Unit 8 Reproduction and Heredity
|
|
|
- Cynthia McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 stone had replaced its tissues. Sediments continued to build up, and rock continued to form. Organism B died. Sediments built up over the dead organism. Minerals seeped into the bones of the organism, transforming it into fossils. Extended Response 18. Sample answer: The four parts of natural selection are overproduction, variation, selection, and adaptation. Overproduction is the tendency of a species to produce more offspring than will survive to adulthood. Overproduction ensures that enough individuals will survive competition, predation, and accidents to allow a healthy breeding population. Variation is the range of characteristics within a population. Individuals within a population have slightly different characteristics. These differences allow the population to adjust to minor changes in the environment by giving different individuals different advantages. Selection is the process or processes by which organisms are removed from the population. Some selective factors include disease, competition, and predation. Individuals that survive the changes are more likely to reproduce and pass on their traits. When they reproduce, these changes are passed to offspring. As this process is repeated, these changes become more widely distributed in the population. The result is called adaptation. Overproduction is the tendency of a population to produce more offspring than are likely to survive to reproduce. Variation is the range in characteristics that exists within a population. Variation increases the likelihood of success of a population. Selection determines which individual organisms are most likely to survive and reproduce in their environment. Adaptation is the process of becoming adapted to an environment (or the acquisition of traits that improve survival and reproduction). Unit 8 Reproduction and Heredity Unit Pretest 1. B 5. B 9. B 2. A 6. C 10. A 3. D 7. B 4. C 8. D 1. B A is incorrect because the recessive trait of tip flower position would be the only trait seen in self-pollinated recessive plants. B is correct because the recessive tip flower position would be seen in every generation. C is incorrect because the stem flower position is the recessive trait and would be observed in every generation. D is incorrect because the plants that were self-pollinated did not have any dominant alleles. So, subsequent generations could not show the dominant trait. 2. A A is correct because the genes are located on the chromosomes of each cell. B is incorrect because genes are located on chromosomes; chromosomes are not located on genes. C is incorrect because the genes come from both parents and are located on the chromosomes. D is incorrect because chromosomes are not made up of cells, and entire chromosomes are not responsible for earlobe attachment. 3. D A is incorrect because a Punnett square cannot identify other traits for which two individuals have alleles in common. B is incorrect because a Punnett square cannot confirm the alleles of adult individuals. C is incorrect because a Punnett square cannot make predictions about acquired traits. D is correct because a Punnett square can be used to predict the possible combinations of alleles that offspring inherit. 4. C A is incorrect because a cross between these parents would produce offspring in a ratio of 1 DD to 1 Dd. B is incorrect because a cross between these parents would produce offspring in a ratio of 1 DD to 2 Dd to 1 dd. C is correct because a cross between these parents would produce offspring in a ratio of 1 Dd to 1 dd. D is incorrect because a cross between these parents would produce only offspring with Dd. 5. B A is incorrect because sexual reproduction requires two parents and does not produce offspring identical to either parent. B is correct because the production of spores is a form of asexual reproduction. C is incorrect because fertilization takes place during sexual reproduction. D is incorrect because vegetative reproduction takes place when a new plant develops from a stem or root of a parent plant. 6. C A is incorrect because after fertilization, the zygote (cell C) is not genetically identical to the egg (cell A). B is incorrect because after fertilization, the zygote (cell C) is not genetically identical to the sperm (cell B). C is correct because after fertilization, the zygote (cell C) has a full set of chromosomes. Half of these chromosomes are from the sperm (cell B), and the other half are from the egg (cell A). D is incorrect because cell B is the sperm, which contributes genes to cell C (the zygote). 7. B A is incorrect because fertilization is the joining of an egg cell and sperm. 319 Grade 7 Guide Florida
2 B is correct because both male and female sex cells are produced through meiosis. C is incorrect because only body cells are produced through mitosis. D is incorrect because pollination is the process whereby pollen is transferred from a male structure (anther) to a female structure (stigma). 8. D A is incorrect because most tissues are made up of body cells, not sex cells. B is incorrect because sex cells contain autosomal chromosomes as well as sex chromosomes. C is incorrect because sex cells have half the chromosomes of a body cell. D is correct because sex cells carry half of the usual number of chromosomes. 9. B A is incorrect because during cytokinesis, Xander would have observed two cells separating from each other. B is correct because during interphase, genetic material is in the form of chromatin, not chromosomes. C is incorrect because during metaphase, chromosomes are aligned at the middle of the cell. D is incorrect because during prophase, chromosomes have condensed. 10. A A is correct because family history of diabetes is a genetic factor, and diet and exercise are examples of acquired factors that contribute to the risk of diabetes. B is incorrect because there is not enough information given to be able to predict the probability of passing a certain allele to offspring. Additionally, there are environmental factors that contribute to the occurrence of diabetes. C is incorrect because there is not enough information provided to know how many genes are associated with diabetes. D is incorrect because there is not enough information provided to know the pattern of dominance associated with diabetes. Lesson 1 Quiz 1. D 4. B 2. A 5. C 3. A 1. D A is incorrect because cytokinesis should be the last step, and metaphase precedes anaphase. B is incorrect because anaphase and prophase are out of order. C is incorrect because the four phases of mitosis are listed in the opposite order. D is correct because interphase is followed by prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and then cytokinesis. 2. A A is correct because if the chromatids did not separate properly during anaphase, one cell could get two chromatids and the other cell could get none. B is incorrect because if the DNA had not been duplicated, the resulting cell could not have had two copies of the chromosome. C is incorrect because if the nuclear membrane had not been broken down properly, the effect would likely not be limited to one chromosome. D is incorrect because separation of the cells occurs after the genetic material has been divided up and enclosed in nuclear membranes. 3. A A is correct because single-celled eukaryotes reproduce through mitosis. B is incorrect because ants are multicellular organisms that rely on mitosis for growth and repair but not for reproduction. C is incorrect because bluebirds are multicellular organisms that rely on mitosis for growth and repair but not for reproduction. D is incorrect because jellyfish are multicellular organisms that rely on mitosis for growth and repair but not for reproduction 4. B A is incorrect because cell division for repair occurs in multicellular, not single-celled, organisms. B is correct because single-celled organisms undergo cell division in order to reproduce. C is incorrect because the new cells have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. D is incorrect because the new cells have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. 5. C A is incorrect because chromosomes would be visible in anaphase, but this is not the first stage of the cell cycle in which they are visible. B is incorrect because chromosomes would be visible during cytokinesis, but this is the last stage in which they are visible. C is correct because during prophase, the first phase of mitosis, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes. D is incorrect because chromosomes are visible during telophase, but this is not the first stage in which they are visible. Lesson 2 Quiz 1. C 4. D 2. B 5. C 1. C A is incorrect because meiosis takes place in reproductive organs, and a bone is not a reproductive organ. B is incorrect because mitosis produces body cells, and not mature sex cells, which are made in the testes. C is correct because meiosis takes place in reproductive organs such as the ovaries. D is incorrect because meiosis takes place in reproductive organs, and the stomach is not a reproductive organ. 2. B A is incorrect because there are four chromatids. Each chromosome consists of two chromatids. B is correct because there are two chromosomes, each consisting of a pair of sister chromatids. C is incorrect because there are only two chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. D is incorrect because there are four chromatids. A is incorrect because four sex cells are produced as a result of meiosis. 320 Grade 7 Guide Florida
3 B is incorrect because there are two cell divisions in meiosis. As a result, one cell produces four cells, each with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell has. C is correct because the two cell divisions in meiosis produce four cells that each have half as many chromosomes as the parent cell has. D is incorrect because each of the four cells produced in meiosis has 23 chromosomes. 4. D A is incorrect because the sister chromatids of a chromosome separate during meiosis II. B is incorrect because the homologous chromosomes pair up in meiosis I when the recombination of genetic material between homologous pairs takes place. C is incorrect because two sex cells are produced as a result of meiosis I, and four sex cells are produced as a result of meiosis II. D is correct because each of the two cells at the end of meiosis I has half the chromosome number. The two chromatids of each chromosome separate during meiosis II. 5. C A is incorrect because mitosis involves replication of chromosomes. B is incorrect because meiosis involves replication of chromosomes. C is correct because fertilization does not involve cell division or the replication of chromosomes. D is incorrect because meiosis is the process of forming the sex cells and involves replication of chromosomes. Lesson 3 Quiz 1. A 4. B 2. B 5. D 3. D 1. A A is correct because sexual reproduction requires two parents and results in offspring that have characteristics of each parent. B is incorrect because this statement describes asexual reproduction. C is incorrect because the offspring of sexual reproduction are not genetically identical to either parent. Instead, they have characteristics of both parents. D is incorrect because sexual reproduction requires two parents, and each parent contributes half of the genes. 2. B A is incorrect because fertilization is required for sexual reproduction. B is correct because all three of these modes of reproduction are asexual. C is incorrect because fertilization is required for sexual reproduction. D is incorrect because egg and sperm join in fertilization as part of sexual reproduction. 3. D A is incorrect because constant, favorable conditions favor asexual reproduction. B is incorrect because conditions that promote the growth of many offspring would favor asexual reproduction. C is incorrect because conditions under which the organism can easily obtain nutrients and water would favor asexual reproduction. D is correct because unfavorable conditions tend to favor sexual reproduction among organisms that can reproduce both sexually and asexually. 4. B A is incorrect because an organism produced by sexual reproduction receives chromosomes equally from each of two parents. B is correct because an organism produced by sexual reproduction receives half of its chromosomes from each parent when a sperm cell fertilizes an egg. C is incorrect because an organism produced by sexual reproduction receives half of its chromosomes from each parent. D is incorrect because an organism produced by sexual reproduction receives half of its chromosomes from each parent. 5. D A is incorrect because only statement II refers to sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction does not enable organisms to increase in number as quickly as asexual reproduction does. B is incorrect because only statement I refers to asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction does not enable organisms to increase in number as quickly as asexual reproduction does, and asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to their parent. C is incorrect because the opposite is true. Statement I refers to asexual reproduction, and statement II refers to sexual reproduction. D is correct because the ability to increase in number very quickly is typical of asexual reproduction, and increasing genetic diversity is typical of sexual reproduction. Lesson 4 Quiz 1. A 4. C 2. D 5. B 1. A A is correct because the genes are located on the chromosomes of each cell. B is incorrect because chromosomes are made up of many genes. C is incorrect because a phenotype is the organism s appearance and not the genes it contains. D is incorrect because the appearance of an organism is its phenotype. 2. D A is incorrect because all of the offspring would have inherited one dominant allele from the parent with purple flowers. B is incorrect because all of the offspring of this cross would inherit a recessive allele for white flowers from one parent and a dominant allele for purple flowers from the other parent. C is incorrect because purple flower color is the dominant trait, so none of the offspring would have white flowers. D is correct because all of the offspring would be heterozygous and have purple flowers. A is incorrect because the phenotype is not determined by a single gene. 321 Grade 7 Guide Florida
4 B is incorrect because most traits are determined by more than one gene. C is correct because some genes determine more than one trait. D is incorrect because each gene can determine more than one trait. 4. C A is incorrect because the alleles are codominant, so both phenotypes are expressed. B is incorrect because both alleles contribute to the phenotype in order to produce blood type AB. C is correct because both alleles contribute to the phenotype in order to produce blood type AB. D is incorrect because individuals with blood type AB produce antigens associated with type A and type B blood. 5. B A is incorrect because a temperature change does not change the alleles that make up the genotype. B is correct because the genotype remains the same, but the phenotype changes depending on environmental conditions. C is incorrect because the cat s alleles do not affect its environment. D is incorrect because the cat s appearance does not change the cat s genetic makeup. Lesson 5 Quiz 1. C 4. D 2. B 5. C 1. C A is incorrect because this choice describes a ratio. B is incorrect because probability does not refer to an actual outcome; it refers to the chances of an outcome. C is correct because probability is the likelihood of a specific outcome in relation to the total number of possible outcomes. D is incorrect because probability gives only the likelihood that something will happen. Probability does not describe what will definitely happen in a given situation. 2. B A is incorrect because in one out of two times, the mouse has the alleles DD and in one out of two times, the mouse has the alleles Dd. B is correct because each of these outcomes has a 50% chance of happening, so they are equally likely to happen. C is incorrect because the mouse is as likely to have DD as it is to have Dd. D is incorrect, These are the only two possible outcomes because their probabilities total 100%. A is incorrect because a pedigree is a diagram of relationships that exist in a family. It does not describe genetic diversity among different species. B is incorrect because a pedigree is a diagram of relationships that exist in a family, but it does not explain dominance. C is correct because a pedigree shows relationships within a family and includes two or more generations. D is incorrect because this choice describes a Punnett square. 4. D A is incorrect because all inherited genetic disorders can be passed from parent to child. B is incorrect because both males and females can be affected by sex-linked disorders. C is incorrect because the inheritance of sex-linked disorders can be traced on a pedigree. D is correct because a sex-linked gene is located on a sex chromosome. 5. C A is incorrect because, as carriers, Alisha and Rob each have an allele for the disease, but they are not immune to the disease. B is incorrect because Alisha and Rob are carriers of the disease, but they will not develop the disease. To be expressed, the disease requires two alleles. C is correct because each parent, as a carrier of the disease, has one allele for the disease. Neither has the disease because, to be expressed, the disease requires two alleles. Each or both parent could pass the allele to a child. D is incorrect because as carriers of the disease, Alisha and Rob do not have the disease. To be expressed, the disease requires two alleles. Lesson 1 Alternative Climb the Ladder: Mitosis Understanding the Cycle: Scrapbooks depict the three stages of the cell cycle, show illustrations of each stages, and describe what occurs during each stage. An Ode to Mitosis: Poems describe the ways that a multicellular organism appreciates mitosis. Tracking Mitosis: Notes and sketches describe the videos. The strengths and weaknesses of the videos are presented. This Just In!: New reports describe a new cell that has just formed, explain how the cell formed (including the three stages of the cell cycle), and identify the cell as a unicellular organism or part of a multicellular organism. To Be DNA: Monologues describe what happens to DNA before and during mitosis. Why, Oh Why?: Videos explain the reasons that unicellular organisms go through cell division and the reasons that multicellular organisms go through cell division. Lesson 2 Alternative Points of View: Meiosis Terms: Terms are defined in students own words, and then by using a dictionary definition. Last, a paragraph uses the terms to describe meiosis. Calculations: Calculations tell how many chromosomes are present in a haploid cell from a squirrel and corn, and how many chromosomes are present in a diploid cell from an alligator. Details: Venn diagrams or other graphic organizers show how meoisis and mitosis are alike and different. Illustrations: Sketches illustrates the differences between the final stages of meiosis I and meiosis II. Analysis: Answers explain why meiosis is important for many living things.. Model: Models show one phase of meiosis, and include cell walls, 322 Grade 7 Guide Florida
5 chromosomes, spindle fibers (if appropriate), and so on. Lesson 3 Alternative Tic-Tac-Toe: Reproduction Plant Detective: Steps explain how to figure out whether the plant reproduces sexually or asexually. Parent Clone: Journal entries describe the advantages of being genetically identical to a parent. Sporific!: Illustrations show the life cycle of a plant that produces spores, and explain in which stage the plant best survives harsh conditions. Diagram It!: Diagram shows how organisms reproduce by mitosis. What re the Advantages?: Charts show the advantages of asexual and sexual reproduction. News Flash!: Reports describe what happens after a giant plant that reproduces by budding is discovered with growing buds. Plan a Garden: Sketches show plants in a garden that reproduce both sexually and asexually, and describe the conditions in which each plant is most likely to succeed. Switching Roles: Explanations tell why the plant may be changing types of reproduction from growing new roots to blooming. Explain It!: Drawings with labels explain fertilization for a person who is learning English. Lesson 4 Alternative Climb the Ladder: It s Hereditary Alien Eyes: Answers explain what color the alien s eyes are, and what alleles the father might have. DNA s Role: Diagrams or sketches explain DNA s role in determining human traits. Diagrams or sketches include labels and descriptions. Dominance Differences: Entries summarize Mendel s findings, and include diagrams or illustrations as needed. Dominance Differences: Charts explain how complete dominance, incomplete dominance, and co-dominance are alike and different. Type Casting: Posters identify the relationship between genotype and phenotype, and include a catchy way to remember what each term means. Genes and Traits: Paragraphs explain how one gene can be responsible for many traits, and how many genes can be responsible for one trait. Lesson 5 Alternative Climb the Pyramid: Make a Flower R = red flower, r = pink flower R r Rr rr r Rr rr L = long stem, l = short stem L r L l Ll Ll l Ll Ll T = thick stem, t = thin stem T T TT Tt t Tt tt O = oval leaf, o = round leaf O t O O OO OO o Oo Oo G = solid green leaf, g = spotted green leaf G g G GG Gg G GG Gg B = big leaf, b = small leaf B B B BB BB b Bb Bb Alleles selected and flowers sketched will vary. Florida Benchmark Review 1. B 5. C 9. C 2. B 6. A 10. C 3. D 7. D 11. C 4. B 8. C 12. D 1. B See Unit 8, Lesson 1 A is incorrect because the order of phases should be prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis, which would be 2, 4, 5, 1, 3. B is correct because the order of phases should be prophase (card 2), metaphase (card 4), anaphase (card 5), telophase (card 1), and cytokinesis (card 3). C is incorrect because the order of phases should be prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis, which would be 2, 4, 5, 1, and 3. D is incorrect because the order of phases should be prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis, which would be 2, 4, 5, 1, and B See Unit 8, Lesson 2 A is incorrect because chromosomes are duplicated during both meiosis and mitosis. B is correct because homologous chromosomes do not pair up during mitosis. C is incorrect because chromosomes line up along the equatorial plate during both types of cell division. D is incorrect because condensation of chromosomes happens before both meiosis and mitosis. 3. D See Unit 8, Lesson 3 A is incorrect because the genetically identical offspring indicate that asexual reproduction rather than sexual reproduction took place. B is incorrect because asexual reproduction requires only one parent. C is incorrect because the genetically identical offspring indicate that asexual reproduction rather than sexual reproduction took place. D is correct. Because the offspring are genetically identical, asexual reproduction took place, and this type of reproduction requires only one parent. 4. B See Unit 8, Lesson 5 A is incorrect because although one parent has the alleles BB, the other is Bb. B is correct because the parental alleles, which are shown at the top and side of the square, are BB and Bb. C is incorrect because although one parent has the alleles Bb, the other is BB. 323 Grade 7 Guide Florida
6 D is incorrect because although one parent has the alleles Bb, the other is BB. 5. C See Unit 8, Lesson 4 A is incorrect because all offspring have the smooth shape, so the smooth shape is a dominant trait. B is incorrect because all offspring have the smooth shape, so the wrinkled shape is a recessive trait. C is correct because only smooth shape shows up in the offspring. Therefore, smooth shape must be the dominant trait. D is incorrect because the offspring do not include any peas with wrinkled seeds. Therefore, wrinkled seeds must be the recessive trait. 6. A See Unit 8, Lesson 4 A is correct because DNA contains the set of instructions that determines traits, such as eye color and hair color. B is incorrect because glucose is a sugar molecule. C is incorrect because cellulose is a starch molecule. D is incorrect because cholesterol is a lipid molecule. 7. D See Unit 8, Lesson 1 A is incorrect because the number of cells produced would be two or less. B is incorrect because the number of chromosomes would be reduced if DNA was not duplicated. C is incorrect because the number of nuclei would likely not be affected by the error. D is correct because if DNA is not duplicated, the chromosome pairs would not separate correctly. The resulting nuclei would have too few chromosomes. 8. C See Unit 8, Lesson 2 A is incorrect because individual 4 is female. B is incorrect because individual 4 is female and is not the offspring of individuals 1 and 2. C is correct because individual 4 is female (the shape representing her is a circle). She is also the mother of individual 3 in generation III because there is a vertical line extending down from the horizontal line connecting individual 4 with individual 3. D is incorrect because individual 4 is not the daughter of individuals 1 and 2. She married the son of individuals 1 and 2 in generation I. 9. C See Unit 8, Lesson 4 A is incorrect because the alleles B and b are two different versions of a gene. B is incorrect because the alleles result in the two different phenotypes: brown fur and white fur. C is correct because each allele is a different version of the same gene. D is incorrect because the alleles both provide different instructions about the same trait. 10. C See Unit 8, Lesson 5 A is incorrect because egg cells are produced by females. B is incorrect because sperm cells are produced by meiosis. C is correct because body cells are produced by mitosis in both males and females. D is incorrect because body cells are not produced by meiosis. 11. C See Unit 8, Lesson 3 A is incorrect because Caryn has a 50% chance of developing Alpha-1 since she will inherit the recessive allele from her mother, and has a 50% chance of inheriting the recessive allele from her father. B is incorrect because Caryn has a 50% chance of becoming a carrier, since she will inherit the recessive allele from her mother but may not inherit the recessive allele from her father. C is correct because Caryn will inherit the recessive allele from her mother, and has a 50% chance of inheriting the allele from her father. So, Caryn has a 50% chance of being a carrier and a 50% chance of developing the disease. D is incorrect because if Caryn does not inherit the recessive allele from her father, she will not develop Alpha-1. She has a 50% chance of becoming a carrier. 12. D See Unit 8, Lesson 3 A is incorrect because budding takes place when a new organism grows from the outside surface of the parent organism, and the resulting offspring are genetically identical. B is incorrect because binary fission takes place when an organism divides into two organisms, and the resulting organisms are genetically identical. C is incorrect because during spore formation, an organism produces a specialized spore that develops into a genetically identical, multicellular organism. D is correct because vegetative reproduction takes place when a new plant develops from a modified stem or root (not a single cell) that is taken from a parent plant. The offspring are genetically identical to the original parent plant. Unit Test A Key Concepts 1. D 6. A 11. C 2. C 7. A 12. B 3. D 8. C 1 4. D 9. B 14. C 5. A 10. D 15. B 1. D A is incorrect because Mendel explained the results by identifying dominant and recessive traits in the plants, not mutations. His studies did not directly address mutations. B is incorrect because Mendel s findings were based on dominant and recessive traits. He did not recognize that the environment could affect the expression of genes. C is incorrect because acquired traits are not inherited, and flower color is an inherited trait. D is correct because Mendel explained the differences in the traits he observed by concluding that plants have both dominant and recessive traits. 2. C A is incorrect because the dominant trait would also be expressed for a codominant trait. B is incorrect because both alleles are expressed in codominance. C is correct because a codominant trait is one in which both alleles are expressed, and the phenotype is a product of the two alleles. D is incorrect because the phenotype is intermediate to both parents in incomplete dominance, but both alleles are expressed in codominance. 324 Grade 7 Guide Florida
7 3. D A is incorrect because eye color is an example of an inherited trait. B is incorrect because wavy, red hair is an inherited trait. C is incorrect because cheek dimples are an inherited trait. D is correct because having long fingernails is a choice, or acquired characteristic. 4. D A is incorrect because this choice describes a pedigree. B is incorrect because a Punnett square does not explain why some genes are recessive; it merely shows how the alleles are passed on. C is incorrect because a Punnett square does not compare inherited and acquired traits; it only shows how alleles are passed on. D is correct because a Punnett square illustrates the probabilities of what alleles offspring will receive from their parents. 5. A A is correct because hemophilia is a sexlinked disorder. B is incorrect because cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease, but it is not sex-linked. C is incorrect because Tay-Sachs disease is a genetic disease, but the gene for this disease is not located on a sex chromosome. D is incorrect because cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease, but it is not sex-linked. The allele for this disease is found on an autosomal chromosome. 6. A A is correct because a ratio compares two quantities and shows the relationship between them. B is incorrect because this choice describes a pedigree diagram. C is incorrect because this choice describes a Punnett square. D is incorrect because this choice describes probability. 7. A A is correct because asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that requires only one parent and results in genetically identical offspring. B is incorrect because asexual reproduction requires only one parent. C is incorrect because asexual reproduction produces genetically identical offspring. D is incorrect because asexual reproduction produces genetically identical offspring and requires only one parent. 8. C A is incorrect because this statement describes binary fission. B is incorrect because this statement describes spore formation. C is correct because vegetative reproduction takes place when new plants develop from modified stems or roots of the parent plant. D is incorrect because this statement describes sexual reproduction 9. B A is incorrect because sexual reproduction increases genetic diversity, but asexual reproduction does not. B is correct because asexual reproduction requires only one parent, and sexual reproduction requires two parents. C is incorrect because sexual reproduction increases a species chances of surviving unfavorable conditions, but asexual reproduction does not. D is incorrect because the offspring produced by sexual reproduction are not identical to each other, but those of asexual reproduction are identical to each other. 10. D A is incorrect because the cell on the left is a body cell. B is incorrect because the cell on the left is a body cell. C is incorrect because the cell on the right is a sex cell, but it does not function in growth or repair of damaged tissue. D is correct because the cell on the right is the sex cell and it passes on genetic information to offspring during sexual reproduction. 11. C A is incorrect because this pair shows the numbers of cells before and after meiosis I or mitosis. B is incorrect because this pair shows the numbers of cells before and after both meiosis I and meiosis II are complete. C is correct because two cells divide to become four cells in meiosis II. D is incorrect because this pair shows no increase in cell number, which indicates that no cell division has taken place. 12. B A is incorrect because chromosomes are not built by instructions from proteins, and proteins do not provide information for building nucleotides. B is correct because during fertilization, an egg cell and a sperm cell each contribute one half of a pair of homologous chromosomes. C is incorrect because one homologous chromosome is inherited from the female parent, and the other is inherited from the male parent. D is incorrect because chromosomes are found in the nucleus, not in the cytoplasm. 1 A is incorrect because cell division for growth takes place in multicellular organisms, not single-celled organisms. B is incorrect because a multicellular organism can undergo cell division to repair an injury, but single-celled organisms cannot. C is correct because single-celled organisms undergo cell division for reproduction, enabling them to transmit their genetic information to the next generation. D is incorrect because multicellular, not single-celled, organisms undergo cell division for specialization. 14. C A is incorrect because chromatin is the loose form of the material that condenses into chromosomes. It is made up of DNA and proteins. B is incorrect because a chromosome is the condensed form of chromatin, and it is designated by letter W. C is correct because DNA is a doublehelix structure along which the genes reside. This structure is shown at position Z in the diagram. D is incorrect because protein is a part of chromatin fiber along with DNA, but letter Z indicates just the DNA. 325 Grade 7 Guide Florida
8 15. B A is incorrect because new cells do not form until cytokinesis is complete. B is correct because mitosis is the process of cell division that results in the formation of two new nuclei. C is incorrect because DNA is copied once during interphase, but each copy of DNA is separated by mitosis into two nuclei. DNA is not copied two times during mitosis. D is incorrect because, although the chromosomes are copied once, each set of chromosomes is separated by mitosis into the two nuclei. The net number of chromosomes in the new nuclei is the same as in the parent cell. Critical Thinking 16. Sample answer: A genotype is the combination of the alleles that determine a trait, and a phenotype is the trait that is observed. Students answers will vary, but correct definition of genotype. correct definition of phenotype. 17. Sample answer: The allele that causes colorblindness is found on the X chromosome. Because women have two X chromosomes, they can carry the allele but still not be colorblind. Men have only one X chromosome, so they will either have the allele (and be colorblind) or not have the allele (and not be a carrier). Color blindness is a sex-linked trait. Women have two X chromosomes and have two alleles for this trait. Men have only one X chromosome, so they cannot be carriers (which requires having two alleles). 18. Sample answer: Binary fission takes place in single-celled organisms such as an amoeba. In this type of asexual reproduction, an organism divides into two equal halves, producing two identical offspring. Students answers will vary but Identifying binary fission as asexual reproduction A brief description of the process An example of an organism that uses this process 19. Sample answer: Both sexual and asexual reproduction result in the production of new organisms. They are different in that asexual reproduction requires only one parent, but sexual reproduction requires two. They are also different in that sexual reproduction produces offspring with genetic diversity. Students answers may vary, but both types of reproduction produce offspring. one parent is needed for asexual reproduction, and two parents are needed for sexual reproduction. sexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically different from the parents, and asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent. 20. Sample answer: This is a sex cell (an egg), because it has 23 chromosomes. This is half the number that is present in a human body cell. Students answers will vary, but an identification of the cell as a sex cell. an explanation that sex cells have 23 chromosomes in humans. 21. Sample answer: As a result of meiosis, each sex cell has half the number of chromosomes that were present in the original cell. During sexual reproduction, fertilization restores the original number of chromosomes. Students answers will vary, but an understanding of the consequences of meiosis. a recognition of the outcome of fertilization. 22. Sample answer: The salamander s tail was replaced by cell division. Multicellular organisms rely on cell division for growth and repair. Cells divided to replace the cells that were lost. They continued dividing until the tail grew back completely. In the case of the salamander s tail, cell division was part of the growth and repair process. Cells divided many times to replace the tail and continued dividing until the tail grew back. Extended Response 23. Sample answer: In sexual reproduction, organisms have to expend energy to find and attract a member of the opposite sex. Many organisms that reproduce sexually also care for their offspring after they are born. This care requires sexually reproducing organisms to expend even more energy. Sexual reproduction requires the expenditure of energy to find and attract a mate. Sexual reproduction may also require the expenditure of energy to raise offspring. 24. Sample answer: It is most likely that one parent has the alleles GG and the other has the alleles gg. This would mean the parent with GG would pass on a G allele to the offspring 100% of the time. The parent with the gg alleles would pass on a g allele to the offspring 100% of the time. So, all of the offspring would have the alleles Gg. If the parents had other allele combinations, such as Gg and Gg, or GG and Gg, they could possibly have offspring that were Gg, but it is highly unlikely that 1,000 out of 1,000 offspring would be Gg. The parents probably have the alleles GG and gg. The parent who is GG would always pass on a G allele. The parent who is gg would always pass on a g allele. Other combinations are not likely because there is a large sample of 1,000 offspring. 326 Grade 7 Guide Florida
Reproduction and Heredity
 Reproduction and Heredity Pretest Edit File Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. One trait that differs in pea plants involves the placement of the flowers. In some plants, flowers grow along the stem
Reproduction and Heredity Pretest Edit File Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. One trait that differs in pea plants involves the placement of the flowers. In some plants, flowers grow along the stem
Genetics & Heredity 11/16/2017
 Genetics & Heredity Biology I Turner College & Career High School 2017 Fertilization is the fusion of an egg and a sperm. Purebred (True breeding plants) are plants that were allowed to selfpollinate and
Genetics & Heredity Biology I Turner College & Career High School 2017 Fertilization is the fusion of an egg and a sperm. Purebred (True breeding plants) are plants that were allowed to selfpollinate and
Sexual Reproduction & Inheritance
 Sexual Reproduction & Sexual Reproduction & Overview Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Meiosis Genetic Diversity Mendel & The Laws of Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Prokaryotes
Sexual Reproduction & Sexual Reproduction & Overview Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Meiosis Genetic Diversity Mendel & The Laws of Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Prokaryotes
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]
![EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]](/thumbs/87/96059079.jpg) EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
1/9/2014. Introduction to Genetics. The Work of Gregor Mendel THE WORK OF GREGOR MENDEL. Some Definitions:
 Introduction to Genetics Chapter 11 Chapter 11 Section 1 THE WORK OF GREGOR MENDEL The Work of Gregor Mendel Some Definitions: Genetics the study of biological inheritance and variation Chromosomes hereditary
Introduction to Genetics Chapter 11 Chapter 11 Section 1 THE WORK OF GREGOR MENDEL The Work of Gregor Mendel Some Definitions: Genetics the study of biological inheritance and variation Chromosomes hereditary
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics. Section 1. Meiosis
 Chromosomes and Chromosome Number! Human body cells have 46 chromosomes! Each parent contributes 23 chromosomes! Homologous chromosomes one of two paired chromosomes, one from each parent Chromosomes and
Chromosomes and Chromosome Number! Human body cells have 46 chromosomes! Each parent contributes 23 chromosomes! Homologous chromosomes one of two paired chromosomes, one from each parent Chromosomes and
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next.
 Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
Mastery. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter Content CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1. Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions.
 Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results?
 CHAPTER 5 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results? National
CHAPTER 5 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results? National
Bell Work 3/8/18. Mitosis: What occurs during mitosis? What are the products of mitosis? What is the purpose of mitosis?
 Bell Work 3/8/18 Mitosis: What occurs during mitosis? What are the products of mitosis? What is the purpose of mitosis? Bell Work: 3/9/18 Complete the pre-assessment on your Anchor Activity Unit 6 sheet.
Bell Work 3/8/18 Mitosis: What occurs during mitosis? What are the products of mitosis? What is the purpose of mitosis? Bell Work: 3/9/18 Complete the pre-assessment on your Anchor Activity Unit 6 sheet.
GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY
 GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS Genetics is the scientific study of heredity Heredity is essentially the study of how traits are passed from parents to their offspring. GREGOR MENDEL
GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS Genetics is the scientific study of heredity Heredity is essentially the study of how traits are passed from parents to their offspring. GREGOR MENDEL
TEST NAME:review TEST ID: GRADE:07 Seventh Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom
 TEST NAME:review TEST ID:1070005 GRADE:07 Seventh Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom review Page 1 of 18 Student: Class: Date: 1. There are four blood types: A, B, AB,
TEST NAME:review TEST ID:1070005 GRADE:07 Seventh Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom review Page 1 of 18 Student: Class: Date: 1. There are four blood types: A, B, AB,
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
The bases on complementary strands of DNA bond with each other in a specific way A-T and G-C
 1 Bio 1101 Lecture 6 (Guided Notes) Ch. 8: Cellular Basis of Reproduction 2 3 4 5 6 Cellular Basis of Reproduction & Inheritance In order for an organism to replace dead cells or to grow and produce new
1 Bio 1101 Lecture 6 (Guided Notes) Ch. 8: Cellular Basis of Reproduction 2 3 4 5 6 Cellular Basis of Reproduction & Inheritance In order for an organism to replace dead cells or to grow and produce new
Go to:
 Name: Period: Go to: http://www2.edc.org/weblabs/mendel/mendel.html 1. What is the guy's name who discovered the basic rules of heredity? 2. In what country and time period did he live? 3. For what reason(s)
Name: Period: Go to: http://www2.edc.org/weblabs/mendel/mendel.html 1. What is the guy's name who discovered the basic rules of heredity? 2. In what country and time period did he live? 3. For what reason(s)
Unit 7 Section 2 and 3
 Unit 7 Section 2 and 3 Evidence 12: Do you think food preferences are passed down from Parents to children, or does the environment play a role? Explain your answer. One of the most important outcomes
Unit 7 Section 2 and 3 Evidence 12: Do you think food preferences are passed down from Parents to children, or does the environment play a role? Explain your answer. One of the most important outcomes
Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity
 Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity ¾ Austrian monk and naturalist. ¾ Conducted research in Brno, Czech Republic from 1856-1863 ¾ Curious about how traits were passed from parents to offspring. Gregor
Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity ¾ Austrian monk and naturalist. ¾ Conducted research in Brno, Czech Republic from 1856-1863 ¾ Curious about how traits were passed from parents to offspring. Gregor
Heredity and Genetics (8%)
 I. Basic Vocabulary a. G Phase Heredity and Genetics (8%) M G2 i. Chromosomes: Threadlike linear strands of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that carry the genes and functions
I. Basic Vocabulary a. G Phase Heredity and Genetics (8%) M G2 i. Chromosomes: Threadlike linear strands of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that carry the genes and functions
Genetics Practice Questions
 Name: ate: 1. If Jessica has light eyes (bb) and both of her parents have dark eyes (b) which statement is true?. Jessica inherited both genes from her father.. Jessica inherited both genes from her mother..
Name: ate: 1. If Jessica has light eyes (bb) and both of her parents have dark eyes (b) which statement is true?. Jessica inherited both genes from her father.. Jessica inherited both genes from her mother..
Name Class Date *PACKET NOTES & WORKSHEETS LAB GRADE
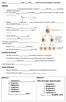 Name Class Date *PACKET NOTES & WORKSHEETS LAB GRADE MEIOSIS is specialized cell division resulting in cells with the genetic material of the parents Sex cells called have exactly set of chromosomes, this
Name Class Date *PACKET NOTES & WORKSHEETS LAB GRADE MEIOSIS is specialized cell division resulting in cells with the genetic material of the parents Sex cells called have exactly set of chromosomes, this
Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS:
 Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS: CHROMOSOME GENE DNA TRAIT HEREDITY INTERPHASE MITOSIS CYTOKINESIS ASEXUAL BINARY FISSION CELL CYCLE GENETIC DIVERSITY
Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS: CHROMOSOME GENE DNA TRAIT HEREDITY INTERPHASE MITOSIS CYTOKINESIS ASEXUAL BINARY FISSION CELL CYCLE GENETIC DIVERSITY
The bases on complementary strands of DNA bond with each other in a specific way A-T and G-C
 1 Bio 1101 Lecture 6 Ch. 8: Cellular Basis of Reproduction 2 3 4 5 6 Cellular Basis of Reproduction & Inheritance In order for an organism to replace dead cells or to grow and produce new cells, existing
1 Bio 1101 Lecture 6 Ch. 8: Cellular Basis of Reproduction 2 3 4 5 6 Cellular Basis of Reproduction & Inheritance In order for an organism to replace dead cells or to grow and produce new cells, existing
Gregor Mendel. What is Genetics? the study of heredity
 Gregor Mendel What is Genetics? the study of heredity Gregor Mendel s Peas Pollen: plant s sperm Egg Cells: plants reproductive cells Fertilization: joining of pollen + egg cells develops into embryo in
Gregor Mendel What is Genetics? the study of heredity Gregor Mendel s Peas Pollen: plant s sperm Egg Cells: plants reproductive cells Fertilization: joining of pollen + egg cells develops into embryo in
VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid homologous chromosome sexual reproduction meiosis
 SECTION 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid
SECTION 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid
GENETICS NOTES. Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16
 GENETICS NOTES Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16 DNA contains the genetic code for the production of PROTEINS. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The
GENETICS NOTES Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16 DNA contains the genetic code for the production of PROTEINS. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance
 Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Patterns of Inheritance
 1 Patterns of Inheritance Bio 103 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Topics Mendel s Principles Variations on Mendel s Principles Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes 3 Experimental
1 Patterns of Inheritance Bio 103 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Topics Mendel s Principles Variations on Mendel s Principles Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes 3 Experimental
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 10
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: HS Genetics Assessment. Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: HS Genetics Assessment Student name: Author: Megan Kitchens School: SHAW HIGH SCHOOL Printed: Monday January 30, 2017 1 In fruit flies, the gray body color (G) is dominant
Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: HS Genetics Assessment Student name: Author: Megan Kitchens School: SHAW HIGH SCHOOL Printed: Monday January 30, 2017 1 In fruit flies, the gray body color (G) is dominant
.the science that studies how genes are transmitted from one generation to the next.
 Genetics .the science that studies how genes are transmitted from one generation to the next. The chromosomes are contained in the nucleus of the cell. Genes and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made of: Gene:
Genetics .the science that studies how genes are transmitted from one generation to the next. The chromosomes are contained in the nucleus of the cell. Genes and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made of: Gene:
Genetic Variation Junior Science
 2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
Genetics. Genetics. True or False. Genetics Vocabulary. Chapter 5. Objectives. Heredity
 Genetics True or False Genes are things you wear on your legs. A priest raising peas in his garden was one of the first to discover how genetics works. Plants can be purebred just like dogs. Dominate alleles
Genetics True or False Genes are things you wear on your legs. A priest raising peas in his garden was one of the first to discover how genetics works. Plants can be purebred just like dogs. Dominate alleles
Meiosis and Introduction to Inheritance
 Meiosis and Introduction to Inheritance Instructions Activity 1. Getting Started: Build a Pair of Bead Chromosomes Materials bag labeled diploid human genome (male) bag labeled diploid human genome (female)
Meiosis and Introduction to Inheritance Instructions Activity 1. Getting Started: Build a Pair of Bead Chromosomes Materials bag labeled diploid human genome (male) bag labeled diploid human genome (female)
What creates variation in the offspring of sexually reproducing organisms?
 What creates variation in the offspring of sexually reproducing organisms? 1. genetic recombination during fertilization 2. mitotic division in body cells 62% 3. crossing over in mitosis 4. homologous
What creates variation in the offspring of sexually reproducing organisms? 1. genetic recombination during fertilization 2. mitotic division in body cells 62% 3. crossing over in mitosis 4. homologous
Patterns of Heredity - Genetics - Sections: 10.2, 11.1, 11.2, & 11.3
 Patterns of Heredity - Genetics - Sections: 10.2, 11.1, 11.2, & 11.3 Genetics = the study of heredity by which traits are passed from parents to offspring Page. 227 Heredity = The passing of genes/traits
Patterns of Heredity - Genetics - Sections: 10.2, 11.1, 11.2, & 11.3 Genetics = the study of heredity by which traits are passed from parents to offspring Page. 227 Heredity = The passing of genes/traits
Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells.
 MEIOSIS Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells. 1. Somatic Cells are body cells and contain the normal number of chromosomes.called the Diploid number (the symbol
MEIOSIS Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells. 1. Somatic Cells are body cells and contain the normal number of chromosomes.called the Diploid number (the symbol
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7
 Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 20 Q. Cystic fibrosis is a disease which affects in 600 babies. (a) What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? (3) Two parents with normal
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 20 Q. Cystic fibrosis is a disease which affects in 600 babies. (a) What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? (3) Two parents with normal
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance
 Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction
 Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Chromosomes Organisms grow by dividing of cells Binary Fission form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring (Bacteria) Eukaryotes have two
Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Chromosomes Organisms grow by dividing of cells Binary Fission form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring (Bacteria) Eukaryotes have two
Unit 5: Genetics Notes
 Unit 5: Genetics Notes https://goo.gl/fgtzef Name: Period: Test Date: Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Date Warm-ups 3-4 Mendelian Genetics Notes 5-6 Mendelian Genetics Lets Practice 7 Monohybrid
Unit 5: Genetics Notes https://goo.gl/fgtzef Name: Period: Test Date: Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Date Warm-ups 3-4 Mendelian Genetics Notes 5-6 Mendelian Genetics Lets Practice 7 Monohybrid
Genetics & The Work of Mendel
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes
 Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes 5.6 Explain how nondisjunction can result in whole chromosomal abnormalities. (Module 5.10) 5.7 Describe the inheritance patterns for strict dominant
Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes 5.6 Explain how nondisjunction can result in whole chromosomal abnormalities. (Module 5.10) 5.7 Describe the inheritance patterns for strict dominant
5Which one of the following occurs in meiosis, but not mitosis?
 Practice Questions: 1Humans possess: a. 22 pairs of sex chromosomes and 1 pair of autosomes b. 23 pairs of autosomes c. equal numbers of autosomes and sex chromosomes d. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair
Practice Questions: 1Humans possess: a. 22 pairs of sex chromosomes and 1 pair of autosomes b. 23 pairs of autosomes c. equal numbers of autosomes and sex chromosomes d. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair
Introduction to Mendelian Genetics
 Introduction to Mendelian Genetics pollen stigma petals anthers Summary of Mendel s First Experiment pollen paintbrush ova ovary Mature male flower A mature pea flower has both male and female parts
Introduction to Mendelian Genetics pollen stigma petals anthers Summary of Mendel s First Experiment pollen paintbrush ova ovary Mature male flower A mature pea flower has both male and female parts
Chromosomes & Cell Division
 Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
Name Period. Keystone Vocabulary: genetics fertilization trait hybrid gene allele Principle of dominance segregation gamete probability
 Name Period BIO B2 GENETICS (Chapter 11) You should be able to: 1. Describe and/or predict observed patterns of inheritance (dominant, recessive, co- dominant, incomplete dominance, sex- linked, polygenic
Name Period BIO B2 GENETICS (Chapter 11) You should be able to: 1. Describe and/or predict observed patterns of inheritance (dominant, recessive, co- dominant, incomplete dominance, sex- linked, polygenic
Genetics & The Work of Mendel. AP Biology
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas u used experimental method u used
Genetics & The Work of Mendel Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas u used experimental method u used
The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Chromosomes
 & Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
& Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
Biology Unit 7 Genetics 7:1 Genetics
 Biology Unit 7 Genetics 7:1 Genetics Gregor Mendel: Austrian monk Studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants His work was not recognized until the 20 th century Between 1856 and 1863, Mendel cultivated
Biology Unit 7 Genetics 7:1 Genetics Gregor Mendel: Austrian monk Studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants His work was not recognized until the 20 th century Between 1856 and 1863, Mendel cultivated
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division. diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
 Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Chromosomes and Cell Cycle
 Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Cell Basics There are trillions of cells in your body Cells are microscopic Cells have DNA inside a structure called the nucleus The nucleus is enclosed by a structure called
Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Cell Basics There are trillions of cells in your body Cells are microscopic Cells have DNA inside a structure called the nucleus The nucleus is enclosed by a structure called
The table to the right shows ALL possible alleles for several traits in pea plants. (Please use it to help you answer #1-6 below.)
 QUIZ: MENDEL S LAWS & PUNNETT SQUARES NAME: PERIOD: DATE: MENDEL S LAWS The table to the right shows ALL possible alleles for several traits in pea plants. (Please use it to help you answer #1-6 below.)
QUIZ: MENDEL S LAWS & PUNNETT SQUARES NAME: PERIOD: DATE: MENDEL S LAWS The table to the right shows ALL possible alleles for several traits in pea plants. (Please use it to help you answer #1-6 below.)
Genes and Inheritance
 Genes and Inheritance Variation Causes of Variation Variation No two people are exactly the same The differences between people is called VARIATION. This variation comes from two sources: Genetic cause
Genes and Inheritance Variation Causes of Variation Variation No two people are exactly the same The differences between people is called VARIATION. This variation comes from two sources: Genetic cause
Guided Reading and Study. Definition a. The scientific study of heredity. b. Physical characteristics
 Genetics: The Science of Heredity Mendel's Work Guided Reading and Study This section describes how Gregor Mendel identified the method by which characteristics are passed from parents to their offspring.
Genetics: The Science of Heredity Mendel's Work Guided Reading and Study This section describes how Gregor Mendel identified the method by which characteristics are passed from parents to their offspring.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 6 Patterns of Inheritance
 Chapter 6 Patterns of Inheritance Genetics Explains and Predicts Inheritance Patterns Genetics can explain how these poodles look different. Section 10.1 Genetics Explains and Predicts Inheritance Patterns
Chapter 6 Patterns of Inheritance Genetics Explains and Predicts Inheritance Patterns Genetics can explain how these poodles look different. Section 10.1 Genetics Explains and Predicts Inheritance Patterns
4. Which of the following cell parts can be found in human cells, but not plant cells? A. mitochondria B. chloroplast C. centrioles D.
 http://chss.sd57.bc.ca/~spearce/science_9/practice%20tests/reproductionpracticetest.htm Sc.9 Biology Practise Test 1. Single-celled organisms use cell division for growth. 2. Chromosomes are made of two
http://chss.sd57.bc.ca/~spearce/science_9/practice%20tests/reproductionpracticetest.htm Sc.9 Biology Practise Test 1. Single-celled organisms use cell division for growth. 2. Chromosomes are made of two
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics
 REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics ACP BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics ACP BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
Pre-AP Biology Unit 7 Genetics Review Outline
 Unit 7 Genetics Review Outline Pre-AP Biology 2017-2018 LT 1 - I can explain the relationships among alleles, genes, chromosomes, genotypes, and phenotypes. This target covers application of the vocabulary
Unit 7 Genetics Review Outline Pre-AP Biology 2017-2018 LT 1 - I can explain the relationships among alleles, genes, chromosomes, genotypes, and phenotypes. This target covers application of the vocabulary
MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes
 1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics
 REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
How do living things Sexually Reproduce?
 How do living things Sexually Reproduce? Besides animals, what other things reproduce sexually? Think of a family that has both biological parents and has 2 or more children #1 Consider what the parents
How do living things Sexually Reproduce? Besides animals, what other things reproduce sexually? Think of a family that has both biological parents and has 2 or more children #1 Consider what the parents
Chapter 17 Genetics Crosses:
 Chapter 17 Genetics Crosses: 2.5 Genetics Objectives 2.5.6 Genetic Inheritance 2.5.10.H Origin of the Science of genetics 2.5.11 H Law of segregation 2.5.12 H Law of independent assortment 2.5.13.H Dihybrid
Chapter 17 Genetics Crosses: 2.5 Genetics Objectives 2.5.6 Genetic Inheritance 2.5.10.H Origin of the Science of genetics 2.5.11 H Law of segregation 2.5.12 H Law of independent assortment 2.5.13.H Dihybrid
Genetics. *** Reading Packet
 Genetics *** Reading Packet 5.4 Mendel and His Peas Learning Objectives Describe Mendel's first genetics experiments. Introduction Why do you look like your family? For a long time people understood that
Genetics *** Reading Packet 5.4 Mendel and His Peas Learning Objectives Describe Mendel's first genetics experiments. Introduction Why do you look like your family? For a long time people understood that
c. Relate Mendelian principles to modern-day practice of plant and animal breeding.
 Course: Biology Agricultural Science & Technology Unit: Genetics in Agriculture STATE STANDARD IV: Students will understand that genetic information coded in DNA is passed from parents to offspring by
Course: Biology Agricultural Science & Technology Unit: Genetics in Agriculture STATE STANDARD IV: Students will understand that genetic information coded in DNA is passed from parents to offspring by
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes
 Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Sexual Reproduction. Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages
 Sexual Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages 72-105 Why Sex? Textbook Read pages 74 77 Sexual Reproduction Is reproduction involving two parents Each parent contributes equal
Sexual Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages 72-105 Why Sex? Textbook Read pages 74 77 Sexual Reproduction Is reproduction involving two parents Each parent contributes equal
Cell Growth and Division
 Name Class Date 10 Cell Growth and Division Big idea Growth, Development, and Reproduction Q: How does a cell produce a new cell? WHAT I KNOW WHAT I LEARNED 10.1 Why do cells divide? 10.2 How do cells
Name Class Date 10 Cell Growth and Division Big idea Growth, Development, and Reproduction Q: How does a cell produce a new cell? WHAT I KNOW WHAT I LEARNED 10.1 Why do cells divide? 10.2 How do cells
Patterns of Heredity Genetics
 Patterns of Heredity Genetics DO NOW Hand in outlines (my desk) Pick up tests from back table and review them. We will be going over the zipgrade and the short answer together. Save your questions for
Patterns of Heredity Genetics DO NOW Hand in outlines (my desk) Pick up tests from back table and review them. We will be going over the zipgrade and the short answer together. Save your questions for
Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel
 Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel What is inheritance? Two uses of the word inheritance Things that are passed down through generations Factors we get from our parents
Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel What is inheritance? Two uses of the word inheritance Things that are passed down through generations Factors we get from our parents
Genetic basis of inheritance and variation. Dr. Amjad Mahasneh. Jordan University of Science and Technology
 Genetic basis of inheritance and variation Dr. Amjad Mahasneh Jordan University of Science and Technology Segment 1 Hello and welcome everyone. My name is Amjad Mahasneh. I teach molecular biology at Jordan
Genetic basis of inheritance and variation Dr. Amjad Mahasneh Jordan University of Science and Technology Segment 1 Hello and welcome everyone. My name is Amjad Mahasneh. I teach molecular biology at Jordan
Mendelian Genetics. Biology 3201 Unit 3
 Mendelian Genetics Biology 3201 Unit 3 Recall: Terms Genetics is a branch of biology dealing with the principles of variation and inheritance in animals and plants. Heredity the passing of traits from
Mendelian Genetics Biology 3201 Unit 3 Recall: Terms Genetics is a branch of biology dealing with the principles of variation and inheritance in animals and plants. Heredity the passing of traits from
Genetics. The study of heredity. Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel (mid 1800 s) Developed set of laws that explain how heredity works
 Genetics The study of heredity Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel (mid 1800 s) Developed set of laws that explain how heredity works Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel original pea plant (input) offspring
Genetics The study of heredity Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel (mid 1800 s) Developed set of laws that explain how heredity works Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel original pea plant (input) offspring
Mendel and Heredity. Chapter 12
 Mendel and Heredity Chapter 12 12.1 Objectives: 1.) summarize the importance of Mendel s experiments 2.)Differentiate between genes and alleles. 3.) Explain that alleles determine what physical traits
Mendel and Heredity Chapter 12 12.1 Objectives: 1.) summarize the importance of Mendel s experiments 2.)Differentiate between genes and alleles. 3.) Explain that alleles determine what physical traits
MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis. (Sections 11-3,11-4;)
 MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis (Sections 11-3,11-4;) RECALL: Mitosis and Meiosis differ in several key ways: MITOSIS: MEIOSIS: 1 round of cell division 2 rounds of cell division Produces
MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis (Sections 11-3,11-4;) RECALL: Mitosis and Meiosis differ in several key ways: MITOSIS: MEIOSIS: 1 round of cell division 2 rounds of cell division Produces
Genetics. by their offspring. The study of the inheritance of traits is called.
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Genetics & The Work of Mendel
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Genetics All somatic cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes 22 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes Genes contained in each pair of chromosomes
 Chapter 6 Genetics and Inheritance Lecture 1: Genetics and Patterns of Inheritance Asexual reproduction = daughter cells genetically identical to parent (clones) Sexual reproduction = offspring are genetic
Chapter 6 Genetics and Inheritance Lecture 1: Genetics and Patterns of Inheritance Asexual reproduction = daughter cells genetically identical to parent (clones) Sexual reproduction = offspring are genetic
NAME: PERIOD: Genetics. Objective 2: Determine the possible outcomes of single crosses using Punnett squares.
 NAME: PERIOD: Genetics Objective 1: Explain the importance of DNA in a cell. Objective 2: Determine the possible outcomes of single crosses using Punnett squares. Objective 3: Compare sexual and asexual
NAME: PERIOD: Genetics Objective 1: Explain the importance of DNA in a cell. Objective 2: Determine the possible outcomes of single crosses using Punnett squares. Objective 3: Compare sexual and asexual
Genes and Inheritance (11-12)
 Genes and Inheritance (11-12) You are a unique combination of your two parents We all have two copies of each gene (one maternal and one paternal) Gametes produced via meiosis contain only one copy of
Genes and Inheritance (11-12) You are a unique combination of your two parents We all have two copies of each gene (one maternal and one paternal) Gametes produced via meiosis contain only one copy of
Pre-Test. 4. Inside of cells, nearly all the genes are located on special structures known as microtubules.
 1 Pre-Test Directions: Answer each question TRUE OR FALSE. 1. Cells in the bodies of multicelled creatures, such as humans, are reproduced in a way that is very similar to the method used by most protozoa.
1 Pre-Test Directions: Answer each question TRUE OR FALSE. 1. Cells in the bodies of multicelled creatures, such as humans, are reproduced in a way that is very similar to the method used by most protozoa.
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. sex cells genotype sex chromosomes
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. sex cells genotype sex chromosomes alleles phenotype meiosis 1.
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. sex cells genotype sex chromosomes alleles phenotype meiosis 1.
Science Olympiad Heredity
 Science Olympiad Heredity Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A Punnett square shows you all the ways in which can combine. a.
Science Olympiad Heredity Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A Punnett square shows you all the ways in which can combine. a.
UNIT 6 GENETICS 12/30/16
 12/30/16 UNIT 6 GENETICS III. Mendel and Heredity (6.3) A. Mendel laid the groundwork for genetics 1. Traits are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. 2. Genetics is the study of biological
12/30/16 UNIT 6 GENETICS III. Mendel and Heredity (6.3) A. Mendel laid the groundwork for genetics 1. Traits are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. 2. Genetics is the study of biological
Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1
 Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1 I. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) a. Austrian monk with a scientific background b. Conducted numerous hybridization experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum,
Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1 I. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) a. Austrian monk with a scientific background b. Conducted numerous hybridization experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum,
Question 2: Which one of the following is the phenotypic monohybrid ratio in F2 generation? (a) 3:1 (b) 1:2:1 (c) 2:2 (d) 1:3 Solution 2: (a) 3 : 1
 Class X Genetics Biology A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option) Which one of the following has the smallest number of chromosomes? (a) Onion (b) Mouse (c) Monkey (d) Ascaris (d)
Class X Genetics Biology A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option) Which one of the following has the smallest number of chromosomes? (a) Onion (b) Mouse (c) Monkey (d) Ascaris (d)
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Name Mitosis: Cell Division by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1.How do children grow? Do
Name Mitosis: Cell Division by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1.How do children grow? Do
You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism.
 Unit 6 Genetics 6.1 Genetics You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism. HEREDITY: traits that are passed from parents
Unit 6 Genetics 6.1 Genetics You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism. HEREDITY: traits that are passed from parents
Labrador Coat Color Similar to coat color in mice: Black lab is BxEx Yellow lab is xxee Chocolate lab is bbex Probable pathway:
 Honors Genetics 1. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) German monk at the Augustine Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno (today in the Czech Republic). He was a gardener, teacher and priest. Mendel conducted experiments
Honors Genetics 1. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) German monk at the Augustine Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno (today in the Czech Republic). He was a gardener, teacher and priest. Mendel conducted experiments
Introduction to Genetics and Heredity
 Introduction to Genetics and Heredity Although these dogs have similar characteristics they are each unique! I. Early Ideas About Heredity A. The Theory of Blending Inheritance Each parent contributes
Introduction to Genetics and Heredity Although these dogs have similar characteristics they are each unique! I. Early Ideas About Heredity A. The Theory of Blending Inheritance Each parent contributes
Biology Unit III Exam» Form C
 Directions: For each of the following questions, decide which of the choices is best and fill in the corresponding space on the answer document. 1. Which of these sets of chromosomes is found in a single
Directions: For each of the following questions, decide which of the choices is best and fill in the corresponding space on the answer document. 1. Which of these sets of chromosomes is found in a single
Summary The Work of Gregor Mendel Probability and Punnett Squares. Oass
 --------------------------- Oass ---------------- Date Chapter 11 Summary Introduction to Genetics 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel The scientific study of heredity is called genetics. Gregor Mendel used
--------------------------- Oass ---------------- Date Chapter 11 Summary Introduction to Genetics 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel The scientific study of heredity is called genetics. Gregor Mendel used
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION
 NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
 The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) telophase b) anaphase c) prometaphase d) metaphase e) prophase 1) DNA begins to coil and
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) telophase b) anaphase c) prometaphase d) metaphase e) prophase 1) DNA begins to coil and
Section Objectives: Pedigrees illustrate inheritance. Pedigrees illustrate inheritance
 What You ll Learn You will compare the inheritance of recessive and dominant traits in humans. You will analyze the inheritance patterns of traits with incomplete dominance and codominance. You will determine
What You ll Learn You will compare the inheritance of recessive and dominant traits in humans. You will analyze the inheritance patterns of traits with incomplete dominance and codominance. You will determine
Unit 11 Test: Genetics Date: /Period:
 Name: 1. Compared to human cells resulting from mitotic cell division, human cells resulting from meiotic cell division would have A) twice as many chromosomes B) the same number of chromosomes C) one-half
Name: 1. Compared to human cells resulting from mitotic cell division, human cells resulting from meiotic cell division would have A) twice as many chromosomes B) the same number of chromosomes C) one-half
Individual Feedback Report for: St#: Test: GENETICS UNIT TEST 2score Grade: 3 Score: % (20.00 of 35.00)
 Individual Feedback Report for: St#: 703709 Test: GENETICS UNIT TEST 2score Grade: 3 Score: 57.14 % (20.00 of 35.00) 26. T F The cell wall controls the transfer of nutrients into animal cells. 27. Mitosis
Individual Feedback Report for: St#: 703709 Test: GENETICS UNIT TEST 2score Grade: 3 Score: 57.14 % (20.00 of 35.00) 26. T F The cell wall controls the transfer of nutrients into animal cells. 27. Mitosis
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION. Cytokinesis. centromere. DNA Replication S-Phase. One Chromosome Two Chromatids. One Chromosome No Chromatids 10.
 MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
Lesson Overview. Human Chromosomes. Lesson Overview. Human Chromosomes
 Lesson Overview Karyotypes A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with chromosomes, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the
Lesson Overview Karyotypes A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with chromosomes, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the
Genetics. the of an organism. The traits of that organism can then be passed on to, on
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
