop, and reproduce. 8. What is metabolism? It is the combination of reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down materials as it carries out its life processes.
7 9. Is the following sentence true or false? All organisms respond to the environment in exactly the same ways. false 10. What is homeostasis? It is the process by which organisms keep their internal conditions fairly constant. 11. A group of organisms that changes over time is said to evolve. Branches of Biology (pages 20 21) Match the different kinds of biologists with the focus of their study. Kinds of Biologists Focus of Study c 12. Zoologist a. Plants a 13. Botanist b. Ancient life b 14. Paleontologist c. Animals 15. Label each of the illustrations below according to the level of study represented. Population Biosphere Cells 16. The largest level of biological study is the biosphere. Biology in Everyday Life (page 22) 17. What kinds of information can the study of biology provide about matters affecting human society? Biology helps you understand all forms of life and helps you understand what affects the quality of your life.
Chapter 1. The Science of Biology. h+p://www.bozemanscience.com/biology
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology h+p://www.bozemanscience.com/biology Section 1: What is Science? The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology h+p://www.bozemanscience.com/biology Section 1: What is Science? The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural
The Science of Biology. Honors Biology I
 The Science of Biology Honors Biology I 1-1 What is Science? Science an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural world Deals only with the natural world Collect and organized
The Science of Biology Honors Biology I 1-1 What is Science? Science an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural world Deals only with the natural world Collect and organized
Designing a Controlled Experiment
 Designing a Controlled Experiment -The independent variable is real vs. artificial trees. The dependent variable is vine growth. -Do vines grow better on real trees? -If vines grow better on real trees,
Designing a Controlled Experiment -The independent variable is real vs. artificial trees. The dependent variable is vine growth. -Do vines grow better on real trees? -If vines grow better on real trees,
5. Living things contain genetic information in the form of DNA and RNA Universal genetic code 6. Living things pass on heritable information to their
 Biology BIOLOGY 102 Lecture 1: Introduction to Biology Scientific study of life From Greek Bios life Logia study of 1. All living things are made of one or more cells 2. Living things carry out metabolism
Biology BIOLOGY 102 Lecture 1: Introduction to Biology Scientific study of life From Greek Bios life Logia study of 1. All living things are made of one or more cells 2. Living things carry out metabolism
Questions. Scientific Inquiry. Why? Model 1 Scientific Inquiry. Observe. Communicate with the wider community. Define the problem
 Why? Scientific Inquiry What do scientists do? Science is a unique way of learning about the natural world. Scientists work hard to explain events, living organisms, and changes we see around us every
Why? Scientific Inquiry What do scientists do? Science is a unique way of learning about the natural world. Scientists work hard to explain events, living organisms, and changes we see around us every
Aim #3: How can we use the scientific method to understand the world around us? Textbook Pgs: I. What is the Scientific Method?
 Name: Date: Aim #3: How can we use the scientific method to understand the world around us? Textbook Pgs: 6-13 I. What is the Scientific Method? 1. The scientific method begins with Scientific Inquiry
Name: Date: Aim #3: How can we use the scientific method to understand the world around us? Textbook Pgs: 6-13 I. What is the Scientific Method? 1. The scientific method begins with Scientific Inquiry
SCIENTIFIC METHOD. Observations: The act of gathering information about a system using one or more of the five senses (sight, sound, touch, etc.
 Observations: The act of gathering information about a system using one or more of the five senses (sight, sound, touch, etc.) Inference: A conclusion based on previous observations Hypothesis: A prediction
Observations: The act of gathering information about a system using one or more of the five senses (sight, sound, touch, etc.) Inference: A conclusion based on previous observations Hypothesis: A prediction
What Is Science? Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 1.1 What Is Science?
 Lesson Overview 1.1 What Science Is and Is Not What are the goals of science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
Lesson Overview 1.1 What Science Is and Is Not What are the goals of science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
Section 1.1: What is Science? Section 1.2: Science in Context Section 1.3: Studying Life
 Section 1.1: What is Science? Section 1.2: Science in Context Section 1.3: Studying Life 1.1 What science is and is not Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural
Section 1.1: What is Science? Section 1.2: Science in Context Section 1.3: Studying Life 1.1 What science is and is not Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural
One ancient evening, lost in the mists of time, someone
 1 1 What Is Science? One ancient evening, lost in the mists of time, someone looked into the sky and wondered for the first time: What are those lights? Where did plants and animals come from? How did
1 1 What Is Science? One ancient evening, lost in the mists of time, someone looked into the sky and wondered for the first time: What are those lights? Where did plants and animals come from? How did
THE SCIENTIFIC WORLD VIEW
 THE SCIENTIFIC WORLD VIEW 1. The Universe Is Understandable. 2. The Universe Is a Vast Single System In Which the Basic Rules Are Everywhere the Same. 3. Scientific Ideas Are Subject To Change. 4. Scientific
THE SCIENTIFIC WORLD VIEW 1. The Universe Is Understandable. 2. The Universe Is a Vast Single System In Which the Basic Rules Are Everywhere the Same. 3. Scientific Ideas Are Subject To Change. 4. Scientific
What Science Is and Is Not
 What Is Science? Key Questions What are the goals of science? What procedures are at the core of scientific methodology? Vocabulary science observation inference hypothesis controlled experiment independent
What Is Science? Key Questions What are the goals of science? What procedures are at the core of scientific methodology? Vocabulary science observation inference hypothesis controlled experiment independent
LIFE & PHYSICAL SCIENCE. Introduction & Scientific Method
 LIFE & PHYSICAL SCIENCE Introduction & Scientific Method What is Life & Physical Science? Life Science: the study of living things; biology. Physical Science: The study of matter, non-living materials;
LIFE & PHYSICAL SCIENCE Introduction & Scientific Method What is Life & Physical Science? Life Science: the study of living things; biology. Physical Science: The study of matter, non-living materials;
Unit 1-Characteristics of Life, Scientific Method and Microscopes
 Unit 1-Characteristics of Life, Scientific Method and Microscopes Section 1.1 Characteristics of Life Look at the following pictures and decide if the object is alive or not. Explain what criteria you
Unit 1-Characteristics of Life, Scientific Method and Microscopes Section 1.1 Characteristics of Life Look at the following pictures and decide if the object is alive or not. Explain what criteria you
What is Science? 1. Science deals only with the natural world. 3. Scientists propose
 Page 1 What is Science? 1. Science deals only with the natural world. 2. Scientists: collect and organize information in a careful, orderly way, looking for patterns and connections between events. The
Page 1 What is Science? 1. Science deals only with the natural world. 2. Scientists: collect and organize information in a careful, orderly way, looking for patterns and connections between events. The
Science is a way of learning about the natural world. The body of knowledge that scientists have is always growing and changing.
 Science is a way of learning about the natural world. The body of knowledge that scientists have is always growing and changing. Thinking Like a Scientist Some of the skills that scientist use are posing
Science is a way of learning about the natural world. The body of knowledge that scientists have is always growing and changing. Thinking Like a Scientist Some of the skills that scientist use are posing
Chapter 1.1. The Process of Science. Essential Questions
 Chapter 1.1 The Process of Science Essential Questions 1. How does scientific inquiry answer questions about the living world? 2. How do observations lead to scientific inferences? 3. How do scientific
Chapter 1.1 The Process of Science Essential Questions 1. How does scientific inquiry answer questions about the living world? 2. How do observations lead to scientific inferences? 3. How do scientific
Key Ideas. Explain how science is different from other forms of human endeavor. Identify the steps that make up scientific methods.
 Key Ideas Explain how science is different from other forms of human endeavor. Identify the steps that make up scientific methods. Analyze how scientific thought changes as new information is collected.
Key Ideas Explain how science is different from other forms of human endeavor. Identify the steps that make up scientific methods. Analyze how scientific thought changes as new information is collected.
1.3. Scientific Thinking and Processes. Teacher Notes and Answers. community, and that explains a wide range of things.
 section 1.3 Scientific Thinking and Processes Teacher Notes and Answers SECTION 3 Instant Replay 1. many possible answers, e.g., observing, because she is looking at something and collecting information,
section 1.3 Scientific Thinking and Processes Teacher Notes and Answers SECTION 3 Instant Replay 1. many possible answers, e.g., observing, because she is looking at something and collecting information,
The Nature of Science
 The Nature of Science To be scientifically literate, science students should have deeper understandings of science that studying the Nature of Science (NOS) provides. Write an account of what you think
The Nature of Science To be scientifically literate, science students should have deeper understandings of science that studying the Nature of Science (NOS) provides. Write an account of what you think
Section 1: The Nature of Science
 Section 1: The Nature of Science Preview Scientific Thought Universal Laws Science and Ethics Why Study Science? Summary Scientific Thought Scientific thought involves making observations, using evidence
Section 1: The Nature of Science Preview Scientific Thought Universal Laws Science and Ethics Why Study Science? Summary Scientific Thought Scientific thought involves making observations, using evidence
Scientific Method. Otter Bowl Diversity Event, December 2, 2006
 Scientific Method Otter Bowl Diversity Event, December 2, 2006 Scientific Method Scientific method is process scientists collectively and over time use to construct an accurate (reliable and consistent)
Scientific Method Otter Bowl Diversity Event, December 2, 2006 Scientific Method Scientific method is process scientists collectively and over time use to construct an accurate (reliable and consistent)
Nature of Science and Scientific Method Guided Notes
 Anything present in the environment, around the world, living, non-living everything is included in science. Science can be knowledge, science can be a fun, it can be a fact, a discovery, a law, a solved
Anything present in the environment, around the world, living, non-living everything is included in science. Science can be knowledge, science can be a fun, it can be a fact, a discovery, a law, a solved
Science is a way of learning about the natural world by observing things, asking questions, proposing answers, and testing those answers.
 Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 The Nature of Science and Scientific Inquiry Online resources: www.science.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe9/centre.html Remember to ask your teacher whether your classroom
Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 The Nature of Science and Scientific Inquiry Online resources: www.science.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe9/centre.html Remember to ask your teacher whether your classroom
Biology Notes Chapter 1 The Study of Life
 Biology Notes Chapter 1 The Study of Life 1.1 Introduction to Biology biology- the study of life bio- greek for life logos- Greek for study Biologists- people who study biology, make discoveries, and seek
Biology Notes Chapter 1 The Study of Life 1.1 Introduction to Biology biology- the study of life bio- greek for life logos- Greek for study Biologists- people who study biology, make discoveries, and seek
Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure (pages 174 181) Key Concept What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? 2. Label the structures
Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure (pages 174 181) Key Concept What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? 2. Label the structures
Chapter 1 About Science. What is Science? When was Science Invented? 4/6/2015
 Chapter 1 About Science What is Science? The body of knowledge which describes order within nature and the causes of that order The ongoing activity of the human race dedicated to gathering knowledge about
Chapter 1 About Science What is Science? The body of knowledge which describes order within nature and the causes of that order The ongoing activity of the human race dedicated to gathering knowledge about
Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages )
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) Key Concepts What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1. Any change,
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) Key Concepts What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1. Any change,
Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages )
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1 Any change, other than
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1 Any change, other than
BIOLOGY the study of life
 BIOLOGY the study of life What is Science? Science - an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural world Knowledge gained through experience Accumulated body of knowledge through
BIOLOGY the study of life What is Science? Science - an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural world Knowledge gained through experience Accumulated body of knowledge through
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Hypothesis-Driven Research
 Hypothesis-Driven Research Research types Descriptive science: observe, describe and categorize the facts Discovery science: measure variables to decide general patterns based on inductive reasoning Hypothesis-driven
Hypothesis-Driven Research Research types Descriptive science: observe, describe and categorize the facts Discovery science: measure variables to decide general patterns based on inductive reasoning Hypothesis-driven
AIM #4: DEFINE SCIENCE AND EXPLAIN THE PROCESS OF THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD
 AIM #4: DEFINE SCIENCE AND EXPLAIN THE PROCESS OF THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD Aim #4: Define science and explain the process of the scientific method Textbook Pages: 11-21 DO NOW: IN YOUR OWN WORDS, DEFINE OBSERVATION:
AIM #4: DEFINE SCIENCE AND EXPLAIN THE PROCESS OF THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD Aim #4: Define science and explain the process of the scientific method Textbook Pages: 11-21 DO NOW: IN YOUR OWN WORDS, DEFINE OBSERVATION:
What is Science? 1. Science deals only with the natural world. 3. Scientists propose
 Page 1 What is Science? 1. Science deals only with the natural world. 2. Scientists: collect and organize information in a careful, orderly way, looking for patterns and connections between events. The
Page 1 What is Science? 1. Science deals only with the natural world. 2. Scientists: collect and organize information in a careful, orderly way, looking for patterns and connections between events. The
The Study of Life. Before You Read. Science Journal
 The Study of Life Before You Read Use the What I Know column to list the things you know about biology. Then list the questions you have about biology in the What I Want to Find Out column. K W L What
The Study of Life Before You Read Use the What I Know column to list the things you know about biology. Then list the questions you have about biology in the What I Want to Find Out column. K W L What
The Scientific Method the process of doing science
 Steps The Scientific Method the process of doing science observation ask a question collect data hypothesis experiment analyze data draw conclusions communicate results Observing and Asking Questions Observation
Steps The Scientific Method the process of doing science observation ask a question collect data hypothesis experiment analyze data draw conclusions communicate results Observing and Asking Questions Observation
GED Preparation Lesson Plan. Module: Science. Lesson Title: Forming a Conclusion. Standards: GED Preparation (Adult General Education)
 GED Preparation Lesson Plan Module: Science Lesson Title: Forming a Conclusion Standards: GED Preparation (Adult General Education) Scientific Practices 2014 Assessment Targets Understand and explain textual
GED Preparation Lesson Plan Module: Science Lesson Title: Forming a Conclusion Standards: GED Preparation (Adult General Education) Scientific Practices 2014 Assessment Targets Understand and explain textual
Name Date Class. The Study of Life
 Chapter Test A CHAPTER 1 The Study of Life Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or answers each question. Part B:
Chapter Test A CHAPTER 1 The Study of Life Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or answers each question. Part B:
1-1 What Is Science? Biology: The study of life!
 1-1 What Is Science? Biology: The study of life! The goal of science is to understand and be able to make predictions about the natural world. 1. Science is the process of trying to understand the natural
1-1 What Is Science? Biology: The study of life! The goal of science is to understand and be able to make predictions about the natural world. 1. Science is the process of trying to understand the natural
Chapter 02 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 02 Lecture Outline William P. Cunningham University of Minnesota Mary Ann Cunningham Vassar College Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
Chapter 02 Lecture Outline William P. Cunningham University of Minnesota Mary Ann Cunningham Vassar College Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
A History of Microbiology
 A History of Microbiology Miasmatic Theory The Miasmatic Theory postulates that disease is caused by "bad air" or "mal aria", known as miasmatic odors. It was thought that these miasmatic odors arose from
A History of Microbiology Miasmatic Theory The Miasmatic Theory postulates that disease is caused by "bad air" or "mal aria", known as miasmatic odors. It was thought that these miasmatic odors arose from
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
Chapter 1: Thinking critically with. Introduction
 Chapter 1: Thinking critically with psychological science Introduction Fact or Falsehood 1. Human intuition is remarkable accurate and free from error. 2. Most people seem to lack confidence in the accuracy
Chapter 1: Thinking critically with psychological science Introduction Fact or Falsehood 1. Human intuition is remarkable accurate and free from error. 2. Most people seem to lack confidence in the accuracy
Biology & The Characteristics of Life
 Biology & The Characteristics of Life Name: Period: Date: I. What is BIOLOGY? The study of WHAT IS THE VALUE OF BIOLOGY? Biological principles are daily being applied for the in controlling disease, improving
Biology & The Characteristics of Life Name: Period: Date: I. What is BIOLOGY? The study of WHAT IS THE VALUE OF BIOLOGY? Biological principles are daily being applied for the in controlling disease, improving
Chapter 1.3b Scientific Method
 Chapter.3b Scientific Method Mrs. Baldessari Biology Objective : Identify and apply the steps of the scientific method. of 2 What is the goal of science? The goal of science is to: investigate and understand
Chapter.3b Scientific Method Mrs. Baldessari Biology Objective : Identify and apply the steps of the scientific method. of 2 What is the goal of science? The goal of science is to: investigate and understand
Lesson 1 Characteristics of Life
 Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Scientific Method Stations
 Stations Mandatory Things You will need: Station instructions and questions. (Attached) Student Response Sheet (Print one from the blog if you were absent or misplaced your copy) Instructions: Follow the
Stations Mandatory Things You will need: Station instructions and questions. (Attached) Student Response Sheet (Print one from the blog if you were absent or misplaced your copy) Instructions: Follow the
Grade 6 Standard 5 Unit Test Microorganisms. 1. Which of the following correctly describes the size of fungi compared to the size of bacteria?
 Grade 6 Standard 5 Unit Test Microorganisms 1. Which of the following correctly describes the size of fungi compared to the size of bacteria? A. Fungi are larger. B. Bacteria are larger. C. They are about
Grade 6 Standard 5 Unit Test Microorganisms 1. Which of the following correctly describes the size of fungi compared to the size of bacteria? A. Fungi are larger. B. Bacteria are larger. C. They are about
Scientific Method in Biology
 Scientific Method in Biology Observations Observations are a critical component of science, because they can lead to scientific questions. Example: Alexander Fleming s observations on a bacterial culture
Scientific Method in Biology Observations Observations are a critical component of science, because they can lead to scientific questions. Example: Alexander Fleming s observations on a bacterial culture
What is Science? What is Science? What is Science? Science is an organized way of using Evidence to learn about the natural world. Chapter 1 pg 3.
 What is Science? Chapter 1 pg 3. What is Science? Science is an organized way of using Evidence to learn about the natural world. What is Science? Goal of Science: To investigate and understand nature,
What is Science? Chapter 1 pg 3. What is Science? Science is an organized way of using Evidence to learn about the natural world. What is Science? Goal of Science: To investigate and understand nature,
UNIT. Experiments and the Common Cold. Biology. Unit Description. Unit Requirements
 UNIT Biology Experiments and the Common Cold Unit Description Content: This course is designed to familiarize the student with concepts in biology and biological research. Skills: Main Ideas and Supporting
UNIT Biology Experiments and the Common Cold Unit Description Content: This course is designed to familiarize the student with concepts in biology and biological research. Skills: Main Ideas and Supporting
Observations & Data! Biology = the Study of Life. ! Data = Recorded Observations. ! Scientific instruments
 What is Science? The Science of BIOLOGY Science is a process of questioning. Science as Inquiry Observations & Data! Biology = the Study of Life! Observations = The use of the senses to gather and record
What is Science? The Science of BIOLOGY Science is a process of questioning. Science as Inquiry Observations & Data! Biology = the Study of Life! Observations = The use of the senses to gather and record
Unit 13.2: Viruses. Vocabulary capsid latency vaccine virion
 Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Scientific Method in Biology
 Scientific Method in Biology Observations Observations are a critical component of science, because they can. Example: Alexander Fleming s observations on a bacterial culture contaminated with mold. Discuss
Scientific Method in Biology Observations Observations are a critical component of science, because they can. Example: Alexander Fleming s observations on a bacterial culture contaminated with mold. Discuss
THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD. Designing Experiments
 THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD Designing Experiments SUCCESS CRITERIA I can create a hypothesis based on a scientific question. I can design a proper scientific experiment based on a hypothesis. I can identify
THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD Designing Experiments SUCCESS CRITERIA I can create a hypothesis based on a scientific question. I can design a proper scientific experiment based on a hypothesis. I can identify
Name Class Date. Infection in which a virus inserts its nucleic acid into the DNA of the host cell and is duplicated with the cell s DNA
 Name Class Date 20.1 Viruses Lesson Objectives Explain how viruses reproduce. Explain how viruses cause infection. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions.
Name Class Date 20.1 Viruses Lesson Objectives Explain how viruses reproduce. Explain how viruses cause infection. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions.
How we see cells Hooke saw cork cells (plant cell) underneath a microscope and described them as cells
 Biology How we see cells Hooke saw cork cells (plant cell) underneath a microscope and described them as cells a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination Because
Biology How we see cells Hooke saw cork cells (plant cell) underneath a microscope and described them as cells a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination Because
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
The Three-Hole Bottle Demo Report
 Name The Three-Hole Bottle Demo Report 1. Compare the bottle used with the diagram at right. Point out any differences noted, or sketch the demo bottle as you see it. Date Per. cap water level tape (covering
Name The Three-Hole Bottle Demo Report 1. Compare the bottle used with the diagram at right. Point out any differences noted, or sketch the demo bottle as you see it. Date Per. cap water level tape (covering
Introduction to Science and the Scientific Method
 I. What is Science? Introduction to Science and the Scientific Method A. The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those
I. What is Science? Introduction to Science and the Scientific Method A. The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those
Pool Canvas. Add. Creation Settings. Chapter 01: Learning About Human Biology. Description Instructions. Add Question Here
 1 of 7 TEST BANK > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add Question drop-down list and click Go to add questions. Use
1 of 7 TEST BANK > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add Question drop-down list and click Go to add questions. Use
Evolution of Populations
 Chapter 16 Evolution of Populations Section 16 1 Genes and Variation (pages 393 396) This section describes the main sources of inheritable variation in a population. It also explains how phenotypes are
Chapter 16 Evolution of Populations Section 16 1 Genes and Variation (pages 393 396) This section describes the main sources of inheritable variation in a population. It also explains how phenotypes are
Designing an experiment 7 TH /8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Designing an experiment 7 TH /8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Scientific inquiry 1. Make an observation 2. Ask a question 3. Create a hypothesis 4. Design an experiment 5. Gather and analyze data 6. Draw conclusions
Designing an experiment 7 TH /8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Scientific inquiry 1. Make an observation 2. Ask a question 3. Create a hypothesis 4. Design an experiment 5. Gather and analyze data 6. Draw conclusions
Disposition. Quantitative Research Methods. Science what it is. Basic assumptions of science. Inductive and deductive logic
 Quantitative Research Methods Sofia Ramström Medicinska vetenskaper, Örebro Universitet Diagnostikcentrum, klinisk kemi, Region Östergötland Disposition I. What is science and what is quantitative science?
Quantitative Research Methods Sofia Ramström Medicinska vetenskaper, Örebro Universitet Diagnostikcentrum, klinisk kemi, Region Östergötland Disposition I. What is science and what is quantitative science?
Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s,
 63 Show Me the Genes! The History of the Germ Theory of Disease Activity 37 r e a d i n g Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s, Mendel knew that the genes had to be in the male
63 Show Me the Genes! The History of the Germ Theory of Disease Activity 37 r e a d i n g Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s, Mendel knew that the genes had to be in the male
NATURE OF SCIENCE. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A
 NATURE OF SCIENCE Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Nature Science Process of asking questions 2 Nature Science Process of asking questions Questions that involve logical reasoning 3 Nature Science
NATURE OF SCIENCE Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Nature Science Process of asking questions 2 Nature Science Process of asking questions Questions that involve logical reasoning 3 Nature Science
Cell Theory HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF CELL THEORY
 Page 1 of 17 Biology: The study of life (living things). Living things are composed of units called cells. Unicellular organism: A one-celled organism. Ex: paramecium, bacteria, amoeba Multicellular organism:
Page 1 of 17 Biology: The study of life (living things). Living things are composed of units called cells. Unicellular organism: A one-celled organism. Ex: paramecium, bacteria, amoeba Multicellular organism:
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 02 Developing and Evaluating Theories of Behavior
 Chapter 02 Developing and Evaluating Theories of Behavior Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n): A. plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the
Chapter 02 Developing and Evaluating Theories of Behavior Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n): A. plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the
Honors Biology Chapter 2. The Science of Biology
 Honors Biology Chapter 2 The Science of Biology Concept 2.1: Discovery Science Emphasizes Inquiry and Observation I. Science as Inquiry A. Science = to know, to answer? s about the natural world 1. 2 main
Honors Biology Chapter 2 The Science of Biology Concept 2.1: Discovery Science Emphasizes Inquiry and Observation I. Science as Inquiry A. Science = to know, to answer? s about the natural world 1. 2 main
Review Sheet. 2) Which branch of science broken into chemistry and physics? a. Life science b. Earth science c. Biology d.
 Multiple Choice: Circle each answer. Review Sheet 1) Which famous scientist was known for his/her work in radioactivity? a. Albert Einstein b. Marie Curie c. Thomas Edison d. Pierre Curie 2) Which branch
Multiple Choice: Circle each answer. Review Sheet 1) Which famous scientist was known for his/her work in radioactivity? a. Albert Einstein b. Marie Curie c. Thomas Edison d. Pierre Curie 2) Which branch
Name Date Class. How the Nervous System Works (pages ) 2. Is the following sentence true or false? You can move without your
 CHAPTER 15 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM SECTION 15 1 How the Nervous System Works (pages 486-490) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Functions
CHAPTER 15 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM SECTION 15 1 How the Nervous System Works (pages 486-490) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Functions
Contents. Pretest...5. Coached Test Posttest Periodic Table Duplicating any part of this book is prohibited by law.
 Contents Pretest...5 Coached Test... 39 Posttest... 75 Periodic Table....111 3 1. As shown below, leaves have small openings called stomata (singular, stoma). The stomata are surrounded by guard cells.
Contents Pretest...5 Coached Test... 39 Posttest... 75 Periodic Table....111 3 1. As shown below, leaves have small openings called stomata (singular, stoma). The stomata are surrounded by guard cells.
Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s,
 63 Activity 37 Show Me the Genes! R E A D I N G Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s, Mendel knew that the genes had to be in the male and female sex cells the sperm (or pollen)
63 Activity 37 Show Me the Genes! R E A D I N G Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s, Mendel knew that the genes had to be in the male and female sex cells the sperm (or pollen)
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS STANDARD REVIEW
 4.B.9.B BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS (B.9) Science concepts. The student knows the significance of various molecules involved in metabolic processes and energy conversions that occur in living organisms.
4.B.9.B BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS (B.9) Science concepts. The student knows the significance of various molecules involved in metabolic processes and energy conversions that occur in living organisms.
One ancient evening, lost in the mists of time, someone
 1 1 What Is Science? One ancient evening, lost in the mists of time, someone looked into the sky and wondered for the first time: What are those lights? Where did plants and animals come from? How did
1 1 What Is Science? One ancient evening, lost in the mists of time, someone looked into the sky and wondered for the first time: What are those lights? Where did plants and animals come from? How did
NOTES CELL UNIT WHAT IS A CELL? cell unicellular multicellular DISCOVERY OF CELLS Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek THE CELL THEORY
 NOTES CELL UNIT WHAT IS A CELL? A cell is the smallest unit of life that can carry out all the functions of a living thing. Living things can be either unicellular (made up entirely of only one cell) or
NOTES CELL UNIT WHAT IS A CELL? A cell is the smallest unit of life that can carry out all the functions of a living thing. Living things can be either unicellular (made up entirely of only one cell) or
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
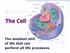 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
Unit 1 History and Methods Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with Psychological Science
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Unit 1 History and Methods Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Fact vs. Falsehood 1. Human intuition is remarkably accurate
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Unit 1 History and Methods Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Fact vs. Falsehood 1. Human intuition is remarkably accurate
It s Alive!!! Or is it??? Book A, Chapter 1 Mrs. Armstrong
 It s Alive!!! Or is it??? Book A, Chapter 1 Mrs. Armstrong It s Alive!! Or Is It? Table of Contents Section 1 Characteristics of Living Things Section 2 The Necessities of Life Section 1 Characteristics
It s Alive!!! Or is it??? Book A, Chapter 1 Mrs. Armstrong It s Alive!! Or Is It? Table of Contents Section 1 Characteristics of Living Things Section 2 The Necessities of Life Section 1 Characteristics
Nature of Science Review
 NOS Quiz 2 Revision 6 Nature of Science Review Name : Class : Date : 1. Marcia did an experiment to find out whether tulips grow faster under fluorescent lighting or incandescent lighting. Under flourescent
NOS Quiz 2 Revision 6 Nature of Science Review Name : Class : Date : 1. Marcia did an experiment to find out whether tulips grow faster under fluorescent lighting or incandescent lighting. Under flourescent
Scientific Thinking Handbook
 Making Observations An observation is an act of noting and recording an event, characteristic, behavior, or anything else detected with an instrument or with the senses. Observations allow you to make
Making Observations An observation is an act of noting and recording an event, characteristic, behavior, or anything else detected with an instrument or with the senses. Observations allow you to make
Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP!
 Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP! Program description: Discover how whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students
Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP! Program description: Discover how whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students
Chapter 13 Summary Experiments and Observational Studies
 Chapter 13 Summary Experiments and Observational Studies What have we learned? We can recognize sample surveys, observational studies, and randomized comparative experiments. o These methods collect data
Chapter 13 Summary Experiments and Observational Studies What have we learned? We can recognize sample surveys, observational studies, and randomized comparative experiments. o These methods collect data
Introduction to Research Methods
 Introduction to Research Methods Updated August 08, 2016 1 The Three Types of Psychology Research Psychology research can usually be classified as one of three major types: 1. Causal Research When most
Introduction to Research Methods Updated August 08, 2016 1 The Three Types of Psychology Research Psychology research can usually be classified as one of three major types: 1. Causal Research When most
The Digestive Process Begins
 Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Introduction to Microbiology The Microbial World and You (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Introduction to Microbiology The Microbial World and You (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Source for figures and content: Eastern Campus
Introduction to Microbiology The Microbial World and You (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Source for figures and content: Eastern Campus
Chapter 13. Experiments and Observational Studies. Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Experiments and Observational Studies Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Observational Studies In an observational study, researchers don t assign choices; they simply observe
Chapter 13 Experiments and Observational Studies Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Observational Studies In an observational study, researchers don t assign choices; they simply observe
Scientific Method. Earth Systems
 Scientific Method Earth Systems What is Science? Scienceis a method for studying the natural world. Scientists use a specific process to investigate their observations. This process is called the scientific
Scientific Method Earth Systems What is Science? Scienceis a method for studying the natural world. Scientists use a specific process to investigate their observations. This process is called the scientific
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with Psychological Science
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers The Need for Psychologists, like all scientists, use the scientific method to construct
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers The Need for Psychologists, like all scientists, use the scientific method to construct
6. A theory that has been substantially verified is sometimes called a a. law. b. model.
 Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n) a. a plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world. b. a well-substantiated explanation
Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n) a. a plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world. b. a well-substantiated explanation
Science and the scientific method. Mr. Banks 7 th and 8 TH grade science
 Science and the scientific method Mr. Banks 7 th and 8 TH grade science What is science? Science is the study of the structure and behavior of the physical and natural universe, to find explanations to
Science and the scientific method Mr. Banks 7 th and 8 TH grade science What is science? Science is the study of the structure and behavior of the physical and natural universe, to find explanations to
LAB 7: THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD
 LAB 7: THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD Making an observation and asking an interesting question The first steps in the scientific method include making an observation, doing some background research on the topic,
LAB 7: THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD Making an observation and asking an interesting question The first steps in the scientific method include making an observation, doing some background research on the topic,
RESEARCH METHODS: PSYCHOLOGY AS A SCIENCE
 RESEARCH METHODS: PSYCHOLOGY AS A SCIENCE TODAY S OBJECTIVE Explain basic methods of psychological research. IMPORTANT KEY TERMS Variable: anything that can change Theory: broad idea or set of closely
RESEARCH METHODS: PSYCHOLOGY AS A SCIENCE TODAY S OBJECTIVE Explain basic methods of psychological research. IMPORTANT KEY TERMS Variable: anything that can change Theory: broad idea or set of closely
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per:
 Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Independent Variable. The Scientific Method and Variables. Dependent Variable. Snappy Practice:
 The Scientific Method and Variables In every experiment, a scientist is trying to explore a problem or answer a question. To do this, you are testing the relationship between two different things called
The Scientific Method and Variables In every experiment, a scientist is trying to explore a problem or answer a question. To do this, you are testing the relationship between two different things called
