Reliability, Validity, and Feasibility of the Mayo Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Questionnaire (GERQ) in a Persian-Speaking Population
|
|
|
- Dustin Boyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 37, No.2, 2008, Iranian pp J Publ Health, Vol. 37, No.2, 2008, pp Original Article Reliability, Validity, and Feasibility of the Mayo Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Questionnaire (GERQ) in a Persian-Speaking Population *S Nasseri-Moghaddam 1, H Razjouyan 1, R Habibi 1, K Rafaat-Zand 1, B Ahrari 1, M Nouraie 1, R Majdzadeh 2, H Vahedi 1, R Malekzadeh 1 1 Digestive Disease Research Center, Shariati Hospital, Medical Sciences/University of Tehran, Iran 2 Tehran University of Medical Sciences, School of Public Health and Institute of Public Health Research, Iran (Received 4 Aug 2007; accepted 16 Feb 2008) Abstract Background: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is prevalent in the West. Mayo-GERQ is one of the most widely used questionnaires for screening GERD. We validated GERQ in an Iranian population. Methods: The Mayo-GERQ was translated into Persian (P-GERQ) and reviewed and commented by two gastroenterologists. Eleven lay-people filled it in and commented on it. Reliability was assessed by test-retest within 2-6 wks in 53 hospital staff. Concurrent-validity was checked in another 53, comparing the results of the self-administered questionnaire with the questionnaires filled in by a gastroenterologist interviewing them. Weighted-kappa (κw) statistics was used. Time needed to complete the questionnaire, practicability of the directions and linguistic eloquence were checked (feasibility indices). Results were used to modify P-GERQ. The modified P-GERQ was tested in another 99 hospital employees in the same manner. Results: Phase-one; One-hundred seventeen subjects were enrolled (46 men). Mean time for completion was 23.7 minutes. Mean kw for reliability was 0.47 and that for validity Sources of poor performance were sought, P-GERQ was revised and underwent validation again (2 nd phase). Phase-two: Ninety-nine individuals were enrolled (37 men). The modified P- GERQ took 15.8+/-11.9 min to complete. κ-values for concurrent-validity of major symptoms (acid-regurgitation, heartburn) were 0.70 and 0.67 respectively. Corresponding κ-values for reliability were 0.57 and Conclusions: P-GERQ was not valid initially. After making appropriate technical and linguistic changes, it achieved acceptable validity, reliability and feasibility. In addition to making available a useful tool for population-based studies, our results underscore the importance of validation before adopting a translated questionnaire. Keywords: Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Questionnaire (GERQ), Feasibility, Reliability, Validity, Weighted Kappa Statistic (κw). Introduction Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a prevalent, chronic condition, with 10-30% of the Western population and 2-20% of the people in the east being affected by weekly symptoms (1-6). Recent studies have shown that GERD and its complications are increasing worldwide (6-10). GERD has already placed a significant burden on healthcare systems, as evidenced by a 3-fold increase in ambulatory care visits to primary care physicians and an almost 5-fold increase in visits to specialists for GERD between 1990 and 2001 (11). Therefore, handling GERD and its complications needs careful planning by the healthcare community. Accurate epidemiological studies will be the cornerstone of this planning. Screening tools are necessary for this type of studies. There are several methods to make a diagnosis of GERD [e.g. ph metry, multi-channel intraluminal impedance measurement (MII), and upper GI endoscopy (UGIE)], but none of them is considered gold standard and most not a feasible screening tool. Currently questionnaires, especially self-administered ones, are the only feasible and reliable method of assessing GERD prevalence. They are relatively easy to administer, inexpensive, noninvasive, and do not need sophisticated tools and personal training procedures. Self-administered questionnaires have been shown to be cost effective methods in screening patients with 64 *Corresponding author: Tel: , Fax: , sianm@ams.ac.ir
2 S Nasseri-Moghaddam et al: Reliability, Validity, and Feasibility... gastrointestinal (GI) complaints (12-18). Symptom assessment, management, and resolution remain the primary goals of medical interventions for both patients and physicians. Therefore, several questionnaires have been developed for this purpose (19), the Mayo gastro-esophageal reflux questionnaire (GERQ) being one of the popular ones (20). The GERQ is a structured questionnaire addressing major and minor GERD symptoms as well as demographic characteristics, habits, medications and past-medical and family history of major upper GI disorders. It has been shown to be valid for this purpose in other communities (21, 22). Patient-Reported Outcomes (PRO) instruments must meet scientific standards (13) and satisfy regulatory criteria, particularly from the perspective of claims for labeling and promotion (23). The regulatory criteria are linguistic, cross-cultural adaptation and psychometric documentation. Persian translation, cross-cultural adaptation and psychometric validation of the Mayo GERQ were the goals of our study. This is done as the pre-requisite of population-based studies in Iran. Materials and Methods The Mayo GERQ The gastroesophageal reflux questionnaire, a self-administered instrument with 80 questions that measures symptoms during the prior year and collects a medical history, has been shown to be reliable (median kappa: 0.70) on test retesting and valid (median kappa, 0.62) in comparison with a physician interview (20). The final structure of the questionnaire is as follows: 1) Four parts assessing major GERD symptoms [namely heartburn (HB), acid regurgitation (AR), chest pain (CP), and dysphagia] during the past 12 months. Each part begins with a screening entry question. Following a positive answer to the screening question, three questions assess duration, frequency, and severity of the symptom and one question seeks the most noxious symptom of the four. Whenever the answer is No to the entry question, the respondent is directed to ignore the rest of the questions of that section and go to the next part. 2) Another part assesses the effect of HB and AR on daily life and medical-care seeking behavior. 3) Nine questions assess various upper GI symptoms including dyspepsia, regurgitation, globus, eructation, nausea, hematemesis, hiccups and early satiety. Five other questions assess respiratory problems, cough, bronchitis, asthma, and hoarseness. These are considered as minor GERD symptoms. 4) The rest of the questions evaluate physician/ hospital referrals during the past 12 months, use of antacids, anti-secretory agents (H-2 blockers and proton pump inhibitors), aspirin, and NSAIDs, as well as pregnancy, presence of hiatal hernias, esophageal dilatation or surgery, history of any esophageal, gastric, cardiac or pulmonary diseases. Coffee and alcohol intake, smoking, general health, and history of esophageal or gastric problems in spouse. The study was performed in two phases: Phase-1 Translation, cultural adaptation and primary validity and reliability testing Preparation & Sampling The permission to use GERQ was obtained from Mayo Clinic authorities, Rochester, Minnesota, USA. It was translated to Persian by a gastroenterologist with special interest in GERD. Since alcohol consumption is legally and religiously forbidden in Iran, the question addressing alcohol consumption was omitted in order to prevent loss of cooperation and compliance. This version was presented to, evaluated and approved by two other gastroenterologists (face validity). Due to lack of an organized national data bank, picking a sample to represent the general population was impractical. The staff of Shariati Hospital, a metropolitan hospital in Tehran (the capital city of Iran), were chosen as the sampling frame (741 subjects). The advantages included better accessibility and follow-up, and presence of a detailed data bank that made randomization and matching possible. A pilot study was conducted on 11 randomly chosen hospital staff. Subjects were asked to fill in 65
3 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 37, No.2, 2008, pp the questionnaire while being timed and write down any ambiguity or difficulties faced. Later, they were individually interviewed. All comments were recorded and used to revise the Persian GERQ. These modifications are detailed in the results section. From the remaining 730 employees, 106 [14.5%, 41 (38.7%) male] were randomly chosen and stratified for gender and educational level. The population s educational profile was as follows: eleven (10.4%) 5 th graders, nine (8.5%) with middle-school degree, 22(20.8%) with high school diploma, 12(11.3%) technicians, 37(34.9%) Bachelor of Science, and 15(14.2%) MDs and higher. Test: Introduced as part of the hospital general health survey, the revised questionnaire was given to all 106 subjects to be completed (self-administered). A separate section was provided for any comments or suggestions. The subjects were intentionally kept unaware of the later re-test or interview step in order to avoid biased patterns of answering and mimic the actual conditions where the questionnaire is to be used. The sample was then divided into two matched groups, 53 subjects each, one for retest and the other for gastroenterologist s interview. The time between the test and the retest/interview step was 2-6 wk. Retest: At this step, which assessed the reliability, the questionnaires were filled in our presence since we intended to time the subjects. As before, the latter was not revealed to the subjects to avoid interference. Upon completion, each subject s questionnaire was compared with the initial one in his/her presence to identify the cause(s) of any disparity between the answers. Interview: To test the concurrent validity, the other 53 subjects were interviewed within 2-6 wk of the initial test by the same gastroenterologist who translated GERQ and who was unaware of the subjects previous responses or medical history. After a structured interview, based on the data obtained, a questionnaire was filled on behalf of the subject by the interviewer. Linguistics: The linguist team was first asked to analyze the translated GERQ per se. After retest they were provided with all the comments, suggestions and ambiguities faced. The linguists report was then generated based upon both the independent review and the information obtained. Statistical Analysis Kappa statistics was used to assess reliability and validity of each question and the questionnaire as a whole. Kappa (κ) statistics and weighted kappa (κw) are used to compare the inter- and intra-rater variability of the reports. Conceptually, κ removes the agreement by chance and informs the clinician of the extent of the possible agreement over and above chance. If the raters agree on every judgment, the total possible agreement is always 100%. Therefore, κ values may vary from -1 (complete disagreement) to +1 (complete agreement), with a zero value pointing to agreement by chance only. Kappa values over 0.8 are considered excellent agreement and those less than 0.2 are considered as very poor. Values of point to good, to moderate, and to weak agreement (24). Kappa statistics fails to differentiate smaller degrees of disagreement from the larger ones. This was compensated for by calculating the weighted kappa statistic (κ w ) where responses could be assigned an ordinal scale. Data were analyzed using the SPSS program and descriptive statistics (means, standard deviation, and percentage) were calculated. Validity and reliability of the questionnaire was assessed by STATA version 7.0 using kappa statistics. Questions with more than two options were analyzed using weighted kappa statitics. STAT transfer 7.0 software was used to transfer SPSS data to STATA. Agreement between answers in the test and retest represented the reliability of each question. The same stood for concurrent validity, which was estimated by comparing the results of the test against the interview. Results of this phase showed that the Persian translation was neither valid nor reliable in this population (details explained in the results section). The sources of incongruity were sought by analyzing the available data and input by the linguist and the questionnaire was reworded and revised. This revised questionnaire was used in the second phase for validation. 66
4 S Nasseri-Moghaddam et al: Reliability, Validity, and Feasibility... Phase-2 The Final Questionnaire Considering the input from phase-1, the following modifications were made and the validation process was repeated. Changes included question appearance, using color papers for each of the entry questions (pink, blue, green, and yellow for pages 3, 5, 7, and 9, respectively), changes of some options of some questions (Q2, 9, 10, 17, 21, 24, 30, 32, 43, 44, 57, 58, 59, 72, 73, 77, 78), deletion of some questions (Q15, 55, 56, 68, 79) and page 18, change in some statements to make them more clear, addition of a question to assess OCP usage in women and two more checking questions to assess AR and HB frequency during the last three months. The final questionnaire was assessed by two gastroenterologists and their comments were considered. The final questionnaire, the Modified Persian Mayo GERQ contained 79 questions and asks the subject to rate how often 16 common symptoms occur and how bothersome they are. Symptom frequency was measured on a scale of 1 to 6 in the following categories: none in the past year, one to ten times in the past year, about once a month, about once a week, several times a week, or daily. Severity of symptoms was classified as mild, moderate, severe, and very severe. We asked about the number of aspirin as well as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs) tablets taken on average each week in the past year. Cigarette use was ascertained as a history of cigarette smoking (yes vs. no) and, for current smokers, the number of packs smoked per day. Current coffee or tea (the commonly used drink in Iran) use (yes or no) and the number of cups per day were measured. Questions assessed whether any of the subject s immediate family members (mother, father, brothers, sisters, and children) or spouse had significant heartburn or disease of the esophagus or stomach. Self-reported current weight (in kilograms) and height (in centimeters) were also asked. Study population Two sets of 50 stratified random subjects from Shariati hospital employees were recruited for the validation of the revised Persian GERQ. The same process of checking reliability and concurrent validity described in the first phase were repeated. Data analysis The same procedure as fore phase-1 was repeated. Results Phase-1 To express the results, we have divided the questionnaire into two functionally distinct sections: Questions 1-38 and questions 39 to 76. The first 38 questions, in 4 clusters, investigate the main symptoms of GERD (heartburn, acid regurgitation, chest pain, and dysphagia) and contain 4 entry (lead) questions. Each lead question is preceded by a definition of the symptom, and followed by a go to direction. Next, there are individual questions that assess GERD s minor & extra-esophageal symptoms, as well as past medical and health status history of the subject. The main reason for this separation is that we believed that the answering patterns in the first section were additionally influenced by the provided definitions and directions. The Pilot study: The Go to directions were modified, complemented by more explanations to render them more user-friendly. A graphic presentation of chest wall, sternum and the area where heartburn is felt was added to the first question to make the heartburn definition more comprehensible. Three out of eleven subjects did not know the organ referred to by the word esophagus, so the proper definition was added prior to the related questions. Sore throat was confused with dysphagia in two cases, and an explanation was offered to avoid confusion. The symptom checklist was omitted from the questionnaire, because the directions were intriguing and difficult to follow. The mean and median for completing the questionnaires were 25.7 and 23.0 minutes respectively (Range: min). Feasibility: The mean and median for completing the questionnaires were 23.7 min and 20.0 min respectively (range: min). Table 67
5 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 37, No.2, 2008, pp details this variable for different educational groups. The translated directions were not understood in the same way by different respondents, therefore aberrant patterns of answering were observed. The linguists assessed the questionnaire as inappropriate for an educational level below middle- school (8 yr of academic education). Table 1: Mean time for completing the questionnaire in different educational groups 5 th graders middle-school High school Diploma Technician B.Sc. M.D. & higher Mean time (min.) Reliability: Table 2 compares some statistics between the original and translated questionnaires while a similar comparison between the two sections of GERQ are presented in table 3. Table 4 illustrates the separate calculations for each major symptom s question cluster. Table 2: Reliability and validity statistics of the original versus translated GERQ κ( w ) for reliability κ( w ) for validity Translated GERQ Original GERQ Translated GERQ Original GERQ Median th percentile th percentile Table 3: Reliability and validity statistics for the two sections of GERQ κ( w ) for reliability κ( w ) for validity 1 st section (qq. 1-38) 2 nd section (qq ) 1 st section (qq. 1-38) 2 nd section (qq ) Mean (SD) 0.36 (0.22) 0.57 (0.25) 0.25 (0.16) 0.26 (0.23) Median Range th percentile th percentile th percentile Heartburn Table 4: Reliability in four question clusters of GERQ κ( w ) for reliability κ( w ) for validity Acid regurgitation Chest pain Dysphagia Heartburn Chest pain Dysphagia Median Range Acid regurgitation
6 S Nasseri-Moghaddam et al: Reliability, Validity, and Feasibility... For this primary study, the median and mean Kw for reliability was 0.48 and 0.47, respectively and the median and mean Kw for validity was 0.29 and According to the results of this study, the questionnaire had moderate reliability and poor validity therefore it was not suitable for epidemiologic studies. These findings led to introducing modifications into the questionnaire as described above. Phase-2 On average, the Modified GERQ took 15.8 min (SD: 11.9, range: 5-60 min) to complete. Ninety nine patients participated in the validation process (mean age: /- 8.1 yr, range: yr) with a female: male ratio of 1.67: 1. More than 72% of participants were high school graduates or had a university degree. Concurrent validity and reliability testing results are presented in Table 5. After considering the first 20 filled questionnaires, we found that the questions do not need further changes to make suitable for performing study. Two cases did not fill out the questionnaire properly, but changing in questionnaire did not seem to avoid the problem. Feasibility: Most interviewees did not have any problem with understanding the questions and responding to them as directed. Mean time for filling the questionnaire was 15.8 (SD: 11.9) min. Table 5: Concurrent validity and reliability of questions Reliability N= 49 Validity N= 50 Overall agreement (%) Κ or Κw 95% CI Overall agreement (%) Κ or Κw 95% CI Heartburn, presence Frequency (12Ms) Frequency (3Ms) Severity * Nocturnal Extension to neck Response to antacid Duration Acid regurgitation, presence Frequency (12Ms) Frequency (3Ms) Severity * Nocturnal * Duration Heartburn and Acid regurgitation, either condition present either condition interrupted daily activities, either condition prompted visit to physician
7 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 37, No.2, 2008, pp No. of physician visits for either condition Reason for physician visits for either condition Table 5: continued... N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A Test done for either condition N.A N.A N.A Chest pain, presence Frequency Severity * * Duration of individual * episodes Exacerbation by cold or warm * drinking Concomitant dysphagia * Pleuritic pain * NA Provoked by heavy exertion * * Provoked by light exertion * * Identified by physician as cardiac * Duration * Dysphagia, presence Frequency * * Severity * Odynophagia * Solids, liquids, or both * Progressive N.A N.A N.A Intermittent (y/n) * Duration * Upper gastrointestinal complain Abdominal pain Pain more than 6 times/yr * Upper or lower abdomen Severity of pain * NA Food regurgitation Nausea Vomiting Hematemesis N.A N.A N.A Main symptom Respiratory symptoms, chest sounded wheezy *
8 S Nasseri-Moghaddam et al: Reliability, Validity, and Feasibility... Table 5: continued... wheezing leading to shortness * of breath Dyspnea on exertion Hoarseness Globus sensation * Burping Early satiety * Hiccups Cough Cough frequency * Nocturnal Cough * Medications, use of aspirin Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agent Use of other medication Past Dx and Rx Hiatal Hernia N.A N.A N.A Disease of the esophagus or stomach Dilation of esophagus N.A N.A N.A Operation of esophagus or N.A N.A N.A stomach Heart disease Diagnosed NA Heart disease treated Asthma NA NA NA Miscellaneous factors Spouse with heartburn Family member with heartburn In general, overall health Elevate head of bed Use of cigarettes Use of tea NA Use of coffee Female specific Pregnancy OCP * Not significant P values 71
9 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 37, No.2, 2008, pp Validity Fifty of 55(91%) invited participants in the validity process accepted to complete the study process. All were interviewed within 2-6 wk after the initial questionnaire was completed. The majority of validity values for the questionnaire were in the fair to excellent range. There was fair to good concordance between the physician interview and the questionnaire for the presence of Heartburn and all the other related aspects of the symptom. The kappa value for the major symptoms including AR, HB, CP, and Dysphagia were 0.70, 0.67, 0.26, and 0.78, respectively. Reliability Forty nine patients participated in the reliability phase of this study. The mean time between completion of the first and second questionnaires was 2-6 wk. Most items had reliability values of good to excellent. The kappa values or the presence of four major symptoms i.e. AR, HB, CP, Dysphagia were 0.57, 0.80, 0.68, and 0.86, respectively. General assessment The mean kappa values for reliability and validity of the questionnaire as a whole were 0.64 (SD: 0.26, 95% CI: ) and 0.44 (SD: 0.29, 95% CI: ), respectively. Median and mean of the questions related to the four major symptoms are shown in Table 6. Table 6: The median and mean values for reliability and validity of major symptoms Reliability Validity Mean Median Mean Median Heartburn Acid Regurgitation Chest pain Dysphagia Discussion We have translated and tested the Mayo GERQ for use in the general Iranian population to assess GERD. The initial translation was not reliable; therefore modifications were made according to the input from the first phase of the study to make the Persian GERQ understandable and more feasible. The general validity and reliability of the questionnaire were fair to good. Kappa values for major GERD symptoms were acceptable, therefore it seems that the modified Persian GERQ in its present format is suitable for population-based studies in Iran. The kappa value for chest pain was rather poor in the initially translated questionnaire. Although it improved with modifications (from 0.07 to 0.27), but it still was not considered valid. This may be due to the low prevalence of this symptom, hence making it unfamiliar to most subjects. In addition, it may have been mistaken with heartburn i.e. heartburn overshadows the chest pain moiety. The reproducibility of minor GERD symptoms was not so good in our final questionnaire. Again this may be due to the fact that theses symptoms are less common and more transient than the major GERD symptoms; therefore assessing their reproducibility in a relatively small sample may be problematic. This study was done in a population with low prevalence of GERD. Had the study been performed in patients referring to a GI clinic, better kappa values may have been achieved and minor symptoms assessed as well. The Modified GERQ is an instrument with fair to excellent validity and reproducibility for the features of GERD. Although a number of validated instruments have been introduced, yet a succinct instrument is lacking (19). No currently available instrument quantitates a number of key GERD elements (including when symptom was first noted, its frequency and severity). The modified GERQ takes sixteen minutes on average to be completed. This is acceptable, but if could be even shortened, it may have been more feasible. Overall, the κ-values of the modified GERQ were high and well acceptable for both reproducibility and validity. Nonetheless, the range between the highest and lowest values was broad, likely due to the sample size of the study. Given that the perception of major symptoms is a very personal experience, and given that the κ ranges of many items were similar to, if not better than, those demonstrated by other validated instruments, we anticipate the Modified GERQ will allow researchers and clinicians to create a uniform language for characterizing patients with GERD symptoms. 72
10 S Nasseri-Moghaddam et al: Reliability, Validity, and Feasibility... GERQ is considered a rather valid and useful tol for assessing GERD in population based studies (20). As demonstrated by our data and supported by others findings, simple translation and peer review of a questionnaire is not adequate to adopt a questionnaire developed for another language and culture regardless of its weight in the original language. Therefore, it is absolutely necessary to test it for appropriateness in measuring the interested items. A self-administered questionnaire should be understood and completed in a reasonable time by the target population, besides being reliable and valid. In summary, the Persian GERQ is a comprehensive instrument with acceptable validity and reproducibility for the diagnosis and measurement of GERD related symptoms. This can be used for population based studies in Persian speaking populations in Iran. Studies to shorten the questionnaire and making it more user-friendly may be warranted. Acknowledgments The authors would like to express their thankfulness to Dr GR Locke from the Mayo clinic for providing the questionnaire and helping in obtaining institution permit to translate and use the GERQ. In addition we hereby express our gratitude to our linguistic team, Dr Kourosh Safavi, Dr Kambiz Mahmoodzadeh and Dr Azita Afrashti for their generous contribution to this work. In addition, we are indebted to Dr Shahin Merat, Mr Mehrdad Shahin-Mehr, and Miss Mina Minapour for their contribution in various parts of the study including the statistical analysis. The present study was supported by a grant from the Digestive Disease Research Center, Shariati Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences. The authors declare that they have no Conflict of Interests. References 1. Dent J, El-Serag H, Wallander M (2005). Epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut, 54: Camilleri M, Dubois D, Coulie B, Jones M, Kahrilas PJ, Rentz AM, et al. (2005) Prevalence and socioeconomic impact of upper gastrointestinal disorders in the United States: results of the US Upper Gastrointestinal Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 3: Nouraie M, Radmard AR, Zaer-Rezaii H, Razjouyan H, Nasseri-Moghaddam S, Malekzadeh R (2007). Hygiene Could Affect GERD Prevalence Independently: A Population-Based Study in Tehran. Am J Gastroenterol, 102 (7): Hu WH, Wong WM, Lam CL, Lam KF, et al. (2002). Anxiety but not depression determines health care-seeking behavior in Chinese patients with dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome: a population-based study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 16: Wang Jin-Hai, Luo Jin-Yan, Dong Lei, Gong Jun, Tong M (2004). Epidemiology of Gastroesophageal reflux disease. A general population-based study in Xi an of Northwest China. World J Gastroenterol, 10: Nouraie M, Razjouyan H, Assady M, Malekzadeh R, Nasseri-Moghaddam S (2007). Epidemiology of Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms in Tehran, Iran; a populationbased Telephone Survey. Arch Iranian Med, 10(3): Holtmann G (2001). Reflux disease: the disorder of the third millennium. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 13(suppl 1):S5 S Delaney B (2004). Review article: prevalence and epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 20(suppl 8): Goh K (2004). Changing epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease in the Asian-Pacific region: an overview. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 19(suppl 3):S22 S Malekzadeh R, Nasseri-Moghaddam S, Sotoudeh M (2003). Gastroesophageal reflux disease: the new epidemic. Arch Iranian Med, 6:
11 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 37, No.2, 2008, pp Altman K, Stephens R, Lyttle C, Weiss KB (2005). Changing impact of gastroesophageal reflux in medical and otolaryngology practice. Laryngoscope, 115: McColl E (2004). Best practice in symptom assessment: a review. Gut, 53(Suppl.4): Lohr K (2002). Assessing health status and quality-of-life instruments: attributes and review criteria. Quality of Life Research, 11: Talley NJ, Zinsmeister AR, Van Dyle C, Melton LJ III (1991). Epidemiology of colonic symptoms and the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology, 101: Talley NJ, Zinsmeister AR, Schleck CD, Melton LJ III (1992). Dyspepsia and dyspepsia subgroups: a population-based study. Gastroenterology, 102: Talley NJ, O Keefe EA, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ III (1992). Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in the elderly: a population-based study. Gastroenterology, 102: Talley NJ, Weaver AL, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ III (1992). Onset and disappearance of gastrointestinal symptoms and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Am J Epidemiol, 136: McColl E, Junghard O, Wiklund I, Revicki DA (2005). Assessing symptoms in gastroesophageal reflux disease: how well do clinicians assessments agree with those of their patients? Am J Gastroenterol, 100: Fass R (2007). Symptom Assessment Tools for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment. J Clin Gastroenterol, 41: Locke GR, Talley NJ, Weaver AL, Zinsmeister AR (1994). A new questionnaire for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Mayo Clin Proc, 69: Wong W, Lam K, Lai K, Hui WM, Hu WH, Lam CL, et al. (2003). A validated symptoms questionnaire (Chinese GERDQ) for the diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in the Chinese population. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 17: Moreno Elola-Olaso C, Rey E, Rodríguez- Artalejo F, Locke GR, Díaz-Rubio M (2002). Adaptation and validation of a gastroesophageal reflux questionnaire for use on a Spanish population. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 94(12): Leidy NK, Revicki DA, Genesté B (1999). Recommendations for evaluating the validity of quality of life claims for labeling and promoting. Value in Health, 2: Maclure M, Willett WC (1987). Misinterpretation and misuse of the kappa statistic. Am J Epidemiol, 126:
Quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease in an Iranian population
 Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2013 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2013 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in Brunei Darussalam
 Gastrointestinal symptoms in Brunei 39 Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in Brunei Darussalam Vui Heng Chong, Gastroenterology Unit, Department of Medicine, Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha (RIPAS)
Gastrointestinal symptoms in Brunei 39 Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in Brunei Darussalam Vui Heng Chong, Gastroenterology Unit, Department of Medicine, Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha (RIPAS)
Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Volume 11 Number 4 2008 VALUE IN HEALTH Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ola Junghard, PhD, 1 Ingela Wiklund, PhD
Volume 11 Number 4 2008 VALUE IN HEALTH Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ola Junghard, PhD, 1 Ingela Wiklund, PhD
Patient-reported Outcomes
 3 Patient-reported Outcomes Ingela Wiklund Key points Many gastrointestinal diseases are symptomdriven, so the patient s perspective is particularly important in this area. Patient-reported outcomes (PROs)
3 Patient-reported Outcomes Ingela Wiklund Key points Many gastrointestinal diseases are symptomdriven, so the patient s perspective is particularly important in this area. Patient-reported outcomes (PROs)
Accepted Article. Questionnaires for the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease: are they really useful? Constanza Ciriza de los Ríos
 Accepted Article Questionnaires for the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease: are they really useful? Constanza Ciriza de los Ríos DOI: 10.17235/reed.2016.4267/2016 Link: PDF Please cite this article
Accepted Article Questionnaires for the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease: are they really useful? Constanza Ciriza de los Ríos DOI: 10.17235/reed.2016.4267/2016 Link: PDF Please cite this article
FDA s GREAT Workshop. Industry Perspective: Development Activities Towards Phase 3 Endpoints. September 19, 2012
 FDA s GREAT Workshop Industry Perspective: Development Activities Towards Phase 3 Endpoints Malcolm Hill, Pharm.D. Meritage Pharma, Inc. San Diego, CA 09/19/12 1 September 19, 2012 Presentation Overview
FDA s GREAT Workshop Industry Perspective: Development Activities Towards Phase 3 Endpoints Malcolm Hill, Pharm.D. Meritage Pharma, Inc. San Diego, CA 09/19/12 1 September 19, 2012 Presentation Overview
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 160-164 ORiginal Article The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal
Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 160-164 ORiginal Article The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion
 Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
MISCONCEPTION OF HEART ATTACK PAIN WITH HEART BURN - HOW COMMON IS IT? Sehrish Khan, Rizwan Aziz Memon, Muhammad Farhan Khan, Mudassir Iqbal Dar
 Pak Heart J ORIGINAL ARTICLE MISCONCEPTION OF HEART ATTACK PAIN WITH HEART BURN - HOW COMMON IS IT? 1 2 3 4 Sehrish Khan, Rizwan Aziz Memon, Muhammad Farhan Khan, Mudassir Iqbal Dar 1 Dow Medical College,
Pak Heart J ORIGINAL ARTICLE MISCONCEPTION OF HEART ATTACK PAIN WITH HEART BURN - HOW COMMON IS IT? 1 2 3 4 Sehrish Khan, Rizwan Aziz Memon, Muhammad Farhan Khan, Mudassir Iqbal Dar 1 Dow Medical College,
PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
 Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT DISCLOSURES 4/18/2018
 GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
Body-Mass Index and Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Women
 The new england journal of medicine original article Body-Mass Index and Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Women Brian C. Jacobson, M.D., M.P.H., Samuel C. Somers, M.D., Charles S. Fuchs, M.D., M.P.H.,
The new england journal of medicine original article Body-Mass Index and Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Women Brian C. Jacobson, M.D., M.P.H., Samuel C. Somers, M.D., Charles S. Fuchs, M.D., M.P.H.,
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES
 SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons https://www.sages.org Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Author : SAGES Webmaster Surgery for Heartburn
SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons https://www.sages.org Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Author : SAGES Webmaster Surgery for Heartburn
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do?
 Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis and Non-Erosive Reflux Disease
 ARC Journal of Hepatology and Gastroenterology Volume 1, Issue 1, 2016, PP 3-8 www.arcjournals.org The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis
ARC Journal of Hepatology and Gastroenterology Volume 1, Issue 1, 2016, PP 3-8 www.arcjournals.org The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation. Introduction. Predisposing factor. Introduction.
 Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Quality Of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) Questionnaire in Iranian Patients with GERD: A Validation Study
 84 Original Article Quality Of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) Questionnaire in Iranian Patients with GERD: A Validation Study S Tofangchiha 1, H Razjouyan 2, S Nasseri-Moghaddam 3* 1. 2. 3. Assistant
84 Original Article Quality Of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) Questionnaire in Iranian Patients with GERD: A Validation Study S Tofangchiha 1, H Razjouyan 2, S Nasseri-Moghaddam 3* 1. 2. 3. Assistant
Disclosures. GI Motility Disorders. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
EXTRAESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR ORAL CAVITY
 EXTRAESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR ORAL CAVITY Crînguţa Paraschiv*, Cristina Gavrilescu, Irina Cotea, Manea Paloma, Rodica Ghiuru Gr. T. Popa" U.M.Ph.
EXTRAESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR ORAL CAVITY Crînguţa Paraschiv*, Cristina Gavrilescu, Irina Cotea, Manea Paloma, Rodica Ghiuru Gr. T. Popa" U.M.Ph.
Cigarette Smoking and its Association with Overlapping Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Functional Dyspepsia, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cigarette Smoking and its Association with Overlapping Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Functional Dyspepsia, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome Yasuhiro Fujiwara, Makiko Kubo, Yukie Kohata,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cigarette Smoking and its Association with Overlapping Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Functional Dyspepsia, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome Yasuhiro Fujiwara, Makiko Kubo, Yukie Kohata,
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540
 Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAGNETIC ESOPHAGEAL RING/ MAGNETIC SPHINCTER AUGMENTATION FOR THE TREATMENT OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAGNETIC ESOPHAGEAL RING/ MAGNETIC SPHINCTER PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAGNETIC ESOPHAGEAL RING/ MAGNETIC SPHINCTER PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial
Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training
 Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training Your pharmacist's advice is required. Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor/ healthcare professional. Pfizer Consumer Healthcare
Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training Your pharmacist's advice is required. Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor/ healthcare professional. Pfizer Consumer Healthcare
Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 483 488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02621.x Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population A. O. O.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 483 488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02621.x Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population A. O. O.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease prevalence among school teachers of Saudi Arabia and its impact on their daily life activities
 Original Article Gastroesophageal reflux disease prevalence among school teachers of Saudi Arabia and its impact on their daily life activities Abdulrahman Mohammed Altwigry 1, Majed Saud Almutairi 1,
Original Article Gastroesophageal reflux disease prevalence among school teachers of Saudi Arabia and its impact on their daily life activities Abdulrahman Mohammed Altwigry 1, Majed Saud Almutairi 1,
ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada
 ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada gerd fact 1 see page 8 Canadian Society of Intestinal Research On average, ARD patients wait over two years before seeking care 1. 1 gerd fact 2 see
ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada gerd fact 1 see page 8 Canadian Society of Intestinal Research On average, ARD patients wait over two years before seeking care 1. 1 gerd fact 2 see
GERD: A linical Clinical Clinical Update Objectives
 GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
Validation of the gastrointestinal symptom score for the assessment of symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 357 363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02572.x Validation of the gastrointestinal symptom score for the assessment of symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia B.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 357 363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02572.x Validation of the gastrointestinal symptom score for the assessment of symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia B.
Original Article Evaluations of life style factors and the severity of Gastroesophageal reflux disease; a case-control study
 Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet 2015;6(1):27-32 www.ijmeg.org /ISSN:1948-1756/IJMEG0014050 Original Article Evaluations of life style factors and the severity of Gastroesophageal reflux disease; a case-control
Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet 2015;6(1):27-32 www.ijmeg.org /ISSN:1948-1756/IJMEG0014050 Original Article Evaluations of life style factors and the severity of Gastroesophageal reflux disease; a case-control
Comparison of Clinical Findings with Symptom Assessment Systems (GerdQ and FSSG) for Functional Gastrointestinal Diseases
 ORIGINAL PAPER Surg. Gastroenterol. Oncol. 2018;23(3):198-203 DOI: 10.21614/sgo-23-3-198 Comparison of Clinical Findings with Symptom Assessment Systems (GerdQ and FSSG) for Functional Gastrointestinal
ORIGINAL PAPER Surg. Gastroenterol. Oncol. 2018;23(3):198-203 DOI: 10.21614/sgo-23-3-198 Comparison of Clinical Findings with Symptom Assessment Systems (GerdQ and FSSG) for Functional Gastrointestinal
Gastrointestinal symptoms are still common in a general Western population
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastrointestinal are still common in a general Western population L.A.S. van Kerkhoven *, T. Eikendal, R.J.F. Laheij, M.G.H. van Oijen, J.B.M.J. Jansen Department of Gastroenterology &
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastrointestinal are still common in a general Western population L.A.S. van Kerkhoven *, T. Eikendal, R.J.F. Laheij, M.G.H. van Oijen, J.B.M.J. Jansen Department of Gastroenterology &
GERD. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the. stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the
 GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
Understanding gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a patient-cluster analysis
 ORIGINAL PAPER Understanding gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a patient-cluster analysis A. King, 1 C. MacDonald, 1 C. Örn 2 doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2008.01929.x OnlineOpen: This article is available
ORIGINAL PAPER Understanding gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a patient-cluster analysis A. King, 1 C. MacDonald, 1 C. Örn 2 doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2008.01929.x OnlineOpen: This article is available
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Paraesophageal Hernias &
 530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
SURGERY LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) SURGERY
 LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) If you suffer from heartburn, your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery to treat this condition, technically referred to as Gastro-oesophageal Reflux
LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) If you suffer from heartburn, your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery to treat this condition, technically referred to as Gastro-oesophageal Reflux
Dr. LEUNG Lok Hang, Will
 Direct access endoscopy booking by family physicians: evaluating a new service model and clinical predictors of positive endoscopy findings at primary care setting Dr. LEUNG Lok Hang, Will Department of
Direct access endoscopy booking by family physicians: evaluating a new service model and clinical predictors of positive endoscopy findings at primary care setting Dr. LEUNG Lok Hang, Will Department of
Patient Interview Form
 Page 1 of 5 Orange Coast Memorial Office: 18111 Brookhurst Ave. Suite 5200, Fountain Valley, CA 92708 * Tel: (714) 962-7705 * Fax: (714) 861-4552 www.unitedgi.com Patient Interview Form Patient Information
Page 1 of 5 Orange Coast Memorial Office: 18111 Brookhurst Ave. Suite 5200, Fountain Valley, CA 92708 * Tel: (714) 962-7705 * Fax: (714) 861-4552 www.unitedgi.com Patient Interview Form Patient Information
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Acid Reflux Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus. Heartburn Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD. It may feel
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Acid Reflux Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus. Heartburn Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD. It may feel
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
Gastroesophageal reflux in children older than years
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:696 701 Determinants of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults With a History of Childhood Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease HASHEM B. EL SERAG,*, PETER
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:696 701 Determinants of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults With a History of Childhood Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease HASHEM B. EL SERAG,*, PETER
Is Rabeprazole A Safe Treatment for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children Ages 1-16 years?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Rabeprazole A Safe Treatment for Gastroesophageal
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Rabeprazole A Safe Treatment for Gastroesophageal
Guidelines for the Management of Dyspepsia and GORD. Gastroenterology/ Acute Adult Governance. Drugs and Therapeutics Committee
 Guidelines for the Management of Dyspepsia and GORD Document type: Version: 3.0 Author (name): Author (designation): Validated by Prescribing Dr. G. Lipscomb Date validated October 2015 Ratified by: Date
Guidelines for the Management of Dyspepsia and GORD Document type: Version: 3.0 Author (name): Author (designation): Validated by Prescribing Dr. G. Lipscomb Date validated October 2015 Ratified by: Date
Barrett s Esophagus. Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI
 Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Impact of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms on health resource usage and work absenteeism in Spain
 1130-0108/2006/98/7/518-526 REVISTA ESPAÑOLA DE ENFERMEDADES DIGESTIVAS Copyright 2006 ARÁN EDICIONES, S. L. REV ESP ENFERM DIG (Madrid) Vol. 98. N. 7, pp. 518-526, 2006 Impact of gastroesophageal reflux
1130-0108/2006/98/7/518-526 REVISTA ESPAÑOLA DE ENFERMEDADES DIGESTIVAS Copyright 2006 ARÁN EDICIONES, S. L. REV ESP ENFERM DIG (Madrid) Vol. 98. N. 7, pp. 518-526, 2006 Impact of gastroesophageal reflux
SASKATCHEWAN REGISTERED NURSES ASSOCIATION
 DEFINITION Reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, which results in esophageal irritation or inflammation. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE FOLLOWING SITUATIONS Dysphagia (solid food, progressive)
DEFINITION Reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, which results in esophageal irritation or inflammation. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE FOLLOWING SITUATIONS Dysphagia (solid food, progressive)
Relationship between Psychological Factors and Quality of Life in Subtypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2009, pp. 259-265 original article Relationship between Psychological Factors and Quality of Life in Subtypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Jung-Hwan Oh*, Tae-Suk
Gut and Liver, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2009, pp. 259-265 original article Relationship between Psychological Factors and Quality of Life in Subtypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Jung-Hwan Oh*, Tae-Suk
Hiatus Hernia. Endoscopy Department. Patient information leaflet
 Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Definition: gas tro e soph a ge al re f lux dis ease (GERD) from Stedman's Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing
 Topic Page: Gastroesophageal reflux Definition: gas tro e soph a ge al re f lux dis ease (GERD) from Stedman's Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing (gas trō-ĕ-sof ă-jē ăl rē flŭks
Topic Page: Gastroesophageal reflux Definition: gas tro e soph a ge al re f lux dis ease (GERD) from Stedman's Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing (gas trō-ĕ-sof ă-jē ăl rē flŭks
June By: Reza Gholami
 ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
HOW TO NATURALLY TREAT INDIGESTION YOGI CAMERON
 HOW TO NATURALLY TREAT INDIGESTION YOGI CAMERON Indigestion is a condition that is often a symptom of another, underlying condition and is associated with various forms of discomfort in the stomach including
HOW TO NATURALLY TREAT INDIGESTION YOGI CAMERON Indigestion is a condition that is often a symptom of another, underlying condition and is associated with various forms of discomfort in the stomach including
Systematic Review on Epidemiology of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Asia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:398 407 REVIEWS Systematic Review on Epidemiology of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Asia BENJAMIN C. Y. WONG* and YOSHIKAZU KINOSHITA *Department of
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:398 407 REVIEWS Systematic Review on Epidemiology of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Asia BENJAMIN C. Y. WONG* and YOSHIKAZU KINOSHITA *Department of
TBURN TBURN BURN ARTBURN EARTBURN EART HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST
 TBURN BURN TBURN ARTBURN. EARTBURN EART N EARTBURN HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST Do you sometimes wake up at night with a sharp, burning sensation in your chest? Does this sometimes happen during
TBURN BURN TBURN ARTBURN. EARTBURN EART N EARTBURN HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST Do you sometimes wake up at night with a sharp, burning sensation in your chest? Does this sometimes happen during
Patient Interview Form
 Page 1 of 5 Gastroenterologists: D.F. Jackson, III, MD William D. McLaughlin, MD Robert P. Albares, MD Jeffrey J. Crittenden, MD Samuel J. Tarwater, MD Travis J. Rutland, MD Gastroenterologists: Marc L.
Page 1 of 5 Gastroenterologists: D.F. Jackson, III, MD William D. McLaughlin, MD Robert P. Albares, MD Jeffrey J. Crittenden, MD Samuel J. Tarwater, MD Travis J. Rutland, MD Gastroenterologists: Marc L.
NEUROLOGICAL SURGERY, P.C.
 NEUROLOGICAL SURGERY, P.C. PATIENT INFORMATION Name Date of Birth Age Address City Sate NY Zip Home ( ) - Cell ( ) - Work ( ) - Ext: Email Address _ Sex M F Soc. Sec. #: / / Single Married Widowed Separated
NEUROLOGICAL SURGERY, P.C. PATIENT INFORMATION Name Date of Birth Age Address City Sate NY Zip Home ( ) - Cell ( ) - Work ( ) - Ext: Email Address _ Sex M F Soc. Sec. #: / / Single Married Widowed Separated
Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature
 Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature Authors Julia L. Pleet 1,SofiaTaboada 2, Arvind Rishi 2,
Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature Authors Julia L. Pleet 1,SofiaTaboada 2, Arvind Rishi 2,
Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Japan: Internet survey using Rome III criteria
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Japan: Internet survey using Rome III criteria Hiroto Miwa Division of Upper Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hyogo College
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Japan: Internet survey using Rome III criteria Hiroto Miwa Division of Upper Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hyogo College
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
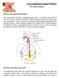 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
What causes GER? How is GERD treated? It is necessary to take these consecutive steps: a) Changes in your lifestyle b) Drug treatment c) Surgery
 When Gastric acids ascend the esophagus, they produce heartburn behind the sternum that can even reach the throat. Other symptoms are chronic cough, frequent vomits, and chronic affectation to the throat
When Gastric acids ascend the esophagus, they produce heartburn behind the sternum that can even reach the throat. Other symptoms are chronic cough, frequent vomits, and chronic affectation to the throat
Is there any association between myocardial infarction, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and acid-suppressing drugs?
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 18: 973 978. doi: 10.1046/j.0269-2813.2003.01798.x Is there any association between myocardial infarction, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and acid-suppressing drugs? S.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 18: 973 978. doi: 10.1046/j.0269-2813.2003.01798.x Is there any association between myocardial infarction, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and acid-suppressing drugs? S.
Achalasia is a rare disease with an annual incidence estimated REVIEWS. Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
Health History Questionaire
 Patient DOB: Patient Name: Date: Health History Questionaire Who referred your consultation? If no one referred you, how did you hear about us? Who is your primary care physician? Have you ever seen a
Patient DOB: Patient Name: Date: Health History Questionaire Who referred your consultation? If no one referred you, how did you hear about us? Who is your primary care physician? Have you ever seen a
Clinical Study Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Review of Medical and Surgical Management
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2014, Article ID 654607, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/654607 Clinical Study Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Review
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2014, Article ID 654607, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/654607 Clinical Study Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Review
Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus. Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery
 Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery Objectives Identify the use of different diagnostic modalities for hiatal hernias List the different types of hiatal hernias
Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery Objectives Identify the use of different diagnostic modalities for hiatal hernias List the different types of hiatal hernias
Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia: what is it? What can we do with these patients? Overview. Dyspepsia Definition. Functional Dyspepsia. Dyspepsia the Basics
 Non-Ulcer : what is it? What can we do with these patients? Temporal Changes and Geographic Variations in Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease Gastric Cancer 1900 Eamonn M M Quigley MD FACG Alimentary Pharmabiotic
Non-Ulcer : what is it? What can we do with these patients? Temporal Changes and Geographic Variations in Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease Gastric Cancer 1900 Eamonn M M Quigley MD FACG Alimentary Pharmabiotic
2. Have your symptoms affected your ability to carry out your daily activities? YES NO
 QUESTIONNAIRE Page 1 of 5 Date: Referring MD (Name, Address, Phone Number): Primary Care Physician (Name and Address, Phone Number): Reason for visit: 1. How long have you had symptoms? Describe your symptoms?
QUESTIONNAIRE Page 1 of 5 Date: Referring MD (Name, Address, Phone Number): Primary Care Physician (Name and Address, Phone Number): Reason for visit: 1. How long have you had symptoms? Describe your symptoms?
GASTROENTEROLOGY PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE - PLEASE PRINT
 GASTROENTEROLOGY PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE - PLEASE PRINT Full name: Date: Telephone Number: Age: Address: Email address: CHIEF COMPLAINTS(List the problems about which you came to see the doctor) 1) 2) 3)
GASTROENTEROLOGY PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE - PLEASE PRINT Full name: Date: Telephone Number: Age: Address: Email address: CHIEF COMPLAINTS(List the problems about which you came to see the doctor) 1) 2) 3)
pissn: eissn: Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 21 No. 3 July, 2015 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm15002 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Original Article Supragastric
JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 21 No. 3 July, 2015 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm15002 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Original Article Supragastric
Title: Home Exposure to Arabian Incense (Bakhour) and Asthma Symptoms in Children: A Community Survey in Two Regions in Oman
 Author's response to reviews Title: Home Exposure to Arabian Incense (Bakhour) and Asthma Symptoms in Children: A Community Survey in Two Regions in Oman Authors: Omar A Al-Rawas (orawas@squ.edu.om) Abdullah
Author's response to reviews Title: Home Exposure to Arabian Incense (Bakhour) and Asthma Symptoms in Children: A Community Survey in Two Regions in Oman Authors: Omar A Al-Rawas (orawas@squ.edu.om) Abdullah
Dyspepsia is a problem commonly seen by primary
 Concise Review for Clinicians Nonulcer Dyspepsia: What It Is and What It Is Not G. RICHARD LOCKE III, MD Nonulcer dyspepsiais a description of persistent or recurrent upper abdominal pain or discomfort
Concise Review for Clinicians Nonulcer Dyspepsia: What It Is and What It Is Not G. RICHARD LOCKE III, MD Nonulcer dyspepsiais a description of persistent or recurrent upper abdominal pain or discomfort
Fairfield County Bariatrics & Surgical Specialists, P.C. Neil R. Floch, M.D. Abraham Fridman, D.O. Craig L. Floch, M.D.
 Fairfield County Bariatrics & Surgical Specialists, P.C. Neil R. Floch, M.D. Abraham Fridman, D.O. Craig L. Floch, M.D. 148 East Avenue, Suite 3-A 2 Trap Falls Road, Suite 100 Norwalk, CT 06851 Shelton,
Fairfield County Bariatrics & Surgical Specialists, P.C. Neil R. Floch, M.D. Abraham Fridman, D.O. Craig L. Floch, M.D. 148 East Avenue, Suite 3-A 2 Trap Falls Road, Suite 100 Norwalk, CT 06851 Shelton,
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD. Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd
 ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
Health-related anxiety and the effect of open-access endoscopy in US patients with dyspepsia
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 23; 17: 835 84. doi: 1.146/j.269-2813.23.1497.x Health-related anxiety and the effect of open-access endoscopy in US patients with dyspepsia A. QUADRI & N. VAKIL University of Wisconsin
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 23; 17: 835 84. doi: 1.146/j.269-2813.23.1497.x Health-related anxiety and the effect of open-access endoscopy in US patients with dyspepsia A. QUADRI & N. VAKIL University of Wisconsin
Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
 Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Mohammed Y Hasosah 1*, Samer A Alamri 2, Faisal A Al-Husayni 2, Rakan M. Aljedaani 2, Mohammad A Zwawy
Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Mohammed Y Hasosah 1*, Samer A Alamri 2, Faisal A Al-Husayni 2, Rakan M. Aljedaani 2, Mohammad A Zwawy
Is Physical Activity Effective In Reducing The Gastrointestinal Symptoms Associated with Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Physical Activity Effective In Reducing
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Physical Activity Effective In Reducing
ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:612 619 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Regurgitation Is Less Responsive to Acid Suppression Than Heartburn in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:612 619 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Regurgitation Is Less Responsive to Acid Suppression Than Heartburn in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux
Past Medical History. Chief Complaint: Patient Name: Appointment Date: Page 1
 Appointment Date: Page 1 Chief Complaint: (Please write reason, symptoms, condition or diagnosis that prompts your appointment) Past Medical History PERSONAL SKIN HISTORY YES NO Yes - Details Melanoma
Appointment Date: Page 1 Chief Complaint: (Please write reason, symptoms, condition or diagnosis that prompts your appointment) Past Medical History PERSONAL SKIN HISTORY YES NO Yes - Details Melanoma
Teaching Diaphragmatic Breathing for Rumination Syndrome
 American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2006 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00801.x Published by Blackwell Publishing THE EXPERT S CORNER Teaching Diaphragmatic
American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2006 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00801.x Published by Blackwell Publishing THE EXPERT S CORNER Teaching Diaphragmatic
ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT. Bravo Catheter-Free ph Monitoring: Normal Values, Concordance, Optimal Diagnostic Thresholds, and Accuracy
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:60 67 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Bravo Catheter-Free ph Monitoring: Normal Values, Concordance, Optimal Diagnostic Thresholds, and Accuracy SHAHIN
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:60 67 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Bravo Catheter-Free ph Monitoring: Normal Values, Concordance, Optimal Diagnostic Thresholds, and Accuracy SHAHIN
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia
 Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
In vitro fertilization-induced pregnancies predispose to gastroesophageal reflux disease
 Original Article In vitro fertilization-induced pregnancies predispose to gastroesophageal reflux disease United European Gastroenterology Journal 2016, Vol. 4(2) 221 228! Author(s) 2016 Reprints and permissions:
Original Article In vitro fertilization-induced pregnancies predispose to gastroesophageal reflux disease United European Gastroenterology Journal 2016, Vol. 4(2) 221 228! Author(s) 2016 Reprints and permissions:
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
 Abdominal pain THEME Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Current concepts in management BACKGROUND Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is defined as recurring symptoms or mucosal damage resulting from
Abdominal pain THEME Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Current concepts in management BACKGROUND Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is defined as recurring symptoms or mucosal damage resulting from
Patient Interview Form
 Page 1 of 5 Physicians: D.F. Jackson, III, MD William D. McLaughlin, MD Robert P. Albares, MD Jeffrey J. Crittenden, MD Physicians: Samuel J. Tarwater, MD Travis J. Rutland, MD Ashwani Kapoor, MD Pathologist:
Page 1 of 5 Physicians: D.F. Jackson, III, MD William D. McLaughlin, MD Robert P. Albares, MD Jeffrey J. Crittenden, MD Physicians: Samuel J. Tarwater, MD Travis J. Rutland, MD Ashwani Kapoor, MD Pathologist:
Original Article. Rattanasupar A Attasaranya S Ovartlarnporn B ABSTRACT
 74 THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) plus Transabdominal Ultrasound (TUS) for Diagnosed Dyspepsia in Elderly Patients Original Article Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) plus Transabdominal
74 THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) plus Transabdominal Ultrasound (TUS) for Diagnosed Dyspepsia in Elderly Patients Original Article Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) plus Transabdominal
Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Refractoriness to Optimal Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Non-erosive Reflux Disease
 www.medscape.com Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Refractoriness to Optimal Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Non-erosive Reflux Disease Mentore Ribolsi; Michele Cicala; Patrizia Zentilin; Matteo
www.medscape.com Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Refractoriness to Optimal Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Non-erosive Reflux Disease Mentore Ribolsi; Michele Cicala; Patrizia Zentilin; Matteo
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that
 Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Digestion. Text. What You Don t Know Can Hurt You!
 Digestion Text What You Don t Know Can Hurt You! Digestive Problems Approximately 36.5 million visits annually to ambulatory care facilities due to the diseases of the digestive system Over 4 million ulcers
Digestion Text What You Don t Know Can Hurt You! Digestive Problems Approximately 36.5 million visits annually to ambulatory care facilities due to the diseases of the digestive system Over 4 million ulcers
Heartburn upper back pain
 P ford residence southampton, ny Heartburn upper back pain Now, you may be thinking isn't acid reflux got something to do with heartburn? You would be absolutely right, however acid reflux disease can
P ford residence southampton, ny Heartburn upper back pain Now, you may be thinking isn't acid reflux got something to do with heartburn? You would be absolutely right, however acid reflux disease can
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/acid-reflux-gastroesophageal-reflux-disease-in-adults-...
 Page 1 of 10 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Page 1 of 10 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Patient Interview Form
 Page 1 of 6 Patient Interview Form Patient Information First Name: MRN: Age: Last Name: Date Of Birth: Notes: Email Please check one as your preferred email for communications Personal: Work: Race Select
Page 1 of 6 Patient Interview Form Patient Information First Name: MRN: Age: Last Name: Date Of Birth: Notes: Email Please check one as your preferred email for communications Personal: Work: Race Select
Hold the Wrap! There is so much more to be done!
 Hold the Wrap! There is so much more to be done! (Well, a few things that can be done.) (Well, not all that much, really ) (But Blair has never killed anyone with a PPI!) Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center
Hold the Wrap! There is so much more to be done! (Well, a few things that can be done.) (Well, not all that much, really ) (But Blair has never killed anyone with a PPI!) Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center
Who may we thank for referring you? Office Only LIST YOUR HEALTH CONCERNS BELOW. If you had the condition before, when? When did this episode start?
 Name Date / / Age Male / Female Address City State Zip Phone: Home Cell Cell Phone Provider Date of Birth / / Email Address Occupation Employer s Name Single / Married / Divorced / Widowed Spouse s Name
Name Date / / Age Male / Female Address City State Zip Phone: Home Cell Cell Phone Provider Date of Birth / / Email Address Occupation Employer s Name Single / Married / Divorced / Widowed Spouse s Name
235 60th Street, West New York, NJ T: (201) F: (201) Main Street, Hackensack, NJ T: (201)
 235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Barrett's Esophagus WHAT IS BARRETTT'S ESOPHAGUS? Barrett's esophagus
235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Barrett's Esophagus WHAT IS BARRETTT'S ESOPHAGUS? Barrett's esophagus
Gastroesophageal reflux disease. The case for improving patient education in primary care
 Original Research Gastroesophageal reflux disease: The case for improving patient education in primary care This study reveals that something as simple as knowing when to take GERD medication is compromised
Original Research Gastroesophageal reflux disease: The case for improving patient education in primary care This study reveals that something as simple as knowing when to take GERD medication is compromised
Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ronnie Fass MD Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Esophageal
Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ronnie Fass MD Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Esophageal
Adult Demographics Form
 Adult Demographics Form Patient s Name: Preferred Name: Age: Patient s Social Security Number: Date of Birth: Sex: M / F Home Address: Apt: City: State: Zip: Cell phone #: Home Phone #: Work phone #: Email:
Adult Demographics Form Patient s Name: Preferred Name: Age: Patient s Social Security Number: Date of Birth: Sex: M / F Home Address: Apt: City: State: Zip: Cell phone #: Home Phone #: Work phone #: Email:
Alternating bowel pattern: what do people mean?
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Alternating bowel pattern: what do people mean? R. S. CHOUNG*, G. R. LOCKE III*, A. R. ZINSMEISTER, L.J.MELTONIIIà &N.J.TALLEY* *Dyspepsia Center and Division of
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Alternating bowel pattern: what do people mean? R. S. CHOUNG*, G. R. LOCKE III*, A. R. ZINSMEISTER, L.J.MELTONIIIà &N.J.TALLEY* *Dyspepsia Center and Division of
