Gender Development and Sexuality
|
|
|
- Bridget Harper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gender Development and Sexuality Reading: Chapter 12 Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 1 Gender Development and Sexuality I. Male/Female Difference Sex and Gender Dimensions of Male/Female Difference Conceptualizing Gender Roles II. Theories of Gender Development Evolutionary Psychology Social Role Theory Psychoanalytic Theory Social Cognitive Theory Cognitive-developmental Theory Gender Schema Theory Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 2
2 Gender Development and Sexuality III. Highlights of Gender Development Infancy and Childhood Adolescence Adulthood and Aging IV. Sexuality and Aging Changes in Frequency of Sexual Activity Reasons for the Decline V. A Bio-psycho-social-developmental Model of Gender and Sexuality Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 3 I. Male/Female Difference Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 4
3 Sex and Gender Sex: Gender: Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 5 Dimensions of Male/Female Difference Dimension 1. Genetic Sex Sex chromosomes 2. Gonadal Sex Gonads -reproductive - sex glands 3. Hormonal Sex Sex hormones Female XX Ovaries Egg cells (ova) Estrogen Progesterone Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 6 Male XY Testes Sperm Androgen Testosterone
4 Dimensions of Male/Female Difference Dimension 4. Genital Sex External genitals Primary sexual characteristics 5. Internal Sexual Organs Female Vulva, clitoris, vaginal opening Uterus, vagina, fallopian tubes, etc. Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 7 Male Penis, scrotum Prostate, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, etc. Video Clip - Nova: Messages in the Genes (to 3:14) Dimensions of Male/Female Difference Dimension 6. Secondary Sexual Characteristics Female Pubic hair, hips widen, breasts develop, etc. 7. Gender Identity I m a girl I m a woman 8. Gender Roles Gender stereotypes Feminine Expressive role Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 8 Male Pubic, facial hair; voice deepens, penis enlarges, etc. I m a boy I m a man Masculine Instrumental role
5 Conceptualizing Gender Roles Older theories one dimension: Masculine Feminine Current two separate dimensions: High Masculine Low Masculine High Feminine Low Feminine The Bem Sex-Role Inventory (BSRI): common measure of the two gender dimensions allows four possible gender statuses: Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 9 Bem Sex Role Inventory 1.self reliant 2.yielding 3.helpful 4.likable 5.cheerful 6.moody 7.independent 8.shy 9.conscientious 10.athletic 11.affectionate 12.theatrical 13.assertive 14.flatterable 15.happy 16.reliable 17.loyal 18.unpredictable 19.forceful 20.feminine 21.strong personality 22.analytical 23.sympathetic 24.willing to take a stand 25.leadership ability 26.sensitive to other's needs 27.truthful 28.willing to take risks 29.understanding 30.acts as a leader 31.makes decisions easily 32.compassionate 33.sincere 34.self-sufficient 35.eager to soothe hurt feelings 36.does not use harsh language 37.dominant 38.soft spoken 39.defends own beliefs 40.masculine Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # warm 42.solemn 43.jealous 44.tender 45.friendly 46.aggressive 47.gullible 48.inefficient 49.secretive 50.childlike 51.adaptable 52.individualistic 53.conceited 54.unsystematic 55.competitive 56.loves children 57.tactful 58.ambitious 59.gentle 60.conventional
6 Conceptualizing Gender Roles Low Feminine (not expressive) High Feminine (expressive) Low Masculine (not instrumental) Undifferentiated Femininity (Feminine) Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 11 High Masculine (instrumental) Masculinity (Masculine) Androgyny (Androgynous) II. Theories of Gender Development Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 12
7 Evolutionary Psychology Natural selection and pressures to adapt early in human history led to psychological and social differences between the sexes Example: Males prefer competition and multiple sexual partners to maximize reproduction Females prefer cooperation and monogamy to insure survival of self and offspring Video clip: Female-male brain differences and love (1:25) Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 13 Social Role Theory Psychological gender differences arise from the different societal roles of men and women In most cultures, men have more economic power and social status, so men adapt by being more assertive, competitive, and goal-oriented and women adapt by becoming more cooperative and nurturing Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 14
8 Psychoanalytic Theory Emphasizes unconscious processes and childhood experience To resolve unconscious sexual conflicts, preschool children develop a sense of gender appropriate behavior though identification with the same-sex parent Gender ideals are part of the superego (a mental representation of society s rules) Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 15 Social Cognitive Theory Children learn gender-role behavior through differential reinforcement and punishment and through observation and imitation of gender behavior of social models Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 16
9 Cognitive-developmental Theory Gender-role behavior stems from gender concept Concept develops in phases: label self as boy or girl later understand gender stable over time finally understand gender constant across situations Video Clip: Development of Gender Concepts (2:12) Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 17 Gender Schema Theory Gender Schema: cognitive structure organizes one s thoughts, concepts regarding gender filter for information processing influences attention, perception, memory Children self-socialize letting schemata guide choices to conform to gender norms Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 18
10 Gender Schema Theory: An Illustration For whom? Truck For boys Doll Gender identity (I m a girl) For whom? For girls Therefore Not for me So So For me Therefore Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 19 Avoid; forget Own sex schema Approach; gather information; remember information III. Highlights of Gender Development Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 20
11 Infancy and Childhood Differential treatment begins at birth Boys usually more intense gender socialization Basic gender identity 2-3 yrs old Concept that gender is stable, constant trait 3-7 yrs old Superego ages 3-6 Grade school children segregate by sex Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 21 During the grade school years, girls and boys tend to strongly prefer their own group Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 22
12 Adolescence Biological changes (puberty) + cognitive advances lead to heightened awareness of gender Gender intensification hypothesis: psychological and behavioral differences between boys and girls become greater during early adolescence because of increased socialization pressures to conform to traditional gender roles Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 23 Adulthood and Aging Debra Tannen: differences in male/female communications rapport talk conversational language establishing connections, relationships women tend to use this style more report talk give information get attention thru stories, jokes, etc. men tend to use this style more Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 24
13 Adulthood and Aging David Gutmann: parental imperative : bearing/raising children pushes men and women toward traditional gender roles once parental imperative ends, men and women take on more opposite-gender traits become more androgynous research shows: couples tend to be more equal in household duties before children, assume more traditional division of labor after having children Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 25 Adulthood and Aging men somewhat more likely to become more expressive than women are to become more instrumental older adults most likely of all age groups to score androgynous on BSRI may be some cohort effects since gender roles have changed in recent decades Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 26
14 IV. Sexuality and Aging Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 27 Frequency of Sexual Activity 85%-90% of yr olds sexually active Begins to decline in late middle age (to ~ 30% after age 70) Percent of U.S. adults of different ages who reported having at least one sexual partner in the past year. Men higher levels sexual activity thru later life than women Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 28
15 Percent Men and Women Reporting Sexual Intercourse by Age Age Age Not at all Once a month Once a week times a week Men Women 21 Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # >2-3 times a week % sexually active Reasons for Age Declines in Sexual Activity Major reason - lack of available, acceptable sexual partners especially problematic for aging women: aging male partner more likely older and in ill health more likely to be widowed female to male sex ratio increases Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 30
16 Population of the U.S. by age and sex. Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 31 Reasons for Age Declines in Sexual Activity Negative attitudes against elderly sexual activity may place restraints on activity become self-fulfilling Declines in physical health Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 32
17 Percent men and women age in good and poor health who report being sexually active Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 33 Lindau et al., 2007 Reasons for Age Declines in Sexual Activity Previous levels of sexual activity: those who are more sexually active in younger, middle adulthood more likely to maintain sexual activity in old age use it or lose it Physiological changes in sexual functioning generally not drastic; can usually be treated or compensated for Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 34
18 V. A Bio-psycho-social Developmental Model of Gender and Sexuality See handout Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 35 A Bio-psycho-social Developmental Model of Gender and Sexuality Biological Influences Prenatal: Genetic predispositions Prenatal hormonal influences Primary sexual characteristics Postnatal: Biological maturation Hormone balance Secondary sexual characteristics Functioning of sexual anatomy Anatomical alterations / medical interventions Social Influences, Culture, and Developmental Context Treatment by and social modeling by parents, other adults, siblings, and peers Media influences Gender-role norms and stereotypes Sexual norms of culture Age norms for sexual behavior Psychological Structures Gender identity Gender schemata Superego / psychosexual stage Gender stereotyping, bias, sexism Sexual identity/orientation Sexual scripts Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 36 Behavior Gender-role behaviors Treatment of others Choice of sexual partners Frequency of sexual activity Choice of sexual activities Use of medication or sexual aids
19 Any Questions on Chapter 12? Lecture: Gender Development and Sexuality (Ch 12) - slide # 37
-There are 2 aspects of sex: genetic sex and anatomical sex. In women, the sex chromosomes are XX. In men, the sex chromosomes are XY.
 111 Chapter 7 Gender Sex vs. Gender sex -refers to biological maleness or femaleness -There are 2 aspects of sex: genetic sex and anatomical sex 1. genetic sex -determined by the sex chromosomes In women,
111 Chapter 7 Gender Sex vs. Gender sex -refers to biological maleness or femaleness -There are 2 aspects of sex: genetic sex and anatomical sex 1. genetic sex -determined by the sex chromosomes In women,
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
Growth and Development 6 th Grade
 Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Sex! Woo Hoo! Finally something interesting!
 Sex! Woo Hoo! Finally something interesting! Males: born with Primary Sex Characteristics like a penis, testes, a scrotum, and a prostate Females: Primary Sex Characteristics include a vagina, a uterus,
Sex! Woo Hoo! Finally something interesting! Males: born with Primary Sex Characteristics like a penis, testes, a scrotum, and a prostate Females: Primary Sex Characteristics include a vagina, a uterus,
Gender. 7 Gender, Gender Identity, and Transgender
 7 Gender 7 Gender, Gender Identity, and Transgender Gender refers to the entire constellation of mental and behavioral traits that differ in males and females; it permeates every aspect of our lives. Gender
7 Gender 7 Gender, Gender Identity, and Transgender Gender refers to the entire constellation of mental and behavioral traits that differ in males and females; it permeates every aspect of our lives. Gender
Gender and Sexuality. Views of Gender. Gender and Sex. Evolutionary Social Cognitive. Gender social dimension of being female or male
 Gender and Sexuality Gender and Sex Gender social dimension of being female or male Gender role: set of expectations prescribing how females and males should act, feel, and think Gender typing: process
Gender and Sexuality Gender and Sex Gender social dimension of being female or male Gender role: set of expectations prescribing how females and males should act, feel, and think Gender typing: process
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 Quiz: Evolution Human Reproduction Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember:
Quiz: Evolution Human Reproduction Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember:
2. Which male target tissues respond to testosterone, and which require dihydrotestosterone?
 308 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 56 Male Pseudohermaphroditism: Sa-Reductase Deficiency Fourteen years ago, Wally and Wanda Garvey, who live in rural North Carolina, had their first child. The baby
308 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 56 Male Pseudohermaphroditism: Sa-Reductase Deficiency Fourteen years ago, Wally and Wanda Garvey, who live in rural North Carolina, had their first child. The baby
PSYCHOLOGICAL ANDROGYNY AND ATTITUDES TOWARDS FEMALES IN SPORTS
 PSYCHOLOGICAL ANDROGYNY AND ATTITUDES TOWARDS FEMALES IN SPORTS Cynthia B. Disotell Ball State University Muncie, Indiana 47306 '.. . Speoll '1"\1eSI :J LO ~!.izq J t.+, f, PSYCHOLOGICAL ANDROGYlN AND
PSYCHOLOGICAL ANDROGYNY AND ATTITUDES TOWARDS FEMALES IN SPORTS Cynthia B. Disotell Ball State University Muncie, Indiana 47306 '.. . Speoll '1"\1eSI :J LO ~!.izq J t.+, f, PSYCHOLOGICAL ANDROGYlN AND
STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases)
 Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
Theoretical Perspectives on Gender. Gender Identity. Gender Identity. Gender Identity. Middle Childhood. Sense of being masculine or feminine
 Sense of being masculine or feminine Well established by preschool years Theoretical Perspectives on Gender Biological Inborn, genetic factors produce gender differences By age 2 years: Consistently label
Sense of being masculine or feminine Well established by preschool years Theoretical Perspectives on Gender Biological Inborn, genetic factors produce gender differences By age 2 years: Consistently label
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
Gender Dimorphism. Lecture 35
 Gender Dimorphism Lecture 35 1 Aspects of Gender Dimorphism Biological Sex Gender Identity Gender Role Sexual Orientation 2 The Human Genome National Geographic 3 Caster Semenya Gold Medal, 800m Race World
Gender Dimorphism Lecture 35 1 Aspects of Gender Dimorphism Biological Sex Gender Identity Gender Role Sexual Orientation 2 The Human Genome National Geographic 3 Caster Semenya Gold Medal, 800m Race World
Motivation IV Sexual Motivation Sexual Reproduction Reproduction is necessary for the survival of the species. Some organisms (e.g., bacteria) reprodu
 Motivation IV Sexual Motivation Sexual Reproduction Reproduction is necessary for the survival of the species. Some organisms (e.g., bacteria) reproduce asexually. Sexual reproduction allows the genes
Motivation IV Sexual Motivation Sexual Reproduction Reproduction is necessary for the survival of the species. Some organisms (e.g., bacteria) reproduce asexually. Sexual reproduction allows the genes
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
Transformation Information elearning Kit Combined Program Lesson Plan Page 1. LESSON TITLE: Combined Program
 Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2008 Bios 90
 Sexual Differentiation Fall 2008 Bios 90 Jennifer Swann, Professor Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Asexual reproduction Budding : offspring develop as a growth on the body of the parent jellyfishes, echinoderms,
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2008 Bios 90 Jennifer Swann, Professor Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Asexual reproduction Budding : offspring develop as a growth on the body of the parent jellyfishes, echinoderms,
11/29/2017. Gender is salient and, not surprisingly, important. Boys and girls have play preferences: By 4 years of age:
 is salient and, not surprisingly, important. Boys and girls have play preferences: By 4 years of age: same sex playfriends social orientations (type of play) What causes these preferences? How does sex-typed
is salient and, not surprisingly, important. Boys and girls have play preferences: By 4 years of age: same sex playfriends social orientations (type of play) What causes these preferences? How does sex-typed
Growing up. W Worksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts
 3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
= add definition here. Definition Slide
 = add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Developmental Psychology = a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span. Zygote = the fertilized
= add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Developmental Psychology = a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span. Zygote = the fertilized
Bios 90/95. Jennifer Swann, PhD
 Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
Title: Sex & Gender Specification: Sex and gender. Sex-role stereotypes. Androgyny and measuring androgyny including the Bem Sex Role Inventory.
 Title: Sex & Gender Specification: Sex and gender. Sex-role stereotypes. Androgyny and measuring androgyny including the Bem Sex Role Inventory. Q1 Define the term androgyny. (2 marks) When an individual
Title: Sex & Gender Specification: Sex and gender. Sex-role stereotypes. Androgyny and measuring androgyny including the Bem Sex Role Inventory. Q1 Define the term androgyny. (2 marks) When an individual
Martin Ritzén. bioscience explained Vol 7 No 2. Girl or boy: What guides gender development and how can this be a problem within
 Martin Ritzén Professor emeritus, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Girl or boy: What guides gender development and how can this be a problem within sport? Introduction During the 2009 athletics
Martin Ritzén Professor emeritus, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Girl or boy: What guides gender development and how can this be a problem within sport? Introduction During the 2009 athletics
Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty
 Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Puberty For Boys Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty 70 minutes Preparing To Teach About Puberty - Teacher Guide Anatomy Review - Teacher Guide Bernie (male
Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Puberty For Boys Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty 70 minutes Preparing To Teach About Puberty - Teacher Guide Anatomy Review - Teacher Guide Bernie (male
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
Genes: Our Biological Blueprint
 Nature--Nurture Genes: Our Biological Blueprint Chromosomes threadlike structures made of DNA that contain the genes DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) complex molecule containing the genetic information that
Nature--Nurture Genes: Our Biological Blueprint Chromosomes threadlike structures made of DNA that contain the genes DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) complex molecule containing the genetic information that
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
NAKED How to understand teenagers x 6 min. minutes
 NAKED How to understand teenagers 2007 6 x 6 min. minutes Program Synopsis: This innovative series of six, six-minute documentaries hears from teens about various issues confronting them at puberty. Breasts,
NAKED How to understand teenagers 2007 6 x 6 min. minutes Program Synopsis: This innovative series of six, six-minute documentaries hears from teens about various issues confronting them at puberty. Breasts,
Defining Sex and Gender & The Biology of Sex
 Defining Sex and Gender & The Biology of Sex Today: -Defining Sex and Gender -Conception of a Child -Chromosomes -Defects in Chromosomes Often we hear the terms sex and gender used in our society interchangeably,
Defining Sex and Gender & The Biology of Sex Today: -Defining Sex and Gender -Conception of a Child -Chromosomes -Defects in Chromosomes Often we hear the terms sex and gender used in our society interchangeably,
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 10 Sex, Gender, and Sexuality 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 1 10.1 How Does Biology Make Us Male or Female?
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 10 Sex, Gender, and Sexuality 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 1 10.1 How Does Biology Make Us Male or Female?
Chapter 18 Development. Sexual Differentiation
 Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Body Wise. Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only
 Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Topic 13 Sex. Being Male and Female
 Topic 13 Sex Being Male and Female Reproduction Asexual (1 individual): more efficient, low genetic variation Sexual: prevalent (2 sexes, separate or not) High genetic variation, need 2 Approaches: External
Topic 13 Sex Being Male and Female Reproduction Asexual (1 individual): more efficient, low genetic variation Sexual: prevalent (2 sexes, separate or not) High genetic variation, need 2 Approaches: External
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Grade 6 Reproduction Review
 Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 16 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 16 1 Chapter in Review 1. Human sexuality includes sex, gender, and sexual behavior. Determining sex at birth includes chromosomal, gonadal, hormonal, and anatomical factors.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 16 1 Chapter in Review 1. Human sexuality includes sex, gender, and sexual behavior. Determining sex at birth includes chromosomal, gonadal, hormonal, and anatomical factors.
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
1. How many parents are involved in sexual reproduction? 2. What are the male and female sex cells called?
 Warm up (3 minutes) 1. Pick up a warm up 2. Pick up the student work from the front table 3. Pick up your binder in the filing cabinet 4. Complete the warm up 5. Secure all handouts in your binder 1. How
Warm up (3 minutes) 1. Pick up a warm up 2. Pick up the student work from the front table 3. Pick up your binder in the filing cabinet 4. Complete the warm up 5. Secure all handouts in your binder 1. How
Let s Talk About Hormones!
 Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY
 HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
Gender and Sexuality. Chapter 4 6/30/2010. Gender Development. Gender Differences in Aggression
 Gender and Sexuality Chapter 4 Gender Development Based on genetic makeup, males and females are alike, since the majority of our inherited genes (45 chromosomes are unisex) are similar. Males and females
Gender and Sexuality Chapter 4 Gender Development Based on genetic makeup, males and females are alike, since the majority of our inherited genes (45 chromosomes are unisex) are similar. Males and females
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
The Reproductive System
 C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
to ensure the. Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion of.
 The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY
 Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Nature and Nurture. What makes us who we are?
 Nature and Nurture What makes us who we are? Chromosomes- threadlike structures made up of DNA that contain genes. Chromosome pair 23 define our gender. How is Gender inherited? Mother can only give X
Nature and Nurture What makes us who we are? Chromosomes- threadlike structures made up of DNA that contain genes. Chromosome pair 23 define our gender. How is Gender inherited? Mother can only give X
Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth
 Revised January 2017 Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth Lesson Goals Explain the Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproduction Systems Review Proper Vocabulary for the
Revised January 2017 Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth Lesson Goals Explain the Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproduction Systems Review Proper Vocabulary for the
Sexual Development. 6 Stages of Development
 6 Sexual Development 6 Stages of Development Development passes through distinct stages, the first of which is fertilization, when one sperm enters one ovum. To enter an ovum, a sperm must undergo the
6 Sexual Development 6 Stages of Development Development passes through distinct stages, the first of which is fertilization, when one sperm enters one ovum. To enter an ovum, a sperm must undergo the
CHAPTER 11: GENDER AND SEXUALITY
 CHAPTER 11: GENDER AND SEXUALITY Gender & Sexuality Jeopardy Category 1 Category 2 Category 3 Category 4 5 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500
CHAPTER 11: GENDER AND SEXUALITY Gender & Sexuality Jeopardy Category 1 Category 2 Category 3 Category 4 5 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500
Psychology. P.1.1 List and explain the reasons for studying the methodology of psychology.
 Standard 1: The Scientific Method Students will understand the development of psychology as an empirical science by describing the scientific method, explaining research strategies, and identifying ethical
Standard 1: The Scientific Method Students will understand the development of psychology as an empirical science by describing the scientific method, explaining research strategies, and identifying ethical
Transitional Phases in childhood Dr Jeané Cloete
 Transitional Phases in childhood Dr Jeané Cloete Children Their development is our future! Children are the touchstone of a healthy and sustainable society. How a culture or society treats its youngest
Transitional Phases in childhood Dr Jeané Cloete Children Their development is our future! Children are the touchstone of a healthy and sustainable society. How a culture or society treats its youngest
Name Class Date. Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter.
 Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Endocrine System and Reproductive System
 Endocrine System and Reproductive System Quick Notes: Endocrine System Reproductive System Responsible for growth and development of the human body Responsible for continuing the species Big Question:
Endocrine System and Reproductive System Quick Notes: Endocrine System Reproductive System Responsible for growth and development of the human body Responsible for continuing the species Big Question:
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System. Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems
 Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
The Reproductive System Responsibility: Continue the species Structure: Pair of Gonads Accessory organs, ducts, hormones, etc.
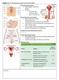 Chapter 11: The Reproductive System and Sexual Health The Reproductive System Responsibility: Continue the species Structure: Pair of Gonads Accessory organs, ducts, hormones, etc. Sexual Autonomy and
Chapter 11: The Reproductive System and Sexual Health The Reproductive System Responsibility: Continue the species Structure: Pair of Gonads Accessory organs, ducts, hormones, etc. Sexual Autonomy and
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Year Five. God loves me in my changing and development. 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5
 Year Five God loves me in my changing and development 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5 Objectives * Know that as we grow we will become different in our bodies feelings love of God 2 A Journey in Love - Year
Year Five God loves me in my changing and development 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5 Objectives * Know that as we grow we will become different in our bodies feelings love of God 2 A Journey in Love - Year
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the Nevada Constitution by repealing the limitation on the recognition of marriage.
 Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada. 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada. 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Overview of Health Curriculum:
 USD 383 Manhattan-Ogden Health Curriculum Map Welcome to the curriculum design maps for Manhattan-Ogden USD 383, striving to produce learners who are: Effective Communicators who clearly express ideas
USD 383 Manhattan-Ogden Health Curriculum Map Welcome to the curriculum design maps for Manhattan-Ogden USD 383, striving to produce learners who are: Effective Communicators who clearly express ideas
Lecture 15 (Nov 16 th ): Hormones and Sexual Behavior Lecture Outline. 4) Gender Phenotype : Organizing Effects of Sex Hormones in Utero and Anomalies
 Lecture 15 (Nov 16 th ): Hormones and Sexual Behavior Lecture Outline 1) Organs / Glands / Hormonal Communication 2) Sex Hormones: Male vs. Female 3) Genetic Gender (XX, XY) 4) Gender Phenotype : Organizing
Lecture 15 (Nov 16 th ): Hormones and Sexual Behavior Lecture Outline 1) Organs / Glands / Hormonal Communication 2) Sex Hormones: Male vs. Female 3) Genetic Gender (XX, XY) 4) Gender Phenotype : Organizing
Lecture Series: Pregnancy
 Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Standard 3 Cognition Students will understand how organisms adapt to their environment through learning, information processing and memory.
 PSYCHOLOGY This course provides students the opportunity to explore psychology as the scientific study of mental processes and behavior. Areas of study include the scientific method, development, cognition,
PSYCHOLOGY This course provides students the opportunity to explore psychology as the scientific study of mental processes and behavior. Areas of study include the scientific method, development, cognition,
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION
 Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION Chapter Summary The male and female reproductive systems produce the sperm and eggs, and promote their meeting and fusion, which results in a fertilized egg.
Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION Chapter Summary The male and female reproductive systems produce the sperm and eggs, and promote their meeting and fusion, which results in a fertilized egg.
Psychology study guide chapter 4
 Psychology study guide chapter 4 Behavior genetics Study how heredity and environment contribute to human differences Genes Building blocks of heredity and development Part of DNA in nucleus Chromosomes
Psychology study guide chapter 4 Behavior genetics Study how heredity and environment contribute to human differences Genes Building blocks of heredity and development Part of DNA in nucleus Chromosomes
17. Sex. Being Male and Female
 17. Sex Being Male and Female Reproduction Asexual: more efficient (Only 1 sex) Low genetic variation Sexual: prevalent (2 sexes, separate or not) High genetic variation Need 2 members of the same species
17. Sex Being Male and Female Reproduction Asexual: more efficient (Only 1 sex) Low genetic variation Sexual: prevalent (2 sexes, separate or not) High genetic variation Need 2 members of the same species
TESTOSTERONE DEFINITION
 DEFINITION A hormone that is a hydroxyl steroid ketone (C19H28O2) produced especially by the testes or made synthetically and that is responsible for inducing and maintaining male secondary sex characteristics.
DEFINITION A hormone that is a hydroxyl steroid ketone (C19H28O2) produced especially by the testes or made synthetically and that is responsible for inducing and maintaining male secondary sex characteristics.
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Communication Skills. Part Ill
 From Comprehensive Counseling for Reproductive Health Participant s Handbook 2003 EngenderHealth Part Ill Communication Skills Good counseling requires good communication skills. The abilities to establish
From Comprehensive Counseling for Reproductive Health Participant s Handbook 2003 EngenderHealth Part Ill Communication Skills Good counseling requires good communication skills. The abilities to establish
Chapter 4 Nature, Nurture, and Human Diversity
 Chapter 4 Nature, Nurture, and Human Diversity Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences The topics in the text: 1.genes 2.twin and adoption studies 3.temperament and heredity 4.gene/environment
Chapter 4 Nature, Nurture, and Human Diversity Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences The topics in the text: 1.genes 2.twin and adoption studies 3.temperament and heredity 4.gene/environment
