Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students will be able to: Describe changes in male and female anatomy and physiology during puberty Identify the parts of the male and female reproductive systems and understand the function of each of these parts Define sex and understand the physical consequences of having sex (pregnancy, HIV, other STIs) Describe menstruation and sperm production and identify their relationship to reproduction Activities: I. Introduction to the Day (3 min) II. Computer Activities III. Wrap-Up 1. Body Moves: Body Development Animation 2. Body Moves: Reproductive Anatomy 3. Body Moves: Menstruation 4. On-The-Air: The Expert s Corner 5. On-The-Air: Reproduction Optional Level I Lesson 8 Quiz (40 min) (2 min) 119
2 Preparation: Review all computer activities prior to the lesson Teacher Aid: Reproductive Anatomy 120
3 Activity I: Introduction to the Day (3 min) A. Welcome students as they come in. Sit each student at a computer and tell students not to touch their mouse or keyboard until they are instructed to do so. B. Explain to students that today they will be using the computers to learn about the reproductive system, puberty, and the definition of sex. C. Ask students who the most important person in their game is. Take a few responses. D. Emphasize that they are the most important person in their game and that s why it is important for them to know how their body works so they can make decisions, especially regarding sex, that will keep their bodies healthy and their game real. E. Tell students to begin today s computer lesson now. F. Remind students to raise their hand if they have a question. 121
4 Activity II: Computer Activities (35 min) NOTE: Monitor time closely. Please remember you will need 8-10 minutes at the end of class to review questions from the computer activities and complete the wrap up. 1. Body Moves: Body Development Animation Description: Using a lighthearted animation, students see the changes that occur in the male and female body during puberty. This animation also focuses on the emotional changes experienced during puberty. Animated scenes also demonstrate the development of a girl s body from age eight through puberty and an eight-year-old boy s body through puberty. Animated scenes are separate for male and female body development. 2. Body Moves: Reproductive Anatomy Description: An interactive animation allows the student to match up a part of the reproductive system with the correct name. When the correct name is identified, reinforcement is given along with an explanation of the function of that reproductive part. If the wrong name is selected, remediation is offered along with redirection to the correct reproductive part. The student performs this activity for both the male and female reproductive systems. (See Teacher Aid on Reproductive Anatomy.) 3. Body Moves: Menstruation Description: Students see an animation that explains how different parts of the female reproductive system work together for menstruation to occur. Students also have the opportunity to read an online fact sheet that answers some common questions about menstruation. 122
5 4. On-The-Air: The Expert s Corner Description: Students watch a video in which an expert hosts a candid discussion about sex and reproduction. The expert provides a definition of sex, including vaginal, oral, and anal sex, and explains the consequences of having sex. In this lesson, the focus is on the physical consequences of having sex pregnancy, HIV, and other STIs. In this activity, the expert talks about STIs, and the student has access to online fact sheets regarding STIs if interested. 5. On-The-Air: Reproduction Description: The expert continues the discussion about another consequence of having sex becoming pregnant. At this point, the student watches an animation of what happens in the female body (menstruation) and in the male body (production of sperm) for reproduction to occur. 6. Arcade: Activity Review Description: Students are able to access the Arcade to review previous lesson activities only after they have completed all the activities for the day. 123
6 Activity III: Wrap-Up (2 min) A. Ask the students to end computer activities. B. Ask students if they have any additional comments they want to make about the activities they did today. Respond as necessary. C. Ask students why they think it s important for them to understand how their bodies work. Take a few responses. D. Tell students that you hope the activities they did in today s class helped them not only understand how their bodies work but also understand some of the consequences (pregnancy, HIV, other STIs) they can experience if they make unhealthy choices regarding sex. E. Remind students that they are the most important person in their game and that s why in the next class they will begin to think about reasons why teens their age choose to wait until they are older to have sex. F. Thank the students for their participation and let them know you look forward to seeing them next time. Optional: Administer Level I Lesson 8 Quiz (located in the Appendix) 124
7 Teacher Aid Teacher Guide to Reproductive Anatomy The interactive animation in the reproductive anatomy computer activity allows the student to match eight parts of the female reproductive system with the correct name: FALLOPIAN TUBE BREAST OVARY UTERUS CERVIX VAGINA VAGINAL OPENING GENITALS Breasts. Breasts, also known as mammary glands, play a part in reproduction because they make milk for the baby. A breast has somewhere between 12 to 20 milk glands, which connect to milk ducts. The milk ducts then lead to the nipple. About 80 percent of breast tissue is made of fat that protects the milk glands. Cervix. The cervix connects the vagina and the uterus. 125
8 Teacher Aid to Reproductive Anatomy continued Fallopian Tubes. The Fallopian tubes are small straw-like tubes. One end connects to the uterus. The other end has fringelike tentacles (fimbriae) that float next to the ovaries. When an egg, or ovum, is released from one of the ovaries, the fimbriae sweep the ovum into the Fallopian tube where it travels to the uterus. Conception, or the fertilization of the egg, occurs in the Fallopian tube. Genitals and Reproductive Anatomy. Genitals is a general word that refers to the reproductive and surrounding organs. Ovaries. Females are born with 2 ovaries, one on each side of the uterus. They are small walnut-sized organs that store egg cells. During puberty the ovaries will begin releasing one egg cell every month, signaling the beginning of the menstrual cycle. The egg cell travels through the Fallopian tubes where fertilization can occur. Uterus. The uterus is a strong muscular organ where a fetus grows until it is ready to be born. The uterus is about the size of a pear and can expand large enough for a 9-month-old baby to live in. After a baby is born, the uterus returns to its original size. When the woman is pregnant the baby is nourished by the blood and tissue built up in the uterus. If the woman s egg is not fertilized, the blood and tissue from the uterine wall are shed, causing her to menstruate. Vagina. The vagina is a muscular organ that has stretchy walls that allow it to expand and recover to its original shape. The vagina is where a penis goes during sex, and it provides a passageway for a baby to come through during childbirth. During menstruation, the vagina provides a way for the blood to pass though from the uterus to the vaginal opening. Vaginal opening. This is the hole between a girl s legs that leads to the vagina. 126
9 Teacher Aid to Reproductive Anatomy continued Further, in the computer lesson, when the Learn More button is selected, eight additional female reproductive system parts are provided: Anus. An opening where feces (or food waste) leaves the body. It is not part of the woman s reproductive organs. Bladder. The bladder is a hollow organ that stores urine until there is an appropriate time to urinate. During urination urine is expelled by the bladder muscles, through the urethra. Clitoris. The clitoris is a small pea-sized mound at the top of the vulva where the labia come together. It is responsible for many of the sexual feelings a woman has. Hymen. The hymen is a thin piece of skin that covers the vaginal opening. The hymen can tear during certain kinds of exercise, by using tampons, or as a result of having sex for the first time. 127
10 Labia Majora. Girls have two pairs of labia. The labia majora are the outer lips that have hair and cover the inner lips or the minora. Labia Minora. Girls have two pairs of labia. The labia minora are the inner lips that are smaller and don t have hair. Urethra. A small opening where urine (pee) leaves the body. It is not part of the woman s sex organs, but it is covered by the vulva and is between the clitoris and the vaginal opening. Vulva. The vulva is the whole area of soft skin between a female's legs that covers the labia, clitoris, the opening to the urethra, and the opening to the vagina. 128
11 Teacher Aid to Reproductive Anatomy continued The interactive animation in the reproductive anatomy computer activity allows the student to match eight parts of the male reproductive system with the correct name: SEMINAL VESICLES GENITALS EPIDIDYMIS Epididymis. A tiny, coiled tube connected to each testicle that stores sperm as they mature. Genitals and Reproductive Anatomy. Genitals is a general word that refers to the reproductive and surrounding organs. Penis. The penis is the male sex organ that hangs down between a boy's legs. The penis may be circumcised, where the foreskin of the penis is removed, or uncircumcised, where the foreskin of the penis is left intact. Although circumcision affects the look of the penis, it does not affect its function. Urine passes through the penis during urination or peeing. The penis usually soft and spongy, but, during 129
12 an erection, it becomes hard. During sexual intercourse, ejaculation, where semen passes through the penis, may occur. Scrotum. The scrotum is a soft, loose wrinkly sac of skin that has two compartments. Each compartment holds one testicle. The skin of the scrotum is darker in color than the rest of a man s skin. When the penis is soft it rests on top of the scrotum. Seminal vesicles. The two seminal vesicles are located under the bladder and make fluids that feed sperm to give them energy. Sperm. Sperm is constantly made in the testes from puberty to the end of a man s life. Sperm are the male s reproductive cells and look like tiny tadpoles. They are only visible through a microscope. If a sperm comes together with an egg from the female fertilization or conception occurs, which can lead to pregnancy. Testicles. The testicles, or testes, are where males begin to produce sperm during puberty. Before puberty, the testes are about the size of a grape. During puberty, the testes grow to the size of a large walnut. Typically before and after puberty, one testicle hangs lower than the other one. Vas deferens. The two vas deferens are long thin tubes that sperm travel through to get from the testicles to the end of the penis. 130
13 Teacher Aide to Reproductive Anatomy continued Prostate. The prostate gland makes fluid that gives sperm an additional energy boost. Cowper s gland. The Cowper s gland is attached to the urethra; it releases a sticky fluid that cleans out the urethra. This fluid is called pre-ejaculate because it comes out the end of the urethra before ejaculation. Urethra. A long tube inside the penis that urine (pee) passes through during urination and semen passes through during sex. Semen. Semen is the combined milky white fluid that squirts out during ejaculation. Semen consists of sperm from the testicles and fluids from other reproductive organs, including the seminal vesicles, prostate, and Cowper's gland. Bladder. The bladder is a hollow organ that stores urine until there is an appropriate time to urinate. During urination urine is expelled by the bladder muscles, through the urethra. 131
14 Anus. An opening where feces (or food waste) leaves the body. It is not part of the man s reproductive organs. 132
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
Purpose. Teaching notes. Procedure. 2. Give each group a bingo card and counters. 4. Explain any words students are unsure of.
 Reproductive bingo Activity: Key Messages Males and females have different reproductive parts, each of which has an important function. It is important to use the correct terminology for reproductive parts
Reproductive bingo Activity: Key Messages Males and females have different reproductive parts, each of which has an important function. It is important to use the correct terminology for reproductive parts
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Lecture Series: Pregnancy
 Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Grade 6 Reproduction Review
 Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Learner Outcomes. Classroom Activities & Timing
 Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook
 Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook Vocabulary Review Anatomy Bingo Exploring Fetal Development Promoting Fetal Development BBI Decision Making Ask an Adult Contents Grade 6 Reproduction Review Vocabulary
Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook Vocabulary Review Anatomy Bingo Exploring Fetal Development Promoting Fetal Development BBI Decision Making Ask an Adult Contents Grade 6 Reproduction Review Vocabulary
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System. Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems
 Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY
 HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
Growth and Development 6 th Grade
 Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3:
 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 1 GRADE 7 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development.
GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 1 GRADE 7 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development.
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Body Wise. Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only
 Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth
 Revised January 2017 Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth Lesson Goals Explain the Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproduction Systems Review Proper Vocabulary for the
Revised January 2017 Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth Lesson Goals Explain the Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproduction Systems Review Proper Vocabulary for the
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS
 DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to describe male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts
DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to describe male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY
 Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Puberty and Reproduction
 Puberty and Reproduction A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end
Puberty and Reproduction A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Chapter 16 Endocrine and Reproductive Health
 Note Taking Lesson 2 The Male Reproductive System Directions: Use the following outline to help organize your notes as you read through the lesson. Key Concept Consider and Reconsider Before reading the
Note Taking Lesson 2 The Male Reproductive System Directions: Use the following outline to help organize your notes as you read through the lesson. Key Concept Consider and Reconsider Before reading the
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty
 Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Puberty For Boys Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty 70 minutes Preparing To Teach About Puberty - Teacher Guide Anatomy Review - Teacher Guide Bernie (male
Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Puberty For Boys Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty 70 minutes Preparing To Teach About Puberty - Teacher Guide Anatomy Review - Teacher Guide Bernie (male
List of Equipment, Tools, Supplies, and Facilities:
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy
 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: Students
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: Students
Anatomy of Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Reproductive System Anatomy of Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Anatomy of Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
Anatomy of Reproductive System Anatomy of Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Anatomy of Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Transformation Information elearning Kit Combined Program Lesson Plan Page 1. LESSON TITLE: Combined Program
 Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
Lecture Series: Puberty
 Lecture Series: Puberty Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will explain the basics of what your
Lecture Series: Puberty Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will explain the basics of what your
Sex Organs - Student Edition (Human Biology)
 Sex Organs - Student Edition (Human Biology) The Program in Human Biology, Stanford Univ- ersity, (HumBio) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access
Sex Organs - Student Edition (Human Biology) The Program in Human Biology, Stanford Univ- ersity, (HumBio) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy
 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
NAKED How to understand teenagers x 6 min. minutes
 NAKED How to understand teenagers 2007 6 x 6 min. minutes Program Synopsis: This innovative series of six, six-minute documentaries hears from teens about various issues confronting them at puberty. Breasts,
NAKED How to understand teenagers 2007 6 x 6 min. minutes Program Synopsis: This innovative series of six, six-minute documentaries hears from teens about various issues confronting them at puberty. Breasts,
Definition One or two sentences giving a brief description of the part. USE A DICTIONARY.
 Reproductive System Project Students will research the Structure, Function, and Pathology of both male and female reproductive system parts. The students will have several periods in the library to research
Reproductive System Project Students will research the Structure, Function, and Pathology of both male and female reproductive system parts. The students will have several periods in the library to research
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Interactive Questions & Exercises
 Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Human Reproduction & Anatomy Breakaway
 Human Reproduction & Anatomy Breakaway Image courtesy of Dream Design at Free Digital Photos Kim Graybill/FamilyConsumerSciences.com Page 1 Challenge #1: Who Do I Belong To? Male? Female? Both? Neither?
Human Reproduction & Anatomy Breakaway Image courtesy of Dream Design at Free Digital Photos Kim Graybill/FamilyConsumerSciences.com Page 1 Challenge #1: Who Do I Belong To? Male? Female? Both? Neither?
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Understanding your body
 71 ch a p t er 4 Understanding your body These 4 women s bodies may look different from each other, but they all go through the same changes. It is important to understand how your body works. The more
71 ch a p t er 4 Understanding your body These 4 women s bodies may look different from each other, but they all go through the same changes. It is important to understand how your body works. The more
Proposed Revisions for the 5th Grade S.H.A.R.E. Sexuality, Health, and Responsibility Education Curriculum Revised February 15, 2017
 Proposed Revisions for the 5th Grade S.H.A.R.E. Sexuality, Health, and Responsibility Education Curriculum Revised February 15, 2017 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of 5th grade,
Proposed Revisions for the 5th Grade S.H.A.R.E. Sexuality, Health, and Responsibility Education Curriculum Revised February 15, 2017 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of 5th grade,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
HEALTH GRADE 11. THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618
 HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
Speak with your IT department to make sure this web address is unblocked for your classroom and that your computer s sound works for the video.
 Everybody s Got Body Parts Part One A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT:
Everybody s Got Body Parts Part One A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT:
GROWING UP AND LIKING IT 2-Hour Assembly/Health Lesson Science-To-Go! Program Grades: 5-6. Growing Up and Liking It: Pondering Puberty
 TEACHER GUIDE GROWING UP AND LIKING IT 2-Hour Assembly/Health Lesson Science-To-Go! Program Grades: 5-6 Growing Up and Liking It: Pondering Puberty Description Hour 1: Learn the science inside a changing
TEACHER GUIDE GROWING UP AND LIKING IT 2-Hour Assembly/Health Lesson Science-To-Go! Program Grades: 5-6 Growing Up and Liking It: Pondering Puberty Description Hour 1: Learn the science inside a changing
Communication Skills. Part Ill
 From Comprehensive Counseling for Reproductive Health Participant s Handbook 2003 EngenderHealth Part Ill Communication Skills Good counseling requires good communication skills. The abilities to establish
From Comprehensive Counseling for Reproductive Health Participant s Handbook 2003 EngenderHealth Part Ill Communication Skills Good counseling requires good communication skills. The abilities to establish
Duration Goal. Learner Outcomes. Standards and Benchmarks Materials Needed
 Duration Goal Learner Outcomes Standards and Benchmarks Materials Needed Activity Overview Module 3: Mōhala Lessons in Puberty and Anatomy 60 minutes To understand the body, specifically the reproductive
Duration Goal Learner Outcomes Standards and Benchmarks Materials Needed Activity Overview Module 3: Mōhala Lessons in Puberty and Anatomy 60 minutes To understand the body, specifically the reproductive
PUBERTY: MY CHANGING BODY Lesson 2
 PUBERTY: MY CHANGING BODY Lesson 2 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify, label and discuss human reproductive body parts. MATERIALS: 1. Public Parts Illustrations (unlabelled &labelled) 2. Private
PUBERTY: MY CHANGING BODY Lesson 2 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify, label and discuss human reproductive body parts. MATERIALS: 1. Public Parts Illustrations (unlabelled &labelled) 2. Private
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 2 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 2 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank
 Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank Objective 6.01 Describe the basic functions of the reproductive system. 1. Which of the following is a function of the reproductive system? a. Production
Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank Objective 6.01 Describe the basic functions of the reproductive system. 1. Which of the following is a function of the reproductive system? a. Production
STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases)
 Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
are some questions. level and Group similar of discussion. the class. somewhere! Avoid offering 1. Is ways to make mean, it means that the a healthy
 Teaching Human Sexuality Answers to Sample Questions Elementary Grade 4, 5, 6 The inquiry process is an important strategy to use for effective human sexuality classes. Here are some tips when answering
Teaching Human Sexuality Answers to Sample Questions Elementary Grade 4, 5, 6 The inquiry process is an important strategy to use for effective human sexuality classes. Here are some tips when answering
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Review and Resources Grades 4-6, Lesson #18
 Review and Resources Grades 4-6, Lesson #18 Time Needed 50-60 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Recognize the definitions of at least 90% of the vocabulary introduced in the unit.
Review and Resources Grades 4-6, Lesson #18 Time Needed 50-60 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Recognize the definitions of at least 90% of the vocabulary introduced in the unit.
Taking Care of Your Sexual Health
 Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey
 From Trainer s Resource Book to accompany Management of Men s Reproductive Health Problems 2003 EngenderHealth Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey In the answer key that follows: The answers appear in
From Trainer s Resource Book to accompany Management of Men s Reproductive Health Problems 2003 EngenderHealth Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey In the answer key that follows: The answers appear in
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Session 4_Girls. Learning about my body: Reproductive system
 Session 4_Girls Learning about my body: Reproductive system Rationale Pubertal changes begin around 9-10 years in girls and around 11 years for boys. Acknowledging the mental, emotional, and physical changes
Session 4_Girls Learning about my body: Reproductive system Rationale Pubertal changes begin around 9-10 years in girls and around 11 years for boys. Acknowledging the mental, emotional, and physical changes
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Human Reproductive Anatomy The female anatomy first just the reproductive parts:
 Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
UNDERSTANDING. Permanent Birth Control for Men
 UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
The Female Reproductive System
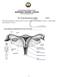 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology. Basic Structure of the Human Body. Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology
 Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
CHAPTER 2: Sexual Anatomy Total Assessment Guide (T.A.G.)
 CHAPTER 2: Sexual Anatomy Total Assessment Guide (T.A.G.) Topic Introduction to Chapter Question Type Remember the Facts Multiple Choice 1 Understand the Concepts Apply What You Know Essay Historical Perspectives
CHAPTER 2: Sexual Anatomy Total Assessment Guide (T.A.G.) Topic Introduction to Chapter Question Type Remember the Facts Multiple Choice 1 Understand the Concepts Apply What You Know Essay Historical Perspectives
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Name Class Date. Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter.
 Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 8-1. Define urogenital systems.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 The Human Urogenital Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-16. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 8-1. Define urogenital systems.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 The Human Urogenital Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-16. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 8-1. Define urogenital systems.
Male Reproductive System
 21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
