AP STATISTICS 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES
|
|
|
- Patrick Craig
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AP STATISTICS 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess students ability to (1) apply terminology related to designing experiments; (2) construct an appropriate plot that could be used to investigate the fit of a linear model; (3) decide, from a graphical display, whether a linear regression model is appropriate for a set of data. Solution Part (a): i. The treatments are the different concentrations of garlic in the food granules. Specifically, there are five treatments: 0 percent, 2 percent, 10 percent, 25 percent and 50 percent. ii. The experimental units are the birds (starlings), each placed in an individual cage. iii. The response is the number of food granules consumed by the bird. Part (b): i. The following scatterplot results from these data. ii. The curved pattern in this scatterplot reveals that a linear regression model would not be appropriate for modeling the relationship between these variables. Scoring Parts (a) and (b) are scored as essentially correct (E), partially correct (P) or incorrect (I). Part (a) is scored as follows: Essentially correct (E) if the student correctly identifies all three subparts the treatments, the experimental units and the response that will be measured. Partially correct (P) if the student identifies two subparts correctly. Incorrect (I) otherwise The College Board.
2 AP STATISTICS 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 (continued) Notes In subpart ii, it is acceptable to identify the experimental units as the cages. In subpart iii, it is not correct to identify the response as the mean number of granules consumed. Part (b) is scored as follows: Essentially correct (E) if the student produces a correct graph (a reasonable scatterplot or residual plot with correct labels and scales) and then concludes, based on one or more features of the graph, that the pattern of the relationship does not appear to be linear. Partially correct (P) if the student produces a correctly shaped graph but concludes that the data are linear OR if the student produces an incorrectly shaped graph but makes a reasonable conclusion based on one or more features of the graph. Incorrect (I) if the student does not include a graph OR if the student produces an incorrect graph and does not make a reasonable conclusion based on one or more features of the graph. Note: Any of the following will result in an incorrect graph. Incorrect scale Reversed axes Missing label(s) Other types of graph (histogram, bar graph, etc.) 4 Complete Response Both parts essentially correct 3 Substantial Response 2 Developing Response One part essentially correct and one part partially correct OR One part essentially correct and one part incorrect Both parts partially correct 1 Minimal Response One part partially correct and one part incorrect 2010 The College Board.
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 AP STATISTICS 2010 SCORING COMMENTARY Question 1 Overview The primary goals of this question were to assess students ability to (1) apply terminology related to designing experiments; (2) construct an appropriate plot that could be used to investigate the fit of a linear model; (3) decide, from a graphical display, whether a linear regression model is appropriate for a set of data. Sample: 1A Score: 4 In part (a), subpart i, the student correctly lists the five treatments. It should be noted that the parenthetical statement (amount of galic [sic] infused in corn) could be viewed as the factor (or variable) involved in the experiment and, if given alone, would not be a correct response for this component. In part (a), subpart ii, the answer is clear and correct. In part (a), subpart iii, although the student identifies the response that will be measured as the birds adverse reaction rather than the amount eaten, it is acceptable to say that the adverse reaction is measured by the amount eaten. As all three subparts are correct, part (a) was scored as essentially correct. In part (b), subpart i, the student draws a well-labeled and correct scatterplot. In part (b), subpart ii, the response correctly states that the linear model is inappropriate because the data exhibits a more exponential pattern. This first sentence is sufficient to answer this subpart correctly. The second sentence presents a nice argument based on a change in the rate of consumption; this also would have been sufficient to correctly answer this subpart. So there are two parallel solutions to this subpart, and both are correct. As both components of part (b) are correct, it was scored as essentially correct. Both parts (a) and (b) were scored as essentially correct, so the response earned a score of 4. Sample: 1B Score: 3 In part (a), subpart i, the five concentrations of garlic oil is sufficient to correctly answer this component. In part (a), subpart ii, the response identifies the 40 birds as the experimental units, so it is correct. The statement dividing the birds into groups is extraneous. In part (a), subpart iii, the response is clear and correct. As all three subparts are correct, part (a) was scored as essentially correct. In part (b), subpart i, the student draws a residual plot but places the wrong variable along the horizontal axis, so this component was scored as incorrect. In part (b), subpart ii, the response identifies the curved shape of the residual plot and therefore correctly concludes that linear regression is not appropriate. With one of the two subparts correct, part (b) was scored as partially correct. Because part (a) was scored as essentially correct and part (b) was scored as partially correct, the response earned a score of 3. Sample: 1C Score: 2 In part (a), subpart i, the student gives a clear and detailed correct response. In part (a), subpart ii, the student identifies two experimental units, the number of food granules and garlic oil concentration. Neither of these is correct. The statement about the explanatory and response variable was considered extraneous and certainly does not improve the answer. This subpart was scored as incorrect. In part (a), subpart iii, the student correctly identifies the response that will be measured in the first sentence. The statements concerning the hypotheses were considered extraneous. As two of the three subparts are correct, part (a) was scored as partially correct. In part (b), subpart i, the student draws a bar chart, 2010 The College Board.
10 AP STATISTICS 2010 SCORING COMMENTARY Question 1 (continued) making this subpart incorrect. In part (b), subpart ii, the response identifies the curved ( roughly negative exponential ) shape of the data by looking at the top left corner of the bars, essentially treating these positions as points on a scatterplot. This interpretation is reasonable for the given graph, so this response was scored as correct. With one of the two subparts correct, part (b) was scored as partially correct. Because both parts (a) and (b) were scored as partially correct, the response earned a score of The College Board.
AP STATISTICS 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP STATISTICS 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) construct an appropriate graphical display for comparing
AP STATISTICS 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) construct an appropriate graphical display for comparing
CHAPTER 3 Describing Relationships
 CHAPTER 3 Describing Relationships 3.1 Scatterplots and Correlation The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Reading Quiz 3.1 True/False 1.
CHAPTER 3 Describing Relationships 3.1 Scatterplots and Correlation The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Reading Quiz 3.1 True/False 1.
AP STATISTICS 2013 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP STATISTICS 2013 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 5 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) recognize the limited conclusions that can be drawn from
AP STATISTICS 2013 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 5 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) recognize the limited conclusions that can be drawn from
Understandable Statistics
 Understandable Statistics correlated to the Advanced Placement Program Course Description for Statistics Prepared for Alabama CC2 6/2003 2003 Understandable Statistics 2003 correlated to the Advanced Placement
Understandable Statistics correlated to the Advanced Placement Program Course Description for Statistics Prepared for Alabama CC2 6/2003 2003 Understandable Statistics 2003 correlated to the Advanced Placement
Chapter 4: Scatterplots and Correlation
 Chapter 4: Scatterplots and Correlation http://www.yorku.ca/nuri/econ2500/bps6e/ch4-links.pdf Correlation text exr 4.10 pg 108 Ch4-image Ch4 exercises: 4.1, 4.29, 4.39 Most interesting statistical data
Chapter 4: Scatterplots and Correlation http://www.yorku.ca/nuri/econ2500/bps6e/ch4-links.pdf Correlation text exr 4.10 pg 108 Ch4-image Ch4 exercises: 4.1, 4.29, 4.39 Most interesting statistical data
AP STATISTICS 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP STATISTICS 2007 SCING GUIDELINES Question 1 Intent of Question The goals of this question are to assess a student s ability to: (1) explain how a commonly used statistic measures variability; (2) use
AP STATISTICS 2007 SCING GUIDELINES Question 1 Intent of Question The goals of this question are to assess a student s ability to: (1) explain how a commonly used statistic measures variability; (2) use
AP STATISTICS 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES
 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) describe why the median might be preferred to the mean in a particular
2014 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) describe why the median might be preferred to the mean in a particular
7. Bivariate Graphing
 1 7. Bivariate Graphing Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=shzvkwwyguk&index=7&list=pl2fqhgedk7yyl1w9tgio8w pyftdumgc_j Section 7.1: Converting a Quantitative Explanatory Variable to Categorical
1 7. Bivariate Graphing Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=shzvkwwyguk&index=7&list=pl2fqhgedk7yyl1w9tgio8w pyftdumgc_j Section 7.1: Converting a Quantitative Explanatory Variable to Categorical
2011 AP STATISTICS FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS (Form B)
 011 AP STATISTICS FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS (Form B) 5. During a flu vaccine shortage in the United States, it was believed that 45 percent of vaccine-eligible people received flu vaccine. The results of
011 AP STATISTICS FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS (Form B) 5. During a flu vaccine shortage in the United States, it was believed that 45 percent of vaccine-eligible people received flu vaccine. The results of
AP STATISTICS 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP STATISTICS 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 1 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess students ability to (1) compare three distributions of a quantitative variable;
AP STATISTICS 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 1 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess students ability to (1) compare three distributions of a quantitative variable;
AP Statistics Practice Test Ch. 3 and Previous
 AP Statistics Practice Test Ch. 3 and Previous Name Date Use the following to answer questions 1 and 2: A researcher measures the height (in feet) and volume of usable lumber (in cubic feet) of 32 cherry
AP Statistics Practice Test Ch. 3 and Previous Name Date Use the following to answer questions 1 and 2: A researcher measures the height (in feet) and volume of usable lumber (in cubic feet) of 32 cherry
Chapter 3: Describing Relationships
 Chapter 3: Describing Relationships Objectives: Students will: Construct and interpret a scatterplot for a set of bivariate data. Compute and interpret the correlation, r, between two variables. Demonstrate
Chapter 3: Describing Relationships Objectives: Students will: Construct and interpret a scatterplot for a set of bivariate data. Compute and interpret the correlation, r, between two variables. Demonstrate
Student Performance Q&A:
 Student Performance Q&A: 2009 AP Statistics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2009 free-response questions for AP Statistics were written by the Chief Reader, Christine Franklin of
Student Performance Q&A: 2009 AP Statistics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2009 free-response questions for AP Statistics were written by the Chief Reader, Christine Franklin of
Metabolic Biochemistry GST and the Effects of Curcumin Practical: Criterion-Referenced Marking Criteria Rubric
 Metabolic Biochemistry GST and the Effects of Curcumin Practical: Criterion-Referenced Marking Criteria Rubric You will be required to present class data in a laboratory report. In the week following the
Metabolic Biochemistry GST and the Effects of Curcumin Practical: Criterion-Referenced Marking Criteria Rubric You will be required to present class data in a laboratory report. In the week following the
INTERPRET SCATTERPLOTS
 Chapter2 MODELING A BUSINESS 2.1: Interpret Scatterplots 2.2: Linear Regression 2.3: Supply and Demand 2.4: Fixed and Variable Expenses 2.5: Graphs of Expense and Revenue Functions 2.6: Breakeven Analysis
Chapter2 MODELING A BUSINESS 2.1: Interpret Scatterplots 2.2: Linear Regression 2.3: Supply and Demand 2.4: Fixed and Variable Expenses 2.5: Graphs of Expense and Revenue Functions 2.6: Breakeven Analysis
Part 1. For each of the following questions fill-in the blanks. Each question is worth 2 points.
 Part 1. For each of the following questions fill-in the blanks. Each question is worth 2 points. 1. The bell-shaped frequency curve is so common that if a population has this shape, the measurements are
Part 1. For each of the following questions fill-in the blanks. Each question is worth 2 points. 1. The bell-shaped frequency curve is so common that if a population has this shape, the measurements are
AP STATISTICS 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP STATISTICS 2008 SCING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) recognize an unbiased estimator and explain why the
AP STATISTICS 2008 SCING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) recognize an unbiased estimator and explain why the
How Faithful is the Old Faithful? The Practice of Statistics, 5 th Edition 1
 How Faithful is the Old Faithful? The Practice of Statistics, 5 th Edition 1 Who Has Been Eating My Cookies????????? Someone has been steeling the cookie I bought for your class A teacher from the highschool
How Faithful is the Old Faithful? The Practice of Statistics, 5 th Edition 1 Who Has Been Eating My Cookies????????? Someone has been steeling the cookie I bought for your class A teacher from the highschool
Section 3.2 Least-Squares Regression
 Section 3.2 Least-Squares Regression Linear relationships between two quantitative variables are pretty common and easy to understand. Correlation measures the direction and strength of these relationships.
Section 3.2 Least-Squares Regression Linear relationships between two quantitative variables are pretty common and easy to understand. Correlation measures the direction and strength of these relationships.
Paper Airplanes & Scientific Methods
 Paper Airplanes & Scientific Methods Scientific Inquiry refers to the many different ways in which scientists investigate the world. Scientific investigations are done to answer questions and solve problems.
Paper Airplanes & Scientific Methods Scientific Inquiry refers to the many different ways in which scientists investigate the world. Scientific investigations are done to answer questions and solve problems.
How to interpret scientific & statistical graphs
 How to interpret scientific & statistical graphs Theresa A Scott, MS Department of Biostatistics theresa.scott@vanderbilt.edu http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/theresascott 1 A brief introduction Graphics:
How to interpret scientific & statistical graphs Theresa A Scott, MS Department of Biostatistics theresa.scott@vanderbilt.edu http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/theresascott 1 A brief introduction Graphics:
Chapter 3: Examining Relationships
 Name Date Per Key Vocabulary: response variable explanatory variable independent variable dependent variable scatterplot positive association negative association linear correlation r-value regression
Name Date Per Key Vocabulary: response variable explanatory variable independent variable dependent variable scatterplot positive association negative association linear correlation r-value regression
STT 200 Test 1 Green Give your answer in the scantron provided. Each question is worth 2 points.
 STT 200 Test 1 Green Give your answer in the scantron provided. Each question is worth 2 points. For Questions 1 & 2: It is known that the distribution of starting salaries for MSU Education majors has
STT 200 Test 1 Green Give your answer in the scantron provided. Each question is worth 2 points. For Questions 1 & 2: It is known that the distribution of starting salaries for MSU Education majors has
Identify two variables. Classify them as explanatory or response and quantitative or explanatory.
 OLI Module 2 - Examining Relationships Objective Summarize and describe the distribution of a categorical variable in context. Generate and interpret several different graphical displays of the distribution
OLI Module 2 - Examining Relationships Objective Summarize and describe the distribution of a categorical variable in context. Generate and interpret several different graphical displays of the distribution
Midterm STAT-UB.0003 Regression and Forecasting Models. I will not lie, cheat or steal to gain an academic advantage, or tolerate those who do.
 Midterm STAT-UB.0003 Regression and Forecasting Models The exam is closed book and notes, with the following exception: you are allowed to bring one letter-sized page of notes into the exam (front and
Midterm STAT-UB.0003 Regression and Forecasting Models The exam is closed book and notes, with the following exception: you are allowed to bring one letter-sized page of notes into the exam (front and
Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data
 Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data Area Principle Bar Chart Boxplot Conditional Distribution Dotplot Empirical Rule Five Number Summary Frequency Distribution Frequency Polygon Histogram Interquartile
Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data Area Principle Bar Chart Boxplot Conditional Distribution Dotplot Empirical Rule Five Number Summary Frequency Distribution Frequency Polygon Histogram Interquartile
AP STATISTICS 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP STATISTICS 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 4 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) design an experiment to compare two treatments
AP STATISTICS 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 4 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) design an experiment to compare two treatments
M 140 Test 1 A Name SHOW YOUR WORK FOR FULL CREDIT! Problem Max. Points Your Points Total 60
 M 140 Test 1 A Name SHOW YOUR WORK FOR FULL CREDIT! Problem Max. Points Your Points 1-10 10 11 3 12 4 13 3 14 10 15 14 16 10 17 7 18 4 19 4 Total 60 Multiple choice questions (1 point each) For questions
M 140 Test 1 A Name SHOW YOUR WORK FOR FULL CREDIT! Problem Max. Points Your Points 1-10 10 11 3 12 4 13 3 14 10 15 14 16 10 17 7 18 4 19 4 Total 60 Multiple choice questions (1 point each) For questions
Lesson 9 Presentation and Display of Quantitative Data
 Lesson 9 Presentation and Display of Quantitative Data Learning Objectives All students will identify and present data using appropriate graphs, charts and tables. All students should be able to justify
Lesson 9 Presentation and Display of Quantitative Data Learning Objectives All students will identify and present data using appropriate graphs, charts and tables. All students should be able to justify
8.SP.1 Hand span and height
 8.SP.1 Hand span and height Task Do taller people tend to have bigger hands? To investigate this question, each student in your class should measure his or her hand span (in cm) and height (in inches).
8.SP.1 Hand span and height Task Do taller people tend to have bigger hands? To investigate this question, each student in your class should measure his or her hand span (in cm) and height (in inches).
AP STATISTICS 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP STATISTICS 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 6 Intent of Question The primary goals of this investigative task were to assess students ability to (1) evaluate whether a double-blind randomized
AP STATISTICS 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 6 Intent of Question The primary goals of this investigative task were to assess students ability to (1) evaluate whether a double-blind randomized
Choosing a Significance Test. Student Resource Sheet
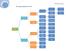 Choosing a Significance Test Student Resource Sheet Choosing Your Test Choosing an appropriate type of significance test is a very important consideration in analyzing data. If an inappropriate test is
Choosing a Significance Test Student Resource Sheet Choosing Your Test Choosing an appropriate type of significance test is a very important consideration in analyzing data. If an inappropriate test is
Lauren DiBiase, MS, CIC Associate Director Public Health Epidemiologist Hospital Epidemiology UNC Hospitals
 Lauren DiBiase, MS, CIC Associate Director Public Health Epidemiologist Hospital Epidemiology UNC Hospitals Statistics Numbers that describe the health of the population The science used to interpret these
Lauren DiBiase, MS, CIC Associate Director Public Health Epidemiologist Hospital Epidemiology UNC Hospitals Statistics Numbers that describe the health of the population The science used to interpret these
AP Statistics. Semester One Review Part 1 Chapters 1-5
 AP Statistics Semester One Review Part 1 Chapters 1-5 AP Statistics Topics Describing Data Producing Data Probability Statistical Inference Describing Data Ch 1: Describing Data: Graphically and Numerically
AP Statistics Semester One Review Part 1 Chapters 1-5 AP Statistics Topics Describing Data Producing Data Probability Statistical Inference Describing Data Ch 1: Describing Data: Graphically and Numerically
Data and Statistics 101: Key Concepts in the Collection, Analysis, and Application of Child Welfare Data
 TECHNICAL REPORT Data and Statistics 101: Key Concepts in the Collection, Analysis, and Application of Child Welfare Data CONTENTS Executive Summary...1 Introduction...2 Overview of Data Analysis Concepts...2
TECHNICAL REPORT Data and Statistics 101: Key Concepts in the Collection, Analysis, and Application of Child Welfare Data CONTENTS Executive Summary...1 Introduction...2 Overview of Data Analysis Concepts...2
Stat 13, Lab 11-12, Correlation and Regression Analysis
 Stat 13, Lab 11-12, Correlation and Regression Analysis Part I: Before Class Objective: This lab will give you practice exploring the relationship between two variables by using correlation, linear regression
Stat 13, Lab 11-12, Correlation and Regression Analysis Part I: Before Class Objective: This lab will give you practice exploring the relationship between two variables by using correlation, linear regression
Chapter 1: Exploring Data
 Chapter 1: Exploring Data Key Vocabulary:! individual! variable! frequency table! relative frequency table! distribution! pie chart! bar graph! two-way table! marginal distributions! conditional distributions!
Chapter 1: Exploring Data Key Vocabulary:! individual! variable! frequency table! relative frequency table! distribution! pie chart! bar graph! two-way table! marginal distributions! conditional distributions!
Preliminary Report on Simple Statistical Tests (t-tests and bivariate correlations)
 Preliminary Report on Simple Statistical Tests (t-tests and bivariate correlations) After receiving my comments on the preliminary reports of your datasets, the next step for the groups is to complete
Preliminary Report on Simple Statistical Tests (t-tests and bivariate correlations) After receiving my comments on the preliminary reports of your datasets, the next step for the groups is to complete
12.1 Inference for Linear Regression. Introduction
 12.1 Inference for Linear Regression vocab examples Introduction Many people believe that students learn better if they sit closer to the front of the classroom. Does sitting closer cause higher achievement,
12.1 Inference for Linear Regression vocab examples Introduction Many people believe that students learn better if they sit closer to the front of the classroom. Does sitting closer cause higher achievement,
Statistics and Probability
 Statistics and a single count or measurement variable. S.ID.1: Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms, and box plots). S.ID.2: Use statistics appropriate to the shape
Statistics and a single count or measurement variable. S.ID.1: Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms, and box plots). S.ID.2: Use statistics appropriate to the shape
Pitfalls in Linear Regression Analysis
 Pitfalls in Linear Regression Analysis Due to the widespread availability of spreadsheet and statistical software for disposal, many of us do not really have a good understanding of how to use regression
Pitfalls in Linear Regression Analysis Due to the widespread availability of spreadsheet and statistical software for disposal, many of us do not really have a good understanding of how to use regression
UNIT 1CP LAB 1 - Spaghetti Bridge
 Name Date Pd UNIT 1CP LAB 1 - Spaghetti Bridge The basis of this physics class is the ability to design an experiment to determine the relationship between two quantities and to interpret and apply the
Name Date Pd UNIT 1CP LAB 1 - Spaghetti Bridge The basis of this physics class is the ability to design an experiment to determine the relationship between two quantities and to interpret and apply the
STP 231 Example FINAL
 STP 231 Example FINAL Instructor: Ela Jackiewicz Honor Statement: I have neither given nor received information regarding this exam, and I will not do so until all exams have been graded and returned.
STP 231 Example FINAL Instructor: Ela Jackiewicz Honor Statement: I have neither given nor received information regarding this exam, and I will not do so until all exams have been graded and returned.
AP STATISTICS 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 5
 AP STATISTICS 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 5 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question are to assess a student s ability to: (1) identify the response variable, treatments, and
AP STATISTICS 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 5 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question are to assess a student s ability to: (1) identify the response variable, treatments, and
STATISTICS & PROBABILITY
 STATISTICS & PROBABILITY LAWRENCE HIGH SCHOOL STATISTICS & PROBABILITY CURRICULUM MAP 2015-2016 Quarter 1 Unit 1 Collecting Data and Drawing Conclusions Unit 2 Summarizing Data Quarter 2 Unit 3 Randomness
STATISTICS & PROBABILITY LAWRENCE HIGH SCHOOL STATISTICS & PROBABILITY CURRICULUM MAP 2015-2016 Quarter 1 Unit 1 Collecting Data and Drawing Conclusions Unit 2 Summarizing Data Quarter 2 Unit 3 Randomness
STATS Relationships between variables: Correlation
 STATS 1060 Relationships between variables: Correlation READINGS: Chapter 7 of your text book (DeVeaux, Vellman and Bock); on-line notes for correlation; on-line practice problems for correlation NOTICE:
STATS 1060 Relationships between variables: Correlation READINGS: Chapter 7 of your text book (DeVeaux, Vellman and Bock); on-line notes for correlation; on-line practice problems for correlation NOTICE:
The graph should contain 5 major parts: the title, the independent variable, the dependent variable, the scales for each variable, and a legend.
 BLIZZARD BAG #2 Please complete the activity below. You will need to print out this activity sheet (pages 2-5 only) OR Write out the answers on a separate piece of paper and graph on a piece of graphing
BLIZZARD BAG #2 Please complete the activity below. You will need to print out this activity sheet (pages 2-5 only) OR Write out the answers on a separate piece of paper and graph on a piece of graphing
Psychology 2015 Scoring Guidelines
 AP Psychology 2015 Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
AP Psychology 2015 Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
Reminders/Comments. Thanks for the quick feedback I ll try to put HW up on Saturday and I ll you
 Reminders/Comments Thanks for the quick feedback I ll try to put HW up on Saturday and I ll email you Final project will be assigned in the last week of class You ll have that week to do it Participation
Reminders/Comments Thanks for the quick feedback I ll try to put HW up on Saturday and I ll email you Final project will be assigned in the last week of class You ll have that week to do it Participation
STATISTICS INFORMED DECISIONS USING DATA
 STATISTICS INFORMED DECISIONS USING DATA Fifth Edition Chapter 4 Describing the Relation between Two Variables 4.1 Scatter Diagrams and Correlation Learning Objectives 1. Draw and interpret scatter diagrams
STATISTICS INFORMED DECISIONS USING DATA Fifth Edition Chapter 4 Describing the Relation between Two Variables 4.1 Scatter Diagrams and Correlation Learning Objectives 1. Draw and interpret scatter diagrams
Year Area Grade 1/2 Grade 3/4 Grade 5/6 Grade 7+ K&U Recognises basic features of. Uses simple models to explain objects, living things or events.
 Assessment Criteria: Science Year 7 (page 1 of 2) K&U Recognises basic features of Uses simple models to explain objects, living things or events. scientific ideas. Makes a comment about scientific Represents
Assessment Criteria: Science Year 7 (page 1 of 2) K&U Recognises basic features of Uses simple models to explain objects, living things or events. scientific ideas. Makes a comment about scientific Represents
Data Analysis, Statistics & Probability - ANSWER KEY DAY 1
 Data Analysis, Statistics & Probability - ANSWER KEY DAY 1 D 1. Dish, vanilla ice cream Sugar cone, vanilla ice cream Regular cone, vanilla ice cream 4. Dish, chocolate ice cream 5. Sugar cone, chocolate
Data Analysis, Statistics & Probability - ANSWER KEY DAY 1 D 1. Dish, vanilla ice cream Sugar cone, vanilla ice cream Regular cone, vanilla ice cream 4. Dish, chocolate ice cream 5. Sugar cone, chocolate
A response variable is a variable that. An explanatory variable is a variable that.
 Name:!!!! Date: Scatterplots The most common way to display the relation between two quantitative variable is a scatterplot. Statistical studies often try to show through scatterplots, that changing one
Name:!!!! Date: Scatterplots The most common way to display the relation between two quantitative variable is a scatterplot. Statistical studies often try to show through scatterplots, that changing one
Unit 7 Comparisons and Relationships
 Unit 7 Comparisons and Relationships Objectives: To understand the distinction between making a comparison and describing a relationship To select appropriate graphical displays for making comparisons
Unit 7 Comparisons and Relationships Objectives: To understand the distinction between making a comparison and describing a relationship To select appropriate graphical displays for making comparisons
Lesson 1: Distributions and Their Shapes
 Lesson 1 Name Date Lesson 1: Distributions and Their Shapes 1. Sam said that a typical flight delay for the sixty BigAir flights was approximately one hour. Do you agree? Why or why not? 2. Sam said that
Lesson 1 Name Date Lesson 1: Distributions and Their Shapes 1. Sam said that a typical flight delay for the sixty BigAir flights was approximately one hour. Do you agree? Why or why not? 2. Sam said that
Regression Discontinuity Design
 Regression Discontinuity Design Regression Discontinuity Design Units are assigned to conditions based on a cutoff score on a measured covariate, For example, employees who exceed a cutoff for absenteeism
Regression Discontinuity Design Regression Discontinuity Design Units are assigned to conditions based on a cutoff score on a measured covariate, For example, employees who exceed a cutoff for absenteeism
Data Analysis with SPSS
 Data Analysis with SPSS A First Course in Applied Statistics Fourth Edition Stephen Sweet Ithaca College Karen Grace-Martin The Analysis Factor Allyn & Bacon Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco
Data Analysis with SPSS A First Course in Applied Statistics Fourth Edition Stephen Sweet Ithaca College Karen Grace-Martin The Analysis Factor Allyn & Bacon Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco
Section 1.2 Displaying Quantitative Data with Graphs. Dotplots
 Section 1.2 Displaying Quantitative Data with Graphs Dotplots One of the simplest graphs to construct and interpret is a dotplot. Each data value is shown as a dot above its location on a number line.
Section 1.2 Displaying Quantitative Data with Graphs Dotplots One of the simplest graphs to construct and interpret is a dotplot. Each data value is shown as a dot above its location on a number line.
This means that the explanatory variable accounts for or predicts changes in the response variable.
 Lecture Notes & Examples 3.1 Section 3.1 Scatterplots and Correlation (pp. 143-163) Most statistical studies examine data on more than one variable. We will continue to use tools we have already learned
Lecture Notes & Examples 3.1 Section 3.1 Scatterplots and Correlation (pp. 143-163) Most statistical studies examine data on more than one variable. We will continue to use tools we have already learned
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables.
 bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
AQA A Level Psychology
 UNIT ASSESSMENT AQA A Level Psychology Unit Assessment Research Methods Year 1 (Edition 1) h 1 hour h The maximum mark for this unit assessment is 48 Name Centre Name AQA A Level Psychology Unit Assessment
UNIT ASSESSMENT AQA A Level Psychology Unit Assessment Research Methods Year 1 (Edition 1) h 1 hour h The maximum mark for this unit assessment is 48 Name Centre Name AQA A Level Psychology Unit Assessment
Unit 1 Outline Science Practices. Part 1 - The Scientific Method. Screencasts found at: sciencepeek.com. 1. List the steps of the scientific method.
 Screencasts found at: sciencepeek.com Part 1 - The Scientific Method 1. List the steps of the scientific method. 2. What is an observation? Give an example. Quantitative or Qualitative Data? 35 grams?
Screencasts found at: sciencepeek.com Part 1 - The Scientific Method 1. List the steps of the scientific method. 2. What is an observation? Give an example. Quantitative or Qualitative Data? 35 grams?
Inferential Statistics
 Inferential Statistics and t - tests ScWk 242 Session 9 Slides Inferential Statistics Ø Inferential statistics are used to test hypotheses about the relationship between the independent and the dependent
Inferential Statistics and t - tests ScWk 242 Session 9 Slides Inferential Statistics Ø Inferential statistics are used to test hypotheses about the relationship between the independent and the dependent
AP Stats Chap 27 Inferences for Regression
 AP Stats Chap 27 Inferences for Regression Finally, we re interested in examining how slopes of regression lines vary from sample to sample. Each sample will have it s own slope, b 1. These are all estimates
AP Stats Chap 27 Inferences for Regression Finally, we re interested in examining how slopes of regression lines vary from sample to sample. Each sample will have it s own slope, b 1. These are all estimates
Statistical Methods and Reasoning for the Clinical Sciences
 Statistical Methods and Reasoning for the Clinical Sciences Evidence-Based Practice Eiki B. Satake, PhD Contents Preface Introduction to Evidence-Based Statistics: Philosophical Foundation and Preliminaries
Statistical Methods and Reasoning for the Clinical Sciences Evidence-Based Practice Eiki B. Satake, PhD Contents Preface Introduction to Evidence-Based Statistics: Philosophical Foundation and Preliminaries
MATH 2560 C F03 Elementary Statistics I LECTURE 6: Scatterplots (Continuation).
 MATH 2560 C F03 Elementary Statistics I LECTURE 6: Scatterplots (Continuation). 1 Outline. adding categorical variables to scatterplots; more examples of scatterplots; categorical explanatory variables;
MATH 2560 C F03 Elementary Statistics I LECTURE 6: Scatterplots (Continuation). 1 Outline. adding categorical variables to scatterplots; more examples of scatterplots; categorical explanatory variables;
Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Physics Level 1
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource 1.1B Physics for Achievement Standard 90935 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Physics Level 1 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Exemplar for internal assessment resource 1.1B Physics for Achievement Standard 90935 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Physics Level 1 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
IAPT: Regression. Regression analyses
 Regression analyses IAPT: Regression Regression is the rather strange name given to a set of methods for predicting one variable from another. The data shown in Table 1 and come from a student project
Regression analyses IAPT: Regression Regression is the rather strange name given to a set of methods for predicting one variable from another. The data shown in Table 1 and come from a student project
3.2 Least- Squares Regression
 3.2 Least- Squares Regression Linear (straight- line) relationships between two quantitative variables are pretty common and easy to understand. Correlation measures the direction and strength of these
3.2 Least- Squares Regression Linear (straight- line) relationships between two quantitative variables are pretty common and easy to understand. Correlation measures the direction and strength of these
Lesson 1 Understanding Science
 Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Content Vocabulary 6 Lesson Outline 7 Content Practice A 9 Content Practice B 10 School to Home 11 Key Concept Builders 12 Enrichment 16 Challenge 17 Scientific
Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Content Vocabulary 6 Lesson Outline 7 Content Practice A 9 Content Practice B 10 School to Home 11 Key Concept Builders 12 Enrichment 16 Challenge 17 Scientific
Table of Contents. Plots. Essential Statistics for Nursing Research 1/12/2017
 Essential Statistics for Nursing Research Kristen Carlin, MPH Seattle Nursing Research Workshop January 30, 2017 Table of Contents Plots Descriptive statistics Sample size/power Correlations Hypothesis
Essential Statistics for Nursing Research Kristen Carlin, MPH Seattle Nursing Research Workshop January 30, 2017 Table of Contents Plots Descriptive statistics Sample size/power Correlations Hypothesis
Table 1: One Year Net Survival Rates for All Cancers Excluding Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer:
 Task 1: Draw a bar chart of the following data. All the data must be on one graph. The data shows yearly survival rates for all types of cancers combined (except non-melanoma skin cancer). Hint: Each period
Task 1: Draw a bar chart of the following data. All the data must be on one graph. The data shows yearly survival rates for all types of cancers combined (except non-melanoma skin cancer). Hint: Each period
Appendix B Statistical Methods
 Appendix B Statistical Methods Figure B. Graphing data. (a) The raw data are tallied into a frequency distribution. (b) The same data are portrayed in a bar graph called a histogram. (c) A frequency polygon
Appendix B Statistical Methods Figure B. Graphing data. (a) The raw data are tallied into a frequency distribution. (b) The same data are portrayed in a bar graph called a histogram. (c) A frequency polygon
Math 075 Activities and Worksheets Book 2:
 Math 075 Activities and Worksheets Book 2: Linear Regression Name: 1 Scatterplots Intro to Correlation Represent two numerical variables on a scatterplot and informally describe how the data points are
Math 075 Activities and Worksheets Book 2: Linear Regression Name: 1 Scatterplots Intro to Correlation Represent two numerical variables on a scatterplot and informally describe how the data points are
Homework #3. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Homework #3 Name Due Due on on February Tuesday, Due on February 17th, Sept Friday 28th 17th, Friday SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Fill
Homework #3 Name Due Due on on February Tuesday, Due on February 17th, Sept Friday 28th 17th, Friday SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Fill
3.2A Least-Squares Regression
 3.2A Least-Squares Regression Linear (straight-line) relationships between two quantitative variables are pretty common and easy to understand. Our instinct when looking at a scatterplot of data is to
3.2A Least-Squares Regression Linear (straight-line) relationships between two quantitative variables are pretty common and easy to understand. Our instinct when looking at a scatterplot of data is to
Lab 4 (M13) Objective: This lab will give you more practice exploring the shape of data, and in particular in breaking the data into two groups.
 Lab 4 (M13) Objective: This lab will give you more practice exploring the shape of data, and in particular in breaking the data into two groups. Activity 1 Examining Data From Class Background Download
Lab 4 (M13) Objective: This lab will give you more practice exploring the shape of data, and in particular in breaking the data into two groups. Activity 1 Examining Data From Class Background Download
5 To Invest or not to Invest? That is the Question.
 5 To Invest or not to Invest? That is the Question. Before starting this lab, you should be familiar with these terms: response y (or dependent) and explanatory x (or independent) variables; slope and
5 To Invest or not to Invest? That is the Question. Before starting this lab, you should be familiar with these terms: response y (or dependent) and explanatory x (or independent) variables; slope and
Big Idea 1 The Practice of Science. Big Idea 2 The Characteristics of Scientific Knowledge
 Big Idea 1 The Practice of Science Big Idea 2 The Characteristics of Scientific Knowledge SC.5.N.1.2 Explain the difference between an experiment and other types of scientific investigation SC.5.N.1.5
Big Idea 1 The Practice of Science Big Idea 2 The Characteristics of Scientific Knowledge SC.5.N.1.2 Explain the difference between an experiment and other types of scientific investigation SC.5.N.1.5
HW 3.2: page 193 #35-51 odd, 55, odd, 69, 71-78
 35. What s My Line? You use the same bar of soap to shower each morning. The bar weighs 80 grams when it is new. Its weight goes down by 6 grams per day on average. What is the equation of the regression
35. What s My Line? You use the same bar of soap to shower each morning. The bar weighs 80 grams when it is new. Its weight goes down by 6 grams per day on average. What is the equation of the regression
Caffeine & Calories in Soda. Statistics. Anthony W Dick
 1 Caffeine & Calories in Soda Statistics Anthony W Dick 2 Caffeine & Calories in Soda Description of Experiment Does the caffeine content in soda have anything to do with the calories? This is the question
1 Caffeine & Calories in Soda Statistics Anthony W Dick 2 Caffeine & Calories in Soda Description of Experiment Does the caffeine content in soda have anything to do with the calories? This is the question
Relationships Between the High Impact Indicators and Other Indicators
 Relationships Between the High Impact Indicators and Other Indicators The High Impact Indicators are a list of key skills assessed on the GED test that, if emphasized in instruction, can help instructors
Relationships Between the High Impact Indicators and Other Indicators The High Impact Indicators are a list of key skills assessed on the GED test that, if emphasized in instruction, can help instructors
Chapter 1: Explaining Behavior
 Chapter 1: Explaining Behavior GOAL OF SCIENCE is to generate explanations for various puzzling natural phenomenon. - Generate general laws of behavior (psychology) RESEARCH: principle method for acquiring
Chapter 1: Explaining Behavior GOAL OF SCIENCE is to generate explanations for various puzzling natural phenomenon. - Generate general laws of behavior (psychology) RESEARCH: principle method for acquiring
FSA Training Papers Grade 7 Exemplars. Rationales
 FSA Training Papers Grade 7 Exemplars Rationales Rationales for Grade 7 Exemplars Reading Grade 7 Reading Exemplar #1: Score 3 Comprehension of the passages and task clearly evident Generally purposeful
FSA Training Papers Grade 7 Exemplars Rationales Rationales for Grade 7 Exemplars Reading Grade 7 Reading Exemplar #1: Score 3 Comprehension of the passages and task clearly evident Generally purposeful
An Introduction to Statistical Thinking Dan Schafer Table of Contents
 An Introduction to Statistical Thinking Dan Schafer Table of Contents PART I: CONCLUSIONS AND THEIR UNCERTAINTY NUMERICAL AND ELEMENTS OF Chapter1 Statistics as a Branch of Human Reasoning Chapter 2 What
An Introduction to Statistical Thinking Dan Schafer Table of Contents PART I: CONCLUSIONS AND THEIR UNCERTAINTY NUMERICAL AND ELEMENTS OF Chapter1 Statistics as a Branch of Human Reasoning Chapter 2 What
A) I only B) II only C) III only D) II and III only E) I, II, and III
 AP Statistics Review Chapters 13, 3, 4 Your Name: Per: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Write the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1.* The Physicians Health Study, a large medical experiment involving 22,000 male
AP Statistics Review Chapters 13, 3, 4 Your Name: Per: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Write the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1.* The Physicians Health Study, a large medical experiment involving 22,000 male
Outline. Practice. Confounding Variables. Discuss. Observational Studies vs Experiments. Observational Studies vs Experiments
 1 2 Outline Finish sampling slides from Tuesday. Study design what do you do with the subjects/units once you select them? (OI Sections 1.4-1.5) Observational studies vs. experiments Descriptive statistics
1 2 Outline Finish sampling slides from Tuesday. Study design what do you do with the subjects/units once you select them? (OI Sections 1.4-1.5) Observational studies vs. experiments Descriptive statistics
WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics. What is Statistics and how does it relate to you?
 WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics Time Interval/ Unit 1: Introduction to Statistics 1.1-1.3 2 weeks S-IC-1: Understand statistics as a process for making inferences about population parameters
WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics Time Interval/ Unit 1: Introduction to Statistics 1.1-1.3 2 weeks S-IC-1: Understand statistics as a process for making inferences about population parameters
Business Statistics Probability
 Business Statistics The following was provided by Dr. Suzanne Delaney, and is a comprehensive review of Business Statistics. The workshop instructor will provide relevant examples during the Skills Assessment
Business Statistics The following was provided by Dr. Suzanne Delaney, and is a comprehensive review of Business Statistics. The workshop instructor will provide relevant examples during the Skills Assessment
14.1: Inference about the Model
 14.1: Inference about the Model! When a scatterplot shows a linear relationship between an explanatory x and a response y, we can use the LSRL fitted to the data to predict a y for a given x. However,
14.1: Inference about the Model! When a scatterplot shows a linear relationship between an explanatory x and a response y, we can use the LSRL fitted to the data to predict a y for a given x. However,
AP Stats Review for Midterm
 AP Stats Review for Midterm NAME: Format: 10% of final grade. There will be 20 multiple-choice questions and 3 free response questions. The multiple-choice questions will be worth 2 points each and the
AP Stats Review for Midterm NAME: Format: 10% of final grade. There will be 20 multiple-choice questions and 3 free response questions. The multiple-choice questions will be worth 2 points each and the
Chapter 14. Inference for Regression Inference about the Model 14.1 Testing the Relationship Signi!cance Test Practice
 Chapter 14 Inference for Regression Our!nal topic of the year involves inference for the regression model. In Chapter 3 we learned how to!nd the Least Squares Regression Line for a set of bivariate data.
Chapter 14 Inference for Regression Our!nal topic of the year involves inference for the regression model. In Chapter 3 we learned how to!nd the Least Squares Regression Line for a set of bivariate data.
Chapter 4. Navigating. Analysis. Data. through. Exploring Bivariate Data. Navigations Series. Grades 6 8. Important Mathematical Ideas.
 Navigations Series Navigating through Analysis Data Grades 6 8 Chapter 4 Exploring Bivariate Data Important Mathematical Ideas Copyright 2009 by the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics, Inc. www.nctm.org.
Navigations Series Navigating through Analysis Data Grades 6 8 Chapter 4 Exploring Bivariate Data Important Mathematical Ideas Copyright 2009 by the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics, Inc. www.nctm.org.
Eating and Sleeping Habits of Different Countries
 9.2 Analyzing Scatter Plots Now that we know how to draw scatter plots, we need to know how to interpret them. A scatter plot graph can give us lots of important information about how data sets are related
9.2 Analyzing Scatter Plots Now that we know how to draw scatter plots, we need to know how to interpret them. A scatter plot graph can give us lots of important information about how data sets are related
Measuring the User Experience
 Measuring the User Experience Collecting, Analyzing, and Presenting Usability Metrics Chapter 2 Background Tom Tullis and Bill Albert Morgan Kaufmann, 2008 ISBN 978-0123735584 Introduction Purpose Provide
Measuring the User Experience Collecting, Analyzing, and Presenting Usability Metrics Chapter 2 Background Tom Tullis and Bill Albert Morgan Kaufmann, 2008 ISBN 978-0123735584 Introduction Purpose Provide
LAB ASSIGNMENT 4 INFERENCES FOR NUMERICAL DATA. Comparison of Cancer Survival*
 LAB ASSIGNMENT 4 1 INFERENCES FOR NUMERICAL DATA In this lab assignment, you will analyze the data from a study to compare survival times of patients of both genders with different primary cancers. First,
LAB ASSIGNMENT 4 1 INFERENCES FOR NUMERICAL DATA In this lab assignment, you will analyze the data from a study to compare survival times of patients of both genders with different primary cancers. First,
Chapter 7: Descriptive Statistics
 Chapter Overview Chapter 7 provides an introduction to basic strategies for describing groups statistically. Statistical concepts around normal distributions are discussed. The statistical procedures of
Chapter Overview Chapter 7 provides an introduction to basic strategies for describing groups statistically. Statistical concepts around normal distributions are discussed. The statistical procedures of
3. For a $5 lunch with a 55 cent ($0.55) tip, what is the value of the residual?
 STATISTICS 216, SPRING 2006 Name: EXAM 1; February 21, 2006; 100 points. Instructions: Closed book. Closed notes. Calculator allowed. Double-sided exam. NO CELL PHONES. Multiple Choice (3pts each). Circle
STATISTICS 216, SPRING 2006 Name: EXAM 1; February 21, 2006; 100 points. Instructions: Closed book. Closed notes. Calculator allowed. Double-sided exam. NO CELL PHONES. Multiple Choice (3pts each). Circle
1. The figure below shows the lengths in centimetres of fish found in the net of a small trawler.
 Bivariate Data 1 IB MATHEMATICS SL Topic: Bivariate Data NAME: DATE: 1. The figure below shows the lengths in centimetres of fish found in the net of a small trawler. Number of fish 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3
Bivariate Data 1 IB MATHEMATICS SL Topic: Bivariate Data NAME: DATE: 1. The figure below shows the lengths in centimetres of fish found in the net of a small trawler. Number of fish 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3
TITLE. Author name Author address (school address) INTRODUCTION
 SCIENTIFIC WRITING Dr. Craig 5/5/12 Skillful scientific writing involves using precise, concise language. Use primarily the first person and active voice (e.g. I conducted the trials, not the trials were
SCIENTIFIC WRITING Dr. Craig 5/5/12 Skillful scientific writing involves using precise, concise language. Use primarily the first person and active voice (e.g. I conducted the trials, not the trials were
