Psychology 101 Exam 1 Fall 2000 Name
|
|
|
- Luke Butler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Psychology 101 Exam 1 Fall 2000 Name 1. Psychology is defined as: a. the scientific investigation of thought processes b. the understanding of abnormal behavior c. the scientific study of behavior and the mind d. the study of mental illness and inner feelings 2. Harry works in a clinic where he often helps couples work through adjustment problems. Harry would most likely be classified as: a. an applied psychologist b. a clinical psychologist c. a research psychologist d. a psychiatrist 3. A psychologist who extends the principles of psychology to practical, everyday problems in the real world would be: a. a clinical psychologist b. a research psychologist c. a psychiatrist d. an applied psychologist 4. A psychologist works for a large company helping to improve employee morale. This person would most likely be classified as: a. a clinical psychologist b. an industrial / organizational psychologist c. a research psychologist d. a psychiatrist 5. Signet Air recently hired a psychologist to help redesign the cockpit of a new aircraft. Their goal is to reduce pilot error when reading the instrument panel. The psychologist the company hired is most likely: a. a human factors psychologist b. a social psychologist c. a developmental psychologist d. an industrial/organizational psychologist 6. Martin is a psychologist who is currently conducting experiments in an attempt to understand how brain biochemistry influences behavior. Martin most likely is: a. a clinical psychologist b. an applied psychologist c. a psychiatrist d. a research psychologist 7. Anne is a psychologist who is currently collecting data in an attempt to understand how groups of people influence and relate to each other. Anne most likely is: a. a clinical psychologist b. a social psychologist c. a counseling psychologist d. a psychiatrist 8. Larry is a graduate student whose major area of interest is cognitive psychology. You should expect that Larry is most interested in: a. understanding mental processes such as memory and learning
2 b. the ways physical or genetic factors influence behavior c. drugs d. how people relate to each other and influence each other 9. The mental health professional who is most likely to prescribe drugs as part of a treatment program for his or her patients is: a. a school psychologist b. a psychiatrist c. a behavioral psychologist d. a cognitive psychologist 10. of the following, the main difference between a clinical psychologist and a psychiatrist is: a. the types of psychological problems they deal with b. the ages of the patients that they treat c. psychologists only have masters degrees d. psychiatrists can give drugs while most psychologists cannot 11. According to lecture, the roots of psychology lie in the disciplines of: a. mathematics and philosophy b. philosophy, physics, and physiology c. biology and physics d. anthropology and sociology 12. Nativism is the view that: a. day-to-day experiences determine what one knows. b. certain kinds of knowledge and ideas are innate c. psychology should be the study of immediate conscious experience d. the mind arises entirely from the physical properties of the brain 13. Which of the following individuals would be considered a Natavist? a. Galen b. Aristotle c. Simonedes d. Plato 14. The goal of Structuralism is to: a. understand the purpose of immediate conscious experience b. understand the elementary elements of consciousness c. discover how environmental changes can cause changes in behavior d. understand how memories and mental process produce problem behavior 15. The individual linked with structuralism was: a. William James b. Wilhelm Wundt c. John Watson d. Sigmund Freud 16. A young man is sitting in a lab giving a detailed account of his subjective experiences concerning the taste of lemonade to discover the basic units of the mind. This is a characteristic of which school? a. behaviorism b. functionalism c. psychoanalysis d. structuralism 17. The individual most clearly linked with functionalism is:
3 a. Wilhelm Wundt b. John Watson c. William James d. Sigmund Freud 18. "Yes, there are four basic tastes, but I am interested in how this has helped us adapt and survive." The type of psychologist who is most likely to make this type of statement would be: a. a structuralist b. a psychoanalyst c. a behaviorist d. a functionalist 19. The person who advocated that psychology should focus on the study of observable behavior was: a. William James b. John Dewey c. John Watson d. Edward Titchener 20. Ruth believes that individuals learn to be aggressive as a result of the experiences they have. Ruth's view is most consistent with the: a. structuralist approach to psychology b. nativist view of psychology c. behavioral approach to psychology d. psychoanalytic view of psychology 21. Gerard believes that individuals act aggressively because of unconscious motives and conflicts. Gerard's view is most consistent with the: a. psychoanalytic view of psychology b. structuralist approach to psychology c. nativist view of psychology d. behavioral approach to psychology 22. Wilma can type very quickly, but when her boss watches her, she types much slower. Wilma's change in typing speed illustrates the concept of: a. experimental control b. negative correlation c. reactivity d. systematic observation 23. A researcher stands on a street corner recording the sex of car drivers and if they stop at a stop sign. This is an example of: a. psychological testing b. naturalistic observation c. experimentation d. survey method 24. Dr. Helmsey investigated the memory changes of an individual who was abducted by a UFO. This individual was tested extensively and questioned in detail about their experience. Dr. Helmsey's is using a a. correlational design b. case study design c. survey design d. experimental design
4 25. The research method where a representative sample of individuals is asked for their opinions is: a. case study research b. correlational research c. a survey d. naturalistic observation 26. When everyone in the target population has an equal likelihood of being selected to take part in a survey, the researcher has selected a: a. biased sample b. a random population c. non-representative sample d. random sample 27. The mode for a data set is: a. the arithmetic average of the set of scores b. the middle point in the set of scores c. the most frequently occurring score d. the difference between the largest and smallest scores 28. The median for a data set is: a. the arithmetic average of the set of scores b. the middle point in the set of scores c. the most frequently occurring score d. the difference between the largest and smallest scores 29. The standard deviation for a data set: a. is the arithmetic average of the set of scores b. is the middle point in the set of scores c. is the difference between the largest and smallest scores d. indicates how much the individual scores vary from the mean 30. Dr. Phillips predicts that if the temperature of a room is increased, then individuals are more likely to act aggressively. This suggests that Dr. Phillips believes room temperature and aggression are: a. negatively correlated b. uncorrelated c. positively correlated d. both dependent variables 31. Of the following, the correlation coefficient that indicates the weakest relationship between the two variables is: a b c d A group of researchers wanted to determine whether people would eat more food in a cool room than in a hot room. Half the participants ate in a warm room (75(F) and half the participants ate in a cool room (65(F). The researchers then measured how much food was consumed in each of the two rooms. In this study, the independent variable is: a. the temperature of the room (75(F or 65(F) b. the type of food the researcher selects for the study c. the amount of food that is consumed d. how hungry the participants are at the start of the study
5 33. The behavior that is observed or measured during an experiment is: a. the dependent variable b. the independent variable c. a confounding variable d. a placebo 34. When Ralph touched a hot candle flame with his finger, the message was carried from his hand to his spinal cord along: a. afferent neurons b. efferent neurons c. affective neurons d. glial cells 35. Efferent neurons: a. carry information inward toward the spinal cord and brain b. convey information from one internal processing site to another c. produce hyperpolarization in glial cells d. carry messages and commands out from the brain and spinal cord 36. The cells in the nervous system that remove waste and help neurons communicate more efficiently are: a. interneurons b. neurotransmitters c. ion pumps d. glial cells 37. The path that information follows in a simple reflex pathway is: a. motor neuron, interneuron, sensory neuron b. sensory neuron, brain, motor neuron c. motor neuron, brain, sensory neuron d. sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron 38. Shyanne was walking along a dark street when he noticed someone following him. His heart rate started to increase and he found himself perspiring. These physical reactions were triggered by Shyanne's: a. somatic nervous system b. parasympathetic nervous system c. sympathetic nervous system d. cerebellum 39. Lori thought she heard a gunshot while she was out walking, but discovered it was only a car down the street backfiring. As she continued on her walk, her heart stopped racing and her blood pressure returned to normal. Lori's blood pressure and heart rate returned to normal levels due to activity in her: a. somatic nervous system b. parasympathetic nervous system c. sympathetic nervous system d. cerebellum 40. A neurologist believes that Derik may have epilepsy. To confirm this diagnosis, the neurologist needs to examine the activity in Derik's brain. The best way to obtain this information would be to use: a. an electroencephalogram (EEG) b. a computerized tomography scan (CT scan) c. positron emission tomography (PET) d. brain lesioning
6 41. One technique that provides pictures of brain structures is: a. an electroencephalogram (EEG) b. computerized tomography scans (CT scans) c. positron emission tomography (PET) d. brain lesioning 42. The imaging technique used to examine brain functioning is: a. an electroencephalogram (EEG) b. computerized tomography scans (CT scans) c. positron emission tomography (PET) d. magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 43. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): a. monitors the overall electrical activity within the brain b. produces extremely detailed, three-dimensional images of the brain c. provides actual pictures of the brain's anatomical structures d. uses radioactive chemicals to produce a pictorial blueprint of brain activity 44. Basic life support functions such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure are associated with: a. the cerebellum b. the medulla c. the reticular formation d. the hippocampus 45. Which midbrain structure is linked to the control of general arousal? a. the amygdala b. the cerebellum c. Wernicke's area d. the reticular formation 46. Larry was recently knocked unconscious when he struck his head on the ice during a figure skating routine. He used to be a world class figure skater, but now he is having difficulty coordinating the motor skills involved in various jumps and spirals. It is likely that when he fell on the ice, Larry sustained damage to his: a. reticular formation b. amygdala c. cerebellum d. temporal lobe 47. The structure that plays an important role in the regulation of eating, drinking, body temperature, and sexual behavior is the: a. thalamus b. medulla c. tectum d. hypothalamus 48. The structure that is basically a relay center in the brain is the: a. the hypothalamus b. the limbic system c. the cerebellum d. the thalamus 49. Which structure is not part of the brain stem
7 a. Thalamus b. Pons c. Reticular Formation d. All of these are part of the brain stem 50. Which structure is involved with hearing a. Inferior colliculus b. Superior colliculus c. Pons d. None of these
8 Answer Key Psychology 101 Exam 1 Fall 2000 Name 1. > c Defining Psychology TYPE: Text Definition Nair2e01 Ch 1 #1 (MC #1) REF: p > b Clinical Psychologist TYPE: Applied Definition Nair2e01 Ch 1 #10 (MC #10) REF: p > d Applied Psychologist TYPE: Text Definition Nair2e01 Ch 1 #13 (MC #13) REF: p > b Applied Psychologist TYPE: Applied Definition Nair2e01 Ch 1 #17 (MC #17) REF: p > a Applied Psychologist TYPE: New Application Nair2e01 Ch 1 #19 (MC #19) REF: p > d Research Psychologist TYPE: Applied Definition Nair2e01 Ch 1 #25 (MC #25) REF: p > b Research Psychologist TYPE: Applied Definition Nair2e01 Ch 1 #26 (MC #26) REF: p > a Research Psychologist TYPE: WWW Nair2e01 Ch 1 #29 (MC #29) REF: p > b Psychiatrist TYPE: WWW Nair2e01 Ch 1 #35 (MC #35) REF: p > d Psychiatrist TYPE: Conceptual Nair2e01 Ch 1 #40 (MC #40) REF: p > b Mind-Body Problem TYPE: Factual Nair2e01 Ch 1 #42 (MC #42) REF: p > b Nativism TYPE: Text Definition Nair2e01 Ch 1 #52 (MC #52) REF: p > d Natural Selection TYPE: Study Guide Nair2e01 Ch 1 #58 (MC #58) REF: p > b
9 Structuralism TYPE: Factual Nair2e01 Ch 1 #61 (MC #61) REF: p > b Structuralism TYPE: WWW Nair2e01 Ch 1 #63 (MC #63) REF: p > d Introspection TYPE: Study Guide Nair2e01 Ch 1 #73 (MC #73) REF: p > c Functionalism TYPE: Factual Nair2e01 Ch 1 #76 (MC #76) REF: p > d Functionalism TYPE: Study Guide Nair2e01 Ch 1 #82 (MC #82) REF: p > c Behaviorism TYPE: Factual Nair2e01 Ch 1 #87 (MC #87) REF: p > c Behaviorism TYPE: Conceptual Nair2e01 Ch 1 #90 (MC #90) REF: p > a Psychoanalysis TYPE: New Application Nair2e01 Ch 1 #94 (MC #94) REF: p > c Reactivity TYPE: New Application Nair2e02 Ch 2 #22 (MC #22) REF: p > b Naturalistic Observation TYPE: New Application Nair2e02 Ch 2 #31 (MC #31) REF: p > b Case Study Method TYPE: New Application Nair2e02 Ch 2 #48 (MC #48) REF: p > c Survey Method TYPE: Text Definition Nair2e02 Ch 2 #51 (MC #51) REF: p > d Sampling TYPE: Text Definition Nair2e02 Ch 2 #59 (MC #59) REF: p > c Central Tendency TYPE: Text Definition Nair2e02 Ch 2 #68 (MC #68) REF: p > b Central Tendency TYPE: Text Definition
10 Nair2e02 Ch 2 #72 (MC #72) REF: p > d Variability TYPE: Text Definition Nair2e02 Ch 2 #80 (MC #80) REF: p > c Positive Correlation TYPE: New Application Nair2e02 Ch 2 #96 (MC #96) REF: p > a Strength of a Correlation TYPE: New Application Nair2e02 Ch 2 #108 (MC #108) REF: p > a Independent Variable TYPE: New Application Nair2e02 Ch 2 #130 (MC #130) REF: p > a Dependent Variable TYPE: Text Definition Nair2e02 Ch 2 #138 (MC #138) REF: p > a Sensory Neurons TYPE: Text Application Nair2e03 Ch 3 #6 (MC #6) REF: p > d Motor Neurons TYPE: Factual Nair2e03 Ch 3 #17 (MC #17) REF: p > d Glial Cells TYPE: Factual Nair2e03 Ch 3 #24 (MC #24) REF: p > d Reflexes TYPE: Factual Nair2e03 Ch 3 #29 (MC #29) REF: p > c Sympathetic Nervous System TYPE: New Application Nair2e03 Ch 3 #125 (MC #125) REF: p > b Parasympathetic Nervous System TYPE: New Application Nair2e03 Ch 3 #128 (MC #128) REF: p > a Studying Brain Function TYPE: Conceptual Nair2e03 Ch 3 #139 (MC #139) REF: p > b Studying Brain Function TYPE: Factual Nair2e03 Ch 3 #141 (MC #141) REF: p > c Studying Brain Function TYPE: Factual Nair2e03 Ch 3 #144 (MC #144) REF: p. 90
11 43. > b Studying Brain Function TYPE: Factual Nair2e03 Ch 3 #146 (MC #146) REF: p > b Medulla and Pons TYPE: Factual Nair2e03 Ch 3 #149 (MC #149) REF: p > d Reticular Formation TYPE: Factual Nair2e03 Ch 3 #154 (MC #154) REF: p > c Cerebellum TYPE: New Application Nair2e03 Ch 3 #162 (MC #162) REF: p > d Hypothalamus TYPE: WWW Nair2e03 Ch 3 #171 (MC #171) REF: p > d Thalamus TYPE: Factual Nair2e03 Ch 3 #169 (MC #169) REF: p > a 50. > a
12
Psychology 100 Exam 1 Spring. 98
 Psychology 100 Exam 1 Spring. 98 Name 1. Which is the first person to contended the mind is a blank slate? a. Pavlov b. Watson c. Plato d. Freud e. Aristotle 2. Which of the following individuals contend
Psychology 100 Exam 1 Spring. 98 Name 1. Which is the first person to contended the mind is a blank slate? a. Pavlov b. Watson c. Plato d. Freud e. Aristotle 2. Which of the following individuals contend
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy
 Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
psychology. experience. mind when Answer the questions, then look up the correct answers in the te xt, course web pages, etc.
 1 Practice Questions for Unit 1 Answer the questions, then look up the correct answers in the te xt, course web pages, etc. 2 The concept of the reflex arc was developed by a. Rene Descartes b. John Locke
1 Practice Questions for Unit 1 Answer the questions, then look up the correct answers in the te xt, course web pages, etc. 2 The concept of the reflex arc was developed by a. Rene Descartes b. John Locke
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
The Brain Studying & Structures. Unit 3
 The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
1. Aristotle suggested that a meal makes us sleepy by causing heat to collect around the
 Module 1 1. Aristotle suggested that a meal makes us sleepy by causing heat to collect around the A. brain. B. throat. C. heart. D. stomach. 2. Wilhelm Wundt's laboratory work involved experimental studies
Module 1 1. Aristotle suggested that a meal makes us sleepy by causing heat to collect around the A. brain. B. throat. C. heart. D. stomach. 2. Wilhelm Wundt's laboratory work involved experimental studies
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
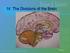 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
The Nervous System. The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind.
 The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
PSY - All Old Quizzes
 PSY - All Old Quizzes 1. John B. Watson believed that psychology should involve the study of. a. Consciousness b. The brain c. The mind d. Behavior 2. A(n) is a measure of how strongly two variables are
PSY - All Old Quizzes 1. John B. Watson believed that psychology should involve the study of. a. Consciousness b. The brain c. The mind d. Behavior 2. A(n) is a measure of how strongly two variables are
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Schools of Psychology
 Schools of Psychology Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. "I am primarily interested in thinking processes; I am a psychologist."
Schools of Psychology Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. "I am primarily interested in thinking processes; I am a psychologist."
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
AP Psychology Ch. 02 The Brain Study Guide
 Name: Period: 1. Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? A) It was ahead of its time and no one believed it could be true. B) The brain is not neatly organized into structures that
Name: Period: 1. Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? A) It was ahead of its time and no one believed it could be true. B) The brain is not neatly organized into structures that
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology
 PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli
 The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology
 Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Ch. 1 The Science of Psychology
 Ch. 1 The Science of Psychology Psychology Scientific study of behavior and mental processes. Behavior outward or overt actions and reactions. Mental processes internal, covert activity of our minds. Psychology
Ch. 1 The Science of Psychology Psychology Scientific study of behavior and mental processes. Behavior outward or overt actions and reactions. Mental processes internal, covert activity of our minds. Psychology
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Ch. 2: The Biological Perspective Take Home Test on Peripheral Nervous System and the Brain Human Behavior Mr. Minervini
 Ch. 2: The Biological Perspective Take Home Test on Peripheral Nervous System and the Brain Human Behavior Mr. Minervini Level 1 Only Name: Period: Please highlight the correct answer/response in yellow
Ch. 2: The Biological Perspective Take Home Test on Peripheral Nervous System and the Brain Human Behavior Mr. Minervini Level 1 Only Name: Period: Please highlight the correct answer/response in yellow
The Nervous System IN DEPTH
 The Nervous System IN DEPTH The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Note taking tips Make sure that you have written
The Nervous System IN DEPTH The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Note taking tips Make sure that you have written
6. When the release of ACh is blocked, the result is A) depression. B) muscular paralysis. C) aggression. D) schizophrenia. E) euphoria.
 Name: Date: 1. Research on left-handedness suggests that A) genes or prenatal factors play a role in handedness. B) a greater proportion of women than men are left-handed. C) left-handers generally demonstrate
Name: Date: 1. Research on left-handedness suggests that A) genes or prenatal factors play a role in handedness. B) a greater proportion of women than men are left-handed. C) left-handers generally demonstrate
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
Gymnázium, Brno, Slovanské nám. 7, WORKBOOK - Biology WORKBOOK. Student:
 WORKBOOK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Teacher: Student: Biology Iva Kubištová.. School year:../ This material was prepared with using http://biologygmh.com/ Topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nervous system, Senses,
WORKBOOK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Teacher: Student: Biology Iva Kubištová.. School year:../ This material was prepared with using http://biologygmh.com/ Topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nervous system, Senses,
Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System. Total 33 points
 Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System Total 33 points Name: Circle the best response to the following: (33 points) 1. What do we call the long fibre that carries impulses away from the nerve cell body? A.
Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System Total 33 points Name: Circle the best response to the following: (33 points) 1. What do we call the long fibre that carries impulses away from the nerve cell body? A.
Will s Pre-Test for Exam IV
 Will s Pre-Test for Exam IV 1) The brain and spinal cord comprise the. (a) autonomic nervous system (b) peripheral nervous system (c) central nervous system (d) efferent nervous system (e) afferent nervous
Will s Pre-Test for Exam IV 1) The brain and spinal cord comprise the. (a) autonomic nervous system (b) peripheral nervous system (c) central nervous system (d) efferent nervous system (e) afferent nervous
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test
 AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
Objectives. ! Describe the major structures of the nervous system. ! Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted.
 Objectives! Describe the major structures of the nervous system.! Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted.! Distinguish between the functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems.! Identify
Objectives! Describe the major structures of the nervous system.! Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted.! Distinguish between the functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems.! Identify
II. HISTORICAL SCHOOLS AND APPROACHES
 Psychology as a science became organized into different branches or schools of thought. First schools: structuralism, functionalism, and behaviorism. Followed by Gestalt psychology and psychoanalysis.
Psychology as a science became organized into different branches or schools of thought. First schools: structuralism, functionalism, and behaviorism. Followed by Gestalt psychology and psychoanalysis.
How do we study the brain? What are the parts of the hindbrain? What is the reticular formation? Parts of the forebrain? Parts of the limbic system?
 How do we study the brain? What are the parts of the hindbrain? What is the reticular formation? Parts of the forebrain? Parts of the limbic system? Lobes of the cerebral cortex? What is the sensory cortex?
How do we study the brain? What are the parts of the hindbrain? What is the reticular formation? Parts of the forebrain? Parts of the limbic system? Lobes of the cerebral cortex? What is the sensory cortex?
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Neuroscience. Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior 1/11/2010. The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
AP PSYCHOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT-2017
 AP PSYCHOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT-2017 Dear Future Students, Welcome to Advanced Placement Psychology! This summer assignment is meant to introduce you to psychology, the perspectives of the field, and the
AP PSYCHOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT-2017 Dear Future Students, Welcome to Advanced Placement Psychology! This summer assignment is meant to introduce you to psychology, the perspectives of the field, and the
Psychology study guide chapter 2
 Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: The Brain Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most obvious difference between the human brain and the brain of a carp
Name: The Brain Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most obvious difference between the human brain and the brain of a carp
Psychology AP Mid-Term Review Packet
 Psychology AP Mid-Term Review Packet How you choose to complete this packet is up to you. I would suggest including more than just a basic definition. Chapter One Psychology Trained Introspection Functionalism
Psychology AP Mid-Term Review Packet How you choose to complete this packet is up to you. I would suggest including more than just a basic definition. Chapter One Psychology Trained Introspection Functionalism
Biological Research Strategies and Hormones
 Biological Research Strategies and Hormones WHS AP Psychology Unit 3: Biological Psychology Essential Task 3-6: Detail historic and contemporary research strategies and technologies that support research
Biological Research Strategies and Hormones WHS AP Psychology Unit 3: Biological Psychology Essential Task 3-6: Detail historic and contemporary research strategies and technologies that support research
Chapter 2 Test. 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. *a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain e.
 Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Chapter 1 Introduction to Psychology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Psychology Main Idea Through the study of human and animal behavior, people can discover psychological principles that have the potential to enrich the lives of humans. Objectives
Chapter 1 Introduction to Psychology Main Idea Through the study of human and animal behavior, people can discover psychological principles that have the potential to enrich the lives of humans. Objectives
True or False. 1. Questions about human nature date back to the speculations of the ancient philosophers Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle.
 True or False Quiz True or False 1. Questions about human nature date back to the speculations of the ancient philosophers Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. True or False 2. Sigmund Freud is generally considered
True or False Quiz True or False 1. Questions about human nature date back to the speculations of the ancient philosophers Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. True or False 2. Sigmund Freud is generally considered
18. The visual cortex is located in the: A) occipital lobe. B) temporal lobe. C) frontal lobe. D) parietal lobe.
 Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
Psychology Unit 1 Test
 1 Psychology Unit 1 Test Choose the best answer. (2 pts each). 1. Of the following, who is a humanistic psychologist? a. Sigmund Freud b. Abraham Maslow c. B. F. Skinner d. John Watson 2. I am primarily
1 Psychology Unit 1 Test Choose the best answer. (2 pts each). 1. Of the following, who is a humanistic psychologist? a. Sigmund Freud b. Abraham Maslow c. B. F. Skinner d. John Watson 2. I am primarily
Forebrain Brain Structures Limbic System. Brain Stem Midbrain Basil Ganglia. Cerebellum Reticular Formation Medulla oblongata
 Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Week 2 Psychology. The Brain and Behavior
 Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]
![Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1] Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]](/thumbs/90/103926552.jpg) Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
II. Nervous System (NS) Organization: can be organized by location/ structure or by function A. Structural Organization 1. Central N.S.
 Nervous System I. Nervous system Functions A. Detect Changes in the environment (stimuli) B. Interpret/evaluate those stimuli C. Initiate responses (trigger muscle contractions or glandular response) II.
Nervous System I. Nervous system Functions A. Detect Changes in the environment (stimuli) B. Interpret/evaluate those stimuli C. Initiate responses (trigger muscle contractions or glandular response) II.
Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How Do Genetic Factors Affect Behavior? II. Does Our Evolutionary Heritage Influence Current Behavior? III. How is the Nervous
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How Do Genetic Factors Affect Behavior? II. Does Our Evolutionary Heritage Influence Current Behavior? III. How is the Nervous
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Brain Structures. Some scientists divide the brain up into three parts. Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain
 The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior. Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed)
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
CNS Tour (Lecture 12)
 A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Nervous Systems. Brain Development
 Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Neurons. Biological Basis of Behavior. Three Types of Neurons. Three Types of Neurons. The Withdrawal Reflex. Transmission of message 10/2/2017
 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Chapter 1. The Evolution of Psychology
 Chapter 1 The Evolution of Psychology The Development of Psychology: From Speculation to Science Prior to 1879 Physiology and philosophy scholars studying questions about the mind Wilhelm Wundt (1832-1920)
Chapter 1 The Evolution of Psychology The Development of Psychology: From Speculation to Science Prior to 1879 Physiology and philosophy scholars studying questions about the mind Wilhelm Wundt (1832-1920)
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
 Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
CR 1: History & Approaches. This Curricular Requirement can be found in Chapter 1 of Myers Psychology for AP.
 CR 1: History & Approaches This Curricular Requirement can be found in Chapter 1 of Myers Psychology for AP. History & Approaches: 2-4% Recognize how philosophical and physiological perspectives shaped
CR 1: History & Approaches This Curricular Requirement can be found in Chapter 1 of Myers Psychology for AP. History & Approaches: 2-4% Recognize how philosophical and physiological perspectives shaped
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
Name Class Date. Read the words in the box. Read the sentences. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Nervous System TWO SYSTEMS WITHIN A SYSTEM 1. What does the nervous system do? a. pump blood b. gather and interpret information c. digest food d. eliminate
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Nervous System TWO SYSTEMS WITHIN A SYSTEM 1. What does the nervous system do? a. pump blood b. gather and interpret information c. digest food d. eliminate
PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY. Art & Philosophy!
 PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY Art & Philosophy! Psychology - is the science of behavior and mental processes. Behavior anything an organism does a recordable action Mental Processes internal subjective experience
PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY Art & Philosophy! Psychology - is the science of behavior and mental processes. Behavior anything an organism does a recordable action Mental Processes internal subjective experience
