Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols
|
|
|
- Gary Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
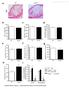
1 Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative images and quantification of Sox1-GFP ESCs differentiated for 5 days as a monolayer. On the 5th day 70.5±6% of the cells were Sox1 positive (c) qrt-pcr analysis showing the decrease in the expression of pluripotency associated genes and the upregulation in the expression of telencephalic markers during the first 4 days of monolayer differentiation. (d) The bar chart indicates the downregulation of the non-neural ectoderm marker cytokeratin14, of the endoderm marker Gata6 and of the mesoderm marker T at day4 of the neural differentiation process. (e) qrt-pcr analysis showing how specifically ventral telencephalic markers are upregulated during the neuronal differentiation by monolayer of ESCs in the absence of Activin. (f) Immunofluorescent microscopy images and quantification of Nestin/Foxg1 double + cells (54.2±4.3), Otx2 (14.69±1.42%), Pax2 (11.62±1.72%) and Pax5 positive cells (3.58±0.13%) after 7 days of monolayer differentiation. (D) For all experiments the average fold change from three independent experiments (±SEM) is shown. Scale bar=25µm (b) and 50µm (f).
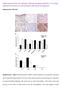
2 Supplementary Figure S2. TGF-ß1 and TGF-ß3 are unable to induce neuronal precursor differentiation. (a) Nestin and β-iii-tubulin double immunostaining and (b) quantifications of cultures treated with control conditions, TGF-ß1 (10ng/ml) or TGF-ß3 (10ng/ml) for 3 days. In these cultures we observe that neither TGF-ß1 nor TGF-ß3 can induce differentiation of ESC derived neural precursors (nestin + / β-iii-tubulin + cells: control 78.3±3.7%/ 19.8±0.9%; TGF-ß1 75.6±4.2%/ 21.6±1.4% and TGF-ß3 treated 76.4±2.6%/ 22.1±0.4%; n=3, mean±sem). ESCs were differentiated for 5 days as a monolayer, then re-plated into poly-d-lysine/laminin coated dishes and cultured in NBB27 media (controls), TGF-ß1 (10ng/ml) or TGF-ß3 (10ng/ml). Scale bar=25µm.
3 Supplementary Figure S3. Gli3 defective neuronal precursors present a hyperactivation of the Shh pathway and don t respond to Activin. (a) The levels of differentiation were analyzed in wild-type (wt) and Gli3 defective cells (Xt) by Nestin and β-iii-tubulin immunostaining after 3 days of control or Activin treatment and (b) the proportion of Nestin + / β-iii-tubulin + wiltypecells plotted (wild-type cells: control 70.5±3.5%/ 22.4±1.91% and Activin treated 42.8%±2.4%/ 57.2±3.63%/; Xt cells: control 84±4.2%/ 15.3±1.53% and Activin treated 76.4%±3.9%/ 20.3±2.18%). In these experiments we observe that the Gli3 defective cells are unable to differentiate in response to Activin. (c) Analysis of the normalized mrna levels of Shh target genes in wild-type and Gli3 -/- cells after 7 days of differentiation. An increase in the expression of Shh target genes is observed in Gli3 defective cells. (d) qrt-pcr analysis of Shh target gene expression in wt and Gli3 -/- cells after 3 days of control or Activin treatment. Activin has only minor effects on the levels of expression of these genes in Gli3 -/- cells compared to controls. For all experiments n=3, mean±sem. ESCs were differentiated for 5 days as a monolayer, then replated into poly-d-lysine/laminin coated dishes and cultured in NBB27 media (controls) or NBB27+10ng/mlActivin for 3 days (a-b and d) or 7 days (c). Scale bar=50µm.
4 Supplementary Figure S4. Combined effects of Cyclopamine and high RA concentrations can mimic Activin induced differentiation. (a) Nestin and β-iii-tubulin immunostaining and (b) quantification of the proportion of positive cells for control, Activin, cyclopamine, RA or RA plus cyclopamine treatments. This data indicates that cyclopamine and RA cooperate to induce neuronal differentiation and the levels of differentiation they induce are similar to those induced by Activin (nestin + /β-iii-tubulin + cells: control 75.1±5.6%/ 22.4±2.3%; Activin 37.8±5.4%/ 58.6±4.3%; 10µM RA 81.34±6.4%/ 15.3±1.2%; cyclopamine 60.8±3.6%/ 32.5±3.2% and cyclopamine +10µM RA treated cells 47.6±2.32%/ 46.7±3.8). ESCs were differentiated for 5 days as a monolayer, then re-plated into poly-d-lysine/laminin coated dishes and cultured in NBB27 media (controls), NBB27+10ng/mlActivin, NBB27+10µM Cyclopamine, NBB27+10µM RA, NBB27+10µM Cyclopamine+5µM RA or NBB27+10µM Cyclopamine+10µM RA. Scale bar=25µm.
5 Supplementary Figure S5. Activin treatment increases the proportion of Dlx2 + interneurons. Immunostaining and quantification for (a) CoupTFII/Nestin (Control 31.48±5.3%; Activin 55.16±4.6%) and CoupTFII/β-III-tubulin (Control 24.3±4.32% and Activin 58.6%±5.17%) indicating that the proportion of CoupTFII positive cells increases upon Activin treatment; (b) β-iii-tubulin/dlx2 (control 36.3±7.1% and Activin 52±5.2%) showing an increase in the proportion of β-iii-tubulin/dlx2 double positive cells upon Activin treatment; (c) calretinin/gaba (76.34%±6.8%) indicating that the majority of calterinin positive cells also stain for GABA and for calretinin/th illustrating how these two markers are very rarely coexpressed (<5%); (c ) high magnification image of (c); (d) calretinin/couptfii indicating that the majority of calretinin expressing neurons are also positive for CoupTFII (95.7±5%) and (e-f) for calretinin/reelin indicating that Activin treatment rarely generates neurons that co-express these markers only (Control 50±3.68% Activin16±1.44%) and that the proportion of reelin positive cells increases upon Activin treatment (Control 6±0.5%, Activin 14.38±1.2%). n=3, mean±sem. ESCs were differentiated as in Fig.S4 but cultured in NBB27 media ±Activin for 5 days (d), 3 days (a and b), 6 days (c) or 7 days (e). For (e) BDNF (10ng/ml) was added from day 2 after re-plating. Scale bar=50µm (a and b), 25µm (c, d and e, except for TH-calretinin where the scale bar=50µm and (c ) where it is 14µm).
6 Supplementary Figure S6. Activin treated telencephalic neural precursors derived from mouse ESCs integrate into the cortex of adult mice. (a) Low magnification composite of images of the injection sites (arrows) in the cortex of animals injected with GFP labelled, Activin treated, telencephalic neural precursors derived from mouse ESCs. The pial surface and white matter (WM) are indicated. (b) Immunostaining for Calretinin to visualize those cells in the cortex that co-express GFP (arrows). (c) 2-photon imaging of a transplanted GFP cell one month after injection into the adult cortex. (c ) High magnification of the area marked by a rectangle in c showing dendritic spines (arrows). Scale bar = 400μm (a), 25μm (b) and 10μm (c-c ).
7 Supplementary Figure S7. A conserved role for Activin in human ESCs. (a) Schematic representation of the protocol used to differentiate human ESCs. (b) qrt-pcr analysis showing the decrease in the expression of pluripotency associated genes and the upregulation in the expression of telencephalic markers during the first 18 days of monolayer differentiation. (c) Representative images of cells expressing Oct3/4, Sox1 and Pax6 during this process and quntification of the percentage of positive cells at each time-point. (d) Representative images of cells expressing calretinin/β-iii-tubulin for the H1 human ESCs line and the 2F8 and 4FHuang ipscs and quatinfication of double positive cells in control conditions and after Activin treatment (H1: control 5.4±1.5%, Activin 70.3±8.8%; 2F8: control 4.9±2.2%, Activin 63.2±15.8%; 4FHuang: control 4.4±1.8%, Activin 58.7±10.9%. (e) Double immunostaining for calretinin and GABA in Activin treated hescs (94.73±2.07% double positive). For all experiments the average fold change from three independent experiments (±SEM) is shown. hescs were differentiated as in Fig.7. Scale bar=50µm (c), 75µm (d) and 14µm (e).
8 Supplementary Figure S8. Activin inhibits Shh signalling and requires RA signalling during the differentiation of human ESCs. (a) qrt-pcr analysis indicating how the levels of Gli1 and Ptch1 change after 24h exposure to the indicated conditions and (b) how the expression of the Aldh1 family of genes are promoted by Activin signaling whilst Cyp26b1 is repressed. (c) Immunohistochemistry and (d) quantification of the proportion of neural precursors and neurons indicates that inhibition of RAR blocks the neural differentiation induced by Activin in hescs. Nestin+/β-III-tubulin + cells: Control=72.1±2.9%/14.6±1.9%; -RA+Act=62.6±5.5%/23.1±2.6%; +RA=64.0±5.5%/16.0±0.9%; +RA+Actv=35.9±5.5%/46.6±3.9%; +RA+Actv+RXRinh=32.0±5.8%/42.5±8.2%; +RA+Actv+RAR inh= 57.1±8.1%/ 31.6±7.1%; +RA+RAR inh= 69.1± 3.6%/ 17.5± 2.1%. For all experiments n=3, mean±sem Student s t test. **p<0.005 for the comparison between +RA+Act versus RA+Act and *p<0.05 for the comparison between +RA+Act versus +RA+Act+RAR inh. hescs were cultured as in Fig.7 until they were re-plated into poly-l-lysine/laminin coated dishes and at this stage they were cultured in N2B27 (controls), N2B27+10ng/ml Activin, N2B27+10µM RXR inhibitor, N2B27+10µM RXR inhibitor+10ng/mlactivin, N2B27+10µM RAR inhibitor or N2B27+10µM RAR inhibitor+10ng/mlactivin for 6 days (H1/iPSCs) or 7 days (H7). The NBB27 media was either VitA deficient or supplemented with VitA for these experiments. Scale bar=50µm.
9 Supplementary Table S1 Primers used for qrt-pcr Primers used for mouse cdnas Forward Reverse Nkx2.1 GGACACCATGCGGAACAGCG CCATGCCACTCATATTCATGCC Gsx2 GGACACCCGCAGCACCACG CCTTTTGCCATTGGGTACCTGG Pax6 CCATCTTTGCTTGGGAAATC GCTTCATCCGAGTCTTCTCC Gli1 CCCAATACATGCTGGTGGTGC CCGTGTGCGACCGAAGGTGC Patched1 CGAGACCAACGTGGAGGAGC GGAGTCTGTATCATGAGTTGAGG GAD1 GGCATCTTCCACTCCTTCGC CACAGATCTTCAGGCCCAGTTTTCT Foxg1 GACCCGTCGAGCGACGACG GGACAGGAAGGGCGACATGG Six3 GGTTTAAGAACCGGCGACAG TACCGAGAGGATCGAAGTGC Sox1 CCTCGGATCTCTGGTCAAGT TACAGAGCCGGCAGTCATAC Oct4 GGTTTAAGAACCGGCGACAG TACCGAGAGGATCGAAGTGC Nano GGTTTAAGAACCGGCGACAG TACCGAGAGGATCGAAGTGC Rex1 CGAGTGGCAGTTTCTTCTTGG GACTCACTTCCAGGGGGCAC Aldh1a1 GCCTGCACAACCTGCAGTCC GCCGCTCACTGAATTGTGCC Aldh1a2 GGTTTAAGAACCGGCGACAG TACCGAGAGGATCGAAGTGC Aldh1a3 GGTTTAAGAACCGGCGACA TACCGAGAGGATCGAAGTGC Cyp26b1 GCTCCATGGGATTCCCGCTC CGACGACTGGAAGCCGGAAC STRA6 GGTGACAGATGACTACAGCAGC GGTGCGGTGAGCTGGCAAAG Dlx2 CTACACCGCCGCGTACACCTCCTAC CGTGGTTTCCGGACTTTCTTTGGCTTCCCG Dlx6 CCTGGCCCTTCCCGAGAGAG GGGTCACTCTCGTGTGGGTTAC Dlx5 CCTCGCCCTGCCAGAACGC GGCATCTCCCCGTTTTTCATGA Er81 GGTCTGCTTGCAGTCAAGAG GGAGTGCTGGATGGTGTCGG Lhx6 CGAGTGCTCCGTGTGTCGCA CCAGTCACTGGCATAGATTTGTC Lhx2 CCCTACTACAACGGCGTGGG GGTAGGGCTGGTCACGATCC Crabp1 GCACACAGACACTTCTTGAGGG CGGACATAAATTCTTGTGCACACC Zcchc12 CCTGGAGGCAGGCTTTCTCAC CGCTTTATCTTCAGCAGTGCAGC β-actin GGTGACAGATGACTACAGCAGC GGTGCGGTGAGCTGGCAAAG Primers used for human cdnas Forward Reverse GSX2 CGCACCTGTCTGCACCGCC CCAGCTCCAGGAGTTGCGTG DLX2 ACTACCCCTGGTACCACCAGAC TCTGCTCTCAGTCTCTGGCGAGTTCTC GAD67 CGTCTTCGACCCCATCTTCGT CGCAGATCTTGAGCCCAGTT Calretinin CCTTACCTGCACCTGGCCGA CCAGAGCCTTTCCTTGCCTTC β-actin TCACCACCACGGCCGAGCG TCTCCTTCTGCATCCTGTCG
Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4
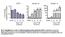 Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4 (n=3 independent differentiation experiments for each
Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4 (n=3 independent differentiation experiments for each
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Supplementary Table 3. Real-time PCR primer sequences.
 Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Human cerebral cortex development from pluripotent stem cells to functional excitatory synapses Yichen Shi 1,2, Peter Kirwan 1,2, James Smith 1,2, Hugh P.C. Robinson 3 and Frederick
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Human cerebral cortex development from pluripotent stem cells to functional excitatory synapses Yichen Shi 1,2, Peter Kirwan 1,2, James Smith 1,2, Hugh P.C. Robinson 3 and Frederick
Supplementary Figure S1: Pial and periventricular vascular networks and the dual GABA neuron streams of the early embryonic mouse telencephalon
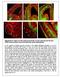 Supplementary Figure S1: Pial and periventricular vascular networks and the dual GABA neuron streams of the early embryonic mouse telencephalon a) The profile of GABA neurons arriving at the pallial-subpallial
Supplementary Figure S1: Pial and periventricular vascular networks and the dual GABA neuron streams of the early embryonic mouse telencephalon a) The profile of GABA neurons arriving at the pallial-subpallial
Table S1. qpcr primer list.
 Table S1. qpr primer list. Genes Forward primer Reverse primer NANOG AAATGGGAAGAATAGA GGTTAGTGGGTTA PAX6 TTTTGTTGGGAAATG TGGTTAAATTTAG ASL1 AAGATGAAAGAAAG GGAGTTTGATTAA NHLH GTGGATAGATATTT ATATTTTGGAATTT
Table S1. qpr primer list. Genes Forward primer Reverse primer NANOG AAATGGGAAGAATAGA GGTTAGTGGGTTA PAX6 TTTTGTTGGGAAATG TGGTTAAATTTAG ASL1 AAGATGAAAGAAAG GGAGTTTGATTAA NHLH GTGGATAGATATTT ATATTTTGGAATTT
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons. As an alternative method to demonstrate the role of shh as a guidance cue
Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons. As an alternative method to demonstrate the role of shh as a guidance cue
Supplemental Information. Induction of Expansion and Folding. in Human Cerebral Organoids
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Induction of Expansion and Folding in Human Cerebral Organoids Yun Li, Julien Muffat, Attya Omer, Irene Bosch, Madeline A. Lancaster, Mriganka Sur, Lee
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Induction of Expansion and Folding in Human Cerebral Organoids Yun Li, Julien Muffat, Attya Omer, Irene Bosch, Madeline A. Lancaster, Mriganka Sur, Lee
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 2 3 4 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table S1. Brain Tumors used in the study Code Tumor Classification Age Gender HuTuP51 Glioblastoma 57 Male HuTuP52 Glioblastoma 53 Male
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 2 3 4 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table S1. Brain Tumors used in the study Code Tumor Classification Age Gender HuTuP51 Glioblastoma 57 Male HuTuP52 Glioblastoma 53 Male
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Short-term coreceptor and costimulation blockade induces tolerance to pluripotent human ESCs. (A) Schematic diagram showing experimental approaches and
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Short-term coreceptor and costimulation blockade induces tolerance to pluripotent human ESCs. (A) Schematic diagram showing experimental approaches and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Supplementary Figure S1: Defective heterochromatin repair in HGPS progeroid cells
 Supplementary Figure S1: Defective heterochromatin repair in HGPS progeroid cells Immunofluorescence staining of H3K9me3 and 53BP1 in PH and HGADFN003 (HG003) cells at 24 h after γ-irradiation. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure S1: Defective heterochromatin repair in HGPS progeroid cells Immunofluorescence staining of H3K9me3 and 53BP1 in PH and HGADFN003 (HG003) cells at 24 h after γ-irradiation. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
TGF-β Signaling Regulates Neuronal C1q Expression and Developmental Synaptic Refinement
 Supplementary Information Title: TGF-β Signaling Regulates Neuronal C1q Expression and Developmental Synaptic Refinement Authors: Allison R. Bialas and Beth Stevens Supplemental Figure 1. In vitro characterization
Supplementary Information Title: TGF-β Signaling Regulates Neuronal C1q Expression and Developmental Synaptic Refinement Authors: Allison R. Bialas and Beth Stevens Supplemental Figure 1. In vitro characterization
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Neocortex Zbtb20 / NFIA / Sox9
 Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Supplementary table I. Real-time primers used in the study. The fold change was obtained by
 Supplementary table I. Real-time primers used in the study. The fold change was obtained by normalizing the gene expression number to those of HPRT, then comparing the samples to untreated or naive mice.
Supplementary table I. Real-time primers used in the study. The fold change was obtained by normalizing the gene expression number to those of HPRT, then comparing the samples to untreated or naive mice.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell extracts were subjected
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Materials. Stromal Modulation Reverses Primary Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Blockade in. Pancreatic Cancer.
 Supplemental Materials Stromal Modulation Reverses Primary Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Pancreatic Cancer Jun Zhao 1, Zhilan Xiao 2, 3, Tingting Li 1, 4, Huiqin Chen 5, Ying Yuan 5, Alan
Supplemental Materials Stromal Modulation Reverses Primary Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Pancreatic Cancer Jun Zhao 1, Zhilan Xiao 2, 3, Tingting Li 1, 4, Huiqin Chen 5, Ying Yuan 5, Alan
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplemental Figure 1. Egr1 expression in adult Achilles tendons. (A,B) Achilles tendons were isolated from 2 month-old Egr1 +/- mice and stained for
 Supplemental Figure 1. Egr1 expression in adult Achilles tendons. (A,B) Achilles tendons were isolated from 2 month-old Egr1 +/- mice and stained for LacZ activity, which reflects Egr1 expression. (A)
Supplemental Figure 1. Egr1 expression in adult Achilles tendons. (A,B) Achilles tendons were isolated from 2 month-old Egr1 +/- mice and stained for LacZ activity, which reflects Egr1 expression. (A)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
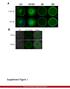 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from
 Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from germ cell mutants (dnrar flox/flox, Stra8-Cre +, RARElacZ) (A ), controls (dnrar flox/flox, RARElacZ) (B ),
Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from germ cell mutants (dnrar flox/flox, Stra8-Cre +, RARElacZ) (A ), controls (dnrar flox/flox, RARElacZ) (B ),
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Otx2 controls neuron subtype identity in ventral tegmental area and antagonizes
 Di Salvio et al. 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Otx2 controls neuron subtype identity in ventral tegmental area and antagonizes vulnerability to MPTP Michela Di Salvio, Luca Giovanni Di Giovannantonio, Dario
Di Salvio et al. 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Otx2 controls neuron subtype identity in ventral tegmental area and antagonizes vulnerability to MPTP Michela Di Salvio, Luca Giovanni Di Giovannantonio, Dario
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3150
 Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated
 Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x
 Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x magnification). B: Second HC skin stained for TSLP receptor in brown
Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x magnification). B: Second HC skin stained for TSLP receptor in brown
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Phosphoinositides Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking to Modulate Hedgehog Signaling
 Developmental Cell Supplemental Information Phosphoinositides Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking to Modulate Hedgehog Signaling Francesc R. Garcia-Gonzalo, Siew Cheng Phua, Elle C. Roberson, Galo Garcia
Developmental Cell Supplemental Information Phosphoinositides Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking to Modulate Hedgehog Signaling Francesc R. Garcia-Gonzalo, Siew Cheng Phua, Elle C. Roberson, Galo Garcia
High expression of cellular retinol binding protein-1 in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis
 High expression of cellular retinol binding protein-1 in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis Supplementary Material Supplementary Figure S1. Representative CRBP-1 immunostaining of non-neoplastic
High expression of cellular retinol binding protein-1 in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis Supplementary Material Supplementary Figure S1. Representative CRBP-1 immunostaining of non-neoplastic
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development
 Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Supplemental Information. Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate. into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling. in Developing Skin Vasculature
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set.
 Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Supplementary Materials for. c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration
 Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC
 Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Notes Note S1 Neonatal grafts consist mainly of mature cortical neurons Very few proliferating or apoptotic cells were found within the graft, and no markers of endodermal, mesodermal, epidermal
Supplementary Notes Note S1 Neonatal grafts consist mainly of mature cortical neurons Very few proliferating or apoptotic cells were found within the graft, and no markers of endodermal, mesodermal, epidermal
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated
 Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
s u p p l e m e n ta ry i n f o r m at i o n
 Figure S1 Characterization of tet-off inducible cell lines expressing GFPprogerin and GFP-wt lamin A. a, Western blot analysis of GFP-progerin- or GFP-wt lamin A- expressing cells before induction (0d)
Figure S1 Characterization of tet-off inducible cell lines expressing GFPprogerin and GFP-wt lamin A. a, Western blot analysis of GFP-progerin- or GFP-wt lamin A- expressing cells before induction (0d)
Differential neuronal vulnerability identifies IGF-2 as a protective factor in
 Supplementary Information Differential neuronal vulnerability identifies IGF-2 as a protective factor in ALS Ilary Allodi 1,3, Laura Comley 1,3, Susanne Nichterwitz 1,3, Monica Nizzardo 2, Chiara Simone
Supplementary Information Differential neuronal vulnerability identifies IGF-2 as a protective factor in ALS Ilary Allodi 1,3, Laura Comley 1,3, Susanne Nichterwitz 1,3, Monica Nizzardo 2, Chiara Simone
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2275
 Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Supplemental Tables and Figures. The metalloproteinase-proteoglycans ADAMTS7 and ADAMTS12 provide an innate,
 Supplemental Tables and Figures The metalloproteinase-proteoglycans ADAMTS7 and ADAMTS12 provide an innate, tendon-specific protective mechanism against heterotopic ossification Timothy Mead et al Supplemental
Supplemental Tables and Figures The metalloproteinase-proteoglycans ADAMTS7 and ADAMTS12 provide an innate, tendon-specific protective mechanism against heterotopic ossification Timothy Mead et al Supplemental
Application of induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in intractable childhood disorders
 10th Annual World Congress on Pediatrics Application of induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in intractable childhood disorders Lessons from Dravet synd. patient-derived ipscs Shinichi Hirose, MD, PhD
10th Annual World Congress on Pediatrics Application of induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in intractable childhood disorders Lessons from Dravet synd. patient-derived ipscs Shinichi Hirose, MD, PhD
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters. motor- and cue- dependent behaviors
 Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters motor- and cue- dependent behaviors Albert Quintana, Elisenda Sanz, Wengang Wang, Granville P. Storey, Ali D. Güler Matthew J. Wanat, Bryan
Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters motor- and cue- dependent behaviors Albert Quintana, Elisenda Sanz, Wengang Wang, Granville P. Storey, Ali D. Güler Matthew J. Wanat, Bryan
Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons by multidirectional repulsion
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2012) 22:697-716. 2012 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/12 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2012) 22:697-716. 2012 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/12 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2638 Figure S1 Morphological characteristics of fetal testes and ovaries from 6.5-20 developmental weeks. Representative images of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of testes and ovaries over
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2638 Figure S1 Morphological characteristics of fetal testes and ovaries from 6.5-20 developmental weeks. Representative images of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of testes and ovaries over
Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and
 Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and exclude YAP from the nucleus. (a) Schematic diagram of an E10.5 mouse embryo. (b,c) Sections at B and C in (a)
Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and exclude YAP from the nucleus. (a) Schematic diagram of an E10.5 mouse embryo. (b,c) Sections at B and C in (a)
Specification of neuronal and glial subtypes from human pluripotent stem cells
 Cell. Mol. Life Sci. (2011) 68:3995 4008 DOI 10.1007/s00018-011-0770-y Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences REVIEW Specification of neuronal and glial subtypes from human pluripotent stem cells Huisheng
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. (2011) 68:3995 4008 DOI 10.1007/s00018-011-0770-y Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences REVIEW Specification of neuronal and glial subtypes from human pluripotent stem cells Huisheng
Ductal pancreatic cancer modeling and drug screening using human pluripotent stem cell and patient-derived tumor organoids
 Ductal pancreatic cancer modeling and drug screening using human pluripotent stem cell and patient-derived tumor organoids Ling Huang 1, Audrey Holtzinger 1,2,11, Ishaan Jagan 1,11, Michael BeGora 1, Ines
Ductal pancreatic cancer modeling and drug screening using human pluripotent stem cell and patient-derived tumor organoids Ling Huang 1, Audrey Holtzinger 1,2,11, Ishaan Jagan 1,11, Michael BeGora 1, Ines
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Current density profiles for backside-plating configuration cells and the cycle stability curve with and without carbon coating. Current density profiles of
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Current density profiles for backside-plating configuration cells and the cycle stability curve with and without carbon coating. Current density profiles of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Long-term protection studies. 45 minutes of ischemia was induced in wild type (S1pr2 +/+ ) and S1pr2 -/- by MCAO. A) 5 days later brains were harvested
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Long-term protection studies. 45 minutes of ischemia was induced in wild type (S1pr2 +/+ ) and S1pr2 -/- by MCAO. A) 5 days later brains were harvested
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Supplementary Figure 1
 Combination index (CI) Supplementary Figure 1 2. 1.5 1. Ishikawa AN3CA Nou-1 Hec-18.5...2.4.6.8 1. Fraction affected (Fa) Supplementary Figure 1. The synergistic effect of PARP inhibitor and PI3K inhibitor
Combination index (CI) Supplementary Figure 1 2. 1.5 1. Ishikawa AN3CA Nou-1 Hec-18.5...2.4.6.8 1. Fraction affected (Fa) Supplementary Figure 1. The synergistic effect of PARP inhibitor and PI3K inhibitor
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Supplemental Information. Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal. Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based. Model of Parkinson's Disease
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based Model of Parkinson's Disease Annika Sommer, Franz Maxreiter, Florian Krach, Tanja Fadler,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based Model of Parkinson's Disease Annika Sommer, Franz Maxreiter, Florian Krach, Tanja Fadler,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells
 Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells Liying Yan,2,5, Mingyu Yang,5, Hongshan Guo, Lu Yang, Jun Wu, Rong Li,2, Ping Liu, Ying Lian, Xiaoying Zheng, Jie
Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells Liying Yan,2,5, Mingyu Yang,5, Hongshan Guo, Lu Yang, Jun Wu, Rong Li,2, Ping Liu, Ying Lian, Xiaoying Zheng, Jie
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Supplemental Table I
 Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4324
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Supplementary Figure 1. Kinetics of SnCs development in surgically-induced OA and effect of GCV-induced SnC clearance on OA disease progression
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Supplementary Figure 1. Kinetics of SnCs development in surgically-induced OA and effect of GCV-induced SnC clearance on OA disease progression
Schwarz et al. Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis
 Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Introduction Kit Components Cat. # # of vials Reagent Quantity Storage
 Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Supplementary Table 2. Plasma lipid profiles in wild type and mutant female mice submitted to a HFD for 12 weeks wt ERα -/- AF-1 0 AF-2 0
 Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
