Rights, Respect, Responsibility
|
|
|
- Erica Hubbard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rights, Respect, Responsibility A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items Elizabeth Schroeder, EdD, MSW Eva Goldfarb, PhD Nora Gelperin, MEd Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 1
2 Elementary School Lessons Assessment Question and Answer of Grade Topic NSES Grade/ Q: Do all families look exactly the same? A: No Q: Circle all of the examples of different ways families might be put together: a. Different numbers of children in the family b. Parents of the same gender or parents of different genders c. Step parents or step children d. Members of the family look alike or look different from each other e. Children living with a grandparent A: a, b, c, d, e Q: Should children be expected to behave certain ways based on their gender (being a boy or a girl)? A: No Q: Circle all of the examples of ways people sometimes expect children to behave based on their gender: a. Boys play sports b. Children should be nice to each other c. Girls like to play princess d. Boys and girls like to laugh A: a and c 2 HR HR.2.CC.1 Identify different kinds of family structures. 2 ID ID.2.CC.1 Describe differences and similarities in how boys and girls may be expected to act. K Different Kinds of Families 1 Gender Roles Q: Is it okay for children of any gender to play baseball? A: Yes Q: Is it okay for children of any gender to play with dolls? A: Yes Q: Circle the letters next to the types of trusted adults a child could tell if someone teased or bullied them or touched them in a way that made the child feel uncomfortable or yucky. a. A parent or guardian b. A friend in school c. A teacher d. A school nurse e. A school principal f. They shouldn t tell anyone. They should keep it a secret. A: a, c, d, e 2 PS PS.2.A1.1 Identify parents and other trusted adults they can tell if they are feeling uncomfortable about being touched. PS.2.A1.2 Identify parents and other trusted adults they can tell if they are being bullied or teased. 2 Seeking Help Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 2
3 of Grade Topic NSES Grade/ Q: What are two strategies a person could use to communicate if they are feeling bullied or harassed? a. Say, I m leaving or You can t treat me like that. b. Say, You re going to get in trouble for treating me like this. or tell your friend c. Say, Please stop being so mean. or write down what s happened in a journal d. Say, My mom is going to get you in trouble or scream at them A: Answer: A Q: Circle the letters next to physical changes that occur during puberty. a. A person gets better balance b. A person gets better at math c. A person gets taller d. Menstruation begins in female bodies e. A person grows hair under their arms and around their genitals A: c, d, e 5 PS PS.5.IC.1 Demonstrate ways to communicate about how one is being treated. 5 PD PD.5.CC.1 Students will be able to explain the physical, social, and emotional changes that occur during puberty and adolescence. 3 Teasing, Harassment and Bullying 4 Making Sense of Puberty Q: Circle the letters next to social changes that occur during puberty. a. A person becomes very popular b. A person may have more conflict with their parents c. Peer pressure increases d. A person might start to become interested in others as more than just friends maybe as a boyfriend or girlfriend e. A person starts thinking about their future career. A: b, c, d Q: Circle the letters next to emotional changes that occur during puberty. a. A person might start to feel self-conscious about how their body looks b. A person might feel like everyone is looking at them or talking about them c. A person might have mood swings d. A person starts feeling great all the time e. A person starts feeling shy A: a, b, c Q: Circle the letters next to the types of trusted adults a child could go to either to answer a question about puberty or to help find a website, book or magazine that has the answer. a. A parent or guardian b. A doctor c. A teacher d. A school nurse e. A librarian A: a, b, c, d, e 5 PD PD.5.AI.2 Identify parents or other trusted adults of whom students can ask questions about puberty and adolescent health issues. 4 Making Sense of Puberty Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 3
4 of Grade Topic NSES Grade/ Q: Write a T for True next to examples of healthy relationships and F for False next to examples of unhealthy relationships. (From Healthy and Unhealthy Relationships Quiz from the grade 4 lesson, Figuring out Friendships. Have students complete these individually, rather than in pairs, and put their names on them). A: Based on the answer key, student should be able to identify the characteristics of Healthy and Unhealthy relationships with no more than 3 incorrect responses. Q: Circle the letters next to examples of sexual abuse a. An adult touches a child s genitals and tells the child to keep it a secret b. An adult forces a child to touch the adult s genitals c. A doctor touches a child s genitals as part of a health exam and the child s parent or other adult family member is in the exam room. d. A child touches their own genitals. A: a, b 5 HR HR.5.CC.1 Describe the characteristics of healthy relationships. 5 PS PS.5.CC.2 Define sexual harassment and sexual abuse. 4 Figuring out Friendships 4 Your Body, Your Rights Q: Circle the letters next to examples of sexual harassment. a. A teenager keeps telling a fifth grader that they are really sexy and that they want to kiss them even though the fifth grader has told them to stop many times. b. A student pays a classmate a compliment one day by telling them that they like their new haircut. c. A group of children keep whispering gay under their breath every time they pass one of their classmates in the hallway d. An adult neighbor loves to watch a middle schooler walk to the bus every morning and shouts out: I can t wait until you are older so I can marry you making the student nervous every time they have to pass the neighbor s house. A: a, c, d Q: Check the box that correctly identifies who has each part. Put the letter from the list on the back of the sheet that correctly identifies the description or main function for each part. (From Body Parts homework in grade 5 lesson Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy): A: Based on the answer sheet from the Body Parts worksheet, student should be able to identify correctly at least 2 parts each of the male and female anatomy and at least 2 functions of each the male and female parts. 5 AP AP.5.CC.1 Describe male and female reproductive systems including body parts and their functions. 5 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 4
5 of Grade Topic NSES Grade/ Q: Circle the letters next to reliable places someone could go if they wanted to learn more about the reproductive system? a. Books from the library b. Teacher c. A classmate d. School nurse e. Parent or guardian f. A friend s teenage family member g. A website that has been recommended by a trusted adult (parent/guardian, teacher, school nurse, or doctor, for example). A: a, b, d, e, g Q: Put the following steps for human reproduction that involves only the male, in the correct order: a. Sperm cells mix with semen b. Sperm is made in the testicles c. Sperm exit the testicles and travel up the vas deferens A: b, c, a 5 AP AP.5.AI.1 Identify medically accurate information about female and male reproductive anatomy. 5 PR PR.5.CC.1 Describe the process of human reproduction. 5 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy 5 Puberty and Reproduction Q: Put the following steps for human reproduction that involves only the female, in the correct order: a. Egg enters the fallopian tube b. Ovulation occurs (egg is released from ovary around every days) c. Lining of the uterus thickens with blood A: c, b, a Q: Put the following steps for human reproduction that involve both the male and the female in the correct order: a. The fertilized egg travels down through the fallopian tube to the uterus b. Cell attaches to the wall of the uterus (implantation) conception complete c. One sperm cell attaches to an egg in the fallopian tube and fertilizes it d. Sperm travel through the cervix, uterus, and into the fallopian tubes e. If the male & female have sexual intercourse then the penis is inserted into the vagina f. Pregnancy begins g. Sperm cells leave the penis and enter the vagina (ejaculation) A: e, g, d, c, a, b, f Student should be able make no more than two errors on this question to be successful. Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 5
6 of Grade Topic NSES Grade/ Q: What is HIV? A: HIV is a virus that is transmitted through bodily fluids and weakens your immune system. Q: What are some ways HIV can be transmitted from one person to another? Circle all that apply: a. Through contact with the blood of someone who is NOT infected with HIV b. Through contact with the blood of someone who IS infected with HIV (including sharing drug needles) c. Through contact with the semen or vaginal fluids of someone who is infected with HIV d. Through hugging someone who is infected with HIV e. Through contact with the tears of someone who is infected with HIV A: b, c 5 SH SH.5.CC.1 Define HIV and identify some age-appropriate methods of transmission, as well as ways to prevent transmission. 5 Learning about HIV Q: How can someone prevent transmission of HIV? A: Make sure that any of the bodily fluids that can transmit HIV from a person who is infected with HIV don t come into contact with a person who is not infected with HIV. Q: Define sexual orientation. A: The gender or genders of the people we feel romantic love and attraction for. Q: Circle the letters next to reliable sources a child could go to to ask questions about sexual orientation. a. Teacher b. Other kids at school c. A website on the internet found through a google search d. Parent/guardian or other adult family member e. Librarian f. Movie star who writes a blog A: a, d, e 5 ID ID.5.CC.1 Define sexual orientation as the romantic attraction of an individual to someone of the same gender or a different gender. ID.5.AI.1 Identify parents or other trusted adults of whom students can ask questions about sexual orientation. 5 What Is Love Anyway? Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 6
7 Middle School Lessons Assessment Question and Answer Q: Is a person who has been raped or sexually assaulted ever at fault? Why or why not? A: No. A person who has been sexually assaulted or raped is never at fault no matter what they say, what they wear or where they go. Everyone has the right to their own boundaries and nobody ever has the right to cross those boundaries without permission. Q: Define sexual intercourse and describe how it is related to human reproduction. A: Sexual intercourse involves a penis going inside a vagina, a penis going inside an anus, or a person s mouth going on a person s vulva or penis. When a penis goes inside a vagina, called vaginal sex, a pregnancy can occur if semen from the penis enters the vagina. Q: Define sexual abstinence and its connection to pregnancy prevention. A: Sexual abstinence is not having sexual intercourse until someone is older, or until some other time. Sexual abstinence is the only 100% sure way to avoid getting pregnant or getting someone pregnant. By the end of grade Topic NSES 8 PS PS.8.CC.4 Explain why a person who has been raped or sexually assaulted is not at fault. 8 PR PR.8.CC.1 Define sexual intercourse and its relationship to human reproduction. 8 PR PR.8.CC.2 Define sexual abstinence as it relates to pregnancy prevention. Grade/ 6 Understanding Boundaries 6 Liking and Loving Now and When I m Older 6 Liking and Loving Now and When I m Older Q: Use the Female Sexual and Reproductive System Crossword Puzzle homework sheet from grade seven lesson, Everybody s Got Body Parts Part One and the Male Sexual and Reproductive System Crossword Puzzle homework sheet from grade seven lesson, Everybody s Got Body Parts Part Two for assessment. A: Based on the answer keys to the crossword puzzles, students should be able to identify the correct male and female sexual and reproductive systems based on their function with no more than three wrong or missing answers on each homework sheet. Q: Define Gender Identity, Gender Expression, and Sexual Orientation. A: A person s gender identity is what they call themselves: Male, female, transgender, or something else. A person s gender expression is how they let people know the gender they are. That can be by the name they use, the clothes they wear, the pronouns (he, she, they) they use, how they carry themselves, etc. Sexual orientation is the gender(s) of the people to whom we are attracted, physically and romantically. 8 AP AP.8.CC.1 Students will be able to describe the male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts and their functions. 8 ID ID.8.CC.1 Differentiate between gender identity, gender expression and sexual orientation. 7 Everybody s Got Body Parts Part One 7 Everybody s Got Body Parts Part Two 7 I Am Who I Am Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 7
8 of Grade Topic NSES Grade/ Q: Were students able to successfully apply a decision-making model to a scenario? A: Teachers will use the Teacher s Guide: The Making SMART Choices Model as a measurement of successful application. Students will need to submit their scenarios individually, and be graded accordingly. (See Appendix B) Q: Did students demonstrate that they understood how to communicate assertively with someone else around sexuality? A: The teacher will need to allocate time for all students to role play in pairs. During these role plays, the teacher will use the definitions given in the lesson for Aggressive, Passive and Assertive communication, and allocate points for each instance of assertive statements and responses. (See Appendix A) Q: Match each of the following three types of communication with its definition: 1. Aggressive 2. Passive 3. Assertive a. When someone says what they want or mean without being hurtful to another person. b. When someone tries to get what they want by bullying another person into it. c. When a person is timid or unclear in expressing their needs or when they won t speak up about what THEY want, but just go along with what the other person wants. A: b, c, a Q: Which contraceptive method is worn on a penis and provides very good protection against both pregnancy and STDs? a. Diaphragm b. The pill c. External condoms d. Internal condoms A: c Q: Which of the following statements about emergency contraception, or Plan B is CORRECT? a. It is a medicine that is inserted into the vagina 3 hours before penis-vagina sex to prevent pregnancy. b. It is a medicine that is taken after unprotected vaginal sex to help prevent pregnancy. c. It is a medicine that can temporarily stop sperm production in order to prevent pregnancy. d. It is a medicine that makes people no longer feel like having sex. A: b 8 PR PR.8.DM.1 Apply a decision-making model to various sexual health decisions. 8 PR PR.8.IC.2 Demonstrate the use of effective communication and negotiation skills about the use of contraception including abstinence and condoms. 8 PR, SH SH.8.IC.1 Demonstrate the use of effective communication skills to reduce or eliminate risk for STDs, including HIV. PR.8.IC.2 Demonstrate the use of effective communication and negotiation skills about the use of contraception including abstinence and condoms. 8 PR PR.8.CC.3 Explain the health benefits, risks and effectiveness rates of various methods of contraception, including abstinence and condoms. 8 PR PR.8.CC.4 Define emergency contraception and its use. 7 Making SMART Choices 7 Let s Talk about Sex 7 Let s Talk about Sex 8 Birth Control Basics 8 Birth Control Basics Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 8
9 of Grade Topic NSES Grade/ Q: All of the following are common mistakes people A: d make when using external condoms, EXCEPT: a. Not checking the expiration date b. Storing condoms someplace that s too hot or too cold c. Putting the condom on wrong side up d. Using a fresh condom for every sex act 8 PR PR.8.SM.1/ SH.8.SM.1 Describe the steps to using a condom correctly. 8 Using Condoms Effectively Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 9
10 High School Lessons Assessment Question and Answer By the end of grade Topic NSES Grade/ Q: What is the difference between gender and sexual orientation? A: Gender has to do with your sense of yourself as male, female, a combination, or neither. Sexual orientation has to do with the gender(s) of the people to whom we are attracted, physically and romantically. 12 ID ID.12.CC.1 Differentiate between biological sex, sexual orientation, and gender identity and expression. ID.12.INF.1 Analyze the influence of friends, family, media, society and culture on the expression of gender, sexual orientation and identity. ID.12.CC.2 Distinguish between sexual orientation, sexual behavior and sexual identity. 9 Understanding Gender 11 Gender and Sexual Orientation: Understanding the Difference 9 Sexual Orientation, Behavior and Identity: How I Feel, What I Do and Who I Am Q: Were students able to successfully apply a decision-making model to a scenario? A: Teachers will use the Teacher s Guide: What s Your Dogma? as a measurement of successful application. Students will need to submit their scenarios individually, and be graded accordingly. (See Appendix C) 12 PD, PR, SH PD.12.DM.1 Apply a decisionmaking model to various situations relating to sexual health. PR.12.IC.1 Demonstrate ways to communicate decisions about whether or when to engage in sexual behaviors. SH.12.DM.1 Apply a decisionmaking model to choices about safer sex practices, including abstinence and condoms. 9 Decisions, Decisions Q: What are two STDs that can be cured, and two that cannot? A: Chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis can be cured; HPV (the virus that causes genital warts and can cause cervical cancer), Herpes and HIV cannot, although they can be treated and managed with medication. 12 SH SH.12.CC.1 Describe common symptoms of and treatments for STDs, including HIV. SH.12.CC.2 Evaluate the effectiveness of abstinence, condoms, and other safer sex methods in preventing the spread of STDs, including HIV. SH.12.AI.2 Access medicallyaccurate prevention information about STDs, including HIV. 9 STD Smarts Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 10
11 of Grade Topic NSES Grade/ Q: Put the following steps to using an external condom in the correct order: a. Carefully open the condom. No teeth! b. Pull the condom off, tie the end in a knot to avoid spillage, and throw it in the garbage. c. Sex act orgasm and ejaculation. d. Roll the condom all the way down the penis. e. Give and obtain consent for having sex. f. Have more than one condom. g. Check whether it s right side up. h. Gently pinch the tip of the condom to get air out. i. Place it on the head of an erect penis. j. Pull the penis out and away from the other person s body. k. Check the expiration date. A: e, f, k, a, g, i, h, d, c, j, b Q: Match each of the following terms to its definition: 1. Consent 2. Coercion 3. Incapacitated a. When someone said they wanted to do something b. When a person doesn t have the ability to do things or say they want to do things, like someone who is asleep, drunk or using drugs c. When someone gets a person to do something by threatening or forcing them to do it A: a, c, b Q: TRUE or FALSE: Possessing a sexually explicit image of someone under 18 is a crime even if the person who receives it is under 18, too. A: TRUE Q: TRUE or FALSE: If you are under 18, sending a sexually explicit image of yourself to someone else is a crime. A: TRUE 12 PR, PR.12.SM.1 Describe the steps to using a condom correctly. SH.12.SM.2 Describe the steps to using a condom correctly. 12 HR HR.12.CC.3 Define sexual consent and explain its implications for sexual decision-making. HR.12.INF.2 Analyze factors, including alcohol and other substances, that can affect the ability to give or perceive the provision of consent to sexual activity. 12 HR HR.12.SM.2 Describe strategies to use social media safely, legally and respectfully. 9 Creating Condom Confidence 10 Rights, Respect, Responsibility 10 Using Technology Respectfully and Responsibly Q: Tricking someone who is under 18 into sending a sexually explicit image is a crime. A: TRUE Q: All of the following are websites for teenagers that provide medically-accurate, age- and developmentally-appropriate information about sexuality for teens, EXCEPT: a. a. b. c. A: b 12 PR PR.12.AI.1 Access medicallyaccurate information about contraceptive methods, including abstinence and condoms. PR.12.AI.2 Access medicallyaccurate information and resources about emergency contraception. 10 Trust it or Trash It? Finding Accurate Sex Ed Info Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 11
12 Q: Name the five categories of relationship abuse. A: Physical, Emotional, Psychological, Sexual and Financial. Q: Put the following abusive behaviors into the appropriate category of relationship abuse: 1. Refusing to practice safer sex 2. Criticizing the person s appearance or intelligence 3. Threatening to hurt the other person 4. Telling the other person they need to spend time with you instead of going to work 5. Pinching 6. Texting nonstop and expecting the other person to text back by a certain time 7. Restraining 8. Sharing sexy photos of the other person without their consent 9. Threatening to hurt yourself if the other person doesn t do what you want 10. Pressuring the other person to do something sexual they don t want to do A: 1. Sexual 2. Emotional 3. Psychological 4. Financial 5. Physical 6. Psychological 7. Physical 8. Sexual 9. Psychological 10. Sexual Q: All of the following are reasons why someone might choose to get tested for STDs, EXCEPT: a. They thought they and their partner were in a monogamous relationship (only having sex with each other) and found out later that their partner was having sex with other people. b. They started to experience some symptoms and didn t know if that meant they had an STD. c. They re thinking about having sex for the first time and think if they get tested in advance it ll keep them from getting an STD. d. Because they were sexually assaulted and need to know whether it resulted in an STD of some kind. A: c Q: All of the following are reasons why someone might choose NOT to get tested for STDs, EXCEPT: a. Because they don t want to know b. Because they think they can tell whether they have an STD by how they are feeling c. Because they are worried about the actual test itself being painful or uncomfortable. d. Because they don t have insurance or think they can t afford to get tested. A: b of Grade Topic NSES 12 PS PS.12.CC.1 Compare and contrast situations and behaviors that may constitute bullying, sexual harassment, sexual abuse, sexual assault, incest, rape and dating violence. 12 SH SH.12.SM.1 Analyze individual responsibility about testing for and informing partners about STDs and HIV status. SH.12.ADV.1 Advocate for sexually active youth to get STD/ HIV testing and treatment. Grade/ 11 Is It Abuse If...? 12 Getting Savvy about STD Testing Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 12
13 Q: All of the following are possible ways in which viewing sexually-explicit materials can affect a young person s attitudes about sex and sexuality, EXCEPT: a. People may expect sex to go a certain way and feel unprepared for or vulnerable when it does not go as expected b. People may assume that because a person looks a particular way they are more or less sexual c. People may assume consent from their partner because they may think everyone of their partner s gender is like that d. People may be more likely to think that they should only have sex if music is playing in the background. of Grade Topic NSES 12 HR HR.12.INF.1 Explain how media can influence one s beliefs about what constitutes a healthy sexual relationship. Grade/ 12 Fantasy or Reality? A: d Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 13
14 APPENDIX A: Rubric for Effective Communication Skills (For use with Let s Talk about Sex, Grade 7) Student Name: Did the Student Possible Points Points Allocated Reflect an accurate understanding of the differences between passive, assertive, and aggressive communication by providing a correct example during the all-class discussion at the beginning of the lesson? Communicate what they did or did not want to do in an assertive manner (rather than passively or aggressively) when playing person B in the activity? Reflect an accurate understanding of the differences between the three communication styles by creating assertive and aggressive pressure lines when playing person A in the activity? Other: Other: Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 14
15 APPENDIX B: Rubric for Effective Use of the SMART Decision-Making Model (For use with Making SMART Choices, Grade 8) Student Name: Did the Student List all steps in the decision-making model and what each letter stands for? Possible Points Points Allocated Explain how someone slows down in order to make a well thought-out decision (S)? List all their options in the given scenario (M)? Analyze their list of options by deleting the less realistic options (A)? Based on the options they eliminate, state the decision they have reached (R)? Explain why it is important to think about and evaluate the decision they reach in their scenario (It is important to check in from time to time, see how things are going, and look at what may need to change in order to stick with or alter the decision made (T)? Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 15
16 APPENDIX C: Rubric for Effective Use of the DOGMA Decision-Making Model (For use with Decisions, Decisions, Grade 9) Student Name: Did the Student Accurately reflect back the situation as described in the given scenario (D)? Possible Points Points Allocated Generated at least three possible options in the given situation (O)? Describe at least two items about which they felt they needed to gather information and named at least two pros and cons to each of those items (G)? Stated a rational decision they d recommend for their chosen character in the scenario that follows the logic of their previous step (M)? Name two things they will do to put the decision into practice (A)? Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Sexuality Education Curriculum Assessment Items 16
FOSE National Sex Ed Standards Grades 9-12 Alignment with HS FLASH
 Strand 1 Anatomy & Physiology AP.12.CC.1 Describe the human sexual response cycle, including the role hormones play Strand 2 Puberty & Adolescent Development PD.12.CC.1 Analyze how brain development has
Strand 1 Anatomy & Physiology AP.12.CC.1 Describe the human sexual response cycle, including the role hormones play Strand 2 Puberty & Adolescent Development PD.12.CC.1 Analyze how brain development has
Key Concepts Guide. Rev. March 2015 Page 1 of 13
 Key Concepts Guide Key concepts are main ideas. They convey big-picture ideas. Birth control is good at preventing pregnancy and Everyone has the right to say who touches their body and how are both key
Key Concepts Guide Key concepts are main ideas. They convey big-picture ideas. Birth control is good at preventing pregnancy and Everyone has the right to say who touches their body and how are both key
Creating Condom Confidence
 A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of 12th grade,
A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of 12th grade,
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Teen Sexual Health Survey
 Instructions Teen Sexual Health Survey Thank you for taking part in our survey. DO NOT write your name on this survey. The answers you give will be kept private. No one will know what you write. Answer
Instructions Teen Sexual Health Survey Thank you for taking part in our survey. DO NOT write your name on this survey. The answers you give will be kept private. No one will know what you write. Answer
Grade 8 Sexual Health Curriculum Overview
 Grade 8 Sexual Health Curriculum Overview Rights, Respect, Responsibility The Advocates for Youth s Rights, Respect, Responsibility curriculum is based on the belief that: Youth have the right to honest
Grade 8 Sexual Health Curriculum Overview Rights, Respect, Responsibility The Advocates for Youth s Rights, Respect, Responsibility curriculum is based on the belief that: Youth have the right to honest
Thinking about the fact that your bodies are maturing -
 Puberty Review Your bodies are rapidly changing, once puberty starts you are on your way to being an adult physically It takes your brain longer to mature, sometimes until age 25 or later Protecting your
Puberty Review Your bodies are rapidly changing, once puberty starts you are on your way to being an adult physically It takes your brain longer to mature, sometimes until age 25 or later Protecting your
Sexual Education for Adults with Disabilities
 Sexual Education for Adults with Disabilities Tool 3 Thematic Card Game The European Commission support for the production of this publication does not constitute an endorsement of the contents which reflects
Sexual Education for Adults with Disabilities Tool 3 Thematic Card Game The European Commission support for the production of this publication does not constitute an endorsement of the contents which reflects
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy
 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: Students
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: Students
What do I need to know about HIV and sex? What are my responsibilities and choices?
 Patient and Family Education HIV: Teens and Sex This handout has information about sex and HIV. This handout answers common questions you might ask about sex. It is important for you to talk to your parents
Patient and Family Education HIV: Teens and Sex This handout has information about sex and HIV. This handout answers common questions you might ask about sex. It is important for you to talk to your parents
Birth Control Basics. TARGET GRADE: Grade 8 Lesson 8 MATERIALS NEEDED: Last Revised: December 17, 2017
 Birth Control Basics A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By
Birth Control Basics A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By
A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum
 Birth Control Basics A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By
Birth Control Basics A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By
Puberty and Reproduction
 Puberty and Reproduction A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end
Puberty and Reproduction A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy
 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that
 The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
ANALYZING CONTRACEPTION OPTIONS
 ANALYZING CONTRACEPTION OPTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to identify and categorize the various forms of contraception and discuss influences on, and reasons why, students may
ANALYZING CONTRACEPTION OPTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to identify and categorize the various forms of contraception and discuss influences on, and reasons why, students may
All Play All Play All Play All Play. All Play All Play All Play All Play
 All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play Role-Play Three girls and boys act out how they might share their hopes and dreams for the future
All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play Role-Play Three girls and boys act out how they might share their hopes and dreams for the future
Protecting Your Health: Understanding and Preventing STDs
 Protecting Your Health: Understanding and Preventing STDs A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality
Protecting Your Health: Understanding and Preventing STDs A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality
PREVENTING PREGNANCY: TALKING ABOUT AND USING CONTRACEPTION
 PREVENTING PREGNANCY: TALKING ABOUT AND USING CONTRACEPTION Lesson 11 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify and describe basic types of contraceptives; i.e., abstinence, condom, foam, birth control
PREVENTING PREGNANCY: TALKING ABOUT AND USING CONTRACEPTION Lesson 11 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify and describe basic types of contraceptives; i.e., abstinence, condom, foam, birth control
High School Sexual Health Curriculum Overview
 High School Sexual Health Curriculum Overview Rights, Respect, Responsibility The Advocates for Youth s Rights, Respect, Responsibility curriculum is based on the belief that: Youth have the right to honest
High School Sexual Health Curriculum Overview Rights, Respect, Responsibility The Advocates for Youth s Rights, Respect, Responsibility curriculum is based on the belief that: Youth have the right to honest
Using Condoms Effectively
 A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of 8th grade,
A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of 8th grade,
17. Preventing pregnancy
 17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
Ohio PREP Region 7: Cuyahoga County Board of Health October 2017 through September 2018 Data Report
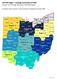 Ohio PREP Region 7: Cuyahoga County Board of Health October 2017 through September 2018 Data Report Provided by Ohio University s Voinovich School of Leadership and Public Affairs 1 P age This report covers
Ohio PREP Region 7: Cuyahoga County Board of Health October 2017 through September 2018 Data Report Provided by Ohio University s Voinovich School of Leadership and Public Affairs 1 P age This report covers
Naturally Curious. Talking to Youth About Sexual Health
 Naturally Curious Talking to Youth About Sexual Health 2 Naturally Curious W e l c o m e! Talking about sex is okay! In fact, it can help young people know healthy sex is normal. This booklet gives you
Naturally Curious Talking to Youth About Sexual Health 2 Naturally Curious W e l c o m e! Talking about sex is okay! In fact, it can help young people know healthy sex is normal. This booklet gives you
MONITORING RESPONSIBILITY: Site administrators or Designees
 TITLE: 5232R Sex Education Instruction PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: To provide guidelines for instruction on acquired immune deficiency syndrome, human reproductive system, related communicable diseases and
TITLE: 5232R Sex Education Instruction PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: To provide guidelines for instruction on acquired immune deficiency syndrome, human reproductive system, related communicable diseases and
THE ANSWER BOX: GRADES 7 AND 8
 THE ANSWER BOX: GRADES 7 AND 8 You may find you are getting a lot of questions from your students about a variety of topics. They are asking these questions because their bodies and minds are changing,
THE ANSWER BOX: GRADES 7 AND 8 You may find you are getting a lot of questions from your students about a variety of topics. They are asking these questions because their bodies and minds are changing,
Gender Roles, Gender Expectations A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum
 Gender Roles, Gender Expectations A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality education. NSES
Gender Roles, Gender Expectations A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering responsibility by respecting young people s rights to honest sexuality education. NSES
Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity
 Unit 7 Lesson 7.1 Notes Introductory Video Video STIs: Running the Risk Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity Section 1: What Are the Risks? Key Terms: Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) an infectious
Unit 7 Lesson 7.1 Notes Introductory Video Video STIs: Running the Risk Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity Section 1: What Are the Risks? Key Terms: Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) an infectious
Love, Sex and You. Love, Sex and You
 Love, Sex and You Love, Sex and You Index Relationships Sex Being safer Your body Where to learn more About this book This is an easy to read book. It has been designed for people who have learning difficulties.
Love, Sex and You Love, Sex and You Index Relationships Sex Being safer Your body Where to learn more About this book This is an easy to read book. It has been designed for people who have learning difficulties.
More info: Your doctor needs to prescribe oral contraceptive pills and will talk to you about the options that are best for you.
 http://share.ceh.org.au/fact-sheet/contraception/ Contraceptives Contraceptives are a way to prevent pregnancy. There are different types of contraceptives, which act in different ways to stop pregnancy.
http://share.ceh.org.au/fact-sheet/contraception/ Contraceptives Contraceptives are a way to prevent pregnancy. There are different types of contraceptives, which act in different ways to stop pregnancy.
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Sexuality/Reproduction CALM Summer 2015
 Female Reproduction Sexuality/Reproduction CALM Summer 2015 Male Reproduction Reproduction https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_7rsh2loiy8 1 About Sex How to use a condom Set Limits Think about how far you
Female Reproduction Sexuality/Reproduction CALM Summer 2015 Male Reproduction Reproduction https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_7rsh2loiy8 1 About Sex How to use a condom Set Limits Think about how far you
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions SEX!! Is it okay if I choose abstinence? I feel weird because my friends are all having sex. Should I lie? It is absolutely OK to wait to have sex, or to decide that you don
Frequently Asked Questions SEX!! Is it okay if I choose abstinence? I feel weird because my friends are all having sex. Should I lie? It is absolutely OK to wait to have sex, or to decide that you don
Risky Stuff. Teacher s Guide. Objectives
 Risky Stuff Teacher s Guide Objectives To define STDs, including HIV/AIDS To explain how various STDs are and are not spread To explain risk-taking behaviors associated with the spread of sexually transmitted
Risky Stuff Teacher s Guide Objectives To define STDs, including HIV/AIDS To explain how various STDs are and are not spread To explain risk-taking behaviors associated with the spread of sexually transmitted
CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY
 Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive Health & Safety. This is from a 1953 Sex Education Curriculum
 Reproductive Health & Safety This is from a 1953 Sex Education Curriculum Reproductive Health & Safety 7 th Grade Our assumptions: Seventh graders are people. This is not your first class in this stuff.
Reproductive Health & Safety This is from a 1953 Sex Education Curriculum Reproductive Health & Safety 7 th Grade Our assumptions: Seventh graders are people. This is not your first class in this stuff.
Sexual Feelings. Having sexual feelings is not a choice, but what you do with your feelings is a choice. Let s take a look at this poster.
 Sexual Feelings It may be your first instinct to deny that your child will ever have sexual feelings. You may even do everything in your power to suppress those feelings if they do surface. You won t succeed
Sexual Feelings It may be your first instinct to deny that your child will ever have sexual feelings. You may even do everything in your power to suppress those feelings if they do surface. You won t succeed
Birth Control -- Especially for Teens
 AP112, June 2011 Birth Control -- Especially for Teens Making the decision whether to have sex can be difficult. You should make up your own mind when the time is right for you. If you are not ready for
AP112, June 2011 Birth Control -- Especially for Teens Making the decision whether to have sex can be difficult. You should make up your own mind when the time is right for you. If you are not ready for
LEARNING NATIONAL CURRICULUM. Herpes virus. This section aims to teach students how sexual activity can lead to the spread of microbes and disease.
 This section aims to teach students how sexual activity can lead to the spread of microbes and disease. Section 2.3, Sexually Transmitted Infections, teaches students how easily potentially harmful microbes
This section aims to teach students how sexual activity can lead to the spread of microbes and disease. Section 2.3, Sexually Transmitted Infections, teaches students how easily potentially harmful microbes
Condoms: Condoms are thin latex caps that cover a man s penis during sex. If you are thinking about using condoms, think about this:
 Vocabulary words The Basics of Birth Control Methods STD Abstinence Penis Vagina Spermicide Birth Control Pills The Shot F O R Y O U R H E A L T H Have you ever heard your friends say: I cannot get pregnant
Vocabulary words The Basics of Birth Control Methods STD Abstinence Penis Vagina Spermicide Birth Control Pills The Shot F O R Y O U R H E A L T H Have you ever heard your friends say: I cannot get pregnant
Lesson 8 STD & Responsible Actions
 Lesson 8 STD & Responsible Actions Overview This lesson reinforces taking care of sexual health by teaching responsible actions around STD prevention. After discussing the responsibilities of a person
Lesson 8 STD & Responsible Actions Overview This lesson reinforces taking care of sexual health by teaching responsible actions around STD prevention. After discussing the responsibilities of a person
Post-Summative Assessment
 Post-Summative Assessment Directions: The following questions will ask you about your knowledge of life skills, human reproduction and making healthy choices. Please answer the questions by circling the
Post-Summative Assessment Directions: The following questions will ask you about your knowledge of life skills, human reproduction and making healthy choices. Please answer the questions by circling the
Having Sex. Some people are heterosexual. Fact Sheet
 Fact Sheet Having Sex Sometimes people who are in a close relationship and like each other a lot, or love each other, like to kiss and cuddle. Sometimes they show how much they like or love each other
Fact Sheet Having Sex Sometimes people who are in a close relationship and like each other a lot, or love each other, like to kiss and cuddle. Sometimes they show how much they like or love each other
SEX? A HEalthy Sexuality Resource
 SEX? A HEalthy Sexuality Resource The information contained in this book is up-to-date as of the date of printing. This information is not a substitute for the advice of a health professional. Always consult
SEX? A HEalthy Sexuality Resource The information contained in this book is up-to-date as of the date of printing. This information is not a substitute for the advice of a health professional. Always consult
Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) Reference Sheet
 Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) Reference Sheet Name Date A Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) is ANY infection people commonly get by having sex with someone who has it. 1. There are more than different
Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) Reference Sheet Name Date A Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) is ANY infection people commonly get by having sex with someone who has it. 1. There are more than different
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-8.13:
 STUDYING STI/HIV Lesson 2 GRADE 8 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-8.13: Describe symptoms, effects, treatments and prevention for common sexually transmitted diseases; i.e., chlamydia, HPV, herpes, gonorrhea, hepatitis
STUDYING STI/HIV Lesson 2 GRADE 8 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-8.13: Describe symptoms, effects, treatments and prevention for common sexually transmitted diseases; i.e., chlamydia, HPV, herpes, gonorrhea, hepatitis
Sex Talk for Self-Advocates #3 Safe Sex Practices - Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
 Sex Talk for Self-Advocates #3 Safe Sex Practices - Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Self-Advocacy Educator - Max Barrows Sex Educator - Katherine McLaughlin www.elevatustraining.com Sex Educator
Sex Talk for Self-Advocates #3 Safe Sex Practices - Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Self-Advocacy Educator - Max Barrows Sex Educator - Katherine McLaughlin www.elevatustraining.com Sex Educator
Pre/Post-Summative Assessment Answer Key
 Pre/Post-Summative Assessment Answer Key Directions: The following questions will ask you about your knowledge of life skills, human reproduction and making healthy choices. Please answer the questions
Pre/Post-Summative Assessment Answer Key Directions: The following questions will ask you about your knowledge of life skills, human reproduction and making healthy choices. Please answer the questions
Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections Storytelling Activity
 Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections Storytelling Activity Trainer s Tips Make the context and characters in the story culturally relevant.» Choose culturally relevant girls and boys names for the
Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections Storytelling Activity Trainer s Tips Make the context and characters in the story culturally relevant.» Choose culturally relevant girls and boys names for the
DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS
 DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to describe male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts
DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to describe male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts
Grade 6 Reproduction Review
 Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.14: Examine abstinence and decisions to postpone sexual activity as healthy choices.
 CHOOSING ABSTINENCE Lesson 1 7 G R A D E LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.14: Examine abstinence and decisions to postpone sexual activity as healthy choices. MATERIALS: 1. HANDOUT: Promoting Abstinence 2. OVERHEAD:
CHOOSING ABSTINENCE Lesson 1 7 G R A D E LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.14: Examine abstinence and decisions to postpone sexual activity as healthy choices. MATERIALS: 1. HANDOUT: Promoting Abstinence 2. OVERHEAD:
Word list of symbols and signs in Sex Education
 Word list of symbols and signs in Sex Education Abbreviations Key: CV Core Vocabulary * Signs Only + Symbols Only Abortion / Termination Abuse, to (2) / Physical Abuse Abuse, to (3) / Verbal Abuse* Adolescence
Word list of symbols and signs in Sex Education Abbreviations Key: CV Core Vocabulary * Signs Only + Symbols Only Abortion / Termination Abuse, to (2) / Physical Abuse Abuse, to (3) / Verbal Abuse* Adolescence
rated sexy smart safe Women Sexy, Smart & Safe
 rated sexy smart safe Women Sexy, Smart & Safe User Instructions These cards were designed to facilitate small group dialog and education on sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and HIV and AIDS. They
rated sexy smart safe Women Sexy, Smart & Safe User Instructions These cards were designed to facilitate small group dialog and education on sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and HIV and AIDS. They
Activity 5.1: Anonymous Question Box (5 minutes)
 Activity 5.1: Anonymous Question Box (5 minutes) Take a moment to check in on the ground rules for the Human Growth and Development unit. If there are questions in the anonymous question box, answer them
Activity 5.1: Anonymous Question Box (5 minutes) Take a moment to check in on the ground rules for the Human Growth and Development unit. If there are questions in the anonymous question box, answer them
Related TeensHealth Links
 Grades 9 to 12 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Grades 9 to 12 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Why Vaccinate Guys Against HPV?
 IN THE KNOW: our health Why Vaccinate Guys Against HPV? By Sam Dercon, 18, Staff Writer I was confused when I first heard that Gardasil, a vaccine that protects against certain strains of the human papillomavirus
IN THE KNOW: our health Why Vaccinate Guys Against HPV? By Sam Dercon, 18, Staff Writer I was confused when I first heard that Gardasil, a vaccine that protects against certain strains of the human papillomavirus
Taking Care of Your Sexual Health
 Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Responsibilities in a sexual relationship - Contact tracing
 P a g e 1 Responsibilities in a sexual relationship - Contact tracing This activity has been designed increase student familiarity with the NSW Health Play Safe website. Suggested duration: 50-60 minutes
P a g e 1 Responsibilities in a sexual relationship - Contact tracing This activity has been designed increase student familiarity with the NSW Health Play Safe website. Suggested duration: 50-60 minutes
Topic 7 Sexual & Reproductive Health
 Topic 7 Sexual & Reproductive Health Introduction The following two activities are designed for Year 8 students and are primarily focused on sexual and reproductive health information. They are adapted
Topic 7 Sexual & Reproductive Health Introduction The following two activities are designed for Year 8 students and are primarily focused on sexual and reproductive health information. They are adapted
Learning about HIV. A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum
 Learning about HIV A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of
Learning about HIV A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of
Grade 6 Sexual Health Curriculum Overview
 Grade 6 Sexual Health Curriculum Overview Rights, Respect, Responsibility The Advocates for Youth s Rights, Respect, Responsibility curriculum is based on the belief that: Youth have the right to honest
Grade 6 Sexual Health Curriculum Overview Rights, Respect, Responsibility The Advocates for Youth s Rights, Respect, Responsibility curriculum is based on the belief that: Youth have the right to honest
9p1 Identify the factors that contribute to positive relationships with others. 9p6 Describe the factors that lead to responsible sexual relationships
 Lesson Eight Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Wrapping up the Sexual Health Unit The 60 minutes * Sexuality Review-Quiz * Sexuality Review-Answer Sheet * Sexual Q & A -Laminated Game Cards * Sexual Q & A
Lesson Eight Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Wrapping up the Sexual Health Unit The 60 minutes * Sexuality Review-Quiz * Sexuality Review-Answer Sheet * Sexual Q & A -Laminated Game Cards * Sexual Q & A
UNDERSTANDING AND PREVENTING SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS
 UNDERSTANDING AND PREVENTING SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Lesson 12 DIFFERING ABILTIES LEARNER OUTCOME Describe symptoms, effects, treatments, prevention for common sexually transmitted diseases; i.e.,
UNDERSTANDING AND PREVENTING SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Lesson 12 DIFFERING ABILTIES LEARNER OUTCOME Describe symptoms, effects, treatments, prevention for common sexually transmitted diseases; i.e.,
What you need to know to: Keep Yourself SAFE!
 What you need to know to: Keep Yourself SAFE! What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? How are they spread? What are the different types of STDs? How do I protect myself? STDs are infections or diseases
What you need to know to: Keep Yourself SAFE! What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? How are they spread? What are the different types of STDs? How do I protect myself? STDs are infections or diseases
HIV/AIDS. National Survey of Teens on PUBLIC KNOWLEDGE AND ATTITUDES ABOUT HIV/AIDS
 PUBLIC KNOWLEDGE AND ATTITUDES ABOUT HIV/AIDS National Survey of Teens on THE KAISER FAMILY FOUNDATION 2000 HIV/AIDS Summary Teens today are concerned about the impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic on the nation
PUBLIC KNOWLEDGE AND ATTITUDES ABOUT HIV/AIDS National Survey of Teens on THE KAISER FAMILY FOUNDATION 2000 HIV/AIDS Summary Teens today are concerned about the impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic on the nation
ADOLESCENT SEXUALITY - SHS Anonymous Survey Results Heather Johnson
 ADOLESCENT SEXUALITY - SHS Anonymous Survey Results Heather Johnson QUICK FACTS: The #1 most spread STD in the USA is Genital Warts (HPV). The most aggressive strands can cause cervical, penile, anal and
ADOLESCENT SEXUALITY - SHS Anonymous Survey Results Heather Johnson QUICK FACTS: The #1 most spread STD in the USA is Genital Warts (HPV). The most aggressive strands can cause cervical, penile, anal and
know!!! you gotta Tips, hints, and all the info you NEED to keep yourself safe from HIV/AIDS
 you gotta know!!! Tips, hints, and all the info you NEED to keep yourself safe from HIV/AIDS Latino HIV/AIDS Behavioral Science Center University Park, PCA 356 11200 SW 8th Street, Miami, Fl, 33199 lhabsc@fiu.edu
you gotta know!!! Tips, hints, and all the info you NEED to keep yourself safe from HIV/AIDS Latino HIV/AIDS Behavioral Science Center University Park, PCA 356 11200 SW 8th Street, Miami, Fl, 33199 lhabsc@fiu.edu
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
HEALTH GRADE 11. THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618
 HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
For Utah Policymakers and Parents: Summary of Comprehensive Sexuality Education
 For Utah Policymakers and Parents: Summary of Comprehensive Sexuality Education Updated February 20, 2016 Comprehensive sexuality education is endorsed around the globe as an international right that should
For Utah Policymakers and Parents: Summary of Comprehensive Sexuality Education Updated February 20, 2016 Comprehensive sexuality education is endorsed around the globe as an international right that should
LET S TALK about Sticking with your treatment plan
 LET S TALK about Sticking with your treatment plan HOW ONGOING HIV CARE HELPS YOU LIVE A LONGER AND HEALTHIER LIFE Your treatment plan is vital to your overall health (and to reducing HIV transmission)
LET S TALK about Sticking with your treatment plan HOW ONGOING HIV CARE HELPS YOU LIVE A LONGER AND HEALTHIER LIFE Your treatment plan is vital to your overall health (and to reducing HIV transmission)
are some questions. level and Group similar of discussion. the class. somewhere! Avoid offering 1. Is ways to make mean, it means that the a healthy
 Teaching Human Sexuality Answers to Sample Questions Elementary Grade 4, 5, 6 The inquiry process is an important strategy to use for effective human sexuality classes. Here are some tips when answering
Teaching Human Sexuality Answers to Sample Questions Elementary Grade 4, 5, 6 The inquiry process is an important strategy to use for effective human sexuality classes. Here are some tips when answering
The Circles of Sexuality
 The Circles of Sexuality Source: http://www.advocatesforyouth.org/lessonplans/circlesofsexuality3.htm An Explanation of the Circles of Sexuality Sexuality is much more than sexual feelings or sexual intercourse.
The Circles of Sexuality Source: http://www.advocatesforyouth.org/lessonplans/circlesofsexuality3.htm An Explanation of the Circles of Sexuality Sexuality is much more than sexual feelings or sexual intercourse.
Contraception. My Sexual Health: Objectives. Vocabulary. Standards Wisconsin Health Education Standards
 Contraception My Sexual Health: This lesson utilizes a game to review and explore the various forms of contraception. Abstinence is included as an option. Students will analyze scenarios to identify influences
Contraception My Sexual Health: This lesson utilizes a game to review and explore the various forms of contraception. Abstinence is included as an option. Students will analyze scenarios to identify influences
20. HIV and AIDS. Objectives. How is HIV transmitted?
 20. HIV and AIDS Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Explain what HIV and AIDS are. Describe how HIV is transmitted. Explain the difference between HIV and AIDS. List
20. HIV and AIDS Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Explain what HIV and AIDS are. Describe how HIV is transmitted. Explain the difference between HIV and AIDS. List
SHOULD I HAVE A. Sexual Health Check? Information for sexually active young people and adults
 SHOULD I HAVE A Sexual Health Check? Information for sexually active young people and adults This brochure tells you about sexual health checks, including where to get them and what s involved. It may
SHOULD I HAVE A Sexual Health Check? Information for sexually active young people and adults This brochure tells you about sexual health checks, including where to get them and what s involved. It may
LARC. sample. ask brook about. Are any of them right for me? How effective is it? How long does it last? long acting reversible contraception
 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09 11:47 Page 1 Are any of them right for me? ask brook about LARC How effective is it? long acting reversible contraception How long does it last? 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09
72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09 11:47 Page 1 Are any of them right for me? ask brook about LARC How effective is it? long acting reversible contraception How long does it last? 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09
Review and Resources Grades 4-6, Lesson #18
 Review and Resources Grades 4-6, Lesson #18 Time Needed 50-60 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Recognize the definitions of at least 90% of the vocabulary introduced in the unit.
Review and Resources Grades 4-6, Lesson #18 Time Needed 50-60 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Recognize the definitions of at least 90% of the vocabulary introduced in the unit.
Sexual Health Jeopardy - Instructions
 1 Sexual Health Jeopardy - Instructions First, choose which topics you wish to cover. You can choose to play with all 10 topics if you have a longer period of time, or you can select as many topics as
1 Sexual Health Jeopardy - Instructions First, choose which topics you wish to cover. You can choose to play with all 10 topics if you have a longer period of time, or you can select as many topics as
How important do you think abstinence is? Very important- 38% Sort of important- 46% Not that important- 16%
 I S H Anonymous Survey Results Have you made a decision to not have sex during your years of high school or longer? Yes- 38% No- 28% Still Deciding- 34% Have you set your sexual limits? Yes- 56% No- 7%
I S H Anonymous Survey Results Have you made a decision to not have sex during your years of high school or longer? Yes- 38% No- 28% Still Deciding- 34% Have you set your sexual limits? Yes- 56% No- 7%
Getting to know. STBBIs. itss.gouv.qc.ca
 Getting to know STBBIs itssgouvqcca 2A STBBIs are Sexually Transmitted and Blood-Borne Infections (STBBIs) They include the following: chlamydia gonorrhoea syphilis genital herpes hepatitis B and hepatitis
Getting to know STBBIs itssgouvqcca 2A STBBIs are Sexually Transmitted and Blood-Borne Infections (STBBIs) They include the following: chlamydia gonorrhoea syphilis genital herpes hepatitis B and hepatitis
Contraceptives. Kim Dawson October 2010
 Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
CALM LEARNER OUTCOMES 1 :
 CALM STI AND HIV LESSON 2 STI AND HIV Lesson 2 GRADE CALM LEARNER OUTCOMES 1 : Examine aspects of healthy sexuality, sexual wellness and responsible sexual behaviour. Describe sexually healthy choices
CALM STI AND HIV LESSON 2 STI AND HIV Lesson 2 GRADE CALM LEARNER OUTCOMES 1 : Examine aspects of healthy sexuality, sexual wellness and responsible sexual behaviour. Describe sexually healthy choices
Child & Adolescent flipchart for HIV Testing, Disclosure & Adherence Counselling
 Child & Adolescent flipchart for HIV Testing, Disclosure & Adherence Counselling Target group Children & adolescents in need of HIV testing, disclosure or adherence counselling, and their caregivers. Use
Child & Adolescent flipchart for HIV Testing, Disclosure & Adherence Counselling Target group Children & adolescents in need of HIV testing, disclosure or adherence counselling, and their caregivers. Use
STI & HIV PRE-TEST ANSWER KEY
 Name: STI & HIV PRE-TEST ANSWER KEY 1. You can catch a STI or HIV from door knobs, toilet seats, or FALSE drinking fountains. STIs are transmitted sexually, requiring sexual contact. Some STIs can be transmitted
Name: STI & HIV PRE-TEST ANSWER KEY 1. You can catch a STI or HIV from door knobs, toilet seats, or FALSE drinking fountains. STIs are transmitted sexually, requiring sexual contact. Some STIs can be transmitted
Curriculum Outline For Health. Health Classes 10 th Grade
 Health Classes 10 th Grade Understanding Health and Wellness Your Total Health What Affects Your Health Health Risks and Your Behavior Promoting Health and Wellness Making Responsible Decisions and Setting
Health Classes 10 th Grade Understanding Health and Wellness Your Total Health What Affects Your Health Health Risks and Your Behavior Promoting Health and Wellness Making Responsible Decisions and Setting
Lesson Sixteen Questions, Summary and Assessment
 Lesson Sixteen Questions, Summary and Assessment Lesson Overview Students are given the opportunity to ask any questions they have regarding sex and human growth and development. They are then given a
Lesson Sixteen Questions, Summary and Assessment Lesson Overview Students are given the opportunity to ask any questions they have regarding sex and human growth and development. They are then given a
Sexual Q & A Game - Birth Control cards - From 5 to 100 Points
 Lesson Eight Sexual Q & A Game - Birth Control cards - From 5 to 100 Points Sexual Jeopardy Birth Control for 10 Points The only 100% effective method for preventing pregnancy and STIs Sexual Jeopardy
Lesson Eight Sexual Q & A Game - Birth Control cards - From 5 to 100 Points Sexual Jeopardy Birth Control for 10 Points The only 100% effective method for preventing pregnancy and STIs Sexual Jeopardy
Teacher Guide For Problem Solving Scenarios. Activity STI and Birth Control
 This lesson contains information that can sometimes make both teachers and students feel embarrassed or uncomfortable. In order to diminish these feelings, some educators find it helpful to provide students
This lesson contains information that can sometimes make both teachers and students feel embarrassed or uncomfortable. In order to diminish these feelings, some educators find it helpful to provide students
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS. fallopian tube instead of the uterus), constant pelvic pain, and other problems.
 PID can be treated and cured with Pelvic antibiotics. If left untreated, PID can lead to serious problems like infertility (not being able to get pregnant), ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy in the Inflammatory
PID can be treated and cured with Pelvic antibiotics. If left untreated, PID can lead to serious problems like infertility (not being able to get pregnant), ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy in the Inflammatory
Power Point Use in EBPs. CAPP & PREP Learning Community May 15, 2018
 Power Point Use in EBPs CAPP & PREP Learning Community May 15, 2018 Objectives Best practices for power point use Why use power point for EBP delivery Examples: the Good, the Bad and the Ugly Recommendations
Power Point Use in EBPs CAPP & PREP Learning Community May 15, 2018 Objectives Best practices for power point use Why use power point for EBP delivery Examples: the Good, the Bad and the Ugly Recommendations
UNDERSTANDING SEXUAL HEALTH AND RISK.
 UNDERSTANDING SEXUAL HEALTH AND RISK. HIV Sexual Health STIs AIDS Semen Violence HIV transmission Sexual activities 25 minutes To understand the different modes of transmission of HIV. To understand risk
UNDERSTANDING SEXUAL HEALTH AND RISK. HIV Sexual Health STIs AIDS Semen Violence HIV transmission Sexual activities 25 minutes To understand the different modes of transmission of HIV. To understand risk
Quiz: Harm Reduction with Latex
 Quiz: Harm Reduction with Latex Name (first name only): Date: 1. HIV can be sexually-transmitted by exchanging which of the following body fluids: a. semen b. vaginal secretions c. blood d. all of the
Quiz: Harm Reduction with Latex Name (first name only): Date: 1. HIV can be sexually-transmitted by exchanging which of the following body fluids: a. semen b. vaginal secretions c. blood d. all of the
A Teacher s Guide Sexually
 sue 3. Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. milk. ed every year. ow stopthesilence TeenZine ol, even once, can Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. men who don't use me pregnant. s. chlamydia.,ghest can among 15 to Contraceptives
sue 3. Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. milk. ed every year. ow stopthesilence TeenZine ol, even once, can Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. men who don't use me pregnant. s. chlamydia.,ghest can among 15 to Contraceptives
Ask at Least Annually. Ask Older Adults. Have you been sexually active in the last year? Have you ever been sexually active?
 Essential Sexual Health Questions to Ask Adults Ask all of your adult patients the sexual health questions on this card. They will help you assess the patient s level of sexual risk and determine whether
Essential Sexual Health Questions to Ask Adults Ask all of your adult patients the sexual health questions on this card. They will help you assess the patient s level of sexual risk and determine whether
