HEALTH GRADE 11. THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618
|
|
|
- Job Armstrong
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The Ewing Public Schools Policy 2230, Course Guides, this curriculum has been reviewed and found to be in compliance with all policies and all affirmative action criteria.
2 Table of Contents Page Unit 1: Healthy Relationships and Family Dynamics 1 Unit 2: Human Reproduction 3 Unit 3: Pregnancy, Birth and Parenthood 6 Unit 4: Contraception 9 Unit 5: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) 11
3 Unit 1: Healthy Relationships and Family Dynamics 1 Why Is This Unit Important? Students will learn the overall importance of healthy relationships and family dynamics. The key points that students will emphasize during this unit are the traits that make a healthy family, the responsibility of marriage and the signs of an unhealthy relationship. Enduring Understanding 1. Students will learn how to form healthy relationships and will be aware of signs of an unhealthy/abusive relationship. 2. Students will learn the signs of a healthy family and the different types of family structure. 3. Students will learn the responsibilities associated with maintaining a successful marriage and family. Essential Questions 1. What are the different types of relationships and the characteristics associated with those relationships? 2. What are the signs of an unhealthy/abusive relationship? 3. Where are some places you could go to get help if you or a friend were involved in an unhealthy relationship? 4. What are traits associated with having and maintaining a healthy marriage? Acquired Knowledge: Students will understand/identify/discuss the following: 1. Relationships 2. Abusive relationship 3. Nuclear family 4. Couple family 5. Single parent family 6. Extended family 7. Dysfunctional family 8. Marriage 9. Physical abuse 10. Emotional abuse 11. Mental abuse 12. Verbal abuse 13. Sexual abuse 14. Neglect 15. Divorce
4 Acquired Skills 2 1. How to recognize when there is a problem in a relationship and how to recognize the qualities of a good, healthy relationship 2. Students will learn how to cope with abusive relationships and the various resources available for help 3. How to recognize the different types of families 4. Students gain an understanding of the accumulating and understanding responsibilities of marriage or a long-term relationship Assessments 1. Marriage project 2. Family structure quiz 3. Class participation 4. Video worksheet Teacher Resources 1. Video: Enough List of Applicable NJCCS: 2.2 Integrated Skills: All students will develop and use personal and interpersonal skills to support a healthy, active lifestyle 2.4 Human Relationships and Sexuality: All students will acquire knowledge about the physical, emotional, and social aspects of human relationships and sexuality and apply these concepts to support a healthy, active lifestyle
5 Unit 2: Human Reproduction 3 Why Is This Unit Important? Students will gain an understanding of the human reproductive systems. The key points that students will be encouraged to emphasize is the understanding of the reproductive system structure and how the reproductive systems function. Students will also be instructed on the various problems or complications that can occur within the human reproductive systems. Enduring Understanding 1. Students will become familiar with the parts and functions of the female reproductive systems 2. Students will become familiar with the parts and functions of the male reproductive systems 3. Students will gain an understanding of diseases and disorders that accompany the reproductive systems and the ways of how early detection can be beneficial Essential Questions 1. What are the internal and external parts of the male reproductive system and their various functions? 2. What are the internal and external parts of the female reproductive system and their various functions? 3. What are the most common disorders that affect the female and male reproductive systems and what are the signs and symptoms associated with these disorders? Acquired Knowledge: Students will understand/identify/discuss the following: 1. Penis 2. Scrotum 3. Testicle 4. Prostate 5. Vas Deferens 6. Epididymis 7. Rectum 8. Seminal vesicles 9. Foreskin 10. Circumcision 11. Bladder 12. Cowper s gland 13. Urethra 14. Sperm
6 15. Semen 16. Erection 17. Nocturnal emission 18. Testicular injury 19. Testicular torsion 20. Inflammation of the penis 21. Prostate cancer 22. Testicular cancer 23. Ovaries 24. Ovulation 25. Mons pubis 26. Labia major 27. Labia minor 28. Clitoris 29. Urethral opening 30. Vaginal opening 31. Vagina 32. Uterus 33. Fallopian tubes 34. Uterine lining 35. Ovum/Egg 36. Cervix 37. Vulva 38. Pre-Menstrual Syndrome (PMS) 39. Vaginitis 40. Ovarian cancer 41. Cervical cancer 42. Ovarian cysts 43. Menstruation 44. Menopause 45. Menstrual cycle 46. Cilia 47. Fimbria 48. Toxic shock syndrome 4 Acquired Skills 1. Recognize the anatomy of the human reproductive systems and the proper functions of the various parts 2. Recognize the disorders and diseases associated with the male reproductive system 3. Recognize the disorders and diseases associated with the female reproductive system 4. Students will learn how to deal and cope with the various disorders and disease associated with the human reproductive systems
7 Assessments 5 1. Male reproductive system quiz 2. Male reproductive system paragraph worksheet 3. Male reproductive system crossword worksheet 4. Female reproductive system paragraph worksheet 5. Female reproductive system crossword worksheet 6. Human reproductive system test 7. Class participation Teacher Resources 1. Video: Stages of Life List of Applicable NJCCS: 2.4 Human Relationships and Sexuality: All students will acquire knowledge about the physical, emotional, and social aspects of human relationships and sexuality and apply these concepts to support a healthy, active lifestyle
8 Unit 3: Pregnancy, Birth and Parenthood 6 Why Is This Unit Important? Students will learn how pregnancy occurs and the stages associated with pregnancy. Key points that students will be encouraged to emphasize is fetal development, problems associated with pregnancy and the stages of birth. Students will also be instructed on the responsibility of parenthood. Enduring Understanding 1. Students will learn about the challenges associated with teenage parenthood 2. Students will learn the stages of pregnancy, what occurs during each trimester, and fetal development 3. Students will learn the possible problems and complications associated with pregnancy and birth Essential Questions 1. What are the signs that a female is pregnant? 2. What are the signs of labor? 3. What are the complications associated with pregnancy? 4. What are the different trimesters and how does the baby develop throughout each trimester? 5. What are some complications and/or problems a teenage parent could face? Acquired Knowledge: Students will understand/identify/discuss the following: 1. Pregnancy 2. Trimesters 3. Fetus 4. Embryo 5. Infertility 6. Ovulation 7. Zygote 8. Implantation 9. Miscarriage 10. Still birth 11. Ectopic pregnancy 12. C Section 13. Vaginal birth 14. Dilation 15. Fertilization 16. Crowning 17. Expulsion
9 18. Water break 19. Amniotic sac 20. Spotting 21. After birth 22. Fertility 23. Placenta 24. Umbilical cord 25. Baby 26. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) 27. Hormones 28. Dilation 29. Premature birth 30. Multiple births 31. Sperm 32. Egg 33. Cervical mucus 34. Blastocyst 35. Basal Body Temperature (BBT) 36. Folic Acid 37. In Vitro Vertilization (IVF) 38. Fraternal twin 39. Identical twin 40. Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, Low Platelet count (HELLP Syndrome) 41. Preeclampsia 7 Acquired Skills 1. Recognizing the early signs of pregnancy 2. Recognize the complications and problems associated with pregnancy 3. Students will understand the trimesters and stages associated with fetal development 4. Students will understand the responsibilities associated with parenthood Assessments 1. Signs of pregnancy worksheet 2. Pregnancy quiz & Pregnant worksheet 4. Class participation Teacher Resources 1. Videos: - Miracle of Life - Stages of Life - 15 & Pregnant
10 List of Applicable NJCCS: Human Relationships and Sexuality: All students will acquire knowledge about the physical, emotional, and social aspects of human relationships and sexuality and apply these concepts to support a healthy, active lifestyle
11 Unit 4: Contraception 9 Why Is This Unit Important? Students will learn various types of contraception methods and how they are used. Key points that students will be emphasized to learn will be proper use and efficiency of various contraceptive methods. Students will be instructed on the pros and cons associated with various contraceptive devices and that the only 100% safe method is practicing abstinence. Enduring Understanding 1. Students will learn the benefits of practicing abstinence during their adolescence and young adulthood. 2. Students will learn the various methods of contraception and how they function. Enduring Questions 1. Describe the most effective method of contraception and actions you could take to practice that method? 2. Why is abstinence the best method of contraception? 3. What are the barrier methods of contraception? 4. What are the chemical methods of contraception? 5. What are the permanent methods of contraception and what makes them permanent? Acquired Knowledge: Students will understand/identify/discuss the following: 1. Abstinence 2. Withdrawal 3. Rhythm method 4. Pre-ejaculation 5. Pill 6. Injections 7. Patch 8. Norplant 9. Spermicidal gels/creams 10. Plan B/Emergency contraception 11. Condom 12. Female condom 13. Diaphragm 14. Sponge 15. Intrauterine device 16. Vasectomy 17. Tubal ligation
12 Acquired Skills How to acquire contraceptive devices 2. Information on how to utilize the best methods of contraception for each individual 3. The proper usage of various contraceptive methods 4. The pros and cons of the various methods of contraception Assessments 1. Pregnancy and Contraception Test 2. Class participation List of Applicable NJCCS: 2.4 Human Relationships and Sexuality: All students will acquire knowledge about the physical, emotional, and social aspects of human relationships and sexuality and apply these concepts to support a healthy, active lifestyle
13 Unit 5: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) 11 Why Is This Unit Important? Students will learn the importance of gaining knowledge of sexually-transmitted infections (STIs) and sexually-transmitted diseases (STDs) and how to stay healthy. Students will be encouraged to emphasize the practice of safe sex and how STIs and STDs are spread. Students will be instructed on how to stay healthy and what to in case of becoming infected with an STI or STD. Enduring Understanding 1. Students will learn the signs and symptoms associated with various sexually transmitted diseases and infections 2. Students will understand why the HIV/AIDS virus is transmitted, how it works and why it is so deadly 3. Students will learn how to cope if they become infected with an STI or STD 4. Students will learn how to treat various types of STIs and STDs Enduring Questions 1. What are the four incurable STIs and why are they incurable? 2. What are the symptoms a person might experience if they are infected with an STI/STD? 3. How would you seek treatment if you suspect that you are infected with an STI/STD? 4. What is the difference between HIV and AIDS? 5. What are some risky behaviors through which you could contract an STI/STD? 6. Explain how a person with HIV could be discriminated against? 7. What are some common myths associated with HIV/AIDS? Acquired Knowledge: Students will understand/identify/discuss the following: 1. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) 2. Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) 3. Genital Herpes 4. Hepatitis B 5. Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) 6. Chlamydia 7. Syphilis 8. Gonorrhea 9. Trichomoniasis 10. Yeast infections 11. Pubic lice 12. Sexual orientation
14 Acquired Skills Recognizing the signs and symptoms of an STI/STD 2. Recognizing how to seek proper treatment if you do contract an STI/STD 3. Understanding the difference between HIV and AIDS 4. Understanding how various STIs and STDs are transmitted from person to person 5. Understanding how to keep yourself healthy through the practice of safe sex Assessments 1. STI/STD quiz 2. She s Too Young worksheet 3. Class participation 4. Posters Teacher Resources 1. Videos: - She s Too Young - Philadelphia - Discovery Channel STDs List of Applicable NJCCS: 2.1 Wellness: All students will acquire health promotion concepts and skills to support a healthy, active lifestyle 2.2 Integrated Skills: All students will develop and use personal and interpersonal skills to support a healthy, active lifestyle 2.4 Human Relationships and Sexuality: All students will acquire knowledge about the physical, emotional, and social aspects of human relationships and sexuality and apply these concepts to support a healthy, active lifestyle
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Rockaway Township Public Schools Health Unit Plan Grade 7
 Unit Title: Time Frame: 21 st Century Theme: Family Life 7 5-6 days Health Literacy, critical thinking and problem solving, communication and collaboration, Information Literacy, Media Literacy, ITC Literacy
Unit Title: Time Frame: 21 st Century Theme: Family Life 7 5-6 days Health Literacy, critical thinking and problem solving, communication and collaboration, Information Literacy, Media Literacy, ITC Literacy
Overview of Health Curriculum:
 USD 383 Manhattan-Ogden Health Curriculum Map Welcome to the curriculum design maps for Manhattan-Ogden USD 383, striving to produce learners who are: Effective Communicators who clearly express ideas
USD 383 Manhattan-Ogden Health Curriculum Map Welcome to the curriculum design maps for Manhattan-Ogden USD 383, striving to produce learners who are: Effective Communicators who clearly express ideas
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook
 Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook Vocabulary Review Anatomy Bingo Exploring Fetal Development Promoting Fetal Development BBI Decision Making Ask an Adult Contents Grade 6 Reproduction Review Vocabulary
Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook Vocabulary Review Anatomy Bingo Exploring Fetal Development Promoting Fetal Development BBI Decision Making Ask an Adult Contents Grade 6 Reproduction Review Vocabulary
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases)
 Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT. Cell Division MITOSIS (P )
 Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT 31 Hours Cell Division MITOSIS (P. 460-469) 1. Describe mitosis in detail; Specifically describe, in detail, the events of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT 31 Hours Cell Division MITOSIS (P. 460-469) 1. Describe mitosis in detail; Specifically describe, in detail, the events of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Contraceptives. Kim Dawson October 2010
 Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Lecture Series: Pregnancy
 Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology. Basic Structure of the Human Body. Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology
 Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS
 DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to describe male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts
DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to describe male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Human Reproduction & Anatomy Breakaway
 Human Reproduction & Anatomy Breakaway Image courtesy of Dream Design at Free Digital Photos Kim Graybill/FamilyConsumerSciences.com Page 1 Challenge #1: Who Do I Belong To? Male? Female? Both? Neither?
Human Reproduction & Anatomy Breakaway Image courtesy of Dream Design at Free Digital Photos Kim Graybill/FamilyConsumerSciences.com Page 1 Challenge #1: Who Do I Belong To? Male? Female? Both? Neither?
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Human Reproductive Anatomy The female anatomy first just the reproductive parts:
 Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
SUMMARY OF LAKEVIEW SCHOOL DISTRICT S REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH CURRICULUM. Philosophy Statement
 SUMMARY OF LAKEVIEW SCHOOL DISTRICT S REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH CURRICULUM Philosophy Statement The primary responsibility for human sexuality education belongs to the family. The schools responsibility is to
SUMMARY OF LAKEVIEW SCHOOL DISTRICT S REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH CURRICULUM Philosophy Statement The primary responsibility for human sexuality education belongs to the family. The schools responsibility is to
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that
 The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
Treating Infertility
 Treating Infertility WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 About 10% of couples in the United States are infertile. Infertility is a condition in which a woman has not been able
Treating Infertility WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 About 10% of couples in the United States are infertile. Infertility is a condition in which a woman has not been able
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 14 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
Biology Homework Chapter 6: Continuity Through Reproduction Pages Answer the questions with complete thoughts!
 Name Biology Homework Chapter 6: Continuity Through Reproduction Pages 143-158 Answer the questions with complete thoughts! Per. * Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Reproduction, Read pages 143 to 146 PART A: Define
Name Biology Homework Chapter 6: Continuity Through Reproduction Pages 143-158 Answer the questions with complete thoughts! Per. * Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Reproduction, Read pages 143 to 146 PART A: Define
WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES?
 CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
Human Reproduction. Human Reproductive System. Scrotum. Male Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Study Guide. Biology 3101B. Science. Reproduction and Development. Adult Basic Education. Biology 2101A Biology 2101C Biology 3101A.
 Adult Basic Education Science Reproduction and Development Prerequisites: Biology 2101A Biology 2101C Biology 3101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003 Biology
Adult Basic Education Science Reproduction and Development Prerequisites: Biology 2101A Biology 2101C Biology 3101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003 Biology
Reproduction Notes. iii. LH stimulates the interstitial cells of testes to produce testosterone c. testes
 I. Asexual Reproduction a a single parent endows its offspring with a set of genes identical to its own (except for mutations) A. Forms 1. Budding a. a part of the parent's body grows and separates from
I. Asexual Reproduction a a single parent endows its offspring with a set of genes identical to its own (except for mutations) A. Forms 1. Budding a. a part of the parent's body grows and separates from
Chapter 17 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 17 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 17 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
BIOLOGY. Animal Reproduction CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 46 Animal Reproduction Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Both
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 46 Animal Reproduction Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Both
Reproductive System. Points to ponder 4/28/2017. Chapter 17 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 17 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 17 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Grade 6 Reproduction Review
 Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Standard: To promote lifelong health and wellness.
 Standard: To promote lifelong health and wellness. Power Benchmark 1: Students will comprehend concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention. Code B Grade Level Benchmark Vocabulary Skills
Standard: To promote lifelong health and wellness. Power Benchmark 1: Students will comprehend concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention. Code B Grade Level Benchmark Vocabulary Skills
Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion
 Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion Infertility Incidence Affects about 10% to 15% of reproductive-age population Subfertility: prolonged time to conceive Sterility: inability to conceive
Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion Infertility Incidence Affects about 10% to 15% of reproductive-age population Subfertility: prolonged time to conceive Sterility: inability to conceive
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE 10 HEALTH
 UNIT: Mental and Emotional Health/Importance of Adequate Sleep NO. OF : 13 KEY LEARNING(S): To know what it means to be emotionally and mentally healthy. To know why adequate sleep is so important for
UNIT: Mental and Emotional Health/Importance of Adequate Sleep NO. OF : 13 KEY LEARNING(S): To know what it means to be emotionally and mentally healthy. To know why adequate sleep is so important for
Special Parts: Gender. Why Have Sex?
 Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity
 Unit 7 Lesson 7.1 Notes Introductory Video Video STIs: Running the Risk Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity Section 1: What Are the Risks? Key Terms: Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) an infectious
Unit 7 Lesson 7.1 Notes Introductory Video Video STIs: Running the Risk Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity Section 1: What Are the Risks? Key Terms: Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) an infectious
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
1.Abstinence no sex (Abstinence only education has been proven ineffective in preventing unwanted pregnancies)
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs 1. Ovary Transplants 2. Freezing Eggs 3. Choosing Gender 4. The Male Pill, parts 1&2 5. Male Birth Control: RISUG 6. Birth Control. 1.Abstinence
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs 1. Ovary Transplants 2. Freezing Eggs 3. Choosing Gender 4. The Male Pill, parts 1&2 5. Male Birth Control: RISUG 6. Birth Control. 1.Abstinence
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings
 Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth
 Revised January 2017 Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth Lesson Goals Explain the Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproduction Systems Review Proper Vocabulary for the
Revised January 2017 Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth Lesson Goals Explain the Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproduction Systems Review Proper Vocabulary for the
The Reproductive System
 The Reproductive System The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete hormones Sperm male gametes Ova (eggs) female
The Reproductive System The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete hormones Sperm male gametes Ova (eggs) female
Review & Post Test Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #30
 Review & Post Test Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #30 Time Needed one class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Recognize the importance of early detection and treatment of all sexual health problems.
Review & Post Test Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #30 Time Needed one class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Recognize the importance of early detection and treatment of all sexual health problems.
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT. Course Description. Instructional Strategies, Learning Practices, Activities, and Experiences.
 SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Health Education Grade Level(s): 10 Units of Credit:.50 Classification: Required Length of Course: 15 cycles Periods Per Cycle: 6
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Health Education Grade Level(s): 10 Units of Credit:.50 Classification: Required Length of Course: 15 cycles Periods Per Cycle: 6
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY
 HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System. Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems
 Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
Birth Control Options Chart
 Hormonal Methods Birth control pills also known as mini-pills 91-99% A daily pill containing hormones that stops you from ovulating. There are combination estrogen or progestin-only (mini-pill) options.
Hormonal Methods Birth control pills also known as mini-pills 91-99% A daily pill containing hormones that stops you from ovulating. There are combination estrogen or progestin-only (mini-pill) options.
100% Highly effective No cost No side effects
 effective? Advantages Disadvantages How do I get Cost Abstinence For some it can mean no sexual contact. For others it is no sexual intercourse or vaginal penetration. A permanent surgical procedure available
effective? Advantages Disadvantages How do I get Cost Abstinence For some it can mean no sexual contact. For others it is no sexual intercourse or vaginal penetration. A permanent surgical procedure available
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
Learner Outcomes. Classroom Activities & Timing
 Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
The reproductive system
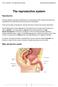 The reproductive system Reproduction All living organisms reproduce. Reproduction is the process by which organisms generate new individuals of the same kind ensuring continuation of the species. There
The reproductive system Reproduction All living organisms reproduce. Reproduction is the process by which organisms generate new individuals of the same kind ensuring continuation of the species. There
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3:
 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 1 GRADE 7 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development.
GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 1 GRADE 7 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development.
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank
 Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank Objective 6.01 Describe the basic functions of the reproductive system. 1. Which of the following is a function of the reproductive system? a. Production
Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank Objective 6.01 Describe the basic functions of the reproductive system. 1. Which of the following is a function of the reproductive system? a. Production
The reproductive system
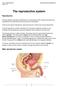 Unit 4. Reproduction (2016-17) Natural Science Department The reproductive system Reproduction All living organisms reproduce. Reproduction is the process by which organisms generate new individuals of
Unit 4. Reproduction (2016-17) Natural Science Department The reproductive system Reproduction All living organisms reproduce. Reproduction is the process by which organisms generate new individuals of
UNDERSTANDING. Permanent Birth Control for Men
 UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
Scrub In. The normal periodic discharge of the endometrial lining in a female is known as:
 Scrub In The normal periodic discharge of the endometrial lining in a female is known as: a. Dysmenorrhea b. Leukorrhea c. Menorrhagia d. Menstruation The scientific name for the beginning of the menses
Scrub In The normal periodic discharge of the endometrial lining in a female is known as: a. Dysmenorrhea b. Leukorrhea c. Menorrhagia d. Menstruation The scientific name for the beginning of the menses
LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS
 LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS LTASEX.INFO! IN AIDS is a treatable complication of advanced HIV infection.
LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS LTASEX.INFO! IN AIDS is a treatable complication of advanced HIV infection.
Chapter 8: How do Organisms Reproduce? 1 What is the primary importance of DNA copying in reproduction? SOLUTION:
 Chapter 8: How do Organisms Reproduce? 1 What is the primary importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA copying in reproduction is important for maintenance of body designs and features. It is also
Chapter 8: How do Organisms Reproduce? 1 What is the primary importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA copying in reproduction is important for maintenance of body designs and features. It is also
Sexual Q & A Game - Birth Control cards - From 5 to 100 Points
 Lesson Eight Sexual Q & A Game - Birth Control cards - From 5 to 100 Points Sexual Jeopardy Birth Control for 10 Points The only 100% effective method for preventing pregnancy and STIs Sexual Jeopardy
Lesson Eight Sexual Q & A Game - Birth Control cards - From 5 to 100 Points Sexual Jeopardy Birth Control for 10 Points The only 100% effective method for preventing pregnancy and STIs Sexual Jeopardy
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis. Regents Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Sperm production. Sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production. Sperm production. Controlling sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Communication Skills. Part Ill
 From Comprehensive Counseling for Reproductive Health Participant s Handbook 2003 EngenderHealth Part Ill Communication Skills Good counseling requires good communication skills. The abilities to establish
From Comprehensive Counseling for Reproductive Health Participant s Handbook 2003 EngenderHealth Part Ill Communication Skills Good counseling requires good communication skills. The abilities to establish
- (Have NO cure yet, but are controllable) - (Can be cured if caught early enough)
 Myths or Facts of STD s 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. 2. Abstinence is the best way to prevent STD s. 3. If you get an STD once, and are treated, you can t get it again. 4. A
Myths or Facts of STD s 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. 2. Abstinence is the best way to prevent STD s. 3. If you get an STD once, and are treated, you can t get it again. 4. A
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers
 Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers Sexual & Reproductive Health Western Australia Chlamydia (bacterial infection) Unprotected vaginal
Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers Sexual & Reproductive Health Western Australia Chlamydia (bacterial infection) Unprotected vaginal
Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Become aware of the magnitude of teen age sexual activity and pregnancy and some of the social and economic effects. 2. Learn about the various means of contraception,
Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Become aware of the magnitude of teen age sexual activity and pregnancy and some of the social and economic effects. 2. Learn about the various means of contraception,
Birth Control- an Overview. Keith Merritt, MD. Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy
 Birth Control- an Overview Keith Merritt, MD Basics Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy Even with perfect use, each method of birth control has a
Birth Control- an Overview Keith Merritt, MD Basics Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy Even with perfect use, each method of birth control has a
Chapter 16 Endocrine and Reproductive Health
 Note Taking Lesson 2 The Male Reproductive System Directions: Use the following outline to help organize your notes as you read through the lesson. Key Concept Consider and Reconsider Before reading the
Note Taking Lesson 2 The Male Reproductive System Directions: Use the following outline to help organize your notes as you read through the lesson. Key Concept Consider and Reconsider Before reading the
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Lesson Four HIV and STIs
 Unit Two Lesson Four Lesson Overview In this activity students learn about the types, symptoms, transmission methods and treatments for various STIs, and are made aware of how easily and comprehensively
Unit Two Lesson Four Lesson Overview In this activity students learn about the types, symptoms, transmission methods and treatments for various STIs, and are made aware of how easily and comprehensively
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS (STIS)
 SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS (STIS) CONTENTS Causes Prevention Methods of Transmission Decisions to Have Sexual Intercourse Signs and symptoms Screening Pop Quiz Diagnosis Management: Public Health
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS (STIS) CONTENTS Causes Prevention Methods of Transmission Decisions to Have Sexual Intercourse Signs and symptoms Screening Pop Quiz Diagnosis Management: Public Health
