THE ANALYSIS OF PECULIARITIES OF PERSONAL ANXIETY EXPERIENCED BY PROFESSIONALS OF SOCIOEDUCATIONAL ACTIVITIES OF LITHUANIA
|
|
|
- Richard Sims
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE ANALYSIS OF PECULIARITIES OF PERSONAL ANXIETY EXPERIENCED BY PROFESSIONALS OF SOCIOEDUCATIONAL ACTIVITIES OF LITHUANIA Trauksmainības īpatnību analīze sociālpedagoģiskajā darbībā Lietuvā Daiva Alifanovienė, Asta Vaitkevičienė Šiauliai University, Lithuania Abstract. The article analyses the peculiarities of the anxiety state of professionals of socioeducational activities (social pedagogues and social workers). Employing Spielberger s and Chanin s personal anxiety scale, the level of personal anxiety was identified, and, using a semi-structured interview, situations provoking anxiety experienced by professionals of socioeducational activities were identified. Data of anxiety experienced by social pedagogues and social workers in 2011 were analysed employing the factor analysis method of multidimensional statistics, the data of the semi-structured interview were processed using the content analysis method. It was identified that about half of the respondents experienced a moderate level of personal anxiety, enabling to mobilise, look for innovative solutions in professional activities. Severe level of personal anxiety was identified for slightly less than half of respondents; it was perceived as dangerous and preventing professionals of socioeducational activities from successful development of professional activities and even warning about possible psychosomatic disorders. Keywords: anxiety, state of anxiety, personal anxiety, professionals of socioeducational activities. Introduction The man often experiences the states of stress and anxiety. According to Izard s (1999) differential emotions theory, anxiety is a combination of several emotions (fear, interest-excitement, guilt, sadness-pain, shame, anger, etc. (The Dictionary of Psychology, 1993). Beck (2005) states that slight restlessness mobilises the man s powers for activity. Continuous anxiety can turn into the feature of a personality restlessness (Izard, 1999, Beck, 2005). Strongly experienced anxiety distorts the perception of reality: flexibility of thinking, will, conscious behaviour control are weakening. Therefore, strongly experienced anxiety can also carry out the destroying function of the person s interaction with the environment. Spielberger, Chanin (2004) differentiate three levels of restlessness. In their opinion, restlessness can be differentiated into mild, moderate and severe. Mild restlessness requires to focus on the activity, its motives and develop the sense of responsibility. Sometimes mild restlessness shows displacement of severe anxiety, which aims to show oneself from the better side (Spielberger, Chanin qtd. in Райгородский, 2004, p.59-63). 11
2 Moderate restlessness is useful because it promotes the process of adaptation, ensuring the person s holistic functioning. Significant deviation from moderate restlessness makes people give thought because severe restlessness shows that in situations, in which the person s competence is evaluated, he/she is inclined to experience anxiety. Seeking to avoid the destroying impact of severe restlessness, it should be necessary to reduce the subjective significance of the situation for a person, transfer attention to consideration of his/her the activity and form self-confidence. Severe personal anxiety is treated as harmful for health, whilst WHO (WHO, 2006) points out that the employee s health should be analysed on the basis of holistic (biopsychosocial) health model (Gustainienė, Pranskevičienė, 2010, p. 137); it should include social, psychological and behavioural factors, which can influence health, become the reasons of suffering, disability and incapacity to work. The analysis of the anxiety state is not a frequent research subject among Lithuanian researchers. School related anxiety of learners is slightly more often analysed (Aramavičiūtė, 2004; Martišauskienė, 2004; Tulickas, Zambacevičienė, 2004; Dagienė, 2006; Nasvytienė, Balnionytė, 2006; Starkuvienė, 2006; Milušauskienė, Zambacevičienė, Dapkevičienė, 2008; Kepalaitė, 2011 et al.) as well as its reasons than anxiety experienced by other social groups. There are also searches for links between anxiety and depression (Germanavičius, 2006; Stanionytė, 2008; Gelumbauskienė, 2009;) or researches on episodic anxiety related to quality of life (Balevičiūtė, 2007; Balsevičius, 2010). Researches on experiencing anxiety in professional activities are also quite rare and solitary (Alifanovienė, Vaitkevičienė, 2007; Alifanovienė, Vaitkevičienė, Lučinskaitė 2011, Kepalaitė, 2011; Loikienė, 2007; Ţydţiūnaitė, Bubnys, Maţuolytė, Mikelskienė, 2009). Research subject: peculiarities of anxiety experienced by professionals of socioeducational activities (social pedagogues and social workers) in professional activities. Research aim: to analyse peculiarities of personal anxiety experienced professionals of socioeducational activities (social pedagogues and social workers). Research objectives: To establish the internal consistency coefficient of Spielberger s, Chanin s personal anxiety scale. To identify levels of anxiety experienced by professionals of socioeducational activities. To identify evaluations of respondents self-feeling, having experienced anxiety. Research methods: a questionnaire using a two-part instrument: the first part contains seven questions to find out demographic data and the second, Spielberger s, Chanin s self-assessment scales with questions representing personal anxiety. To analyse quantitative research data, statistical methods were used (descriptive mathematical statistics: frequencies (N), percentages (%), means (M), 12
3 multi-dimensional statistics (factor analysis). During the qualitative in-depth semistructured interview (according to different diagnostic areas) the respondents approach to the situations arousing anxiety, to impact of anxiety on professional activities and self-feeling was analysed. Participants of the survey (respondents). The qualitative survey was attended by 6 respondents, the quantitative, by 113 respondents social pedagogues and social workers working in different Lithuanian educational, treatment and child care institutions. There were 108 women and 5 men, the average age of the respondents was 37,7. The respondents were selected using targeted selection, this was determined by the research aim. The main selection criteria were social pedagogue s, social worker s professional qualifications. Peculiarities of Anxiety Experienced by Professionals of Socioeducational Activities The experienced state of personal anxiety reflects the person s self-feeling, which has formed and is characteristic to the person regardless of the existing impact of social environment. Personal anxiety is perceived as a person s constant inclination to perceive many life situations as dangerous, react to such situations by the state of anxiety. Very severe personal anxiety directly correlates with the existence of neurotic conflict, emotional explosions and psychosomatic illnesses (Raigorodskij, 1998). The structure of variables of personal anxiety consists of 15 statements. Factorisation of these statements was sufficiently meaningful; it enabled to discover the structure of the investigated phenomenon. These 15 statements were generalised by three factor models (other variables of personal anxiety were rejected due to too low weight of test items (L)) (see Table 1). The results disclosed three factors: strongly expressed excitement and emotional sensitivity, the feeling of satisfaction and happiness, passiveness and lack of self-confidence, encompassing from 3 to 9 statements. Fluctuation limits of correlation coefficient values (0,26 r 0,70) witness that obtained correlations of scores of empirical statements with distinguished factors were quite high. Descriptive power (dispersion) of factors fluctuates between 10,33 per cent and 17,3 per cent. Suitability of the matrix for factor analysis is proved by Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) coefficient which is high (0,73). Internal consistency of solitary factors, evaluated using Cronbach s alpha coefficient, fluctuates from 0,49 to 0,81; therefore, all factors are sufficiently homogenous. The first factor discloses that respondents are often characterised by strongly expressed excitement and emotional sensitivity (M = 2,23). Comparing these data with the model of reactive anxiety factors, a certain paradox is noticed: the model of reactive anxiety factors discloses that strong psychic tension is not characteristic to respondents, and the model of personal anxiety factors witnesses that respondents confess that they often experience excitement and despair. This can be explained only by the respondents good perception of the task. Feeling safe and 13
4 Name of the factor Initial statements Weight of the test item, L Item to total correlation, r/itt KMO Cronbach s α Descriptive dispersion of the factor, % ISSN calm at the present moment, they both gave corresponding answers to the statements of the reactive anxiety scale and adequately evaluated the dominating personal state, noting statements of the personal anxiety scale. Table 1 Factor Analysis Data of Social Pedagogues and Social Workers Reactive Anxiety Scale Strongly expressed excitement and emotional sensitivity (M = 2,23) Feeling of satisfaction and happiness (M = 2,83) Passiveness and lack of selfconfidence (M = 1,86) I am too nervous about trivia 0,636 0,65 I am usually very worried about expected difficulties 0,541 0,48 I take too much to heart 0,530 0,52 I am overwhelmed with strong excitement when I think about my matters and 0,519 0,52 worries I experience despair so long, I can t forget it for a long time 0,501 0,58 I start crying easily 0,498 0,42 I would like to be as happy as others 0,484 0,31 All kinds of trivia distract and affect me 0,478 0,51 I often lose because I make decisions insufficiently 0,305 0,34 quickly I am happy 0,866 0,70 I am satisfied 0,792 0,69 I feel satisfaction 0,606 0,57 Melancholy is characteristic to me 0,670 0,37 I lack self-confidence 0,470 0,30 I get tired very quickly 0,324 0, ,73 0,79 17,13 0,81 12, 34 0,49 10,33 The second factor again as of contradicts the first because it indicates the existence of specialists feeling of satisfaction and happiness (M = 2,83). Passiveness and lack of self-confidence is the weakest of the obtained factors but anyway it indicates that this feature is characteristic to specialists.
5 To sum up the model of personal anxiety, it can be stated that social pedagogues and social workers experience contradictory feelings in their professional activities. However, evaluating specialists reactive and personal anxiety, more attention should be focused on the values of personal anxiety because they are the reflection of dominating self-feeling and not a onetime evaluation of the situation. Peculiarities of respondents experienced personal anxiety are represented by the diagram given below (Figure 1) Mild anxiety Moderate anxiety Severe anxiety Figure 1. Peculiarities of Personal Anxiety Experienced by Professionals of Socioeducational Activities (N=113) The research on the personal anxiety state demonstrates that the share of respondents who experience mild personal anxiety is not large. Mild level of anxiety requires to focus on the motives of activity and increase the feeling of responsibility (Raigorodskij, 1998). Therefore, it could be concluded that a very small share of social pedagogues and social workers lack motivation in their professional activities. Optimal; i.e., moderate personal anxiety is experienced by about 50 % of respondents. The moderate level of anxiety helps to look for novelties, move on, encourages a personality to function and develop. Severe level of personal anxiety is reached by about 40 per cent of respondents. Severe personal anxiety level is the most dangerous. It warns about the danger impendent to the specialists eventually to experience neurosis and psychosomatic disorders. Vaitkevičius (1995) has noticed that social pedagogues, social workers have to be able to cope with bigger nervous-psychic loads, be proactive, patient, persistent seeking their aim, ready for psychic discomfort; therefore, the severe level of personal anxiety is incompatible with professional characteristics of specialists of socioeducational activities. Meanwhile research data disclose that respondents quite intensively (M = 37,513, Sdt.D = 7.422) experienced personal anxiety. 15
6 Evaluation of Self-Feeling of Specialists of Socioeducational Activities, Having Experienced Anxiety The research aimed to analyse evaluations of personal self-feelings of social educators and social workers (N=6) after manifestation of anxiety. To do this, qualitative in-depth survey was carried out employing the semi-structured interview. Research data were processed employing the content analysis method according to diagnostic areas: situations arousing the state of anxiety, impact of anxiety on work, self-feeling after experiencing anxiety and other. In this article we shall present only the latter diagnostic area. Analysing evaluations of specialists self-feeling in the situation of anxiety, three qualitative categories showed up (see Table 2): 1) Physical reactions and feelings aroused by anxiety 2) Manifestation of negative, haunting thoughts 3) Psychological problems Table 2 Self-Feeling of Specialists of Socioeducational Activities after Manifestation of Anxiety (N=6) Category Subcategory Examples of empirical statements External physical reactions and feelings aroused by anxiety Manifestation of negative, haunting thoughts Experienced unpleasant physical reactions Experienced feeling of helplessness Social educator s inability to dissociate from negative thoughts face reddenes..., cheeks burst..., blood pressure goes up, hands shake, I am getting hot flashes, hands start shaking, hands tremble, blood pressure starts going up, heart is beating very hard, you can t stay in one place, I feel as if something enchains all body, hands are shaking, physical strength is exhausting, it is very difficult to do anything feeling helplessness, you feel as a caught nestling, sometimes it seems that we have to put up with it, that we are not omnipotent, I don t know exactly or doubt in my powers or the very situation: maybe it is hopeless haunting, I do my best to get rid of them, but I can t do anything with it, sometimes that anxiety is so strong, in the morning again having opened my eyes again these thoughts haunt me, when something worries me, I m not able even to do these exercises calmly, the right way, because my thoughts are already at work, about this or other problems, thoughts are obsessive, all kinds of thoughts and obsessive, even inadequate to the situation, thoughts are no good, awful thoughts come into my mind, I was very worried and thought about leaving the job 16 Number of statements
7 Psychological problems Psychological tiredness Feeling of fear Lack of selfconfidence Sleep disorders you also feel psychologically tired, I feel sad..., I feel very deeply, I react to such things very sensitively, I plug, I am distressed, I am overwhelmed with bad mood, stress there appears fear, there appears fear at once, although you still don t know what will be, there is fear already, but fear exists you start doubting your abilities if you will succeed, if everything will go well, you test 110 times if you took that presentation, you check everything so that you shall not get reproaches, you check everything I don t sleep at night, I am thinking how I could help, I feel sleep disorders very severely,...i am trying to get good sleep Loss of balance I feel being off balance, you are feeling not like yourself 2 In terms of distribution of categories by frequency, physical reactions (face reddens, hands shake, blood pressure goes up) and helplessness (the caught nestling, it is necessary to put up...) clearly distinguish themselves. These statements of respondents confirm physical reactions caused by anxiety, which are described in literature, such as sweaty palms, reddened cheeks, faster heart beat and similar. Most often they accompany the person that is overwhelmed by anxiety and are as if a warning that it is necessary to look for a way out quickly, change the emerged situation (Greenberger, Padesky, 2000). Negative, haunting thoughts are another category that is most often referred to by the respondents (in the morning I open my eyes and again these thoughts haunt me...). Social pedagogues and social workers disclose an insufficient ability to cope with anxiety, difficulties to get rid of haunting, obsessive thoughts related to the situation arousing anxiety. Psychological problems aroused by anxiety most often manifest themselves by bad mood, apathy. According to the above mentioned authors (Greenberger, Padesky, 2000), the situation of anxiety is characterised by restless, variable, irritable, nervous mood. The feeling of fear, mentioned by the responder, experiencing the state of anxiety, can be related to the emotional model of anxiety described by Izard (1999), where fear is one of the key emotions constituting the state of anxiety. According to Mahoney, Chapman (2004), the feeling of fear is caused by interpersonal anxiety; it is a state when the personality feels fear to be negatively evaluated, feels discomfort interacting with the team, with the unpleasant or new superior person. The statements of the above mentioned scientists are confirmed by data of interviews with specialists of socioeducational activities because namely unpleasant communication with the person that has higher qualification, with the hostile team causes the feeling of fear. Respondents 17
8 state that experiencing the state of anxiety the person starts to lack self-confidence. In this case anxiety carries out a negative function and it is likely that it aggravates the process of professional activity, takes time constantly checking if everything is done well. Conclusions 1. Factor analysis of data of social pedagogues and social workers experienced anxiety disclosed that internal consistency coefficient of Spielberger s, Chanin s personal and reactive anxiety scales was high; therefore, it can be stated that the employed instrument enabled to collect reliable data about social pedagogues and social workers emotional state. 2. Severe level of personal anxiety, which can be dangerous to health and eventually form neurosis and psychosomatic disorders, is experienced by more than one third of respondents. About half of investigated social pedagogues and social workers experienced moderate reactive anxiety. This manifestation of anxiety is to be treated as optimal, enabling the professional to improve, set new goals, have perspective future plans. Mild level of anxiety was experienced by a very small share of respondents. 3. Social pedagogues and social workers experience physical and psychological features of personal anxiety. Physical features include reddening of face, shaking of hands, increasing blood pressure. Psychological features are negative, haunting thoughts, bad mood, apathy, the feeling of fear, and lack of self-confidence. Bibliography 1. Aramavičiūtė, V. (2004). Kai kurie vyresniųjų mokinių gyvenimo mokykloje aspektai. Acta Paedagogica Vilnensia, 12, Alifanovienė, D., Vaitkevičienė, A. (2007). Socialinių pedagogų, socialinių darbuotojų išgyvenamo nerimo ypatumai profesinėje veikloje. Specialusis ugdymas, 2 (17), Alifanovienė, D., Vaitkevičienė, A., Lučinskaitė L. (2011). Socialinių pedagogų ir socialinių darbuotojų profesinėje veikloje išgyvenamas nerimas. Specialusis ugdymas, 2 (25), Balevičiūtė, I. (2007). Rizikingų finansinių sprendimų priėmimo ryšys su juos priimančių darbuotojų gyvenimo kokybe, nerimastingumu ir pinigų kokybinėmis schemomis. (Magistro darbas, Mykolo Romerio universitetas). 5. Balsevičius, T. (2010). Radiodažnuminės termoabliacijos veiksmingumas gydant knarkiančiuosius ir sergančiuosius lengvu ir vidutinio sunkumo obstrukcinės miego apnėjos hipopnėjos sindromu (Daktaro disertacija, Kauno medicinos universitetas). 6. Dagienė, A. (2006). Mokyklos baimė kaip socializacijos mokykloje problema (Magistro darbas, Vilniaus pedagoginis universitetas). 7. Gelumbauskienė, B. (2009). Pacientų nerimo ir depresiškumo sąsajos su ligos suvokimu reabilitacijos laikotarpiu (Magistro darbas, Vytauto Didţiojo universitetas). 8. Germanavičius, A. (2006). Nerimo ir depresinių susirgimų epidemiologija ir patofiziologija. Neurologijos seminarai, 10 (27),
9 9. Gustainienė, L., Pranskevičienė, A. (2010). Kokie veiksniai skatina darbuotojų gerovę ir palankią darbo aplinką? Tarptautinis psichologijos žurnalas: biopsichosocialinis požiūris, 7, Loikienė, O. (2007). Aukštųjų mokyklų dėstytojų bei bendrojo lavinimo mokyklų patofiziologija. Neurologijos seminarai, 10 (27), Lučinskaitė, L. (2011). Socialinių pedagogų ir socialinių darbuotojų išgyvenamo nerimo ypatumai profesinėje veikloje. Šiaulių universitetas (vadovė soc. m. dr. Daiva Alifanovienė). 12. Kardelis, K. (2002). Mokslinių tyrimų metodologija ir metodai. Kaunas: JUDEX. 13. Kepalaitė, A. (2011). Vyresniųjų paauglių savęs vertinimo ir nerimo pokyčiai taikant psichologinį poveikį. Specialusis ugdymas, 2 (25), Martišauskienė, E. (2004). Mokyklinio nerimo ir dvasinės sklaidos paralelės paauglystėje. Pedagogika, 73, Milušauskienė, J., Zambacevičienė, E., Dapkevičienė, V. (2008). Priešmokyklinio amţiaus vaikų intelektinio brandumo, mokyklinio nerimo ir auklėjimo šeimoje stilių sąsajos. Jaunųjų mokslininkų darbai, 4 (20), Nasvytienė, D., Balnionytė, R. (2006) metų paauglių emocinių problemų ir nerimo lygio įvertinimo ypatumai. Ugdymo psichologija, 16, Pikturnaitė, R. (2007). Socialinių pedagogų ir socialinių darbuotojų išgyvenamo nerimo ypatumai profesinėje veikloje (Magistro darbas, Šiaulių universitetas). 18. Stanionytė, V. (2008). Linkusių save žaloti įkalintų asmenų nerimo, depresiškumo ir stresogeninių situacijų įveikos strategijų tarpusavio sąsajos (Magistro darbas, Vytauto Didţiojo universitetas). 19. Starkuvienė, D. (2006). Paauglių nerimo, pažangumo ir problemiško elgesio sąryšis (Magistro darbas, Vilniaus pedagoginis universitetas). 20. Tulickas, E., Zambacevičienė, E. (2004). Mokyklinio nerimo apraiškos skirtingose ugdymo pakopose. Jaunųjų mokslininkų darbai, 3, Vaitkevičius, V. (1995). Socialinės pedagogikos pagrindai. Vilnius: Evalda. Daiva Alifanovienė Šiauliai University P.Višinskio str. 25, LT Šiauliai, Lithuania daiva.alif@delfi.lt Asta Vaitkevičienė Šiauliai University P.Višinskio str. 25, LT Šiauliai, Lithuania 19
Depression: what you should know
 Depression: what you should know If you think you, or someone you know, might be suffering from depression, read on. What is depression? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness and
Depression: what you should know If you think you, or someone you know, might be suffering from depression, read on. What is depression? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness and
Mr. Stanley Kuna High School
 Mr. Stanley Kuna High School Stress What is Stress? Stress is - The mental, emotional, and physiological response of the body to any situation that is new, threatening, frightening, or exciting. Stress
Mr. Stanley Kuna High School Stress What is Stress? Stress is - The mental, emotional, and physiological response of the body to any situation that is new, threatening, frightening, or exciting. Stress
NCFE Level 2 Certificate in Awareness of Mental Health Problems SAMPLE. Part A
 NCFE Level 2 Certificate in Awareness of Mental Health Problems Part A Certificate in Awareness of Mental Health Problems Welcome to this Level 2 Certificate in Awareness of Mental Health Problems. We
NCFE Level 2 Certificate in Awareness of Mental Health Problems Part A Certificate in Awareness of Mental Health Problems Welcome to this Level 2 Certificate in Awareness of Mental Health Problems. We
MS the invisible war on emotion
 MS the invisible war on emotion So you have been diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis. Like every other serious health diagnosis, the news is really hard to take in, especially if you are feeling relatively
MS the invisible war on emotion So you have been diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis. Like every other serious health diagnosis, the news is really hard to take in, especially if you are feeling relatively
Self-confidence can increase or decrease according to the context (situation, time, people) we are in.
 Self Confidence 1 SELF-CONFIDENCE Self-confidence can be described as one's trust in his/her own thoughts, feelings and learning ability. Self-confident people can evaluate their experience in a correct
Self Confidence 1 SELF-CONFIDENCE Self-confidence can be described as one's trust in his/her own thoughts, feelings and learning ability. Self-confident people can evaluate their experience in a correct
Mental Health First Aid at a Glance
 Mental Health First Aid at a Glance Candice M. Haines, LCPC Program Supervisor Mental Health First Aid Instructor Pilsen Wellness Center chaines@pilsenmh.org Overview Address myths vs facts Warning signs
Mental Health First Aid at a Glance Candice M. Haines, LCPC Program Supervisor Mental Health First Aid Instructor Pilsen Wellness Center chaines@pilsenmh.org Overview Address myths vs facts Warning signs
Understanding Complex Trauma
 Understanding Complex Trauma Frightening events can have lasting effects Trauma and Homelessness Team Carswell House Dennistoun Glasgow G31 2HX Tel: 0141 232 0114 Fax: 0141 232 0131 General enquiries email:
Understanding Complex Trauma Frightening events can have lasting effects Trauma and Homelessness Team Carswell House Dennistoun Glasgow G31 2HX Tel: 0141 232 0114 Fax: 0141 232 0131 General enquiries email:
Module 3 - How Pain Affects You
 Module 3 - How Pain Affects You You have learned that pain is produced as a result of all of the incoming electrical or danger signals which reach your brain. Example: Mum Watching Her Son Play Footy Think
Module 3 - How Pain Affects You You have learned that pain is produced as a result of all of the incoming electrical or danger signals which reach your brain. Example: Mum Watching Her Son Play Footy Think
Your Safety System - a User s Guide.
 1 Your Safety System - a User s Guide. Human beings are designed for safety SO: You have 2 settings: 1. An ordinary everyday setting And 2. An emergency threat setting. This gets the body ready for immediate
1 Your Safety System - a User s Guide. Human beings are designed for safety SO: You have 2 settings: 1. An ordinary everyday setting And 2. An emergency threat setting. This gets the body ready for immediate
Finding common ground with people who have diabetes
 Finding common ground with people who have diabetes Dr Jess Brown Senior Clinical Psychologist Department of Psychological Medicine York Community Diabetes Team Aims for today Why common ground? What might
Finding common ground with people who have diabetes Dr Jess Brown Senior Clinical Psychologist Department of Psychological Medicine York Community Diabetes Team Aims for today Why common ground? What might
Coping with Advanced Stage Heart Failure and LVAD/Transplant. Kristin Kuntz, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
 Coping with Advanced Stage Heart Failure and LVAD/Transplant Kristin Kuntz, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Health What is Health Psychology? Health psychology focuses on how biology, psychology,
Coping with Advanced Stage Heart Failure and LVAD/Transplant Kristin Kuntz, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Health What is Health Psychology? Health psychology focuses on how biology, psychology,
Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide
 Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide Anxiety Anxiety can be a very normal and healthy response to stressful situations, such as paying bills or sitting an exam. However, it becomes a problem when
Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide Anxiety Anxiety can be a very normal and healthy response to stressful situations, such as paying bills or sitting an exam. However, it becomes a problem when
GENERAL BEHAVIOR INVENTORY Self-Report Version Never or Sometimes Often Very Often
 GENERAL BEHAVIOR INVENTORY Self-Report Version Here are some questions about behaviors that occur in the general population. Think about how often they occur for you. Using the scale below, select the
GENERAL BEHAVIOR INVENTORY Self-Report Version Here are some questions about behaviors that occur in the general population. Think about how often they occur for you. Using the scale below, select the
SOCIAL DYSFUNCTION AND AGGRESSION SCALE (SDAS)
 sychiatric Research Unit SOCIAL DYSFUNCTION AND ARESSION SCALE (SDAS) 1. IRRITABILITY 0 =Not present 1 = doubtful 2 = mild 3 = moderate 4 = severe lease mark appropriate field under and with an X This
sychiatric Research Unit SOCIAL DYSFUNCTION AND ARESSION SCALE (SDAS) 1. IRRITABILITY 0 =Not present 1 = doubtful 2 = mild 3 = moderate 4 = severe lease mark appropriate field under and with an X This
Reference document STRESS MANAGEMENT
 Reference document STRESS MANAGEMENT Table of Contents Introduction 2 Definition of stress 2 Causes of stress at work 2 Categories of stress: positive and negative stress 2 Forms of stress: physiological
Reference document STRESS MANAGEMENT Table of Contents Introduction 2 Definition of stress 2 Causes of stress at work 2 Categories of stress: positive and negative stress 2 Forms of stress: physiological
Reference document. Stress management
 Reference document Stress management Contents Introduction 2 Definition of stress 2 Causes of stress at work 2 Categories of stress: positive and negative stress 2 Forms of stress: physiological and psychological
Reference document Stress management Contents Introduction 2 Definition of stress 2 Causes of stress at work 2 Categories of stress: positive and negative stress 2 Forms of stress: physiological and psychological
What is Stress? What causes stress?
 What is Stress? Stress is the physical and mental response of the body to demands made upon it by everyday life, especially if we are struggling to cope with pressured or difficult tasks or circumstances.
What is Stress? Stress is the physical and mental response of the body to demands made upon it by everyday life, especially if we are struggling to cope with pressured or difficult tasks or circumstances.
Chapter 3 Self-Esteem and Mental Health
 Self-Esteem and Mental Health How frequently do you engage in the following behaviors? SCORING: 1 = never 2 = occasionally 3 = most of the time 4 = all of the time 1. I praise myself when I do a good job.
Self-Esteem and Mental Health How frequently do you engage in the following behaviors? SCORING: 1 = never 2 = occasionally 3 = most of the time 4 = all of the time 1. I praise myself when I do a good job.
THE LIVING STRESS FREE STRESS MODEL
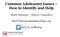
 http://livingstressfree.org/ THE LIVING STRESS FREE STRESS MODEL LIVING STRESS FREE EBOOK LIBRARY Louis and Marilyn Guadagnino MEDICAL DISCLAIMER The Materials are provided for informational and educational
http://livingstressfree.org/ THE LIVING STRESS FREE STRESS MODEL LIVING STRESS FREE EBOOK LIBRARY Louis and Marilyn Guadagnino MEDICAL DISCLAIMER The Materials are provided for informational and educational
Recognising the Warning Signs of Emotional Distress. Claire Doonan and David Watson Clinical Nurse Practitioners, CAMHS
 Recognising the Warning Signs of Emotional Distress Claire Doonan and David Watson Clinical Nurse Practitioners, CAMHS Parents as teenagers or Oh No I have become my mother 1) Did you ever argue with your
Recognising the Warning Signs of Emotional Distress Claire Doonan and David Watson Clinical Nurse Practitioners, CAMHS Parents as teenagers or Oh No I have become my mother 1) Did you ever argue with your
These questionnaires are used by psychology services to help us understand how people feel. One questionnaire measures how sad people feel.
 ADAPTED PHQ-9 & GAD-7 QUESTIONNAIRES How to fill in these questionnaires: These questionnaires are used by psychology services to help us understand how people feel. One questionnaire measures how sad
ADAPTED PHQ-9 & GAD-7 QUESTIONNAIRES How to fill in these questionnaires: These questionnaires are used by psychology services to help us understand how people feel. One questionnaire measures how sad
Determining Major Depressive Disorder in Youth.
 Co-parenting chapter eight. Watching for Depression in Yourself and Your Child. by Yvonne Sinclair M.A. If you notice your child has been feeling sad most of the day and can t seem to shake that down feeling,
Co-parenting chapter eight. Watching for Depression in Yourself and Your Child. by Yvonne Sinclair M.A. If you notice your child has been feeling sad most of the day and can t seem to shake that down feeling,
Common Adolescent Issues How to Identify and Help
 Common Adolescent Issues How to Identify and Help Mark Samways School Counsellor Mark.Samways@dubaicollege.org @DCol_wellbeing Dates of all talks Tuesday 21 st November: Screen Time Tuesday 28 th November:
Common Adolescent Issues How to Identify and Help Mark Samways School Counsellor Mark.Samways@dubaicollege.org @DCol_wellbeing Dates of all talks Tuesday 21 st November: Screen Time Tuesday 28 th November:
Taking Control of Anger. About Anger
 Taking Control of Anger About Anger About the course This course is for anyone who is concerned about his or her anger. Throughout the course you can expect to learn: How to reduce the frequency and intensity
Taking Control of Anger About Anger About the course This course is for anyone who is concerned about his or her anger. Throughout the course you can expect to learn: How to reduce the frequency and intensity
Adapted from Segal Williams and Teasdale (2007). Copyright by the Guilford Press.
 Adapted from Segal Williams and Teasdale (2007). Copyright by the Guilford Press. TURNING TOWARD THE DIFFICULT In Session 5 we extended our formal practice to begin deliberately to turn toward and approach
Adapted from Segal Williams and Teasdale (2007). Copyright by the Guilford Press. TURNING TOWARD THE DIFFICULT In Session 5 we extended our formal practice to begin deliberately to turn toward and approach
BBMS PARENT-TEACHER INSTITUTE PRESENTS= STRESS MANAGEMENT LEARN TO LET IT GO
 BBMS PARENT-TEACHER INSTITUTE PRESENTS= STRESS MANAGEMENT LEARN TO LET IT GO HTTPS://WWW.YOUTUBE.COM/WATCH?V=MOSFLVXNBGK BY: CHRISTINA COLLINS & LAUREN MURPHY MULTI- TASKING = THE DIVISION OF ATTENTION
BBMS PARENT-TEACHER INSTITUTE PRESENTS= STRESS MANAGEMENT LEARN TO LET IT GO HTTPS://WWW.YOUTUBE.COM/WATCH?V=MOSFLVXNBGK BY: CHRISTINA COLLINS & LAUREN MURPHY MULTI- TASKING = THE DIVISION OF ATTENTION
The Revised Treatment Manual for the Brief Behavioral Activation Treatment for Depression (BATD-R) Pre - Session
 The Revised Treatment Manual for the Brief Behavioral Activation Treatment for Depression (BATD-R) Pre-Session Key Elements: 1. Discussion of Depression Pre - Session 2. Introduction to Treatment Rationale
The Revised Treatment Manual for the Brief Behavioral Activation Treatment for Depression (BATD-R) Pre-Session Key Elements: 1. Discussion of Depression Pre - Session 2. Introduction to Treatment Rationale
Pain-related Distress: Recognition and Appropriate Interventions. Tamar Pincus Professor in psychology Royal Holloway University of London
 Pain-related Distress: Recognition and Appropriate Interventions Tamar Pincus Professor in psychology Royal Holloway University of London Remit (and limitations) of presentation Mostly, research in low
Pain-related Distress: Recognition and Appropriate Interventions Tamar Pincus Professor in psychology Royal Holloway University of London Remit (and limitations) of presentation Mostly, research in low
Zone of Positive Stress
 Stress What is Stress? A stressor is any demand on mind and body. It is our response to anxiety provoking events. Stress is arousal of mind and body in response to demands made upon the individual. Positive
Stress What is Stress? A stressor is any demand on mind and body. It is our response to anxiety provoking events. Stress is arousal of mind and body in response to demands made upon the individual. Positive
Bounce Back. Stronger! Being Emo-chic INFLUENCE INSPIRE IGNITE
 INSPIRE IGNITE Bounce Back INFLUENCE Stronger! Being Emo-chic Managing your emotions can sometimes be harder than getting out of bed for school in the mornings. There s always the snooze button if you
INSPIRE IGNITE Bounce Back INFLUENCE Stronger! Being Emo-chic Managing your emotions can sometimes be harder than getting out of bed for school in the mornings. There s always the snooze button if you
RELAPSE PREVENTION THERAPY
 RELAPSE PREVENTION THERAPY Stages of Change Model (Prochaska & Diclemente, 1992) Relapse Prevention Abstinence Lapse- first episode of drug intake after a period of abstinance Relapse- episode of backsliding
RELAPSE PREVENTION THERAPY Stages of Change Model (Prochaska & Diclemente, 1992) Relapse Prevention Abstinence Lapse- first episode of drug intake after a period of abstinance Relapse- episode of backsliding
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Teena Jain 2017 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder What is post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD? PTSD is a disorder that some people develop after experiencing a shocking,
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Teena Jain 2017 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder What is post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD? PTSD is a disorder that some people develop after experiencing a shocking,
WORD WALL. Write 3-5 sentences using as many words as you can from the list below.
 WORD WALL Write 3-5 sentences using as many words as you can from the list below. Suicide Phobia Bipolar Obsessive compulsive disorder(ocd) Anxiety Depression Mood Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
WORD WALL Write 3-5 sentences using as many words as you can from the list below. Suicide Phobia Bipolar Obsessive compulsive disorder(ocd) Anxiety Depression Mood Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
HAMILTON DEPRESSION RATING SCALE (HAM-D) (HAM)
 HAMILTON DEPRESSION RATING SCALE (HAM-D) (HAM) www.cnsforum.com 1 Patient Information Patient Date Day Mth. Year Time Hour Min Personal notes TICK APPROPRIATE BOX FOR EACH ITEM 1. Depressed mood This item
HAMILTON DEPRESSION RATING SCALE (HAM-D) (HAM) www.cnsforum.com 1 Patient Information Patient Date Day Mth. Year Time Hour Min Personal notes TICK APPROPRIATE BOX FOR EACH ITEM 1. Depressed mood This item
Mindset For Optimal Performance: Essential Mental Skills DR. RICK MCGUIRE DIRECTOR OF SPORT PSYCHOLOGY ANNE SHADLE M.ED.
 Mindset For Optimal Performance: Essential Mental Skills DR. RICK MCGUIRE DIRECTOR OF SPORT PSYCHOLOGY ANNE SHADLE M.ED. THINKING RIGHT IN SPORT It s all about FOCUS! Outline For Today: 1. Thinking Right
Mindset For Optimal Performance: Essential Mental Skills DR. RICK MCGUIRE DIRECTOR OF SPORT PSYCHOLOGY ANNE SHADLE M.ED. THINKING RIGHT IN SPORT It s all about FOCUS! Outline For Today: 1. Thinking Right
Managing Mental Health (at Work)
 Managing Mental Health (at Work) So what do you hope to get from this session? Can you name some types of Mental Health Conditions? Depression Eating problems Phobias Anxiety Schizophrenia Stress Post-traumatic
Managing Mental Health (at Work) So what do you hope to get from this session? Can you name some types of Mental Health Conditions? Depression Eating problems Phobias Anxiety Schizophrenia Stress Post-traumatic
STRESS KUON? AUR KAISE KARE MANAGE? Dr. NAYNA KADAM (Dept. Of Engg. Mathematics)
 STRESS KUON? AUR KAISE KARE MANAGE? Dr. NAYNA KADAM (Dept. Of Engg. Mathematics) Outline What is Stress? Causes of Stress Check your anxiety level Symptoms of stress Stress Management What is Stress? Stress
STRESS KUON? AUR KAISE KARE MANAGE? Dr. NAYNA KADAM (Dept. Of Engg. Mathematics) Outline What is Stress? Causes of Stress Check your anxiety level Symptoms of stress Stress Management What is Stress? Stress
Improve Your... Mental Training - SELF TALK
 Improve Your... Mental Training - SELF TALK Published May 2016 version 1.0 This document is part of "Mental Preparation for Basketball Referees" CHAPTER 4: SELF TALK When you think about something and
Improve Your... Mental Training - SELF TALK Published May 2016 version 1.0 This document is part of "Mental Preparation for Basketball Referees" CHAPTER 4: SELF TALK When you think about something and
A-Z of Mental Health Problems
 Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Mental Health: Subjective evaluation of overall quality of life (QOL) Happiness, life satisfaction, morale, trait effect, etc. Quality of Life (QOL)
 Mental Health: Subjective evaluation of overall quality of life (QOL) Happiness, life satisfaction, morale, trait effect, etc. Quality of Life (QOL) Multidimensional concept Includes: Physical health Cognitive
Mental Health: Subjective evaluation of overall quality of life (QOL) Happiness, life satisfaction, morale, trait effect, etc. Quality of Life (QOL) Multidimensional concept Includes: Physical health Cognitive
Mental Health. Borderline Personality Disorder
 Mental Health Borderline Personality Disorder a) Borderline Personality Disorder b) I want to go into detail because I feel that many addicts with Complex Trauma have this i. BPD comes out of more severe
Mental Health Borderline Personality Disorder a) Borderline Personality Disorder b) I want to go into detail because I feel that many addicts with Complex Trauma have this i. BPD comes out of more severe
2018 Texas Focus: On the Move! Let s Talk: Starting the Mental Health Conversation with Your Teen Saturday, March 3, :45-11:15 AM
 Texas School for the Blind & Visually Impaired Outreach Programs www.tsbvi.edu 512-454-8631 1100 W. 45 th St. Austin, TX 78756 2018 Texas Focus: On the Move! Let s Talk: Starting the Mental Health Conversation
Texas School for the Blind & Visually Impaired Outreach Programs www.tsbvi.edu 512-454-8631 1100 W. 45 th St. Austin, TX 78756 2018 Texas Focus: On the Move! Let s Talk: Starting the Mental Health Conversation
Recovering from a difficult birth
 Fife Clinical Psychology Department Recovering from a difficult birth Reviewed: June 2010 1 Recovering from a difficult birth This leaflet aims to give you information about recovering from a difficult
Fife Clinical Psychology Department Recovering from a difficult birth Reviewed: June 2010 1 Recovering from a difficult birth This leaflet aims to give you information about recovering from a difficult
Understanding Chronic Pain: An Educational Session on Chronic Pain
 Understanding Chronic Pain: An Educational Session on Chronic Pain Matilda Nowakowski, Ph.D., C.Psych. Linette Savage Chronic Pain Clinic, St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Objectives To better understand
Understanding Chronic Pain: An Educational Session on Chronic Pain Matilda Nowakowski, Ph.D., C.Psych. Linette Savage Chronic Pain Clinic, St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Objectives To better understand
Neurotic and Personality Disorders
 Neurotic and Personality Disorders LPT Gondar Mental Health Group www.le.ac.uk Neurosis Originally coined by the Scottish physician William Cullen in 1769. Included a range of conditions e.g. epilepsy,
Neurotic and Personality Disorders LPT Gondar Mental Health Group www.le.ac.uk Neurosis Originally coined by the Scottish physician William Cullen in 1769. Included a range of conditions e.g. epilepsy,
Live patient discussion Sandra Ros (MA), Dr Lluís Puig
 Department of Dermatology Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau op yr ig ht I P C N O V A R T I S P S O R I A S I S P R E C E P T O R S H I P C Live patient discussion Sandra Ros (MA), Dr Lluís Puig Barcelona,
Department of Dermatology Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau op yr ig ht I P C N O V A R T I S P S O R I A S I S P R E C E P T O R S H I P C Live patient discussion Sandra Ros (MA), Dr Lluís Puig Barcelona,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Baby Blues and More DRAFT. Knowing About This in Advance Can Help
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Recognizing and coping with postpartum mood disorders Some women have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. It helps to know about these
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Recognizing and coping with postpartum mood disorders Some women have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. It helps to know about these
Converting change fatigue into workplace success
 Converting change fatigue into workplace success Dr. William Howatt 2018 Greetings from Dr. Bill 25+ years of experience Author: Certified Management Essentials (CME), 10-course program Pathway to Coping
Converting change fatigue into workplace success Dr. William Howatt 2018 Greetings from Dr. Bill 25+ years of experience Author: Certified Management Essentials (CME), 10-course program Pathway to Coping
Other significant mental health complaints
 Other significant mental health complaints 2 Session outline Introduction to other significant mental health complaints Assessment of other significant mental health complaints Management of other significant
Other significant mental health complaints 2 Session outline Introduction to other significant mental health complaints Assessment of other significant mental health complaints Management of other significant
Your Safety System - a User s Guide.
 THE WOODHAVEN ANXIETY/STRESS MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME. Your Safety System - a User s Guide. Isabel Clarke and Becky Mallery. Woodhaven Psychological Therapies Service. 1 Your Safety System - a User s Guide.
THE WOODHAVEN ANXIETY/STRESS MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME. Your Safety System - a User s Guide. Isabel Clarke and Becky Mallery. Woodhaven Psychological Therapies Service. 1 Your Safety System - a User s Guide.
UNDERSTANDING THE PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPACT OF A COLORECTAL CANCER DIAGNOSIS
 UNDERSTANDING THE PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPACT OF A COLORECTAL CANCER DIAGNOSIS Dr Claire Delduca, Macmillan Clinical Psychologist Velindre Cancer Centre, Cardiff Aims Understanding the impact of a diagnosis of
UNDERSTANDING THE PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPACT OF A COLORECTAL CANCER DIAGNOSIS Dr Claire Delduca, Macmillan Clinical Psychologist Velindre Cancer Centre, Cardiff Aims Understanding the impact of a diagnosis of
Suicide and the Military Amy Menna, Ph.D., LMHC, CAP Giftfromwithin.org
 Suicide and the Military Amy Menna, Ph.D., LMHC, CAP Giftfromwithin.org When someone commits suicide, it is a tragedy. When we are losing more soldiers to suicide than the Afghanistan war, it is an epidemic.
Suicide and the Military Amy Menna, Ph.D., LMHC, CAP Giftfromwithin.org When someone commits suicide, it is a tragedy. When we are losing more soldiers to suicide than the Afghanistan war, it is an epidemic.
EMOTIONAL SUPPORT ANIMAL (ESA) PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION PART I: PERSONAL INFORMATION STREET ADDRESS CITY/STATE
 EMOTIONAL SUPPORT ANIMAL (ESA) PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION PART I: PERSONAL INFORMATION FIRST NAME LAST NAME EMAIL PHONE # STREET ADDRESS CITY/STATE ZIP GENDER: MALE FEMALE TRANSGENER MARITAL STATUS: MARRIED
EMOTIONAL SUPPORT ANIMAL (ESA) PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION PART I: PERSONAL INFORMATION FIRST NAME LAST NAME EMAIL PHONE # STREET ADDRESS CITY/STATE ZIP GENDER: MALE FEMALE TRANSGENER MARITAL STATUS: MARRIED
CREATING A MORE VALIDATING FAMILY ENVIRONMENT
 Page 13 CREATING A MORE VALIDATING FAMILY ENVIRONMENT FOR YOURSELF AND YOUR LOVED ONES Definition of a Validating Family Environment What is a VALIDATING FAMILY ENVIRONMENT? IT: Legitimizes family members
Page 13 CREATING A MORE VALIDATING FAMILY ENVIRONMENT FOR YOURSELF AND YOUR LOVED ONES Definition of a Validating Family Environment What is a VALIDATING FAMILY ENVIRONMENT? IT: Legitimizes family members
Understanding and Managing Change
 www.working-minds.org.uk Understanding and Managing Change Understanding and Managing Change This leaflet is designed to assist you in understanding some of the normal emotions that we feel when we are
www.working-minds.org.uk Understanding and Managing Change Understanding and Managing Change This leaflet is designed to assist you in understanding some of the normal emotions that we feel when we are
Development. summary. Sam Sample. Emotional Intelligence Profile. Wednesday 5 April 2017 General Working Population (sample size 1634) Sam Sample
 Development summary Wednesday 5 April 2017 General Working Population (sample size 1634) Emotional Intelligence Profile 1 Contents 04 About this report 05 Introduction to Emotional Intelligence 06 Your
Development summary Wednesday 5 April 2017 General Working Population (sample size 1634) Emotional Intelligence Profile 1 Contents 04 About this report 05 Introduction to Emotional Intelligence 06 Your
Neurobiology of Sexual Assault Trauma: Supportive Conversations with Victims
 Neurobiology of Sexual Assault Trauma: Supportive Conversations with Victims Jim Hopper, Ph.D. November 2017 Handout 1: Using Neurobiology of Trauma Concepts to Validate, Reassure, and Support Note: In
Neurobiology of Sexual Assault Trauma: Supportive Conversations with Victims Jim Hopper, Ph.D. November 2017 Handout 1: Using Neurobiology of Trauma Concepts to Validate, Reassure, and Support Note: In
Optimal Health Questionnaire
 Optimal Health Questionnaire This questionnaire is intended to help you assess how well you are balancing the various elements in your life. The basis of the process is that we have 5 dimensions which
Optimal Health Questionnaire This questionnaire is intended to help you assess how well you are balancing the various elements in your life. The basis of the process is that we have 5 dimensions which
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Baby Blues and More. Postpartum mood disorders DRAFT. Emotional Changes After Giving Birth
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Postpartum mood disorders Some new mothers have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. This chapter gives ideas for things you can do to
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Postpartum mood disorders Some new mothers have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. This chapter gives ideas for things you can do to
Biology Change Pressure Identity and Self-Image
 Victoria L Foster Biology Change Pressure Identity and Self-Image Sadness Sadness is something we all experience. Sadness is usually tied to one event or reason. Sadness is what happens when normal
Victoria L Foster Biology Change Pressure Identity and Self-Image Sadness Sadness is something we all experience. Sadness is usually tied to one event or reason. Sadness is what happens when normal
Postnatal anxiety and depression
 What Dads and Mums need to know Postnatal anxiety and depression What Dads and Mums need to know 1 Postnatal anxiety and depression Feelings and emotions after birth Having a baby can be an exciting time,
What Dads and Mums need to know Postnatal anxiety and depression What Dads and Mums need to know 1 Postnatal anxiety and depression Feelings and emotions after birth Having a baby can be an exciting time,
THOUGHTS, ATTITUDES, HABITS AND BEHAVIORS
 THOUGHTS, ATTITUDES, HABITS AND BEHAVIORS Ellen Freedman, CLM Law Practice Management Coordinator Pennsylvania Bar Association I ve been thinking a lot lately about how we think, what we think, and what
THOUGHTS, ATTITUDES, HABITS AND BEHAVIORS Ellen Freedman, CLM Law Practice Management Coordinator Pennsylvania Bar Association I ve been thinking a lot lately about how we think, what we think, and what
STRESSED? What is Stress? What is Stress? Healthy Stress and the Biology of Stress
 What is Stress? What is Stress? Stress is a person s response to any situation or event that requires adjustment or change. The stress reaction prepares the mind and body to react to any situation that
What is Stress? What is Stress? Stress is a person s response to any situation or event that requires adjustment or change. The stress reaction prepares the mind and body to react to any situation that
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) FACTS Families and Carers Training and Support Programme
 FACTS : Participants handouts Module 2 Mindfulness and Emotion Management Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) FACTS Families and Carers Training and Support Programme A short course for family members
FACTS : Participants handouts Module 2 Mindfulness and Emotion Management Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) FACTS Families and Carers Training and Support Programme A short course for family members
Healthy Coping. Learning You Have Diabetes. Stress. Type of Stress
 Healthy Coping Learning You Have Diabetes Learning you have diabetes changes your life forever. You may feel scared, shocked, angry or overwhelmed. You may not want to believe it. These are normal reactions.
Healthy Coping Learning You Have Diabetes Learning you have diabetes changes your life forever. You may feel scared, shocked, angry or overwhelmed. You may not want to believe it. These are normal reactions.
Why does someone develop bipolar disorder?
 Bipolar Disorder Do you go through intense moods? Do you feel very happy and energized some days, and very sad and depressed on other days? Do these moods last for a week or more? Do your mood changes
Bipolar Disorder Do you go through intense moods? Do you feel very happy and energized some days, and very sad and depressed on other days? Do these moods last for a week or more? Do your mood changes
Depression. Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Trust (Revised Jan 2002) An Information Leaflet
 Depression Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Trust (Revised Jan 2002) An Information Leaflet practical ldren 1 7XR isle, d n. ocial These are the thoughts of two people who are depressed: I feel so alone,
Depression Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Trust (Revised Jan 2002) An Information Leaflet practical ldren 1 7XR isle, d n. ocial These are the thoughts of two people who are depressed: I feel so alone,
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Abnormal Behavior/Mental Disorders. How do we define these?
 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Abnormal Behavior/Mental Disorders How do we define these? Abnormality is identified from three vantage points: 1. That of society 2. That of the individual 3. That of the mental
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Abnormal Behavior/Mental Disorders How do we define these? Abnormality is identified from three vantage points: 1. That of society 2. That of the individual 3. That of the mental
Psychosocial Outcome Severity Guide Instructor s Guide
 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Instructor s Guide 2006 Prepared by: American Institutes for Research 1000 Thomas Jefferson St, NW Washington, DC 20007 Slide 1 Psychosocial Outcome Severity
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Instructor s Guide 2006 Prepared by: American Institutes for Research 1000 Thomas Jefferson St, NW Washington, DC 20007 Slide 1 Psychosocial Outcome Severity
What are you going to focus on?
 What are you going to focus on? DO YOU FOCUS ON what you can or can t control? Do you focus on things that excite you or things that you fear? Realize that whatever you focus on, you experience because,
What are you going to focus on? DO YOU FOCUS ON what you can or can t control? Do you focus on things that excite you or things that you fear? Realize that whatever you focus on, you experience because,
Non-epileptic attacks
 Non-epileptic attacks A short guide for patients and families Information for patients Neurology Psychotherapy Service What are non-epileptic attacks? Non-epileptic attacks are episodes in which people
Non-epileptic attacks A short guide for patients and families Information for patients Neurology Psychotherapy Service What are non-epileptic attacks? Non-epileptic attacks are episodes in which people
Recovering from a difficult birth.
 NHS Fife Department of Psychology Recovering from a difficult birth. Help Yourself @ moodcafe.co.uk Recovering from a difficult birth This leaflet aims to give you information about recovering from a difficult
NHS Fife Department of Psychology Recovering from a difficult birth. Help Yourself @ moodcafe.co.uk Recovering from a difficult birth This leaflet aims to give you information about recovering from a difficult
What are the Sources of Stress? Going for the 3 Increases: Increase in Health, Increase in Happiness & Increase in Energy
 What are the Sources of Stress? Going for the 3 Increases: Increase in Health, Increase in Happiness & Increase in Energy Strategies for Success in Health Management By: James J. Messina, Ph.D. 1. Change
What are the Sources of Stress? Going for the 3 Increases: Increase in Health, Increase in Happiness & Increase in Energy Strategies for Success in Health Management By: James J. Messina, Ph.D. 1. Change
LOUDOUN ACADEMY PHYSICAL EDUCATION DEPARTMENT NATIONAL 5 PORTFOLIO PREPARATION
 LOUDOUN ACADEMY PHYSICAL EDUCATION DEPARTMENT NATIONAL 5 PORTFOLIO PREPARATION Section 1: Understanding factors that impact on performance In this section you will learn about various Physical (Fitness)
LOUDOUN ACADEMY PHYSICAL EDUCATION DEPARTMENT NATIONAL 5 PORTFOLIO PREPARATION Section 1: Understanding factors that impact on performance In this section you will learn about various Physical (Fitness)
Presented by Wendy Rawlings MS LMHC I Can Do This Can t I?
 Presented by Wendy Rawlings MS LMHC www.wendyrawlings@gmail.com 253-661-0181 I Can Do This Can t I? Your Reason For Weight Loss Surgery What s your goal? The Two Predictors of Success On a scale of 1-10
Presented by Wendy Rawlings MS LMHC www.wendyrawlings@gmail.com 253-661-0181 I Can Do This Can t I? Your Reason For Weight Loss Surgery What s your goal? The Two Predictors of Success On a scale of 1-10
Managing Your Emotions
 Managing Your Emotions I love to ask What s your story? (pause) You immediately had an answer to that question, right? HOW you responded in your mind is very telling. What I want to talk about in this
Managing Your Emotions I love to ask What s your story? (pause) You immediately had an answer to that question, right? HOW you responded in your mind is very telling. What I want to talk about in this
Introduction into Psychiatric Disorders. Dr Jon Spear- Psychiatrist
 Introduction into Psychiatric Disorders Dr Jon Spear- Psychiatrist Content Stress Major depressive disorder Adjustment disorder Generalised anxiety disorder Post traumatic stress disorder Borderline personality
Introduction into Psychiatric Disorders Dr Jon Spear- Psychiatrist Content Stress Major depressive disorder Adjustment disorder Generalised anxiety disorder Post traumatic stress disorder Borderline personality
Caring for the Caregiver
 Caring for the Caregiver Understanding and Managing the effects of caregiving Finding Your Caregiving Stress Index Define the Role of Stress and its Negative Effects Creating a Wellness Model Ten Step
Caring for the Caregiver Understanding and Managing the effects of caregiving Finding Your Caregiving Stress Index Define the Role of Stress and its Negative Effects Creating a Wellness Model Ten Step
How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Patient information leaflet Follow us on
 Coping with Anxiety How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in
Coping with Anxiety How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in
DEPRESSION. There are a couple of kinds, or forms. The most common are major depression and dysthymic disorder.
 DEPRESSION OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class, you will be able to: 1.list and describe several kinds of depression, 2.discuss the signs of depression, and 3.relate the treatment of depression. INTRODUCTION
DEPRESSION OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class, you will be able to: 1.list and describe several kinds of depression, 2.discuss the signs of depression, and 3.relate the treatment of depression. INTRODUCTION
What is stress? A type of response that typically involves an unpleasant state, such as anxiety or tension (page 469).
 LP 11B stress and coping 1 What is stress? Stress: A type of response that typically involves an unpleasant state, such as anxiety or tension (page 469). Stressors: Something in the environment that is
LP 11B stress and coping 1 What is stress? Stress: A type of response that typically involves an unpleasant state, such as anxiety or tension (page 469). Stressors: Something in the environment that is
Look to see if they can focus on compassionate attention, compassionate thinking and compassionate behaviour. This is how the person brings their
 Compassionate Letter Writing Therapist Notes The idea behind compassionate mind letter writing is to help people engage with their problems with a focus on understanding and warmth. We want to try to bring
Compassionate Letter Writing Therapist Notes The idea behind compassionate mind letter writing is to help people engage with their problems with a focus on understanding and warmth. We want to try to bring
THE EFFECTS AND MITIGATIONS OF STRESS. Joanne Wong, M.A., PsyD Candidate California Pacific Medical Center - Outpatient Psychiatry
 THE EFFECTS AND MITIGATIONS OF STRESS Joanne Wong, M.A., PsyD Candidate California Pacific Medical Center - Outpatient Psychiatry ACKNOWLEDGMENT CPMC s Kalmanovitz Child Development Center Integrated Health
THE EFFECTS AND MITIGATIONS OF STRESS Joanne Wong, M.A., PsyD Candidate California Pacific Medical Center - Outpatient Psychiatry ACKNOWLEDGMENT CPMC s Kalmanovitz Child Development Center Integrated Health
Depression, Anxiety, and the Adolescent Athlete: Introduction to Identification and Treatment
 Depression, Anxiety, and the Adolescent Athlete: Introduction to Identification and Treatment Jamie E. Pardini, PhD Sports Medicine and Concussion Specialists Banner University Medical Center-Phoenix University
Depression, Anxiety, and the Adolescent Athlete: Introduction to Identification and Treatment Jamie E. Pardini, PhD Sports Medicine and Concussion Specialists Banner University Medical Center-Phoenix University
ALLIANCE COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SLEEP DISORDERS CENTER PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE/HISTORY PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING WITH YOU ON THE NIGHT OF YOUR TEST.
 ALLIANCE COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SLEEP DISORDERS CENTER PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE/HISTORY PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING WITH YOU ON THE NIGHT OF YOUR TEST. NAME DATE: HEIGHT: WEIGHT: DOB: SEX: HOME PHONE #: REFERRING
ALLIANCE COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SLEEP DISORDERS CENTER PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE/HISTORY PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING WITH YOU ON THE NIGHT OF YOUR TEST. NAME DATE: HEIGHT: WEIGHT: DOB: SEX: HOME PHONE #: REFERRING
COUPLE & FAMILY INSTITUTE OF TRI-CITIES AMEN ADULT GENERAL SYMPTOM CHECKLIST
 COUPLE & FAMILY INSTITUTE OF TRI-CITIES AMEN ADULT GENERAL SYMPTOM CHECKLIST Please rate yourself on each symptom listed below. Please use the following scale: 0--------------------------1---------------------------2--------------------------3--------------------------4
COUPLE & FAMILY INSTITUTE OF TRI-CITIES AMEN ADULT GENERAL SYMPTOM CHECKLIST Please rate yourself on each symptom listed below. Please use the following scale: 0--------------------------1---------------------------2--------------------------3--------------------------4
Overview. what is anxiety? when is anxiety a problem? diagnoses, prevalence, causes
 Anxiety in Children Kawartha Pine Ridge District School Board Parent Conference on Mental Health October 18, 2014 Presented by: Christine Flindall and Suzanne Steele (School Board Counsellors) Overview
Anxiety in Children Kawartha Pine Ridge District School Board Parent Conference on Mental Health October 18, 2014 Presented by: Christine Flindall and Suzanne Steele (School Board Counsellors) Overview
HAMILTON ANXIETY RATING SCALE (HAM-A)
 HAMILTON ANXIETY RATING SCALE (HAM-A) Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit www.mdpu.ca 1 Patient Information Patient Date Day Mth. Year Time Hour Min Personal notes 1. Anxious mood This item covers the
HAMILTON ANXIETY RATING SCALE (HAM-A) Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit www.mdpu.ca 1 Patient Information Patient Date Day Mth. Year Time Hour Min Personal notes 1. Anxious mood This item covers the
Understanding Depression
 Understanding Depression What causes Depression? Family History Having family members who have depression may increase a person s risk Deficiencies of certain chemicals in the brain may lead to depression
Understanding Depression What causes Depression? Family History Having family members who have depression may increase a person s risk Deficiencies of certain chemicals in the brain may lead to depression
The eight steps to resilience at work
 The eight steps to resilience at work Derek Mowbray March 2010 derek.mowbray@orghealth.co.uk www.orghealth.co.uk Introduction Resilience is the personal capacity to cope with adverse events and return
The eight steps to resilience at work Derek Mowbray March 2010 derek.mowbray@orghealth.co.uk www.orghealth.co.uk Introduction Resilience is the personal capacity to cope with adverse events and return
Pain Self-Management Strategies Wheel
 Pain Self-Management Strategies Wheel Each strategy has its own wedge on this wheel. Each wedge is divided into three sections. After you read about a strategy, use the key below to rate how well you think
Pain Self-Management Strategies Wheel Each strategy has its own wedge on this wheel. Each wedge is divided into three sections. After you read about a strategy, use the key below to rate how well you think
Mental Health and Stress Management
 Mental Health and Stress Management In recent years, psychologists have become more interested in positive psychology Focus on positive emotions, characteristics, strengths, and conditions that create
Mental Health and Stress Management In recent years, psychologists have become more interested in positive psychology Focus on positive emotions, characteristics, strengths, and conditions that create
Procrastination and the College Student: An Analysis on Contributing Factors and Academic Consequences
 Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Education Undergraduate Research Education and Psychology Fall 12-11-2014 Procrastination and the College Student: An Analysis on Contributing Factors
Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Education Undergraduate Research Education and Psychology Fall 12-11-2014 Procrastination and the College Student: An Analysis on Contributing Factors
Is an Energy Balancing Modality that releases your trapped and toxic Emotions, and can replace them with abundant Health, Love and Happiness!
 The Emotion Code Is an Energy Balancing Modality that releases your trapped and toxic Emotions, and can replace them with abundant Health, Love and Happiness! Emotional Baggage Some people have more then
The Emotion Code Is an Energy Balancing Modality that releases your trapped and toxic Emotions, and can replace them with abundant Health, Love and Happiness! Emotional Baggage Some people have more then
Effects of Traumatic Experiences
 Effects of Traumatic Experiences A National Center for PTSD Fact Sheet By Eve B. Carlson, Ph.D. and Josef Ruzek, Ph.D When people find themselves suddenly in danger, sometimes they are overcome with feelings
Effects of Traumatic Experiences A National Center for PTSD Fact Sheet By Eve B. Carlson, Ph.D. and Josef Ruzek, Ph.D When people find themselves suddenly in danger, sometimes they are overcome with feelings
How To Win Your War Against Depression
 Page 1 of 1 Contents Depression Treatment Without Side Effects... 9 Depression Treatment: Natural Treatments... 10 Depression Treatment: Helping Someone Else... 11 Depression Treatment: Talking Therapies...
Page 1 of 1 Contents Depression Treatment Without Side Effects... 9 Depression Treatment: Natural Treatments... 10 Depression Treatment: Helping Someone Else... 11 Depression Treatment: Talking Therapies...
The first step to managing stress is to understand its nature
 Excerpted from 5 Steps to Reducing Stress: Recognizing What Works Recognizing Stress The first step to managing stress is to understand its nature as well as your preferred way of initiating a relaxation
Excerpted from 5 Steps to Reducing Stress: Recognizing What Works Recognizing Stress The first step to managing stress is to understand its nature as well as your preferred way of initiating a relaxation
Handout One Understanding Your Approach to Emotions
 Handout One Understanding Your Approach to Emotions Adapted from John Gottman's Raising an Emotionally Intelligent Child: The Heart of Parenting It's important to understand why you approach emotions the
Handout One Understanding Your Approach to Emotions Adapted from John Gottman's Raising an Emotionally Intelligent Child: The Heart of Parenting It's important to understand why you approach emotions the
Procrastination: The art of postponing
 Procrastination: The art of postponing The Academic Support Centre Student Health 16 th October 2017 What is procrastination? Today: Why me? Mapping the problem. What can I do about it? Concrete strategies
Procrastination: The art of postponing The Academic Support Centre Student Health 16 th October 2017 What is procrastination? Today: Why me? Mapping the problem. What can I do about it? Concrete strategies
