FRAMING MENTAL DISORDERS
|
|
|
- Carmella Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FRAMING MENTAL DISORDERS 23 August 2012 CTF 2012 Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Patrice Soom (HHUD)
2 OUTLINE 1. Project outline 2. The DSM-IV definition of delusions 3. A Frame analysis of delusions 4. Framing neuropsychological explanations of delusions 5. Conclusions
3 1. PROJECT OUTLINE Frame analysis of mental disorders 3
4 1. PROJECT OUTLINE Frame analysis of mental disorders frames provide the fundamental representation of knowledge in human cognition (Barsalou 1992, 21). Two research directions: 1. Descriptive psychological thesis: mental representations are cognitive frames. Cognition represents and operates by means of frames and frame based mental simulations. 2. Methodological thesis : explicit frames should be used in order to represent explicitly the structure of our scientific knowledge, i.e. psychological, psychiatric, neuroscientific knowledge. 4
5 1. PROJECT OUTLINE Frame analysis of mental disorders frames provide the fundamental representation of knowledge in human cognition (Barsalou 1992, 21). Two research directions: 1. Descriptive psychological thesis: mental representations are cognitive frames. Cognition represents and operates by means of frames and frame based mental simulations. 2. Methodological thesis : explicit frames should be used in order to represent explicitly the structure of our scientific knowledge, i.e. psychological, psychiatric, neuroscientific knowledge. 5
6 1. PROJECT OUTLINE Frame analysis of mental disorders What are frames? Barsalou (1992) Recursive attribute-value structures Superordinate category concepts are individuated by their relations to subordinate attribute concepts. Values are subordinate concepts of attributes concepts. Frames might represent further relations: Structural invariants: systematic relations between attributes Attribute constraints: systematic relations between attributes values
7 1. PROJECT OUTLINE Example of a frame for vacation (Barsalou 1992)
8 1. PROJECT OUTLINE Frame as directed graphs (Petersen 2007) Vacation [high; low] [fast; slow] [hills; beach] [close; far] sport
9 1. PROJECT OUTLINE Frame as directed graphs (Petersen 2007) Vacation Transpor tation [high; low] Location [fast; slow] [hills; beach] [close; far] sport Attributes constraints grasping dependencies between attributes values.
10 1. PROJECT OUTLINE Frame analysis of mental disorders Complexity of clinical phenomena Multiple cognitive, behavioral, neuropsychological, ( ), dimensions of mental disorders. Heterogeneity of clinical phenomena Disjunctive character of diagnosis criteria. Heterogeneity of classification criteria Categorical and dimensional systems of classification.
11 1. PROJECT OUTLINE Frame analysis of the classification of mental disorders Complexity of clinical phenomena Heterogeneity of clinical phenomena Heterogeneity of classification criteria Focus on one key concept: delusion.
12 2. THE DSM-IV DEFINITION OF DELUSIONS A delusion is a false belief based on incorrect inference about external reality that is firmly sustained despite what almost everyone else believes and despite what constitutes incontrovertible and obvious proof or evidence to the contrary (APA 2000: 821).
13 2. THE DSM-IV DEFINITION OF DELUSIONS External world A delusion is a false belief based on incorrect inference about external reality that is firmly sustained despite what almost everyone else believes and despite what constitutes incontrovertible and obvious proof or evidence to the contrary (APA 2000: 821). delusion Belief Incorrect False No Firm No
14 2. THE DSM-IV DEFINITION OF DELUSIONS Delusions are symptoms of several mental disorders: Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorders Schizoaffective disorders Alzheimer dementia Mood disorders Huntigton s disease Parkinson s disease Multiple sclerosis Traumatic brain injuries Substance-induced disorders Delusional disorders
15 2. THE DSM-IV DEFINITION OF DELUSIONS Delusions are symptoms of several mental disorders External world delusion Belief Incorrect False No Firm No
16 2. THE DSM-IV DEFINITION OF DELUSIONS Delusions are classified depending on their content: My closest relative has been replaced by an imposter (Capgras delusion). I am followed around by people who are known to me but who are unrecognizable because they are in disguise (Fregoli delusion) I am dead (Cotard delusion). The person I see in the mirror is not really me (mirrored selfidentification). A person I knew who died is nevertheless in the hospital ward today (reduplicative paramnesia). This arm is not mine; it is yours. You have three arms (somatoparaphrenia). Someone else is able to control my actions (delusion of alien control). Someone else s thoughts are being inserted into my mind (delusion of thought insertion). But also persecution, grandiosity, jealousy, erotomania, etc.
17 2. THE DSM-IV DEFINITION OF DELUSIONS Delusions are classified according to their content. External world Belief Content Attribute constraint: [content sub-type] delusion Incorrect False No Firm No
18 2. THE DSM-IV DEFINITION OF DELUSIONS Bizarre vs Non-Bizarre Delusions: Delusions are deemed bizarre if they are clearly implausible and not understandable and do not derive from ordinary life experiences An example of a bizarre delusion is a person's belief that a stranger has removed his or her internal organs and has replaced them with someone else's organs without leaving any wounds or scars An example of a non-bizarre delusion is a person's false belief that he or she is under surveillance by the police. If the delusions are judged to be bizarre, only this single symptom is needed to satisfy Criterion A for Schizophrenia (APA 2000, p. 299)
19 2. THE DSM-IV DEFINITION OF DELUSIONS Depending on content, delusions might be said bizarre, which impacts on the diagnosis. External world Yes/No Attribute constraint [bizarreness type of mental disorder] Content delusion Belief Incorrect False No Firm No
20 3. FRAME ANALYSIS OF DELUSIONS External world Yes/No Attribute constraint [bizarreness type of mental disorder] Content delusion Belief Incorrect False No Firm No
21 3. FRAME ANALYSIS OF DELUSIONS DSM-IV definition: theoretically inadequate elements External world Yes/No Content delusion Belief Incorrect False No Firm No
22 3. FRAME ANALYSIS OF DELUSIONS delusion No Delusions are contentful conceptual mental representations, that are insensitive to counterevidence and thus immune to revision.
23 3. FRAME ANALYSIS OF DELUSIONS delusion Asymetrical Delusions are contentful conceptual mental representations, that are insensitive to counterevidence and thus immune to revision. Delusions have an asymmetric inferential profile: they might impact on the rest of the system of mental properties, whereas this does not hold the other way round.
24 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS delusion Psychological level Asymetrical Psychological definition: delusions are contentful conceptual mental representations that have an asymmetrical inferential profile.
25 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS delusion Psychological level Asymetrical Psychological definition: delusions are contentful conceptual mental representations that have an asymmetrical inferential profile. Neuropsychological accounts aims to provide reductive explanations of theses features of delusions. How to integrate neuropsychological reductive explanations?
26 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS According to the Two-Factor Account (TFA; Coltheart 2007, 2011), delusions occur as a result of the conjunction of two factors, which respectively explain: a) Why delusions are tokened? b) Why delusions are not rejected in reasons of their inconsistency with the other mental properties of the deluded patient? 26
27 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS Abductive reasoning prompts an explanatory belief P. Delusional explanatory belief Explanatory adequacy: if P was the case, then E would be expectable. Fact-A Fact-B Neuropsychological fact. generating an abnormal experience E. Impairment in belief evaluation prevents the rejection of P.
28 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS Abductive reasoning prompts an explanatory belief P. Delusional explanatory belief Explanatory adequacy: if P was the case, then E would be expectable. Fact-A Fact-B Capgras Delusion Neuropsychological fact. generating an abnormal experience E. Reduced autonomic response to familiar faces. Impairment in belief evaluation prevents the rejection of P. Right prefrontal impairment.
29 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS Abductive reasoning prompts an explanatory belief P. Delusional explanatory belief Explanatory adequacy: if P was the case, then E would be expectable. Fact-A Fact-B Fregoli Delusion Neuropsychological fact. generating an abnormal experience E. Enhanced autonomic response to faces. Impairment in belief evaluation prevents the rejection of P. Right prefrontal impairment.
30 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS TFA on several famous delusions: Delusion type Factor A Factor B Capgras Reduced auto resp. to familiar faces RPF Def. Fregoli Enhanced autonomic resp. to faces RPF Def. Cotard Abolished autonomic responses RPF Def. MSMI Mirror agnosia or face agnosia RPF Def. Somatopara. Paralysis of a limb RPF Def. Alien Control Disrupted self-monitoring RPF Def. (Coltheart, Langdon and McKay (2011), Delusional belief. Annual Review of Psychology, pp )
31 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS delusion Psychological level Asymetrical Cognitive level A-Factor B-Factor
32 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS delusion Psychological level Asymetrical Cognitive level A-Factor B-Factor Neurological level??
33 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS Psychological level My wife has been replaced Capgras delusion Cognitive level Neurological level Asymetrical Autonomus hyporeactivity Abnormal STS connectivity Belief rev. sys. impaired Right prefrontal imp. A Frame for the Capgras delusion
34 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS Psychological level I am surrounded by friends Fregoli delusion Asymetrical Cognitive level Neurological level Autonomus hyperreactivity Not yet known Belief rev. sys. impaired Right prefrontal imp. A Frame for the Fregoli delusion
35 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS Psychological level List of possible values List of subtypes of delusions List of possible values Asymetrical Cognitive level Neurological level List of possible values List of possible values Belief rev. sys. impaired Right prefrontal imp. The variability of delusions might be represented by means of integrating possible values in a generalized frame for the concept of delusion.
36 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS Psychological level List of possible values List of subtypes of delusions List of possible values Asymetrical Cognitive level Neurological level List of possible values List of possible values Belief rev. sys. impaired Right prefrontal imp. Attribute constraints enable to represent different (types of) dependencies between the values of the attributes.
37 4. FRAMING NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXPLANATIONS OF DELUSIONS Psychological level List of possible values List of subtypes of delusions List of possible values Asymetrical Cognitive level Neurological level List of possible values List of possible values Belief rev. sys. impaired Right prefrontal imp. Example of attribute constraints: if the value of central node is [capgras], then the value of the attribute [content] fall under the description [a close relative as been replaced].
38 5. CONCLUSIVE REMARKS The complexity and the heterogeneity of mental disorders impose to work on simple cases. Frames enable to represent accurately key concepts of psychiatry. Integrating possible values allows to represent the variability of psychiatric symptoms. Dependencies between values might be represented using attribute constraints.
39 Thank you for your attention! SFB 991 B06 Team: PD Dr. J. Zielasek Prof. Dr. G. Vosgerau Prof. Dr. W. Gaebel O. Beldanova, dipl. -Psych. Dr. P. Soom
Chapter 2, Wondrous Strange: The Neuropsychology of Abnormal Beliefs
 PHIL 5983: Irrational Belief Seminar Prof. Funkhouser 1/30/13 Pathologies of Belief, Chapters 2-4 Chapter 2, Wondrous Strange: The Neuropsychology of Abnormal Beliefs 1. * Delusions are bizarre and not
PHIL 5983: Irrational Belief Seminar Prof. Funkhouser 1/30/13 Pathologies of Belief, Chapters 2-4 Chapter 2, Wondrous Strange: The Neuropsychology of Abnormal Beliefs 1. * Delusions are bizarre and not
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network
 Positive and Negative Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart
From the internal lexicon to delusional belief 5
 AVANT, Vol. V, No. 3/2014 ISSN: 2082-6710 avant.edu.pl/en DOI: 10.26913/50302014.0112.0002 Max Coltheart Department of Cognitive Science Macquarie University max.coltheart[]mq.edu.au From the internal
AVANT, Vol. V, No. 3/2014 ISSN: 2082-6710 avant.edu.pl/en DOI: 10.26913/50302014.0112.0002 Max Coltheart Department of Cognitive Science Macquarie University max.coltheart[]mq.edu.au From the internal
Index 1. The Author(s) 2018 L. Bortolotti (ed.), Delusions in Context,
 Index 1 A Abductive inferences, 42 Abuse, 3, 14, 15, 101, 105 Action, 2, 3, 10, 20, 39, 48, 50, 54, 75, 79, 87, 100, 108, 112, 113 Adaptiveness, 48, 53, 76, 83, 98,,, n8, 110 Adjustment heuristic, 45,
Index 1 A Abductive inferences, 42 Abuse, 3, 14, 15, 101, 105 Action, 2, 3, 10, 20, 39, 48, 50, 54, 75, 79, 87, 100, 108, 112, 113 Adaptiveness, 48, 53, 76, 83, 98,,, n8, 110 Adjustment heuristic, 45,
The neuropsychology of delusions
 Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: The Year in Cognitive Neuroscience The neuropsychology of delusions Max Macquarie Centre for Cognitive Science, Macquarie
Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: The Year in Cognitive Neuroscience The neuropsychology of delusions Max Macquarie Centre for Cognitive Science, Macquarie
Gold and Hohwy, Rationality and Schizophrenic Delusion
 PHIL 5983: Irrational Belief Seminar Prof. Funkhouser 2/6/13 Gold and Hohwy, Rationality and Schizophrenic Delusion There are two plausible departments of rationality: procedural and content. Procedural
PHIL 5983: Irrational Belief Seminar Prof. Funkhouser 2/6/13 Gold and Hohwy, Rationality and Schizophrenic Delusion There are two plausible departments of rationality: procedural and content. Procedural
DELUSION: COGNITIVE APPROACHES BAYESIAN INFERENCE AND COMPARTMENTALIZATION
 Chapter 42 DELUSION: COGNITIVE APPROACHES BAYESIAN INFERENCE AND COMPARTMENTALIZATION Martin Davies and Andy Egan Delusions in individuals with schizophrenia are personal-level phenomena and no account
Chapter 42 DELUSION: COGNITIVE APPROACHES BAYESIAN INFERENCE AND COMPARTMENTALIZATION Martin Davies and Andy Egan Delusions in individuals with schizophrenia are personal-level phenomena and no account
Cognitive Psychopathology: An essential tool for the frame analysis of mental disorders Olga Beldanova, Jürgen Zielasek, Wolfgang Gaebel
 Cognitive Psychopathology: An essential tool for the frame analysis of mental disorders Olga Beldanova, Jürgen Zielasek, Wolfgang Gaebel LVR Klinikum Düsseldorf Dept. of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy Heinrich-Heine-University
Cognitive Psychopathology: An essential tool for the frame analysis of mental disorders Olga Beldanova, Jürgen Zielasek, Wolfgang Gaebel LVR Klinikum Düsseldorf Dept. of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy Heinrich-Heine-University
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis
 Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Psychosis. Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah
 Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
 Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy Delusion First published Wed Sep 16, 2009; substantive revision Fri Oct 11, 2013 This entry focuses on the phenomenon of clinical delusions. Although the nature of delusions
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy Delusion First published Wed Sep 16, 2009; substantive revision Fri Oct 11, 2013 This entry focuses on the phenomenon of clinical delusions. Although the nature of delusions
By Jason H. King DECONSTRUCTING THE DSM-5 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS THE NEW LANDSCAPE
 DECONSTRUCTING THE DSM-5 By Jason H. King ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS Happy New Year as you engage in your counseling, research, supervision or educational endeavors. I
DECONSTRUCTING THE DSM-5 By Jason H. King ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS Happy New Year as you engage in your counseling, research, supervision or educational endeavors. I
Young s paper (2007) identifies fundamental. If You Did Not Care, You Would Not Notice: Recognition and Estrangement in Psychopathology
 If You Did Not Care, You Would Not Notice: Recognition and Estrangement in Psychopathology Lisa Bortolotti and Matthew R. Broome Keywords: psychopathology, emotions, neuropsychology, delusions, cognitive
If You Did Not Care, You Would Not Notice: Recognition and Estrangement in Psychopathology Lisa Bortolotti and Matthew R. Broome Keywords: psychopathology, emotions, neuropsychology, delusions, cognitive
Chapter 12. Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders. PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception
 Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness
 Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness A Psychosis refers to a state where a person loses contact with reality. The word is derived from the Latin words "psyche" meaning mind and "osis" meaning illness.
Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness A Psychosis refers to a state where a person loses contact with reality. The word is derived from the Latin words "psyche" meaning mind and "osis" meaning illness.
Uncommon Psychiatric Syndromes
 Uncommon Psychiatric Syndromes Capgras delusion Delusional Misinterpretation described by Capgras and Reboul-Lachaux in 1923 they called it l illusion des sosies (illusion of doubles) also associated with
Uncommon Psychiatric Syndromes Capgras delusion Delusional Misinterpretation described by Capgras and Reboul-Lachaux in 1923 they called it l illusion des sosies (illusion of doubles) also associated with
Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes
 Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes Psychotic Disorders- Week 7- Chapter 4 Narrow definitions of psychosis only require the presence of hallucinations and delusions, whereas broad definitions of psychosis incorporate
Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes Psychotic Disorders- Week 7- Chapter 4 Narrow definitions of psychosis only require the presence of hallucinations and delusions, whereas broad definitions of psychosis incorporate
Delusion: Cognitive approaches Bayesian inference and compartmentalisation *
 Production version To appear in KWM Fulford, M Davies, RGT Gipps, G Graham, J Sadler, G Stanghellini and T Thornton (eds), The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy and Psychiatry (Oxford: Oxford University Press,
Production version To appear in KWM Fulford, M Davies, RGT Gipps, G Graham, J Sadler, G Stanghellini and T Thornton (eds), The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy and Psychiatry (Oxford: Oxford University Press,
The psychological disorders
 The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
Psychiatric Discourse: Scientific reductionism for the autonomous person
 Psychiatric Discourse: Scientific reductionism for the autonomous person Stephan Heckers, MD MSc Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Vanderbilt University Psychiatric discourse 1) Historical/current
Psychiatric Discourse: Scientific reductionism for the autonomous person Stephan Heckers, MD MSc Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Vanderbilt University Psychiatric discourse 1) Historical/current
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA
 Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
Delusion. Delusions 27/09/13. Types of Hypnosis Research DSM- IV (2000): Intrinsic Exploring the nature of hypnosis itself
 Types of Hypnosis Research Intrinsic Exploring the nature of hypnosis itself Instrumental Using hypnoac suggesaons to explore psychological processes Using hypnosis to create analogues of clinical condiaons
Types of Hypnosis Research Intrinsic Exploring the nature of hypnosis itself Instrumental Using hypnoac suggesaons to explore psychological processes Using hypnosis to create analogues of clinical condiaons
Abnormal Psychology Notes
 Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
A break with reality. Hallucinations. Disorganized speech and thinking
 Other Psychotic Disorders István Bitter 28 October 2009 Psychosis A break with reality Hallucinations Delusions Disorganized speech and thinking Psychosis Negative Symptoms blunted affect decreased motivation
Other Psychotic Disorders István Bitter 28 October 2009 Psychosis A break with reality Hallucinations Delusions Disorganized speech and thinking Psychosis Negative Symptoms blunted affect decreased motivation
Managing Psychotic Disorders in the Primary Care Setting
 Managing Psychotic Disorders in the Primary Care Setting Anne Dohrenwend, Ph.D., ABPP McLaren Regional Medical Center Heather Kirkpatrick, Ph.D., ABPP Genesys Regional Medical Center Presentation Outline!
Managing Psychotic Disorders in the Primary Care Setting Anne Dohrenwend, Ph.D., ABPP McLaren Regional Medical Center Heather Kirkpatrick, Ph.D., ABPP Genesys Regional Medical Center Presentation Outline!
Tips & Techniques for Supporting Residents with Mental Illness in Senior Housing
 Tips & Techniques for Supporting Residents with Mental Illness in Senior Housing Marsha Frankel, LICSW JF&CS Caren Silverlieb, MMHS JCHE reserved 2017 1 Objectives Be able to identify three behavioral
Tips & Techniques for Supporting Residents with Mental Illness in Senior Housing Marsha Frankel, LICSW JF&CS Caren Silverlieb, MMHS JCHE reserved 2017 1 Objectives Be able to identify three behavioral
Schizophrenia. Delusion or Reality
 Schizophrenia Delusion or Reality Why Diagnose? We would even argue that the sole reason as to why clinicians should undertake a diagnostic assessment is to develop a management plan for the patient. Otherwise
Schizophrenia Delusion or Reality Why Diagnose? We would even argue that the sole reason as to why clinicians should undertake a diagnostic assessment is to develop a management plan for the patient. Otherwise
Agoraphobia. An anxiety disorder marked by fear of being in situations in which escape may be difficult or impossible.
 Agoraphobia An anxiety disorder marked by fear of being in situations in which escape may be difficult or impossible. (See page 634) Antisocial personality disorder (APD) A personality disorder marked
Agoraphobia An anxiety disorder marked by fear of being in situations in which escape may be difficult or impossible. (See page 634) Antisocial personality disorder (APD) A personality disorder marked
Bizarre delusions and DSM-IV schizophrenia
 Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences (2002), 56, 391 395 Regular Article Bizarre delusions and DSM-IV schizophrenia MAKOTO NAKAYA, md, phd, 1 KATSUNORI KUSUMOTO, md, phd, 2 TAKAYUKI OKADA, md, phd 3 AND
Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences (2002), 56, 391 395 Regular Article Bizarre delusions and DSM-IV schizophrenia MAKOTO NAKAYA, md, phd, 1 KATSUNORI KUSUMOTO, md, phd, 2 TAKAYUKI OKADA, md, phd 3 AND
A frame-based analysis of synaesthetic metaphors
 A frame-based analysis of synaesthetic metaphors Wiebke Petersen, Jens Fleischhauer, Hakan Beseoglu, Peter Bücker Institute of Language and Information Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Abstract The
A frame-based analysis of synaesthetic metaphors Wiebke Petersen, Jens Fleischhauer, Hakan Beseoglu, Peter Bücker Institute of Language and Information Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Abstract The
Mental Health Disorders Civil Commitment UNC School of Government
 Mental Health Disorders 2017 Civil Commitment UNC School of Government Edward Poa, MD, FAPA Chief of Inpatient Services, The Menninger Clinic Associate Professor, Baylor College of Medicine NC statutes
Mental Health Disorders 2017 Civil Commitment UNC School of Government Edward Poa, MD, FAPA Chief of Inpatient Services, The Menninger Clinic Associate Professor, Baylor College of Medicine NC statutes
BADDS Appendix A: The Bipolar Affective Disorder Dimensional Scale, version 3.0 (BADDS 3.0)
 BADDS Appendix A: The Bipolar Affective Disorder Dimensional Scale, version 3.0 (BADDS 3.0) General information The Bipolar Affective Disorder Dimension Scale (BADDS) has been developed in order to address
BADDS Appendix A: The Bipolar Affective Disorder Dimensional Scale, version 3.0 (BADDS 3.0) General information The Bipolar Affective Disorder Dimension Scale (BADDS) has been developed in order to address
Chapter 02 Developing and Evaluating Theories of Behavior
 Chapter 02 Developing and Evaluating Theories of Behavior Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n): A. plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the
Chapter 02 Developing and Evaluating Theories of Behavior Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n): A. plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the
DBS and the patient s lived experience: What can we saiy about the comparison between neurology and psychiatry?
 DBS and the patient s lived experience: What can we saiy about the comparison between neurology and psychiatry? B a p t i s t e M o u t a u d ( CNRS- L E S C ) Some PD patients: were not satisfied or did
DBS and the patient s lived experience: What can we saiy about the comparison between neurology and psychiatry? B a p t i s t e M o u t a u d ( CNRS- L E S C ) Some PD patients: were not satisfied or did
Recognition memory in psychotic patients
 Behavioural Neurology (1992), S, 23-26 Recognition memory in psychotic patients H. Ellis1, K. De Pauw2, G.N. Christodoulou3, J.-P. Luaute4, E. Bidault 4 and K. Szulecka 5 1 School of Psychology, University
Behavioural Neurology (1992), S, 23-26 Recognition memory in psychotic patients H. Ellis1, K. De Pauw2, G.N. Christodoulou3, J.-P. Luaute4, E. Bidault 4 and K. Szulecka 5 1 School of Psychology, University
Megan Testa, MD. Proponent Testimony on H.B. 81 SMI and the Death Penalty. May 9, 2017
 Megan Testa, MD On behalf of the Ohio Psychiatric Physicians Association Before Members of the House Criminal Justice Committee Proponent Testimony on H.B. 81 SMI and the Death Penalty May 9, 2017 Chairman
Megan Testa, MD On behalf of the Ohio Psychiatric Physicians Association Before Members of the House Criminal Justice Committee Proponent Testimony on H.B. 81 SMI and the Death Penalty May 9, 2017 Chairman
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Detecting and Disrupting Criminal Networks. A Data Driven Approach. P.A.C. Duijn
 Detecting and Disrupting Criminal Networks. A Data Driven Approach. P.A.C. Duijn Summary Detecting and Disrupting Criminal Networks A data-driven approach It is estimated that transnational organized crime
Detecting and Disrupting Criminal Networks. A Data Driven Approach. P.A.C. Duijn Summary Detecting and Disrupting Criminal Networks A data-driven approach It is estimated that transnational organized crime
Basel München Paris London New York New Delhi Singapore Tokyo Sydney
 The Delusional Misidentification Syndromes Bibliotheca Psychiatrica No. 164 Series Editors P. Berner, Wien E. Gabriel, Wien KARGER Basel München Paris London New York New Delhi Singapore Tokyo Sydney The
The Delusional Misidentification Syndromes Bibliotheca Psychiatrica No. 164 Series Editors P. Berner, Wien E. Gabriel, Wien KARGER Basel München Paris London New York New Delhi Singapore Tokyo Sydney The
Early Stages of Psychosis. Learning Objectives
 Early Stages of Psychosis Stephan Heckers, MD MSc Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Vanderbilt University Learning Objectives Summarize the five domains of psychosis Describe how psychotic
Early Stages of Psychosis Stephan Heckers, MD MSc Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Vanderbilt University Learning Objectives Summarize the five domains of psychosis Describe how psychotic
Severe Mental Disorders. Etheldreda Nakimuli-Mpungu, MMed (Psych), MBChB Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Schizophrenia. Nikita Verma 2017 Page 1
 Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Examiner concern with the use of theory in PhD theses
 Examiner concern with the use of theory in PhD theses (Presenter) Professor Allyson Holbrook Professor Sid Bourke Paper 2 - Symposium: The role of theory in doctoral education 15 th Biennial EARLI Conference
Examiner concern with the use of theory in PhD theses (Presenter) Professor Allyson Holbrook Professor Sid Bourke Paper 2 - Symposium: The role of theory in doctoral education 15 th Biennial EARLI Conference
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders?
 Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Dr. Fred Rose. Schizophrenia. Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview. Prevalence of Schizophrenia 10/20/10. Schizophrenia vs.
 Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Lecture 2: Foundations of Concept Learning
 Lecture 2: Foundations of Concept Learning Cognitive Systems - Machine Learning Part I: Basic Approaches to Concept Learning Version Space, Candidate Elimination, Inductive Bias last change October 18,
Lecture 2: Foundations of Concept Learning Cognitive Systems - Machine Learning Part I: Basic Approaches to Concept Learning Version Space, Candidate Elimination, Inductive Bias last change October 18,
10. Psychological Disorders & Health
 10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
9/3/2014. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
D. Exclusion of schizoaffective disorder and mood disorder with psychotic features.
 65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Note: See my PinterestBoard for more articles and videos on Psychological Disorders: www.pinterest.com/carmcmurray Psychology 40S C. McMurray Source: PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David
Psychological Disorders Note: See my PinterestBoard for more articles and videos on Psychological Disorders: www.pinterest.com/carmcmurray Psychology 40S C. McMurray Source: PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David
Durham E-Theses. Reasoning biases and delusions. Dudley, Robert Edward James
 Durham E-Theses Reasoning biases and delusions Dudley, Robert Edward James How to cite: Dudley, Robert Edward James (1996) Reasoning biases and delusions, Durham theses, Durham University. Available at
Durham E-Theses Reasoning biases and delusions Dudley, Robert Edward James How to cite: Dudley, Robert Edward James (1996) Reasoning biases and delusions, Durham theses, Durham University. Available at
Schizophrenia and Monothematic Delusions
 Schizophrenia Bulletin vol. 33 no. 3 pp. 642 647, 2007 doi:10.1093/schbul/sbm017 Advance Access publication on March 19, 2007 Schizophrenia and Monothematic Delusions Max Coltheart 1,2, Robyn Langdon 2,3,
Schizophrenia Bulletin vol. 33 no. 3 pp. 642 647, 2007 doi:10.1093/schbul/sbm017 Advance Access publication on March 19, 2007 Schizophrenia and Monothematic Delusions Max Coltheart 1,2, Robyn Langdon 2,3,
6. A theory that has been substantially verified is sometimes called a a. law. b. model.
 Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n) a. a plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world. b. a well-substantiated explanation
Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n) a. a plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world. b. a well-substantiated explanation
Schizophrenia. Delusional disorders are characterized by a persistent belief that is contrary to reality. Why do people stalk?
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Delusional disorders are characterized by a persistent belief that is contrary to reality. There are several subtypes recognized by the DSM IV: - - Grandiose
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Delusional disorders are characterized by a persistent belief that is contrary to reality. There are several subtypes recognized by the DSM IV: - - Grandiose
Autonomy as a Positive Value Some Conceptual Prerequisites Niklas Juth Dept. of Philosophy, Göteborg University
 Philosophical Communications, Web Series, No. 28 Dept. of Philosophy, Göteborg University, Sweden ISSN 1652-0459 Autonomy as a Positive Value Some Conceptual Prerequisites Niklas Juth Dept. of Philosophy,
Philosophical Communications, Web Series, No. 28 Dept. of Philosophy, Göteborg University, Sweden ISSN 1652-0459 Autonomy as a Positive Value Some Conceptual Prerequisites Niklas Juth Dept. of Philosophy,
The cancer of mental illness
 The cancer of mental illness KWL Chart and Hearing Voices Simulations De-brief on activity What is schizophrenia? Recognition of Schizophrenia Symptoms Anderson Cooper Simulation Diagnosis and Treatment
The cancer of mental illness KWL Chart and Hearing Voices Simulations De-brief on activity What is schizophrenia? Recognition of Schizophrenia Symptoms Anderson Cooper Simulation Diagnosis and Treatment
Your experiences. It s all in the brain? Deciphering Neurological Presentations a Perspective From Neuropsychiatry
 Your experiences Deciphering Neurological Presentations a Perspective From Neuropsychiatry Mike Dilley Maudsley Hospital michael.dilley@slam.nhs.uk Think about the last patient that your saw with a neurological
Your experiences Deciphering Neurological Presentations a Perspective From Neuropsychiatry Mike Dilley Maudsley Hospital michael.dilley@slam.nhs.uk Think about the last patient that your saw with a neurological
Chapter 5 - Somatic Symptom, Dissociative, and Factitious Disorders
 Chapter 5 - Somatic Symptom, Dissociative, and Factitious Disorders SOMATIC SYMPTOM AND RELATED DISORDERS -Physical symptoms (eg. pain) or concerns about an illness cannot be explained by a medical or
Chapter 5 - Somatic Symptom, Dissociative, and Factitious Disorders SOMATIC SYMPTOM AND RELATED DISORDERS -Physical symptoms (eg. pain) or concerns about an illness cannot be explained by a medical or
Delusion and Motivationally Biased Belief: Self-Deception in the Two-Factor Framework *
 To appear in T. Bayne and J. Fernandez (eds), Delusions and Self-Deception: Affective Influences on Belief- Formation. Hove, East Sussex: Psychology Press. Delusion and Motivationally Biased Belief: Self-Deception
To appear in T. Bayne and J. Fernandez (eds), Delusions and Self-Deception: Affective Influences on Belief- Formation. Hove, East Sussex: Psychology Press. Delusion and Motivationally Biased Belief: Self-Deception
Final Exam: PSYC 300. Multiple Choice Items (1 point each)
 Final Exam: PSYC 300 Multiple Choice Items (1 point each) 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three fundamental features of science? a. empirical questions b. public knowledge c. mathematical equations
Final Exam: PSYC 300 Multiple Choice Items (1 point each) 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three fundamental features of science? a. empirical questions b. public knowledge c. mathematical equations
The Paranoid Patient: Perils and Pitfalls
 The Paranoid Patient: Perils and Pitfalls Phillip J. Resnick, MD Professor of Psychiatry Case Western Reserve University Director of Forensic Psychiatry University Hospitals Case Medical Center Cleveland,
The Paranoid Patient: Perils and Pitfalls Phillip J. Resnick, MD Professor of Psychiatry Case Western Reserve University Director of Forensic Psychiatry University Hospitals Case Medical Center Cleveland,
PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders
 PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders Chapter 10 Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders Outline/Overview Schizophrenia Statistics/Impact/History Criteria Prognostic indicators/ suicide Epidemiology/correlates
PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders Chapter 10 Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders Outline/Overview Schizophrenia Statistics/Impact/History Criteria Prognostic indicators/ suicide Epidemiology/correlates
Nuplazid. Nuplazid (pimavanserin) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.60.03 Subject: Nuplazid Page: 1 of 4 Last Review Date: June 22, 2018 Nuplazid Description Nuplazid (pimavanserin)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.60.03 Subject: Nuplazid Page: 1 of 4 Last Review Date: June 22, 2018 Nuplazid Description Nuplazid (pimavanserin)
INTERVIEWS II: THEORIES AND TECHNIQUES 5. CLINICAL APPROACH TO INTERVIEWING PART 1
 INTERVIEWS II: THEORIES AND TECHNIQUES 5. CLINICAL APPROACH TO INTERVIEWING PART 1 5.1 Clinical Interviews: Background Information The clinical interview is a technique pioneered by Jean Piaget, in 1975,
INTERVIEWS II: THEORIES AND TECHNIQUES 5. CLINICAL APPROACH TO INTERVIEWING PART 1 5.1 Clinical Interviews: Background Information The clinical interview is a technique pioneered by Jean Piaget, in 1975,
Schizophrenia. Class Objectives. Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia? 12/7/2011. Other psychotic disorders and causes
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Class Objectives What are Delusional Disorders? What causes Schizophrenia? How can Schizophrenia be treated? Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Class Objectives What are Delusional Disorders? What causes Schizophrenia? How can Schizophrenia be treated? Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia?
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents
 Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
COURSE: NURSING RESEARCH CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION
 COURSE: NURSING RESEARCH CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1. TERMINOLOGY 1.1 Research Research is a systematic enquiry about a particular situation for a certain truth. That is: i. It is a search for knowledge
COURSE: NURSING RESEARCH CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1. TERMINOLOGY 1.1 Research Research is a systematic enquiry about a particular situation for a certain truth. That is: i. It is a search for knowledge
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Behavioral Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Behavioral Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS: Behavior - how a person functions or acts in response to
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Behavioral Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS: Behavior - how a person functions or acts in response to
Alzheimer Disease and Related Dementias
 Alzheimer Disease and Related Dementias Defining Generic Key Terms and Concepts Mild cognitive impairment: (MCI) is a state of progressive memory loss after the age of 50 that is beyond what would be expected
Alzheimer Disease and Related Dementias Defining Generic Key Terms and Concepts Mild cognitive impairment: (MCI) is a state of progressive memory loss after the age of 50 that is beyond what would be expected
4. General overview Definition
 4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH (PYC 304-C) Lecture 4
 4. Constructs PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH (PYC 304-C) 4.1 Relationships between constructs Lecture 4 As mentioned in Lecture 3, introversion-extroversion is a construct that is as abstract as anxiety. Here,
4. Constructs PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH (PYC 304-C) 4.1 Relationships between constructs Lecture 4 As mentioned in Lecture 3, introversion-extroversion is a construct that is as abstract as anxiety. Here,
Clinical Study First- and Third-Person Perspectives in Psychotic Disorders and Mood Disorders with Psychotic Features
 Schizophrenia Research and Treatment Volume 2011, Article ID 769136, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/769136 Clinical Study First- and Third-Person Perspectives in Psychotic Disorders and Mood Disorders with Psychotic
Schizophrenia Research and Treatment Volume 2011, Article ID 769136, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/769136 Clinical Study First- and Third-Person Perspectives in Psychotic Disorders and Mood Disorders with Psychotic
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY. Descriptions of Symptoms & Signs. Dr. Janaka Pushpakumara Department of Psychiatry FMAS/RUSL
 PSYCHOPATHOLOGY Descriptions of Symptoms & Signs Dr. Janaka Pushpakumara Department of Psychiatry FMAS/RUSL Symptoms & Signs In General Medicine, there is a clear definition of, and separation between,
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY Descriptions of Symptoms & Signs Dr. Janaka Pushpakumara Department of Psychiatry FMAS/RUSL Symptoms & Signs In General Medicine, there is a clear definition of, and separation between,
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
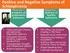 Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Chapter 13
 Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Erotomanic type- central theme of the delusion is that another person is in love with the individual. Grandiose type- central theme of the delusion
 A. Presence of one or more non-bizarre delusions that persist for at least one month B. Diagnosis of Delusional Disorder is not given if person has had symptom presentation that met criterion A for Schizophrenia
A. Presence of one or more non-bizarre delusions that persist for at least one month B. Diagnosis of Delusional Disorder is not given if person has had symptom presentation that met criterion A for Schizophrenia
Eliminative materialism
 Michael Lacewing Eliminative materialism Eliminative materialism (also known as eliminativism) argues that future scientific developments will show that the way we think and talk about the mind is fundamentally
Michael Lacewing Eliminative materialism Eliminative materialism (also known as eliminativism) argues that future scientific developments will show that the way we think and talk about the mind is fundamentally
CSC2130: Empirical Research Methods for Software Engineering
 CSC2130: Empirical Research Methods for Software Engineering Steve Easterbrook sme@cs.toronto.edu www.cs.toronto.edu/~sme/csc2130/ 2004-5 Steve Easterbrook. This presentation is available free for non-commercial
CSC2130: Empirical Research Methods for Software Engineering Steve Easterbrook sme@cs.toronto.edu www.cs.toronto.edu/~sme/csc2130/ 2004-5 Steve Easterbrook. This presentation is available free for non-commercial
Phenomenology and delusions: Who put the alien in alien control?
 Consciousness and Cognition xxx (2006) xxx xxx Consciousness and Cognition www.elsevier.com/locate/concog Phenomenology and delusions: Who put the alien in alien control? Elisabeth Pacherie a, *, Melissa
Consciousness and Cognition xxx (2006) xxx xxx Consciousness and Cognition www.elsevier.com/locate/concog Phenomenology and delusions: Who put the alien in alien control? Elisabeth Pacherie a, *, Melissa
Dr Rikaz Sheriff. Senior Medical Officer, Western Hospital
 Dr Rikaz Sheriff MBBS Senior Medical Officer, Western Hospital Transplant & Employee Counselor PGIM Trainee MSc in Biomedical Informatics PGIM Trainee Certificate in Medical Education Outline Psychological
Dr Rikaz Sheriff MBBS Senior Medical Officer, Western Hospital Transplant & Employee Counselor PGIM Trainee MSc in Biomedical Informatics PGIM Trainee Certificate in Medical Education Outline Psychological
The Erotetic Theory of Delusional Thinking (Forthcoming: Cognitive Neuropsychiatry) Non-citable Draft
 The Erotetic Theory of Delusional Thinking (Forthcoming: Cognitive Neuropsychiatry) Non-citable Draft Dr Matthew Parrott (corresponding author) Department of Philosophy King s College London The Strand
The Erotetic Theory of Delusional Thinking (Forthcoming: Cognitive Neuropsychiatry) Non-citable Draft Dr Matthew Parrott (corresponding author) Department of Philosophy King s College London The Strand
우측전두정엽뇌경색환자에서발생한재생가능성기억착오증 증례보고
 Brain & NeuroRehabilitation Vol. 6, No. 1, March, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.12786/bn.2013.6.1.41 우측전두정엽뇌경색환자에서발생한재생가능성기억착오증 증례보고 고려대학교안암병원재활의학과 최태웅ㆍ편성범 Reduplicative Paramnesia after Right Frontoparietal
Brain & NeuroRehabilitation Vol. 6, No. 1, March, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.12786/bn.2013.6.1.41 우측전두정엽뇌경색환자에서발생한재생가능성기억착오증 증례보고 고려대학교안암병원재활의학과 최태웅ㆍ편성범 Reduplicative Paramnesia after Right Frontoparietal
Audio: In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2
 Psychology 312: Lecture 2 Psychology as a Science Slide #1 Psychology As A Science In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2 Outline Psychology is an empirical science.
Psychology 312: Lecture 2 Psychology as a Science Slide #1 Psychology As A Science In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2 Outline Psychology is an empirical science.
How many speakers? How many tokens?:
 1 NWAV 38- Ottawa, Canada 23/10/09 How many speakers? How many tokens?: A methodological contribution to the study of variation. Jorge Aguilar-Sánchez University of Wisconsin-La Crosse 2 Sample size in
1 NWAV 38- Ottawa, Canada 23/10/09 How many speakers? How many tokens?: A methodological contribution to the study of variation. Jorge Aguilar-Sánchez University of Wisconsin-La Crosse 2 Sample size in
Schizophrenia. Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia? 11/30/2008. Name that Psychotic Disorder! Other psychotic disorders and causes
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Name that Psychotic Disorder! Chris has started spending large amounts of time guarding his home. They have bugged his phone and are sending cars past
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Name that Psychotic Disorder! Chris has started spending large amounts of time guarding his home. They have bugged his phone and are sending cars past
Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia: Treatments
 Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia: Treatments Nowadays we tend to think of the various symptoms of schizophrenia as falling into two groups. There are the positive symptoms such as delusions and hallucinations
Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia: Treatments Nowadays we tend to think of the various symptoms of schizophrenia as falling into two groups. There are the positive symptoms such as delusions and hallucinations
SAMPLE HLTEN510A. Implement and monitor nursing care for consumers with mental health conditions
 TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank HLTEN510A Implement and monitor nursing care for consumers with mental health conditions Version 1.0 Flexible Learning Resource
TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank HLTEN510A Implement and monitor nursing care for consumers with mental health conditions Version 1.0 Flexible Learning Resource
Schizophrenia. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Psychological Disorders. Module 51. Schizophrenia
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Schizophrenia Module 51 2 Psychological Disorders Schizophrenia Symptoms
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Schizophrenia Module 51 2 Psychological Disorders Schizophrenia Symptoms
Child and Adolescent Screening and Assessment Tools
 Child and Adolescent Screening and Assessment Tools Randall Stiles, PhD. State of Nevada Division of Child and Family Services The views, opinions, and content expressed in this presentation do not necessarily
Child and Adolescent Screening and Assessment Tools Randall Stiles, PhD. State of Nevada Division of Child and Family Services The views, opinions, and content expressed in this presentation do not necessarily
AVAILABLE COURSES FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR (GREEK COURSES)
 1 AVAILABLE COURSES FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2017-2018 (GREEK COURSES) FALL SEMESTER Course Code Course Title ECTS credits ΨΥ-324 Neuropsychology I 6 ΨΥ-560 Community Clinical Psychology 5 ΨΥ-564 Intergroup
1 AVAILABLE COURSES FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2017-2018 (GREEK COURSES) FALL SEMESTER Course Code Course Title ECTS credits ΨΥ-324 Neuropsychology I 6 ΨΥ-560 Community Clinical Psychology 5 ΨΥ-564 Intergroup
Rating Mental Impairment with AMA Guides 6 th edition:
 Rating Mental Impairment with AMA Guides 6 th edition: Practical Considerations and Strategies CSME/CAPDA C-CAT Course, March 24, 2018 William H. Gnam, PhD, MD, FRCPC (william.gnam@gmail.com) Consultant
Rating Mental Impairment with AMA Guides 6 th edition: Practical Considerations and Strategies CSME/CAPDA C-CAT Course, March 24, 2018 William H. Gnam, PhD, MD, FRCPC (william.gnam@gmail.com) Consultant
DSM-5 UPDATE FOR THOSE WORKING WITH OLDER ADULTS
 DSM-5 UPDATE FOR THOSE WORKING WITH OLDER ADULTS Ole J. Thienhaus, MD Professor and Chair Department of Psychiatry College of Medicine The University of Arizona, Tucson Learning Objectives: Discuss the
DSM-5 UPDATE FOR THOSE WORKING WITH OLDER ADULTS Ole J. Thienhaus, MD Professor and Chair Department of Psychiatry College of Medicine The University of Arizona, Tucson Learning Objectives: Discuss the
Beliefs about delusions
 FROM TAXI DRIVER.COLUMBIA PICTURES (COURTESY KOBAL) Beliefs about delusions VAUGHAN BELL,PETER HALLIGAN and HADYN ELLIS on the sometimes fine line between normality and abnormality. EARLY in his third
FROM TAXI DRIVER.COLUMBIA PICTURES (COURTESY KOBAL) Beliefs about delusions VAUGHAN BELL,PETER HALLIGAN and HADYN ELLIS on the sometimes fine line between normality and abnormality. EARLY in his third
SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited
 SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 II. A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited agitation), hebephrenia (i.e., silly and immature
SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 II. A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited agitation), hebephrenia (i.e., silly and immature
Psychological Disorders
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 16 Psychological Disorders James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 16 Psychological Disorders James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Concerns with Identity Theory. Eliminative Materialism. Eliminative Materialism. Eliminative Materialism Argument
 Eliminative Materialism Concerns with Identity Theory Churland The main concern with the Identity Theory is not whether a material account of the mental is correct It is thought to be correct The main
Eliminative Materialism Concerns with Identity Theory Churland The main concern with the Identity Theory is not whether a material account of the mental is correct It is thought to be correct The main
Psychotic Disorders. There is a loss of contact with and difficulty in recognizing reality.
 Psychotic Disorders A psychosis or psychotic disorder, involves a major disorganization of thought processes, confused and extreme emotional responses, and distorted perceptions of the world. There is
Psychotic Disorders A psychosis or psychotic disorder, involves a major disorganization of thought processes, confused and extreme emotional responses, and distorted perceptions of the world. There is
