SpikerBox Neural Engineering Workshop
|
|
|
- Mervyn Bryant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SpikerBox Neural Engineering Workshop A Workshop Curriculum for Grades 9-12 Developed as a two-day, two hours/day workshop Developed by UW Graduate Students: Stephanie Seeman, Bethany Kondiles, and Katherine Manbeck November 2014 Copyright 2014, Center for Sensorimotor Neural Engineering, University of Washington
2 Workshop Time: 2-2 hour sessions or 1-3 hour session Background: The nervous system operates by taking in natural stimuli (sound, vision, touch, etc.) and responding in the form of electrical action potentials among groups of neurons. The nature of this stimulus-response relationship is dependent on both input into the system (stimuli) and the output of the system (response by a group of neurons), and thus is a defining feature of that particular system. Scientists and clinicians can take advantage of the input-output relationship by recording a neural response and reconstructing the stimulus that likely evoked that response. In the motor system, the activity of a group of neurons is what contracts muscles and allows us to move. If you record from the brain of a paralyzed patient, you would see that their neurons are active just like an able-bodied person even though they can t actually make the intended movement. However, since we know what the inputoutput relationship is between neural activity and movement, we can use the recorded neurons to artificially create the encoded movement. This is the basis for neural engineering; understanding the relationship between an input and an output so that we may use one to engineer the other. Session 1: Objective: To understand how the nervous system uses action potentials to code responses to sensory stimuli. Today you will be learning how action potentials encode sensory information by recording from neurons in a cockroach leg in response to sensory stimuli. Key Words: Input Output Action potential (AP) Electrode o Recording Encoding Decoding Key Concepts: 1. A system can be defined by its input-output relationship 2. Neurons facilitate the inputs and outputs of the nervous system 3. We can directly measure the nervous system by recording from neurons 4. The nervous system encodes information about the world Key Questions: 1. What is the input-output relationship of any system? 2. How do you record from the nervous system? 2
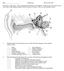
3 3. What ways can you stimulate the nervous system? 4. How does the response of the cockroach leg encode information about the stimulus? Materials List: Per group, 2-4 students/group Backyard Brains SpikerBox Bundle, which includes: o Recording Electrode o Smartphone Data Cable (green cable, Macs and mobile devices) o Laptop Data Cable (blue cable, PCs) o Stimulation Cable Y-splitter 2 x audio cables Mini audio amplifier/speaker, can be found at RadioShack Laptop, tablet, or smartphone Audacity, freely available for download for laptops Backyard Brains App, freely available for Apple devices Cockroach leg or Cricket leg (which you can get at a local pet store) Toothpicks Tweezers Extra sewers pins Exercises: READ THROUGH ALL OF THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY! A cockroach leg contains sensory spines that are innervated by neurons. We can record the activity of these neurons and how they respond to stimuli. Setting up the SpikerBox Open your kit and remove the SpikerBox from the bottom compartment Remove one of the Speakers - turn it on just past the click (don t turn the volume all the way up). Take out the black Y splitter cable - plug the male (unsplit) end into the Spiker Box (green arrow in Fig 1). Take out black audio cable and plug into INPUT of speakerconnect speaker to one female end of the splitter cable. MAC: Remove the GREEN cable and plug SpikerBox end into the other splitter cable jack, and the Smartphone end into the headphone jack of the computer. 3
4 PC: Remove the BLUE cable and plug one end into the other splitter cable jack, and the other end into the microphone jack of the computer. Carefully pick up the cockroach leg and place it on the cork pad of the SpikerBox. Position it so that the tibia (Fig 2) is hanging off the RIGHT edge a little bit. You want to be able to access the tibia for stimulating later. Remove the recording electrode from your box and place one pin (lead) into the coxa and the second lead into the femur. Push all the way through so that the leg is secure on the cork. a. There are 2 pins that comprise your recording electrode. What is the role of each pin? Plug the electrode into the SpikerBox (Fig. 1 yellow arrow) and turn it on by flipping the switch (a green light should come on and you should hear a noise). You are now recording from a cockroach leg! Listen for the little pops in the recording that happen above the general noise. If you re having trouble getting a good recording try repositioning the electrodes ever so slightly. Also to reduce noise and hear the spikes better keep talking to a minimum. b. What are you recording in the leg? Go into Audacity on the computer, it should already be open Hit the record button (red circle). Go to View Fit Vertically This will allow you to look at your spikes. You can zoom in two ways; use both to make the action potentials big enough to easily see. o Click on the zero on the y-axis. You may need to click several times. This zooms vertically. (note: if you zoom in too much you can hold shift and then click to zoom back out. 4
5 o Click on the + magnifying glass on the right hand side of the screen. This zooms horizontally, in time, and will make the recording move faster or slower across your screen. Once you are consistently seeing good action potentials, hit the stop button (yellow square). You will now be able to scroll through your recording. Identifying different neurons Find a section of your recording that has a few big action potentials. Use the zoom tool (the magnifying glass with no plus or minus toward the left of the screen) to draw a window around the action potentials. Pick out action potentials from 2-3 different neurons. c. How are the action potentials from one neuron different from the action potentials of another? (Ex. Size, shape) Why might action potentials differ between neurons? Calculating the firing rate and amplitude of a neuron: Once you have identified a couple of neurons find a section of your recording that has action potentials from each of your neurons. Zoom in so that the width of the window (x-axis) is 1 second long! Count the number of action potentials you see FROM 1 NEURON! This is the baseline firing rate! It is measured in spikes/second or Hertz. You can get a feel for the firing rate just by listening to the recording as well. Find the peak and trough of the action potential. Calculate the amplitude by subtracting the y- axis values of the peak and the trough. Do this for 2-3 DIFFERENT NEURONS. Find different sections of recording if necessary to help answer the questions in the table below. 5
6 d. Fill in the table for each of your different neurons: number each neuron for reference. When you are done call over an instructor to go over your answers. Neuron Peak value Trough value Amplitude Baseline Firing Rate (spikes/sec) 3. Sensory stimulation The neurons in the spine respond to sensory stimulation such as physical bending and air movement. Restart the recording of your cockroach leg in Audacity by clicking the record button again. This will start a new recording window. Stimulate the spines on the leg by following the instructions below and answering the questions. Work as a group to note where in the recording the stimulation started and ended so that you can zoom in on the section and calculate the firing rate. Pick the biggest, or most obvious action potential in your recording to analyze a. Blow on the leg gently. In general what happened to the firing rate when you tried blowing on it, did it go up, down, no change? Stop your recording. Select a section of your recording during the blowing that is 1 second long. b. Calculate and record the firing rate. Compared to the baseline firing rate did it increase, decrease, no change? c. Gently deflect a spine on the leg with your toothpick. Make sure to touch just one spine and not disrupt the whole leg. What is the firing rate of the neuron now? What happened to the firing rate here: up, down, no change? 6
7 d. What is the input and what is the output in this system for each type of stimulation? 7
8 e. Spine Stimulation Work together to fill in the table trying different stimuli. Before performing each experiment make a prediction of what the result will be based on what you have done so far. Write your prediction in the Prediction column. Do this as a group. For the experiments try having one person apply the stimuli, and a second person recording the results in the Response column. Measure your response as firing rate in Hertz as you did above. Compare the response firing rate to the baseline you calculated earlier when discussing a Change in firing rate. Instructions Stimulus (input) Prediction Response (output) Record firing rate (spikes/sec) Deflect a spine in one direction for a set amount of time, as in Figure A on the right. Then deflect the spine in the opposite direction (as in Figure B) for the same amount of time. Direction of spine deflection A. B. A. Will firing rate: (circle one) CHANGE NOT CHANGE B. Will firing rate: (circle one) CHANGE NOT CHANGE A: B: If there was a change did it increase or decrease, compared to baseline? 8
9 Touch the spine as lightly as you can. Deflect a lot vs. a little A. Which direction will you deflect the spine and why? A. Small deflection: Deflect the spine as far as you can Large deflection: B. Which will produce a greater change in firing rate, a small deflection or a large one? B. Was your prediction right? Deflect the spine as you have in previous experiments so that you observe a change in firing rate. Hold the spine there for various amounts of time, returning to no bend in between. Deflect for a long time vs. a short time 5 sec 10 sec 30 sec Do you expect the change in firing rate to last the duration of the hold? 5 sec: YES NO 10 sec: YES NO 30 sec: YES NO Record the firing rate in the first and last second of your hold and compare. 5 sec: 10 sec: 30 sec: 9
10 BEFORE MOVING ON TO THE NEXT SECTION WE WILL ALL REGROUP AND DEMONSTRATE STIMULATING WITH MUSIC. Up until now you have been stimulating the sensory neurons in your leg by mechanically activating the spines with your toothpick. There are also motor neurons in your leg which, when active, cause the leg to move. You can stimulate these motor neurons by injecting stimulation, in the form of music, into the leg itself. What happened when we started playing the song? Did the leg move? Did the leg seem to move to only certain parts of the song? Over the next week, think about what in the song is activating the motor neurons and causing the leg to move. Come next week with a list of songs you want to try using as stimulation for the leg. Think about why you chose those songs and what you expect the response in the leg will be. Also think of songs that may not cause leg movement. Here are some ideas to try: Songs with a lot of bass vs little bass Songs with more speaking (rap) vs more instrumental Loud songs vs soft songs Homework for next session: 1. Choose your list of songs 2. Fill in first 3 columns of the table on the last page. 10
11 Session 2: Objective: To understand how the nervous system uses action potentials to drive motor output. Today you will be stimulating neurons to produce action potentials which will cause a cockroach leg to move. Review: Peripheral nerves, those that go to legs, arms, and other extremities, contain both sensory neurons and motor neurons. Last week you manually stimulated the nerve in the cockroach leg. This stimulation elicited action potentials in the sensory neurons which travels to the brain and tells the cockroach something about the external world. Neurons can also be stimulated by electricity to produce action potentials. Today you will use electrical stimulation in the form of music, sound waves, to elicit action potentials in the motor neurons. Activity in motor neurons causes muscles to contract, resulting in movement. You will explore how different songs activated motor neurons and thus cause the cockroach leg to move. As a review and preview fill in the table below highlighting the difference between sensory and motor neurons. A. What is the input? Sensory Neuron Motor Neuron B. What is the output? Key Words: - Stimulating electrode - Encoding - Decoding - Sensory neurons - Motor neurons Key Concepts: 1. Stimulating a sensory neuron vs. stimulating a motor neuron 2. Scientists and clinicians can use this information encoding to simulate neural intent for motor output in injured patients or prosthetics. Key Questions: 1. How is electrical stimulation like/unlike sensory stimulation? 2. How might you use sensory responses from one cockroach to control the leg movement of a second cockroach? 11
12 Setting up the SpikerBox Open your kit and remove the SpikerBox from the bottom compartment Carefully pick up the cockroach leg and place it on the cork pad of the SpikerBox. Position it so that the tibia (Fig 2) is hanging off the RIGHT edge a little bit. You want to be able to access the tibia with your manipulator for stimulating later. Remove the recording electrode from your box and place one pin (lead) into the coxa and the second lead into the femur. Push all the way through so that the leg is secure on the cork. Plug the electrode into the SpikerBox (Fig. 1 yellow arrow) and turn it on by flipping the switch (a green light should come on and you should hear a noise). You are now recording from a cockroach leg! Use the speaker on the SpikerBox to listen for the little pops in the recording that happen above the general noise. If you re having trouble getting a good recording try repositioning the electrodes ever so slightly. Also to reduce noise and hear the spikes better keep talking to a minimum. Setting up electrical stimulation Now that you know you have good electrical contact with the neurons in the leg, it s time to start stimulating electrically! Turn your SpikerBox off and unplug the recording electrode from the box, BUT NOT FROM YOUR LEG! Plug the Y-splitter into the audio jack of the computer Remove the stimulating cable from your kit. Attach the red and black clips to each pin in the leg. Plug one end of the audio cable into the Y-splitter and the other into the INPUT of the RadioShack speaker. Turn the volume on the Radio Shack speaker all the way down (just above the click) Turn the volume on the device controlling the music to HALF WAY! When controlling the volume of the music use the computer or phone, NOT the RadioShack speaker (these two volume sources will multiple together so you need to keep one very low) 12
13 What is your general hypothesis based on the songs you have chosen? (Ex. Songs with bass will cause movement while songs without bass will not). When you have your hypothesis show an instructor. Hypothesis: Conclusions: How would you describe the movements of the leg in reaction to the songs you picked? Did the leg deflect a lot? Did it move fast? Why do you think each song caused the leg to act the way it did? Was your initial hypothesis correct? 13
14 Song Stimulation: Cue up your songs and work through the table. Start the volume of the song at half way. If the leg doesn t move turn to ¾ and full until you see movement. This is the threshold volume of the motor neurons you are stimulating for that particular song. If the leg is already moving at ½ volume, turn down to ¼ or until movement stops. After you ve tested all of your songs fill in the Conclusions below your hypothesis. Think about the results of each of your songs individually as well as a whole how the leg responded to stimulation. What song did you pick? Why did you pick it? Do you expect the leg to move when you play this song? Did it move? Threshold volume How did it move? To a beat? Randomly? Describe YES NO YES NO ¼ ½ ¾ FULL YES NO YES NO ¼ ½ ¾ FULL YES NO YES NO ¼ ½ ¾ FULL YES NO YES NO ¼ ½ ¾ FULL 14
iworx Sample Lab Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors
 Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors Exercise 1: Chordotonal Organs Aim: To explore the basic characteristics of the chordotonal organs, their response to direction and intensity of leg movement,
Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors Exercise 1: Chordotonal Organs Aim: To explore the basic characteristics of the chordotonal organs, their response to direction and intensity of leg movement,
Section 4. Intro to Neurophysiology
 Section 4. Intro to Neurophysiology 4.1 Action potentials at work (Cockroach Receptive Fields) Overview The goals of this unit are to: 1) introduce you to the basic concepts, equipment, and methodology
Section 4. Intro to Neurophysiology 4.1 Action potentials at work (Cockroach Receptive Fields) Overview The goals of this unit are to: 1) introduce you to the basic concepts, equipment, and methodology
LAB 3. Neurophysiology Electrical Activity of Neurons
 LAB 3 Neurophysiology Electrical Activity of Neurons The following lab manuals were adapted and written by Veronique Boucquey, Derek Huffman, Joyce Lacy of the Dept. of Neurobiology and Behavior at the
LAB 3 Neurophysiology Electrical Activity of Neurons The following lab manuals were adapted and written by Veronique Boucquey, Derek Huffman, Joyce Lacy of the Dept. of Neurobiology and Behavior at the
>Talko. Have your modular speak out the CV, the LPC, 8 bits, vintage way. Page 1
 >Talko Have your modular speak out the CV, the LPC, 8 bits, vintage way. Page 1 Table of Contents 1Short description...3 2Technical details... 3 3Banks... 4 4Panel... 4 4.1Mode Switch...4 4.2Sound jack
>Talko Have your modular speak out the CV, the LPC, 8 bits, vintage way. Page 1 Table of Contents 1Short description...3 2Technical details... 3 3Banks... 4 4Panel... 4 4.1Mode Switch...4 4.2Sound jack
QUICK START GUIDE TYMPANOMETRY AND AUDIOMETRY FOR SENTIERO DESKTOP DEVICES
 DEVICE CONNECTORS On/off button Headphones or second transducer Power supply Air pump USB cable Label printer Patient response Probe button Make sure all your appropriate transducers are connected (Tymp
DEVICE CONNECTORS On/off button Headphones or second transducer Power supply Air pump USB cable Label printer Patient response Probe button Make sure all your appropriate transducers are connected (Tymp
LAB ONE: SPIKES FOR ALL! A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE SPIKERBOX
 LAB ONE: SPIKES FOR ALL! A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE SPIKERBOX OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. learn how to prepare a cockroach leg for electrophysiological readings; 2. observe and record action potentials
LAB ONE: SPIKES FOR ALL! A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE SPIKERBOX OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. learn how to prepare a cockroach leg for electrophysiological readings; 2. observe and record action potentials
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM III
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM III Small Review Review What is this? A neuron What does it do? Receives and transmits information Sending a signal How are signals sent in the nervous system? Message travels from neuron
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM III Small Review Review What is this? A neuron What does it do? Receives and transmits information Sending a signal How are signals sent in the nervous system? Message travels from neuron
Bio-logic AuDX PRO FLEX Screening tympanometry and audiometry Quick start guide
 AuDX PRO FLEX Screening tympanometry and audiometry Quick start guide Doc. No.7-26-1374-EN/00 Part No.7-26-13704-EN Natus Medical Denmark ApS. +45 45 75 55 55. otoinfo@natus.com Natus Medical Incorporated.
AuDX PRO FLEX Screening tympanometry and audiometry Quick start guide Doc. No.7-26-1374-EN/00 Part No.7-26-13704-EN Natus Medical Denmark ApS. +45 45 75 55 55. otoinfo@natus.com Natus Medical Incorporated.
EKG and Sound.
 I. Before coming to lab Read this handout and the supplemental. Visit the following website: blaufuss.org then click on the "START" button next to "Heart Sounds Tutorial." Do not worry so much about the
I. Before coming to lab Read this handout and the supplemental. Visit the following website: blaufuss.org then click on the "START" button next to "Heart Sounds Tutorial." Do not worry so much about the
Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease
 Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease Lab #10 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes...... 83 Introduction....... 84 Activity 1: Collecting ECG Data..... 85 Activity
Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease Lab #10 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes...... 83 Introduction....... 84 Activity 1: Collecting ECG Data..... 85 Activity
Frequently asked questions to Oticon ConnectClip
 Frequently asked questions to Oticon ConnectClip 1. Pairing Question Answer How many devices can ConnectClip be paired to? ConnectClip can be paired to up to 8 Bluetooth devices. What happens when a 9th
Frequently asked questions to Oticon ConnectClip 1. Pairing Question Answer How many devices can ConnectClip be paired to? ConnectClip can be paired to up to 8 Bluetooth devices. What happens when a 9th
1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002
 1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002 I. Introduction. Read the introductory material in your lab manual Marieb Ex 16A: Skeletal Muscle Physiology Frog
1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002 I. Introduction. Read the introductory material in your lab manual Marieb Ex 16A: Skeletal Muscle Physiology Frog
Connevans.info. DeafEquipment.co.uk. This product may be purchased from Connevans Limited secure online store at
 Connevans.info Solutions to improve the quality of life Offering you choice Helping you choose This product may be purchased from Connevans Limited secure online store at www.deafequipment.co.uk DeafEquipment.co.uk
Connevans.info Solutions to improve the quality of life Offering you choice Helping you choose This product may be purchased from Connevans Limited secure online store at www.deafequipment.co.uk DeafEquipment.co.uk
Roger at work. Bridging the understanding gap
 Roger at work Bridging the understanding gap Concentrate on excelling, not your hearing The modern workplace can be a complicated listening environment, with its challenging open-plan spaces, group meetings,
Roger at work Bridging the understanding gap Concentrate on excelling, not your hearing The modern workplace can be a complicated listening environment, with its challenging open-plan spaces, group meetings,
Guess: Correct or Incorrect. Trial (perform in random order)
 AP Biology Senses Lab Names Per. Our senses are constantly bombarded with various stimuli from the environment, which are relayed to the central nervous system where the information is interpreted. In
AP Biology Senses Lab Names Per. Our senses are constantly bombarded with various stimuli from the environment, which are relayed to the central nervous system where the information is interpreted. In
Evolve 3 & 5 Service Manual
 Evolve 3 & 5 Service Manual 1 Product Browse 2 Contents CHAPTER 1: SERIAL NUMBER LOCATION... 5 CHAPTER 2: CONSOLE INSTRUCTIONS 2.1 Console Overview... 6 2.1.1 Evolve 3 Console Overview... 6 2.1.2 Evolve
Evolve 3 & 5 Service Manual 1 Product Browse 2 Contents CHAPTER 1: SERIAL NUMBER LOCATION... 5 CHAPTER 2: CONSOLE INSTRUCTIONS 2.1 Console Overview... 6 2.1.1 Evolve 3 Console Overview... 6 2.1.2 Evolve
Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 5.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 5.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42
Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation
 Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation Text Reading: Silverthorn, 5 th ed. 412 419, 425 427; 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 In this exercise, we will investigate the physiology of contraction in the
Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation Text Reading: Silverthorn, 5 th ed. 412 419, 425 427; 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 In this exercise, we will investigate the physiology of contraction in the
MedRx HLS Plus. An Instructional Guide to operating the Hearing Loss Simulator and Master Hearing Aid. Hearing Loss Simulator
 MedRx HLS Plus An Instructional Guide to operating the Hearing Loss Simulator and Master Hearing Aid Hearing Loss Simulator The Hearing Loss Simulator dynamically demonstrates the effect of the client
MedRx HLS Plus An Instructional Guide to operating the Hearing Loss Simulator and Master Hearing Aid Hearing Loss Simulator The Hearing Loss Simulator dynamically demonstrates the effect of the client
Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography
 Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography Readings: Silverthorn, 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 Your brain communicates with your muscles through action potentials on the motor neurons, which are then transmitted
Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography Readings: Silverthorn, 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 Your brain communicates with your muscles through action potentials on the motor neurons, which are then transmitted
Quick guide to connectivity and the ReSound Smart 3D app
 Quick guide to connectivity and the ReSound Smart 3D app 2 Content Compatibility: Hearing aids and mobile devices...4 Get started with your iphone, ipad or ipod touch...6 Pair with your ReSound Smart Hearing
Quick guide to connectivity and the ReSound Smart 3D app 2 Content Compatibility: Hearing aids and mobile devices...4 Get started with your iphone, ipad or ipod touch...6 Pair with your ReSound Smart Hearing
Voice Switch Manual. InvoTek, Inc Riverview Drive Alma, AR USA (479)
 Voice Switch Manual InvoTek, Inc. 1026 Riverview Drive Alma, AR 72921 USA (479) 632-4166 www.invotek.org info@invotek.org Voice Switch DESCRIPTION OF FUNCTION The Voice Switch is designed to provide a
Voice Switch Manual InvoTek, Inc. 1026 Riverview Drive Alma, AR 72921 USA (479) 632-4166 www.invotek.org info@invotek.org Voice Switch DESCRIPTION OF FUNCTION The Voice Switch is designed to provide a
Sound Interfaces Engineering Interaction Technologies. Prof. Stefanie Mueller HCI Engineering Group
 Sound Interfaces 6.810 Engineering Interaction Technologies Prof. Stefanie Mueller HCI Engineering Group what is sound? if a tree falls in the forest and nobody is there does it make sound?
Sound Interfaces 6.810 Engineering Interaction Technologies Prof. Stefanie Mueller HCI Engineering Group what is sound? if a tree falls in the forest and nobody is there does it make sound?
SOUNDS LIKE FUN SCIENCE GRADE 4 STELLA BIZZIO. TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class.
 SOUNDS LIKE FUN TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class. OVERVIEW: Using hands-on activities and demonstrations the lesson will focus on the production of sound as energy that can make matter vibrate. Students
SOUNDS LIKE FUN TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class. OVERVIEW: Using hands-on activities and demonstrations the lesson will focus on the production of sound as energy that can make matter vibrate. Students
IHearYou The award-winning self-fit hearing aid system. A detailed guide (April 2018).
 Discover the system that puts you in control of your hearing health. IHearYou The award-winning self-fit hearing aid system. A detailed guide (April 2018). Better hearing is at your f i nger tips. I will
Discover the system that puts you in control of your hearing health. IHearYou The award-winning self-fit hearing aid system. A detailed guide (April 2018). Better hearing is at your f i nger tips. I will
Quick Guide - eabr with Eclipse
 What is eabr? Quick Guide - eabr with Eclipse An electrical Auditory Brainstem Response (eabr) is a measurement of the ABR using an electrical stimulus. Instead of a traditional acoustic stimulus the cochlear
What is eabr? Quick Guide - eabr with Eclipse An electrical Auditory Brainstem Response (eabr) is a measurement of the ABR using an electrical stimulus. Instead of a traditional acoustic stimulus the cochlear
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
5. Which word refers to making
 Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Nerve Cell Communication
 Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 40 minutes if Part 4 is completed for homework. Teacher Provides:
Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 40 minutes if Part 4 is completed for homework. Teacher Provides:
Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG
 Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Manual Revision PL3.7.0 080706 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Manual Revision PL3.7.0 080706 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
(Visual) Attention. October 3, PSY Visual Attention 1
 (Visual) Attention Perception and awareness of a visual object seems to involve attending to the object. Do we have to attend to an object to perceive it? Some tasks seem to proceed with little or no attention
(Visual) Attention Perception and awareness of a visual object seems to involve attending to the object. Do we have to attend to an object to perceive it? Some tasks seem to proceed with little or no attention
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab. Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine
Regulation of Human Heart Rate
 Name: Date: Period: Regulation of Human Heart Rate Pre-Lab 1. List some activities or stimuli that you think may increase a person s heart rate. An activity is something a person does, and a stimulus is
Name: Date: Period: Regulation of Human Heart Rate Pre-Lab 1. List some activities or stimuli that you think may increase a person s heart rate. An activity is something a person does, and a stimulus is
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
The Gaze Cueing Paradigm with Eye Tracking Background Set-up Lab
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-17 The Gaze Cueing Paradigm with Eye Tracking Background Set-up Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-17 The Gaze Cueing Paradigm with Eye Tracking Background Set-up Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
Humans make voluntary decisions to talk, walk, stand up, or sit down. The
 2 E X E R C I S E Skeletal Muscle Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define motor unit, twitch, latent period, contraction phase, relaxation phase, threshold, summation, tetanus, fatigue, isometric contraction,
2 E X E R C I S E Skeletal Muscle Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define motor unit, twitch, latent period, contraction phase, relaxation phase, threshold, summation, tetanus, fatigue, isometric contraction,
AMBCO 1000+P AUDIOMETER
 Model 1000+ Printer User Manual AMBCO 1000+P AUDIOMETER AMBCO ELECTRONICS 15052 REDHILL AVE SUITE #D TUSTIN, CA 92780 (714) 259-7930 FAX (714) 259-1688 WWW.AMBCO.COM 10-1004, Rev. A DCO 17 008, 11 13 17
Model 1000+ Printer User Manual AMBCO 1000+P AUDIOMETER AMBCO ELECTRONICS 15052 REDHILL AVE SUITE #D TUSTIN, CA 92780 (714) 259-7930 FAX (714) 259-1688 WWW.AMBCO.COM 10-1004, Rev. A DCO 17 008, 11 13 17
Tune in on life with SCOLAbuddy. A new fm receiver from Widex
 Tune in on life with SCOLAbuddy A new fm receiver from Widex Meet your new buddy The latest member of the Scola FM family The successful Widex SCOLA FM product series has acquired a new family member:
Tune in on life with SCOLAbuddy A new fm receiver from Widex Meet your new buddy The latest member of the Scola FM family The successful Widex SCOLA FM product series has acquired a new family member:
Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm
 Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm Background During almost all social interactions, people s eyes convey information about their direction of attention as well as their emotional and mental status.
Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm Background During almost all social interactions, people s eyes convey information about their direction of attention as well as their emotional and mental status.
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
This series of Sensory Questionnaires are designed to enable you to support your child s progress with particular areas of sensory development.
 This series of Sensory Questionnaires are designed to enable you to support your child s progress with particular areas of sensory development. YOUR SENSE OF HEARING Listening to the world around us helps
This series of Sensory Questionnaires are designed to enable you to support your child s progress with particular areas of sensory development. YOUR SENSE OF HEARING Listening to the world around us helps
Biology 325 Fall 2003 Human anatomy and physiology
 SKELETAL MUSCLE PROPERTIES Background : In this experiment, you will investigate the physiological properties of skeletal muscle from the isolated amphibian gastrocnemius. You will examine skeletal muscle
SKELETAL MUSCLE PROPERTIES Background : In this experiment, you will investigate the physiological properties of skeletal muscle from the isolated amphibian gastrocnemius. You will examine skeletal muscle
Norwood Science Center
 Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Reaction Times: A POGIL Introduction to the Nervous System
 Reaction Times: A POGIL Introduction to the Nervous System Original POGIL developed during July 2011 POGIL Workshop; revised by Nancy Cripe, Minnehaha Academy Student Content Outcomes Summarize the organization
Reaction Times: A POGIL Introduction to the Nervous System Original POGIL developed during July 2011 POGIL Workshop; revised by Nancy Cripe, Minnehaha Academy Student Content Outcomes Summarize the organization
Custom instruments. Insio primax User Guide. Hearing Systems
 Custom instruments Insio primax User Guide Hearing Systems Content Welcome 4 Your hearing instruments 5 Instrument type 5 Getting to know your hearing instruments 5 Components and names 6 Controls 8 Settings
Custom instruments Insio primax User Guide Hearing Systems Content Welcome 4 Your hearing instruments 5 Instrument type 5 Getting to know your hearing instruments 5 Components and names 6 Controls 8 Settings
SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT. Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction
 SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction 1 Overview of course and requirements Lecture/discussion; lecture notes on website http://faculty.washington.edu/lawerner/sphsc462/
SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction 1 Overview of course and requirements Lecture/discussion; lecture notes on website http://faculty.washington.edu/lawerner/sphsc462/
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Hearing Control App User Guide
 Hearing Control App User Guide Introduction to Audibel s Smart Hearing Aids Android Listed below are Audibel s smartphone compatible hearing aids that work with the TruLink Hearing Control app: We are
Hearing Control App User Guide Introduction to Audibel s Smart Hearing Aids Android Listed below are Audibel s smartphone compatible hearing aids that work with the TruLink Hearing Control app: We are
Design Folio Stay Tuned! Comparing the effects of long and short-term auditory stimulation for increasing the sensitivity of a person s hearing.
 Design Folio Stay Tuned! Comparing the effects of long and short-term auditory stimulation for increasing the sensitivity of a person s hearing. Page 1 of 12 Need or problem For my scientific research
Design Folio Stay Tuned! Comparing the effects of long and short-term auditory stimulation for increasing the sensitivity of a person s hearing. Page 1 of 12 Need or problem For my scientific research
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Product Model #: Digital Portable Radio XTS 5000 (Std / Rugged / Secure / Type )
 Rehabilitation Act Amendments of 1998, Section 508 Subpart 1194.25 Self-Contained, Closed Products The following features are derived from Section 508 When a timed response is required alert user, allow
Rehabilitation Act Amendments of 1998, Section 508 Subpart 1194.25 Self-Contained, Closed Products The following features are derived from Section 508 When a timed response is required alert user, allow
Set-up Instructions. MANUFACTURED BY COMMUNICATIONS-APPLIED TECHNOLOGY CO., INC. RESTON, VA. CAGE CODE: 0EEY2
 Set-up Instructions C-AT Level A/B Radio Interface with: Push-to-Talk Assembly, Shaped Audio Throat Microphone Bi-aural Speaker Assembly (two configurations) MANUFACTURED BY COMMUNICATIONS-APPLIED TECHNOLOGY
Set-up Instructions C-AT Level A/B Radio Interface with: Push-to-Talk Assembly, Shaped Audio Throat Microphone Bi-aural Speaker Assembly (two configurations) MANUFACTURED BY COMMUNICATIONS-APPLIED TECHNOLOGY
Each student should record the ECG of one of the members of the lab group and have their own ECG recorded.
 EXPERIMENT 1 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment is to introduce you to the techniques of electrocardiography and the interpretation of electrocardiograms. In Part A of the experiment, you
EXPERIMENT 1 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment is to introduce you to the techniques of electrocardiography and the interpretation of electrocardiograms. In Part A of the experiment, you
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION KEY TERMS
 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION KEY TERMS BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING refers to processing sensory information as it is coming in. In other words, if I flash a random picture on the screen, your
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION KEY TERMS BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING refers to processing sensory information as it is coming in. In other words, if I flash a random picture on the screen, your
Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue
 Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 080706 Richard Pflanzer,
Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 080706 Richard Pflanzer,
Demo Mode. Once you have taken the time to navigate your RPM 2 app in "Demo mode" you should be ready to pair, connect, and try your inserts.
 Demo Mode RPM 2 is supported with a "demonstration (Demo) mode" that easily allows you to navigate the app. Demo mode is intended for navigation purposes only. Data in Demo mode are simply random data
Demo Mode RPM 2 is supported with a "demonstration (Demo) mode" that easily allows you to navigate the app. Demo mode is intended for navigation purposes only. Data in Demo mode are simply random data
SENDING SECRET MESSAGES (1 Hour)
 SENDING SECRET MESSAGES (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound
SENDING SECRET MESSAGES (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound
The Nervous System. Two Systems Within a System. 526 Chapter 17
 1 The Nervous System Key Concept Your nervous system is an organ system that gathers, interprets, and responds to sensory information. What You Will Learn The central nervous system processes and responds
1 The Nervous System Key Concept Your nervous system is an organ system that gathers, interprets, and responds to sensory information. What You Will Learn The central nervous system processes and responds
Hear Better With FM. Get more from everyday situations. Life is on
 Hear Better With FM Get more from everyday situations Life is on We are sensitive to the needs of everyone who depends on our knowledge, ideas and care. And by creatively challenging the limits of technology,
Hear Better With FM Get more from everyday situations Life is on We are sensitive to the needs of everyone who depends on our knowledge, ideas and care. And by creatively challenging the limits of technology,
Platinum Series Sound Processor
 Platinum Series Sound Processor We encourage you to review the processor components before proceeding. Choose from the item below that best describes your situation: I want to learn how to perform a task
Platinum Series Sound Processor We encourage you to review the processor components before proceeding. Choose from the item below that best describes your situation: I want to learn how to perform a task
Nord.cTracICA.Cr USER'S MANUAL A CAUTION QUESTIONS? .. Visit our website'at. new products, prizes, fitness tips, and much more!
 Nord.cTracICA.Cr Model No. NTCW90907.1 Serial No. Write the serial number in the space above for reference. _ USER'S MANUAL Serial Number Decal (under frame) QUESTIONS? As a manufacturer, we are committed
Nord.cTracICA.Cr Model No. NTCW90907.1 Serial No. Write the serial number in the space above for reference. _ USER'S MANUAL Serial Number Decal (under frame) QUESTIONS? As a manufacturer, we are committed
BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject
 Updated 12-22-03 BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject This PRO lesson describes hardware and software setup of the BSL PRO System to record and measure
Updated 12-22-03 BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject This PRO lesson describes hardware and software setup of the BSL PRO System to record and measure
User Manual Verizon Wireless. All Rights Reserved. verizonwireless.com OM2260VW
 User Manual 2010 Verizon Wireless. All Rights Reserved. verizonwireless.com OM2260VW Home Phone Connect Welcome to Verizon Wireless Thank you for choosing Verizon Wireless Home Phone Connect. You re now
User Manual 2010 Verizon Wireless. All Rights Reserved. verizonwireless.com OM2260VW Home Phone Connect Welcome to Verizon Wireless Thank you for choosing Verizon Wireless Home Phone Connect. You re now
QuickTIPS REMOTE CONTROL TRULINK FOR APPLE DEVICES VOLUME CHANGES MEMORY CHANGES. PRODUCT AVAILABILITY: Halo iq, Halo 2, and Halo Devices
 QuickTIPS TRULINK FOR APPLE DEVICES PRODUCT AVAILABILITY: Halo iq, Halo 2, and Halo Devices For the most up-to-date information regarding Apple devices and ios versions that are supported for use with
QuickTIPS TRULINK FOR APPLE DEVICES PRODUCT AVAILABILITY: Halo iq, Halo 2, and Halo Devices For the most up-to-date information regarding Apple devices and ios versions that are supported for use with
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide
 E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
Phonak Wireless Communication Portfolio Product information
 Phonak Wireless Communication Portfolio Product information The accessories of the Phonak Wireless Communication Portfolio offer great benefits in difficult listening situations and unparalleled speech
Phonak Wireless Communication Portfolio Product information The accessories of the Phonak Wireless Communication Portfolio offer great benefits in difficult listening situations and unparalleled speech
Phonak Wireless Communication Portfolio Product information
 Phonak Wireless Communication Portfolio Product information We have been listening to ensure we fully understand what matters to you. Each new generation of products is based on these insights. This understanding
Phonak Wireless Communication Portfolio Product information We have been listening to ensure we fully understand what matters to you. Each new generation of products is based on these insights. This understanding
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
Restoring Communication and Mobility
 Restoring Communication and Mobility What are they? Artificial devices connected to the body that substitute, restore or supplement a sensory, cognitive, or motive function of the nervous system that has
Restoring Communication and Mobility What are they? Artificial devices connected to the body that substitute, restore or supplement a sensory, cognitive, or motive function of the nervous system that has
Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves
 The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
This series of Sensory Questionnaires are designed to enable you to support your child s progress at different stages of sensory development.
 This series of Sensory Questionnaires are designed to enable you to support your child s progress at different stages of sensory development. YOUR SENSE OF HEARING Listening to the world around us helps
This series of Sensory Questionnaires are designed to enable you to support your child s progress at different stages of sensory development. YOUR SENSE OF HEARING Listening to the world around us helps
Table of Contents Science Action Labs
 Table of Contents Science Action Labs 1: Vibrating Sound......................................5 2: Sound Fun..........................................8 3: How Sound Travels..................................11
Table of Contents Science Action Labs 1: Vibrating Sound......................................5 2: Sound Fun..........................................8 3: How Sound Travels..................................11
Controlling Worries and Habits
 THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
How to use mycontrol App 2.0. Rebecca Herbig, AuD
 Rebecca Herbig, AuD Introduction The mycontrol TM App provides the wearer with a convenient way to control their Bluetooth hearing aids as well as to monitor their hearing performance closely. It is compatible
Rebecca Herbig, AuD Introduction The mycontrol TM App provides the wearer with a convenient way to control their Bluetooth hearing aids as well as to monitor their hearing performance closely. It is compatible
Lecture 1: Neurons. Lecture 2: Coding with spikes. To gain a basic understanding of spike based neural codes
 Lecture : Neurons Lecture 2: Coding with spikes Learning objectives: To gain a basic understanding of spike based neural codes McCulloch Pitts Neuron I w in Σ out Θ Examples: I = ; θ =.5; w=. - in = *.
Lecture : Neurons Lecture 2: Coding with spikes Learning objectives: To gain a basic understanding of spike based neural codes McCulloch Pitts Neuron I w in Σ out Θ Examples: I = ; θ =.5; w=. - in = *.
[TRANSCRANIAL DC STIMULATION] [PROTOCOL GUIDE] For use with the Oasis Pro
![[TRANSCRANIAL DC STIMULATION] [PROTOCOL GUIDE] For use with the Oasis Pro [TRANSCRANIAL DC STIMULATION] [PROTOCOL GUIDE] For use with the Oasis Pro](/thumbs/87/95996779.jpg) [TRANSCRANIAL DC STIMULATION] [PROTOCOL GUIDE] For use with the Oasis Pro W A R N I N G / W A I V E R Transcranial DC Stimulation is very powerful and if applied improperly, may cause mental impairments
[TRANSCRANIAL DC STIMULATION] [PROTOCOL GUIDE] For use with the Oasis Pro W A R N I N G / W A I V E R Transcranial DC Stimulation is very powerful and if applied improperly, may cause mental impairments
Practical Guidelines For the Enraf-Nonius Commercial Training Myomed 632
 Practical Guidelines For the Enraf-Nonius Commercial Training Myomed 632 Copyright: & Exclusive Sales and Service: Enraf-Nonius B.V. P.O. Box 12080 3004 GB ROTTERDAM The Netherlands Tel: +31 (0)10 20 30
Practical Guidelines For the Enraf-Nonius Commercial Training Myomed 632 Copyright: & Exclusive Sales and Service: Enraf-Nonius B.V. P.O. Box 12080 3004 GB ROTTERDAM The Netherlands Tel: +31 (0)10 20 30
Cochlear Implant The only hope for severely Deaf
 Cochlear Implant The only hope for severely Deaf By: Dr. M. Sohail Awan, FCPS (ENT) Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi - Pakistan For centuries, people believed that only a miracle could restore hearing
Cochlear Implant The only hope for severely Deaf By: Dr. M. Sohail Awan, FCPS (ENT) Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi - Pakistan For centuries, people believed that only a miracle could restore hearing
Cochlear True Wireless Accessories Experience True Wireless Freedom
 Cochlear True Wireless Accessories Experience True Wireless Freedom Experience the convenience of our exclusive wireless technology. Cochlear hearing implants can help you extend your hearing experience,
Cochlear True Wireless Accessories Experience True Wireless Freedom Experience the convenience of our exclusive wireless technology. Cochlear hearing implants can help you extend your hearing experience,
SENSES: VISION. Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014
 SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
The Golf Swing Speed Challenge (103) - First 3 Weeks
 103 The Golf Swing Speed Challenge (103) - First 3 Weeks In the first three weeks of this elite program you're going to be predominantly doing two things 1. Improving your flexibility through a range of
103 The Golf Swing Speed Challenge (103) - First 3 Weeks In the first three weeks of this elite program you're going to be predominantly doing two things 1. Improving your flexibility through a range of
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Posner s Attention Test
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-18 Posner s Attention Test Background Setup Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-18 Posner s Attention Test Background Setup Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
Connectivity guide for ReSound Smart 3D app
 Connectivity guide for ReSound Smart 3D app Table of contents Introduction to ReSound Smart Hearing Aids... 3 Mobile Devices that Work with ReSound Smart Hearing Aids... 3 Connectivity and ReSound Smart
Connectivity guide for ReSound Smart 3D app Table of contents Introduction to ReSound Smart Hearing Aids... 3 Mobile Devices that Work with ReSound Smart Hearing Aids... 3 Connectivity and ReSound Smart
Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings. Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014
 Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014 Goals for the lecture Be able to: Conceptually understand some of the analysis and jargon encountered in a typical (sensory)
Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014 Goals for the lecture Be able to: Conceptually understand some of the analysis and jargon encountered in a typical (sensory)
Source and Description Category of Practice Level of CI User How to Use Additional Information. Intermediate- Advanced. Beginner- Advanced
 Source and Description Category of Practice Level of CI User How to Use Additional Information Randall s ESL Lab: http://www.esllab.com/ Provide practice in listening and comprehending dialogue. Comprehension
Source and Description Category of Practice Level of CI User How to Use Additional Information Randall s ESL Lab: http://www.esllab.com/ Provide practice in listening and comprehending dialogue. Comprehension
Testing FM Systems on the 7000 Hearing Aid Test System
 Testing FM Systems on the 7000 Hearing Aid Test System Introduction Testing FM Systems on the 7000 Hearing Aid Test System This workbook describes how to test FM systems with the 7000 Hearing Aid Test
Testing FM Systems on the 7000 Hearing Aid Test System Introduction Testing FM Systems on the 7000 Hearing Aid Test System This workbook describes how to test FM systems with the 7000 Hearing Aid Test
Appendix: Instructions for Treatment Index B (Human Opponents, With Recommendations)
 Appendix: Instructions for Treatment Index B (Human Opponents, With Recommendations) This is an experiment in the economics of strategic decision making. Various agencies have provided funds for this research.
Appendix: Instructions for Treatment Index B (Human Opponents, With Recommendations) This is an experiment in the economics of strategic decision making. Various agencies have provided funds for this research.
Biological Information Neuroscience
 Biological Information Neuroscience The Nervous System Sensory neurons Motor neurons Interneurons Gathers, stores, process, and communicate vast amounts of information and uses it successfully. 10/25/2012
Biological Information Neuroscience The Nervous System Sensory neurons Motor neurons Interneurons Gathers, stores, process, and communicate vast amounts of information and uses it successfully. 10/25/2012
TEAK Bioengineering Artificial Hearing Lesson Plan Page 1 TEAK Traveling Engineering Activity Kits
 TEAK Bioengineering Artificial Hearing Lesson Plan Page 1 TEAK Traveling Engineering Activity Kits Biomedical Engineering Kit: Artificial Sensory Artificial Hearing Activity TEAK Bioengineering Artificial
TEAK Bioengineering Artificial Hearing Lesson Plan Page 1 TEAK Traveling Engineering Activity Kits Biomedical Engineering Kit: Artificial Sensory Artificial Hearing Activity TEAK Bioengineering Artificial
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted
 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted for recording; dark black line indicates electrode. Stereotactic
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted for recording; dark black line indicates electrode. Stereotactic
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997
 ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
Trouble hearing? Do you have trouble hearing in some situations?
 Trouble hearing? Do you have trouble hearing in some situations? At home. Does your partner often need to speak up to get her point across? With friends. Do you have trouble following the conversation
Trouble hearing? Do you have trouble hearing in some situations? At home. Does your partner often need to speak up to get her point across? With friends. Do you have trouble following the conversation
1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms may be used more than once.
 THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMS Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system, nerves STUDENT BOOK Ch. 7, pp. 202 206 1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms
THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMS Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system, nerves STUDENT BOOK Ch. 7, pp. 202 206 1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms
Adventure 3 Plus Service Manual
 Adventure 3 Plus Service Manual 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: SERIAL NUMBER LOCATION...3 CHAPTER 2: PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE 2.1 Preventative Maintenance. 4 2.2 Tension and Centering the Running Belt....6
Adventure 3 Plus Service Manual 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: SERIAL NUMBER LOCATION...3 CHAPTER 2: PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE 2.1 Preventative Maintenance. 4 2.2 Tension and Centering the Running Belt....6
Hand on a Hot Stove Teacher Information
 STO-135 Hand on a Hot Stove Teacher Information Summary Kit contains Students model the neuron pathways involved in reflex actions, conscious sensations, voluntary movements, and memories. They apply their
STO-135 Hand on a Hot Stove Teacher Information Summary Kit contains Students model the neuron pathways involved in reflex actions, conscious sensations, voluntary movements, and memories. They apply their
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study
 Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study What is Biofeedback? Biofeedback is a technique that people can use to learn to control their body's physiological functions. The definition
Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study What is Biofeedback? Biofeedback is a technique that people can use to learn to control their body's physiological functions. The definition
Chapter 5 Test Review. Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line
 Chapter 5 Test Review Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line Printing game plan Put six slides on a page Select pure black and white as the printing option Okay, now wade into the answers>>>>
Chapter 5 Test Review Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line Printing game plan Put six slides on a page Select pure black and white as the printing option Okay, now wade into the answers>>>>
How to use mycontrol App 2.0. Rebecca Herbig, AuD
 Rebecca Herbig, AuD Introduction The mycontrol TM App provides the wearer with a convenient way to control their Bluetooth hearing aids as well as to monitor their hearing performance closely. It is compatible
Rebecca Herbig, AuD Introduction The mycontrol TM App provides the wearer with a convenient way to control their Bluetooth hearing aids as well as to monitor their hearing performance closely. It is compatible
