The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
|
|
|
- June Allison Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones. A hormone is a chemical substance secreted by a gland.
3 Hormones are secreted by one part of the body to control one or more organs. The organs which the hormones control could be directly next to the gland which releases them or in a completely different part of the body. A hormone will only work on an organ which is sensitive to that hormone.
4 A small list of hormones in the human body Testosterone Estrogen Adrenaline (epinephrine) HGH (human growth hormone) Insulin Etc.
5 Two hormones play a major role in puberty secreted by the pituitary gland. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) These hormones stimulate the maturation of the ova and the production of sperm. They also stimulate the ovaries and testicles to produce the male and female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone (female) and testosterone (male)
6 The sex hormones initiate significant physical and psychological changes. These are more commonly referred to as primary and secondary sexual characteristics. We will list the primary and secondary changes in men and women.
7 Oogenesis is the process of an ovum production by meiosis. Puberty is the beginning of the fertile phase of a woman s life. A woman has all of her oocytes (precursor to an ovum) at birth. At puberty, a girl has approximately 700,000 oocytes.
8 The oocytes are diploid cells, meaning that they have 23 pairs of chromosomes each. Typically there is 1 ovum produced for each cycle of the menstrual system. During a woman s life, approximately 400 oocytes change into ova (plural of ovum)
9 The diploid oocyte undergoes a process call meiosis where the diploid cells become two haploid cells Haploid means that their only have one set of chromosomes, so 23 chomosomes. The oocyte does not split into two equal cells, one gets all the nutrients and the second dies quickly after.
10
11 Each oocyte gives rise to one ovum. If this ovum is not fertilized, it is then expelled by the body during menstruation If the ovum is fertilized, the zygote forms and implants itself into the wall of the uterus to develop into a embryo.
12 The ovarian cycle is the process where a single ovarian follicle matures to produce an ovum and changes into a corpus luteum. At the beginning of the cycle, the pituitary gland secretes FSH which stimulates the development and growth of the ovarian follicle. As the follicle develops, it secretes more and more estrogen.
13 The increased estrogen leads to an increase of LH. This causes the ovum to be released from the follicle. The follicle then turns into a corpus luteum which then secretes progesterone. This hormone prepares the body for implantation of the zygote.
14 If there is no zygote present, then the lining of the endometrium is shed through menstruation. If the zygote does implant then the progesterone levels are maintained. The corpus keeps secreting progesterone until the placenta takes over.
15
16 The menstrual cycle represents all of the periodic changes in the uterine endometrium. The menstrual cycle begins on the first day of menstruation. If a zygote is not implanted, then the drop of progesterone triggers menstruation.
17 After menstruation, the body begins the proliferation phase until ovulation occurs. The endometrium thickens again due to stimulation of estrogen. The final phase is the secretory phase which is marked by the thickening of the endometrium further.
18 An ovum lives for between hours and a spermatozoan lives for hours which means that a woman s fertile period is roughly 4 days. Hormone levels fluctuates throughout the ovarian and menstrual cycles.
19
20 When a boy reaches puberty, the pituitary gland releases FSH, which stimulates spermatogenesis. Cells called spermatogonia cover the walls of the seminiferous tubules. These cells undergo meiosis to form spermatozoan (sperm) Each spermatogonia gives rise to four sperm. Men produce 120 million sperm per day.
21 As we saw, an erection is the process by which blood collects and is trapped in the penis. After spermatogenesis, the sperm collect in the vas deferens until ready to be expelled. When the erect penis is stimulated, the sperm are pushed through the ejaculatory duct towards the urethra.
22 Urine and sperm are enemies and urine will kill sperm on contact. To ensure that the urethra is clean, a man s body produces a pre-ejaculatory fluid to clean out the urethra. For ejaculation, the sperm is mixed with seminal fluid to create semen.
23 Semen then collects in the bulge of the urethra near the prostate. At the moment of ejaculation, the muscles around the urethra as well as the contraction of the penis serve to project the semen. The average ejaculation contains 3.5 ml of fluid and 350 million sperm.
to ensure the. Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion of.
 The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 Quiz: Evolution Human Reproduction Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember:
Quiz: Evolution Human Reproduction Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember:
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
1 The cell. Checkup Chapter 5. (pp ) 1. Look at the following illustration.
 Checkup Chapter 5 1 The cell (pp. 126 131) 1. Look at the following illustration. a) What three cell components are visible under a light (optical) microscope? Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus b) What is
Checkup Chapter 5 1 The cell (pp. 126 131) 1. Look at the following illustration. a) What three cell components are visible under a light (optical) microscope? Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus b) What is
a. the tail disappears b. they become spermatids c. they undergo capacitation d. they have been stored in the uterus for several days
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Physiology of Male Reproductive System
 Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Animal Reproduction Chapter 46. Fission. Budding. Parthenogenesis. Fragmentation 11/27/2017
 Animal Reproduction Chapter 46 Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Sexual reproduction is the creation of an offspring by fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete
Animal Reproduction Chapter 46 Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Sexual reproduction is the creation of an offspring by fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis. Regents Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
REPRODUCTION The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis.
 1. The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis. Which cell produces testosterone? 2. A function of the interstitial cells in the testes is to produce A sperm B testosterone
1. The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis. Which cell produces testosterone? 2. A function of the interstitial cells in the testes is to produce A sperm B testosterone
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
Female Reproductive System. Lesson 10
 Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
Sperm production. Sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production. Sperm production. Controlling sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Human Reproduction. Human Reproductive System. Scrotum. Male Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive Anatomy The female anatomy first just the reproductive parts:
 Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Investigation: The Human Menstrual Cycle Research Question: How do hormones control the menstrual cycle?
 Investigation: The Human Menstrual Cycle Research Question: How do hormones control the menstrual cycle? Introduction: The menstrual cycle (changes within the uterus) is an approximately 28-day cycle that
Investigation: The Human Menstrual Cycle Research Question: How do hormones control the menstrual cycle? Introduction: The menstrual cycle (changes within the uterus) is an approximately 28-day cycle that
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
1. During the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, the hypothalamus releases GnRH.
 1. During the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, the hypothalamus releases GnRH. 2. This causes the anterior pituitary to secrete small quantities of FSH and LH. 3. At this time, the follicles in the
1. During the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, the hypothalamus releases GnRH. 2. This causes the anterior pituitary to secrete small quantities of FSH and LH. 3. At this time, the follicles in the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
LIFE SCIENCES Grade 12 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014
 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
To General Embryology Dr: Azza Zaki
 Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Male Reproductive System
 21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
The Reproductive System
 The Reproductive System The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete hormones Sperm male gametes Ova (eggs) female
The Reproductive System The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete hormones Sperm male gametes Ova (eggs) female
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 14 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Chapter 27 The Reproductive System. MDufilho
 Chapter 27 The Reproductive System 1 Figure 27.19 Events of oogenesis. Before birth Meiotic events 2n Oogonium (stem cell) Mitosis Follicle development in ovary Follicle cells Oocyte 2n Primary oocyte
Chapter 27 The Reproductive System 1 Figure 27.19 Events of oogenesis. Before birth Meiotic events 2n Oogonium (stem cell) Mitosis Follicle development in ovary Follicle cells Oocyte 2n Primary oocyte
Special Parts: Gender. Why Have Sex?
 Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into 2
 Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction
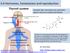 6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
The Human Menstrual Cycle
 The Human Menstrual Cycle Name: The female human s menstrual cycle is broken into two phases: the Follicular Phase and the Luteal Phase. These two phases are separated by an event called ovulation. (1)
The Human Menstrual Cycle Name: The female human s menstrual cycle is broken into two phases: the Follicular Phase and the Luteal Phase. These two phases are separated by an event called ovulation. (1)
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
2. Which of the following factors does not contribute to ion selectivity?
 General Biology Summer 2014 Exam II Sample Answers 1. Which of the following is TRUE about a neuron at rest? A. The cytosol is positive relative to the outside B. Na+ concentrations are higher inside C.
General Biology Summer 2014 Exam II Sample Answers 1. Which of the following is TRUE about a neuron at rest? A. The cytosol is positive relative to the outside B. Na+ concentrations are higher inside C.
Reproductive System. Testes. Accessory reproductive organs. gametogenesis hormones. Reproductive tract & Glands
 Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
The Reproductive System
 A+ NURSING TEAM The Reproductive System Chapter 28 Page1129-1181 2012 A PLUS TEAM ~ فريقك األكاديمي في كليتك التمريض ~. *`'. A+ team. *`'. ما هى إال وسيلة لتفعيل دور كل واحد منا في تيسير المعرفة بطريقة
A+ NURSING TEAM The Reproductive System Chapter 28 Page1129-1181 2012 A PLUS TEAM ~ فريقك األكاديمي في كليتك التمريض ~. *`'. A+ team. *`'. ما هى إال وسيلة لتفعيل دور كل واحد منا في تيسير المعرفة بطريقة
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
Embryology Lecture # 4
 1 Quick Review: Oogenesis : - Oogonia start appear in the ovary when the age of the fetus 1 is th (5 week). - Then the Oogonia transformed into 1ry Oocyte. - 1ry Oocyte is surrounded by a follicle (cover).
1 Quick Review: Oogenesis : - Oogonia start appear in the ovary when the age of the fetus 1 is th (5 week). - Then the Oogonia transformed into 1ry Oocyte. - 1ry Oocyte is surrounded by a follicle (cover).
BIOLOGY. Animal Reproduction CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 46 Animal Reproduction Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Both
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 46 Animal Reproduction Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Both
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 27.3 Using Figure 27.3, match the following: 1) The stage called ovulation. 2) Corpus
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 27.3 Using Figure 27.3, match the following: 1) The stage called ovulation. 2) Corpus
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2
 Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23
 AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
Unit 4 - Reproduction
 Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Which cell process occurs only in organisms that reproduce sexually? A) mutation B) replication C) meiosis D) mitosis 2. Which sequence represents the
Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Which cell process occurs only in organisms that reproduce sexually? A) mutation B) replication C) meiosis D) mitosis 2. Which sequence represents the
Reproduction Worksheet
 Name: Date: Reproduction Worksheet Directions: Base your answers to questions 1-4 on the diagram below and your knowledge of biology. 1. Identify the structure in which sperm is produced. What is the name
Name: Date: Reproduction Worksheet Directions: Base your answers to questions 1-4 on the diagram below and your knowledge of biology. 1. Identify the structure in which sperm is produced. What is the name
describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it
 You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
Growing up. W Worksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts
 3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
Fig Chapter 46. Animal Reproduction
 Fig. 46-1 Chapter 46 Animal Reproduction Overview: Pairing Up for Sexual Reproduction Each earthworm produces sperm and eggs; Aspects of animal form and function can be viewed broadly as adaptations contributing
Fig. 46-1 Chapter 46 Animal Reproduction Overview: Pairing Up for Sexual Reproduction Each earthworm produces sperm and eggs; Aspects of animal form and function can be viewed broadly as adaptations contributing
The Reproductive System
 C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Unit 2 Physiology and Health Part (a) The Reproductive System HOMEWORK BOOKLET
 Unit 2 Physiology and Health Part (a) The Reproductive System HOMEWORK BOOKLET Name: Homework Date Due Mark % Key Area 1 The structure and function of reproductive organs Key Area 2 Hormonal control of
Unit 2 Physiology and Health Part (a) The Reproductive System HOMEWORK BOOKLET Name: Homework Date Due Mark % Key Area 1 The structure and function of reproductive organs Key Area 2 Hormonal control of
2 - male hormones/ female system
 2 - male hormones/ female system May 7, 2012 5:08 PM I) Testosterone: main androgen (male sex hormone) A) Intro to Testosterone: -steroid hormone produced by interstitial cells in testes -produced in response
2 - male hormones/ female system May 7, 2012 5:08 PM I) Testosterone: main androgen (male sex hormone) A) Intro to Testosterone: -steroid hormone produced by interstitial cells in testes -produced in response
Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank
 Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank Objective 6.01 Describe the basic functions of the reproductive system. 1. Which of the following is a function of the reproductive system? a. Production
Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank Objective 6.01 Describe the basic functions of the reproductive system. 1. Which of the following is a function of the reproductive system? a. Production
