100 mm Sucrose. +Berberine +Quinine
|
|
|
- Julie Shavonne Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies. Proboscis Extension Response (PER) of Gr32a / to mm sucrose (first graph) and sucrose containing various bitter compounds (graph 2 to 5) is the same as in wild type flies. Probability of Extension represents the number of times flies from a given strain extended their proboscis when presented with a tastant, divided by the total number of times that the tastant was presented. Each graph represents data from at least four experiments. Error bars represent SEM (3-11 flies per experiment, 2-5 flies total for each strain and tastant tested). No differences (p<.5) were detected between the strains using the Student s t-test. Caffeine and quinine was present at mm, berberine at mm and Denatonium at 1 mm.
2 a Courtship to male b Female receptivity Courtship index Gr32a 5.9 ** * * * +/+ +/ / / / / #1 #2 #1/#2 Non-maters (%) 15 5 Gr32a +/+ / Copulation latency (min) 15 5 Gr32a +/+ / c 6 Courtship to female Courtship index * * * W: DTI Gr32a[1]: W Gr32a[1]: DTI Gr32a[2]: DTI Gr66a[1]: DTI Gr66a[2]: DTI Gr22e[1]: DTI Gr22e[2]: DTI d 6 Courtship to female 5 Courtship to male 5 Courtship index * * Courtship index Gr32a / / / / / / GAL4 + + GAL4VP UAS-Gr32a Gr32a / / / / / / GAL4 + + GAL4VP UAS-Gr32a + + +
3 Supplementary Figure 2: Courtship analyses of various Gr32a mutant genotypes. (a) Courtship index of males towards decapitated males. Experiments were carried out as described in Figure 2a. Gr32a +/ mutant males and Gr32a / males with either one of the two Gr32a_5.9 transgenes show intermediate male-directed courtship phenotype. (b) Gr32a / females mate with wild type males as efficiently as wild type females in one on one mating assays. A single male was provided with a single virgin female in a courtship chamber (n=2). No statistically significant difference in fraction of non-maters (left panel) and latency time (time to copulation; right panel) was observed between wild type and Gr32a / (p>.5; chi-square test for non-maters, ANOVA for copulation latency). (c) Courtship index of males lacking various Gr expressing neurons towards decapitated females. Experiments were carried out as described in Figure 3a. (n>3 for each genotype tested). All males expressing DTI show the same level of courtship as control males (containing only the UAS:DTI transgene). The Gr32a driver line exhibits slightly higher courtship than the other strains. (d) Courtship index of males towards decapitated males or females. Experiments were carried out as described in Figure 2a. Male-male courtship is significantly decreased only if the tested male has both Gr32a- Gal4/Gr32a-Gal4VP16 and UAS-Gr32a cdna. Error bars represent SEM. Statistical significance was measured by ANOVA (* p<.5, ** p<.1).
4 a b c Male GAL4VP16 Whole (1-29 µm) Male Female GAL4 Surface (1-13 µm) Inside (14-29 µm) Supplementary Figure 3: Projection pattern of Gr32a-expressing neurons beyond the SOG. (a) Individual flies (2 males and 1 female) show slightly different axonal projection patterns and position of the termini, visualized in whole mount antibody staining of brains from Gr32a-GAL4VP16; UAS-mCD8::GFP flies using anti-gfp antibody (see also Supplementary Table 4). (b) Live GFP images of male tarsi expressing a UAS-mCD8::GFP reporter under the control of the Gr32a-Gal4VP16 or Gr32a-Gal4 driver, respectively. Because Gal4VP16 is much more potent and leads to higher expression of the reporter, the signal was adjusted to obtain similar visual images in the two panels. Note that both drivers are expressed in the same set of neurons. (c) Visualization of projections of Gr32a expressing neurons and FRUM expressing nuclei. In contrast to the axons of Gr32a neurons, almost all cell body of fruitless neurons are on or close to the surface of the brain, and no termini of Gr32a neuron contact FRUM-positive cell bodies.
5 Tapping Wing vibration Attempting Wild 7.9 ± ± ±.9 Gr32a / 6.4 ± ± 2.4 * 6.6 ± 1.7 * Gr32a / : 5.9 #1/#2 8.9 ± ± ±.4 Supplementary Table 1: Gr32a / males exhibit late courtship steps towards males (wing vibration and attempting) much more frequently than wild type and Gr32a rescued males. Individual courtship steps towards decapitated males were quantified. In contrast to Gr32a / males, wild type and Gr32a / males carrying rescue transgenes rarely extend courtship beyond tapping. Numbers represent how many times each courtship step was carried out during an experiment of five minutes. n>2. * p<.5 (ANOVA).
6 Gr32a:Gal4/UAS mcd8-gfp DTI +DTI labial palp 6.8 ±.9.6 ±.6 ** foreleg 3.9 ±.2.2 ±.1 ** Gr66a:Gal4/UAS mcd8-gfp DTI +DTI labial palp 16. ± ±.6 ** foreleg.9 ±.2. ±. * Supplementary Table 2: Diphtheria toxin efficiently ablates GRNs. Cell numbers were counted based on GFP expression in flies of the indicated genotypes in the absence or presence UAS-DTI. n=5-. * p<.5, ** p<.1 (ANOVA).
7 treatment Total (n) beyond SOG (n) intact foreleg ablation 4* mid+hindleg ablation 9 9 Supplementary Table 3: The axonal projection pattern of Gr32a-expressing neuron with and without foreleg. Ablations were performed between one to days after eclosion and flies were kept for another 8 to days in vials to allow effective deafferentiation to occur. Only the fourth and fifth tarsal segments were cut off (harboring all Gr32a-expressing cell bodies) to achieve the highest possible survival rate. Compared to intact flies, and flies lacking mid and hindlegs, foreleg-ablated flies showed a significant reduction of projections into the ventrolateral protocerebrum (* p<.5; chisquare test).
8 Gr32a neuron projection status Between VP and SOG Border of VP and AL Inside of VP Total Male Female Supplementary Table 4: Projection patterns of Gr32a-expressing neurons beyond the SOG. The end positions of Gr32a axon beyond the SOG were analyzed in detail. In general, the axons are shorter in male than in female and termini were more difficult to visualize in males. This is likely due to somewhat more robust CNS staining in females than males due to better antibody penetration in the former. Intensity of GFP expression in the cellbodies on the foreleg did not show any apparent difference between the sexes.
9 Supplementary Video: Movie of a mating competition experiment. A wild type and a Gr32a / male are let to compete for a virgin female. The mutant, but not the wild type, male performs occasionally courtship towards the male competitor. The female is easily discernable by the white eye. Both males have red eyes, but the mutant male was marked by a blue dot on thorax, which is difficult to see in the movie, but easily recognizable when directly viewed under a stereomicroscope. Methods: Movie was recorded by COLOUR C/CS MOUNT CAMERA.
10 Methods Gr32a targeting: Upstream (5 arm; ) and downstream (3 arm; ) regions of Gr32a were amplified by Elongase (Invitrogen) from Oregon R DNA. These fragments were cloned into BsiWI SpeI sites and NotI NheI sites, respectively, of CMC5 vector (a gift from C. M. Chen and G. Struhl). This vector contains two polylinkers flanking the mini white gene with a I SceI site, flanked by FRT sites and containing conventional P element repeats. This construct was designed to replace the 2/3 of Gr32a coding region with the eye color marker, white. Virgin female flies carrying targeting construct insertions on 3rd chromosome were crossed to w 1118 ;7FLP; 7I SceI, and 3 day old progeny were heat shocked at 38 C for 6 min. Approximately 8 white eyed adult virgin females were crossed to w 1118 ;7FLP males and progeny were heat shocked as described above. Of the 28 red eyed flies that were obtained, 6 were simple gene replacements. Genomic DNAs from wild type Ore R and Gr32a mutant flies were subjected to PCR amplification primers annealing to sequences within the Gr32a coding region ( ) and the 5 upstream arm ( ). We also confirmed the gene replacement with genomic Southern hybridization. Genomic DNA was digested with BglII or XmaI, fragments were separated on 1 % agarose gels by electrophoresis and transferred to nictorcellulose membranes (Amersham, Inc.), which were hybridized with probes derived from regions upstream of the 5 arm or downstream of the 3 arm (corresponding to nucleotides and , respectively). Transgenesis: The Gr32a_5.9 rescuing constructs contain genomic fragments from 3776 nt upstream of the Gr32a translation initiation codon to 585 nt downstream of the Gr32a translation termination codon. They were obtained by PCR, sequenced and cloned into the pcaspr 4 transformation vector to generate two independently derived transgenic lines (#1 and #2). For the generation of a Gr32a GAL4VP16 driver, a segment containing the 378 nt upstream of the Gr32a translation initiation codon was inserted into a transformation vector containing the GAL4VP16 coding sequence (a gift from Michael Green). Courtship assays: All mutant males, mutant males rescued with transgenes and DTI expressing males used in mating assays carried a w + containing X chromosome to
11 eliminate any effects of different eye pigmentation on mating performance (except for Gr32a[2] Gal4; UAS dti males). Wild type males (control) derived from a cross of Ore R females to w 1118 males. w 1118 males and females were used as mating targets. They were collected as virgins shortly after eclosion, kept separately for 2 5 (female) or 3 7 days (male), unless indicated otherwise. Male subjects were kept in isolation until used for mating behavior. All flies were kept at 25 C on 12:12 light:dark cycle. Copulation latency and non maters experiments were performed in a small Plexiglas mating chamber (4 3 mm). Copulation latency was measured from the time a single male was aspirated into the mating chamber until he successfully mounted the female. A male was considered a non mater if he did failed to copulate within 3 min. The courtship index (CI) is given as percentage of time a male performs vigorous courtship behaviors (wing vibration, licking, and attempting) during 3 seconds. Competition experiments were performed by placing two males in a chamber with a single female and scoring the male which successfully mated. One of the males was marked with a dot of blue ink on the thorax shortly after eclosion at the time of collection in order to distinguish between genotypes. The blue dot did not affect success rate (data not shown). Courtship experiments with fertilized females were carried out as follows: Females were mated and kept in food vials for 1 day. They were then decapitated and used in as described above. Females exposed to males were kept with fru 3 mutant males under heavily crowded conditions to facilitate hydrocarbon exchange between the male and females. females were placed with fru 3 mutant males in 21 mm diameter and a 3 mm high food vial for 1 day. fru 3 mutant males court females at very low intensity and cannot copulate. Immunostaining: UAS mcd8::gfp was driven by Gr32a Gal4VP16 to visualize axonal projections. Animals were aged for at least days before dissection. Antibody staining was conducted as described by Laissue et al. 15, except that 5% heat inactivated goat serum was added to the blocking solution (protocol provided by Leslie Vosshall). Primary antibodies were rabbit anti GFP (Molecular Probes; A 6455) and mouse anti nc82 as a neuropil marker. Secondly antibodies were goat anti rabbit
12 ALEXA 488 and goat anti mouse Cy3. Confocal Microscopy was performed on a Zeiss LSM. For leg ablations, both fore legs or all four mid/hindlegs were cut off above the third tarsal segment with a razor blade, removing all Gr32a expressing cell bodies, which are located on the fourth and fifth tarsal segments. The flies were let to recover for 8 to days, before their brain was dissected and used for immunostaining. Statistical analyses: Statistical analysis of behavioral assays was done using ANOVA. To determine statistically significant differences between genotypes for non maters and for statistically significant differences in established projection beyond the SOG in normal and leg ablated animals, we employed the chi square test. 15. Laissue, P.P., et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the antennal lobe in Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Neurol 45, (1999).
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed
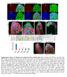 Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
A subset of octopaminergic neurons are important for Drosophila aggression
 28 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/natureneuroscience A subset of octopaminergic neurons are important for Drosophila aggression Chuan Zhou 1,2, Yong Rao 1 & Yi Rao 1,3 Aggression is an innate
28 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/natureneuroscience A subset of octopaminergic neurons are important for Drosophila aggression Chuan Zhou 1,2, Yong Rao 1 & Yi Rao 1,3 Aggression is an innate
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary s Supplementary 1 All three types of foods suppress subsequent feeding in both sexes when the same food is used in the pre-feeding test feeding. (a) Adjusted pre-feeding
Supplementary Information Supplementary s Supplementary 1 All three types of foods suppress subsequent feeding in both sexes when the same food is used in the pre-feeding test feeding. (a) Adjusted pre-feeding
Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state Thirsty but not sated wild-type flies form robust 3 min memory. For the thirsty group, the flies were water-deprived
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state Thirsty but not sated wild-type flies form robust 3 min memory. For the thirsty group, the flies were water-deprived
Secondary Taste Neurons that Convey Sweet Taste and Starvation in the Drosophila Brain
 Article Secondary Taste Neurons that Convey Sweet Taste and Starvation in the Drosophila Brain Highlights d d d d Gustatory projection neurons (sgpns) are involved in sweet taste behaviors sgpn dendrites
Article Secondary Taste Neurons that Convey Sweet Taste and Starvation in the Drosophila Brain Highlights d d d d Gustatory projection neurons (sgpns) are involved in sweet taste behaviors sgpn dendrites
Development Supplementary information
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Mosaic clonal analysis GSC and SP clones were induced with the FLP/FRT-mediated mitotic recombination technique (Xu and Rubin, 1993) in files with following genotypes:
Supplemental Materials and Methods Mosaic clonal analysis GSC and SP clones were induced with the FLP/FRT-mediated mitotic recombination technique (Xu and Rubin, 1993) in files with following genotypes:
marker. DAPI labels nuclei. Flies were 20 days old. Scale bar is 5 µm. Ctrl is
 Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Overexpression of Fto leads to increased food intake and results in obesity Chris Church, Lee Moir, Fiona McMurray, Christophe Girard, Gareth T Banks, Lydia Teboul, Sara Wells,
Supplementary Information Overexpression of Fto leads to increased food intake and results in obesity Chris Church, Lee Moir, Fiona McMurray, Christophe Girard, Gareth T Banks, Lydia Teboul, Sara Wells,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
A Drosophila model for alcohol reward. Supplemental Material
 Kaun et al. Supplemental Material 1 A Drosophila model for alcohol reward Supplemental Material Kaun, K.R. *, Azanchi, R. *, Maung, Z. *, Hirsh, J. and Heberlein, U. * * Department of Anatomy, University
Kaun et al. Supplemental Material 1 A Drosophila model for alcohol reward Supplemental Material Kaun, K.R. *, Azanchi, R. *, Maung, Z. *, Hirsh, J. and Heberlein, U. * * Department of Anatomy, University
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
The Drosophila Pox neuro gene: control of male courtship behavior and fertility as revealed by a complete dissection of all enhancers
 Development 129, 5667-5681 2002 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:10.1242/dev.00157 5667 The Drosophila Pox neuro gene: control of male courtship behavior and fertility as revealed by a complete dissection
Development 129, 5667-5681 2002 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:10.1242/dev.00157 5667 The Drosophila Pox neuro gene: control of male courtship behavior and fertility as revealed by a complete dissection
Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice
 Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
50mM D-Glucose. Percentage PI. L-Glucose
 Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a
Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a
Isoform-Specific Control of Male Neuronal Differentiation and Behavior in Drosophila by the fruitless Gene
 Current Biology 16, 1063 1076, June 6, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2006.04.039 Isoform-Specific Control of Male Neuronal Differentiation and Behavior in Drosophila by
Current Biology 16, 1063 1076, June 6, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2006.04.039 Isoform-Specific Control of Male Neuronal Differentiation and Behavior in Drosophila by
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
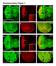 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
COMPARATIVE BEHAVIOURAL ANALYSIS OF MATING BETWEEN YELLOW AND WILD TYPE DROSOPHILA OF MELANOGASTER SPECIES GROUP
 Journal of Scientific Research Vol. 58, 2014 : 45-50 Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi ISSN : 0447-9483 COMPARATIVE BEHAVIOURAL ANALYSIS OF MATING BETWEEN YELLOW AND WILD TYPE DROSOPHILA OF MELANOGASTER
Journal of Scientific Research Vol. 58, 2014 : 45-50 Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi ISSN : 0447-9483 COMPARATIVE BEHAVIOURAL ANALYSIS OF MATING BETWEEN YELLOW AND WILD TYPE DROSOPHILA OF MELANOGASTER
Two Gr Genes Underlie Sugar Reception in Drosophila
 Article Two Gr Genes Underlie Sugar Reception in Drosophila Anupama Dahanukar, 1 Ya-Ting Lei, 1 Jae Young Kwon, 1 and John R. Carlson 1, * 1 Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology,
Article Two Gr Genes Underlie Sugar Reception in Drosophila Anupama Dahanukar, 1 Ya-Ting Lei, 1 Jae Young Kwon, 1 and John R. Carlson 1, * 1 Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology,
Linkage Mapping in Drosophila Melanogaster
 Linkage Mapping in Drosophila Melanogaster Genetics: Fall 2012 Joshua Hanau Introduction: An experiment was performed in order to determine the presence and degree of gene linkage in Drosophila Melanogaster.
Linkage Mapping in Drosophila Melanogaster Genetics: Fall 2012 Joshua Hanau Introduction: An experiment was performed in order to determine the presence and degree of gene linkage in Drosophila Melanogaster.
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
doi: /nature09554
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
- -. I ANIMAL BEHAVIOR
 LAB L- - -. I ANIMAL BEHAVIOR OVERVIEW In this lab you will observe some aspects of animal behavior. 1. In Exercise 11A you will observe pillbugs and design an experiment to investigate their responses
LAB L- - -. I ANIMAL BEHAVIOR OVERVIEW In this lab you will observe some aspects of animal behavior. 1. In Exercise 11A you will observe pillbugs and design an experiment to investigate their responses
Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states.
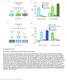 Supplementary Figure 1 Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states. (a) Protocol to produce exclusively hungry or thirsty flies for 6 h water memory retrieval. (b) Consumption assays
Supplementary Figure 1 Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states. (a) Protocol to produce exclusively hungry or thirsty flies for 6 h water memory retrieval. (b) Consumption assays
Labeled lines. Drosophila avoid ingesting alkaloids. Bitter modulated sugar detection in Drosophila melanogaster
 2/2/213 Drosophila avoid ingesting alkaloids Bitter modulated sugar detection in Drosophila melanogaster nl/fly/h 3 2 1 Females Males Frédéric MARION POLL AgroParisTech, Paris INRA UMR 1272 PISC multicafe
2/2/213 Drosophila avoid ingesting alkaloids Bitter modulated sugar detection in Drosophila melanogaster nl/fly/h 3 2 1 Females Males Frédéric MARION POLL AgroParisTech, Paris INRA UMR 1272 PISC multicafe
Sensory Integration Regulating Male Courtship Behavior in Drosophila
 Sensory Integration Regulating Male Courtship Behavior in Drosophila Dimitrije Krstic 1,2, Werner Boll 1, Markus Noll 1 * 1 Institute for Molecular Biology, University of Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2
Sensory Integration Regulating Male Courtship Behavior in Drosophila Dimitrije Krstic 1,2, Werner Boll 1, Markus Noll 1 * 1 Institute for Molecular Biology, University of Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11905 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of integrated chorda tympani nerve responses. Quantification
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11905 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of integrated chorda tympani nerve responses. Quantification
Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions
 nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text:
nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text:
The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
Octopamine Neuromodulatory Effects on a Social Behavior Decision- Making Network in Drosophila Males
 Octopamine Neuromodulatory Effects on a Social Behavior Decision- Making Network in Drosophila Males The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Octopamine Neuromodulatory Effects on a Social Behavior Decision- Making Network in Drosophila Males The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
LABORATÓRIUMI GYAKORLAT SILLABUSZ SYLLABUS OF A PRACTICAL DEMOSTRATION. financed by the program
 TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 projekt Az élettudományi-klinikai felsőoktatás gyakorlatorientált és hallgatóbarát korszerűsítése a vidéki képzőhelyek nemzetközi versenyképességének erősítésére program
TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 projekt Az élettudományi-klinikai felsőoktatás gyakorlatorientált és hallgatóbarát korszerűsítése a vidéki képzőhelyek nemzetközi versenyképességének erősítésére program
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Figure S1. Molecular confirmation of the precise insertion of the AsMCRkh2 cargo into the kh w locus.
 Supporting Information Appendix Table S1. Larval and adult phenotypes of G 2 progeny of lines 10.1 and 10.2 G 1 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S2. List of oligonucleotide primers. Table S3.
Supporting Information Appendix Table S1. Larval and adult phenotypes of G 2 progeny of lines 10.1 and 10.2 G 1 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S2. List of oligonucleotide primers. Table S3.
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1: nlp-22 is expressed in the RIA interneurons and is secreted. (a) An animal expressing both the RIA specific reporter
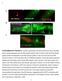 1 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1: nlp-22 is expressed in the RIA interneurons and is secreted. (a) An animal expressing both the RIA specific reporter Pglr-3:mCherry (red) and Pnlp-22:gfp (green) shows co-localization
1 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1: nlp-22 is expressed in the RIA interneurons and is secreted. (a) An animal expressing both the RIA specific reporter Pglr-3:mCherry (red) and Pnlp-22:gfp (green) shows co-localization
Biology 164 Laboratory
 Biology 164 Laboratory Transmission Genetics: Inheritance of Mutant Traits in Drosophila Fruit Flies Introduction To reinforce your understanding of basic eukaryotic genetic principles, you will study
Biology 164 Laboratory Transmission Genetics: Inheritance of Mutant Traits in Drosophila Fruit Flies Introduction To reinforce your understanding of basic eukaryotic genetic principles, you will study
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Experiment 1. The aim here is to understand the pattern of
 H A Ranganath and M T Tanuja Drosophila Stock Centre Department of Studies in Zoology University of Mysore Manasagangotri Mysore 570006, India. E-mail:drosrang@bgl.vsnl.net.in hranganath@hotmail.com Part
H A Ranganath and M T Tanuja Drosophila Stock Centre Department of Studies in Zoology University of Mysore Manasagangotri Mysore 570006, India. E-mail:drosrang@bgl.vsnl.net.in hranganath@hotmail.com Part
Experimental evolution under hyperpromiscuity in Drosophila melanogaster
 Perry et al. BMC Evolutionary Biology (2016) 16:131 DOI 10.1186/s12862-016-0699-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Experimental evolution under hyperpromiscuity in Drosophila melanogaster Jennifer C. Perry
Perry et al. BMC Evolutionary Biology (2016) 16:131 DOI 10.1186/s12862-016-0699-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Experimental evolution under hyperpromiscuity in Drosophila melanogaster Jennifer C. Perry
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Supplemental Information. Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate. into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling. in Developing Skin Vasculature
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal
 Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal hydrocephalus Fadel TISSIR, Yibo QU, Mireille MONTCOUQUIOL, Libing ZHOU, Kouji KOMATSU, Dongbo SHI, Toshihiko FUJIMORI,
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal hydrocephalus Fadel TISSIR, Yibo QU, Mireille MONTCOUQUIOL, Libing ZHOU, Kouji KOMATSU, Dongbo SHI, Toshihiko FUJIMORI,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Inheritance of Aldehyde Oxidase in Drosophila melanogaster
 Inheritance of Aldehyde Oxidase in Drosophila melanogaster (adapted from Morgan, J. G. and V. Finnerty. 1991. Inheritance of aldehyde oxidase in Drosophilia melanogaster. Pages 33-47, in Tested studies
Inheritance of Aldehyde Oxidase in Drosophila melanogaster (adapted from Morgan, J. G. and V. Finnerty. 1991. Inheritance of aldehyde oxidase in Drosophilia melanogaster. Pages 33-47, in Tested studies
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Central Brain Neurons Expressing doublesex Regulate Female Receptivity in Drosophila
 Article Central Brain Neurons Expressing doublesex Regulate Female Receptivity in Drosophila Chuan Zhou, 1 Yufeng Pan, 1 Carmen C. Robinett, 1 Geoffrey W. Meissner, 1 and Bruce S. Baker 1, 1 Janelia Farm
Article Central Brain Neurons Expressing doublesex Regulate Female Receptivity in Drosophila Chuan Zhou, 1 Yufeng Pan, 1 Carmen C. Robinett, 1 Geoffrey W. Meissner, 1 and Bruce S. Baker 1, 1 Janelia Farm
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Factors and Genes Mendel s model of inheritance was based on the idea of factors that were independently assorted and segregated into gametes We now know that these
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Factors and Genes Mendel s model of inheritance was based on the idea of factors that were independently assorted and segregated into gametes We now know that these
Ch 8 Practice Questions
 Ch 8 Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What fraction of offspring of the cross Aa Aa is homozygous for the dominant allele?
Ch 8 Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What fraction of offspring of the cross Aa Aa is homozygous for the dominant allele?
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Head of College Scholars List Scheme. Summer Studentship Report Form
 Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Supplemental Information. Proprioceptive Opsin Functions. in Drosophila Larval Locomotion
 Neuron, Volume 98 Supplemental Information Proprioceptive Opsin Functions in Drosophila Larval Locomotion Damiano Zanini, Diego Giraldo, Ben Warren, Radoslaw Katana, Marta Andrés, Suneel Reddy, Stephanie
Neuron, Volume 98 Supplemental Information Proprioceptive Opsin Functions in Drosophila Larval Locomotion Damiano Zanini, Diego Giraldo, Ben Warren, Radoslaw Katana, Marta Andrés, Suneel Reddy, Stephanie
Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8
 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10643 Supplementary Table 1. Identification of hecw-1 coding polymorphisms at amino acid positions 322 and 325 in 162 strains of C. elegans. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 Supplementary Figure
doi:10.1038/nature10643 Supplementary Table 1. Identification of hecw-1 coding polymorphisms at amino acid positions 322 and 325 in 162 strains of C. elegans. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplemental Information. Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body. Output Synapses Are Cholinergic
 Neuron, Volume 89 Supplemental Information Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body Output Synapses Are Cholinergic Oliver Barnstedt, David Owald, Johannes Felsenberg, Ruth Brain, John-Paul Moszynski, Clifford B.
Neuron, Volume 89 Supplemental Information Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body Output Synapses Are Cholinergic Oliver Barnstedt, David Owald, Johannes Felsenberg, Ruth Brain, John-Paul Moszynski, Clifford B.
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h)
 Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
Conditional disruption of synaptic transmission induces male male courtship behavior in Drosophila
 Conditional disruption of synaptic transmission induces male male courtship behavior in Drosophila Toshihiro Kitamoto* Division of Neurosciences, Beckman Research Institute of the City of Hope, 1450 East
Conditional disruption of synaptic transmission induces male male courtship behavior in Drosophila Toshihiro Kitamoto* Division of Neurosciences, Beckman Research Institute of the City of Hope, 1450 East
Supplementary Figures
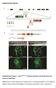 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing hybridization signals for chicken (left) and quail (right) genomic DNA analyzed by Chicken GeneChip (n=3). www.nature.com/nature 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Independent
Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing hybridization signals for chicken (left) and quail (right) genomic DNA analyzed by Chicken GeneChip (n=3). www.nature.com/nature 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Independent
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Associative learning and memory in Drosophila: beyond olfactory conditioning
 Behavioural Processes 64 (2003) 225 238 Associative learning and memory in Drosophila: beyond olfactory conditioning Kathleen K. Siwicki, Lisa Ladewski Department of Biology, Swarthmore College, 500 College
Behavioural Processes 64 (2003) 225 238 Associative learning and memory in Drosophila: beyond olfactory conditioning Kathleen K. Siwicki, Lisa Ladewski Department of Biology, Swarthmore College, 500 College
PEER REVIEW FILE. Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In this manuscript entitled "Neural circuits for long-term water-reward memory processing in thirsty Drosophila", the authors
PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In this manuscript entitled "Neural circuits for long-term water-reward memory processing in thirsty Drosophila", the authors
Contact Chemoreceptors Mediate Male-Male Repulsion and Male-Female Attraction during Drosophila Courtship
 Contact Chemoreceptors Mediate Male-Male Repulsion and Male-Female Attraction during Drosophila Courtship Robert Thistle, 2,3 Peter Cameron, 2,3,4 Azeen Ghorayshi, 2 Lisa Dennison, 2 and Kristin Scott
Contact Chemoreceptors Mediate Male-Male Repulsion and Male-Female Attraction during Drosophila Courtship Robert Thistle, 2,3 Peter Cameron, 2,3,4 Azeen Ghorayshi, 2 Lisa Dennison, 2 and Kristin Scott
Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc.
 Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc. a,b, Test of put RNAi. a, In wildtype discs the Dpp target gene Sal (red) is expressed in a broad stripe in the centre of the ventral
Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc. a,b, Test of put RNAi. a, In wildtype discs the Dpp target gene Sal (red) is expressed in a broad stripe in the centre of the ventral
Supplementary Figure 1: Co-localization of reconstituted L-PTC and dendritic cells
 a CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-y CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-z c b x-y view BoNT NAPs CD11c BoNT CD11c NAPs BoNT NAPs CD11c 90 x-z view Apical Basolateral Supplementary
a CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-y CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-z c b x-y view BoNT NAPs CD11c BoNT CD11c NAPs BoNT NAPs CD11c 90 x-z view Apical Basolateral Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang and Page-McCaw, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403084/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Extracellular anti-wg staining is specific. Note
Supplemental material Wang and Page-McCaw, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403084/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Extracellular anti-wg staining is specific. Note
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Parameters and consequences of mononuclear cardiomyocyte frequency.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Parameters and consequences of mononuclear cardiomyocyte frequency. (a) Correlation of the frequency of mononuclear cardiomyocytes to the frequency of cardiomyocytes with three or
Supplementary Figure 1 Parameters and consequences of mononuclear cardiomyocyte frequency. (a) Correlation of the frequency of mononuclear cardiomyocytes to the frequency of cardiomyocytes with three or
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila Ayako Kohyama-Koganeya, 1,2 Takuji Nabetani, 1 Masayuki Miura, 2,3 Yoshio Hirabayashi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila Ayako Kohyama-Koganeya, 1,2 Takuji Nabetani, 1 Masayuki Miura, 2,3 Yoshio Hirabayashi
Supplementary Figures
 J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni eee Supplementary Figure 1
 eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
Targeted Manipulation of Serotonergic Neurotransmission Affects the Escalation of Aggression in Adult Male Drosophila Melanogaster
 Targeted Manipulation of Serotonergic Neurotransmission Affects the Escalation of Aggression in Adult Male Drosophila Melanogaster The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Targeted Manipulation of Serotonergic Neurotransmission Affects the Escalation of Aggression in Adult Male Drosophila Melanogaster The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples.
 Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/326/5951/443/dc1 Supporting Online Material for The Taste of Carbonation Jayaram Chandrashekar, David Yarmolinsky, Lars von Buchholtz, Yuki Oka, William Sly, Nicholas
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/326/5951/443/dc1 Supporting Online Material for The Taste of Carbonation Jayaram Chandrashekar, David Yarmolinsky, Lars von Buchholtz, Yuki Oka, William Sly, Nicholas
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Structural Variation and Medical Genomics
 Structural Variation and Medical Genomics Andrew King Department of Biomedical Informatics July 8, 2014 You already know about small scale genetic mutations Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) Deletions,
Structural Variation and Medical Genomics Andrew King Department of Biomedical Informatics July 8, 2014 You already know about small scale genetic mutations Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) Deletions,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh
 Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa
Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 7040/01 London Examinations GCE Biology Ordinary Level Paper 1
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 7040/01 London Examinations GCE Biology Ordinary Level Paper 1 Friday 15 January 2010 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Nil
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 7040/01 London Examinations GCE Biology Ordinary Level Paper 1 Friday 15 January 2010 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Nil
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
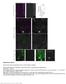 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Ahtiainen et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
