Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1
|
|
|
- Lily Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1 I. Unit 13: The Respiratory System A. Organs of the Respiratory System 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. Bronchi 6. Lungs - alveoli B. Functions of the Respiratory System 1. Gas exchanges between the blood and external environment a) Occurs in the alveoli of the lungs 2. Passageways to the lungs purify, humidify, and warm the incoming air C. The Nose 1. Only externally visible part of the respiratory system 2. Air enters the nose through the external nostrils (nares) 3. Interior of the nose consists of a nasal cavity divided by a nasal septum D. Upper Respiratory Tract 1. Anatomy of the Nasal Cavity a) Olfactory receptors are located in the mucosa on the superior surface b) The rest of the cavity is lined with respiratory mucosa that (1) Moisten air (2) Trap incoming foreign particles c) Lateral walls have projections called conchae (1) Increase surface area (2) Increase air turbulence within the nasal cavity d) The nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity by the palate (1) Anterior hard palate (bone) (2) Posterior soft palate (muscle) 2. Paranasal Sinuses a) Cavities within bones surrounding the nasal cavity are called sinuses
2 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 2 b) Sinuses are located in the following bones (1) Frontal bone (2) Sphenoid bone (3) Ethmoid bone (4) Maxillary bone c) Function of the sinuses (1) Lighten the skull (2) Act as resonance chambers for speech (3) Produce mucus that drains into the nasal cavity 3. Pharynx (Throat) a) Muscular passage from nasal cavity to larynx b) Three regions of the pharynx (1) Nasopharynx - superior region behind nasal cavity (2) Oropharynx - middle region behind mouth (3) Laryngopharynx - inferior region attached to larynx c) The oropharynx and laryngopharynx are common passageways for air and food d) Structures of the Pharynx (1) Pharyngotympanic tubes open into the nasopharynx (2) Tonsils of the pharynx (a) Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids) are located in the nasopharynx (b) Palatine tonsils are located in the oropharynx (c) Lingual tonsils are found at the base of the tongue 4. Larynx (Voice Box) a) Routes air and food into proper channels b) Plays a role in speech c) Made of eight rigid hyaline cartilages and a spoon-shaped flap of elastic cartilage (epiglottis) d) Structures of the Larynx (1) Thyroid cartilage
3 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 3 (a) Largest of the hyaline cartilages (b) Protrudes anteriorly (Adam s apple) (2) Epiglottis (a) Protects the superior opening of the larynx (b) Routes food to the esophagus and air toward the trachea (c) When swallowing, the epiglottis rises and forms a lid over the opening of the larynx (3) Vocal folds (true vocal cords) (a) Vibrate with expelled air to create sound (speech) (4) Glottis - opening between vocal cords 5. Trachea (Windpipe) a) Four-inch-long tube that connects larynx with bronchi b) Walls are reinforced with C-shaped hyaline cartilage c) Lined with ciliated mucosa (1) Beat continuously in the opposite direction of incoming air (2) Expel mucus loaded with dust and other debris away from lungs 6. Respiratory Membrane (Air-Blood Barrier) a) Thin squamous epithelial layer lines alveolar walls b) Alveolar pores connect neighboring air sacs c) Pulmonary capillaries cover external surfaces of alveoli d) On one side of the membrane is air and on the other side is blood 7. Gas Exchange a) Gas crosses the respiratory membrane by diffusion b) Oxygen enters the blood c) Carbon dioxide enters the alveoli d) Alveolar macrophages ( dust cells ) add protection by picking up bacteria, carbon particles, and other debris e) Surfactant (a lipid molecule) coats gas-exposed alveolar surfaces 8. Main (Primary) Bronchi a) Formed by division of the trachea
4 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 4 b) Enters the lung at the hilum (medial depression) c) Right bronchus is wider, shorter, and straighter than left d) Bronchi subdivide into smaller and smaller branches 9. Lungs a) Occupy most of the thoracic cavity (1) Heart occupies central portion called mediastinum b) Apex is near the clavicle (superior portion) c) Base rests on the diaphragm (inferior portion) d) Each lung is divided into lobes by fissures (1) Left lung - two lobes (2) Right lung - three lobes e) Coverings of the Lungs (1) Serosa covers the outer surface of the lungs (a) Pulmonary (visceral) pleura covers the lung surface (b) Parietal pleura lines the walls of the thoracic cavity (2) Pleural fluid fills the area between layers of pleura to allow gliding (3) These two pleural layers resist being pulled apart 10. Bronchial (Respiratory) Tree Divisions a) All but the smallest of these passageways have reinforcing cartilage in their walls (1) Primary bronchi (2) Secondary bronchi (3) Tertiary bronchi (4) Bronchioles (5) Terminal bronchioles 11. Respiratory Zone a) Structures (1) Respiratory bronchioles (2) Alveolar ducts (3) Alveolar sacs
5 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 5 (4) Alveoli (air sacs) b) Site of gas exchange = alveoli only E. Four Events of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation - moving air in and out of the lungs (commonly called breathing) 2. External respiration - gas exchange between pulmonary blood and alveoli a) Oxygen is loaded into the blood b) Carbon dioxide is unloaded from the blood 3. Respiratory gas transport - transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide via the bloodstream 4. Internal respiration - gas exchange between blood and tissue cells in systemic capillaries F. Four Events of Respiration 1. Mechanics of Breathing (Pulmonary Ventilation) a) Completely mechanical process that depends on volume changes in the thoracic cavity (1) Volume changes lead to pressure changes, which lead to the flow of gases to equalize pressure b) Two phases (1) Inspiration = inhalation (a) flow of air into lungs (b) Diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract (c) The size of the thoracic cavity increases (d) External air is pulled into the lungs due to (i) Increase in intrapulmonary volume (ii) Decrease in gas pressure (2) Expiration = exhalation (a) air leaving lungs (b) Largely a passive process which depends on natural lung elasticity (c) As muscles relax, air is pushed out of the lungs due to (i) Decrease in intrapulmonary volume
6 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 6 (ii) Increase in gas pressure (d) Forced expiration can occur mostly by contracting internal intercostal muscles to depress the rib cage c) Pressure Differences in the Thoracic Cavity (1) Normal pressure within the pleural space is always negative (intrapleural pressure) (2) Differences in lung and pleural space pressures keep lungs d) Nonrespiratory Air (Gas) Movements (1) Can be caused by reflexes or voluntary actions (2) Examples: (a) Cough and sneeze - clears lungs of debris (b) Crying - emotionally induced mechanism (c) Laughing - similar to crying (d) Hiccup - sudden inspirations (e) Yawn - very deep inspiration e) Respiratory Volumes and Capacities (1) Normal breathing moves about 500 ml of air with each breath (a) This respiratory volume is tidal volume (TV) (2) Many factors that affect respiratory capacity (a) A person s size (b) Sex (c) Age (d) Physical condition (3) Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) (a) Amount of air that can be taken in forcibly over the tidal volume (i) Usually between 2100 and 3200 ml (4) Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) (a) Amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled (b) Approximately 1200 ml (5) Residual volume
7 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 7 (a) Air remaining in lung after expiration (b) About 1200 ml (6) Vital capacity (a) The total amount of exchangeable air (i) Vital capacity = TV + IRV + ERV (7) Dead space volume (a) Air that remains in conducting zone and never reaches alveoli (i) About 150 ml (8) Functional volume (a) Air that actually reaches the respiratory zone (i) Usually about 350 ml (9) Respiratory capacities are measured with a spirometer f) Respiratory Sounds (1) Sounds are monitored with a stethoscope (2) Two recognizable sounds can be heard with a stethoscope (a) Bronchial sounds - produced by air rushing through trachea and bronchi (b) Vesicular breathing sounds - soft sounds of air filling alveoli 2. External Respiration a) Oxygen loaded into the blood (1) The alveoli always have more oxygen than the blood (2) Oxygen moves by diffusion towards the area of lower concentration (3) Pulmonary capillary blood gains oxygen b) Carbon dioxide unloaded out of the blood (1) Blood returning from tissues has higher concentrations of carbon dioxide than air in the alveoli (2) Pulmonary capillary blood gives up carbon dioxide to be exhaled c) Blood leaving the lungs is oxygen-rich and carbon dioxide-poor 3. Gas Transport in the Blood a) Oxygen transport in the blood
8 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 8 (1) Most oxygen attached to hemoglobin to form oxyhemoglobin (HbO2) (2) A small dissolved amount is carried in the plasma b) Carbon dioxide transport in the blood (1) Most is transported in the plasma as bicarbonate ion (HCO3 ) (2) A small amount is carried inside red blood cells on hemoglobin, but at different binding sites than those of oxygen (3) For carbon dioxide to diffuse out of blood into the alveoli, it must be released from its bicarbonate form: (a) Bicarbonate ions enter RBC (b) Combine with hydrogen ions (c) Form carbonic acid (H2CO3) (d) Carbonic acid splits to form water + CO2 (e) Carbon dioxide diffuses from blood into alveoli 4. Internal Respiration a) Exchange of gases between blood and body cells b) An opposite reaction to what occurs in the lungs (1) Carbon dioxide diffuses out of tissue to blood (called loading) (2) Oxygen diffuses from blood into tissue (called unloading) G. Neural Regulation of Respiration 1. Activity of respiratory muscles is transmitted to and from the brain by phrenic and intercostal nerves 2. Neural centers that control rate and depth are located in the medulla and pons a) Medulla - sets basic rhythm of breathing and contains a pacemaker called the self-exciting inspiratory center b) Pons - appears to smooth out respiratory rate 3. Normal respiratory rate (eupnea) a) respirations per minute 4. Hyperpnea a) Increased respiratory rate often due to extra oxygen needs H. Non-Neural Factors Influencing Respiratory Rate and Depth 1. Physical factors
9 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 9 a) Increased body temperature b) Exercise c) Talking d) Coughing e) Volition (conscious control) f) Emotional factors 2. Chemical factors: CO2 levels a) The body s need to rid itself of CO2 is the most important stimulus b) Increased levels of carbon dioxide (and thus, a decreased or acidic ph) in the blood increase the rate and depth of breathing c) Changes in carbon dioxide act directly on the medulla oblongata 3. Chemical factors: oxygen levels a) Changes in oxygen concentration in the blood are detected by chemoreceptors in the aorta and common carotid artery b) Information is sent to the medulla I. Hyperventilation and Hypoventilation 1. Hyperventilation a) Results from increased CO2 in the blood (acidosis) b) Breathing becomes deeper and more rapid c) Blows off more CO2 to restore normal blood ph 2. Hypoventilation a) Results when blood becomes alkaline (alkalosis) b) Extremely slow or shallow breathing c) Allows CO2 to accumulate in the blood J. Respiratory Disorders: 1. Respiratory Disorders: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) a) Exemplified by chronic bronchitis and emphysema b) Major causes of death and disability in the United States c) Features of these diseases (1) Patients almost always have a history of smoking
10 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 10 (2) Labored breathing (dyspnea) becomes progressively more severe (3) Coughing and frequent pulmonary infections are common (4) Most victims are hypoxic, retain carbon dioxide, and have respiratory acidosis (5) Those infected will ultimately develop respiratory failure 2. Respiratory Disorders: Chronic Bronchitis a) Mucosa of the lower respiratory passages becomes severely inflamed b) Mucus production increases c) Pooled mucus impairs ventilation and gas exchange d) Risk of lung infection increases e) Pneumonia is common f) Called blue bloaters due to hypoxia and cyanosis 3. Respiratory Disorders: Emphysema a) Alveoli enlarge as adjacent chambers break through b) Chronic inflammation promotes lung fibrosis c) Airways collapse during expiration d) Patients use a large amount of energy to exhale e) Overinflation of the lungs leads to a permanently expanded barrel chest f) Cyanosis appears late in the disease; sufferers are often called 4. Respiratory Disorders: Lung Cancer a) Accounts for one-third of all cancer deaths in the United States b) Increased incidence is associated with smoking c) Three common types (1) Squamous cell carcinoma (2) Adenocarcinoma (3) Small cell carcinoma K. Developmental Aspects of the Respiratory System 1. Lungs are filled with fluid in the fetus 2. Lungs are not fully inflated with air until two weeks after birth 3. Surfactant is a fatty molecule made by alveolar cells
11 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 11 a) Lowers alveolar surface tension so that lungs do not collapse b) Not present until late in fetal development and may not be present in premature babies 4. Appears around weeks of pregnancy 5. Homeostatic imbalance a) Infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS) - surfactant production is inadequate b) Cystic fibrosis - oversecretion of thick mucus clogs the respiratory system c) Respiratory rate changes throughout life (1) Newborns: 40 to 80 respirations per minute (2) Infants: 30 respirations per minute (3) Age 5: 25 respirations per minute (4) Adults: 12 to 18 respirations per minute (5) Rate often increases somewhat with old age d) Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) (1) Apparently healthy infant stops breathing and dies during sleep (2) Some cases are thought to be a problem of the neural respiratory control center (3) One third of cases appear to be due to heart rhythm abnormalities (4) Recent research shows a genetic component e) Asthma (1) Chronic inflamed hypersensitive bronchiole passages (2) Response to irritants with dyspnea, coughing, and wheezing f) Aging effects (1) Elasticity of lungs decreases (2) Vital capacity decreases (3) Blood oxygen levels decrease (4) Stimulating effects of carbon dioxide decrease (5) Elderly are often hypoxic and exhibit sleep apnea (6) More risks of respiratory tract infection
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
Unit 13: The Respiratory System
 Unit 13: The Respiratory System I. Organs of the Respiratory System A. Nose B. Pharynx C. Larynx D. Trachea E. Bronchi F. Lungs alveoli II. Functions of the Respiratory System A. Gas exchanges between
Unit 13: The Respiratory System I. Organs of the Respiratory System A. Nose B. Pharynx C. Larynx D. Trachea E. Bronchi F. Lungs alveoli II. Functions of the Respiratory System A. Gas exchanges between
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Respiratory System 13PART A Organs of the Respiratory System Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Respiratory System 13PART A Organs of the Respiratory System Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Overview Oxygen is important to our body. The cardiovascular and respiratory system share responsibility for supplying the body with oxygen and disposing of carbon dioxide. Functional
The Respiratory System Overview Oxygen is important to our body. The cardiovascular and respiratory system share responsibility for supplying the body with oxygen and disposing of carbon dioxide. Functional
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous
 I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
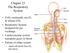 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Phases of Respiration
 Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
Chapter 16. The Respiratory System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Bio 104 Respiratory System 81
 81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 9
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Lab Activity 27. Anatomy of the Respiratory System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms
 131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
Chapter 22: The Respiratory System
 Chapter 22: The Respiratory System Four processes = pulmonary ventilation; external respiration; gas transport; internal respiration. I. Functional Anatomy Conduction zones lead into respiratory zones.
Chapter 22: The Respiratory System Four processes = pulmonary ventilation; external respiration; gas transport; internal respiration. I. Functional Anatomy Conduction zones lead into respiratory zones.
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models.
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Name: Date: Class: Unit 6 Outline: The Lymphatic and Respiratory Systems
 Name: Date: Class: Unit 6 Outline: The Lymphatic Respiratory Systems Lymphatic Vessels, Tissue, Organs The Lymphatic System Consists of Lymphatic Lymphoid tissues Lymphatic system functions Transport fluids
Name: Date: Class: Unit 6 Outline: The Lymphatic Respiratory Systems Lymphatic Vessels, Tissue, Organs The Lymphatic System Consists of Lymphatic Lymphoid tissues Lymphatic system functions Transport fluids
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Pages and
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
NAME PER DATE. membrane
 NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
Chapter 11. The respiratory system. Glossary. Anthony Wheeldon
 Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE.
 BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
Karachi King s College of Nursing
 Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
Structural Plan. Respiratory System. ose. Upper Respiratory Tract. Upper Respiratory Tract ose, nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx, and larynx
 Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
The Respiratory System:
 The Respiratory System: Respiration Involves both the respiratory and the circulatory systems Four processes that supply the body with O 2 and dispose of CO 2 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing):
The Respiratory System: Respiration Involves both the respiratory and the circulatory systems Four processes that supply the body with O 2 and dispose of CO 2 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing):
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Respiratory System
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Respiratory System I. Overview of the Respiratory System A. The respiratory system functions as an air distributor and gas exchanger supplying oxygen and removing carbon dioxide
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Respiratory System I. Overview of the Respiratory System A. The respiratory system functions as an air distributor and gas exchanger supplying oxygen and removing carbon dioxide
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
Gas exchange Regulate blood ph Voice production Olfaction Innate immunity
 Respiration Functions Gas exchange: Grab O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate immunity: physical protection
Respiration Functions Gas exchange: Grab O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate immunity: physical protection
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
The respiratory system
 Inspiration: Inhalation or breathing in air. The respiratory system Expiration: Exhalation or breathing out of air Ventilation (both) CVS carry the O2 to cells where Cellular respiration is taking place
Inspiration: Inhalation or breathing in air. The respiratory system Expiration: Exhalation or breathing out of air Ventilation (both) CVS carry the O2 to cells where Cellular respiration is taking place
The Respiratory System. Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration
 C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Objectives. Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology. Function of the Lungs/Heart. The lung is for gas exchange. Failure of the Lungs/Heart
 Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Anatomy of the Lungs. Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy
 Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23
 The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiration. Functions Anatomy
 Respiration Functions Anatomy Major Functions Gas exchange: absorb O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate
Respiration Functions Anatomy Major Functions Gas exchange: absorb O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate
Respiratory System. All I need is the air that I breathe
 Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Respiratory System. BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number.
 Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Overview. The Respiratory System. Chapter 18. Respiratory Emergencies 9/11/2012
 Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
The RESPIRATORY System
 The RESPIRATORY System Respira5on The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ven5la5on - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary) Respira5on
The RESPIRATORY System Respira5on The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ven5la5on - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary) Respira5on
Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from?
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
The Respiratory System
 Elaine N. Marieb Katja Hoehn Human Anatomy & Physiology SEVENTH EDITION C H A P T E R PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Vince Austin, Bluegrass Technical and Community College 22P A R T B The Respiratory
Elaine N. Marieb Katja Hoehn Human Anatomy & Physiology SEVENTH EDITION C H A P T E R PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Vince Austin, Bluegrass Technical and Community College 22P A R T B The Respiratory
