Fatigue in primary biliary cirrhosis
|
|
|
- Derek Wells
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gut 998;:0 0 0 Fatigue in primary biliary cirrhosis Department of Medicine K Cauch-Dudek E J Heathcote Department of Psychiatry, Toronto Hospital, University of Toronto, Canada S Abbey D E Stewart Correspondence to: Mrs K Cauch-Dudek, Toronto Hospital, Western Division, 99 Bathurst St, West Wing 8, Toronto, Ontario MT S8, Canada. Accepted for publication May 998 K Cauch-Dudek, S Abbey, D E Stewart, E J Heathcote Abstract Background Fatigue is a frequent and debilitating symptom in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). Aims To study fatigue in relation to sleep,, and liver disease severity. Methods Patients with PBC completed validated self report questionnaires measuring fatigue, sleep quality,, and functional capacity. Verbally reported fatigue and observer rated measure of and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) use were recorded. Liver biochemistry and tests to rule out metabolic causes of fatigue were performed. Results Mean age of the 88 patients enrolled was years; 8% were female and mean duration of disease was. years. Median bilirubin was µmol/l (mean 8.). Verbally reported fatigue (for more than six months) was present in 0 patients (8%). The self rated Fatigue Severity Score (FSS) correlated well with verbally reported fatigue (p=0.000). The FSS did not correlate with age, duration of disease, serum bilirubin, Mayo Risk Score, or UDCA use, but correlation was seen with sleep quality. Fatigued patients had more sleep problems and higher scores than non-fatigued patients. Self rated was present in 8% (/0) of fatigued compared with % (/8) of non-fatigued patients. Conclusions Long term fatigue avected 8% of the patients with PBC but it was not related to the severity of their liver disease. Poor sleep quality and were commonly associated with fatigue. (Gut 998;:0 0) Keywords: primary biliary cirrhosis; fatigue; ; sleep Fatigue, perceived as a persistent sense of exhaustion, inability to perform usual routines, and a decreased capacity for physical and mental work, is often one of the most debilitating symptoms of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). The Canadian demographic study found that 8% of patients reported fatigue as their most prevalent symptom, with deleterious evects on quality of life. These patients reported that their fatigue interfered with physical activity (%), family life (%), and job performance (0%). Recent clinical trials involving a total of 8 patients with PBC have shown that % report fatigue at entry to the studies. Yet despite its prevalence, there have been no studies to date focusing directly on the issue of fatigue and its impact on the quality of life in patients with PBC. The aetiology of fatigue in PBC is not known. In a previous study we have shown that fatigue did not correlate with liver histology in PBC patients; % of patients with PBC reported fatigue and no correlation with histological stage of disease was observed. In addition, treatments found to be evective in influencing the course of PBC do not necessarily improve the fatigue. Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) may currently be considered the best treatment for PBC as its evect on survival has now been shown. 8 However, UDCA trials have failed to show that this therapy leads to any improvement in fatigue. A recent editorial focused on fatigue as an important determinant of the quality of life in patients with chronic liver disease and emphasised the importance of studying fatigue. 9 The aims of this study were to assess factors associated with fatigue in PBC, and simultaneously assess liver function and the physical and emotional aspects of quality of life. This paper reports on sleep,, and cognitive function in relation to fatigue. Patients and methods Between January and May 99, of the patients with liver biopsy proved antimitochondrial, antibody positive PBC actively followed at that time by The Toronto Hospital (Western Division) Liver Clinic, were overed participation in the study. Participation was not overed to patients either because of an inadequate understanding of the English language or an inability to travel to clinic due to the long distance or sickness. Of the patients approached, chose not to participate ( were not interested in the study, nine were unable to travel, and a further two lacked an adequate understanding of English). The study was approved by the institutional review board (The Toronto Hospital Committee for Research on Human Subjects) and informed written consent was obtained from each patient. During a visit to the outpatient liver clinic, patients completed previously validated self report questionnaires measuring fatigue, sleep disturbance,, and cognitive and functional capacity. 0 Verbally reported fatigue was recorded and an observer rated measure of completed by a single observer (KC-D). Standard liver biochemistry was performed along with other standard tests (thyroid and renal function, haemoglobin, calcium) to rule out recognised metabolic causes of fatigue. Use of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA, Ursofalk, mg/kg/day) at the time of study and the amount of weekly physical
2 0 Cauch-Dudek, Abbey, Stewart, et al With verbally reported fatigue (n = 0) Without verbally reported fatigue (n = 8) Total bilirubin (µmol/l) 0 80 r = 0.0 p > Mayo Risk Score Figure Fatigue Severity Scale score versus total serum bilirubin and Mayo Risk Score. There is some overlap of points within the figure. Table exercise (in hours) were recorded. The Mayo Risk score, a validated prognostic index developed to predict survival in PBC, was calculated for each patient as an indirect measure of disease severity. Data were analysed with SAS using the Wilcoxon rank sum test, correlation, and linear regression. Non-parametric statistics were used as the data were not normally distributed. However, means (SD) are reported in order to compare results with work done in previously reported populations where large standard deviations were observed presumably due to skewness of data. Fatigue, sleep and in primary biliary cirrhosis Patients verbally reporting fatigue (n=0) 0 Patients verbally reporting no fatigue (n=8) r = 0.08 p > 0.0 Normal population controls (FSS) Mean (SD). (.)*. (.). (.8) Range. Global sleep quality (PSQI) Mean (SD) 8. (.9).0 (.). (.) Range Depressive symptoms Observer rated HDRS Mean (SD) 9. (.)*.89 (.9) Range Self rated CES-D Mean (SD). (9.). (.0) 9. (8.)** Range *p<0.000, p<0.000 v patients with PBC verbally reporting no fatigue. Schwartz et al. 0 Buysse et al. Hamilton et al. **RadloV, maximum of three general population means,.9, 8., 9.. INSTRUMENTS Fatigue Two measures of fatigue were used in this study. Verbally reported fatigue was assessed as being present if noted for more than six months by the patient. Fatigue was also measured by the self rated Fatigue Assessment Instrument (FAI), 0 developed to measure both the qualitative and quantitative aspects of respondents fatigue during the previous two weeks. This 9 item questionnaire was designed for, and validated in, large groups of medical and psychiatric patients and includes subscales of fatigue severity (FSS), situation specificity, consequences of fatigue, and response to rest and sleep. Sleep The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) was used to assess sleep quality and disturbances in sleep patterns during the previous month. Designed and validated to discriminate between good and poor sleepers in clinical populations, this 9 item self rated questionnaire generates seven component scores of subjective sleep quality, sleep latency, sleep duration, habitual sleep eyciency, sleep disturbances, daytime dysfunction, and use of sleeping medication. Each component score is weighted equally on a 0 scale. The frequency with which pruritus interfered with sleep was also recorded as part of the PSQI. A global PSQI sleep quality score with a range of 0 is generated by summing the component scores, with a higher score indicating worse overall sleep quality. Depression Two well validated scales were used to assess. Observer rated was measured by the item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS). Although originally developed to assess the severity of in psychiatric populations, use of this scale is no longer restricted to this group. There are standard cut point scores which have been used to identify divering levels of depressive symptomatology in research studies. The HDRS has a possible range of scores from 0 to. Scores of are described as indicating mild, 8 as moderate, and scores of greater than as. A score of 8 or more is typically required for entry into clinical trials of antidepressant therapy. The self rated 0 item Centre for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Rating Scale (CES-D) was designed to assess depressive symptomatology within the previous week in general population groups. Each of the items is scored from 0 to on a scale of frequency of occurrence of the symptom. Scores on the CES-D range from 0 to 0. In studies which have used the CES-D, means for three general population samples of Caucasian respondents were.9, 8., and 9., while the mean for psychiatric patients was.. 8 A cut point score of is commonly used to indicate the likely presence of.
3 Fatigue in primary biliary cirrhosis 0 Severe difficulty Sleep subscale score No difficulty 0 Subjective sleep quality PBC patients with verbally reported fatigue (n = 0) PBC patients without verbally reported fatigue (n = 8) Normal control population (n = ) Habitual sleep efficiency Sleep disturbances Daytime dysfunction Sleep latency Sleep components Figure Comparison of sleep in patients with and without verbally reported fatigue and a normal control population. Cognitive function During patient interviews, the Folstein Mini Mental State was used to assess cognitive function. This item test focuses on patient orientation to time and place, registration, attention and calculation, recall and language. Function was also determined by timed performance on the Trails A and B tests, where patients were asked to connect sequential letters and numbers. Results A total of 88 patients with PBC was enrolled in the study. The mean age was () years (range 80); 8% were female and the mean duration of disease, from date of diagnosis, was () years (range ). Fifty per cent of the patients were receiving UDCA treatment for their PBC at the time of study entry. Median bilirubin was.0 µmol/l (mean 8. (.0), range ) and the mean Mayo Risk Score was () (range ). Only two of the 88 patients had decompensated liver disease and they were the only subjects taking diuretics for ascites. Haemoglobin, thyroid stimulating hormone, creatinine, or calcium levels did not With verbally reported fatigue (n = 0) Without verbally reported fatigue (n = 8) r = 0.9 p = No difficulty Severe difficulty Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index: global score Figure Fatigue Severity Scale score versus global sleep quality. The PSQI global score range for normal controls is 0.. There is some overlap of points within the figure. indicate a metabolic basis for fatigue in any study patient. FATIGUE On clinical interview, verbally reported fatigue lasting longer than six months was present in 0 patients (8%). The 0% of patients receiving UDCA treatment had identical rates of verbally reported fatigue to those in nontreated patients. Using the self rated fatigue severity score (FSS) from the Fatigue Assessment Instrument (FAI), patients who had verbally reported fatigue also had significantly higher FSS scores than those with no verbally reported fatigue (p<0.000) (table ). UDCA treated and non-treated patients had similar FSS scores (means of.0 and.8 respectively). There was no correlation of FSS with patient age, duration of disease, or hours of weekly physical exercise. PBC severity as indicated by total serum bilirubin and Mayo Risk Score did not correlate with FSS (fig ). SLEEP Patients who verbally reported fatigue had significantly more diyculty with global sleep quality as measured by the PSQI than those not reporting fatigue (p<0.000) (table ). Those with fatigue reported greater impairment than non-fatigued patients in subjective sleep quality, habitual sleep eyciency, sleep disturbances, and daytime dysfunction (fig ). PSQI sleep quality score was found to be highly correlated with the FSS (fig ). Total sleep duration (in hours) was similar for patients reporting and those not reporting fatigue: % (/0) of fatigued and 9% (8/8) of non-fatigued patients reported less than six hours of sleep (this % diverence is not significant; 9% confidence interval to ). Global sleep quality was similar for UDCA treated and non-treated patients. Pruritus reported by the patients was not found to correlate with PSQI sleep quality or the specific aspects of sleep noted above; % (/0) of patients with fatigue had no pruritus. Medications to assist sleep were used more than twice per week by (%) of the patients with fatigue versus three (%) of those without fatigue. DEPRESSION Patients reporting fatigue had significantly more depressive symptomatology than those not reporting fatigue, both on the observer rated HDRS and self rated CES-D (table ). On the HDRS, which is generally considered to be the gold standard rating scale for measuring clinical, % (/9) of fatigued patients had at least some evidence of depressive symptomatology (HDRS score of seven or more) whereas these symptoms were only present in 8% (/8) of patients without fatigue (this % diverence is significant; 9% confidence interval to ). Using classic cut points for this scale, % of fatigued patients were mildly depressed (score of ), % were moderately depressed (score of 8 ), and % were ly depressed (score greater than ). In the non-fatigued patients, the
4 08 Cauch-Dudek, Abbey, Stewart, et al No 0 0 With verbally reported fatigue (n = 0) Without verbally reported fatigue (n = 8) Mild 0 0 Total Hamilton Depression Rating Scale score No Depression Total CES-D score Figure Fatigue Severity Scale score versus. There is some overlap of points within the figure. Moderate r = 0. p = Severe figures for these same indexes were 8%, 0%, and 0% respectively. The CES-D, which recorded self rated depressive symptomatology, found 8% (/ 0) of fatigued patients had depressive symptoms comparable in severity (CES-D score of or more) to that reported in depressed patients undergoing psychiatric consultation, 8 whereas only % (/8) of the patients reporting no fatigue had depressive symptoms of similar severity (this % diverence is significant; 9% confidence interval to 8). Both measurements were highly correlated with fatigue severity as measured by the FSS subscale of the FAI (fig ). Both the observer rated and self rated scores were similar for the fatigued patients being treated with UDCA and those receiving no treatment (observer rated mean scores of 9. and 0.0 and self rated mean scores of 0. and. respectively). Both scores remained within the normal range for patients without fatigue, regardless of UDCA use. The correlation of fatigue severity with both measures of was similar for both UDCA treated and non-treated groups. COGNITIVE FUNCTION The fatigued and non-fatigued groups did not diver significantly on screening tests for cognitive dysfunction, total score on the 0 r = 0. p = Folstein Mini Mental State Examination, and time on Trail Making A and B tests. The scores for both groups were well within the normal range and no patients scored in the abnormal range. Discussion Fatigue lasting for more than six months was reported on interview by 8% of our PBC patients; there was no correlation with UDCA use. The fatigue severity scores of our PBC patients reporting fatigue (. (.)) were comparable to scores published for patients with multiple sclerosis (.8 (.)) and systemic lupus erythematosus (. (.)). 9 Patients with PBC reporting no fatigue on interview had fatigue severity scores comparable to those of normal healthy adults (. (.) versus. (0.)). 9 Both our fatigued and non-fatigued patients had global PSQI sleep quality scores that indicated worse sleep than normal population controls ; only % (/0) of our patients with fatigue reported sleep quality comparable to normal controls, whereas % (/8) of those without fatigue had normal sleep quality (fig ). The pruritus reported by our patients was not associated with global sleep quality score; thus it seems that poor sleep quality could not be simply attributed to itching. Our patients did not compensate for their fatigue by sleeping longer nor was rest found to be restorative to those with fatigue. Sleep duration of at least six hours reported by % of our fatigued and % of our non-fatigued patients is comparable to the duration of sleep reported by normal population controls. Gross cognitive dysfunction was not found in our screening tests or on interview with our patients, and as only two patients had clinical evidence of hepatic decompensation, we conclude that none had hepatic encephalopathy to account for their poor sleep quality. However, despite the absence of hepatic encephalopathy, daytime dysfunction was a significant problem for many of the patients; 9% of fatigued patients had higher daytime dysfunction scores on the PSQI than normal controls, compared with % of those patients without fatigue. Many factors may cause daytime dysfunction, aside from poor sleep quality. Depression was common in our fatigued patients, regardless of UDCA use. The minimum score on the observer rated HDRS required for the study of antidepressant medications in outpatients is 8. Thus using this scale, 9% (/9) of our fatigued PBC patients had scores suycient to warrant therapy with antidepressants, whereas none of the patients without fatigue had scores in this range (fig ). The rate of in our PBC patients is higher than that observed in a recent Ontario study which reported that.% of middle aged women (aged to years) suvered from. 0 The combination of and fatigue is not unusual and has been found in the general population, in primary care samples, in medically unexplained syndromes such as the chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), as well as in well defined
5 Fatigue in primary biliary cirrhosis 09 disease groups such as survivors of Hodgkin s disease and end stage renal disease. Fatigue has been studied in few patients with liver disease, 8 but there have been studies reporting fatigue in association with other chronic autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. A multivariate model of fatigue was proposed in an attempt to sort out the contributions of disease activity,, sleep patterns, and fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus. It was postulated that, through reciprocal evects on each other, both and sleep act as mechanisms through which fatigue is increased by disease activity. However, as in this study of PBC patients no correlation was observed between severity of disease (serum bilirubin and Mayo Risk Score) and fatigue, it would seem that it is not the liver disease directly that is causative. This study has raised some interesting questions about the relations between sleep,, and fatigue. It remains to be determined whether fatigue induces sleep disturbance and/or or vise versa in PBC patients. Based on the assumption that fatigue and other behavioural changes are part of a natural homoeostatic reaction used by the body in response to stressful conditions, Swain and Maric have recently studied the role of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) in bile duct resected cholestatic rats and sham resected controls. Defective CRH mediated responses were found in the cholestatic rats, and they conclude that the altered CRH mediated behaviours resulting from the cholestasis may contribute to fatigue and other non-specific symptoms of PBC. These same authors have reported evidence of an altered pituitaryadrenal axis in PBC patients who were found to have elevated serum cortisol levels. Long term fatigue can have a debilitating evect on the quality of life in PBC patients. We found that the fatigue is similar in UDCA treated and non-treated patients, and a previous study by our group failed to show that UDCA aleviates fatigue. Sleep disturbance, which is often a symptom of, 8 can compound this evect. Studies of sleep architecture in patients with PBC are required to determine whether sleep disturbances induce fatigue, as sleep disturbances are treatable. Similarly, this study has shown that is a major factor associated with fatigue, but it is not clear whether fatigue leads to or vice versa. As PBC is primarily a disease of women and in epidemiological studies, is twice as common in women as in 9 0 men, may explain in part why fatigue is a predominant symptom of PBC. Given that is eminently treatable and may result in alleviation of fatigue and general improvement in quality of life, studies of antidepressant therapy may be indicated to assess the evect on the and fatigue associated with PBC. Barofsky I, Legro MW. Definition and measurement of fatigue: approaches to data collection. Rev Infect Dis 99;:S9. Witt-Sullivan H, Heathcote EJL, Cauch K, et al. The demography of primary biliary cirrhosis in Ontario, Canada. Hepatology 990;:98 0. Poupon RE, Balkau B, Eschwege E, Poupon R, and the UDCA-PBC Study Group. A multicentre, controlled trial of ursodiol for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 99;:8. Heathcote EJL, Cauch-Dudek K, Walker V, et al. The Canadian multi-centre double blind randomized controlled trial of ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 99;9:9. Lindor KD, Dickson ER, Baldus WP, et al. Urosdeoxycholic acid in the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 99;0:8 90. Wanless IR, Heathcote EJ, Cauch K, et al. Detailed histologic grading as a predictor of morbidity and mortality in primary biliary cirrhosis [abstract]. Hepatology 99;8: A. Lindor KD, Therneau TM, Jorgensen RA, et al. EVects of ursodeoxycholic acid on survival in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 99;0: 8. 8 Poupon RE, Lindor KD, Cauch-Dudek K, et al. Randomized controlled trials of ursodiol treatment in primary biliary cirrhosis: combined analysis of French, American and Canadian data. Gastroenterology 99;: Jones EA. Fatigue associated with chronic liver disease: a riddle wrapped in a mystery inside an enigma [editorial]. Hepatology 99;: Schwartz JE, Krupp LB. The measurement of fatigue: a new instrument. J Psychosom Res 99;:. Buysse DJ, Reynolds III CF, Monk TH, et al. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiat Res 989;8:9. Hamilton M. A rating scale for. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90;:. RadloV LS. CES-D scale: a self-report scale for research in the general population. Psychol Meas 9;: 8 0. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini-mental state: a practical method of grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiat Res 9;: Reitan RM. Validity of the Trail Making test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Percept Motor Skills 98;8:. Dickson ER, Grambsch PM, Fleming TR,et al. Prognosis in primary biliary cirrhosis: model for decision making. Hepatology 989;0:. Endicott J, Cohen J, Nee J, et al. Hamilton Depression Rating Scale: extracted from regular and changed versions of the Schedule for AVective Disorders and Schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiat 98;8: Corcoran K, Fischer J. Centre for Epidemiologic Studies Depressed Mood Scale. In: Measures for clinical practice: a sourcebook. New York: The Free Press, 98: Krupp LB, LaRocca NG, Muir-Nash J, et al. The Fatigue Severity Scale. Application to patients with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Neurol 989;:. 0 OVord DR, Boyle MH, Campbell D, et al. One-year prevalence of psychiatric disorder in Ontarians to years of age. Can J Psychiatry 99;:9. Chen MK. The epidemiology of self-perceived fatigue among adults. Prevent Med 98;: 8. Pawlikowska T, Chalder T, Hirsch SR, et al. Population based study of fatigue and psychological distress. BMJ 99;08:. Cathebras PJ, Robbins JM, Kirmayer LJ, et al. Fatigue in primary care: prevalence, psychiatric comorbidity, illness behavior, and outcome. J Gen Intern Med 99;: 8. Walker EA, Katon WJ, Jemelka RP. Psychiatric disorders and medical care utilization among people in the general population who report fatigue. J Gen Intern Med 99;8: 0. Wessely S. The epidemiology of chronic fatigue syndrome. Epidemiol Rev 99;:9. Fobair P, Hoppe RT, Bloom J, et al. Psychosocial problems among survivers of Hodgkin s disease. J Clin Oncol 98;: 80. Cardenas DD, Kutner NG. The problem of fatigue in dialysis patients. Nephrology 98;0: 0. 8 Nelles S, Abbey S, Stewart DE, et al. Fatigue assessment in patients with hepatitis C [abstract]. Gastroenterology 99; 0:A. 9 Huet PM, Deslauriers J. Impact of fatigue on quality of life of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis [abstract]. Gastroenterology 99;0:A. 0 Merican I, Sherlock S, McIntyre N, et al. Clinical, biochemical and histologic features in 0 patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. QJMed99;8:9. Mahl TC, Daniels K, Dahhan W, et al. Fatigue in patients with chronic hepatitis C [abstract]. Gastroenterology 99; 0:A. McCoy A, Callahan LF, Pincus T. Quantitative assessment of fatigue in routine care of patients with rheumatic diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Care Research 99;:S. Krupp LB, LaRocca NG, Muir J, et al. A study of fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 990;:0. Krupp LB, LaRocca NG, Muir-Nash J, et al. The fatigue severity scale: application to patients with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Neurol 989;:.
6 0 Cauch-Dudek, Abbey, Stewart, et al McKinley PS, Ouellette SC, Winkel GH. The contributions of disease activity, sleep patterns, and to fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus: a proposed model. Arthritis Rheum 99;8:8. Swain MG, Maric M. Defective corticotropin-releasing hormone mediated neuroendocrine and behavioral responses in cholestatic rats: implications for cholestatic liver diseaserelated sickness behaviors. Hepatology 99;:0. Swain MG, Mogiakou M, Bergasa NV, et al. Facilitation of ACTH and cortisol responses to corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) [abstract]. Hepatology 99;0:A. 8 American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. th edn. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, Myers JK, Weissman MM, Tischler GL, et al. Six-month prevalence of psychiatric disorders in three communities: 980 to 98. Arch Gen Psychiatry 98;:99. 0 Robins LN, Heizer JE, Weissman MM, et al. Lifetime prevalence of specific psychiatric disorders in three sites. Arch Gen Psychiatry 98;:99 8. Gut: first published as 0./gut...0 on November 998. Downloaded from on March 09 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Prolonged Follow-Up of Patients in the U.S. Multicenter Trial of Ursodeoxycholic Acid for Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2004 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j1572-0241.2004.04047.x Published by Blackwell Publishing Prolonged Follow-Up of Patients in the
American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2004 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j1572-0241.2004.04047.x Published by Blackwell Publishing Prolonged Follow-Up of Patients in the
Presentation and mortality of primary biliary cirrhosis in older patients
 Age and Ageing 2000; 29: 305 309 Presentation and mortality of primary biliary cirrhosis in older patients JULIA L. NEWTON 1,DAVID E. JONES 2,JANE V. METCALF 2,JAY B. PARK 2,ALISTAIR D. BURT 2, MARGARET
Age and Ageing 2000; 29: 305 309 Presentation and mortality of primary biliary cirrhosis in older patients JULIA L. NEWTON 1,DAVID E. JONES 2,JANE V. METCALF 2,JAY B. PARK 2,ALISTAIR D. BURT 2, MARGARET
Obeticholic Acid for the treatment of Primary Biliary Cholangitis: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks
 Obeticholic Acid for the treatment of Primary Biliary Cholangitis: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks Draft Background and Scope Background: April 21, 2016 Primary biliary cholangitis
Obeticholic Acid for the treatment of Primary Biliary Cholangitis: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks Draft Background and Scope Background: April 21, 2016 Primary biliary cholangitis
Clinical Significance of Serum Bilirubin Levels Under Ursodeoxycholic Acid Therapy in Patients With Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 Clinical Significance of Serum Bilirubin Levels Under Ursodeoxycholic Acid Therapy in Patients With Primary Biliary Cirrhosis ANNE-MARIE BONNAND, 1 E. JENNY HEATHCOTE, 2 KEITH D. LINDOR, 3 AND RENÉE EUGÉNIE
Clinical Significance of Serum Bilirubin Levels Under Ursodeoxycholic Acid Therapy in Patients With Primary Biliary Cirrhosis ANNE-MARIE BONNAND, 1 E. JENNY HEATHCOTE, 2 KEITH D. LINDOR, 3 AND RENÉE EUGÉNIE
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Ocaliva (obeticholic acid) Page 1 of 6 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Ocaliva (obeticholic acid) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
Ocaliva (obeticholic acid) Page 1 of 6 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Ocaliva (obeticholic acid) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
TREATMENT OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS (PBC)
 TREATMENT OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS (PBC) URSO not indicated Therapy for PBC Difficulties Etiology is uncertain Therapies are based on ideas regarding pathogenesis Present medical therapies have a limited
TREATMENT OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS (PBC) URSO not indicated Therapy for PBC Difficulties Etiology is uncertain Therapies are based on ideas regarding pathogenesis Present medical therapies have a limited
Fatigue is common in primary biliary cirrhosis
 LIVER DISEASE A Randomized, Controlled Crossover Trial of Ondansetron in Patients With Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and Fatigue Jeremy J. Theal, 1 Mohssen N. Toosi, 1 Larisa Girlan, 1 Ronald J. Heslegrave,
LIVER DISEASE A Randomized, Controlled Crossover Trial of Ondansetron in Patients With Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and Fatigue Jeremy J. Theal, 1 Mohssen N. Toosi, 1 Larisa Girlan, 1 Ronald J. Heslegrave,
Diagnosis and Management of PBC
 Diagnosis and Management of PBC Cynthia Levy, MD, FAASLD University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Miami, Florida 1 Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) Chronic cholestatic liver disease Autoimmune in
Diagnosis and Management of PBC Cynthia Levy, MD, FAASLD University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Miami, Florida 1 Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) Chronic cholestatic liver disease Autoimmune in
New insights in pathogenesis and therapy of primary biliary cholangitis. Keith D. Lindor Dean Professor of Medicine
 New insights in pathogenesis and therapy of primary biliary cholangitis Keith D. Lindor Dean Professor of Medicine OUTLINE PBC Epidemiology Diagnosis Treatment Incidence of PBC and PSC Trends Boonstra
New insights in pathogenesis and therapy of primary biliary cholangitis Keith D. Lindor Dean Professor of Medicine OUTLINE PBC Epidemiology Diagnosis Treatment Incidence of PBC and PSC Trends Boonstra
R ecent estimates suggest that there are
 865 LIVER Asymptomatic primary biliary cirrhosis: clinical features, prognosis, and symptom progression in a large population based cohort M I Prince, A Chetwynd, W L Craig, J V Metcalf, O F W James...
865 LIVER Asymptomatic primary biliary cirrhosis: clinical features, prognosis, and symptom progression in a large population based cohort M I Prince, A Chetwynd, W L Craig, J V Metcalf, O F W James...
The True Impact of Fatigue in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: A Population Study
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2002;122:1235 1241 The True Impact of Fatigue in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: A Population Study JENNIFER GOLDBLATT,* PHILIP J. S. TAYLOR, TOBY LIPMAN, MARTIN I. PRINCE,* ANNA BARAGIOTTA,*
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2002;122:1235 1241 The True Impact of Fatigue in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: A Population Study JENNIFER GOLDBLATT,* PHILIP J. S. TAYLOR, TOBY LIPMAN, MARTIN I. PRINCE,* ANNA BARAGIOTTA,*
Ocaliva (obeticholic acid tablets)
 Ocaliva (obeticholic acid tablets) Policy Number: 5.01.619 Last Review: 11/2018 Origination: 11/2016 Next Review: 11/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
Ocaliva (obeticholic acid tablets) Policy Number: 5.01.619 Last Review: 11/2018 Origination: 11/2016 Next Review: 11/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features?
 22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
Cost and health consequences of treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis with ursodeoxycholic acid
 Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics Cost and health consequences of treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis with ursodeoxycholic acid K. M. Boberg*,, T. Wisløff, K. S. Kjøllesdal, H. Støvring & I.
Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics Cost and health consequences of treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis with ursodeoxycholic acid K. M. Boberg*,, T. Wisløff, K. S. Kjøllesdal, H. Støvring & I.
Morning Report Presentation. Sarah Hughes, MD January 11, 2005
 Morning Report Presentation Sarah Hughes, MD January 11, 2005 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis! PBC is a chronic, progressive, cholestatic liver disease of unknown cause that usually affects middle-aged women
Morning Report Presentation Sarah Hughes, MD January 11, 2005 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis! PBC is a chronic, progressive, cholestatic liver disease of unknown cause that usually affects middle-aged women
ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT A
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:228 233 ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT A Predictive Model for Fatigue and Its Etiologic Associations in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis JULIA
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:228 233 ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT A Predictive Model for Fatigue and Its Etiologic Associations in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis JULIA
PBC features and management in the era of UDCA and Budesonide
 PBC features and management in the era of UDCA and Budesonide Raoul Poupon, MD Université P&M Curie, AP-Hôpitaux de Paris, Inserm, Paris, France The changing pattern of PBC Over the last 2 decades: More
PBC features and management in the era of UDCA and Budesonide Raoul Poupon, MD Université P&M Curie, AP-Hôpitaux de Paris, Inserm, Paris, France The changing pattern of PBC Over the last 2 decades: More
LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:769 775 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Factors That Reduce Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis MARIA BENITO
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:769 775 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Factors That Reduce Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis MARIA BENITO
Hangzhou, 15 March Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical Center University of Amsterdam
 Clinical Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Hangzhou, 15 March 2008 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical Center University of Amsterdam Epidemiology of Primary
Clinical Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Hangzhou, 15 March 2008 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical Center University of Amsterdam Epidemiology of Primary
Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
 Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN 2012 Annual Conference PSC Partners Seeking a Cure May 5, 2012 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Multifocal
Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN 2012 Annual Conference PSC Partners Seeking a Cure May 5, 2012 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Multifocal
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a rare chronic inflammatory CLINICAL LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2005;128:297 303 CLINICAL LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT The Effect of Ursodeoxycholic Acid Therapy on the Natural Course of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis CHRISTOPHE CORPECHOT,* FABRICE
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2005;128:297 303 CLINICAL LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT The Effect of Ursodeoxycholic Acid Therapy on the Natural Course of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis CHRISTOPHE CORPECHOT,* FABRICE
A Prospective Trial of Colchicine and Methotrexate in the Treatment of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1999;117:1173 1180 A Prospective Trial of Colchicine and Methotrexate in the Treatment of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis MARSHALL M. KAPLAN, CHRISTOPHER SCHMID, DAWN PROVENZALE, ARCHNA SHARMA,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1999;117:1173 1180 A Prospective Trial of Colchicine and Methotrexate in the Treatment of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis MARSHALL M. KAPLAN, CHRISTOPHER SCHMID, DAWN PROVENZALE, ARCHNA SHARMA,
Adverse health effects of industrial wind turbines: a preliminary report
 Adverse health effects of industrial wind turbines: a preliminary report Michael Nissenbaum MD 1, Jeff Aramini PhD 2, Chris Hanning MD 3 1 Northern Maine Medical Center, Fort Kent, Maine, USA, mnissenbaum@att.net
Adverse health effects of industrial wind turbines: a preliminary report Michael Nissenbaum MD 1, Jeff Aramini PhD 2, Chris Hanning MD 3 1 Northern Maine Medical Center, Fort Kent, Maine, USA, mnissenbaum@att.net
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
 Primary Biliary Cholangitis What is primary biliary cholangitis? Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic liver disease. When a person has PBC, the immune
Primary Biliary Cholangitis What is primary biliary cholangitis? Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic liver disease. When a person has PBC, the immune
Risk stratification in PBC
 Risk stratification in PBC Christophe Corpechot Reference Center for Inflammatory Biliary Diseases Saint-Antoine hospital, Paris, France What is currently known (background) PBC : chronic, progressive
Risk stratification in PBC Christophe Corpechot Reference Center for Inflammatory Biliary Diseases Saint-Antoine hospital, Paris, France What is currently known (background) PBC : chronic, progressive
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Once Rare, Now Common in the United Kingdom?
 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Once Rare, Now Common in the United Kingdom? OLIVER F. W. J AMES, 1 RAJ BHOPAL, 2 DENISE HOWEL, 2 JACKIE GRAY, 2 ALASTAIR D. BURT, 1 AND JANE V. METCALF 1 There is a widespread
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Once Rare, Now Common in the United Kingdom? OLIVER F. W. J AMES, 1 RAJ BHOPAL, 2 DENISE HOWEL, 2 JACKIE GRAY, 2 ALASTAIR D. BURT, 1 AND JANE V. METCALF 1 There is a widespread
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES No conflict of interest Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES No conflict of interest Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic, potentially. Assessing Quality of Life in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2004;2:164 174 Assessing Quality of Life in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis ANNE RANNARD,* DEBORAH BUCK,* DAVID E. J. JONES, OLIVER F. W. JAMES, and ANN JACOBY* *Department
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2004;2:164 174 Assessing Quality of Life in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis ANNE RANNARD,* DEBORAH BUCK,* DAVID E. J. JONES, OLIVER F. W. JAMES, and ANN JACOBY* *Department
Development of a self-reported Chronic Respiratory Questionnaire (CRQ-SR)
 954 Department of Respiratory Medicine, University Hospitals of Leicester, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester LE3 9QP, UK J E A Williams S J Singh L Sewell M D L Morgan Department of Clinical Epidemiology and
954 Department of Respiratory Medicine, University Hospitals of Leicester, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester LE3 9QP, UK J E A Williams S J Singh L Sewell M D L Morgan Department of Clinical Epidemiology and
Fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomized controlled trial of exercise
 Rheumatology 2003;42:1050 1054 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg289, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Advance Access publication 16 April 2003 Fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus: a
Rheumatology 2003;42:1050 1054 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg289, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Advance Access publication 16 April 2003 Fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus: a
Comparison of seven performance scales for differentiating individuals with Myalgic
 Comparison of seven performance scales for differentiating individuals with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) from other patient groups Authors Ruth R. Miller, PhD 1 (Corresponding)
Comparison of seven performance scales for differentiating individuals with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) from other patient groups Authors Ruth R. Miller, PhD 1 (Corresponding)
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
 Primary Biliary Cholangitis PBC Foundation (UK) Ltd 6 Hill Street Edinburgh EH2 3JZ Tel: +44 (0) 131 556 6811 info@pbcfoundation.org.uk www.pbcfoundation.org.uk PBC for Healthcare Practitioners Introduction
Primary Biliary Cholangitis PBC Foundation (UK) Ltd 6 Hill Street Edinburgh EH2 3JZ Tel: +44 (0) 131 556 6811 info@pbcfoundation.org.uk www.pbcfoundation.org.uk PBC for Healthcare Practitioners Introduction
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is an autoimmune
 Early Biochemical Response to Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Long-Term Prognosis of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: Results of a 14-Year Cohort Study Li-Na Zhang, 1,2 * Tian-Yan Shi, 1,2 * Xu-Hua Shi, 1,2 Li Wang,
Early Biochemical Response to Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Long-Term Prognosis of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: Results of a 14-Year Cohort Study Li-Na Zhang, 1,2 * Tian-Yan Shi, 1,2 * Xu-Hua Shi, 1,2 Li Wang,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Janssen CW, Lowry CA, Mehl MR, et al. Whole-body hyperthermia for the treatment of major depressive disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. Published online
Supplementary Online Content Janssen CW, Lowry CA, Mehl MR, et al. Whole-body hyperthermia for the treatment of major depressive disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. Published online
PBC treatment: the present and future. Maggie Bassendine Professor of Hepatology
 PBC treatment: the present and future Maggie Bassendine Professor of Hepatology Primary biliary cirrhosis 20-25yrs OLT/ Death Symptoms: Fatigue, itching, jaundice Autoimmune disease: Focal small bile duct
PBC treatment: the present and future Maggie Bassendine Professor of Hepatology Primary biliary cirrhosis 20-25yrs OLT/ Death Symptoms: Fatigue, itching, jaundice Autoimmune disease: Focal small bile duct
Quality of sleep in patients with chronic kidney disease
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2004) 19: 95 99 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg423 Original Article Quality of sleep in patients with chronic kidney disease Eduard A. Iliescu, Karen E. Yeates and David C. Holland Department
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2004) 19: 95 99 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg423 Original Article Quality of sleep in patients with chronic kidney disease Eduard A. Iliescu, Karen E. Yeates and David C. Holland Department
Prognosis of untreated Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Erik Christensen Copenhagen, Denmark
 Prognosis of untreated Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Erik Christensen Copenhagen, Denmark Study of Prognosis of PSC Difficulties: Disease is rare The duration of the course of disease may be very
Prognosis of untreated Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Erik Christensen Copenhagen, Denmark Study of Prognosis of PSC Difficulties: Disease is rare The duration of the course of disease may be very
URSODIOL FOR PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS URSODIOL FOR PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS. Patients
 KEITH D. LINDOR, M.D., FOR THE MAYO PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS URSODEOXYCHOLIC ACID STUDY GROUP* ABSTRACT Background There is no satisfactory medical therapy for patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis.
KEITH D. LINDOR, M.D., FOR THE MAYO PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS URSODEOXYCHOLIC ACID STUDY GROUP* ABSTRACT Background There is no satisfactory medical therapy for patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Subject: Obeticholic Acid (Ocaliva ) Tablet
 09-J2000-65 Original Effective Date: 09/15/16 Reviewed: 07/11/18 Revised: 08/15/18 Subject: Obeticholic Acid (Ocaliva ) Tablet THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION, EXPLANATION
09-J2000-65 Original Effective Date: 09/15/16 Reviewed: 07/11/18 Revised: 08/15/18 Subject: Obeticholic Acid (Ocaliva ) Tablet THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION, EXPLANATION
GEOEPIDEMIOLOGY OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS IN CENTRAL GREECE
 GEOEPIDEMIOLOGY OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS IN CENTRAL GREECE Kalliopi Azariadis 1, Nikolaos K. Gatselis 1, Kalliopi Zachou 1, Vasiliki Lygoura 1, Pinelopi Arvaniti 1, Eirini I. Rigopoulou 1, Georgia
GEOEPIDEMIOLOGY OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS IN CENTRAL GREECE Kalliopi Azariadis 1, Nikolaos K. Gatselis 1, Kalliopi Zachou 1, Vasiliki Lygoura 1, Pinelopi Arvaniti 1, Eirini I. Rigopoulou 1, Georgia
Single Technology Appraisal (STA) Obeticholic acid for treating primary biliary cirrhosis ID785
 Single Technology Appraisal (STA) Obeticholic acid for treating primary biliary cirrhosis ID785 Response to consultee and commentator comments on the draft remit and draft scope (pre-referral) Comment
Single Technology Appraisal (STA) Obeticholic acid for treating primary biliary cirrhosis ID785 Response to consultee and commentator comments on the draft remit and draft scope (pre-referral) Comment
Living Donor Liver Transplantation Patients Follow-up : Health-related Quality of Life and Their Relationship with the Donor
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 1, 9 15, March 2017 Original Living Donor Liver Transplantation Patients Follow-up : Health-related Quality of Life and Their Relationship with the Donor Shinji IRIE Abstract :
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 1, 9 15, March 2017 Original Living Donor Liver Transplantation Patients Follow-up : Health-related Quality of Life and Their Relationship with the Donor Shinji IRIE Abstract :
Study on sleep quality and associated psychosocial factors among elderly in a rural population of Kerala, India
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health George S et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2018 Feb;5(2):526-531 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original Research
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health George S et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2018 Feb;5(2):526-531 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original Research
CLINICAL ADVANCES IN LIVER PANCREAS AND BILIARY TRACT
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;135:1552 1560 IN LIVER PANCREAS Portal Hypertension and Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: Effect of Long-Term Ursodeoxycholic Acid Treatment PIERRE MICHEL HUET,*, CATHERINE VINCENT,* JULIE
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;135:1552 1560 IN LIVER PANCREAS Portal Hypertension and Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: Effect of Long-Term Ursodeoxycholic Acid Treatment PIERRE MICHEL HUET,*, CATHERINE VINCENT,* JULIE
Sleep Insomnia Severity Index (SISI) Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Inventory. POMS Vigor subscale
 Physical GLOBAL HEALTH PROMIS completed already Sleep PROMIS-Sleep Sleep Insomnia Severity Index () Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Inventory 8 items 7 items 18 items Vigor Vigor subscale 6 items 1 Sleep- PROMIS
Physical GLOBAL HEALTH PROMIS completed already Sleep PROMIS-Sleep Sleep Insomnia Severity Index () Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Inventory 8 items 7 items 18 items Vigor Vigor subscale 6 items 1 Sleep- PROMIS
Pediatric PSC A children s tale
 Pediatric PSC A children s tale September 8 th PSC Partners seeking a cure Tamir Miloh Assistant Professor Pediatric Hepatology Mount Sinai Hospital, NY Incidence Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) ;
Pediatric PSC A children s tale September 8 th PSC Partners seeking a cure Tamir Miloh Assistant Professor Pediatric Hepatology Mount Sinai Hospital, NY Incidence Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) ;
Fatigue and Psychiatric Morbidity Among Hodgkin s Disease Survivors
 Vol. 19 No. 2 February 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 91 Original Article Fatigue and Psychiatric Morbidity Among Hodgkin s Disease Survivors Jon Håvard Loge, MD, Arne Foss Abrahamsen, MD,
Vol. 19 No. 2 February 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 91 Original Article Fatigue and Psychiatric Morbidity Among Hodgkin s Disease Survivors Jon Håvard Loge, MD, Arne Foss Abrahamsen, MD,
Liver Disease That Presents with Jaundice (PBC, Alcohol and Drugs): Diagnosis and Patient Management. Emma Pham, PA-C
 Liver Disease That Presents with Jaundice (PBC, Alcohol and Drugs): Diagnosis and Patient Management Emma Pham, PA-C Case: JL (jaundiced lady) A 72 year old woman presents to her primary care provider
Liver Disease That Presents with Jaundice (PBC, Alcohol and Drugs): Diagnosis and Patient Management Emma Pham, PA-C Case: JL (jaundiced lady) A 72 year old woman presents to her primary care provider
Suitable dose and duration of fluvoxamine administration to treat depression
 PCN Psychiatric and Clinical Neurosciences 1323-13162003 Blackwell Science Pty Ltd 572April 2003 1098 Dose and duration of fluvoxamine S. Morishita and S. Arita 10.1046/j.1323-1316.2002.01098.x Original
PCN Psychiatric and Clinical Neurosciences 1323-13162003 Blackwell Science Pty Ltd 572April 2003 1098 Dose and duration of fluvoxamine S. Morishita and S. Arita 10.1046/j.1323-1316.2002.01098.x Original
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Medical Management
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Medical Management Kapil Chopra M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Transplant Medicine Mayo Clinic Arizona PSC Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a progressive
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Medical Management Kapil Chopra M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Transplant Medicine Mayo Clinic Arizona PSC Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a progressive
Current Concepts in the Management and Treatment of PBC & PSC
 Current Concepts in the Management and Treatment of PBC & PSC Michael A Heneghan, MD, MMedSc, FRCPI. Institute of Liver Studies, King s College Hospital, London A family affair? Central vein Hepatocytes
Current Concepts in the Management and Treatment of PBC & PSC Michael A Heneghan, MD, MMedSc, FRCPI. Institute of Liver Studies, King s College Hospital, London A family affair? Central vein Hepatocytes
PSYCHIATRIC MORBIDITY AMONG OVERSEAS STUDENTS
 ABSTRACT PSYCHIATRIC MORBIDITY AMONG OVERSEAS STUDENTS Pages with reference to book, From 115 To 117 Muhammad Afzal Javed ( Department of Psychiatry, Mayo Hospital, Lahore. ) Cohn M. Shapiro ( Department
ABSTRACT PSYCHIATRIC MORBIDITY AMONG OVERSEAS STUDENTS Pages with reference to book, From 115 To 117 Muhammad Afzal Javed ( Department of Psychiatry, Mayo Hospital, Lahore. ) Cohn M. Shapiro ( Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validation of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the psychological disorder among premature ejaculation subjects
 (2007) 19, 321 325 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijir ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validation of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the psychological
(2007) 19, 321 325 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijir ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validation of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the psychological
Beck depression inventory in general practice
 Beck depression inventory in general practice M. R. SALKIND, M.R.C.S., L.R.C.P., M.R.C.G.P. London THE early diagnosis of depression has become increasingly important to family doctors. The majority of
Beck depression inventory in general practice M. R. SALKIND, M.R.C.S., L.R.C.P., M.R.C.G.P. London THE early diagnosis of depression has become increasingly important to family doctors. The majority of
Suicide Risk and Melancholic Features of Major Depressive Disorder: A Diagnostic Imperative
 Suicide Risk and Melancholic Features of Major Depressive Disorder: A Diagnostic Imperative Robert I. Simon, M.D.* Suicide risk is increased in patients with Major Depressive Disorder with Melancholic
Suicide Risk and Melancholic Features of Major Depressive Disorder: A Diagnostic Imperative Robert I. Simon, M.D.* Suicide risk is increased in patients with Major Depressive Disorder with Melancholic
ACG Clinical Guideline: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Keith D. Lindor, MD, FACG 1, Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FACG 2, and M. Edwyn Harrison, MD 3 1 College of Health Solutions, Arizona State University, Phoenix,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Keith D. Lindor, MD, FACG 1, Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FACG 2, and M. Edwyn Harrison, MD 3 1 College of Health Solutions, Arizona State University, Phoenix,
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Treatment
 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Treatment Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Treatment Edited by Keith D. Lindor Professor of Medicine MayoClinic 200 First
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Treatment Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Treatment Edited by Keith D. Lindor Professor of Medicine MayoClinic 200 First
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic
 Predicting Clinical and Economic Outcomes After Liver Transplantation Using the Mayo Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Model and Child-Pugh Score Jayant A. Talwalkar, * Eric Seaberg, W. Ray Kim, * and Russell
Predicting Clinical and Economic Outcomes After Liver Transplantation Using the Mayo Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Model and Child-Pugh Score Jayant A. Talwalkar, * Eric Seaberg, W. Ray Kim, * and Russell
Number of Items. Response Categories. Part V: Specific Behavior Scales-Sleep Scales. Based on past month
 Part V: Specific Behavior Scales-Sleep Scales Based on past month First 4 items ask for time or amount of sleep 41. Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) Sleep quality Sleep latency Sleep duration Habitual
Part V: Specific Behavior Scales-Sleep Scales Based on past month First 4 items ask for time or amount of sleep 41. Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) Sleep quality Sleep latency Sleep duration Habitual
Depression intervention via referral, education, and collaborative treatment (Project DIRECT): a pilot study
 Executive summary of completed research Depression intervention via referral, education, and collaborative treatment (Project DIRECT): a pilot study Principal Investigator Jane McCusker, MD DrPH Co-investigators
Executive summary of completed research Depression intervention via referral, education, and collaborative treatment (Project DIRECT): a pilot study Principal Investigator Jane McCusker, MD DrPH Co-investigators
THE LONG TERM PSYCHOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF DAILY SEDATIVE INTERRUPTION IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS
 THE LONG TERM PSYCHOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF DAILY SEDATIVE INTERRUPTION IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS John P. Kress, MD, Brian Gehlbach, MD, Maureen Lacy, PhD, Neil Pliskin, PhD, Anne S. Pohlman, RN, MSN, and
THE LONG TERM PSYCHOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF DAILY SEDATIVE INTERRUPTION IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS John P. Kress, MD, Brian Gehlbach, MD, Maureen Lacy, PhD, Neil Pliskin, PhD, Anne S. Pohlman, RN, MSN, and
Impact of Chronic Pain
 BURDEN OF ILLNESS Overview Impact of Chronic Pain Healthcare costs 6 Sleep disturbances 2 Depression 2 Presenteeism and absenteeism 4,5 Chronic pain 1 Anxiety 2 Disability 4 Decreased quality of life 3
BURDEN OF ILLNESS Overview Impact of Chronic Pain Healthcare costs 6 Sleep disturbances 2 Depression 2 Presenteeism and absenteeism 4,5 Chronic pain 1 Anxiety 2 Disability 4 Decreased quality of life 3
POST TRANSPLANT OUTCOMES IN PSC
 POST TRANSPLANT OUTCOMES IN PSC Kidist K. Yimam, MD Medical Director, Autoimmune Liver Disease Program Division of Hepatology and Liver Transplantation California Pacific Medical Center (CPMC) PSC Partners
POST TRANSPLANT OUTCOMES IN PSC Kidist K. Yimam, MD Medical Director, Autoimmune Liver Disease Program Division of Hepatology and Liver Transplantation California Pacific Medical Center (CPMC) PSC Partners
The Relationships between Sleep-Wake Cycle and Academic Performance in Medical Students
 Biological Rhythm Research 0165-0424/01/3202-263$16.00 2001, Vol. 32, No. 2, pp. 263 270 Swets & Zeitlinger The Relationships between Sleep-Wake Cycle and Academic Performance in Medical Students Ana Ligia
Biological Rhythm Research 0165-0424/01/3202-263$16.00 2001, Vol. 32, No. 2, pp. 263 270 Swets & Zeitlinger The Relationships between Sleep-Wake Cycle and Academic Performance in Medical Students Ana Ligia
CLINICAL LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT. Epidemiology of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis in Victoria, Australia: High Prevalence in Migrant Populations
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2004;127:470 475 CLINICAL LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Epidemiology of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis in Victoria, Australia: High Prevalence in Migrant Populations SIDDHARTH SOOD, PAUL
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2004;127:470 475 CLINICAL LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Epidemiology of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis in Victoria, Australia: High Prevalence in Migrant Populations SIDDHARTH SOOD, PAUL
The Natural History of Small-Duct Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;134:975 980 The Natural History of Small-Duct Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis EINAR BJÖRNSSON,* ROLF OLSSON,* ANNIKA BERGQUIST, STEFAN LINDGREN, BARBARA BRADEN, ROGER W. CHAPMAN, KIRSTEN
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;134:975 980 The Natural History of Small-Duct Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis EINAR BJÖRNSSON,* ROLF OLSSON,* ANNIKA BERGQUIST, STEFAN LINDGREN, BARBARA BRADEN, ROGER W. CHAPMAN, KIRSTEN
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis What is Primary Biliary Cirrhosis? Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic liver disease resulting from progressive destruction of the bile ducts in the liver called the
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis What is Primary Biliary Cirrhosis? Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic liver disease resulting from progressive destruction of the bile ducts in the liver called the
OCALIVA (obeticholic acid) oral tablet
 OCALIVA (obeticholic acid) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
OCALIVA (obeticholic acid) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
NEUROPSYCHOMETRIC TESTS
 NEUROPSYCHOMETRIC TESTS CAMCOG It is the Cognitive section of Cambridge Examination for Mental Disorders of the Elderly (CAMDEX) The measure assesses orientation, language, memory, praxis, attention, abstract
NEUROPSYCHOMETRIC TESTS CAMCOG It is the Cognitive section of Cambridge Examination for Mental Disorders of the Elderly (CAMDEX) The measure assesses orientation, language, memory, praxis, attention, abstract
Definition of Acute Insomnia: Diagnostic and Treatment Implications. Charles M. Morin 1,2. Keywords: Insomnia, diagnosis, definition
 Acute Insomnia Editorial 1 Definition of Acute Insomnia: Diagnostic and Treatment Implications Charles M. Morin 1,2 1 Université Laval, Québec, Canada 2 Centre de recherche Université Laval/Robert-Giffard,
Acute Insomnia Editorial 1 Definition of Acute Insomnia: Diagnostic and Treatment Implications Charles M. Morin 1,2 1 Université Laval, Québec, Canada 2 Centre de recherche Université Laval/Robert-Giffard,
Is Serum Bilirubin Concentration the Only Valid Prognostic Marker in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
 Is Serum Bilirubin Concentration the Only Valid Prognostic Marker in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis? PIOTR KRZESKI, 1 WLODZIMIERZ ZYCH, 1 EWA KRASZEWSKA, 2 BOHDAN MILEWSKI, 3 EUGENIUSZ BUTRUK, 1 AND ANDRZEJ
Is Serum Bilirubin Concentration the Only Valid Prognostic Marker in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis? PIOTR KRZESKI, 1 WLODZIMIERZ ZYCH, 1 EWA KRASZEWSKA, 2 BOHDAN MILEWSKI, 3 EUGENIUSZ BUTRUK, 1 AND ANDRZEJ
CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED YEARS
 CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED 60 94 YEARS AM. J. GERIATR. PSYCHIATRY. 2013;21(7):631 635 DOI:
CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED 60 94 YEARS AM. J. GERIATR. PSYCHIATRY. 2013;21(7):631 635 DOI:
4/26/2017. Liver Transplant and Palliative Care: Teaming up to improve care
 Liver Transplant and Palliative Care: Teaming up to improve care Jody C. Olson, M.D., FACP Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery Hepatology and Critical Care Medicine All patients with end-stage
Liver Transplant and Palliative Care: Teaming up to improve care Jody C. Olson, M.D., FACP Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery Hepatology and Critical Care Medicine All patients with end-stage
Aberrant Expression of Keratin 7 in Hepatocytes as a Predictive Marker of Rapid Progression to Hepatic Failure in Asymptomatic Primary Biliary
 2015 69 3 137144 Aberrant Expression of Keratin 7 in Hepatocytes as a Predictive Marker of Rapid Progression to Hepatic Failure in Asymptomatic Primary Biliary Cirrhosis a a,b* a a a a a,b a a a,b c d
2015 69 3 137144 Aberrant Expression of Keratin 7 in Hepatocytes as a Predictive Marker of Rapid Progression to Hepatic Failure in Asymptomatic Primary Biliary Cirrhosis a a,b* a a a a a,b a a a,b c d
Reliability and Validity of the Chinese Translation of Insomnia Severity Index and Comparison with Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index
 ORIGINAL PAPER Reliability and Validity of the Chinese Translation of Insomnia Severity Index and Comparison with Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index Shapour BA 1, Gang CK 2 1 Complementary Medicine Research
ORIGINAL PAPER Reliability and Validity of the Chinese Translation of Insomnia Severity Index and Comparison with Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index Shapour BA 1, Gang CK 2 1 Complementary Medicine Research
Screening for depressive symptoms: Validation of the CES-D scale in a multi-ethnic group of patients with diabetes in Singapore
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online March 25, 2008 Screening for depressive symptoms: Validation of the CES-D scale in a multi-ethnic group of patients with diabetes in Singapore Stahl
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online March 25, 2008 Screening for depressive symptoms: Validation of the CES-D scale in a multi-ethnic group of patients with diabetes in Singapore Stahl
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis at Hospital Kuala Lumpur: A Study of 11 Cases Seen Between
 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis at Hospital Kuala Lumpur: A Study of 11 Cases Seen Between 1992 and 1999 R Kananathan, MRCPI, R L Suresh, MRCP, I Merican, FRCP, Department of Medicine, Hospital Kuala Lumpur,
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis at Hospital Kuala Lumpur: A Study of 11 Cases Seen Between 1992 and 1999 R Kananathan, MRCPI, R L Suresh, MRCP, I Merican, FRCP, Department of Medicine, Hospital Kuala Lumpur,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Lam RW, Levitt AJ, Levitan RD, et al. Efficacy of bright light treatment, fluoxetine, and the combination in patients with nonseasonal major depressive disorder: a randomized
Supplementary Online Content Lam RW, Levitt AJ, Levitan RD, et al. Efficacy of bright light treatment, fluoxetine, and the combination in patients with nonseasonal major depressive disorder: a randomized
Ursodeoxycholic Acid for the Treatment of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 T h e n e w e ng l a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical therapeutics Ursodeoxycholic Acid for the Treatment of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Keith Lindor, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case
T h e n e w e ng l a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical therapeutics Ursodeoxycholic Acid for the Treatment of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Keith Lindor, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case
Review of self-reported instruments that measure sleep dysfunction in patients suffering from temporomandibular disorders and/or orofacial pain
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 Review of self-reported instruments that measure sleep dysfunction in
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 Review of self-reported instruments that measure sleep dysfunction in
Summary ID# Clinical Study Summary: Study B4Z-MC-LYBX
 CT Registry ID#7068 Page 1 Summary ID# 7068 Clinical Study Summary: Study B4Z-MC-LYBX A Randomized, Double-Blind Comparison of Hydrochloride and Placebo in Child and Adolescent Outpatients with Attention-
CT Registry ID#7068 Page 1 Summary ID# 7068 Clinical Study Summary: Study B4Z-MC-LYBX A Randomized, Double-Blind Comparison of Hydrochloride and Placebo in Child and Adolescent Outpatients with Attention-
CBT in the Treatment of Persistent Insomnia in Patients with Cancer
 CBT in the Treatment of Persistent Insomnia in Patients with Cancer Colin A Espie University of Glasgow Sleep Centre Sackler Institute of Psychobiological Research University of Glasgow Scotland UK Outline
CBT in the Treatment of Persistent Insomnia in Patients with Cancer Colin A Espie University of Glasgow Sleep Centre Sackler Institute of Psychobiological Research University of Glasgow Scotland UK Outline
Growth analysis in children with PFIC treated with the ASBT inhibitor maralixibat
 Growth analysis in children with PFIC treated with the ASBT inhibitor maralixibat INDIGO Study Richard Thompson, Deirdre Kelly, Sanjay Rajwal, Alexander Miethke, Nisreen Soufi, Christine Rivet, Irena Jankowska,
Growth analysis in children with PFIC treated with the ASBT inhibitor maralixibat INDIGO Study Richard Thompson, Deirdre Kelly, Sanjay Rajwal, Alexander Miethke, Nisreen Soufi, Christine Rivet, Irena Jankowska,
Keywords: neurological disease; emotional disorder
 202 Psychiatry, University of Edinburgh, Royal Edinburgh Hospital, Morningside Park, A J Carson B Ringbauer M Sharpe Medical Neurology, University of C Warlow Psychological Medicine M Sharpe Clinical Neurology,
202 Psychiatry, University of Edinburgh, Royal Edinburgh Hospital, Morningside Park, A J Carson B Ringbauer M Sharpe Medical Neurology, University of C Warlow Psychological Medicine M Sharpe Clinical Neurology,
Is the Mayo Model for Predicting Survival Useful After the Introduction of Ursodeoxycholic Acid Treatment for Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
 Is the Mayo Model for Predicting Survival Useful After the Introduction of Ursodeoxycholic Acid Treatment for Primary Biliary Cirrhosis? MATTHEW R. KILMURRY, 1 E. JENNY HEATHCOTE, 1 KAREN CAUCH-DUDEK,
Is the Mayo Model for Predicting Survival Useful After the Introduction of Ursodeoxycholic Acid Treatment for Primary Biliary Cirrhosis? MATTHEW R. KILMURRY, 1 E. JENNY HEATHCOTE, 1 KAREN CAUCH-DUDEK,
Standing up for fatigue the role of autonomic function in the symptom of fatigue
 Standing up for fatigue the role of autonomic function in the symptom of fatigue Julia Newton Professor of Ageing and Medicine, Newcastle University Deputy Medical Director Newcastle Hospitals NHS Foundation
Standing up for fatigue the role of autonomic function in the symptom of fatigue Julia Newton Professor of Ageing and Medicine, Newcastle University Deputy Medical Director Newcastle Hospitals NHS Foundation
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic cholestatic
 AUTOIMMUNE, CHOLESTATIC AND BILIARY DISEASE Epidemiology and Natural History of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis in a Canadian Health Region: A Population-Based Study Robert P. Myers, 1,2 Abdel Aziz M. Shaheen,
AUTOIMMUNE, CHOLESTATIC AND BILIARY DISEASE Epidemiology and Natural History of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis in a Canadian Health Region: A Population-Based Study Robert P. Myers, 1,2 Abdel Aziz M. Shaheen,
Key Points: Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective. Jenny Heathcote, MD. University of Toronto
 Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective Jenny Heathcote, MD University of Toronto Key Points: AILD comprise autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis
Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective Jenny Heathcote, MD University of Toronto Key Points: AILD comprise autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis
Factors affecting health status in COPD patients with co-morbid anxiety or depression
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Factors affecting health status in COPD patients with co-morbid anxiety or depression Minna J Hynninen¹ Ståle Pallesen² Inger Hilde Nordhus¹ ¹Department of Clinical Psychology, University
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Factors affecting health status in COPD patients with co-morbid anxiety or depression Minna J Hynninen¹ Ståle Pallesen² Inger Hilde Nordhus¹ ¹Department of Clinical Psychology, University
Improving the Lives of Patients with Liver Diseases
 Improving the Lives of Patients with Liver Diseases Corporate Presentation March 2019 Safe Harbor Statement This presentation contains "forward-looking" statements that involve risks, uncertainties and
Improving the Lives of Patients with Liver Diseases Corporate Presentation March 2019 Safe Harbor Statement This presentation contains "forward-looking" statements that involve risks, uncertainties and
BILIARY ATRESIA. What is biliary atresia?
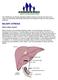 The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. BILIARY ATRESIA What is
The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. BILIARY ATRESIA What is
Role of Sleep Disturbance in Chronic Hepatitis C Infection
 Curr Hepatitis Rep (2010) 9:25 29 DOI 10.1007/s11901-010-0030-x Role of Sleep Disturbance in Chronic Hepatitis C Infection Meghan D. Carlson & Robin C. Hilsabeck & Fatma Barakat & William Perry Published
Curr Hepatitis Rep (2010) 9:25 29 DOI 10.1007/s11901-010-0030-x Role of Sleep Disturbance in Chronic Hepatitis C Infection Meghan D. Carlson & Robin C. Hilsabeck & Fatma Barakat & William Perry Published
An integrated care pathway improves quality of life in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 Q J Med 2008; 101:535 543 doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcn043 Advance Access published on 3 April 2008 An integrated care pathway improves quality of life in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis DAVID E.J. JONES, KATY SUTCLIFFE,
Q J Med 2008; 101:535 543 doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcn043 Advance Access published on 3 April 2008 An integrated care pathway improves quality of life in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis DAVID E.J. JONES, KATY SUTCLIFFE,
Fatigue in chronic migraine patients
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleFatigue in chronic migraine MFP Peres et al. Fatigue in chronic migraine patients MFP Peres 1, E Zukerman
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleFatigue in chronic migraine MFP Peres et al. Fatigue in chronic migraine patients MFP Peres 1, E Zukerman
Development of a Japanese Version of the Mental Health-Related Self-Care Agency Scale
 J. Jpn. Acad. Nurs. Sci., Vol. 31, No. 4, pp. 24 33, 2011 Development of a Japanese Version of the Mental Health-Related Self-Care Agency Scale 1 2 3 Kumiko Kasuya, Akiko Funakoshi, Miyoko Nagae Key words
J. Jpn. Acad. Nurs. Sci., Vol. 31, No. 4, pp. 24 33, 2011 Development of a Japanese Version of the Mental Health-Related Self-Care Agency Scale 1 2 3 Kumiko Kasuya, Akiko Funakoshi, Miyoko Nagae Key words
Depression and anxiety are reported to have a
 Validation of Mood Measures for People with Multiple Sclerosis Tessa M. Watson, DClinPsy; Emma Ford, BSc; Esme Worthington, PhD; Nadina B. Lincoln, PhD Background: Valid assessments are needed in order
Validation of Mood Measures for People with Multiple Sclerosis Tessa M. Watson, DClinPsy; Emma Ford, BSc; Esme Worthington, PhD; Nadina B. Lincoln, PhD Background: Valid assessments are needed in order
P rimary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic cholestatic liver
 265 LIVER DISEASE Hyperlipidaemic state and cardiovascular in primary biliary cirrhosis M Longo, A Crosignani, P M Battezzati, C Squarcia Giussani, P Invernizzi, M Zuin, M Podda... See end of article for
265 LIVER DISEASE Hyperlipidaemic state and cardiovascular in primary biliary cirrhosis M Longo, A Crosignani, P M Battezzati, C Squarcia Giussani, P Invernizzi, M Zuin, M Podda... See end of article for
Prognostic indicators in primary biliary cirrhosis: significance of revised IAHG (International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group) score
 pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 2012;18:375-382 Prognostic indicators in primary biliary cirrhosis: significance of revised IAHG (International Autoimmune
pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 2012;18:375-382 Prognostic indicators in primary biliary cirrhosis: significance of revised IAHG (International Autoimmune
Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases
 Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases - EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines - Rome, 8 October 2010 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Tytgat Institute of Liver and Intestinal Research
Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases - EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines - Rome, 8 October 2010 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Tytgat Institute of Liver and Intestinal Research
