Osteoporosis: assessing the risk of fragility fracture
|
|
|
- Oliver Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Osteoporosis: assessing the risk of fragility fracture Issued: August 2012 NICE clinical guideline 146 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg146 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Clinical Practice at NICE to produce guidelines. Accreditation is valid for 5 years from September 2009 and applies to guidelines produced since April 2007 using the processes described in NICE's 'The guidelines manual' (2007, updated 2009). More information on accreditation can be viewed at NICE 2012
2 Contents Introduction... 4 Patient-centred care Guidance... 7 Targeting risk assessment... 7 Methods of risk assessment Notes on the scope of the guidance Implementation Research recommendations Using GP practice lists to identify people at high risk FRAX and QFracture in adults receiving bone protective therapy FRAX and QFracture in adults with secondary causes of osteoporosis BMD with FRAX FRAX and QFracture in adults living in residential care Other versions of this guideline Full guideline NICE pathway Information for the public Related NICE guidance Updating the guideline Appendix A: The Guideline Development Group, National Clinical Guideline Centre and NICE project team Guideline Development Group National Clinical Guideline Centre NICE project team Changes after publication NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 2 of 24
3 About this guideline NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 3 of 24
4 Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease characterised by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, with a consequent increase in bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture. Osteoporosis leads to nearly 9 million fractures annually worldwide [1], and over 300,000 patients present with fragility fractures to hospitals in the UK each year [2]. Fragility fractures are fractures that result from mechanical forces that would not ordinarily result in fracture, known as low-level (or 'low energy') trauma [3]. The World Health Organization (WHO) has quantified this as forces equivalent to a fall from a standing height or less. Reduced bone density is a major risk factor for fragility fracture. Other factors that may affect the risk of fragility fracture include the use of oral or systemic glucocorticoids, age, sex, previous fractures and family history of osteoporosis. Because of increased bone loss after the menopause in women, and age-related bone loss in both women and men, the prevalence of osteoporosis increases markedly with age, from 2% at 50 years to more than 25% at 80 years in women. As the longevity of the population increases, so will the incidence of osteoporosis and fragility fracture. Fragility fractures occur most commonly in the spine (vertebrae), hip (proximal femur) and wrist (distal radius). They may also occur in the arm (humerus), pelvis, ribs and other bones. Osteoporotic fractures are defined as fractures associated with low bone mineral density (BMD) and include clinical spine, forearm, hip and shoulder fractures. Osteoporotic fragility fractures can cause substantial pain and severe disability, often leading to a reduced quality of life, and hip and vertebral fractures are associated with decreased life expectancy. Hip fracture nearly always requires hospitalisation, is fatal in 20% of cases and permanently disables 50% of those affected; only 30% of patients fully recover [4]. Projections suggest that, in the UK, hip fracture incidence will rise from 70,000 per year in 2006 to 91,500 in 2015 and 101,000 in 2020 [5]. Direct medical costs from fragility fractures to the UK healthcare economy were estimated at 1.8 billion in 2000, with the potential to increase to 2.2 billion by 2025, and with most of these costs relating to hip fracture care [6]. There are a number of therapies and treatments available for the prevention of fragility fractures in people who are thought to be at risk, or to prevent further fractures in those who have already had one or more fragility fractures. However, identifying who will benefit from preventative treatment is imprecise. A number of risk assessment tools are available to predict fracture incidence over a period of time, and these may be used to aid decision-making. These tools are NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 4 of 24
5 limited in that they may not include all risk factors, or may lack details of some risk factors. Tools are dependent on the accuracy of the epidemiological data used to derive them and tools validated in other populations may not apply to the UK. Two tools, FRAX and QFracture, are available for use in the UK. It is not clear whether these tools are equally accurate and whether choice of tool should depend on circumstances. This short clinical guideline aims to provide guidance on the selection and use of risk assessment tools in the care of people who may be at risk of fragility fractures in all settings in which NHS care is received. [1] Johnell O, Kanis JA (2006) An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporosis International 17: [2] British Orthopaedic Association (2007). The care of patients with fragility fracture. [3] Kanis JA, Oden A, Johnell O et al. (2001) The burden of osteoporotic fractures: a method for setting intervention thresholds. Osteoporosis International 12: [4] Sernbo I, Johnell O (1993). Consequences of a hip fracture: a prospective study over 1 year. Osteoporosis International 3: [5] Department of Health. Hospital episode statistics (England) [6] Burge RT, Worley D, Johansen A, et al. The cost of osteoporotic fractures in the UK: projections for Journal of Medical Economics 4: NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 5 of 24
6 Patient-centred care This guideline offers best practice advice on the assessment of fragility fracture risk in adults. Treatment and care should take into account patients' needs and preferences. People at risk of fragility fracture should have the opportunity to make informed decisions about their care and treatment, in partnership with their healthcare professionals. If patients do not have the capacity to make decisions, healthcare professionals should follow the Department of Health's advice on consent and the code of practice that accompanies the Mental Capacity Act. In Wales, healthcare professionals should follow advice on consent from the Welsh Government. Good communication between healthcare professionals and patients is essential. It should be supported by evidence-based written information tailored to the patient's needs. Treatment and care, and the information patients are given about it, should be culturally appropriate. It should also be accessible to people with additional needs such as physical, sensory or learning disabilities, and to people who do not speak or read English. If the patient agrees, families and carers should have the opportunity to be involved in decisions about treatment and care. Families and carers should also be given the information and support they need. NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 6 of 24
7 1 Guidance The following guidance is based on the best available evidence. The full guideline gives details of the methods and the evidence used to develop the guidance. Targeting risk assessment 1.1 Consider assessment of fracture risk: In all women aged 65 years and over and all men aged 75 years and over in women aged under 65 years and men aged under 75 years in the presence of risk factors, for example: previous fragility fracture current use or frequent recent use of oral or systemic glucocorticoids history of falls family history of hip fracture other causes of secondary osteoporosis [7] low body mass index (BMI) (less than 18.5 kg/m 2 ) smoking alcohol intake of more than 14 units per week for women and more than 21 units per week for men. 1.2 Do not routinely assess fracture risk in people aged under 50 years unless they have major risk factors (for example, current or frequent recent use of oral or systemic glucocorticoids, untreated premature menopause or previous fragility fracture), because they are unlikely to be at high risk. NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 7 of 24
8 Methods of risk assessment 1.3 Estimate absolute risk when assessing risk of fracture (for example, the predicted risk of major osteoporotic or hip fracture over 10 years, expressed as a percentage). 1.4 Use either FRAX [8] (without a bone mineral density [BMD] value if a dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry [DXA] scan has not previously been undertaken) or QFracture [9], within their allowed age ranges, to estimate 10-year predicted absolute fracture risk when assessing risk of fracture. Above the upper age limits defined by the tools, consider people to be at high risk. 1.5 Interpret the estimated absolute risk of fracture in people aged over 80 years with caution, because predicted 10-year fracture risk may underestimate their short-term fracture risk. 1.6 Do not routinely measure BMD to assess fracture risk without prior assessment using FRAX (without a BMD value) or QFracture. 1.7 Following risk assessment with FRAX (without a BMD value) or QFracture, consider measuring BMD with DXA in people whose fracture risk is in the region of an intervention threshold [10] for a proposed treatment, and recalculate absolute risk using FRAX with the BMD value. 1.8 Consider measuring BMD with DXA before starting treatments that may have a rapid adverse effect on bone density (for example, sex hormone deprivation for treatment for breast or prostate cancer). 1.9 Measure BMD to assess fracture risk in people aged under 40 years who have a major risk factor, such as history of multiple fragility fracture, major osteoporotic fracture, or current or recent use of high-dose oral or high-dose systemic glucocorticoids (more than 7.5 mg prednisolone or equivalent per day for 3 months or longer) Consider recalculating fracture risk in the future: NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 8 of 24
9 if the original calculated risk was in the region of the intervention threshold [11] for a proposed treatment and only after a minimum of 2 years, or when there has been a change in the person's risk factors Take into account that risk assessment tools may underestimate fracture risk in certain circumstances, for example if a person: has a history of multiple fractures has had previous vertebral fracture(s) has a high alcohol intake is taking high-dose oral or high-dose systemic glucocorticoids (more than 7.5 mg prednisolone or equivalent per day for 3 months or longer) has other causes of secondary osteoporosis [7] Take into account that fracture risk can be affected by factors that may not be included in the risk tool, for example living in a care home or taking drugs that may impair bone metabolism (such as anti-convulsants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, thiazolidinediones, proton pump inhibitors and antiretroviral drugs). [7] Causes of secondary osteoporosis include endocrine (hypogonadism in either sex including untreated premature menopause and treatment with aromatase inhibitors or androgen deprivation therapy; hyperthyroidism; hyperparathyroidism; hyperprolactinaemia; Cushing's disease; diabetes), gastrointestinal (coeliac disease; inflammatory bowel disease; chronic liver disease; chronic pancreatitis; other causes of malabsorption), rheumatological (rheumatoid arthritis; other inflammatory arthropathies), haematological (multiple myeloma; haemoglobinopathies; systemic mastocytosis), respiratory (cystic fibrosis; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), metabolic (homocystinuria), chronic renal disease and immobility(due for example to neurological injury or disease). [8] FRAX, the WHO fracture risk assessment tool, can be used for people aged between 40 and 90 years, either with or without BMD values, as specified. NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 9 of 24
10 [9] QFracture can be used for people aged between 30 and 84 years. BMD values cannot be incorporated into the risk algorithm. [10] An intervention threshold is the level of risk at which an intervention is recommended. People whose risk is in the region from just below to just above the threshold may be reclassified if BMD is added to assessment. It is out of the scope of this guideline to recommend intervention thresholds. Healthcare professionals should follow local protocols or other national guidelines for advice on intervention thresholds. [11] An intervention threshold is the level of risk at which an intervention is recommended. It is out of the scope of this guideline to recommend intervention thresholds. Healthcare professionals should follow local protocols or other national guidelines for advice on intervention thresholds. NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 10 of 24
11 2 Notes on the scope of the guidance NICE guidelines are developed in accordance with a scope that defines what the guideline will and will not cover. How this guideline was developed NICE commissioned the National Clinical Guideline Centre to develop this guideline. The Centre established a Guideline Development Group (see appendix A), which reviewed the evidence and developed the recommendations. There is more information about how NICE clinical guidelines are developed on the NICE website. A booklet, 'How NICE clinical guidelines are developed: an overview for stakeholders, the public and the NHS' is available. NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 11 of 24
12 3 Implementation NICE has developed tools to help organisations implement this guidance. NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 12 of 24
13 4 Research recommendations The Guideline Development Group has made the following recommendations for research, based on its review of evidence, to improve NICE guidance and patient care in the future. The Guideline Development Group's full set of research recommendations is detailed in the full guideline. 4.1 Using GP practice lists to identify people at high risk What is the clinical and cost effectiveness of using GP practice lists to identify people at high risk of fracture, leading to formal risk assessment and possible treatment? Why this is important Fracture risk is currently assessed opportunistically. GP records are now universally computerised and contain information that may be useful in identifying patients at high risk of fracture (for example, age, record of prescriptions, major diagnoses and previous fracture). A study is needed to assess whether people at higher risk can be identified by using risk assessment tools to obtain an estimate of risk based on pre-existing information and inviting people at highest risk for a clinical assessment and risk-factor estimation. This could result in a more effective and efficient use of staff time and health service resources than an opportunistic approach. 4.2 FRAX and QFracture in adults receiving bone protective therapy What is the utility of FRAX and QFracture in adults receiving bone protective therapy? Why this is important Because of concerns about rare but serious side-effects of long-term anti-resorptive therapy, many physicians prescribe these drugs for a finite period of time, usually 3 5 years. Reassessment of fracture risk at the end of this treatment period is important, since some people remain at high risk of fracture and require continued treatment whereas others may benefit from a 'drug holiday' for 1 or more years. Neither FRAX nor QFracture has been examined in treated NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 13 of 24
14 patients, and it is not known whether the ability of clinical risk factors with or without measurement of BMD to predict fracture risk is similar in untreated and treated patients. There is therefore a need for prospective studies to investigate the predictive power of these tools to assess fracture risk in patients after a period of bone protective therapy. 4.3 FRAX and QFracture in adults with secondary causes of osteoporosis What is the utility of FRAX and QFracture in detecting risk of fragility fracture in adults with secondary causes of osteoporosis? Why this is important If secondary osteoporosis is entered as a risk factor in FRAX, the algorithm assumes that the effect is mediated solely through effects on BMD. Input of BMD into the questionnaire in such patients will therefore generate the same fracture risk whether or not secondary osteoporosis is entered. However, it is likely that at least some causes of secondary osteoporosis (for example, inflammatory bowel disease) affect fracture risk by mechanisms that are partially independent of BMD and fracture risk may therefore be underestimated in such patients. There is therefore a need to investigate the accuracy of FRAX in predicting fracture risk in patients with causes of secondary osteoporosis other than rheumatoid arthritis and to establish whether their effect on fracture risk is mediated solely through effects on BMD. 4.4 BMD with FRAX What is the added prognostic value of BMD in the assessment of fracture risk with FRAX? Why this is important The 10-year fracture risk as estimated by FRAX is calculated using clinical risk factors with or without BMD. The clinical risk factors are routinely available, making calculation of fracture risk possible at the time of consultation. However, refinement of a patient's 10-year fracture risk using BMD requires assessment using DXA scanning equipment. Currently, there are no definitive studies in primary or secondary care evaluating whether the addition of BMD to FRAX improves the accuracy of the predicted fracture risk. There is a need NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 14 of 24
15 for studies to examine whether adding BMD to FRAX results in the correct reclassification of patients from low risk to high risk (and vice-versa). Furthermore, studies are also needed to evaluate the clinical usefulness (net benefit) of adding BMD to FRAX; that is, how many more patients are correctly classified as high risk (true positives) and low risk (true negatives). 4.5 FRAX and QFracture in adults living in residential care What is the utility of FRAX and QFracture in detecting risk of fragility fracture in adults living in residential care? Why this is important Care home residents are at high risk of fragility fracture. This is probably related to increased age and frailty with multiple comorbidities, which increase fracture risk. There is also evidence that care home residents have lower BMD, with 70% assessed as having osteoporosis using densitometry criteria alone. However, tools such as FRAX and QFracture, which only estimate fracture risk up to the 9th decade and use 10-year fracture risk, may underestimate short-term risk in care home residents, who have a mean age of approximately 85 years and a life expectancy of less than 5 years. A study is required to assess whether care home residents should have targeted fracture risk assessment and whether residents at higher risk of fracture can be identified, using FRAX or QFracture. This could result in a more effective and efficient strategy for fracture prevention, targeting health service resources on those at the very highest fracture risk. NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 15 of 24
16 5 Other versions of this guideline 5.1 Full guideline The full guideline, Osteoporosis: assessing the risk of fragility fracture, contains details of the methods and evidence used to develop the guideline. It is published by the National Clinical Guideline Centre. 5.2 NICE pathway The recommendations from this guideline have been incorporated into a NICE pathway. 5.3 Information for the public NICE has produced information for the public explaining this guideline. We encourage NHS and voluntary sector organisations to use text from this information in their own materials about assessment of fragility fracture. NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 16 of 24
17 6 Related NICE guidance Patient experience in adult NHS services. NICE clinical guideline 138 (2012). Alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene, strontium ranelate and teriparatide for the secondary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women. NICE technology appraisal guidance 161 (2011). Alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and strontium ranelate for the primary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women. NICE technology appraisal guidance 160 (2011). The management of hip fracture in adults. NICE clinical guideline 124 (2011). Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women. NICE technology appraisal guidance 204 (2010). Falls. NICE clinical guideline 21 (2004). NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 17 of 24
18 7 Updating the guideline NICE clinical guidelines are updated so that recommendations take into account important new information. New evidence is checked 3 years after publication, and healthcare professionals and patients are asked for their views; we use this information to decide whether all or part of a guideline needs updating. If important new evidence is published at other times, we may decide to do a more rapid update of some recommendations. Please see our website for information about updating the guideline. NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 18 of 24
19 Appendix A: The Guideline Development Group, National Clinical Guideline Centre and NICE project team Guideline Development Group Peter Barry (GDG Chair) Honorary Lecturer in Child Health, University of Leicester Terry Aspray Consultant in Metabolic Bone Disease, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle Kathleen Briers Patient and carer member Gary Collins Senior Medical Statistician, University of Oxford Juliet Compston Professor of Bone Medicine, University of Cambridge Frances Dockery Consultant Geriatrician, St. Thomas's Hospital, London Sheila Ruddick Osteoporosis Specialist Nurse, County Durham and Darlington Foundation Trust Peter Selby Consultant Physician, Senior Lecturer in Medicine, Manchester Royal Infirmary David Stephens Portfolio GP, Scotland Angela Thornhill Patient and carer member NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 19 of 24
20 Jonathan Tobias Professor of Rheumatology, University of Bristol National Clinical Guideline Centre Lina Gulhane Joint Head of Information Science Rosa Lau Research Fellow Lilian Li Health Economist Norma O'Flynn Clinical Director Silvia Rabar Senior Project Manager and Research Fellow NICE project team Sharon Summers-Ma Centre for Clinical Practice Associate Director Michael Heath Guideline Commissioning Manager Emma Banks Guideline Coordinator (until February 2012) Anthony Gildea Guideline Coordinator (from February 2012) Judith Thornton Technical Lead NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 20 of 24
21 Prashanth Kandaswamy Health Economist Catharine Baden-Daintree Editor NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 21 of 24
22 Changes after publication November 2013: minor maintenance. October 2012: minor maintenance. NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 22 of 24
23 About this guideline NICE clinical guidelines are recommendations about the treatment and care of people with specific diseases and conditions in the NHS in England and Wales. The guideline was developed by the National Clinical Guideline Centre, which is based at the Royal College of Physicians. The Collaborating Centre worked with a group of healthcare professionals (including consultants, GPs and nurses), patients and carers, and technical staff, who reviewed the evidence and drafted the recommendations. The recommendations were finalised after public consultation. The methods and processes for developing NICE clinical guidelines are described in The guidelines manual. The recommendations from this guideline have been incorporated into a NICE pathway. We have produced information for the public explaining this guideline. Tools to help you put the guideline into practice and information about the evidence it is based on are also available. Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of NICE, which was arrived at after careful consideration of the evidence available. Healthcare professionals are expected to take it fully into account when exercising their clinical judgement. However, the guidance does not override the individual responsibility of healthcare professionals to make decisions appropriate to the circumstances of the individual patient, in consultation with the patient and/or guardian or carer, and informed by the summary of product characteristics of any drugs they are considering. Implementation of this guidance is the responsibility of local commissioners and/or providers. Commissioners and providers are reminded that it is their responsibility to implement the guidance, in their local context, in light of their duties to avoid unlawful discrimination and to have regard to promoting equality of opportunity. Nothing in this guidance should be interpreted in a way that would be inconsistent with compliance with those duties. Copyright National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence All rights reserved. NICE copyright material can be downloaded for private research and study, and may be reproduced for NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 23 of 24
24 educational and not-for-profit purposes. No reproduction by or for commercial organisations, or for commercial purposes, is allowed without the written permission of NICE. Contact NICE National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Level 1A, City Tower, Piccadilly Plaza, Manchester M1 4BT NICE All rights reserved. Last modified August 2012 Page 24 of 24
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 : assessing the risk of fragility fracture bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new
: assessing the risk of fragility fracture bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new
Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk. Costing report. Implementing NICE guidance
 Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk Costing report Implementing NICE guidance August 2012 NICE clinical guideline 146 1 of 15 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline: Osteoporosis: assessing
Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk Costing report Implementing NICE guidance August 2012 NICE clinical guideline 146 1 of 15 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline: Osteoporosis: assessing
Case Finding and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis
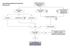 Case Finding and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis Patient may present as a fragility fracture or risk fracture Fragility fracture age 50 Clinical risk factors aged 50 Very strong clinical risk factors
Case Finding and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis Patient may present as a fragility fracture or risk fracture Fragility fracture age 50 Clinical risk factors aged 50 Very strong clinical risk factors
nice bulletin NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised
 nice bulletin NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised nice bulletin Welcome In August 2012, the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
nice bulletin NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised nice bulletin Welcome In August 2012, the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
DEXA SCAN POLICY CRITERIA BASED ACCESS
 DEXA SCAN POLICY Version: 1718.v2 Recommendation by: Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum (CCPF) Date Ratified: 01 November 2017 Name of Originator/Author: Approved by Responsible Committee/Individual:
DEXA SCAN POLICY Version: 1718.v2 Recommendation by: Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum (CCPF) Date Ratified: 01 November 2017 Name of Originator/Author: Approved by Responsible Committee/Individual:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Health and social care directorate Quality standards and indicators Briefing paper
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Health and social care directorate Quality standards and indicators Briefing paper Quality standard topic: Osteoporosis Output: Prioritised quality improvement
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Health and social care directorate Quality standards and indicators Briefing paper Quality standard topic: Osteoporosis Output: Prioritised quality improvement
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 9 August 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta464
 Bisphosphonates for treating osteoporosis Technology appraisal guidance Published: 9 August 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta464 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Bisphosphonates for treating osteoporosis Technology appraisal guidance Published: 9 August 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta464 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 9 August 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta464
 Bisphosphonates for treating osteoporosis Technology appraisal guidance Published: 9 August 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta464 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Bisphosphonates for treating osteoporosis Technology appraisal guidance Published: 9 August 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta464 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
FRAX, NICE and NOGG. Eugene McCloskey Professor of Adult Bone Diseases University of Sheffield
 FRAX, NICE and NOGG Eugene McCloskey Professor of Adult Bone Diseases University of Sheffield Disclosures Research funding and/or honoraria and/or advisory boards for: o ActiveSignal, Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer
FRAX, NICE and NOGG Eugene McCloskey Professor of Adult Bone Diseases University of Sheffield Disclosures Research funding and/or honoraria and/or advisory boards for: o ActiveSignal, Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer
nogg Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK
 nogg NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE GROUP Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK Produced by J Compston, A Cooper,
nogg NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE GROUP Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK Produced by J Compston, A Cooper,
Understanding NICE guidance. NICE technology appraisal guidance advises on when and how drugs and other treatments should be used in the NHS.
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, strontium ranelate and raloxifene for preventing bone fractures in postmenopausal women with
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, strontium ranelate and raloxifene for preventing bone fractures in postmenopausal women with
Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk
 Fragility fracture risk Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk Osteoporosis: assessing the risk of fragility fracture Short clinical guideline Evidence and recommendations January 0 Draft for consultation
Fragility fracture risk Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk Osteoporosis: assessing the risk of fragility fracture Short clinical guideline Evidence and recommendations January 0 Draft for consultation
Advanced medicine conference. Monday 20 Tuesday 21 June 2016
 Advanced medicine conference Monday 20 Tuesday 21 June 2016 Osteoporosis: recent advances in risk assessment and management Juliet Compston Emeritus Professor of Bone Medicine Cambridge Biomedical Campus
Advanced medicine conference Monday 20 Tuesday 21 June 2016 Osteoporosis: recent advances in risk assessment and management Juliet Compston Emeritus Professor of Bone Medicine Cambridge Biomedical Campus
An audit of osteoporotic patients in an Australian general practice
 professional Darren Parker An audit of osteoporotic patients in an Australian general practice Background Osteoporosis is a major contributor to morbidity and mortality in Australia, and is predicted to
professional Darren Parker An audit of osteoporotic patients in an Australian general practice Background Osteoporosis is a major contributor to morbidity and mortality in Australia, and is predicted to
Costing statement: Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women
 Costing statement: Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women Resource impact The guidance Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women
Costing statement: Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women Resource impact The guidance Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women
SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES. A. Service Specifications
 SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES A. Service Specifications Service Specification No. 04/MSKT/0013 Service PAN DORSET FRACTURE LIAISON SERVICE Commissioner Lead CCP for Musculoskeletal & Trauma Provider Lead Deputy
SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES A. Service Specifications Service Specification No. 04/MSKT/0013 Service PAN DORSET FRACTURE LIAISON SERVICE Commissioner Lead CCP for Musculoskeletal & Trauma Provider Lead Deputy
May Professor Matt Stevenson School of Health and Related Research, University of Sheffield
 ASSESSING THE FEASIBILITY OF TRANSFORMING THE RECOMMENDATIONS IN TA160, TA161 AND TA204 INTO ABSOLUTE 10-YEAR RISK OF FRACTURE A REPORT PRODUCED BY THE DECISION SUPPORT UNIT IN THE CONTEXT OF THE REVIEW
ASSESSING THE FEASIBILITY OF TRANSFORMING THE RECOMMENDATIONS IN TA160, TA161 AND TA204 INTO ABSOLUTE 10-YEAR RISK OF FRACTURE A REPORT PRODUCED BY THE DECISION SUPPORT UNIT IN THE CONTEXT OF THE REVIEW
Osteoporosis. Open Access. John A. Kanis. Diseases, University of Sheffield, UK
 Journal of Medical Sciences (2010); 3(3): 00-00 Review Article Osteoporosis Open Access John A. Kanis WHO Collaborating Centre for Metabolic Bone Diseases, University of Sheffield, UK incorporated into
Journal of Medical Sciences (2010); 3(3): 00-00 Review Article Osteoporosis Open Access John A. Kanis WHO Collaborating Centre for Metabolic Bone Diseases, University of Sheffield, UK incorporated into
Validation of QFracture. Analysis prepared for NICE 2011
 Validation of QFracture compared with FRAX Analysis prepared for NICE 2011 Authors: Julia Hippisley-Cox & Carol Coupland Email: Julia.hippisley-cox@nottingham.ac.uk Julia Hipisley-Cox, University of Nottingham,
Validation of QFracture compared with FRAX Analysis prepared for NICE 2011 Authors: Julia Hippisley-Cox & Carol Coupland Email: Julia.hippisley-cox@nottingham.ac.uk Julia Hipisley-Cox, University of Nottingham,
Clinical guideline Published: 23 March 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg118
 Colorectal cancer prevention: ention: colonoscopic surveillance in adults with ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease or adenomas Clinical guideline Published: March 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg118 NICE 2018.
Colorectal cancer prevention: ention: colonoscopic surveillance in adults with ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease or adenomas Clinical guideline Published: March 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg118 NICE 2018.
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention
 Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention NATIONAL GUIDELINE SUMMARY This guideline was developed using an evidence-based methodology by the KP National Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Guideline Development Team
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention NATIONAL GUIDELINE SUMMARY This guideline was developed using an evidence-based methodology by the KP National Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Guideline Development Team
Osteoporosis challenges
 Osteoporosis challenges Osteoporosis challenges Who should have a fracture risk assessment? Who to treat? Drugs, holidays and unusual adverse effects Fracture liaison service? The size of the problem 1
Osteoporosis challenges Osteoporosis challenges Who should have a fracture risk assessment? Who to treat? Drugs, holidays and unusual adverse effects Fracture liaison service? The size of the problem 1
Horizon Scanning Centre March Denosumab for glucocorticoidinduced SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 6329
 Horizon Scanning Centre March 2014 Denosumab for glucocorticoidinduced osteoporosis SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 6329 This briefing is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature
Horizon Scanning Centre March 2014 Denosumab for glucocorticoidinduced osteoporosis SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 6329 This briefing is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature
Osteoporosis: assessing the risk of fragility fracture
 Fragility fracture risk Osteoporosis: assessing the risk of fragility fracture Appendices Short clinical guideline 27 January 2012 Commissioned by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
Fragility fracture risk Osteoporosis: assessing the risk of fragility fracture Appendices Short clinical guideline 27 January 2012 Commissioned by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis
 Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis Yeap SS, Hew FL, Chan SP, on behalf of the Malaysian Osteoporosis Society Committee Working Group for the Clinical Guidance on the Management of Osteoporosis,
Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis Yeap SS, Hew FL, Chan SP, on behalf of the Malaysian Osteoporosis Society Committee Working Group for the Clinical Guidance on the Management of Osteoporosis,
Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment. William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC
 Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC Case #1 Age 53: 3 years post-menopause Has always enjoyed excellent health with
Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC Case #1 Age 53: 3 years post-menopause Has always enjoyed excellent health with
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles tendinopathy
 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Costing report: Lipid modification Implementing the NICE guideline on lipid modification (CG181)
 Putting NICE guidance into practice Costing report: Lipid modification Implementing the NICE guideline on lipid modification (CG181) Published: July 2014 This costing report accompanies Lipid modification:
Putting NICE guidance into practice Costing report: Lipid modification Implementing the NICE guideline on lipid modification (CG181) Published: July 2014 This costing report accompanies Lipid modification:
Barrett's oesophagus. Ablative therapy for the treatment of Barrett's oesophagus. Issued: August NICE clinical guideline 106
 Barrett's oesophagus Ablative therapy for the treatment of Barrett's oesophagus Issued: August 2010 NICE clinical guideline 106 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg106 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre
Barrett's oesophagus Ablative therapy for the treatment of Barrett's oesophagus Issued: August 2010 NICE clinical guideline 106 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg106 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre
NICE SCOOP OF THE DAY FRAX with NOGG. Eugene McCloskey Professor of Adult Bone Diseases University of Sheffield
 NICE SCOOP OF THE DAY FRAX with NOGG Eugene McCloskey Professor of Adult Bone Diseases University of Sheffield Disclosures Consultant/Advisor/Speaker for: o ActiveSignal, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Consilient
NICE SCOOP OF THE DAY FRAX with NOGG Eugene McCloskey Professor of Adult Bone Diseases University of Sheffield Disclosures Consultant/Advisor/Speaker for: o ActiveSignal, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Consilient
Guideline for the investigation and management of osteoporosis. for hospitals and General Practice
 Guideline for the investigation and management of osteoporosis for hospitals and General Practice Background Low bone density is an important risk factor for fracture. The aim of assessing bone density
Guideline for the investigation and management of osteoporosis for hospitals and General Practice Background Low bone density is an important risk factor for fracture. The aim of assessing bone density
Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women
 Issue date: October 2010 Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women This guidance was developed using the single technology appraisal process NICE technology appraisal
Issue date: October 2010 Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women This guidance was developed using the single technology appraisal process NICE technology appraisal
Pathway from Fracture or Risk Factor to Treatment
 Appendix 6A - Guidance on Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis Pathway from Fracture or Risk Factor to Treatment Fragility Fracture = fracture sustained from a low energy fall from standing height
Appendix 6A - Guidance on Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis Pathway from Fracture or Risk Factor to Treatment Fragility Fracture = fracture sustained from a low energy fall from standing height
Arthroscopic knee washout, with or without debridement, for the treatment of osteoarthritis
 Arthroscopic knee washout, with or without debridement, for the treatment of osteoarthritis Issued: August 2007 www.nice.org.uk/ipg230 Copyright NICE 2007 Contents 1 Guidance... 3 2 The procedure... 4
Arthroscopic knee washout, with or without debridement, for the treatment of osteoarthritis Issued: August 2007 www.nice.org.uk/ipg230 Copyright NICE 2007 Contents 1 Guidance... 3 2 The procedure... 4
Interpreting DEXA Scan and. the New Fracture Risk. Assessment. Algorithm
 Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Summary. Background. Diagnosis
 March 2009 Management of post-menopausal osteoporosis This bulletin focuses on the pharmacological management of patients with post-menopausal osteoporosis both those with clinically evident disease (e.g.
March 2009 Management of post-menopausal osteoporosis This bulletin focuses on the pharmacological management of patients with post-menopausal osteoporosis both those with clinically evident disease (e.g.
Overview. Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases. People Centred Positive Compassion Excellence
 Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Osteoporosis Clinical Guideline. Rheumatology January 2017
 Osteoporosis Clinical Guideline Rheumatology January 2017 Introduction Osteoporosis is a condition of low bone mass leading to an increased risk of low trauma fractures. The prevalence of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis Clinical Guideline Rheumatology January 2017 Introduction Osteoporosis is a condition of low bone mass leading to an increased risk of low trauma fractures. The prevalence of osteoporosis
1
 www.osteoporosis.ca 1 2 Overview of the Presentation Osteoporosis: An Overview Bone Basics Diagnosis of Osteoporosis Drug Therapies Risk Reduction Living with Osteoporosis 3 What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis:
www.osteoporosis.ca 1 2 Overview of the Presentation Osteoporosis: An Overview Bone Basics Diagnosis of Osteoporosis Drug Therapies Risk Reduction Living with Osteoporosis 3 What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis:
Costing Report: atrial fibrillation Implementing the NICE guideline on atrial fibrillation (CG180)
 Putting NICE guidance into practice Costing Report: atrial fibrillation Implementing the NICE guideline on atrial fibrillation (CG180) Published: June 2014 This costing report accompanies the clinical
Putting NICE guidance into practice Costing Report: atrial fibrillation Implementing the NICE guideline on atrial fibrillation (CG180) Published: June 2014 This costing report accompanies the clinical
Quality and Outcomes Framework Programme NICE cost impact statement July Indicator area: Osteoporosis - fragility fracture
 Quality and Outcomes Framework Programme NICE cost impact statement July 2011 Indicator area: Osteoporosis - fragility fracture Indicators NM29: The practice can produce a register of patients: 1. Aged
Quality and Outcomes Framework Programme NICE cost impact statement July 2011 Indicator area: Osteoporosis - fragility fracture Indicators NM29: The practice can produce a register of patients: 1. Aged
Analyses of cost-effective BMD scanning and treatment strategies for generic alendronate, and the costeffectiveness
 Analyses of cost-effective BMD scanning and treatment strategies for generic alendronate, and the costeffectiveness of risedronate and strontium ranelate in those people who would be treated with generic
Analyses of cost-effective BMD scanning and treatment strategies for generic alendronate, and the costeffectiveness of risedronate and strontium ranelate in those people who would be treated with generic
Delirium. Quick reference guide. Issue date: July Diagnosis, prevention and management
 Issue date: July 2010 Delirium Diagnosis, prevention and management Developed by the National Clinical Guideline Centre for Acute and Chronic Conditions About this booklet This is a quick reference guide
Issue date: July 2010 Delirium Diagnosis, prevention and management Developed by the National Clinical Guideline Centre for Acute and Chronic Conditions About this booklet This is a quick reference guide
Infracoccygeal sacropexy using mesh for uterine prolapse repair
 Infracoccygeal sacropexy using mesh for uterine Issued: January 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg280 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Infracoccygeal sacropexy using mesh for uterine Issued: January 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg280 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic kidney disease: early identification and management of adults with chronic kidney disease in primary and secondary
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic kidney disease: early identification and management of adults with chronic kidney disease in primary and secondary
Skeletal Manifestations
 Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
Horizon Scanning Technology Briefing. Zoledronic Acid (Aclasta) once yearly treatment for postmenopausal. National Horizon Scanning Centre
 Horizon Scanning Technology Briefing National Horizon Scanning Centre Zoledronic Acid (Aclasta) once yearly treatment for postmenopausal osteoporosis December 2006 This technology summary is based on information
Horizon Scanning Technology Briefing National Horizon Scanning Centre Zoledronic Acid (Aclasta) once yearly treatment for postmenopausal osteoporosis December 2006 This technology summary is based on information
Review of bisphosphonate prescribing May 2014
 Title of Project: NHS Dumfries & Galloway Review of bisphosphonate prescribing May 2014 1 Reason for the review The aim of this audit is to review patients prescribed a bisphosphonate for the prophylaxis
Title of Project: NHS Dumfries & Galloway Review of bisphosphonate prescribing May 2014 1 Reason for the review The aim of this audit is to review patients prescribed a bisphosphonate for the prophylaxis
Clinical Specialist Statement Template
 Clinical Specialist Statement Template Thank you for agreeing to give us a statement on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS. Healthcare professionals can
Clinical Specialist Statement Template Thank you for agreeing to give us a statement on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS. Healthcare professionals can
Using the FRAX Tool. Osteoporosis Definition
 How long will your bones remain standing? Using the FRAX Tool Gary Salzman M.D. Director Banner Good Samaritan/ Hayden VAMC Internal Medicine Geriatric Fellowship Program Phoenix, Arizona Using the FRAX
How long will your bones remain standing? Using the FRAX Tool Gary Salzman M.D. Director Banner Good Samaritan/ Hayden VAMC Internal Medicine Geriatric Fellowship Program Phoenix, Arizona Using the FRAX
Haemorrhoidal artery ligation
 Haemorrhoidal artery ligation Issued: May 2010 NICE interventional procedure guidance 342 www.nice.org.uk/ipg342 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme
Haemorrhoidal artery ligation Issued: May 2010 NICE interventional procedure guidance 342 www.nice.org.uk/ipg342 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme
Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on
 Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on Strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis by The Society for Endocrinology
Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on Strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis by The Society for Endocrinology
Recent advances in the management of osteoporosis
 CONFERENCE SUMMARIES Clinical Medicine 2009, Vol 9, No 6: 565 9 Recent advances in the management of osteoporosis Juliet Compston Introduction Osteoporotic fractures are a major cause of morbidity and
CONFERENCE SUMMARIES Clinical Medicine 2009, Vol 9, No 6: 565 9 Recent advances in the management of osteoporosis Juliet Compston Introduction Osteoporotic fractures are a major cause of morbidity and
Prostate artery embolisation for benign prostatic hyperplasia
 Prostate artery embolisation for benign prostatic Issued: April 2013 guidance.nice.org.uk/ipg NICE has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Prostate artery embolisation for benign prostatic Issued: April 2013 guidance.nice.org.uk/ipg NICE has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Bisphosphonate treatment break
 Bulletin 110 December 2015 Bisphosphonate treatment break Bisphosphonates have been widely used in the treatment of osteoporosis with robust data demonstrating efficacy in fracture risk reduction over
Bulletin 110 December 2015 Bisphosphonate treatment break Bisphosphonates have been widely used in the treatment of osteoporosis with robust data demonstrating efficacy in fracture risk reduction over
Costing tool: Osteoarthritis Implementing the NICE guideline on osteoarthritis (CG177)
 Putting NICE guidance into practice Costing tool: Osteoarthritis Implementing the NICE guideline on osteoarthritis (CG177) Published: February 2014 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline
Putting NICE guidance into practice Costing tool: Osteoarthritis Implementing the NICE guideline on osteoarthritis (CG177) Published: February 2014 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline
Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women
 Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in Issued: October 2010 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta204 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Health Technology Evaluation at NICE to
Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in Issued: October 2010 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta204 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Health Technology Evaluation at NICE to
Strong bones after 50 Fracture liaison services explained A guide for patients, carers and families
 Strong bones after 50 Fracture liaison services explained A guide for patients, carers and families What the NHS should provide for people over 50 who have broken a bone after falling from standing height
Strong bones after 50 Fracture liaison services explained A guide for patients, carers and families What the NHS should provide for people over 50 who have broken a bone after falling from standing height
Initial Pathway for DEXA Referral and Treatment for Fracture Risk Reduction in Postmenopausal Women and Men Age 50 or Above
 Initial Pathway for DEXA Referral and Treatment for Fracture Risk Reduction in Postmenopausal Women and Men Age 50 or Above 2 or > vertebral fractures Low trauma fracture In past 5 years Risk Factors (table1)
Initial Pathway for DEXA Referral and Treatment for Fracture Risk Reduction in Postmenopausal Women and Men Age 50 or Above 2 or > vertebral fractures Low trauma fracture In past 5 years Risk Factors (table1)
Issue date: October Review date: July 2010
 Issue date: October 2008 Review date: July 2010 Alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and strontium ranelate for the primary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal
Issue date: October 2008 Review date: July 2010 Alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and strontium ranelate for the primary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal
Strong bones after 50 Fracture liaison services explained A guide for patients, carers and families
 What the NHS should provide for people over 50 who have broken a bone after falling from standing height or less. Feedback Strong bones after 50 A guide for patients, carers and families What the NHS should
What the NHS should provide for people over 50 who have broken a bone after falling from standing height or less. Feedback Strong bones after 50 A guide for patients, carers and families What the NHS should
Clinical guideline Published: 23 May 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg140
 Palliative care for adults: strong opioids for pain relief Clinical guideline Published: 23 May 12 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg140 NICE 18. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Palliative care for adults: strong opioids for pain relief Clinical guideline Published: 23 May 12 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg140 NICE 18. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Clinical guideline Published: 11 August 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg106
 Barrett's oesophagus: ablative therapy Clinical guideline Published: 11 August 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg106 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Barrett's oesophagus: ablative therapy Clinical guideline Published: 11 August 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg106 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This guideline incorporates some of the recommendations from SIGN, NICE, National Group (NOGG) and local expert opinion. It adopts
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This guideline incorporates some of the recommendations from SIGN, NICE, National Group (NOGG) and local expert opinion. It adopts
IMPROVING BONE HEALTH AND FRACTURE PREVENTION
 IMPROVING BONE HEALTH AND FRACTURE PREVENTION Helen Ridley, Programme Lead, North East & North Cumbria Academic Health Science Network NORTH EAST REGION 2014/15 AHSN Single Sponsored Project Hadrian Primary
IMPROVING BONE HEALTH AND FRACTURE PREVENTION Helen Ridley, Programme Lead, North East & North Cumbria Academic Health Science Network NORTH EAST REGION 2014/15 AHSN Single Sponsored Project Hadrian Primary
O. Bruyère M. Fossi B. Zegels L. Leonori M. Hiligsmann A. Neuprez J.-Y. Reginster
 DOI 10.1007/s00296-012-2460-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the proportion of patients potentially treated with an anti-osteoporotic drug using the current criteria of the Belgian national social security
DOI 10.1007/s00296-012-2460-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the proportion of patients potentially treated with an anti-osteoporotic drug using the current criteria of the Belgian national social security
Dumfries and Galloway. Treatment Protocol for Osteoporosis
 Dumfries and Galloway Treatment Protocol for Osteoporosis DIAGNOSIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS 2 Diagnostic Criteria 2 REFERRAL CRITERIA FOR DEXA 3 TREATMENT 4 Non-Drug Therapy : for all 4 Non-Drug Therapy : in the
Dumfries and Galloway Treatment Protocol for Osteoporosis DIAGNOSIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS 2 Diagnostic Criteria 2 REFERRAL CRITERIA FOR DEXA 3 TREATMENT 4 Non-Drug Therapy : for all 4 Non-Drug Therapy : in the
Audit on follow-up of patients with primary Osteoporosis
 Abstract Aim: To document the frequency of Dual-energy X- ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scanning and Rheumatology clinic follow-up visits of patients with primary osteoporosis, and compare these with recommended
Abstract Aim: To document the frequency of Dual-energy X- ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scanning and Rheumatology clinic follow-up visits of patients with primary osteoporosis, and compare these with recommended
Clinical Practice. Presented by: Internist, Endocrinologist
 Clinical Practice Management of Osteoporosis Presented by: SaeedBehradmanesh, h MD Internist, Endocrinologist Iran, Isfahan, Feb. 2017 Definition: A disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural
Clinical Practice Management of Osteoporosis Presented by: SaeedBehradmanesh, h MD Internist, Endocrinologist Iran, Isfahan, Feb. 2017 Definition: A disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural
Clinical guideline Published: 27 July 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg125
 Chronic kidney disease (stage 5): peritoneal dialysis Clinical guideline Published: 27 July 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg1 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Chronic kidney disease (stage 5): peritoneal dialysis Clinical guideline Published: 27 July 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg1 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Fragile Bones and how to recognise them. Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey
 Fragile Bones and how to recognise them Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder characterised by compromised bone
Fragile Bones and how to recognise them Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder characterised by compromised bone
Practical Management Of Osteoporosis
 Practical Management Of Osteoporosis CONFERENCE 2012 Education Centre, Bournemouth.19 November The following companies have given funding towards the cost of this meeting but have no input into the agenda
Practical Management Of Osteoporosis CONFERENCE 2012 Education Centre, Bournemouth.19 November The following companies have given funding towards the cost of this meeting but have no input into the agenda
Thank you for agreeing to give us a statement on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS.
 Appendix I - Thank you for agreeing to give us a statement on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS. Healthcare professionals can provide a unique perspective
Appendix I - Thank you for agreeing to give us a statement on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS. Healthcare professionals can provide a unique perspective
BEST PRACTICE FRAMEWORK QUESTIONNAIRE
 CAPTURE the FRACTURE BEST PRACTICE FRAMEWORK QUESTIONNAIRE INTRODUCTION Capture the Fracture invites Fracture Liaison Services (FLS) to apply for Capture the Fracture Best Practice Recognition programme.
CAPTURE the FRACTURE BEST PRACTICE FRAMEWORK QUESTIONNAIRE INTRODUCTION Capture the Fracture invites Fracture Liaison Services (FLS) to apply for Capture the Fracture Best Practice Recognition programme.
Dumfries and Galloway. Treatment Protocol for Osteoporosis
 Dumfries and Galloway Treatment Protocol for Osteoporosis DIAGNOSIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS 2 Diagnostic Criteria 2 Multiple low trauma vertebral fractures in the absence of myeloma or metastatic disease. 2 T-score
Dumfries and Galloway Treatment Protocol for Osteoporosis DIAGNOSIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS 2 Diagnostic Criteria 2 Multiple low trauma vertebral fractures in the absence of myeloma or metastatic disease. 2 T-score
DENOSUMAB SHARED CARE GUIDLINES
 DENOSUMAB LICENSING Denosumab (PROLIA ) is licensed for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at increased risk of fractures and for bone loss associated with hormone ablation in men with
DENOSUMAB LICENSING Denosumab (PROLIA ) is licensed for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at increased risk of fractures and for bone loss associated with hormone ablation in men with
Osteoporosis: An Overview. Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, MS
 Osteoporosis: An Overview Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, MS Osteoporosis: An Overview Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, MS Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Objectives Review osteoporosis
Osteoporosis: An Overview Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, MS Osteoporosis: An Overview Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, MS Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Objectives Review osteoporosis
Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions
 Putting NICE guidance into practice Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions Implementing the NICE guidance on Patient Group Directions (MPG2) Published: March 2014 [updated March 2017] These case scenarios
Putting NICE guidance into practice Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions Implementing the NICE guidance on Patient Group Directions (MPG2) Published: March 2014 [updated March 2017] These case scenarios
Guidelines for the Pharmaceutical Management of Osteoporosis in Adult WA Public Hospitals
 WA.DRUG EVALUATION PANEL Guidelines for the Pharmaceutical Management of Osteoporosis in Adult WA Public Hospitals Introduction Osteoporotic fracture-related hospitalisations impose a substantial financial
WA.DRUG EVALUATION PANEL Guidelines for the Pharmaceutical Management of Osteoporosis in Adult WA Public Hospitals Introduction Osteoporotic fracture-related hospitalisations impose a substantial financial
Disclosures. Diagnostic Challenges in Osteoporosis: Whom To Treat 9/25/2014
 Disclosures Diagnostic Challenges in Osteoporosis: Whom To Treat Ethel S. Siris, MD Columbia University Medical Center New York, NY Consultant on scientific issues for: AgNovos Amgen Eli Lilly Merck Novartis
Disclosures Diagnostic Challenges in Osteoporosis: Whom To Treat Ethel S. Siris, MD Columbia University Medical Center New York, NY Consultant on scientific issues for: AgNovos Amgen Eli Lilly Merck Novartis
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540
 Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Analyses of the cost-effectiveness of pooled alendronate and risedronate, compared with strontium ranelate, raloxifene, etidronate and teriparatide
 Analyses of the cost-effectiveness of pooled alendronate and risedronate, compared with strontium ranelate, raloxifene, etidronate and teriparatide Dr Matt Stevenson Sarah Davis July 2006 1 Page Executive
Analyses of the cost-effectiveness of pooled alendronate and risedronate, compared with strontium ranelate, raloxifene, etidronate and teriparatide Dr Matt Stevenson Sarah Davis July 2006 1 Page Executive
Clinical guideline Published: 14 December 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg134
 Anaphylaxis: assessment and referral after emergency treatment Clinical guideline Published: 14 December 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg134 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Anaphylaxis: assessment and referral after emergency treatment Clinical guideline Published: 14 December 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg134 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
FRAX-based assessment and intervention thresholds an exploration of thresholds in women aged 50 years and older in the UK
 Osteoporos Int (1) 26:91 99 DOI.7/s198-1-3176- POSITION PAPER FRAX-based assessment and intervention thresholds an exploration of thresholds in women aged years and older in the UK E. McCloskey 1 & J.
Osteoporos Int (1) 26:91 99 DOI.7/s198-1-3176- POSITION PAPER FRAX-based assessment and intervention thresholds an exploration of thresholds in women aged years and older in the UK E. McCloskey 1 & J.
Alcohol interventions in secondary and further education
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Guideline version (Draft for Consultation) Alcohol interventions in secondary and further education NICE guideline: methods NICE guideline Methods
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Guideline version (Draft for Consultation) Alcohol interventions in secondary and further education NICE guideline: methods NICE guideline Methods
FRiSCy Oxford Fracture Prevention Service
 FRiSCy Oxford Fracture Prevention Service MK Javaid Lecturer in Metabolic Bone Disease, University of Oxford Hon Consultant Rheumatologist, Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Lead Clinician for FRiSCy Declaration
FRiSCy Oxford Fracture Prevention Service MK Javaid Lecturer in Metabolic Bone Disease, University of Oxford Hon Consultant Rheumatologist, Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Lead Clinician for FRiSCy Declaration
Bone Mass Measurement BONE MASS MEASUREMENT HS-042. Policy Number: HS-042. Original Effective Date: 8/25/2008
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Make your. first break. your last.
 www.iofbonehealth.org Make your first break your last WHAT IS OSTEOPOROSIS? Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become more fragile and weak, leading to an increased risk of fractures (broken bones).
www.iofbonehealth.org Make your first break your last WHAT IS OSTEOPOROSIS? Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become more fragile and weak, leading to an increased risk of fractures (broken bones).
1. UK List Price of Zoledronic acid (Zoledronate) 5 mg (Aclasta )
 Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd Frimley Business Park Frimley Camberley Surrey GU16 7SR Dr C M Longson Director, Centre for Health Technology Evaluation National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd Frimley Business Park Frimley Camberley Surrey GU16 7SR Dr C M Longson Director, Centre for Health Technology Evaluation National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
Osteoporosis. Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease
 Osteoporosis Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease Marc K. Drezner, MD Senior Associate Dean Emeritus Professor of Medicine Emeritus University of Wisconsin-Madison Auditorium The Forest at Duke October
Osteoporosis Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease Marc K. Drezner, MD Senior Associate Dean Emeritus Professor of Medicine Emeritus University of Wisconsin-Madison Auditorium The Forest at Duke October
S H A R E D C A R E G U I D E L I N E Drug: Denosumab 60mg injection Indication: treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women
 S H A R E D C A R E G U I D E L I N E Drug: Denosumab 60mg injection Indication: treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women Introduction Indication: Denosumab (Prolia ) is recommended in NICE TA204
S H A R E D C A R E G U I D E L I N E Drug: Denosumab 60mg injection Indication: treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women Introduction Indication: Denosumab (Prolia ) is recommended in NICE TA204
AMERICAN COLLEGE OF RHEUMATOLOGY POSITION STATEMENT. Committee on Rheumatologic Care
 AMERICAN COLLEGE OF RHEUMATOLOGY POSITION STATEMENT SUBJECT: PRESENTED BY: FOR DISTRIBUTION TO: Bone Mineral Density Measurement and the Role of Rheumatologists in the Management of Osteoporosis Committee
AMERICAN COLLEGE OF RHEUMATOLOGY POSITION STATEMENT SUBJECT: PRESENTED BY: FOR DISTRIBUTION TO: Bone Mineral Density Measurement and the Role of Rheumatologists in the Management of Osteoporosis Committee
Osteoporosis. Overview
 v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
Men and Osteoporosis So you think that it can t happen to you
 Men and Osteoporosis So you think that it can t happen to you Jonathan D. Adachi MD, FRCPC Alliance for Better Bone Health Chair in Rheumatology Professor, Department of Medicine Michael G. DeGroote School
Men and Osteoporosis So you think that it can t happen to you Jonathan D. Adachi MD, FRCPC Alliance for Better Bone Health Chair in Rheumatology Professor, Department of Medicine Michael G. DeGroote School
Pharmacy Management Drug Policy
 SUBJECT: - Forteo (teriparatide), Prolia (denosumab), Tymlos (abaloparatide) POLICY NUMBER: Pharmacy-35 EFFECTIVE DATE: 9/07 LAST REVIEW DATE: 9/29/2017 If the member s subscriber contract excludes coverage
SUBJECT: - Forteo (teriparatide), Prolia (denosumab), Tymlos (abaloparatide) POLICY NUMBER: Pharmacy-35 EFFECTIVE DATE: 9/07 LAST REVIEW DATE: 9/29/2017 If the member s subscriber contract excludes coverage
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 October 2008 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta160
 Raloxifene for the primary prevention ention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 October 2008 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta160 NICE 2018. All
Raloxifene for the primary prevention ention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 October 2008 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta160 NICE 2018. All
Quality Standards for Osteoporosis and Prevention of Fragility Fractures
 Draft for consultation Quality Standards for Osteoporosis and Prevention of Fragility Fractures September 0 Have your say We would welcome your views and opinions. Please use the consultation response
Draft for consultation Quality Standards for Osteoporosis and Prevention of Fragility Fractures September 0 Have your say We would welcome your views and opinions. Please use the consultation response
SCORECARD Questionnaire September 2012
 Introduction SCORECARD Questionnaire September 2012 The Osteoporosis Advisory Panel is an independent project chaired by our president Professor John Kanis, supported by a multi-stakeholder group of experts
Introduction SCORECARD Questionnaire September 2012 The Osteoporosis Advisory Panel is an independent project chaired by our president Professor John Kanis, supported by a multi-stakeholder group of experts
8/6/2018. Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? Disclosure. Objectives. Overview
 Disclosure Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? I have no financial disclosure relevant to this presentation Tasma Harindhanavudhi, MD Division of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Disclosure Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? I have no financial disclosure relevant to this presentation Tasma Harindhanavudhi, MD Division of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Hip fracture. The management of hip fracture in adults. Issued: June 2011 last modified: March NICE clinical guideline 124
 Hip fracture The management of hip fracture in adults Issued: June 2011 last modified: March 2014 NICE clinical guideline 124 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg124 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre
Hip fracture The management of hip fracture in adults Issued: June 2011 last modified: March 2014 NICE clinical guideline 124 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg124 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre
