Unit 2 Brain & Behavior
|
|
|
- Leonard O’Connor’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 2 Brain & Behavior
2 Brain & Behavior Unit Guide REV 2017 Essential Questions: Why is studying biology important to understanding psychology? Which brain structures are necessary for survival? What are the functions of the cerebral cortex and its lobes? How has split-brain research helped us understand the functions of each brain hemisphere? How does biology play a role in behavior? 5-2 Brainstem, medulla, reticular formation, cerebellum, limbic system, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala 5-3 Cerebral cortex, corpus callosum, frontal lobes, parietal lobes, occipital lobes, temporal lobes, motor cortex, somatosensory (sensory) cortex, plasticity 5-4 Broca s area, Wernicke s area
3 BRAIN GAMES QUIZ 1. How do shadows affect our perception of color? Name: 2. Describe the rubber hand illusion. 3. Why were people wearing special body suits in the video? 4. When asked to count the number of f s in a sentence, why might people get the wrong answer?
4
5 Broccoli Lab You will be exploring the main parts of the Central Nervous System in this activity. In order to perform this lab you need the following items: 1 Broccoli Bunch 1 White Gummy 1 Red Gummy 1 Green Gummy 1 Gummy Worm 3 Toothpicks Your textbook Use your textbook and answer the questions. Then, follow the directions for labeling your broccoli. 1. What are the 2 Parts of the Central Nervous System? 2. What 2 things does the Medulla control? 3. Where is the Medulla located? Label the Medulla on your broccoli stem by using the white gummy and a toothpick. 4. What 2 functions does the Cerebellum control? 5. Where is the Cerebellum located? 6. What problems does a person experience if the Cerebellum is damaged? Label the Cerebellum on your broccoli stem using the red gummy and a toothpick. 7. Where is the Thalamus located? Label the Thalamus with your green gummy.
6 8. What does the Thalamus control? 9. What does the Reticular Formation control? 10. Where is the Reticular Formation located? Label the Reticular Formation with your gummy worm. 11. The lower part of the brain is the first part to develop. Why do you think this part of the brain develops first?
7 Grapefruit Lab Now it s time to move to the Cerebral Cortex and Cerebral Hemispheres. The Cerebral Hemisphere is divided into 4 lobes: the Frontal Lobe, Parietal Lobe, Temporal Lobe, and Occipital Lobe. In order to perform this lab you need the following items: 1 Grapefruit 2 Orange / Clear Gummies 2 Yellow Gummies 1 gummy worm 2 Red Gummies 2 Green Gummies 8 Toothpicks 1 Piece of Wax Paper Use your textbook to answer the following questions. Then, follow the directions to label your grapefruit. 1. What is the job of the Cerebral Cortex? Expose your Cerebral Cortex by removing the outer layer of your grapefruit. Please be sure to keep your ingredients on the wax paper. Now, separate the grapefruit in 2 equal sections(1/2) approximately 2/3 of the way down the grapefruit. Be careful that the lower 1/3 of the grapefruit is still intact. o You have just created the 2 Cerebral Hemispheres. The left hemisphere and the right hemisphere are mirror images of each other and yet they have separate functions. Place the gummy worm at the base of where the left and right hemispheres meet. This is the Corpus Callosum. 2. What job does the Corpus Callosum have in a whole brain individual? 3. What is the function of the Occipital Lobe? 4. What occurs if this lobe is damaged? The lobe at the very back of the Left and Right Hemispheres is called the Occipital Lobe. Label each side of this Lobe with the orange gummies and 2 toothpicks. Remember that the Left Hemisphere and Right Hemisphere are mirrored images of each other, so you have 2 Occipital Lobes 1 in the Left Hemisphere and 1 in the Right Hemisphere.
8 5. What is the function of the Temporal Lobe? The lobe in front of the Occipital Lobe and on the sides of the brain is the Temporal Lobe. Label the Temporal Lobe in each hemisphere with the yellow gummies and 2 toothpicks. 6. What is the function of the Parietal Lobe? The Parietal Lobe sits on top of the Temporal and Occipital Lobes in each hemisphere. Label the Parietal Lobes with the red gummies and 2 toothpicks. 7. What are the jobs of the Frontal Lobe? The largest part of the human brain just behind the forehead is the Frontal Lobe. Label the Frontal Lobe in each hemisphere with the green gummies and 2 toothpicks. 8. Who was Phineas Gage? Why is he important to our study of the brain? 9. What is the function of the Motor Cortex? 10. What is the function of the Sensory Cortex? 11. What is the function of the Broca s Area? 12. What is the function of the Wernicke s Area? 13. Teens don t have fully developed frontal lobes. Using evidence from your own life, explain why this is true.
9 Brain Injury Review Activity Metea psychology students were on their way to the zoo for a field trip. In the excitement to get there 1 st and hear the animal trainers talk, all the buses got into a fender-bender outside the school. Everyone survived the crash, but many students had minor injuries. Using the description of each person s symptoms, determine the probable location(s) of the damage and explain their function(s). 1. Katie had problems coordinating her movement and keeping her balance. Area of Damage Function 2. David lost the ability to move his right arm. 3. Lauren and Toni suffered from an impaired ability to plan, and make good judgments. 4. Sara often kept falling asleep at odd times and in odd places. 5. Jeremy and Drew seemed to always be hungry and their temperatures ran high. 6. Danielle suffered from an inability to form new memories. 7. Tyler and Hayden both often flew into a rage and started picking fights with each other.
10 8. Natalie could no longer respond to her teacher because she didn t understand what she was asking. Area of Damage Function 9. Sammy s speech was choppy, slow, and a grammatical mess. 10. Amanda experienced irregularities in heartbeat and respiration rates.
11 Test Yourself! Are you right-brained or left-brained? In each item, different styles of learning or thinking are described. Circle the letter that best describes your strength or preference. 1. a. Not good at remembering faces. b. Not good at remembering names. c. Equally good at remembering names and faces. 2. a. Respond best to verbal instructions. b. Respond best to instruction by example. c. Equally responsive to verbal instruction and instruction by example. 3. a. Able to express feelings and emotions freely. b. Not easily able to express feelings and emotions. 4. a. Prefer classes where I have one assignment at a time. b. Prefer classes where I am studying many things at once. c. I have equal preference for the above type classes. 5. a. Preference for multiple-choice tests. b. Preference for essay tests. c. Equal preference for multiple-choice, essay tests. 6. a. Good at thinking up funny things to say and/or do. b. Poor at thinking up funny things to say and/or do. c. Moderately good at thinking up funny things to say and/or do. 7. a. Prefer classes in which I am moving and doing things. b. Prefer classes in which I listen to others. c. Equal preference for above type classes. 8. a. Use factual, objective information in making judgments. b. Use personal experiences and feelings in making judgments. c. Make equal use of factual information and personal experiences. 9. a. Almost always use whatever tools are available to get work done. b. At times am able to use whatever is available to get work done. c. Prefer working with proper materials for use they are intended for. 10. a. Like classes or work to be planned, know exactly what I am to do. b. Like classes or work to be open-ended, allowing for different interpretations. c. Equal preferences for classes or work to be planned or open-ended. 11. a. Very inventive. b. Occasionally inventive. c. Never inventive. 12. a. Preference for intuitive approach in solving problems. b. Preference for logical approach in solving problems. c. Equal preference for intuitive, logical approaches.
12 13. a. Like classes where the work has clear and immediate applications (such as mechanical drawing, shop, home economics). b. Like classes where the work does not have a clearly practical application (such as literature, algebra, history). c. Equal preference for both types of classes. 14. a. Responsive to emotional appeals. b. Responsive to emotional and verbal appeals. 15. a. Think best when lying flat on back. b. Think best while sitting upright. 16. a. Preference for solving problems logically. b. Preference for solving problems through experience. c. Equal preference for using logic, experience in problem-solving. 17. a. Skilled in giving verbal explanations. b. Skilled in showing by movement and action. c. Equally able to explain verbally and through actions. 18. a. Learn best from teaching that uses verbal explanation. b. Learn best from teaching that uses visual presentation. c. Equal preferences for verbal explanation, visual presentation. 19. a. Easily lost even in familiar surroundings. b. Easily find directions even in strange surroundings. c. Moderately skilled in finding directions. 20. a. Like to be in noisy place where lots of things are happening. b. Like to be where I can concentrate on one activity to my best ability. c. Sometimes like both of the above, have no preference. 21. a. Prefer to learn details and specific facts. b. Prefer a general overview of a subject, looking at the whole picture. c. Prefer overview intermixed with specific facts and details. Are You Right-Brained or Left-Brained? Count up how many "R"'s, "L"'s, and "I"'s you have. The letter with the highest number is your answer! R = RIGHT BRAIN, L = LEFT BRAIN, I = BOTH SIDES OF BRAIN ARE INTERACTIVE 1. A=L, B=R, C=I 2. A=L, B=R, C=I 3. A=R, B=L 4. A=L, B=R, C=I 5. A=R, B=L, C=I 6. A=R, B=L, C=I 7. A=R, B=L, C=I 8. A=L, B=R, C=I KEY 9. A=R, B=I, C=L 10. A=L, B=R, C=I 11. A=R, B=I, C=L 12. A=R, B=L, C=I 13. A=R, B=L, C=I 14. A=R, B=L 15. A=R, B=L 16. A=L, B=R, C=I 17. A=L, B=R, C=I 18. A=L, B=R, C=I 19. A=L, B=R, C=I 20. A=R, B=L, C=I 21. A=L, B=R, C=I
13 Gabby Giffords 20/20 Video Guide 1. What percent of people with brain injuries survive? Name 2. Why did doctors remove part of Gabby s skull? 3. What was Gaby s first word? 4. Why was music easier for Gabby than speaking? 5. What does Gabby remember about the day of the shooting? 6. What does the future hold for Gabby s recovery? 7. Describe the 2 things that were most meaningful to you from this video & explain WHY
14 LEAGUE OF DENIAL: THE NFL S CONCUSSION CRISIS 1. In what ways was former Pittsburgh Steeler Mike Webster s body affected by his time playing in the NFL? What was initially surprising about his brain at his autopsy? 2. How did family members and others who knew Mike describe his personality and behavior after his injuries? 3. What are some concerns sports agents and doctors share about the NFL s focus on a tough guy image in such a violent game? 4. How did the NFL respond to the pack journalism concerns about brain trauma? 5. In your opinion, how important is it for high schools and colleges to keep track of concussions for student athletes? Does this inhibit their growth as athletes, or is this an appropriate protection? Explain.
15 A BRAINTASTIC PROJECT For this project you may work either with one partner or by yourself. You may use your textbook as a resource, but the goal of this assignment is to describe the functions of the brain structures IN YOUR OWN WORDS. For this reason, no outside sources may be used. Objective: As a new children s book author, you are to write an original story about the brain using 12 of the brain structures listed below. Your story should be entertaining, yet also educational. It should not be written as a textbook, but rather as a story about the brain (ie. The Adventures of Billy s Brain). 1. You Choose: You may create any of the following: -Recreate a children s book -Create a pop-up book -Create a comic strip 2. Define: Your story must also include the function of those 12 brain structures-- Incorporate the definition INTO the story it should not be in definition format. Medulla Occipital Lobe Cerebral Cortex Hypothalamus Frontal Lobe Wernicke s Area Temporal Lobe Corpus Callosum Left Hemisphere Parietal Lobe Hippocampus Right Hemisphere Sensory Cortex Motor Cortex Cerebellum Reticular Formation Amygdala Broca s Area 1. You may ONLY include illustrations (NOT clipart)! --- Though you may trace. 2. For full credit be sure to highlight the structures within your story. Remember that you must include the functions in your project! REQUIREMENTS BRAINTASTIC Rubric DUE DATE: ACCURACY of 12 structures & functions utilized /24 FOR ALL PROJECTS: CREATIVITY, NEATNESS, ENTHUSIASM Total /30 pts /6 Please type a list of the 12 brain structures you included in your project in the order they appear!
16 BRAIN BOOK EXCHANGE BOOK 1 TITLE: AUTHORS: BOOK 2 TITLE: AUTHORS: Briefly describe the plot of the story: Briefly describe the plot of the story: Score the number of brain parts that are accurately used: Are any of the parts possibly not being used appropriately based on their function: Score the number of brain parts that are accurately used: Are any of the parts possibly not being used appropriately based on their function: Which character was your favorite/will help you remember the function of that part of the brain the best? Which character was your favorite/will help you remember the function of that part of the brain the best?
Unit 2 The Brain, Biology & Sleep
 Unit 2 The Brain, Biology & Sleep Brain, Biology, & Sleep Unit Guide MV AP Psych 2017-18 Essential Questions What are the subdivisions and structures of the nervous system? How did they evolve and what
Unit 2 The Brain, Biology & Sleep Brain, Biology, & Sleep Unit Guide MV AP Psych 2017-18 Essential Questions What are the subdivisions and structures of the nervous system? How did they evolve and what
Unit 2 The Brain, Biology and Sleep
 Unit 2 The Brain, Biology and Sleep PONS The Pons portion of the brain lying above the medulla and below the cerebellum and the cavity of the fourth ventricle. The pons is a broad, horseshoe-shaped mass
Unit 2 The Brain, Biology and Sleep PONS The Pons portion of the brain lying above the medulla and below the cerebellum and the cavity of the fourth ventricle. The pons is a broad, horseshoe-shaped mass
Brain Structures. Some scientists divide the brain up into three parts. Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain
 The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1
 Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Unit 2 The Brain, Biology & Sleep
 Unit 2 The Brain, Biology & Sleep Brain, Biology, & Sleep Unit Guide Essential Questions What are the subdivisions and structures of the nervous system? How did they evolve and what are their functions?
Unit 2 The Brain, Biology & Sleep Brain, Biology, & Sleep Unit Guide Essential Questions What are the subdivisions and structures of the nervous system? How did they evolve and what are their functions?
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Forebrain Brain Structures Limbic System. Brain Stem Midbrain Basil Ganglia. Cerebellum Reticular Formation Medulla oblongata
 Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
AP Psychology Exam Review. The Brain. Brain Mnemonics by Michael Britt
 AP Psychology Exam Review The Brain Brain Mnemonics by Michael Britt www.thepsychfiles.com Figure 2.2, p. 67 Pons - regulates waking and relaxing. Put a d in pons and you have ponds. Ponds are relaxing
AP Psychology Exam Review The Brain Brain Mnemonics by Michael Britt www.thepsychfiles.com Figure 2.2, p. 67 Pons - regulates waking and relaxing. Put a d in pons and you have ponds. Ponds are relaxing
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system:
 Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER
 BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Biology Partnership (A Teacher Quality Grant) Lesson Plan Construction Form
 Biology Partnership (A Teacher Quality Grant) Lesson Plan Construction Form Identifying Information: (Group Members and Schools, Title of Lesson, Length in Minutes, Course Level) Group Members: Marilyn
Biology Partnership (A Teacher Quality Grant) Lesson Plan Construction Form Identifying Information: (Group Members and Schools, Title of Lesson, Length in Minutes, Course Level) Group Members: Marilyn
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Activity Overview. A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity 1A. The Brain: It s All In Your Mind
 A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity Objectives: Using diagrams of the brain, students will be able to: Observe the basic anatomy of the brain and its components Identify the parts
A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity Objectives: Using diagrams of the brain, students will be able to: Observe the basic anatomy of the brain and its components Identify the parts
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Chapter 2 Test. 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. *a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain e.
 Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Explainer: This is your brain
 Explainer: This is your brain By The Conversation, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.24.17 Word Count 803 TOP: There are many different parts of the brain with their own specific function. There are times
Explainer: This is your brain By The Conversation, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.24.17 Word Count 803 TOP: There are many different parts of the brain with their own specific function. There are times
Learning Objectives.
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
CNS Tour (Lecture 12)
 A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
Lesson Plan in Brief What To Know What To Do What To Say
 Lesson Plan Leader s Guide Lesson Plan in Brief What To Know What To Do What To Say Children and parents need to know about alcohol and its effects to make good decisions about drinking. They need to
Lesson Plan Leader s Guide Lesson Plan in Brief What To Know What To Do What To Say Children and parents need to know about alcohol and its effects to make good decisions about drinking. They need to
Hemispheric Specialization (lateralization) Each lobe of the brain has specialized functions (Have to be careful with this one.)
 Cerebral Cortex Principles contralaterality the right half of your brain controls the left half of your body and vice versa. (contralateral control.) Localization of function Specific mental processes
Cerebral Cortex Principles contralaterality the right half of your brain controls the left half of your body and vice versa. (contralateral control.) Localization of function Specific mental processes
Lab 12 Nervous System II
 Lab 12 Nervous System II Laboratory Objectives Identify the structural components of the central nervous system Label the functional areas of human cerebral cortex. Given a deficit affecting one or more
Lab 12 Nervous System II Laboratory Objectives Identify the structural components of the central nervous system Label the functional areas of human cerebral cortex. Given a deficit affecting one or more
Neocortex. Hemispheres 9/22/2010. Psychology 472 Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs. Structures are divided into several section or lobes.
 Neocortex Psychology 472 Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs 1 Is the most developed in Humans Has many folds and fissures The folds of tissue are called gyri or a gyrus (single) The fissures or valleys
Neocortex Psychology 472 Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs 1 Is the most developed in Humans Has many folds and fissures The folds of tissue are called gyri or a gyrus (single) The fissures or valleys
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Disorders affecting region: depression anxiety
 Amygdala Involved in learning, and the processing of emotional memories. Measures sensory input for potential threat level, then hypothalamus Regulates volatile emotions like fear and anger. Disorders
Amygdala Involved in learning, and the processing of emotional memories. Measures sensory input for potential threat level, then hypothalamus Regulates volatile emotions like fear and anger. Disorders
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System
 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Prof. Greg Francis 5/23/08
 Brain parts The brain IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Greg Francis Lecture 02 The source of cognition (consider transplant!) Weighs about 3 pounds Damage to some parts result in immediate death or disability
Brain parts The brain IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Greg Francis Lecture 02 The source of cognition (consider transplant!) Weighs about 3 pounds Damage to some parts result in immediate death or disability
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version
 Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD? People with ADHD have brains that may function a little differently in some
Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD? People with ADHD have brains that may function a little differently in some
The Brain Puzzle. A set of the brain coloured sections puzzle pieces for each pair/small group
 34 The Brain Puzzle ITEMS REQUIRED A set of the brain coloured sections puzzle pieces for each pair/small group BRAIN PUZZLE INSTRUCTIONS Put the coloured brain section pieces together to form the correct
34 The Brain Puzzle ITEMS REQUIRED A set of the brain coloured sections puzzle pieces for each pair/small group BRAIN PUZZLE INSTRUCTIONS Put the coloured brain section pieces together to form the correct
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
[RG online edits added ; updated ] Unit 3: The Nervous System. Introduction
![[RG online edits added ; updated ] Unit 3: The Nervous System. Introduction [RG online edits added ; updated ] Unit 3: The Nervous System. Introduction](/thumbs/79/79754305.jpg) [RG online edits added 6-23-04; updated 6-30-04] Unit 3: The Nervous System Introduction Everything you do, everything you feel, every thought that you have, every sensation that you experience, involves
[RG online edits added 6-23-04; updated 6-30-04] Unit 3: The Nervous System Introduction Everything you do, everything you feel, every thought that you have, every sensation that you experience, involves
Chapter 14, Part 2! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial Nerves! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
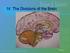 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Higher Cortical Function
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13
 Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
3/20/13. :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
PSY 215 Lecture 17 (3/28/2010) (Lateralization in the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215
 PSY 215 Lecture 17 Topic: Lateralization in the Brain Chapter 14.1, pages 403-414 Corrections: Lecture 16 (page 4) Broca s Area: trouble producing language, comprehension is okay. Announcements: Review
PSY 215 Lecture 17 Topic: Lateralization in the Brain Chapter 14.1, pages 403-414 Corrections: Lecture 16 (page 4) Broca s Area: trouble producing language, comprehension is okay. Announcements: Review
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
The Nervous System. Two Systems Within a System. 526 Chapter 17
 1 The Nervous System Key Concept Your nervous system is an organ system that gathers, interprets, and responds to sensory information. What You Will Learn The central nervous system processes and responds
1 The Nervous System Key Concept Your nervous system is an organ system that gathers, interprets, and responds to sensory information. What You Will Learn The central nervous system processes and responds
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT: HELPING ALL CHILDREN DO AND BE THEIR BEST. February 9, :30 8:00 p.m. (Delicious Dinner First!)
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT: HELPING ALL CHILDREN DO AND BE THEIR BEST February 9, 2012 5:30 8:00 p.m. (Delicious Dinner First!) Most annoying thing about learning about the brainmom was right! Everything we talk
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT: HELPING ALL CHILDREN DO AND BE THEIR BEST February 9, 2012 5:30 8:00 p.m. (Delicious Dinner First!) Most annoying thing about learning about the brainmom was right! Everything we talk
Module 1 An Introduction to the Brain and Nervous System
 Module 1 An Introduction to the Brain and Nervous System Overview Summary This introductory module of the Brain Power! Challenge Program is designed to help students learn about the parts of the brain,
Module 1 An Introduction to the Brain and Nervous System Overview Summary This introductory module of the Brain Power! Challenge Program is designed to help students learn about the parts of the brain,
Test Bank. Multiple Choice
 Chapter 2: The Brain: An Overview of Structure and Function Test Bank Multiple Choice 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain Answer
Chapter 2: The Brain: An Overview of Structure and Function Test Bank Multiple Choice 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain Answer
Seniors Helping Seniors September 7 & 12, 2016 Amy Abrams, MSW/MPH Education & Outreach Manager Alzheimer s San Diego
 Dementia Skills for In-Home Care Providers Seniors Helping Seniors September 7 & 12, 2016 Amy Abrams, MSW/MPH Education & Outreach Manager Alzheimer s San Diego Objectives Familiarity with the most common
Dementia Skills for In-Home Care Providers Seniors Helping Seniors September 7 & 12, 2016 Amy Abrams, MSW/MPH Education & Outreach Manager Alzheimer s San Diego Objectives Familiarity with the most common
SECTION 1: as each other, or as me. THE BRAIN AND DEMENTIA. C. Boden *
 I read all the available books by other [people with] Alzheimer s disease but they never had quite the same problems as each other, or as me. I t s not like other diseases, where there is a standard set
I read all the available books by other [people with] Alzheimer s disease but they never had quite the same problems as each other, or as me. I t s not like other diseases, where there is a standard set
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE
 THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
CEREBRUM. Dr. Jamila EL Medany
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: The Brain Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most obvious difference between the human brain and the brain of a carp
Name: The Brain Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most obvious difference between the human brain and the brain of a carp
Brain-Behavior Network. Central Nervous System. Cerebral Cortex Gyrus and Sulcus. Nervous System
 Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
The brain and behaviour
 The brain and behaviour Alzheimer's disease is a degenerative condition associated with a progressive loss of nerve cells or neurons. The disease gradually pervades most areas of the brain. However, the
The brain and behaviour Alzheimer's disease is a degenerative condition associated with a progressive loss of nerve cells or neurons. The disease gradually pervades most areas of the brain. However, the
P O D C A S T Transcript. Dr. Gary Small. Author of 2 Weeks to a Younger Brain
 P O D C A S T Transcript Dr. Gary Small Author of 2 Weeks to a Younger Brain Dr. Small, what is your first memory of being interested in the subject of memory? Well, I think I got interested in it when
P O D C A S T Transcript Dr. Gary Small Author of 2 Weeks to a Younger Brain Dr. Small, what is your first memory of being interested in the subject of memory? Well, I think I got interested in it when
A Healthy Brain. An Injured Brain
 A Healthy Brain Before we can understand what happens when a brain is injured, we must realize what a healthy brain is made of and what it does. The brain is enclosed inside the skull. The skull acts as
A Healthy Brain Before we can understand what happens when a brain is injured, we must realize what a healthy brain is made of and what it does. The brain is enclosed inside the skull. The skull acts as
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Nervous System and Special Senses HEALTH SCIENCE
 Nervous System and Special Senses HEALTH SCIENCE Bellwork!! What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-time-test/ State Standards 8) Outline
Nervous System and Special Senses HEALTH SCIENCE Bellwork!! What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-time-test/ State Standards 8) Outline
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
The New Normal: Understanding Family and Individual Dynamics Following Brain Injury. Deborah Gutteridge, MS, CBIST Clinical Evaluator
 The New Normal: Understanding Family and Individual Dynamics Following Brain Injury Deborah Gutteridge, MS, CBIST Clinical Evaluator The Most Challenging Issue. for survivors for families for professionals
The New Normal: Understanding Family and Individual Dynamics Following Brain Injury Deborah Gutteridge, MS, CBIST Clinical Evaluator The Most Challenging Issue. for survivors for families for professionals
MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU
 If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following
If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following
How We Grow & Change
 How We Grow & Change Neural Development What makes up nerves? Neurons! (single cells) Interesting Facts About Neurons: Average brain has approx 100 billion neurons and we only use 10% (10 billion neurons)!
How We Grow & Change Neural Development What makes up nerves? Neurons! (single cells) Interesting Facts About Neurons: Average brain has approx 100 billion neurons and we only use 10% (10 billion neurons)!
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Specific Sulci/Fissures:
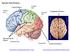 Specific Sulci/Fissures: Central Sulcus Longitudinal Fissure Sylvian/Lateral Fissure Transverse Fissure http://www.bioon.com/book/biology/whole/image/1/1-8.tif.jpg http://www.dalbsoutss.eq.edu.au/sheepbrains_me/human_brain.gif
Specific Sulci/Fissures: Central Sulcus Longitudinal Fissure Sylvian/Lateral Fissure Transverse Fissure http://www.bioon.com/book/biology/whole/image/1/1-8.tif.jpg http://www.dalbsoutss.eq.edu.au/sheepbrains_me/human_brain.gif
Lesson #2: My Amore: My Amygdala
 Lesson #2: My Amore: My Amygdala Objectives 1. Students will be able to identify the function of the amygdala and hippocampus in the limbic system. 2. Students will be able to identify the roles and tasks
Lesson #2: My Amore: My Amygdala Objectives 1. Students will be able to identify the function of the amygdala and hippocampus in the limbic system. 2. Students will be able to identify the roles and tasks
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology
 Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System
 Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
 Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Autism, my sibling, and me
 ORGANIZATION FOR AUTISM RESEARCH Autism, my sibling, and me Brothers and sisters come in all shapes and sizes. They have a lot in common, and they can be really different from each other. Some kids even
ORGANIZATION FOR AUTISM RESEARCH Autism, my sibling, and me Brothers and sisters come in all shapes and sizes. They have a lot in common, and they can be really different from each other. Some kids even
Ant. Bite-size Science
 Bite-size Science Trying new things can be hard. When you play a new sport, you have to learn and remember a whole new set of rules. When you try new food, you may end up not liking it (and you may even
Bite-size Science Trying new things can be hard. When you play a new sport, you have to learn and remember a whole new set of rules. When you try new food, you may end up not liking it (and you may even
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
NCFE Level 2 Certificate in The Principles of Dementia Care
 The Principles of Dementia Care S A M P LE NCFE Level 2 Certificate in The Principles of Dementia Care Part A 1 These learning resources and assessment questions have been approved and endorsed by ncfe
The Principles of Dementia Care S A M P LE NCFE Level 2 Certificate in The Principles of Dementia Care Part A 1 These learning resources and assessment questions have been approved and endorsed by ncfe
Composed of gray matter and arranged in raised ridges (gyri), grooves (sulci), depressions (fissures).
 PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
IT S ALL IN YOUR MIND
 An Elementary Brain Hat Activity Activity 1G: Atop Your Head Grades 4 & 5 ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION In this activity, you will make a brain hat as you learn about the brain. You will discuss the location and
An Elementary Brain Hat Activity Activity 1G: Atop Your Head Grades 4 & 5 ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION In this activity, you will make a brain hat as you learn about the brain. You will discuss the location and
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
BIOL Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain
 BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
